Changes and Driving Factors of Ecological Environment Quality in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China from 2000 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
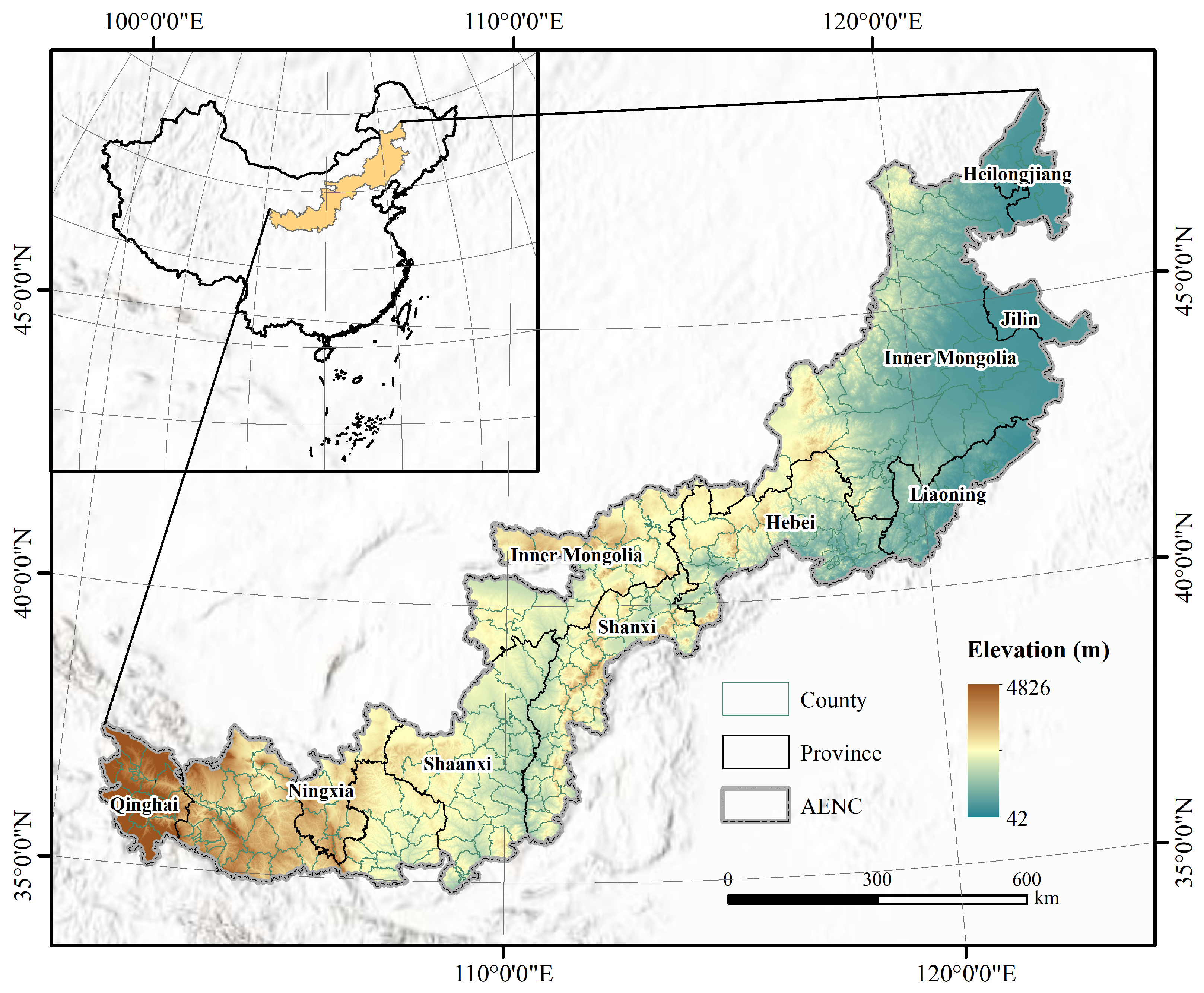
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
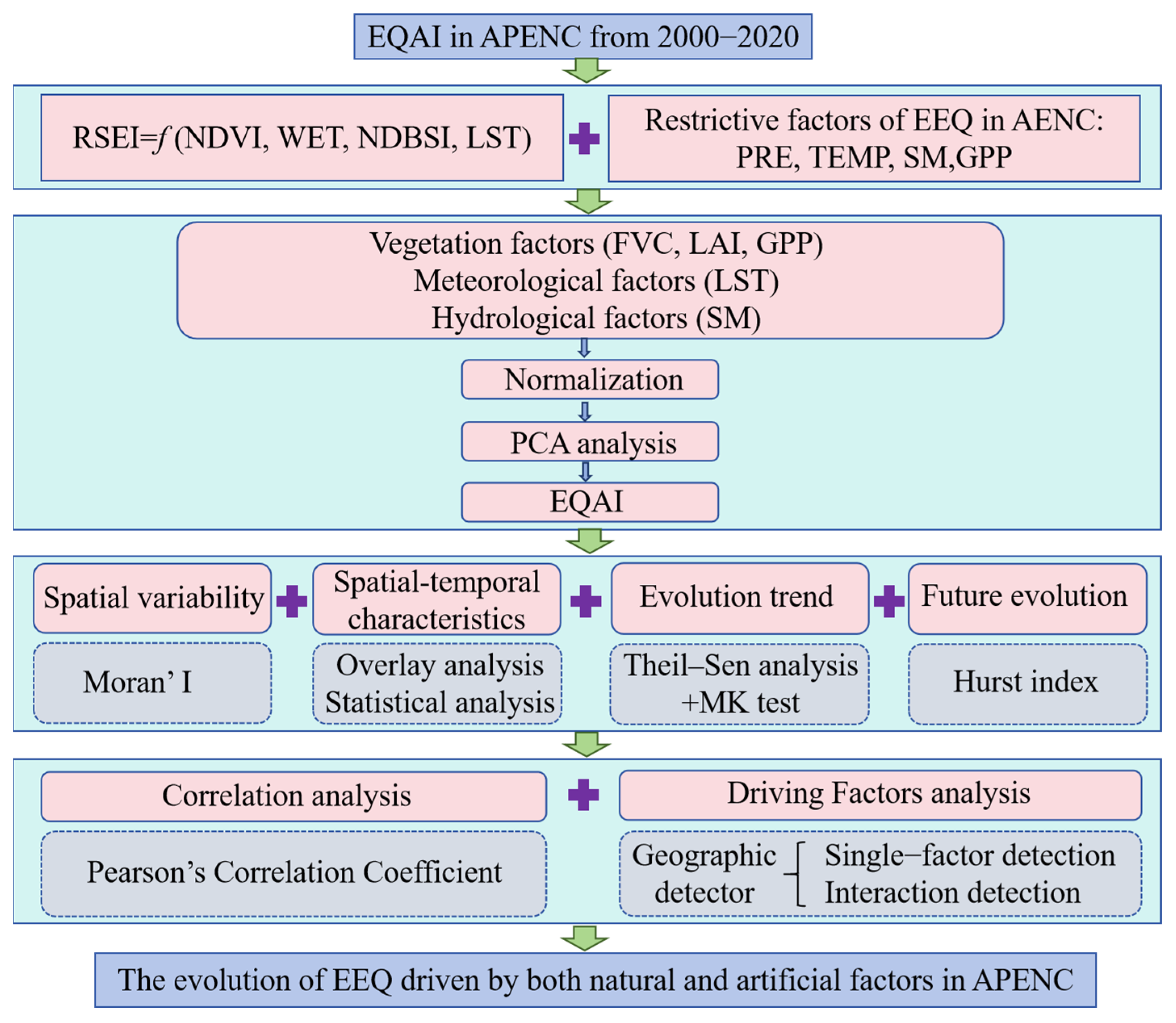
2.3.1. Eco-Environmental Quality Assessment Index (EQAI)
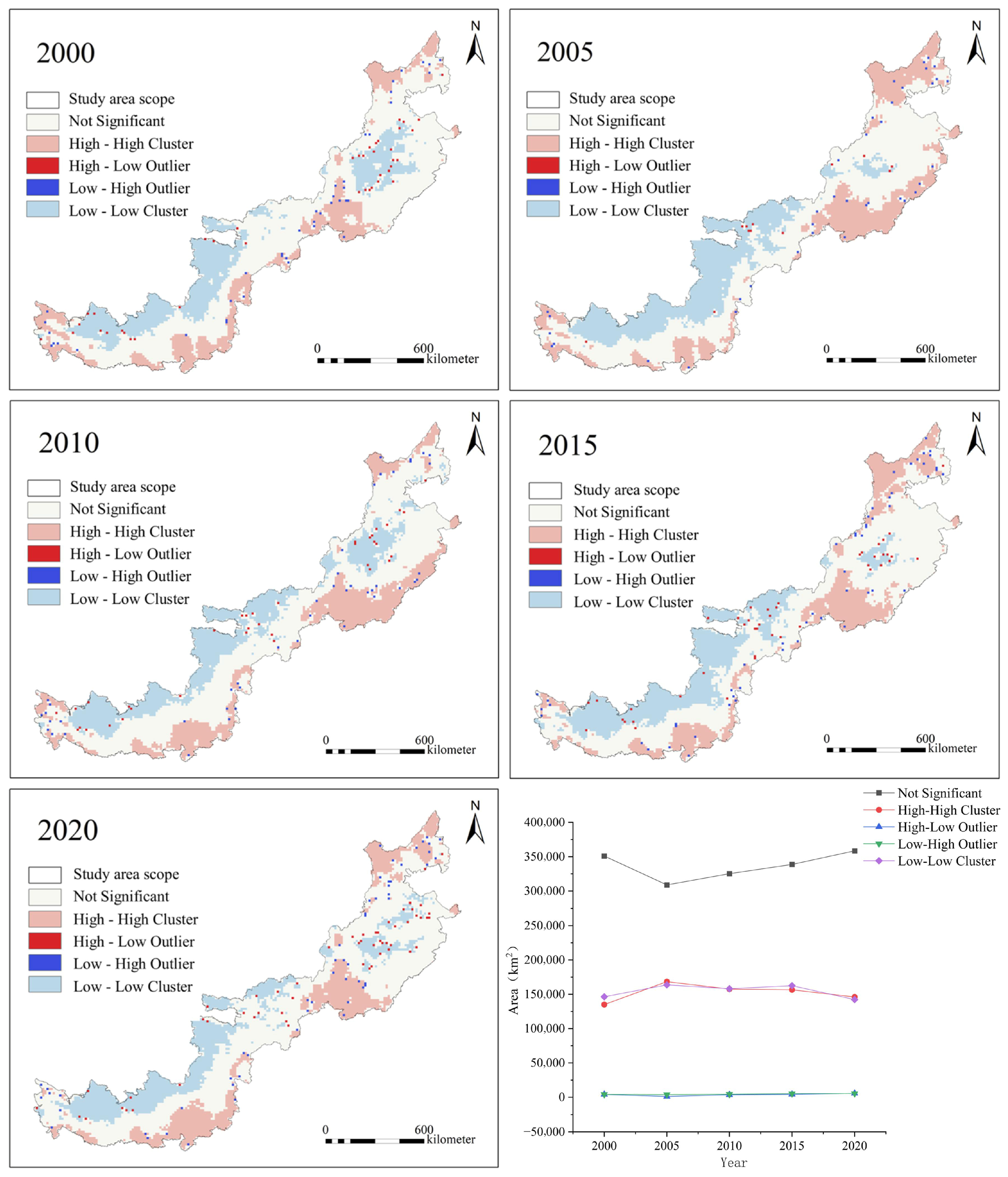
2.3.2. Moran’s I
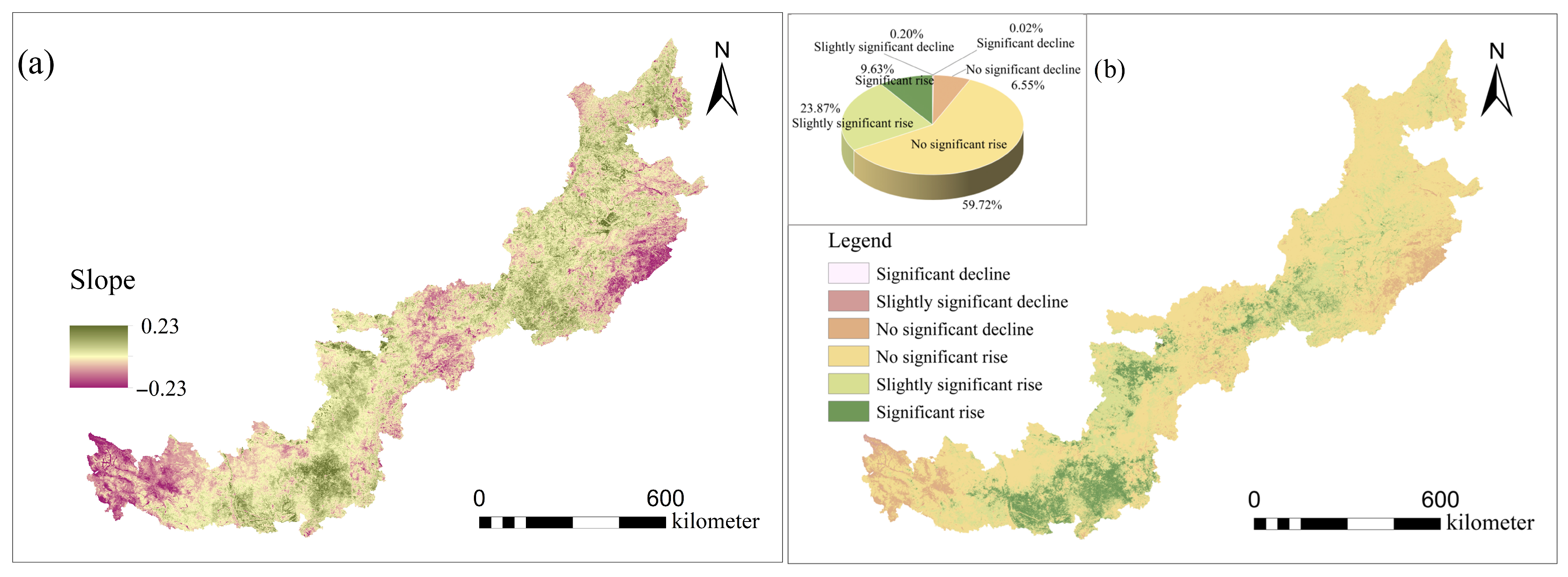
2.3.3. Theil–Sen Slope Estimator and Mann–Kendall Test
2.3.4. Hurst Index
2.3.5. Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient Method
2.3.6. Geographic Detector
- (1)
- Single-factor detection
- (2)
- Interaction detection
2.3.7. Analysis of the Transfer Matrix of LUCC
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of EQAI
3.2. Evolution of EQAI
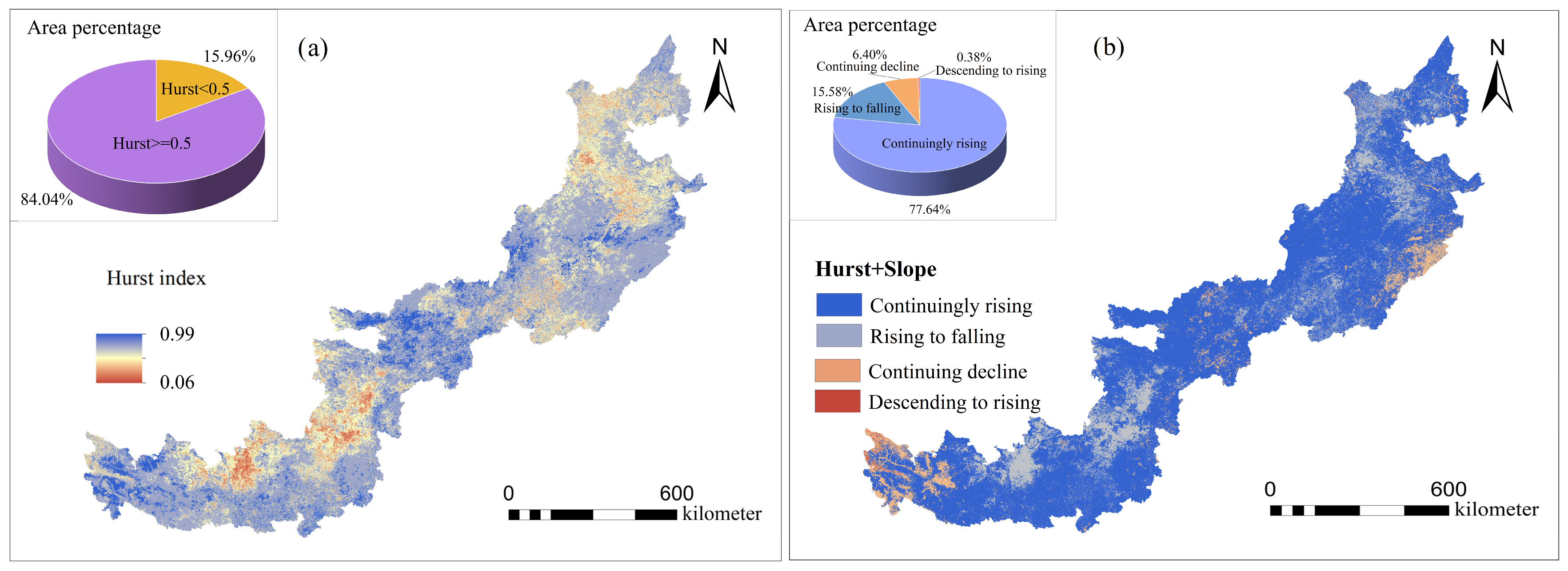
3.3. Changing Trend of EEQ
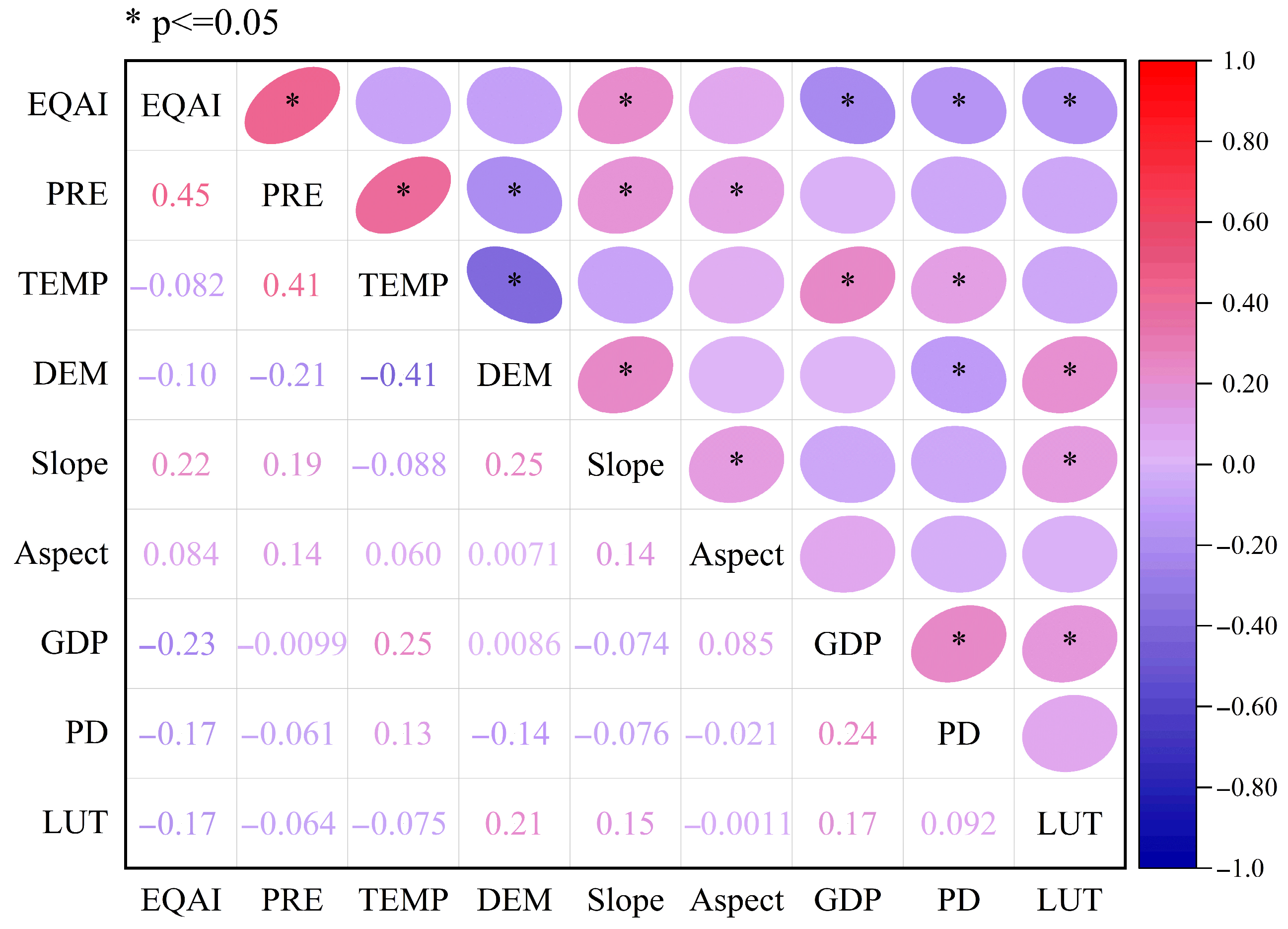
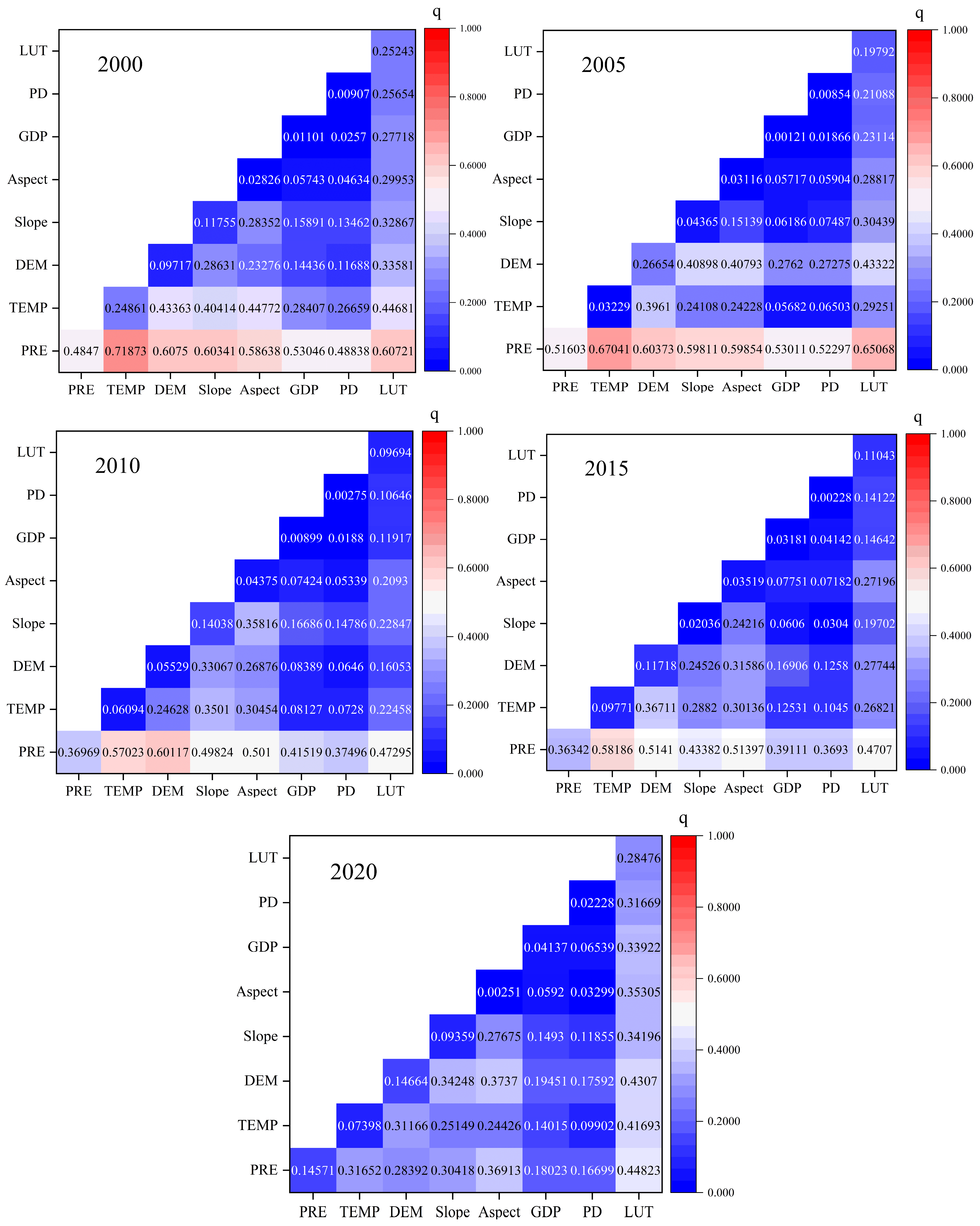
3.4. Influencing Factors of EEQ in the APENC
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution of EQAI in the APENC
4.2. Driving Factors of the EEQ in the APENC
4.3. Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Pei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Revegetation projects significantly improved ecosystem service values in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China in recent 20 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147756–147769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yu, G.; Chen, Z.; Yang, M.; Hao, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Q.; Liu, Z.; Han, L.; et al. Cascade effects of climate and vegetation influencing the spatial variation of evapotranspiration in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 344, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Wang, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal variations in eco-environmental quality and responses to drought and human activities in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China from 1990 to 2022. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, A.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Han, X.; Yang, B. Exploring the long-term vegetation dynamics of different ecological zones in the farming-pastoral ecotone in northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 27914–27932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, Y.; Yin, X.; Alexandrov, G.; Qiu, L. Toward sustainable revegetation in the Loess Plateau using coupled water and carbon management. Engineering 2022, 15, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Wei, F.; Chen, P.; Grünzweig, J. Locating hydrologically unsustainable areas for supporting ecological restoration in China’s drylands. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Jiao, L.; Lian, X.; Wang, W. Linking supply-demand balance of ecosystem services to identify ecological security patterns in urban agglomerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 92, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Liu, C.; Gu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Akhtar, M.; Bashir, B.; et al. A comprehensive framework for evaluating ecosystem quality changes and human activity contributions in Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang, China. Land Use Policy 2025, 151, 107494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, B.; Bayfield, N. Developing sustainability indicators for mountain ecosystems: A study of the Cairngorms, Scotland. J. Environ. Manag. 1998, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fano, E.; Mistri, M.; Rossi, R. The ecofunctional quality index (EQI): A new tool for assessing lagoonal ecosystem impairment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, L. Spatiotemporal distribution and influencing factors of Ulva prolifera and Sargassum and their coexistence in the South Yellow Sea, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1070–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Piao, S.; Myneni, R.; Huang, M.; Zeng, Z.; Canadell, J.; Ciais, P.; Sitch, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; Arneth, A.; et al. Greening of the earth and its drivers. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Jin, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Gu, Z.; Hong, C.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Y. Ecological environment quality assessment based on remote sensing data for land consolidation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Yan, H.; Wu, M.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Cheng, L. Dynamic monitoring and evaluation model for spatio-temporal change of comprehensive ecological quality of vegetation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 6573–6583. [Google Scholar]
- Caccamo, G.; Chisholm, L.; Bradstock, R.; Puotinen, M. Assessing the sensitivity of MODIS to monitor drought in high biomass ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2626–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego, P.; Polyanna da, C.; Dayana, A.; Maryam, I.; Heiko, B.; Luiz, E. Environmental vulnerability index: An evaluation of the water and the vegetation quality in a Brazilian Savanna and Seasonal Forest biome. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Dong, L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Ecosystem Quality in Shule River Basin from 2001 to 2010. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Ye, B.; Jiang, D. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of 11 unheeded metals in sediments of the Chinese Xiangjiang River. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, A.; Zhang, Z. Analysis and research on ecological situation change based on EI value. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2018, 14, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, W. Evaluation of the Spatiotemporal Change of Ecological Quality under the Context of Urban Expansion—A Case Study of Typical Urban Agglomerations in China. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Shi, T.; Hu, X. Detecting Ecological Changes with a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI) Produced Time Series and Change Vector Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Gao, M.; Yu, C.; Gong, E.; Long, H.; Hu, H. Dynamic Monitoring of Environmental Quality in the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2020 Using the Google Earth Engine Platform and the Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yu, K.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ai, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Variation and Drivers of Ecological Quality in Fuzhou Based on RSEI. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Jia, X.; Zhao, Y.; Han, L.; Ma, C.; Bai, Y. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Factors of Ecological Environment Quality on the Loess Plateau in China from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, L.; Fa, K.; Liu, X.; Hou, Z.; Huang, G. A shift in the dominant role of atmospheric vapor pressure deficit and soil moisture on vegetation greening in China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, Z.; An, P. Aridification in a farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China from 2 perspectives: Climate and soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mara, N.; Skonieczny, C.; McGee, D.; Winckler, G.; Bory, A.; Bradtmiller, L.; Malaizé, B.; Polissar, P. Pleistocene drivers of Northwest African hydroclimate and vegetation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Zhao, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yan, J.; Lu, N. Promoting ecological sustainability in the arid farming-pastoral ecotone through optimal water allocation. J. Hydrol. 2025, 652, 132609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y. The trend of vegetation greening and its drivers in the Agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China, 2000–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Tian, W.; Tian, J.; He, C. Contribution of climate change and vegetation restoration to interannual variability of evapotranspiration in the agropastoral ecotone in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabhane, V.; Ramteke, P.; Chary, G.; Patode, R.; Ganvir, M.; Chorey, A.; Tupe, A. Effects of long-term nutrient management in semi-arid Vertisols on soil quality and crop productivity in a cotton-greengram intercropping system. Field Crops Res. 2023, 303, 109115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Sonnenborg, O.; Andreasen, M.; He, C. Effect of ecological restoration on evapotranspiration and water yield in the agro-pastoral ecotone in northern China during 2000–2018. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y. The hidden costs of land use transformation: Ecological degradation in arid and semi-arid areas. J. Arid. Environ. 2025, 230, 105433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Shi, J.; Lv, T.; Zhou, C.; Liu, W. Assessing Changes in Ecosystem Service Values in Response to Land Cover Dynamics in Jiangxi Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, P. Theory and practice of marginal ecosystem management-establishment of optimized ecoproductive paradigm of grassland and farming-pastoral zone of North China. Acta Bot. Sin. 2003, 45, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L. Dynamic Monitoring of Ecological Environmental Quality in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: Disparities Among Central Asian Countries and Analysis of Key Driving Factors. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Gu, L.; Zhao, T. Global Surface Soil Moisture Data Set 1 km Resolution (2000–2020); National Data Center of Tibet Plateau: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Deng, X.; Ren, C.; Deng, M.; Wang, S.; Lai, X.; Long, A. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Trends of Ecological Environment Quality and Influencing Factors in Xinjiang Oasis. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, H.; Huang, N.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ding, Z.; Xie, J. A comprehensive assessment of MODIS-derived GPP for forest ecosystems using the site-level FLUXNET database. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5907–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Chen, S.; Su, H. Climate dynamics of the spatiotemporal changes of vegetation NDVI in northern China from 1982 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I. Pearson correlation coefficient. In Noise Reduction in Speech Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, W. Using the geodetector method to characterize the spatiotemporal dynamics of vegetation and its interaction with environmental factors in the qinba mountains, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, F.; Xu, C.; Li, B.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z. Evaluating the suitability of urban development land with a Geodetector. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geographic Detector: Principles and Prospects. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Ye, Z.; Li, Z. Anomaly detection based on a dynamic Markov model. Inf. Sci. 2017, 411, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horion, S.; Cornet, Y.; Erpicum, M.; Tychon, B. Studying interactions between climate variability and vegetation dynamic using a phenology based approach. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 20, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Tian, J.; Gao, B.; Zhao, Y. Differentiating climate and human-induced drivers of grassland degradation in the Liao River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Anthropogenic contributions dominate trends of vegetation cover change over the farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, L. Vegetation Degradation and Its Driving Factors in the Farming–Pastoral Ecotone over the Countries along Belt and Road Initiative. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloat, L.; Gerber, S.; Samberg, H.; Smith, K.; Herrero, M.; Ferreira, L.; Godde, M.; West, C. Increasing importance of precipitation variability on global livestock grazing lands. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mu, S.; Sun, Z.; Gang, C.; Li, J.; Padarian, J.; Groisman, P.; Chen, J.; Li, S. Grassland carbon sequestration ability in China: A new perspective from terrestrial aridity zones. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 69, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowll, W.; Blumenthal, D.; Cherwin, K.; Smith, A.; Symstad, A.; Vermeire, L.; Collins, S.; Smith, M.; Knapp, A. Climatic controls of aboveground net primary production in semi-arid grasslands along a latitudinal gradient portend low sensitivity to warming. Oecologia 2015, 177, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.; Lin, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Grassland degradation remote sensing monitoring and driving factors quantitative assessment in China from 1982 to 2010. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, E.; Webber, H.; Asseng, S.; Boote, K.; Durand, J.; Ewert, F.; Martre, P.; MacCarthy, D. Climate change impacts on crop yields. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, X. Human-induced grassland degradation/restoration in the central Tibetan Plateau: The effects of ecological protection and restoration projects. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Sun, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, K. Effects of climate change and anthropogenic activity on the vegetation greening in the Liaohe River Basin of northeastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Kappas, M.; Wyss, D.; Wang, C.; Putzenlechner, B.; Thi, N.; Chen, J. Assessment of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Development in Northeast China. Sensors 2022, 22, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Yu, D.; Georgescu, M.; Han, Z.; Wu, J. Impacts of land use and land cover change on regional climate: A case study in the agro-pastoral transitional zone of China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chang, Q.; Jia, K.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, T. Temporal-spatial variability of desertification in an agro-pastoral transitional zone of northern Shaanxi Province, China. Catena 2012, 88, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ling, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Hao, J.; et al. Dynamic Monitoring and Analysis of Ecological Environment Quality in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas Based on a Modified Remote Sensing Ecological Index (MRSEI): A Case Study of the Qilian Mountain National Nature Reserve. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batunacun Ralf, W.; Tobia, L.; Claas, N. Using Shapley additive explanations to interpret extreme gradient boosting predictions of grassland degradation in Xilingol, China. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 1493–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Chen, L.; Shankman, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Excessive reliance on afforestation in China’s arid and semi-arid regions: Lessons in ecological restoration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 104, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, G.; Liu, G. Afforestation may accelerate the depletion of deep soil moisture on the Loess Plateau: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3829–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Jin, S.; Chen, J.; Li, T. Evolution and Driving Forces of Ecological Service Value in Anhui Based on Landsat Land Use and Land Cover Change. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Factors | Driving Types | Data Type | Index | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Time Period | Data Sources/ References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Driving Factors | Internal factor | Vegetation factors | Vegetation coverage (FVC) | 500 m | 8 days | June–September in 2000–2020 | NASA (https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/, accessed on 5 June 2024) |
| Leaf area index (LAI) | |||||||
| Gross primary productivity (GPP) | |||||||
| Meteorological factors | Precipitation (PRE) | 1000 m | Monthly | 2000–2020 | China National Qinghai– Tibet Plateau Data Center | ||
| Air temperature (TEMP) | |||||||
| Land surface temperature (LST) | |||||||
| Hydrological factors | Soil moisture (SM) | ||||||
| Artificial Driving Factors | External factor | Geographical factors | Digital elevation model (DEM) | 90 m | Yearly | China National Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Data Center/(Zheng et al., 2022 [37]) | |
| Slope and aspect | |||||||
| Land use type (LUT) | 30 m | China Land Cover Dataset/(Yang et al., 2021 [38]) | |||||
| Social and economic factors | Gross domestic product (GDP) | 1000 m | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.Geodata.cn/, accessed on 5 June 2024) | ||||
| Population density (PD) |
| Criterion of Interval | Interaction |
|---|---|
| q(X1∩X2) < Min[q(X1), q(X2)] | Nonlinear weakening |
| Min[q(X1), q(X2)] < q(X1∩X2) < Max[q(X1), q(X2)] | Single-factor nonlinear weakening |
| q(X1∩X2) > Max[q(X1), q(X2)] | Dual-factor enhancement |
| q(X1∩X2) = q(X1) + q(X2) | Independence |
| q(X1∩X2) > q(X1) + q(X2) | Nonlinear enhancement |
| Year | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 0.7717 | 0.8367 | 0.7853 | 0.7760 | 0.7557 |
| Variance | 0.000037 | 0.000037 | 0.000037 | 0.000037 | 0.000037 |
| z-score | 126.4087 | 137.0467 | 128.6455 | 127.1068 | 123.7980 |
| p value | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Driving Factor | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q Value | Sequence | q Value | Sequence | q Value | Sequence | q Value | Sequence | q Value | Sequence | |
| PRE | 0.4084 | 1 | 0.6182 | 1 | 0.3940 | 1 | 0.3931 | 1 | 0.3532 | 1 |
| TEMP | 0.1797 | 2 | 0.0996 | 3 | 0.0646 | 3 | 0.1064 | 2 | 0.0946 | 2 |
| DEM | 0.0702 | 4 | 0.1691 | 2 | 0.0634 | 4 | 0.0755 | 3 | 0.0476 | 5 |
| Slope | 0.1341 | 3 | 0.0687 | 4 | 0.0870 | 2 | 0.0709 | 4 | 0.0769 | 3 |
| Aspect | 0.0008 | 6 | 0.0010 | 7 | 0.0014 | 7 | 0.0010 | 8 | 0.0014 | 8 |
| LUT | 0.0211 | 5 | 0.0243 | 5 | 0.0324 | 5 | 0.0368 | 5 | 0.0500 | 4 |
| GDP | 0.0000 | 8 | 0.0001 | 8 | 0.0003 | 8 | 0.0012 | 7 | 0.0028 | 7 |
| PD | 0.0006 | 7 | 0.0015 | 6 | 0.0085 | 6 | 0.0170 | 6 | 0.0066 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X. Changes and Driving Factors of Ecological Environment Quality in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China from 2000 to 2020. Land 2025, 14, 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122309
Yang S, Zhao M, Zhao M, Zhang Q, Liu X. Changes and Driving Factors of Ecological Environment Quality in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China from 2000 to 2020. Land. 2025; 14(12):2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122309
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shuqing, Ming Zhao, Maolin Zhao, Qiutong Zhang, and Xiang Liu. 2025. "Changes and Driving Factors of Ecological Environment Quality in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China from 2000 to 2020" Land 14, no. 12: 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122309
APA StyleYang, S., Zhao, M., Zhao, M., Zhang, Q., & Liu, X. (2025). Changes and Driving Factors of Ecological Environment Quality in the Agro-Pastoral Ecotone of Northern China from 2000 to 2020. Land, 14(12), 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122309





