Abstract
Antibody fragments, especially single-chain Fv fragments, have been established for the generation of immunoliposomes for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy and other applications. Bispecific immunoliposomes should be useful for dual targeting addressing inter- and intratumoral heterogeneity of tumor antigen expression. Here, we established a protocol to generate dual-targeted immunoliposomes using genetically engineered scFv molecules recognizing two different tumor-associated antigens, EGFR and CEA (CEACAM5), applying a step-wise insertion of antibody-coupled micelles into preformed PEGylated liposomes. The dual-targeted immunoliposomes retained binding activity for both antigens and combined the selectivity of both antibodies within one liposome. Thus, these dual-targeted immunoliposomes should be suitable to deliver therapeutic payloads to tumor cells expressing EGFR or CEA, or both antigens.
1. Introduction
Liposomes have been extensively studied as drug carrier systems [1,2,3]. The composition of liposomes allows encapsulation of hydrophilic drugs into the aqueous interior as well as the incorporation of hydrophobic drugs into the lipophilic lipid bilayer(s) [4]. Several liposomal formulations, e.g., liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil®), are approved for cancer therapy [5,6]. In order to maintain an extended circulation in the blood stream, liposomes are sterically stabilized by incorporation of PEG chains into the liposomal surface (PEGylated liposomes) [7,8]. Therapeutic efficacy is mainly due to delivery of drugs to the tumor sites by means of an enhanced permeability and retention (EPR effect), caused by an irregular and defective tumor vasculature and a compromised lymphatic drainage [5,9,10]. This effect is passive and does not lead to a selective binding and uptake of the liposomal formulation into tumor cells. However, therapeutic efficacy should benefit from a targeted (active) delivery of the liposomes to tumor cells, thus increasing the local concentration of the drug in the tumor and facilitating intracellular delivery of the drug [11,12,13]. This can be achieved by coupling of tumor-selective ligands to the liposomal surface, for example using antibodies [14,15,16].
Immunoliposomes are generated by coupling whole antibodies or antibody fragments such as Fab or single-chain Fv fragments (scFv) directly to the liposomal surface [15]. Alternatively, ligands can be coupled to micellar lipids and subsequently inserted into preformed liposomes (postinsertion method) [17]. The use of Fab and scFv fragments avoids Fc-mediated interactions and elimination by the reticulo-endothelial systems. A site-directed and defined coupling of scFv fragments can be achieved by introducing an additional cysteine residue at the C-terminus or at the linker connecting the VH and VL domain, which can be used for coupling to maleimide-functionalized lipids [18,19,20].
Extensive studies have been performed with immunoliposomes targeting single antigens [15,16]. These studies demonstrated that immunoliposomes are able to bind selectively to antigen-specific target cells and to deliver therapeutic compounds to the cell. However, solid tumors are characterized by an intra- and intertumoral heterogeneity caused by genetic instability and clonal evolution, e.g., as described for breast cancer [21,22,23,24,25]. Furthermore, tumor cells often upregulate different cell surface antigens, which can be used to discriminate tumor cells from normal cells. Dual targeting of tumor cells has been proposed to improve therapy and several approaches, e.g., using a combination of monoclonal antibodies or bispecific antibodies, have demonstrated its feasibility to improve efficacy [26]. Dual targeting should also be applicable for liposomes and other nanoparticles.
Several strategies have already been explored to generate dual-targeted nanoparticles using combinations of antibodies, natural ligands, and peptides [27,28,29,30,31]. For example, dual-targeted immunoliposomes were generated coupling thiolated monoclonal antibodies directed against CD19 and CD20 to the surface of PEGylated liposomes that showed improved binding, uptake and cytotoxic activity compared with the individually targeted immunoliposomes [27].
Dual targeting should also be possible using recombinant antibody fragments such as cysteine-modified single-chain Fv fragments (scFv') [20]. Here, we applied two recombinant scFv' molecules directed against EGFR and CEA (CEACAM5) for the generation of bispecific immunoliposomes. Both antigens have been described to be over-expressed by cells from various tumor types including colon carcinoma [32,33,34]. The dual-targeted immunoliposomes (dt-IL) were generated applying an adapted postinsertion protocol utilizing a step-by-step insertion of antibody fragments coupled to micellar maleimide-PEG-DSPE lipids. We show that the dual-targeted immunoliposomes retain antigen binding for both antigens, thus are capable of recognizing tumor cells expressing both or only one of the tumor-associated antigens.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Egg phosphatidylcholine (EPC) was purchased from Lipoid (Ludwigshafen, Germany), cholesterol was purchased from Calbiochem (Darmstadt, Germany). 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-(7-nitro-2-1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl) (ammonium salt) (NBD-DOPE) and 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-(lissamine rhodamine B sulfonyl) (ammonium salt) (rhodamine-DPPE) and all other lipids were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL, USA). DiI was purchased from Sigma (Taufkirchen, Germany). HRP-conjugated anti-His-tag antibody was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA) and FITC-conjugated anti-His antibody from Dianova (Hamburg, Germany). The PE-labeled monoclonal anti-EGFR antibody (EGFR R-1) was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. The BW 431/26 (mouse anti-CEA) antibody was provided by Behringwerke (Marburg, Germany). The polyclonal anti-moIgG-FITC IgG was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA. The human colon carcinoma cell line LS174T, the human epidermoid carcinoma cell line A431 and the human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line A549 were cultured in RPMI1640 containing 5% FCS, 2 mM L-glutamine and 100 units/mL penicillin G and 100 µg/mL streptomycin. The human breast cancer cell lines SKBR3 and MCF7 and the human colon adenocarcinoma cell line LoVo were cultured in RPMI1640 containing 10% FCS, 2 mM L-glutamine and 100 units/mL penicillin G and 100 µg/mL streptomycin. Cells were cultured at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2 incubator.
2.2. Generation of scFv' Fragments
An anti-EGFR scFv' was generated by cloning a humanized version of scFv C225 (hu225) into vector pABC4 [19]. An anti-CEA scFv' was described previously [19]. Antibody fragments (anti-EGFR scFv' hu225, anti-CEA scFv' MFE23) were purified by immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) as described elsewhere [35]. Protein concentration was determined by measuring the absorbance at 280 nm. Purified scFv' were analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing and non-reducing conditions and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue G250 or immunoblotted with an HRP-conjugated anti-His-tag antibody.
2.3. Protein Melting Points
Purified scFv' (100–150 µg) was diluted in PBS to a total volume of 1 mL and sterile filtered (0.2 µm) into a quartz cuvette. Dynamic laser light scattering intensity was measured with a Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern, Herrenberg, Germany) while the temperature was increased in 1 °C intervals from 30 to 70 °C with 2 min equilibration for each temperature step. The melting point was defined as the temperature at which the light scattering intensity dramatically increased.
2.4. Preparation of Immunoliposomes
Immunoliposomes were generated by postinsertion of scFv'-conjugated micelles into preformed PEG-liposomes [20]. Liposomes composed of EPC:Chol:mPEG2000-DSPE at a molar ratio of 6.75:3:0.25 were prepared by the film hydration-extrusion method as described previously [19]. All liposomes further contained 0.3 mol% fluorescent dye (DiI). Mal-PEG2000-DSPE micelles were generated by removal of chloroform under a stream of nitrogen at RT. The dried lipid was dissolved in double distilled water to a final concentration of 10 mg/mL and incubated for 5 min at 65 °C in a water bath to form micelles. Purified scFv were reduced in 8 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) for 2 h at room temperature followed by removal of TCEP by dialysis against degassed 10 mM Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4 buffer, 0.2 mM EDTA, 30 mM NaCl (pH 6.7) overnight at 4 °C. Micellar lipid and reduced scFv' were mixed at a molar ratio of 5:1. Coupling reaction was performed at room temperature for 30 min. The reaction was quenched with 1 mM L-cysteine, 0.02 mM EDTA, pH 5.5. The scFv'-coupled micelles were inserted into preformed PEGylated liposomes by incubation at 45 °C for 2 h (anti-CEA scFv') or at 55 °C for 30 min (anti-EGFR scFv'). Dual targeted immunoliposomes were prepared by step-wise post-insertion. Firstly, anti-EGFR scFv'-coupled micelles were inserted at 55 °C for 30 min afterwards anti-CEA scFv'-coupled micelles were added to the dispersion and again incubated at 45 °C for 2 h in a water bath. Unbound scFv molecules were removed by gel-filtration using a Sepharose CL4B column (Amersham, Braunschweig, Germany). Liposome size was measured using a ZetaSizer Nano ZS (Malvern). To monitor the synchronized post-insertion of two different micelle species the Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles were stained either with NBD-DOPE or with rhodamine-DPPE as indicated. The fluorescently-labeled phospholipids were added to the Mal-PEG2000-DSPE in chloroform before the organic solvent was evaporated.
2.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Cell Binding
For analyzing the binding of monoclonal antibodies, cells were resuspended to a concentration of 2.5 × 106 cells/mL in PBA (PBS, 2% FCS, 0.02% sodium azide) containing the diluted primary antibody (anti-EGFR: 1:100, anti-CEA: 1:100). After incubation at 4 °C for 1 h in the dark, the plate was washed three times with 150 μL PBA. To detect unlabeled primary antibodies 100 μL 1:500 diluted anti-mouse IgG-FITC was applied to the respective wells and incubated at 4 °C for 45 min in the dark. Cells incubated with a fluorescently labeled antibody were resuspended in 100 μL PBA. The cells were washed twice in 150 μL PBA, resuspended in 500 μL PBA and transferred into FACS tubes. A total of 10,000 cells were analyzed using a Cytomics FC500 (Beckmann Coulter, Krefeld, Germany). Analysis of the obtained data was performed using FlowJo 7.6.1 and Microsoft Office Excel 2011. Binding of purified scFv' molecules was determined by incubating detached cells with antibody molecules in PBA buffer for 1 h at 4 °C. Cells were then washed three times with PBA and incubated with FITC-conjugated anti-His-tag antibody diluted 1:200. Binding of liposomes was analyzed by incubating cells (2.5 × 105) with DiI-labeled immunoliposomes (1–1,000 nmol lipid) per 100 µL PBA for 1 h at 4 °C. After washing cells three times with PBA (4 °C) cells were resuspended in 300 µL PBA buffer and analyzed by flow cytometry. Data was evaluated with WinMDI, version 2.9. The relative mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) plotted in the binding experiment analysis was calculated according to the following formula: relative MFI = MFIsample − (MFInt − MFIcells)/MFIcells.
2.6. ELISA
Binding of the immunoliposomes to CEA and EGFR was analyzed by a sandwich ELISA. CEA was coated onto a microtiter plate at a concentration of 3 µg/mL. After blocking remaining binding sites with MPBS (PBS, 2% skimmed milk powder), liposomes were added at varying concentrations and incubated for 1 h. After washing with PBS, an EGFR-Fc fusion protein (10 µg/mL) was added and incubated for 1 h. After washing, bound EGFR-Fc was detected with an HRP-conjugated anti-human Fc antibody (Sigma-Aldrich) and subsequent addition of TMB substrate.
2.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Liposomes
The flow cytometer was adjusted for counting small liposomes at a size range between 100–150 nm by modifying the voltage of the front and side scatter detectors. Furthermore, the overlapping fluorescence signals in fluorescence detector one (FL1) and detector two (FL2) of single fluorescently labeled liposomes (NBD-DOPE or rhodamine-DPPE) were compensated for the detection of double stained vesicles (NBD-DOPE and rhodamine-DPPE). All liposomes were measured at a phospholipid concentration of approximately 1 mM analyzing 10,000 vesicles.
3. Results
3.1. Expression of EGFR and CEA by Tumor Cell Lines
A panel of human tumor cell lines was analyzed by flow cytometry for the expression of EGFR and CEA (Figure 1). The two human colon carcinoma cell lines LS174T and LoVo showed strong staining for EGFR and CEA. Three other cell lines, A549, MCF-7 and SKBR3 showed medium to weak expression of the two antigens. The human squamous carcinoma cell line A431 exhibited strong expression of EGFR and was negative for CEA. Thus, these cell lines express the two antigens to varying extent and should therefore be suitable for the analysis of dual targeting of immunoliposomes.
3.2. Post-Insertion of Micellar Lipid/Dye Preparations
For the generation of dual-targeted immunoliposomes we applied the post-insertion of Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles conjugated with two scFv' molecules of different specificity. Principally, this can be performed with micelles prepared by the simultaneous conjugation of both different ligands. Alternatively, the preparation and insertion of individual ligand-coupled micelles can be applied, with the insertion performed simultaneously or step-wise. In order to monitor the behavior of Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles during the post-insertion into preformed liposomes (plain liposomes), we analyzed micelles containing either the fluorescent phospholipid NBD-DOPE (green fluorescence) or rhodamine-DPPE (red fluorescence), respectively. During insertion, these lipids will be transferred into the liposomes, thus acting as surrogate for the ligand-coupled lipids. Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles were prepared containing between 1 to 30 mol% of the fluorescent phospholipid NBD-DOPE (Figure 2a). The size (zeta average) of Mal-PEG2000-DSPE micelles containing 1, 3, 10, and 30 mol% NBD-DOPE, respectively, remained stable at around 15 to 18 nm, in accordance with values described for PEG2000-DSPE micelles [36]. The size of the plain liposomes was 138 nm with a PDI of 0.11. After post-insertion, no micellar structures were detected by dynamic light scattering. The size of the liposomes increased slightly to 143–159 nm (Figure 2a). The poly-dispersity index (PDI) of all formulations after post-insertion was below 0.2. An increase in fluorescence intensity of the liposomes was observed after post-insertion of 1 mol% Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles that directly correlated with the amount of dye contained within the micelles (Figure 2b,c). No remaining (free) Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles were detected via dynamic light scattering implying a complete insertion of micellar lipids into the outer layer of the preformed liposomes.
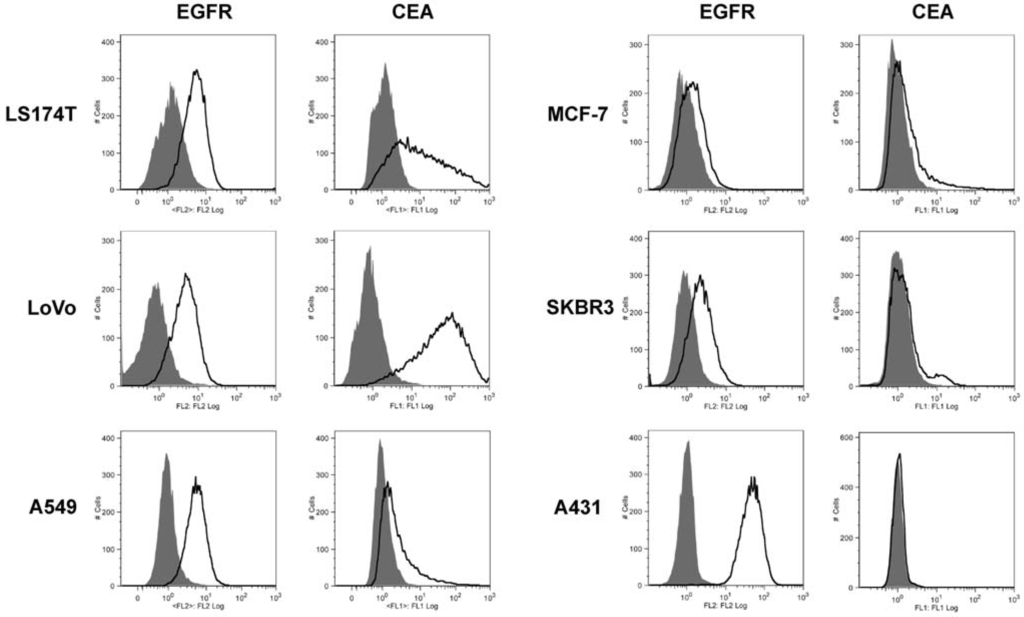
Figure 1.
Flow cytometry analysis of the expression of EGFR and CEA on various tumor cell lines (grey filled, cells alone; black line, cells incubated with either anti-EGFR or anti-CEA monoclonal antibodies).
Next, we analyzed the effects of inserting two differently labeled micelles (containing 10 mol% NBD-DOPE or rhodamine-DPPE, respectively) into preformed liposomes. The post-insertion of 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1 mol% Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles containing either NBD-DOPE or rhodamine-DPPE into liposomes caused a concentration-dependent shift in fluorescence intensity (Figure 2d). Thus, insertion of NBD-DOPE-labeled micelles caused an increase in green fluorescence and insertion of rhodamine-DPPE-labeled micelles caused an increase in red fluorescence, respectively. The simultaneous post-insertion of both differently labeled Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles into liposomes led to a similar concentration-dependent shift of green and red fluorescence intensities. No liposomes exhibiting only green or red fluorescence could be detected even at very low concentration of micellar lipid used for post-insertion (e.g., 0.03 mol% corresponding to approximately 40 to 50 micellar lipids per liposome). According to this finding, the post-insertion of differently labeled micelles results in the insertion of lipids from both kinds of micelles into one liposome, thus should be applicable for the generation of dual-targeted immunoliposomes even at low micelle to liposome ratios.
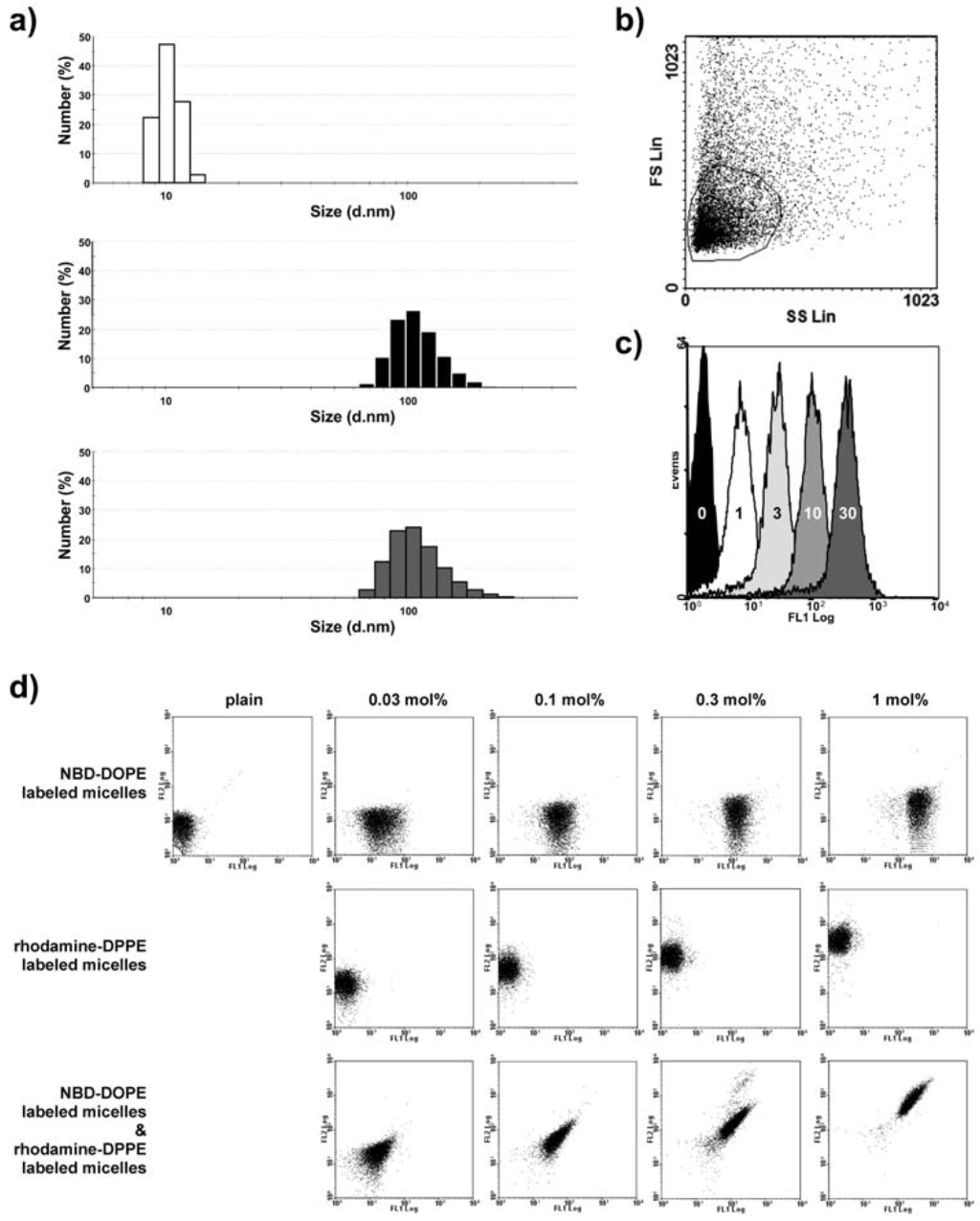
Figure 2.
Postinsertion of dye-labeled Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles into preformed liposomes. (a) Particle size distributions (numbers) of Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles containing 10 mol% NBD-DOPE (white), plain liposomes before post-insertion (black), liposomes after post-insertion (grey); (b) Titration of micellar NBD-DOPE post-inserted into plain liposomes. Liposomes were detected using the flow cytometer showing the population of vesicles used for the analysis; (c) Liposomal fluorescence intensity after post-insertion using 1 mol% Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles containing indicated amounts of NBD-DOPE (0 to 30 mol%); (d) Flow cytometry analysis of liposomes after post-insertion using indicated amounts of Mal-PEG2000-DSPE-micelles containing 10 mol% dye (NBD-DOPE or rhodamine-DPPE).
3.3. Antibody Fragments for the Generation of Immunoliposomes
For the generation of immunoliposomes, we produced two scFv' fragments containing a C-terminal cysteine for side-directed coupling. ScFv' hu225 is directed against human EGFR and scFv' MFE23 is directed against human CEA. Both antibody fragments were produced in E. coli and purified from the periplasm with yields in the range of 0.2–0.5 mg/L. In SDS-PAGE, the molecules migrated with an apparent molecular mass of 30–35 kDa under reducing conditions. Under non-reducing conditions, an additional band of approximately 55–60 kDa was visible, indicating the formation of disulfide-linked dimers (Figure 3a). Thermal stability of the antibody fragments was determined by dynamic light scattering, which revealed a melting point of approximately 62 °C for scFv' hu225 and of 48 °C for scFv' MFE23 (Figure 3b). Both antibody fragments were capable of binding to EGFR- and CEA-expressing tumor cell lines (LS174T, A549) in a concentration-dependent manner with EC50 values of 0.3–1 nM for scFv' hu225 and 3–10 nM for scFv' MFE23 (Figure 3).
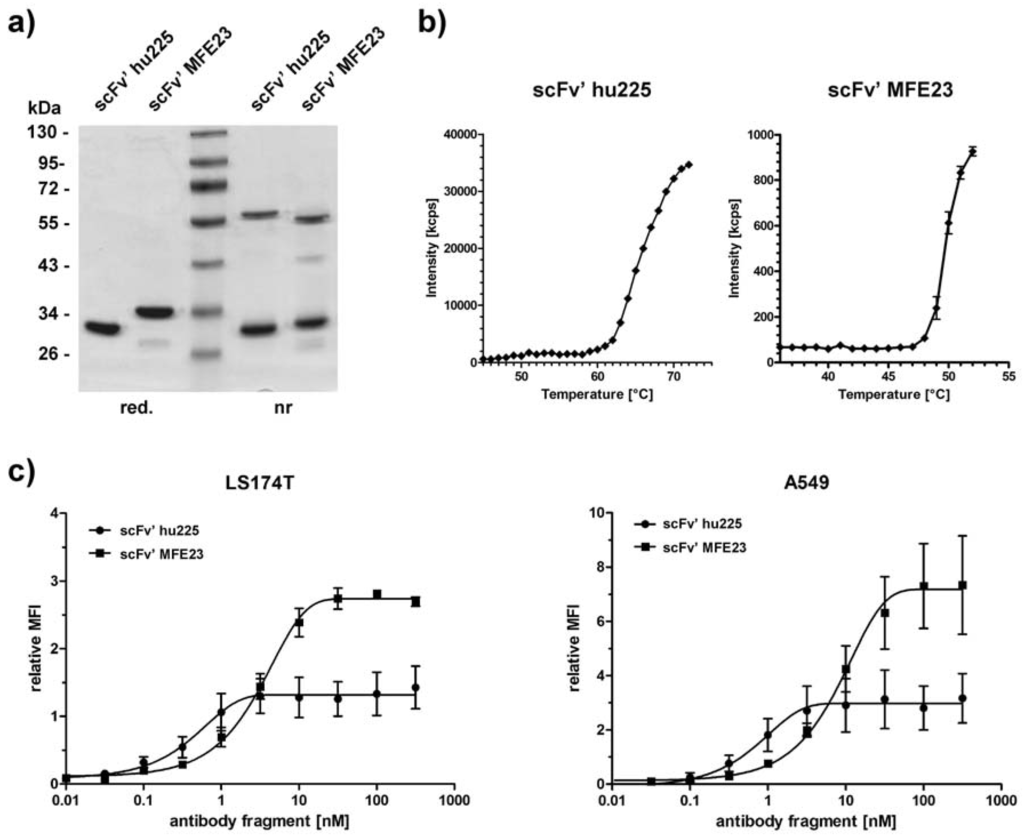
Figure 3.
Characterization of scFv'-fragments targeting EGFR- or CEA-expressing tumor cells. (a) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified anti-EGFR scFv' hu225 and anti-CEA scFv' MFE23 analyzed under reducing (red.) or non-reducing (nr) conditions; (b) Thermal stability of scFv' hu225 and scFv' MFE23 analyzed by dynamic light scattering; (c) Flow cytometry analysis of binding of the two scFv fragments to LS174T and A549 cells.
3.4. Immunoliposomes
In order to determine the amount of scFv-coupled micellar lipids required for a strong immunoliposomal binding to target cells, we generated immunoliposomes by inserting between 0.01 mol% and 1 mol% of scFv-MalPEG2000-DSPE-conjugates. Coupling efficiencies to Mal-PEG2000-DSPE were approximately 95% for scFv' hu225 and 50% for scFv' MFE23 as determined by SDS-PAGE (Figure 4a). Hu225-ILs were generated by post-insertion at 55 °C for 30 min and MFE23-ILs were generated performing the post-insertion step at 45 °C for approximately 2 h. Both types of immunoliposomes (hu225-IL, MFE23-IL) showed a concentration-dependent binding to EGFR- and CEA-positive tumor cell lines analyzed by flow cytometry (Figure 4b). For hu225-IL, strongest signals were observed using 0.1 to 0.3 mol% inserted lipid. MFE23-ILs showed strong binding with 0.03 to 0.1 mol% inserted lipid.
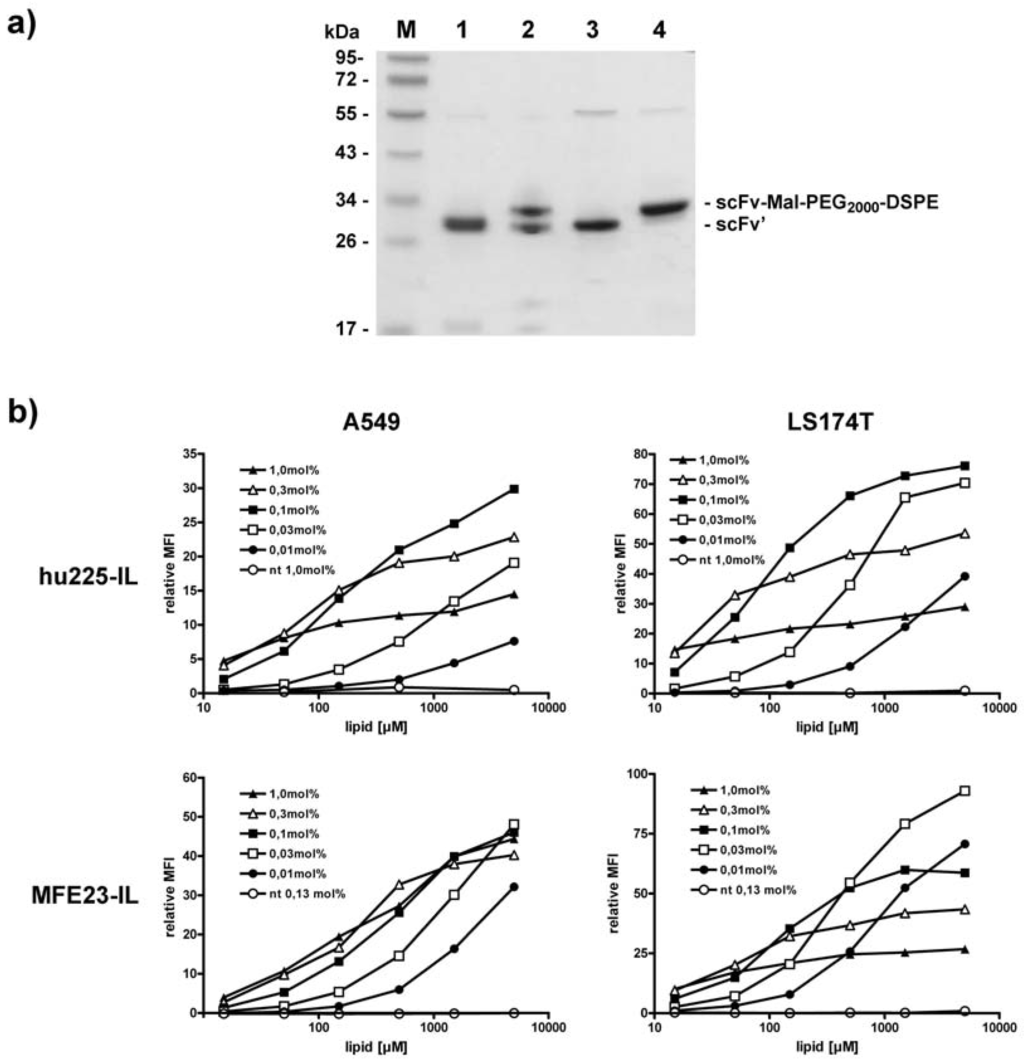
Figure 4.
Generation and analysis of monospecific immunoliposomes. (a) Coupling efficiency of scFv' hu225 and MFE23 to Mal-PEG2000-DSPE was analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. 1, scFv' MFE23; 2, scFv' MFE23 coupled to Mal-PEG2000-DSPE micelles; 3, scFv' hu225; 4, scFv' hu225 coupled to Mal-PEG2000-DSPE micelles; (b) Binding of hu225-IL and MFE23-IL to A549 and LS174T cells.
3.5. Dual-Targeted Immunoliposomes
Because the two scFv' molecules showed different thermal stability, we established a two-step post-insertion protocol for the generation of dual-targeted immunoliposomes, which also allowed to use different amounts of the two antibody-coupled micellar lipids for insertion (Figure 5).
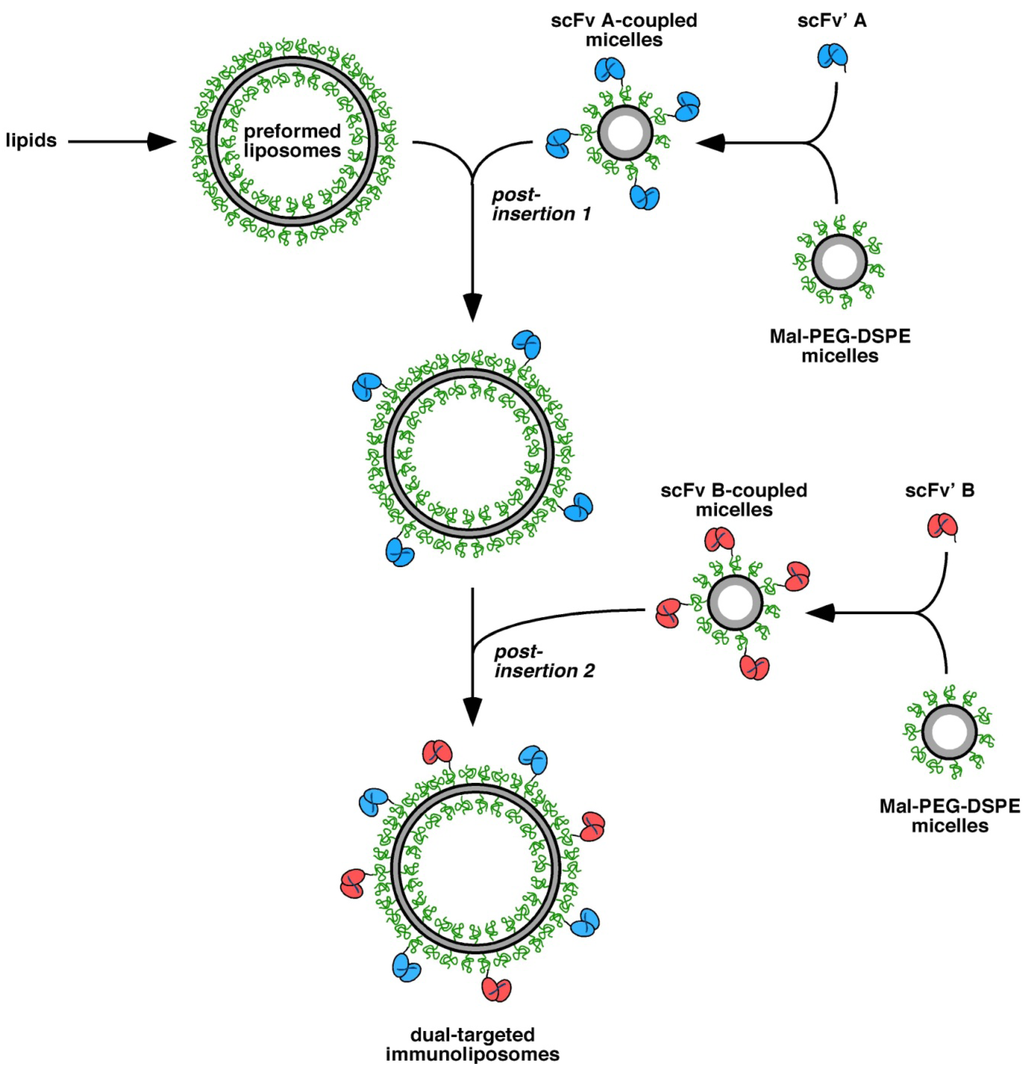
Figure 5.
Schematic presentation of the generation of dual-targeted immunoliposomes applying a two-step post-insertion approach.
In a first step, 0.3 mol% scFv' hu225-coupled lipids were inserted into preformed liposomes at 55 °C for 30 min. In a second step, 0.03 mol% scFv' MFE23-coupled lipids were then inserted into these immunoliposomes at 45 °C for approximately 2 h. Bispecificity of the dual-targeted ILs was confirmed by ELISA. CEA was immobilized onto microtiter plates and subsequently incubated with liposomes followed by soluble EGFR-Fc fusion protein, which was then detected with an anti-Fc antibody (Figure 6). Thus, only liposomes containing anti-CEA and anti-EGFR scFvs in their lipid bilayer are capable of binding both antigens. Accordingly, anti-EGFR-ILs (hu225-IL), anti-CEA-ILs (MFE23-IL) as well as non-targeted liposomes (nt) gave no signals in ELISA, while dt-ILs caused a concentration-dependent increase in ELISA signal.
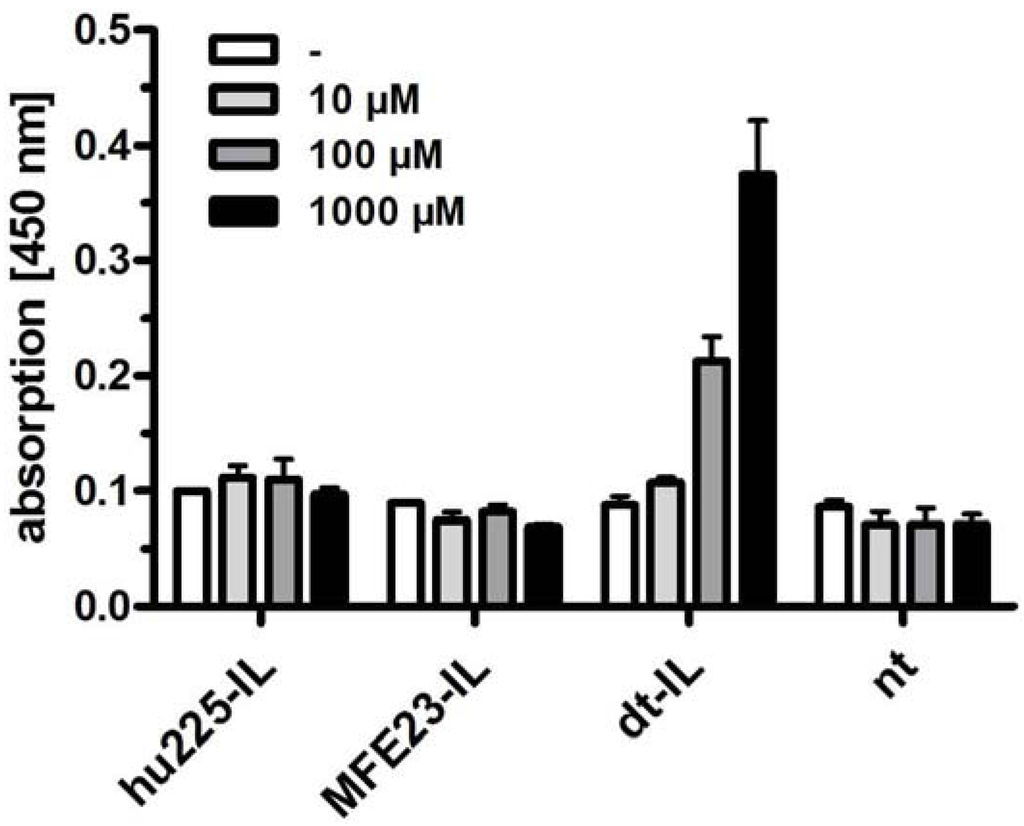
Figure 6.
ELISA analyzing the binding of monospecific ILs (hu225-IL, MFE23-IL), dual-targeted immunoliposomes (dt-ILs) as well as non-targeted liposomes (nt) to immobilized CEA and detection of bound liposomes by incubation with EGFR-Fc and an anti-Fc antibody. Only the dt-ILs caused a signal confirming bispecificity.
The dt-ILs as well as the monospecific ILs were then tested for binding to a panel of different tumor cell lines (Figure 7). Binding of the monospecific ILs correlated with expression of EGFR and CEA on these cell lines. Thus, MFE23-ILs showed strong binding to LS174T, LoVo and A549 cells, while weak binding was seen with MCF-7 and no binding with A431 and SKBR3 cells. Hu225-ILs showed strong binding to all cell lines except MCF-7 for which only a weak binding was observed. Interestingly, the dt-ILs combined the binding activities of the monospecific ILs. Thus, strong binding was observed with all cell lines tested. Signals obtained with the dt-ILs were also concentration-dependent and always similar or slightly better than the signals observed for either hu225-ILs or MFE23-ILs alone.
4. Discussion
The attachment of two different ligands to nanoparticles offers the possibility to combine two target cell specificities within one carrier system. This allows to broaden the specificity for different target cells, thus addressing the inter- but also intratumoral heterogeneity, and to improve delivery of a payload into the tumor. Here, we adopted the post-insertion method routinely used to generate immunoliposomes for the generation of dual-targeted immunoliposomes. The two-step protocol allows to vary the coupling and insertion conditions as well as adapting the amount of inserted antibodies for each specificity. We found that the two antibody fragments used in this study exhibit different thermal stability. Routinely, post-insertion is performed for 30 to 60 min at 55 °C or even higher temperatures, parameters that are mainly influenced by the lipid composition and the phase transition temperature of the preformed liposomes [17,20,37,38]. However, this requires that the ligands are stable under these conditions. Recently, we found that scFv' molecules with melting points below 50 °C can be inserted into PEGylated EPC/Chol liposomes at lower temperatures (37–45 °C) using an extended insertion time of 2 to 24 h. Consequently, we performed insertion of the first scFv' molecule (hu225) at 55 °C for 30 min followed by insertion of the second scFv' (MFE23) at 45 °C for 2 h. Binding experiments confirmed transfer of the scFv molecules into liposomes retaining antigen-binding activity.
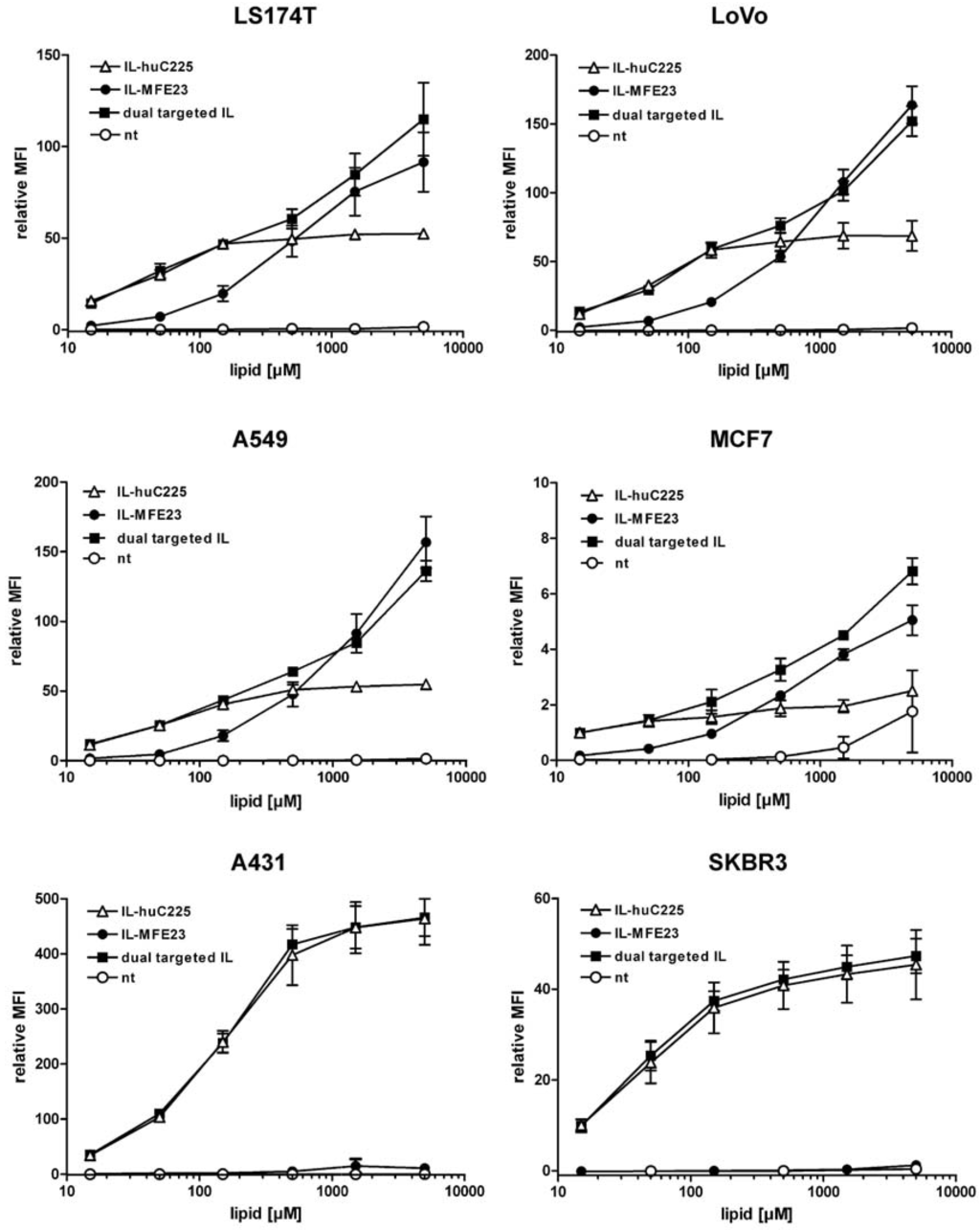
Figure 7.
Flow cytometry analysis of binding of monospecific (hu225-IL, MFE23-IL) and dual-targeted immunoliposomes (dt-IL) to various tumor cell lines (n = 3). Non-targeted (nt) liposomes were included as negative control.
Binding experiments performed with the monospecific immunoliposomes revealed that antigen binding is dependent on the amount of liposomes but also the amount of inserted antibody molecules. Of note, we found that especially at higher lipid concentrations (>100 to 1,000 µM) increased binding was observed using lower antibody concentrations, indicating an optimum antibody concentration in respect to target cell binding. For the two antibody molecules used in this study, this concentration was in the range of 0.03 to 0.3 mol% of inserted scFv-coupled lipid, corresponding to approximately 8 to 80 scFv molecules per liposome (assuming 100% coupling). In the present study, we used different amounts for insertion of the two antibodies, which can be easily adapted by the two-step post-insertion protocol. In our experiments with fluorescent-labeled micelles, we found that even at low ratios of micellar to liposomal lipids, i.e., 0.03 mol% corresponding to approximately 40–50 micellar lipids, the dyes from two different micelles insert into one liposome resulting in liposomes containing both dyes. Assuming an aggregation number of approximately 90 [36,39], this indicates that lipids from one micelle insert into several liposomes.
The prepared dual-targeted immunoliposomes exhibited specific binding to cells expressing either EGFR or CEA, or both antigens. Interestingly, a comparison of the dual-targeted immunoliposomes with the monospecific immunoliposomes did not indicate synergistic or additive binding effects by the presence of both antibodies on one liposome. However, the dual-targeted immunoliposomes always showed the same or a slightly better binding than either one of the monospecific immunoliposomes. This finding clearly shows that the dual-targeted immunoliposomes combine the binding activities of the monospecific immunoliposomes within one liposome. Thus, these dual-targeted immunoliposomes might be suitable to deliver therapeutic payloads to a panel of different tumor cells expressing EGFR and/or CEA. Furthermore, the modular composition and preparation methods allows to use antibodies or other ligands against other targets, for example, receptors and cell adhesion molecules on tumor cells, cancer stem cells, and cells of the tumor microenvironment [40,41,42]. Recently, dual-targeted liposomes were described using folate and the anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody C225 [31]. These dual-targeted liposomes were prepared by a sequential process of DSPE-PEG3350-folate insertion into preformed liposomes followed by coupling of the thiolated anti-EGFR IgG to free maleimide groups of the Mal-PEG2000-DSPE contained within the liposomes. An enhanced targeting selectivity of the dual-targeted liposomes against a cell line expressing EGFR and the folate receptor was reported. In another study, dual-targeted immunoliposomes were generated coupling anti-VCAM1 and anti-E-selectin antibodies to the surface of preformed liposomes [43]. These liposomes demonstrated complementary targeting to activated endothelial cells via IL-1 and TNF-induced transient expression of VCAM1 and E-selectin. Interestingly, in this study an increased binding of the dual-targeted immunoliposomes was observed at a 1:1 ratio of both antibodies, while the attachment of 4- or 8-fold amounts of the anti-E-selectin antibody reduced the binding activity to that observed for the monospecific immunoliposomes. Similar findings were described for dual-targeted immunoliposomes directed against ICAM and ELAM [44]. In this study, it was shown that fluidity of the liposomal membrane influences target cell binding. In another study by the same group using liposomes targeting the cell adhesion molecules ICAM and E-selectin, it was revealed that cooperative binding was also dependent on co-localization of the two cell adhesion molecules within lipid rafts [45]. These findings indicate that several parameters including the ratio and mobility of the two ligands present on dual-targeted liposomes but also the choice and localization of the antigen on the target cells influence cooperative binding and, thus represent parameters for further development and optimization of dual-targeted liposomes.
5. Conclusions
Dual-targeted immunoliposomes directed against two tumor-associated antigens can be generated using recombinant single-chain Fv fragments and applying the post-insertion method to incorporate scFv-coupled PEGylated lipids into preformed liposomes. The step-wise insertion allows to adapt the insertion conditions to the thermal stability of the scFv fragments and to adjust the inserted amounts of antibody for optimal binding. The dual targeted immunoliposomes combine the antigen specificities of the two antibodies allowing targeting of tumor cells expressing either one or both antigens, thus broaden the applicability of immunoliposomes for targeting of different tumor cell types and subtypes.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) and the Deutsche Krebshilfe.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fenske, D.B.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal nanomedicines. Expert Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2008, 5, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malam, Y.; Loizidou, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Liposomes and nanoparticles: Nanosized vehicles for drug delivery in cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.; El-Aneed, A. Properties, engineering and applications of lipid-based nanoparticle drug-delivery systems: Current research and advances. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 1237–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jamal, W.T.; Kostarelos, K. Liposomes: From a clinically established drug delivery system to a nanoparticle platform for theranostic nanomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1094–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabizon, A.; Shmeeda, H.; Grenader, T. Pharmacological basis of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin: impact on cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodle, M.C. Sterically stabilized liposome therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995, 16, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Szebeni, J. Stealth liposomes and long circulating nanoparticles: Critical issues in pharmacokinetics, opsonization and protein-binding properties. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H. Tumor-selective delivery of macromolecular drugs via the EPR effect: Background and future prospects. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Styllanopoulos, T. Delivering nanomedicine to solid tumors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Murray, J.C. Long-circulating and target-specific nanoparticles: Theory to practice. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 283–318. [Google Scholar]
- Bryne, J.D.; Betancourt, T.; Brannon-Peppas, L. Active targeting schemes for nanoparticle systems in cancer therapeutics. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Thanou, M. Targeting nanoparticles to cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Ishida, O.; Takizawa, T.; Moribe, K. Possibility of active targeting to tumor tissues with liposomes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 40, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontermann, R.E. Immunoliposomes for cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2006, 8, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Torchilin, V. Antibody-modified liposomes for cancer chemotherapy. Expert Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2008, 5, 1003–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Iden, D.L.; Allen, T.M. A combinatorial approach to producing sterically stabilized (Stealth) immunoliposomal drugs. FEBS Lett. 1999, 460, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, U.B.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Pickering, E.M.; Hong, K.; Park, J.W.; Shalaby, M.R.; Shao, Y.; Benz, C.C.; Marks, J.D. Therapeutic efficacy of anti-erbB2 immunoliposomes targeted by a phage antibody selected for cellular endocytosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1591, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, P.; Müller, D.; Rüger, R.; Kontermann, R.E. Single-chain Fv immunoliposomes for the targeting of fibroblast activation protein-expressing tumor stromal cells. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerschmidt, S.K.E.; Kolbe, A.; Müller, D.; Knoll, M.; Pleiss, J.; Kontermann, R.E. Novel single-chain Fv' formats for the generation of immunoliposomes by site-directed coupling. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhieng, D.C.; Frost, A.R.; Niwas, S.; Weiss, H.; Grizzle, W.E.; Beeken, S. Intratumoral heterogeneity of biomoarker expression in breast carcinomas. Biotech. Histochem. 2004, 79, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.L.; Polyak, K. Breast tumor heterogeneity: cancer stem cells or clonal evolution? Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2332–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.; Ribeiro, F.R.; Pandis, N.; Andersen, J.A.; Heim, S.; Teixeira, M.R. Intratumor genomic heterogenity in breast cancer with clonal divergence between primary carcinomas and lymph node metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 102, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Cabrero, I.A.; Cotsonis, G.A.; Cohen, C. Intratumoral heterogeneity of immunohistochemical marker expression in breast carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2010, 18, 433–441. [Google Scholar]
- Marusyk, A.; Polyak, K. Tumor heterogeneity: Causes and consequences. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1805, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kontermann, R.E. Dual targeting strategies using bispecific antibodies. mAbs 2012, 4, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laginha, K.; Mumbengegwi, D.; Allen, T. Liposomes targeted via two different antibodies: Assay, B-cell binding and cytotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1711, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante, E.A.; Pickard, J.E.; Rychak, J.; Klibanov, A.; Ley, K. Dual targeting improves microbubble contras agent adhesion to VCAM-1 and P-selectin under flow. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Su, B.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, W.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, C. Enhanced antitumor effect of novel dual-targeted paclitaxel liposomes. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 415103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, B.; Yang, Z. Dual targeting of glioma U251 cells with nanoparticles prevents tumor angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2012. Epup ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Saul, J.M.; Annapragada, A.V.; Bellamkonda, R.V. A dual-ligand approach for enhancing targeting selectivity of therapeutic nanocarriers. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Lima, C.M.; Soares, H.P.; Raez, L.E.; Singal, R. EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control 2007, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Wieduwilt, M.J.; Moasser, M.M. The epidermal growth factor receptor family: Biology driving targeted therapeutics. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1566–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarström, S. The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family: Structure, suggested fucntions and expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1999, 9, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüger, R.; Müller, D.; Fahr, A.; Kontermann, R.E. Generation of immunoliposomes using recombinant single-chain Fv fragments bound to Ni-NTA-liposomes. J. Drug Target. 2005, 13, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastantin, M.; Ananthanarayanan, B.; Karmali, P.; Ruoslahti, E.; Tirrell, M. Effect of the lipid chain melting transition on the stability of DSPE-PEG(2000) micelles. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7279–7286. [Google Scholar]
- Iden, D.L.; Allen, T.M. In vitro and in vivo comparison of immunoliposomes made by conventional coupling techniques with those made by a new post-insertion approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1513, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, T.M.; Sapra, P.; Moase, E. Use of the post-insertion method for the formation of ligand-coupled liposomes. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2002, 7, 889–894. [Google Scholar]
- Arleth, L.; Ashok, B.; Onyuksel, H.; Thiyagarajan, P.; Jacob, J.; Hjelm, R.P. Detailed structure of hairy mixed micelles fomred by phosphatidylcholine and PEGylated phospholipids in aqueous media. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.P.; Weiner, L.M. Monoclonal antibody therapy of cancer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deonarain, M.P.; Kousparou, C.A.; Epenetos, A.A. Antibodies targeting cancer stem cells: A new paradigm in immunotherapy? mAbs 2005, 1, 12–27. [Google Scholar]
- Schliemann, C.; Neri, D. Antibody-based vascular tumor targeting. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010, 180, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, R.C.; Almeda, D.; Augute, D.T. Complementary targeting of liposomes to IL-1a and TNF-a activated endothelial cells via the transient expression of VCAM1 and E-selectin. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9848–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, R.C.; Auguste, D.T. The role of antibody synergy and membrane fluidity in the vascular targeting of immunoliposomes. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, R.C.; Auguste, D.T. Immunoliposomes that targeted endothelium in vitro are dependent on lipid raft formation. Mol. Pharma. 2010, 7, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).