Abstract
Agriculture in Africa is not only exposed to climate change impacts but is also a source of greenhouse gases (GHGs). While GHG emissions in Africa are relatively minimal in global dimensions, agriculture in the continent constitutes a major source of GHG emissions. In Ghana, agricultural emissions are accelerating, mainly due to ensuing deforestation of which smallholder cocoa farming is largely associated. The sector is also bedevilled by soil degradation, pests, diseases and poor yields coupled with poor agronomic practices. Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) thus offers a way to reduce the sector’s GHG emissions and to adapt the sector to the adverse impacts of climate change. This study assesses the potential of CSA vis-à-vis conventional cocoa systems to enhance production, mitigate and/or remove GHG emissions and build resilience, in addition to understanding key determinants influencing CSA practices. Using a mixed methods approach, data was collected in Ghana’s Juabeso and Atwima Mponua districts through semi-structured household questionnaires administered to 80 household heads of cocoa farms, two focus group discussions and expert interviews. A farm budget analysis of productivity and economic performance for both scenarios show that CSA practitioners had a 29% higher income per ha compared to the conventional farmers. Estimations using the FAO Ex-Ante Carbon-Balance Tool (EX-ACT) indicate CSA practices preserve forest resources without which the effect on carbon balance as presented by conventional farming would remain a source of GHG emissions. Farm tenure, age of farmers, location of farm, residential status and access to extension services were the main determining factors influencing CSA practices among cocoa farmers. An in-depth understanding of these indicators can help identify ways to strengthen CSA strategies in the cocoa sector and their contributions to climate change mitigation and resilience.
Keywords:
climate smart agriculture; resilience; carbon balance; cocoa; mitigation; Ghana; Ex-ACT; agroforestry 1. Introduction
Agriculture is the primary source of livelihood in many African countries, employing more than 60% of the population and often the largest contributor to Gross Domestic Product [1,2].
Yet the sector faces various challenges including market system failures and trade barriers, unstable and ineffective socio-economic policies, poor information, infrastructural and financial accessibility, increasing population pressure and resources scarcity, unsustainable agronomic practices and environmental degradation [3,4]. These challenges are further compounded by the effects of climate variability and change as the sector is mainly rain-fed and climate dependent [2,5]. Thus, agriculture in Africa remains one of the most vulnerable sectors to climate variability and change.
Yet African agriculture is not only exposed to climate change impacts but can also be a source of greenhouse gases [6]. Although in global dimensions, GHG emissions in Africa are relatively minimal, a key concern is that major parts of these emissions emanate from the agriculture sectors with high growth rates [7]. For instance, between 1990 and 2014 annual agricultural emissions from Africa increased by 46.4% from 569.3 to 833.6 Megatonnes of Carbon dioxide equivalents (Mt CO2e) making up nearly 16% of global agricultural emissions over the period [7]. As many African economies like Ghana expand, it is crucial to initiate measures to reduce emissions from the agricultural sector while adapting the sector to the impacts of climate change.
Ghana’s agriculture is the second largest contributor to total national GHG emissions, constituting approximately 38%, only after the energy sector’s 41% [8]. Moreover, agricultural emissions in Ghana are growing at a faster rate, considering trends between 1990 and 2006, of 44.2% as opposed to a 39% growth rate of energy sector emissions [8]. Although cocoa production is the most important economic activity in Ghana’s agriculture sector, it is associated with significant contributions to national agricultural GHG emissions [9,10]. The expansion of cocoa cultivation into the high forest zones in the 1990s in order to increase national production levels has resulted in biodiversity loss, massive forest degradation and associated GHG emissions [11,12].
Furthermore, the Ghanaian cocoa landscape is plagued with ecological problems such as declining soil fertility, high incidence of pests and diseases and high exposure to droughts and temperature extremes, coupled with poor agronomic practices and inadequate farm maintenance by characteristically aged farmers [13,14]. Yields are estimated to be 350 kg/ha on average and are far lower than other major producing countries like Cote d’Ivoire with an average yield of 800 kg/ha and Malaysia’s 1700 kg/ha [15]. Consequently, livelihood conditions of many of the approximately 800,000 smallholder cocoa farmers [16] have deteriorated over the decades with lower returns from cocoa farming leaving them impoverished [17].
Despite high commitments to meeting its objectives, the state-owned Ghana Cocoa Board (COCOBOD) charged with nationwide sustainability of the sub-cocoa sector, is yet to achieve necessary synergies between emerging socio-economic and environmental trade-offs such as increasing productivity/income vis-à-vis reducing extensive cultivation and deforestation. To address the challenges of adapting the cocoa sector to climate change and reducing the sector’s emissions, Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) is increasingly being promoted especially for cocoa production in Ghana [10,18,19]. CSA integrates economic, social and environmental dimensions of sustainable development to build on three main pillars as follows: (1) sustainably increasing agricultural productivity and incomes; (2) adapting and building resilience to climate change and; (3) reducing and/or removing greenhouse gases emissions relative to conventional practices [4]. Hence, the World Bank programme to reduce emission from deforestation and forest degradation (REDD+) is strongly focused on cocoa and expected to drive sustainability in the sector post 2016 [10,20]. However, a majority of the predominant smallholder cocoa farmers still employ conventional methods of production [10,21]. Antwi-Agyei et al. (2013) [22] attribute this situation to the limited understanding of the barriers to effective implementation of adaptation strategies faced by farm households across sub-Saharan Africa.
Furthermore, knowledge on the extent to which existing agricultural practices are climate smart in terms of increasing productivity/income and building resilience does not exist. There is thus a need to identify factors that contribute to livelihood resilience, which has been characterized to encompass buffer capacity (as portrayed by livelihood capitals and their dynamics) and actors’ capacity to self-organise and to learn [23]. There is also no information on the conditions and factors that influence climate-smart cocoa practices. Thus, we aim to analyse the potential of cocoa farming systems to maintain or enhance cocoa production, reduce and/or remove GHG emissions and build resilience. Further, we aim to identify and analyse the factors that influence CSA practices from the individual and household as well as the institutional and policy perspectives. We therefore seek to answer the following questions: What is the level of increase in productivity, farm income and GHG balance due to CSA practices compared to conventional cocoa production? What factors influence CSA practices in cocoa farming systems in Ghana?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Area
The cocoa landscapes of Juabeso and Atwima Mponua districts in the Western and Ashanti regions respectively (Figure 1) were selected for this study. These sites were considered suitable primarily because of the predominance of smallholder cocoa farming households, engaging in either ‘business-as-usual’ or improved cocoa farming systems based on scientific recommendations. The area also embodies successful implementation of major voluntary standards and certification schemes in Ghana including Rainforest Alliance (RA) and UTZ certified (an abbreviation for “Utz Kapeh”: ‘Good Coffee’ in the Mayan Quiché language; global certification program for sustainable coffee, cocoa and tea production) [24]. While conventional farming systems are common in each district, the presence of the Rainforest Alliance certified Climate Cocoa Project in Juabeso and Organic Cocoa Project in the Atwima Mponua Districts represent essential classifications that allowed the study to explore and compare different dimensions to adoption and practices of CSA, as well as determinant factors in different locations.
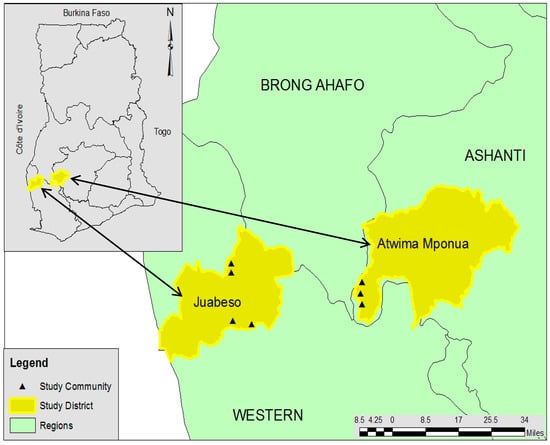
Figure 1.
Map of the Study Area (Source: Authors (2015)). The Juabeso district is in the Western Region of Ghana while the Atwima Mponua district is located in the Ashanti Region. The characteristics of both regions are displayed in Table 1.
The study area is composed of a rural population of which growth rates reflect high immigration mainly by migrant cocoa farmers who are estimated to own about 70% of cocoa farms in the districts [9,24]. The Juabeso district is host to the Krokosua Hills forest reserve, which is one of the remaining forest patches surrounded by vast areas of low or no shade cocoa farms with negative implications for biodiversity and ecosystem services [9]. Similarly, encroachment also threatens the forest reserves in Atwima Mponua district, which cover over half of the land area making it one of the biggest forest reserves in Ghana [30].
Recognised as very productive, Juabeso district is a hub of recent cocoa expansion, illegal logging and associated encroachment into protected areas [9,29]. Bush fires are frequent in the dry seasons resulting from the activities of farmers practicing slash and burn, as well as from hunting and palm wine tapping activities [25]. With annual deforestation rate of 2.2% compared to a 2% per annum national rate, land, forest, wildlife and water resources remain under threat of degradation [31].
2.2. Data Collection
Data for the study was collected using a mixed methods approach. Semi-structured household questionnaires were administered to 80 household heads of cocoa farms to elicit information on household characteristics and farm management in the two study areas. In addition, two Focus Group Discussions (FGDs), each targeting cocoa farmers in the respective districts were conducted to explore perceptions about climate change and cocoa production as well as factors influencing adoption of CSA practices. The FGDs helped to verify and build consensus on conflicting data. Lastly, interviews with selected experts provided further data on the study area. These various sources also served to triangulate collected data.
In each study area, two categories of cocoa farmers were identified, namely, farmers practicing conventional models of cultivation and those engaged in CSA/Agroecology as illustrated in Table 2 below. CSA/Agroecology farming systems were selected from the cocoa certification projects by the RA or AgroEco Louis Bolk Institute. Following this stratification, 20 farmers were selected under each of the categories in each location of the study. Four communities were randomly selected in each location. These included Anasu, Pasoro, Gyereso and Wurubegu in the Atwima Mponua District and Cashiekrom, Komeamaa, Breman and Addaekrom in the Juabeso district, from which five respondents under each stratum of conventional and CSA/Agroecology farming categories were respectively selected.

Table 2.
Characteristics of CSA/Agroecology juxtaposed Conventional Practices in Ghana.
Asare (2014) outlines the following justification by experts and practitioners for recommended CSA/Agroecology practices over conventional practices: During land preparation, leaving cleared weeds to mulch increases soil organic carbon via decomposition and improves soil fertility, avoiding emissions associated with burning in the context of conventional practices. Planting hybrid seedlings increases yield as well as disease resistance, while applying recommended fertilizer regime not only significantly increases yield but also increases root and shoot growth of cocoa causing enhancement of soil carbon stocks. Applying pesticides four times per year, if needed, helps control black pod, other fungal diseases and pests affecting cocoa. Grafting, lining and pegging seedlings at a three square meter spacing reduces intra cocoa competition associated with planting at stake and enhances yield. Allowing natural regeneration and planting shade trees lead to modest carbon sequestration, while planting cocoa under forest-tree or shade produces no emissions from clearing. Weeding regimes reduce competition for soil nutrients, enhances carbon sequestration from cocoa and shade growth. Pruning practices improve cocoa growth and reduces incidence of pest and diseases thereby ensuring healthy cocoa and greater resilience. Cocoa intensification as production strategy ensures higher resource efficiency, climate adaptation and mitigation co-benefits in contrast to extensive practices.
One community representing each study district was selected for a Focus Group Discussion. Anansu and Komeamaa communities were selected in Atwima Mponua and Juabeso districts respectively. In each case, the groups were limited to a randomly selected sample of 10 participants to enable effective facilitation.
We interviewed one targeted expert each from the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA), Rainforest Alliance (RA) and Nature Conservation Research Centre (NCRC). These institutions were considered due to their technical know-how on the theme of this paper and also due to convenience and resource constraints.
2.3. Data Analysis
Statistical software (SPSS and STATA) were used to analyse quantitative data on productivity, income and factors framing CSA practices. Qualitative data from focus group discussions and expert interviews were analysed using content analysis. The FAO Ex-Ante Carbon Balance Tool (EX-ACT) was used to estimate climate change mitigation potentials of the two farming systems.
2.3.1. Farm Budget Analysis
A farm budget analysis was carried out for both conventional and CSA/Agroecology farming categories. This was to assess respective levels of productivity in average yield per hectare (ha) and economic performance through average income per hectare expressed in Ghana Cedis per hectare (GHS/ha). To realise this, income indicators such as Gross Output Value and Total Production Cost were calculated and set in the function below.
Income (I) = Gross Output Value (GOV) − Total Production Cost (TPC)
The GOV is defined as the total value of cocoa and associated intercrops harvested per hectare over the 2014/2015 farming season. For the purpose of this study, fixed costs were held as a constant factor and TPCs were therefore limited to total variable costs incurred during the same season consisting of variables such as costs for labour (both hired and permanent), pesticides and herbicides, farm maintenance (pruning, weeding etc.), harvesting (pod plucking and breaking), post-harvest (drying and bagging) and transportation.
2.3.2. Estimation of Greenhouse Gases as Part of Natural Capital
The FAO Ex-Ante Carbon-Balance Tool (EX-ACT) was used for the estimation of GHGs emission and/or sequestration from farming systems (conventional and CSA/Agroecology). The EX-ACT is a land-based accounting system for measuring the impact of agriculture, forestry and other land use on carbon (C) stocks, stock changes per unit land and methane (CH4) and Nitrogen oxide (N2O) emissions expressed in tonnes per hectare of carbon dioxide equivalent (t CO2-eq/ha) [32]. The difference between two scenarios; with or without project interventions, which in the study’s context is considered as with or without CSA/Agroecology intervention, defines the C balance, which is the main output of the tool.
2.3.3. Logistic Regression for Identifying Factors Framing CSA/Agroecology Practices
A binomial logistic regression was used to identify factors framing CSA/Agroecology practices among cocoa farmers in the study area. The logistic model was estimated using the following equation:
where is the dependent variable measured as a dummy, 1 if farmer practiced CSA/Agroecology, 0 if farmer practiced conventional farming; is the constant term; to represent the coefficients of the explanatory variables; and the error term. In relation to the following a priori expectations as presented in Table 3, the coefficients were estimated using STATA software [33].

Table 3.
A Priori Expectations for Explanatory Variables.
2.3.4. Content Analysis
Qualitative data that was collected in focus group discussions and expert interviews were analysed via content analysis. Voice recordings obtained via these processes were transcribed and manually synthesised to retrieve information to complement the quantitative data.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Socio-Economic Characteristics of Household Respondents
Demographic and socio-economic characteristics considered include age, gender, education, household size, farm tenure, number of farms and size, among others (Table 4). The age of respondents ranged from 24 to 75 years with a mean of 45 and modal age of 40 years, whereas 63% of respondents were male. On average, farming experience (number of years engaged in cocoa farming) was about 18 years. Table 4 shows a similar distribution of farmers with primary education while those with secondary education are more among the CSA/agroecology farmers.

Table 4.
Characteristics of Cocoa Farming Household Respondents.
The average number of persons per household is 8 persons. About 72% of respondents employ both household and hired labour. Average farm size cultivated is 2.7 ha with conventional farming having the largest farm size (8 ha) in the range. With respect to farm tenure, 69% of the farmers own their farms while 20% managed family farms and 11% operated as share croppers under equal share of proceeds (abunum) agreements. However, 60% of farmers interviewed had access to only one cocoa farm and 29% operated 2 different cocoa farms while 11% operated 3 to 4 cocoa farms. In general, 59% of the respondents were members of farmer organizations but only 23% of conventional farmers belonged to a farmer organization compared to 95% of farmers in CSA/Agroecology with membership in at least one farmer organization. Furthermore, 64% of respondents who had access to extension services in the previous farming season (2014/2015) comprised 90% and 38% of CSA and conventional farmers respectively.
Further, only 10% and 13% of respective farmers under conventional and CSA/Agroecology categories had access to farm credits, which made up 11% of respondents who obtained access to credit. Despite the government’s support with free cocoa fertilizer distribution and free pests and disease control exercises, 71% of respondents claimed no access to farm inputs in the previous (2014/2015) farming season. Only 15% of conventional farmers had access to pesticides and fertilizer compared to 43% CSA/Agroecology farmers.
3.2. Assessing Productivity, Income and Resilience as Dimensions of CSA/Agroecology
3.2.1. Farm Production Input and Costs
Farm investments in inputs and other costs incurred for cocoa production in the 2014/2015 farming season links to the value of assets at the disposal of cocoa farmers. Cocoa production costs per hectare (Table 5) ranged from GHS 65 (USD 17) in the conventional category to GHS 1962 (USD 516) in CSA/Agroecology with an overall mean of GHS 715 (US $188). Averages of total production costs (without fixed costs) per hectare for Conventional and CSA/Agroecology practices were GHS 621 (USD 163) and GHS 920 (USD 242) respectively. Labour constituted the largest cost component in both categories representing 42% and 51% of total cost respectively.

Table 5.
Share of Average Cocoa Production Costs in Ghana Cedis per Hectare (GHS/Ha).
3.2.2. Farm Productivity of Cocoa
A total average yield of 432 kg/ha was achieved for the entire study area. Average yield per hectare for the whole study area was 37% higher in CSA/agroecology (500 kg/ha) than in conventional farming (363 kg/ha). We use the difference between CSA/Agroecology and conventional cocoa yields as an indicator of resilience. The performance of CSA/agroecology in Juabeso and Atwima Mponua indicates 50% and 22% improvements in productivity and by extension improvements in resilience compared to respective cases of conventional cocoa. In CSA/Agroecology, yields in both Juabeso and Atwima Mponua were 594 kg/ha and 406 kg/ha respectively. Conventional cocoa yields in Juabeso and Atwima Mponua were 394 kg/ha and 332 kg/ha respectively. Independent sample t-test of yields showed a significant difference between yields from CSA/Agroecology and conventional farming (t(78) = −3933, p = 0.000), with yields from CSA/Agroecology being higher than yields from conventional farming.
3.2.3. Value of Produced Cocoa
With reference to the producer price of cocoa as set by Ghana’s cocoa governing institution (COCOBOD) for the 2014/2015 farming season of GHS 5.47 (USD 1.4) for 1 kg (Ministry of Finance 2014) and additional 3.5% premium paid for organic cocoa beans, the value of cocoa output per hectare ranged from GHS 1050 (USD 276) to GHS 6394 (USD 1683) with a mean of GHS 2382 (UD $627). Farmers practicing CSA/Agroecology produced higher output per hectare with an average value of GHS 2786 (USD 733) compared to GHS 1978 (UD $521) for conventional cocoa.
3.2.4. Farm Income from Cocoa and Non-Cocoa Farm Production
Considering farm productivity and value of output, respondents in the study generally made profits for the 2014/2015 farming season, indicating improvement in their buffer capacity (resilience) with results (Table 6) showing an average income per hectare of GHS 1726 (USD 454). With farm sizes averaging 2.7 hectares, farmer income from cocoa production for the season ranged from GHS 658.40 (UD $173) to GHS 5865 (USD 1543) per hectare. CSA/Agroecology farmers earned higher incomes with a mean of GHS 1983 (USD 522) per hectare, 29% above that of conventional farmers’ (GHS 1470 (UD $387)).

Table 6.
Average Farm Size in Hectares and Income Indicators in Ghana Cedis per Hectare (GHS/Ha).
With these mean income values for CSA/Agroecology and conventional farming categories associated with a standard deviation of 871.3 and 516.3 respectively, results of the independent sample t-test showed a statistically significant effect, t(62.9) = −3.334, p = 0.002. Thus, income levels from cocoa were statistically higher among farmers practicing CSA/Agroecology than among farmers practicing conventional farming.
Furthermore, an assessment of diversity in household income shows that the average on-farm income from non-cocoa related farm activities was 11% higher in CSA/Agroecology (GHS 930) compared to conventional farming (GHS 840). For instance, intercropping annual food crops on cocoa farms is a common practice in both farming systems. However, CSA/Agroecology had a higher diversity of 3 crops on average in contrast to 2 crops in the conventional cocoa farms. Animal rearing (e.g., grass-cutter; Greater cane-rat: Thryonomys swinderianus), bee keeping and economic trees on-farm such as citrus and avocado, augmented household income and hence contribute to their economic resilience. Although statistically not significant (t(47) = −0.280, p = 0.781), non-cocoa farm income levels were higher among farmers practicing CSA/Agroecology than among farmers practicing conventional farming.
3.3. Assessing Climate Change Mitigation and Resilience as Dimensions of CSA/Agroecology
3.3.1. Land Use Change
Both conventional (87.5%) and CSA/Agroecology (80%) cocoa farmers in the study area cultivated cocoa mainly by slashing and burning secondary forests (Deforestation by fire). Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the results from the carbon balance analysis of conventional and CSA/Agroecology cocoa production. While deforestation affected 133 hectares of forests via conventional farming systems in Juabeso, 111 hectares of forest were affected by CSA/Agroecology interventions. Consequently, the study estimated emissions of 64,493 tCO2-eq (2150 tCO2-eq yearly) with CSA/Agroecology interventions and 76,876 tCO2-eq (2563 tCO2-eq yearly) with conventional practices over a 30-year period ex-ante. For this period, a carbon sink of 12,383 tCO2-eq (413 tCO2-eq yearly) is estimated from avoided deforestation as a result of CSA interventions (Figure 2).
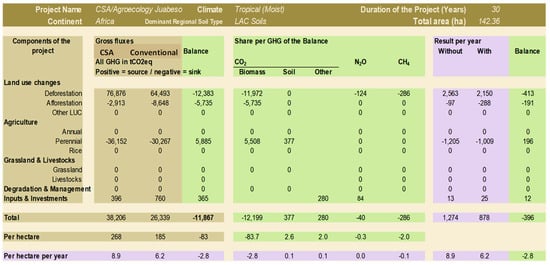
Figure 2.
EX-ACT results showing fluxes per relevant component in cocoa farm projects in Juabeso Source: Field Data (2015).
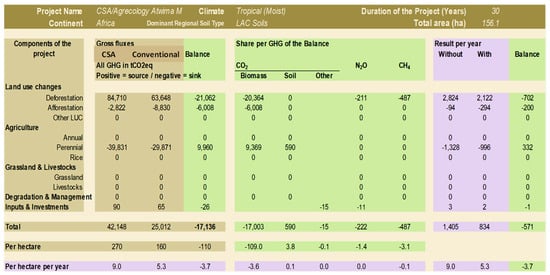
Figure 3.
EX-ACT results showing fluxes per relevant component in cocoa farm projects in Atwima Mponua. Source: Field Data (2015).
Similarly, results from Atwima Mponua indicate 110 and 146 hectares of deforested area with and without CSA/Agroecology interventions respectively. Over a 30-year ex-ante period of consideration, these results indicate future emissions of 63,648 tCO2-eq (2122 tCO2-eq yearly) with and 84,710 tCO2-eq (2824 tCO2-eq yearly) without CSA/Agroecology (Figure 3). The estimated balance of 21,062 tCO2-eq (702 tCO2-eq yearly) represents a carbon sink from avoided deforestation (Figure 3). Thus, CSA/Agroecology practices preserve forest resources (natural capital) without which the effect on carbon balance as presented by conventional farming would remain a source of GHG emissions.
Furthermore, in Juabeso (Figure 2), afforestation activities of planting shade trees as engendered in CSA/Agroecology was higher with an average of 11 trees per hectare, in contrast to results shown from conventional practices with 5 trees per hectare. Consequently, CSA/Agroecology was responsible for an estimated sequestration of 8648 tCO2-eq compared to only 2913 tCO2-eq resulting from the fewer trees planted in conventional systems. Hence a carbon balance reflected a sink of 5735 tCO2-eq over a 30 year period (191 tCO2-eq yearly), resulting from improvement via CSA/agroecology interventions beyond the conventional or business as usual practices. Similarly, over the same period in Atwima Mponua (Figure 3), a sink carbon balance of 6008 tCO2-eq (200 tCO2-eq yearly) was estimated from afforestation activities. CSA/Agroecology was responsible for sequestration of 8830 tCO2-eq compared to only 2822 tCO2-eq by conventional or business as usual practices.
3.3.2. Crop Production and Farm Input
The study also analysed crop systems and farm inputs under CSA/Agroecology and Conventional systems, using the EX-ACT, to further understand associated GHG mitigation potentials. As a perennial crop, the production of cocoa in Juabeso over a 30 year period of analysis generally sequestered an estimated 36,152 tCO2eq in conventional systems compared to 30,267 tCO2eq in CSA/Agroecology (Figure 2). Due to expansive production with closely spaced cocoa trees, typical in conventional farming systems, more cocoa trees were cultivated per hectare and hence the higher carbon sequestration estimates associated with growing the perennial crop compared to CSA/Agroecology. The same situation held true in Atwima Mponua, where over a 30 year period of analysis, cocoa cultivation generally accounted for an estimated sequestration of 39,831 tCO2eq in conventional systems compared to 29,871 tCO2eq in CSA/Agroecology (Figure 3).
Despite the resulting emission source balance of 5885 tCO2eq (196 tCO2eq yearly) and 9960 tCO2eq (332 tCO2eq yearly), linked to the intervention of CSA/Agroecology practices in Juabeso and Atwima Mponua respectively, its overall mitigation impact is yet greater considering benefits from avoided deforestation and afforestation practices as explained above.
Emissions from farm investments and inputs such as application of fertilizer, pesticides, spraying and fuel use were higher at 760 tCO2eq (25 tCO2eq yearly) with practices under CSA/Agroecology compared to 396 tCO2eq (13 tCO2eq yearly) in conventional systems at Juabeso. This is justified from the observation that cocoa farms under CSA/Agroecology were more intensified with relatively higher inputs, compared to those in the conventional systems. In the case of Atwima Mponua, a sink balance of 26 tCO2eq (1 tCO2eq yearly) is projected and accounted for by a carbon source of 90 tCO2eq (3 tCO2eq yearly) due to farm input under conventional systems and 65 tCO2eq (2 tCO2eq yearly) from farm input approaches under CSA/Agroecology. This was due to lower or no input organic farming practices, typical with CSA/Agroecology systems in that part of the study area.
3.4. Assessing Farmer Self-Organisation as a Dimension of Livelihood Resilience
Though CSA/Agroecology groups were historically formed by external project organizations (Rainforest Alliance and Agro-Eco Louis Bolk Institute), these groups have thrived over time through institutions created by farmers themselves.
Farmers indicated in the focus group discussions that they introduced their own rules and regulations, ways of enforcements and related punitive measures such as fines for non-compliance to these introduced organizational rules by members. These local institutions also worked to improve knowledge and skills of members and access to their rights and entitlements mainly through their own initiatives. Through fellow members whom they had selected and promoted with the groups’ resources as lead farmers, they interact with stakeholders at various levels and information and skills acquired through this process is shared within the groups. Further 90% of CSA/Agroecology farmers compared to only 38% of Conventional farmers had access to extension and advisory services; and 45% of CSA/Agroecology farmers compared to 15% of conventional farmers had access to government’s free improved planting materials.
The integration of CSA/Agroecology farmers, into their respective farmer organizations is also driven by trust. Thus, farmers who are believed to be trustworthy and could trust others, worked together to enhance their livelihood. 25% of farmers who were not members of any farmer organization identified mistrust in others as an important reason, while 25% were refused admission into their desired groups. Through such processes, CSA/Agroecology farmers in different instances collectively organized assets at their disposal to support enhancements of their livelihoods such as through buying spraying machines, training lead farmers and maintaining demonstration farms.
These interrelations between farmers’ abilities (buffer capacities), in terms of ownership of livelihood capitals and exercise of necessary utility rights, highlight the contribution of farmer self-organization to livelihood resilience. Majority of CSA/Agroecology cocoa farmers (95%) rather than conventional farmers (23%) however, have willingly become group members in order to secure their livelihoods.
3.5. Assessing Farmer Capacity for Learning as a Dimension of Livelihood Resilience
Results from the FGDs indicated that farmers were generally aware of what constituted threats (mainly high temperatures and rainfall variability) and opportunities to their livelihoods. However, transfer of new ideas and technology is challenged mostly in conventional farming due to limited interaction among conventional farmers and key stakeholders. In contrast, CSA/Agroecology farmers demonstrated commitment to learning through creation and use of existing group-managed demonstration farms for experimentations and transfer of knowledge and technology. They also engaged visiting extension officers and their lead farmers acquired training from relevant agencies.
Based on previous experiences with unfavourable tree tenure, CSA/Agroecology farmer groups have engaged with the officials of the Forestry Commission of Ghana to register trees they have planted on-farm to protect their ownership and rights. However, conventional farmers have not exercised such agency to take advantage of this collaboration but are rather demotivated to plant trees on their farms due to illegal logging by chainsaw operators without appropriate compensation to the conventional farmers. In addition, analysis of selected farm management practices (Figure 4), underscored that CSA systems indicated higher commitments for learning, by following and implementing recommended best practices better than in conventional systems, although this strategy may be tied to the conditions set by the organizations for CSA/Agroecology farmers to access farm inputs.
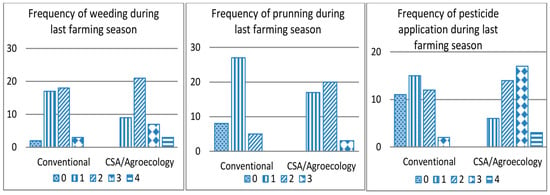
Figure 4.
Frequency of selected farm management practices per farming systems. Source: Field Data (2015).
Despite a general awareness of climate risks on cocoa production, livelihoods diversification was moderately undertaken in each of the farming systems. While CSA/Agroecology systems showed more diversity on-farm in terms of non-cocoa crops and forest/shade tree cover, conventional systems were averagely more diversified with respect to non-farm economic activities
3.6. Factors Affecting Practice of CSA/Agroecology
Results of the logistic regression model to identify the factors affecting CSA/Agroecology practices are presented in Table 7. Using the specifications with the dependent variable measured as 1 if farmer practiced CSA/Agroecology and 0 if farmer practiced conventional farming, a maximum likelihood procedure was used to estimate the parameters. The co-efficient of determination, Pseudo R2 of 0.446, indicate that about 44.6% of variation in the practice of CSA/Agroecology could be explained by the explanatory variables. The model is statistically significant at 1%.

Table 7.
Estimations of regression models for framing factors of CSA/Agroecology practice.
Farm tenure, age of farmer, location (district), residential status and access to extension services were the main determining factors influencing CSA/Agroecology practices. Farm Tenure was statistically significant at 5% indicating that farmers who owned their farms were 39% more likely to adopt CSA/Agroecology practices than those who managed family farms and 43% more likely to practice CSA than share croppers. While age of farmer was positively significant at 10%, results showed non-linearity in the variable as the square of farmer age was negatively significant at 10%. Thus, farmers are more likely to practice CSA/Agroecology with increase in their age but this tendency of CSA practice eventually drops with further age increase.
Location has an influence on the practice of CSA/Agroecology. ‘District’ as a variable was significant at 10%, showing a 37% likelihood of CSA/Agroecology practice in Juabeso more than in Atwima Mponua District. However, with residential status remaining positively significant at 5%, native farmers are 39% less likely to practice CSA/Agroecology than settlers. Further, access to extension services has a positive significant effect at 1% on the practice of CSA/Agroecology in cocoa production. It is 73% likely that increasing farmer access to extension services increases farmer adoption of CSA/Agroecology practices. Nevertheless, farmer level of education, household dependency ratio and access to credit were positively related to CSA/Agroecology but were not statistically significant.
4. Discussion
4.1. Contributions of CSA/Agroecology to Productivity and Income
The results indicate higher income in CSA agroecology systems. The average yield for conventional systems (363 kg/ha) identified in this study is validated by the national average of 350–400 kg/ha [15,35], mainly reflecting the conventional cocoa production practiced by most farmers in Ghana. The relatively higher yields (501 kg/ha) attributed to CSA/Agroecology, is confirmed by Aidoo and Fromm (2015) [39], who reported similar results for farmers engaged in certification for implementing more sustainable practices in the Ashanti Region of Ghana.
CSA/Agroecology farmers also had higher financial capital as evidenced in their average incomes (29% more) and hence increased their purchasing power as observed in their average farm investments (32% more) compared to conventional farmers. Incremental financial capital can buffer livelihood risks (such as poor soil fertility, pests and diseases, etc.), since farmers are more capable to finance their strategies (such as fertilizer application, spraying pesticides, etc.) to reduce or cope with the risks, which is a crucial dimension of livelihood resilience [40].
Through intercropping of diverse non-cocoa crops (particularly food crops), respective CSA/Agroecology households invariably have access to food and are additionally provided with income (10% more than conventional) mainly due to higher cropping intensities and diversities. Such farm households earn additional incomes directly from the sale of food products including plantain, yams, fruits, honey, vegetables etc., and indirectly from monies saved that would have been otherwise used to buy food [41]. Furthermore, through agroforestry practices that increase carbon stocks on-farm and hence reduce GHG emissions, CSA/Agroecology provides a potential opportunity for additional household incomes from carbon credits through the result-based national REDD+ programme [42]. However, this potential raises questions on equity concerning how farmers would be fairly rewarded from carbon credits and other related benefits for achieving mitigation benefits. This is because there is not yet clarity on key issues around the development of a fair and transparent benefit sharing scheme and carbon rights definition, land and tree tenure and gender mainstreaming mechanisms are still outstanding, which have dominated the REDD+ implementation discourse [41].
While CSA/Agroecology contributed to increased yields and incomes which in turn build resilience of farmers’ livelihoods through improved food security (also from higher variety and output of food crops) and enhanced buffer capacity [39], the study also considers the hypothetical diminishing of this buffer capacity given the susceptibility of cocoa to reduction in rainfall particularly during the dry season and increased temperatures which have worsened due to increase climate variability and change [16]. The following further places the discussions in this context to highlight the potential of CSA/Agroecology to mitigate such climatic risks and adapt to associated impacts.
4.2. Contributions of CSA/Agroecology to Climate Change Mitigation
Although farmers clear fell and burn secondary forests to plant cocoa crops before the adoption of recommended practices, the emission effect was lower with the intervention of CSA/Agroecology. This is explained by the effect of avoided deforestation for the purposes of farm expansions as CSA/Agroecology farmers were rather shifting to intensification practices. Unlike conventional farmers who typically employ low input and aim to increase yields by expanding the area of land cultivated and hence further deforest secondary or virgin forests [9], CSA farmers rather intensify input investment in relatively smaller areas of land to increase productivity thereby saving carbon stock in forest, which would have otherwise been burnt.
According to Cambell et al. (2014) the approach of sustainable intensification is an essential means of adapting to climate change, also resulting in lower emissions per unit of output and is highly complementary with CSA [43]. Gockowski and Sonwa (2011) further observed in their study of rural livelihoods in the Guinea rain forest of West Africa that this strategy not only mitigate deforestation and carbon emissions but also biodiversity loss and enhance poverty alleviation and rural development [44], all of which are essential ingredients for strengthening adaptive capacities against and building resilience to climate variability and change.
4.3. Contributions of CSA/Agroecology to Farmer Social Capital and Learning
Increase in income among CSA/Agroecology farmers was inextricably linked to their respective higher value in social capital (increase in other assets due to membership or participation in social networks; labour support from group members and income gained through membership in groups) and vice versa. This also influenced their higher capacities for learning via institutionalising group processes and their ability to further mobilise more resources to protect their livelihoods as a collective. To protect and enhance their livelihoods, CSA/Agroecology farmers actively self-organised and integrated into farmer based groups such that they subject themselves to rules and regulation, offer themselves to trust and be trusted and pulling resources together as well as remaining open to information and new ideas for the achievement of livelihood outcomes. Hence enhancement in not only their buffer capacities but also their social capital and capacity for learning as dimensions of resilience [39] This is further supported by Mohammed et al.’s (2013) [45] observation of a positive relationship between social capital and access to credit.
CSA/Agroecology farmers have also generally demonstrated agency through resources at their disposal including increased economic power from higher incomes and political influences through the functioning group dynamics. These represented the foundation on which they engaged with the officials of the Forestry Commission of Ghana and which was instrumental in protecting their interest in established tree tenure for example. Asare (2014) argues that making the shift to a sustainable and climate resilient cocoa landscape will require significant changes, including extensive coordination and collaboration between key stakeholders, many of which have traditionally not collaborated, like the Cocoa Board and the Forestry Commission [10]. These forms of cooperation have implicitly been initiated by CSA practices.
4.4. Conditions and Processes Framing Practice of CSA/Agroecology
4.4.1. Land and Farm Tenure
In accordance to the a priori expectations of the study, farm tenure influenced the practice of CSA/Agroecology in the study area showing that farmers are more likely to invest time and resources on their own farms than on farms where ownership right is insecure [16,35]. Secure land tenure thus has a significant effect on agricultural production and the ways in which rural livelihoods are sustained. According to Acheampong et al. (2014) [35], the security and quality of land tenure rights directly affect how respective resources are used and managed.
Linking this situation to resilience, up-scaling the practice of CSA in the study areas will require the processes of land and farm right acquisition to foster farmers with greater security in terms of ownership and rights to use (entitlement). Freudenberger (1994) [46] argues that local land and farm tenure system in Ghana is complex, adaptive and evolves over time in response to changing ecological and socio-economic conditions. Given that this is a product of the interaction of customary laws as guaranteed by government statute [47], local and public institutions are crucial as they influence options and strategies available to farmers to sustain their livelihoods. Therefore, institutional reforms must create conducive environments that reduce farmers’ risk associated with accessibility of farmlands. Short term interests acquired by migrant farmers in lands or in farms as well as the resources on them should therefore be ensured by capitalising on Customary Land Secretariat systems to enhance enabling contractual agreements between them and their respective land or farm owners [44].
4.4.2. Age of Farmer
According to the results, the adoption and practice of CSA/Agroecology grew with increase in farmers’ age but only up to a threshold beyond which adoption of CSA/Agroecology practices declined as farmers grew older. Farmers also tend to reduce farm investments as well as the propensity to experiment or employ new technologies as they grow older. Knowler and Bradshaw (2007), Aneani et al. (2012), Obuobisa-Darko (2015) [21,33,34] indicated that older cocoa farmers in Ghana are more resistant to shift from traditional practices to improved ones as they are risk averse.
However, it needs to be considered that younger farmers are less likely to have the necessary endowments in livelihood assets or capitals compared to older farmers. Thus, access to natural capital (farmlands), financial capital (credit, bank loans), human capital (farm experience, know-how), social capital (household control, trust) and physical capital (access to technologies) are more likely to be limited among younger farmers than older ones. These have implications for the extent of practice of CSA/Agroecology among younger farmers despite their will to change considering that Mumuni and Oladele (2016) [48] observed young farmers are more likely to develop entrepreneurial abilities than aged ones. To overcome these barriers, institutions and policies governing the sector need to not only target CSA/Agroecology technologies among young farmers but also enhance their capacities to improve their relatively weak buffer capacities and livelihood resilience [39,49].
4.4.3. Location (District) of Farmer
The location of farmers also influenced their tendency to practice CSA/Agroecology with farmers in Juabeso District being more engaged in CSA/Agroecology systems than those of Atwima Mponua. This can be explained by the status of Juabeso district as part of the Western Region, which is recognised as the cocoa hub of the country and produces more than half of the country’s cocoa [9]. This comparative advantage could also be linked to government and private sector interventions to support cocoa farmers through fertilizer distribution, free cocoa farm spraying exercises, extension and technical support services and other important facilities, skewed towards the Juabeso district. Thus, significant variations in socio-economic and ecological contexts can explain the success of CSA/Agroecology interventions.
4.4.4. Residential Status of Farmer
Farmers’ residential status was identified to be a significantly influential factor determining farmers’ capacity to practice CSA/Agroecology in Ghana. Contrary to a priori expectations, the results showed that native farmers rather have lower tendencies to practice CSA/Agroecology than migrant farmers. This contradicts other findings [37,50] that associate unsustainable land management practices with migrant farmers because of their short-term insecure land access and interests in faster and higher returns, than natives with more secured interest and as such greater incentive to sustainably preserve the quality of land.
Van der Geest (2011) [51] also challenged findings attributing unsustainable land management practices to Dagara migrants in Ghana’s Brong Ahafo Region. Given that migrant farmers in Ghana have mostly been displaced by environmental change [49], their experiences and awareness of previous threats are likely to define their capacity for learning in their new locations to build livelihood resilience. According to Marney et al. (2014) [49], migration of farmers in Ghana is mostly an adaptation strategy and in the process migrants expand their social networks with stronger ties through which they access information, while deploying social-ecological memory as potential agents of innovation and adaptation. Thus, there is a need to revise unpopular perceptions that associate migrant farmers with growing forest degradation in Ghana, while enabling their adaptation as they have potentials to be agents of change through innovation, technological transfer and adoption. In cases of environmentally induced migration, recognition should be given to migrant farmers in Ghana’s climate change adaptation policies to provide them with adaptation opportunities and rights, similar to non-migrant farmers.
4.4.5. Farmer Access to Extension Services
It is expected that increased access to extension services by farmers will correspondingly increase CSA/Agroecology adoption and practice [34,36]. Anim-Kwapong and Frimpong (2010) [16] argued in this relation that cocoa farmers in Ghana are quite conservative and as such require very effective extension systems to motivate them adopt innovations and new technologies. Yet the processes of extension in Ghana have not been effective mainly due to financial constraints [36]. This condition also produces risks in adaptation to climate change.
However, with institutional bottlenecks, processes of agricultural extension initiated out of the agency of farmers to build their own capacities as evidenced by the CSA/Agroecology farmer groups should be encouraged. Collaborations between farmers and responsible institutions for extension service delivery would be instrumental in closing this gap. For instance, involving farmers in extension delivery through the concept of “Lead Farmers” where selected farmers from farmer groups are equipped with extension delivery skills in order to train and educate their colleagues would be a vital strategy towards reducing livelihood risks under current conditions among cocoa farmers in Ghana.
5. Conclusions
This study has shown that average farm productivity and average income is significantly higher among farmers practicing CSA/Agroecology, who also incur higher farm investment costs required to meet recommended practices, than conventional cocoa farmers. Premiums additionally paid to cocoa CSA/Agroecology farmers for undertaking these recommended practices under certification schemes also augmented their incomes, in addition to income from non-cocoa farm production. The relatively high income is linked to enhancements in other livelihood capitals and hence increased ownership of livelihood assets and utility rights such as in land tenure for example. With enhanced buffer capacity and resilience, farmers practicing CSA/Agroecology also indicated better self-organisation with higher capacity for learning in an inter-linked fashion, contributing more to livelihood resilience than in conventional farming systems. Further, the study highlights that trade-offs may exist between practicing CSA/Agroecology cocoa production and diversification of farmer livelihoods as a climate change adaptation strategy.
The estimations of carbon balance due to land-use change, crop production and farm input use, using the EX-ACT tool varied with different production systems. While farm input intensification practices of CSA/Agroecology have negative implications for climate mitigation, CSA/Agroecology practices, overall have positive impacts on GHG mitigation without which cocoa landscapes would be a source of emission. The contributions of CSA to climate mitigation however showed no direct impact on farmers’ livelihood resilience. The study however found that the institutional processes of obtaining land or farm ownership and rights (land/farm tenure system) in Ghana, age of farmers, geographical location of farmers (district), farmers’ residential status and their access to agricultural extension services were the main factors influencing the practice of CSA/Agroecology in the study area and by extension resilience to climate change impacts on cocoa production.
While the study assessed resilience with selected proxy indicators, the analysis hints that a comprehensive resilience profile of cocoa production systems integrating all relevant indicators and related proxies under each of the three components of resilience (buffer capacity, self-organization and capacity for learning) should be further studied. This also means re-examining the concept of CSA that captures resilience as one of its components. It is also instrumental to research existing trade-offs that exist with practice of CSA by cocoa farmers and to assess the extent to which they can be minimised.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Rebecca Ashley Asare (Nature Conservation Research Centre), Christian Mensah (Rainforest Alliance) and Sander Muilerman (International Institute for Tropical Agriculture) for their invaluable insights. We also appreciate the support of Anthony Adom and Abraham Yelley of Rainforest Alliance, as well as Israel Kuadzi and Selasse Gidiglo of Agro Eco-Louis Bolk Institute. “This work was implemented as part of the CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), which is carried out with support from CGIAR Fund Donors and through bilateral funding agreements. For details please visit https://ccafs.cgiar.org/donors. The views expressed in this document cannot be taken to reflect the official opinions of these organizations.”
Author Contributions
F.A.-A. conceived and designed the research; performed literature review, managed the field data collection processes; analysed the data; and wrote the paper. C.I.S. designed and shaped the research as well as analysing supporting literature, writing and reviewing the paper to finalize it. L.B. contributed to the research design and provided the Ex-Ante Carbon Balance Tool as well as supporting the estimation and analysis of Greenhouse Gas Emission resulting from farming activities. R.A. contributed to the research design and the data collection tools and processes, as well as reviewing the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Branca, G.; Tennigkeit, T.; Mann, W.; Lipper, L. Identifying Opportunities for Climate Smart Agriculture Investment in Africa; Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.O.; Mul, M.; Cofie, O.; Kinyangi, J.; Zougmore, R.; Wamukoya, G.; Nyasimi, M.; Mapfumo, P.; Speranza, C.I.; Amwata, D.; et al. Climate Smart Agriculture in the African Context—Background Paper. In Proceedings of the Feeding Africa Conference—Unlocking Africa’s Agricultural Potentials for Transformation to Scale, Dakar, Senegal, 21–23 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Campbell, B.M.; Ingram, J.S.I. Climate Change and Food Systems. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Climate Smart Agriculture Sourcebook; Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. In Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Fifth Assessment Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, C.; Chacon, M.; Donatti, C.; Garen, E.; Lee, H.; Andrade, A.; Bede, A.L.; Brown, D.; Calle, A.; Chara, J.; et al. Climate-Smart Landscapes: Opportunities and Challenges for Integrating Adaptation and Mitigation in Tropical Agriculture. Conserv. Lett. 2013, 7, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTATS—Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations, Statistics Division. Emissions: Agriculture. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#compare (accessed on 31 August 2017).
- EPA. National Greenhouse Gas Inventory Report for 1990–2006; Environmental Protection Agency: Accra, Ghana, 2013.
- Gockowski, J.; Robiglio, V.; Muilerman, S.; Agyema, N.F. Agricultural Intensification as a Strategy for Climate Mitigation in Ghana: An Evaluative Study of the COCOBOD High Tech Programmes, Rural Incomes and Forest Resources Bia (Juabeso) District of Ghana; International Institute for Tropical Agriculture (IITA): Accra, Ghana, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Asare, R.A. Understanding and Defining Climate-Smart Cocoa: Extensions, Inputs, Yields and Farming Practices; Natural Conservation Research Center—Forest Trends: Accra, Ghana, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gockowski, J.; Sonwa, D. Biodiversity and Smallholder Cocoa Production Systems in West Africa; International Institute for Tropical Agriculture (IITA): Accra, Ghana, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.; Robinson, J.; Midmore, D.; Verhoef, A. Carbon Storage in Ghanaian Cocoa Ecosystems; Springer: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dormon, E.; Huis, A.V.; Leeuwis, C.; Obeng-Ofori, D.; Sakyi-Dawson, O. Causes of Low Productivity of Cocoa in Ghana; Farmers’ Perspective and Insight From Research and the Socio-Political Establishment. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2004, 52, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyeiwu, S.; Pallant, E.; Hanlon, M. Sustainable and Unsustainable Agriculture in Ghana and Nigeria: 1960–2009. Ecosyst. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 3, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Danso-Abbeam, G.; Aidoo, R.; Agyemang, K.O.; Ohene-Yankyera, K. Technical Efficiency in Ghana’s Cocoa Industry: Evidence From Bibiani-Anhwiaso-Bekwai District. J. Dev. Agric. Econ. 2012, 4, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Anim-Kwapong, G.J.; Frimpong, E.B. Vulnerability and Adaptation Assessment under the Netherlands Climate Change Studies Assistance Programme Phase 2 (NCCSAP2) Vulnerability of Agriculture to Climate Change-Impact of Climate Change on Cocoa Production; Cocoa Research Institute of Ghana: New Tafo Akim, Ghana, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, M. Cocoa and Food Security. 2011. Available online: http://cocoasustainability.com/2011/11/cocoa-and-food-security/ (accessed on 19 May 2016).
- Zougmoré, R. Climate Smart Agriculture Integrated into Decision-Making in Ghana. 2014. Available online: https://ccafs.cgiar.org/blog/climate-smart-agriculture-integrated-decision-making-ghana#.VuAuAPnnVyN (accessed on 20 December 2015).
- Amlalo, D.S.; Oppong-Boadi, K.Y. Ghana’s Third National Communication Report to the UNFCCC: 2015 Climate Change Report; Environmental Protection Agency: Accra, Ghana, 2015.
- Hutchins, A.; Tamargo, A.; Bailey, C.; Kim, Y. Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Cocoa Production and Approaches to Adaptation and Mitigation: A Contextual View of Ghana and Costa Rica. 2015. Available online: https://elliott.gwu.edu/sites/elliott.gwu.edu/files/World%20Cocoa%20Foundation.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2015).
- Aneani, F.; Anchirinah, V.M.; Owusu-Ansah, F.; Asamoah, M. Adoption of Some Cocoa Production Technologies by Cocoa Farmers in Ghana. Sustain. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Agyei, P.; Dougill, A.J.; Stringer, L.C. Barriers to Climate Change Adaptation in Sub-Sahara Africa: Evidence from Northeast Ghana and Systematic Literature Review. Clim. Dev. 2014, 7, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifejika Speranza, C.; Wiesmann, U.; Risk, S. An Indicator Framework for Assessing Livelihood Resilience in the Contexst of Social-Ecological Dynamics. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 28, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addae-Boadu, S.; Aikins, S.; Alhassan, A.S. The Cocoa Certification Program and Its Effect on Sustainable Cocoa Production in Ghana: A Case Study in Upper Denkyira West District. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 7, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Atwima Mponua District Assembly. The Composite Budget of the Atwima Mponua District Assembly for the 2012 Fiscal Year. 2012. Available online: http://www.mofep.gov.gh/sites/default/files/budget/Atwima%20Mponua.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2016).
- Ghanadistricts.com. Ashanti: Atwima Mponua & Western: Juabeso. 2006. Available online: http://ghanadistricts.com/districts/?news&r=5&_=136 (accessed on 16 January 2016).
- Ghana Statistical Service. 2010 Population and Housing Census: Juaboso District; Ghana Statistical Service: Accra, Ghana, 2014.
- Ghana Statistical Service. 2010 Population and Housing Census: Atwima Mponua District; Ghana Statistical Service: Accra, Ghana, 2013.
- Juaboso District Assembly. District Information. 2012. Available online: http://juaboso.ghanadistricts.gov.gh/?arrow=dnf&_=136&r=5&rlv=location (accessed on 14 January 2016).
- ITTO. Enrichment of Young Forest Plantations with Selected NTFPs for Livelihood Improvement and Support of Forest Fringe Communities in Atwima Mponua District, Ghana; International Tropical Timber Organization (IITO): Yokohama, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- GoG. 2015 Juaboso District Composite Budget and Economic Statement. Government of Ghana, 2015. Available online: http://www.mofep.gov.gh/sites/default/files/budget/2015/Composite/WR/Juaboso.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2016).
- Bernoux, M.; Branca, G.; Carro, A.; Lipper, L.; Smith, G.; Bockel, L. Ex-Ante Greenhouse Gas Balance of Agriculture and Forestry Development Programs. Sci. Agricola 2010, 67, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 13; StataCorp LP.: College Station, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Knowler, D.; Bradshaw, B. Farmers’ Adoption of Conservation Agriculture: A Review and Synthesis of Recent Research. Food Policy 2007, 32, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuobisa-Darko, E. Credit Access and Adoption of Cocoa Research Innovations in Ghana. Res. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2015, 5, 16–29. [Google Scholar]
- Acheampong, E.; Dawoe, E.; Bosu, P.; Asante, W. Moving forward with REDD+ in Ghana: Shade Systems, Crown Cover, Carbon Stocks and Socio-Economic Dynamics of Smallholder Cocoa Agroforestry Systems; SNV World: Accra, Ghana, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Aseidu-Darko, E. Agricultural Extension Delivery in Ghana: A Case Study of Factors Affecting it in Ashanti, Eastern and Northern Regions of Ghana. J. Agric. Ext. Rural Dev. 2013, 5, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Antwi-Agyei, P.; Dougill, A.J.; Stringer, L.C. Impacts of Land Tenure Arrangements on the Adaptive Capacity of Marginalized Groups: The case of Ghana’s Ejura Sekyedumase and Bongo Districts. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidoo, R.; Fromm, I. Willingness to Adopt Certifications and Sustainable Production Methods among Small-Scale Cocoa Farmers in the Ashanti Region of Ghana. J. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 8, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifejika Speranza, C. Buffer Capacity: Capturing a Dimension of Resilience to Climate Change in African Smallholder Agriculture. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokoto, J.; Afari-Sefa, V.; Addo-Quaye, A. Vegetable Diversification in Cocoa-Based Farming Systems in Ghana. Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foli, E.; Dumenu, W. Background Paper for Ghana’s REDD+ Benefit Sharing Dialogue; The Forest Dialogue: Elmina, Ghana, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, B.; Thornton, P.; Zougmoreé, R.; van Asten, P.; Lipper, L. Sustainable Intensification: What is the Role of Climate Smart Agriculture? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 8, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gockowski, J.; Sonwa, D. Cocoa Intensification Scenarios and their Predicted Impacts on CO2 Emissions, Biodiversity, Conservation and Rural Livelihoods in Guinea rain forest of West Africa. Environ. Manag. 2011, 8, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudenberger, K.S. Tree and Land Tenure: Rapid Appraisal Tools; Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Larbi, W.O. Tenure Transformation and Land Valorisation Processes at the Urban Periphery of Ghana. Proceeding of the International Conference on Land Tenure in the Developing World with a Focus on Southern Africa, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 27–29 January 1998; pp. 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mumuni, E.; Oladele, O.I. Access to Livelihood Capitals and Propensity for Entrepreneurship amongst Rice Farmers in Ghana. Agric. Food Secur. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILO. Research to Identify Practical Measures to Enhance Productivity in Cocoa Growing Communities in Ghana; International Labour Organization (ILO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP. Environmental Sustainability and Policy for Cocoa Production in Ghana; United Nations Development Programme (UNDP): Nairobi, Kenya, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Geest, K. The Dagara Farmer at Home and Away: Migration, Environment and Development in Ghana; African Studies Centre: Leiden, Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marney, I.E.; Anglaaere, L.N.; Akoto, D.S.; Dawoe, E. Migrant Farmers as Information Brokers: Agroecosystems Management in the Transition Zone of Ghana. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 56. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).