Multi-Scenario Assessment of Ecological Network Resilience and Community Clustering in the Yellow River Delta
Abstract
1. Introduction
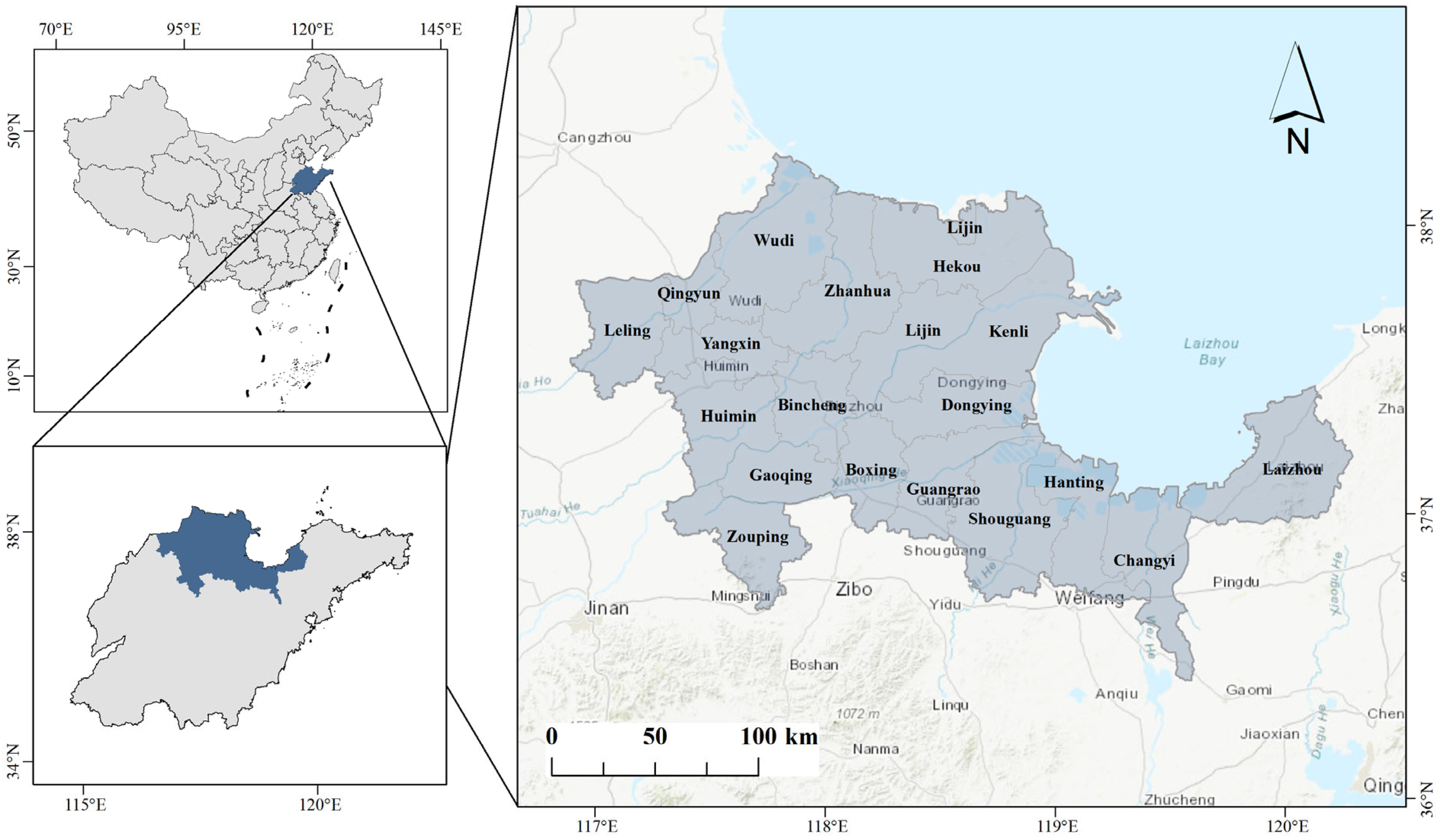
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
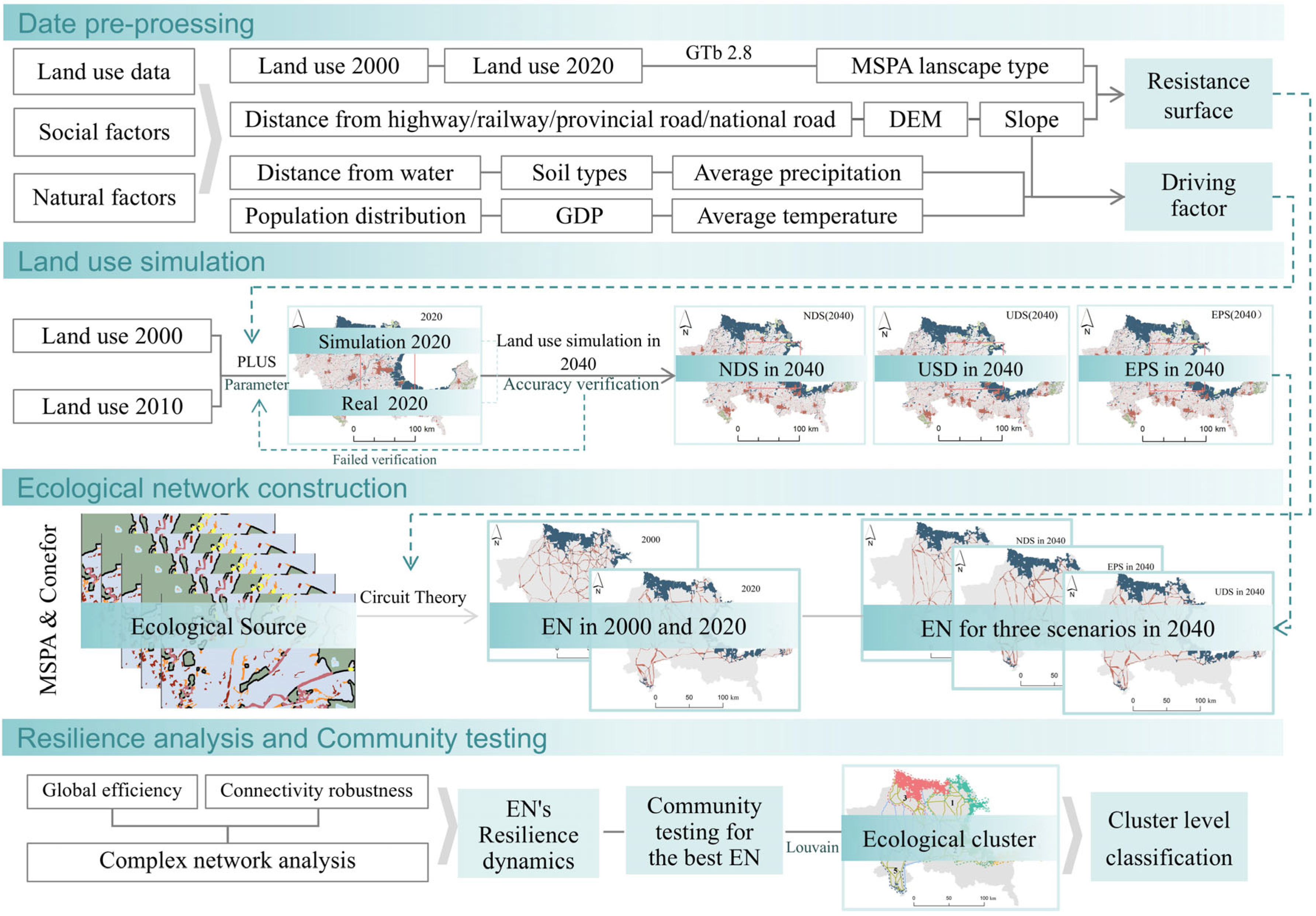
3. Methods
3.1. Simulation of Land Use
3.1.1. Land Use Simulation and Accuracy Assessment
3.1.2. Scenarios Settings
3.2. Process of Building an EN
3.2.1. Selection of Ecological Source
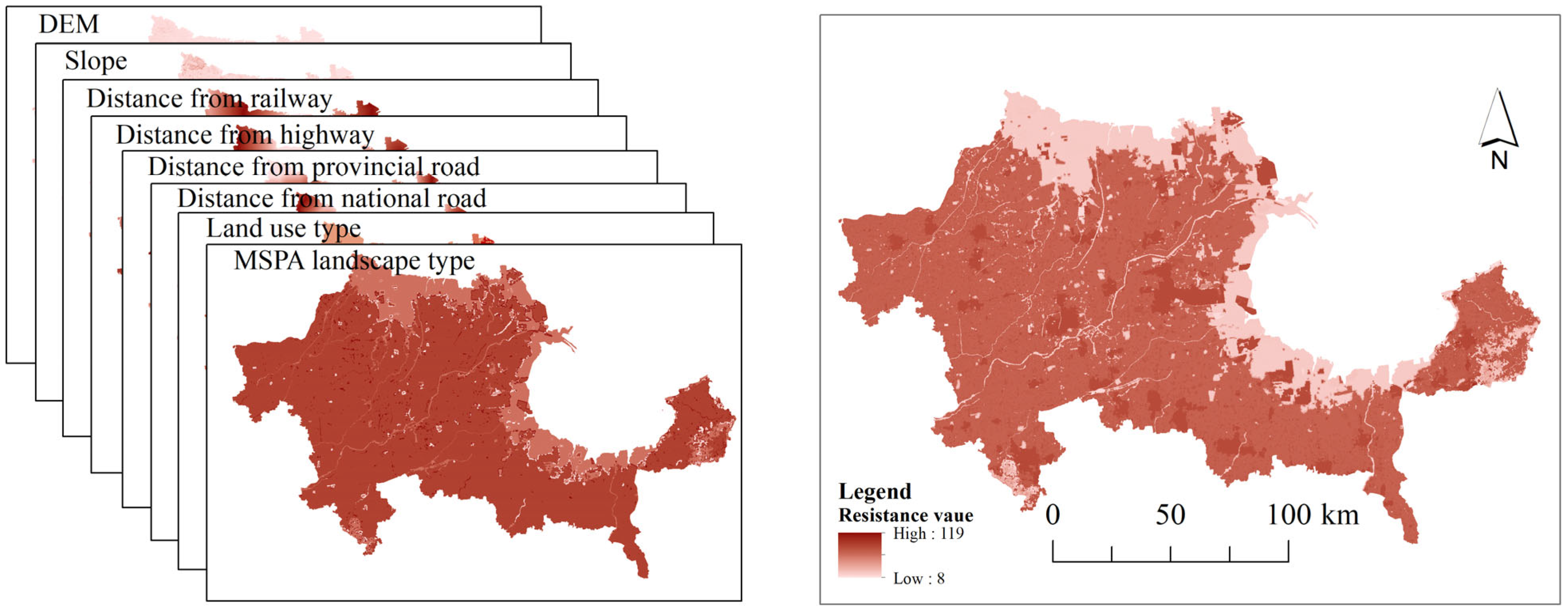
3.2.2. Construction Procedures of Resistance Surface
3.2.3. Selection of Ecological Corridors
3.3. Resilience Analysis of EN
3.4. Cluster Identification and Classification
4. Results
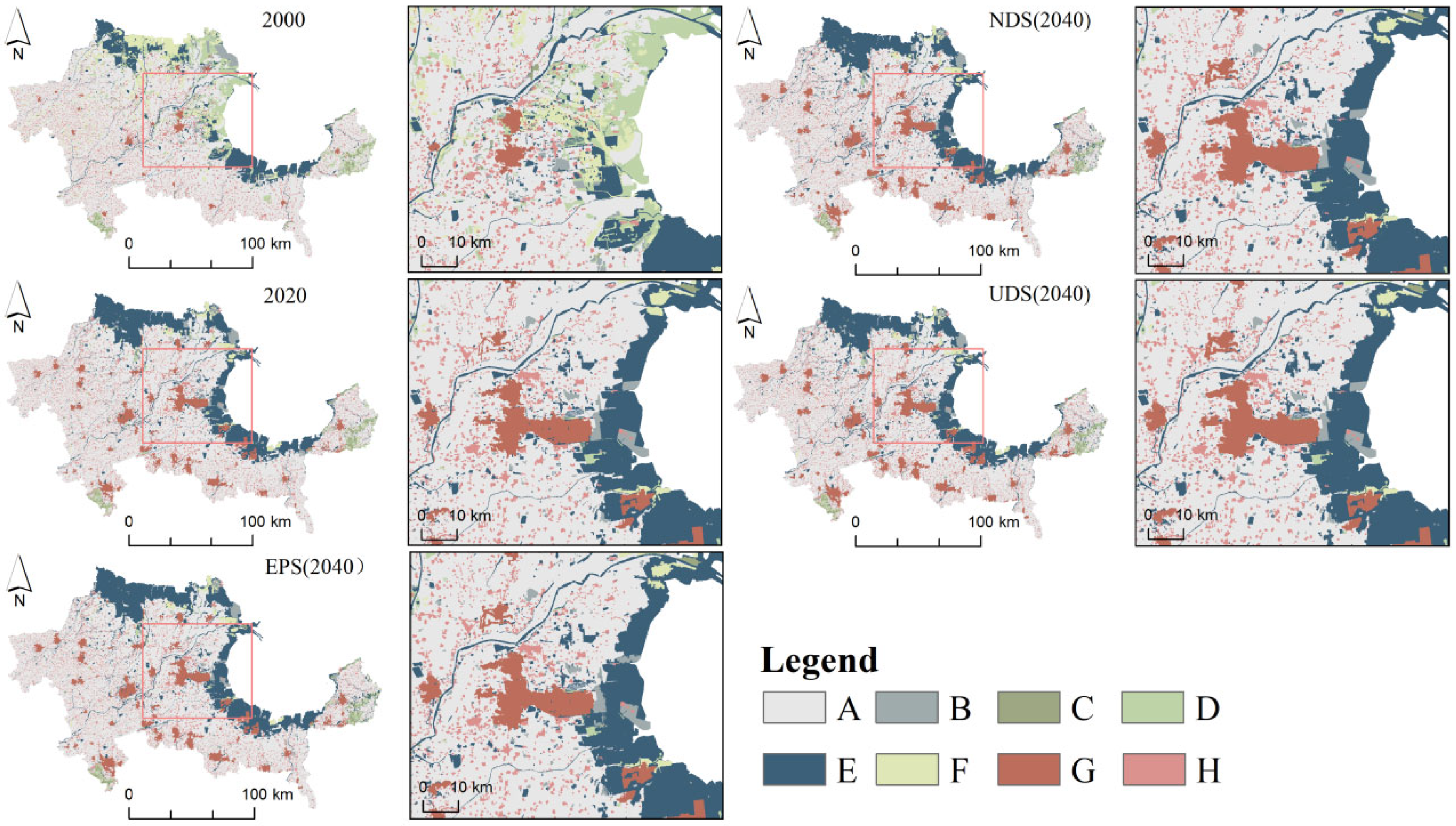
4.1. Simulation Results of Land Use
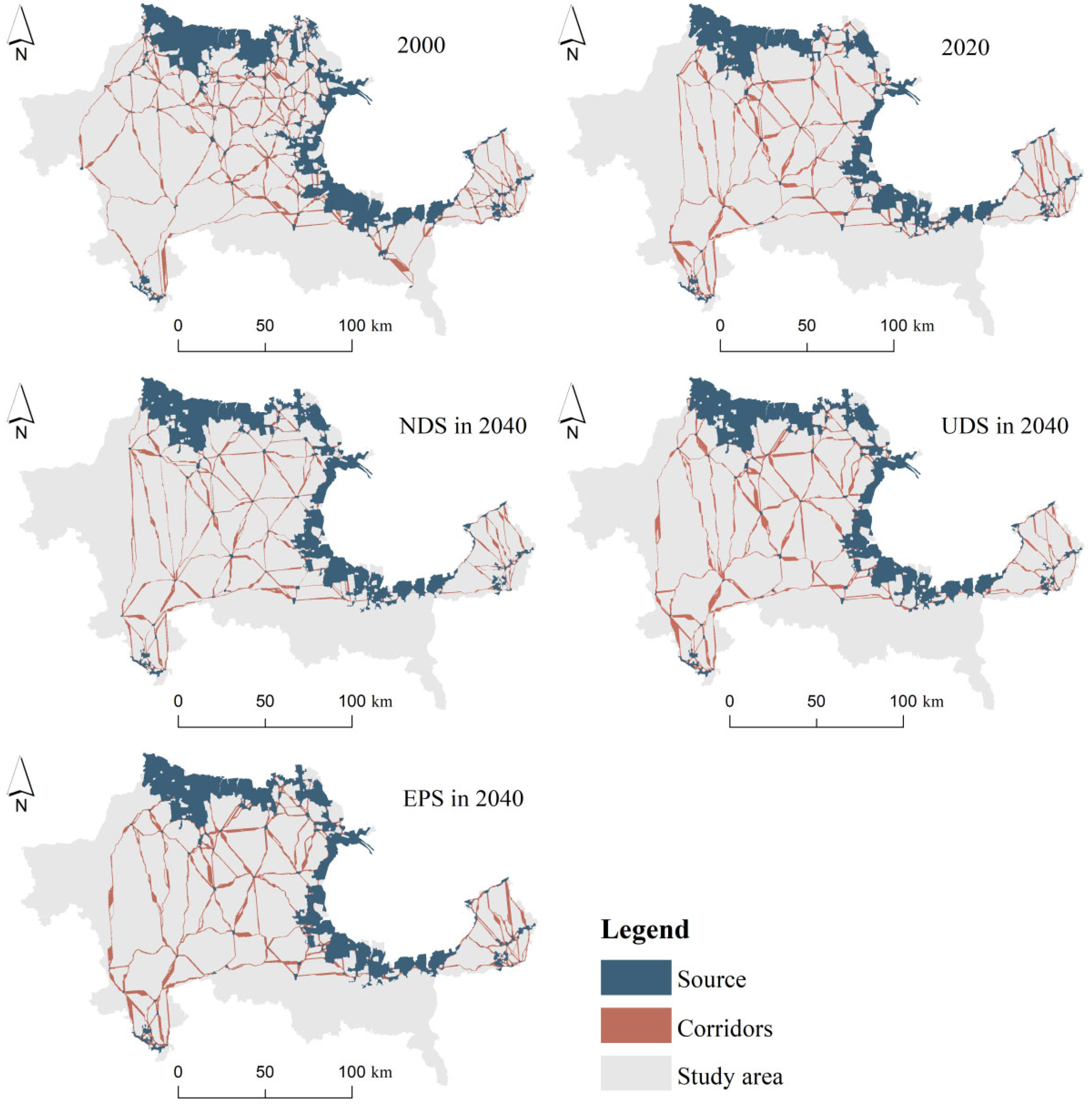
4.2. Construction of EN Across Different Scenarios and Periods
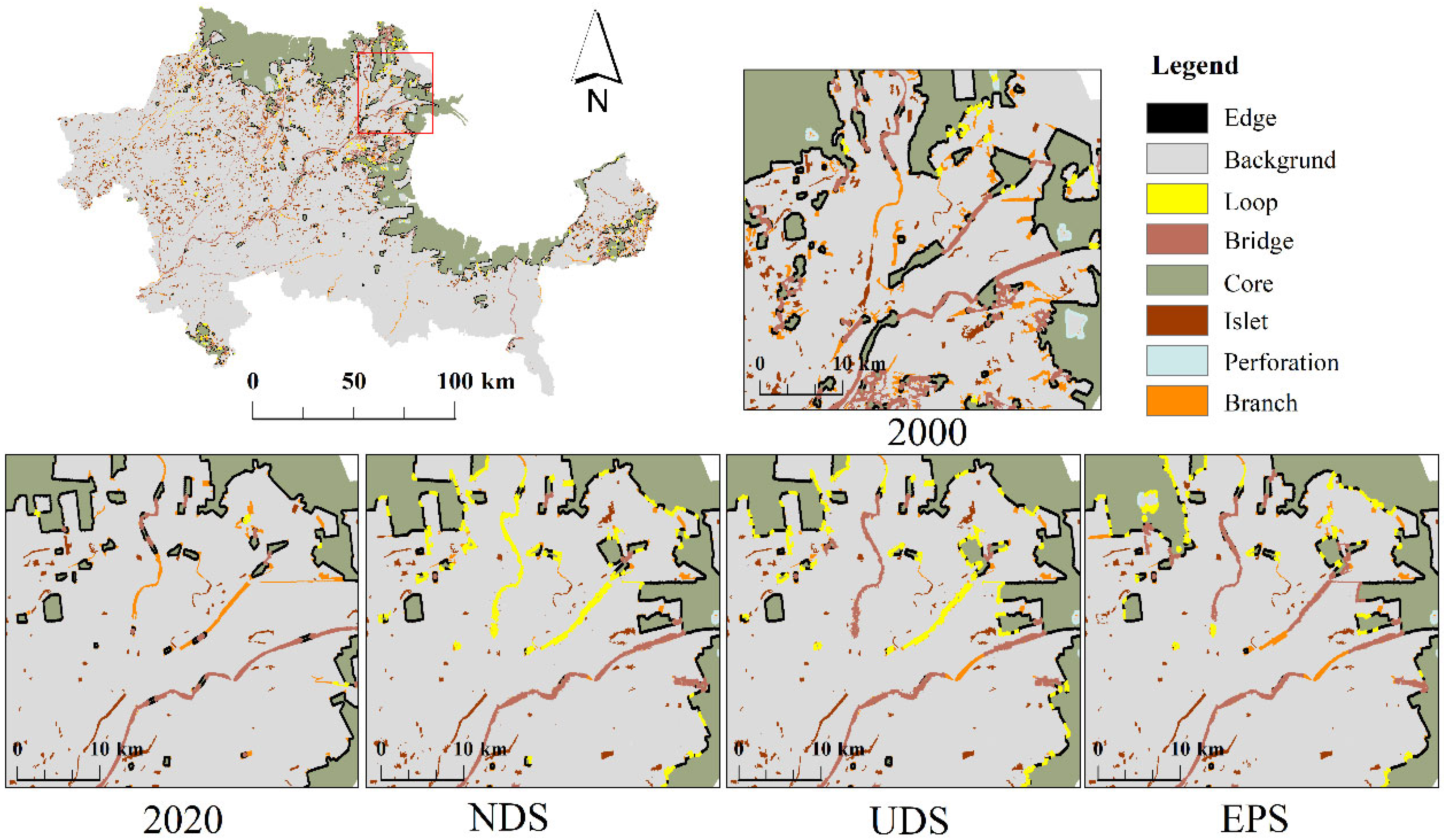
4.2.1. Identification of Ecological Sources
4.2.2. Construction of Resistance Surface
4.2.3. Extraction of Ecological Corridor and Construction of EN
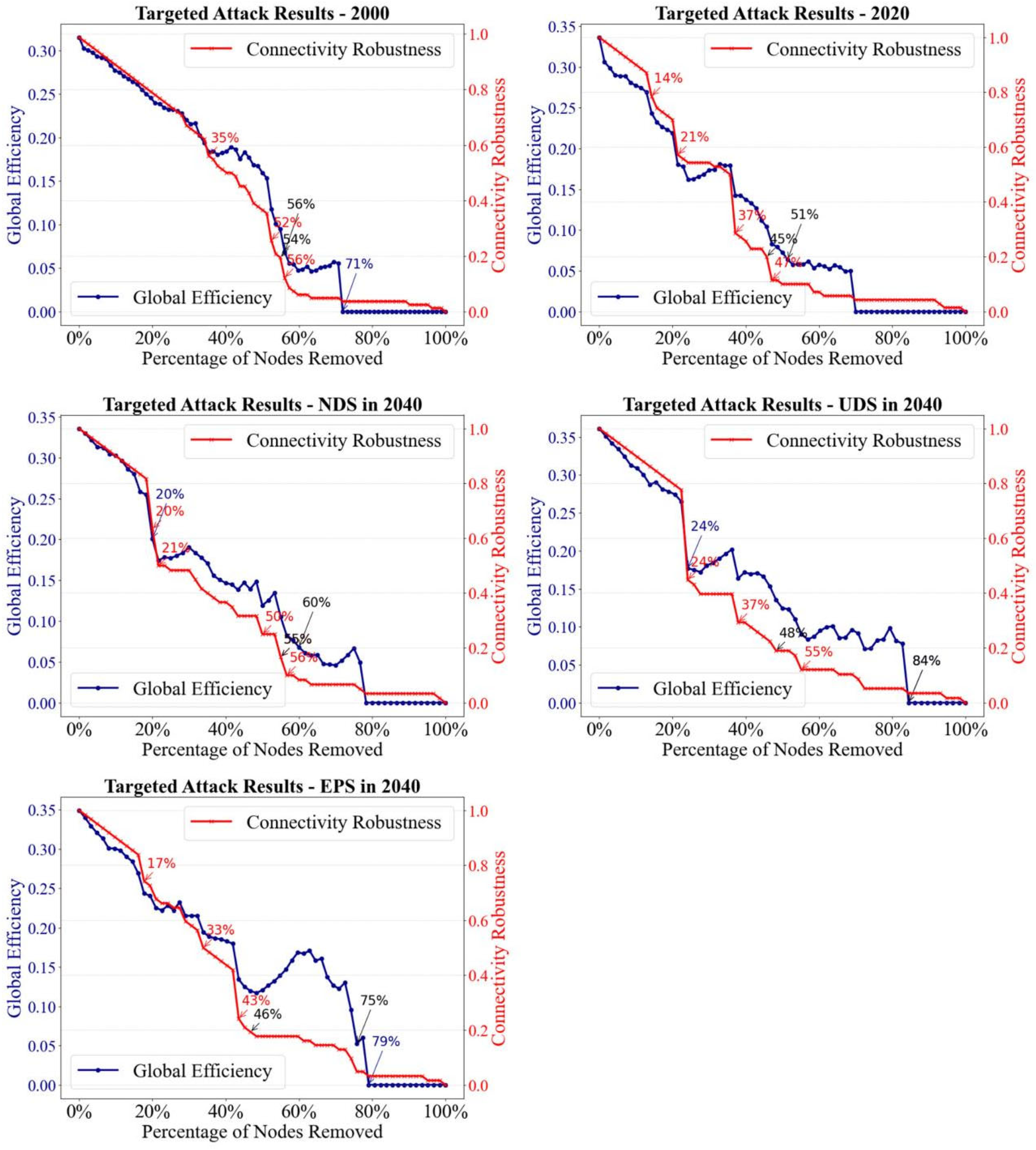
4.3. EN Resilience Analysis
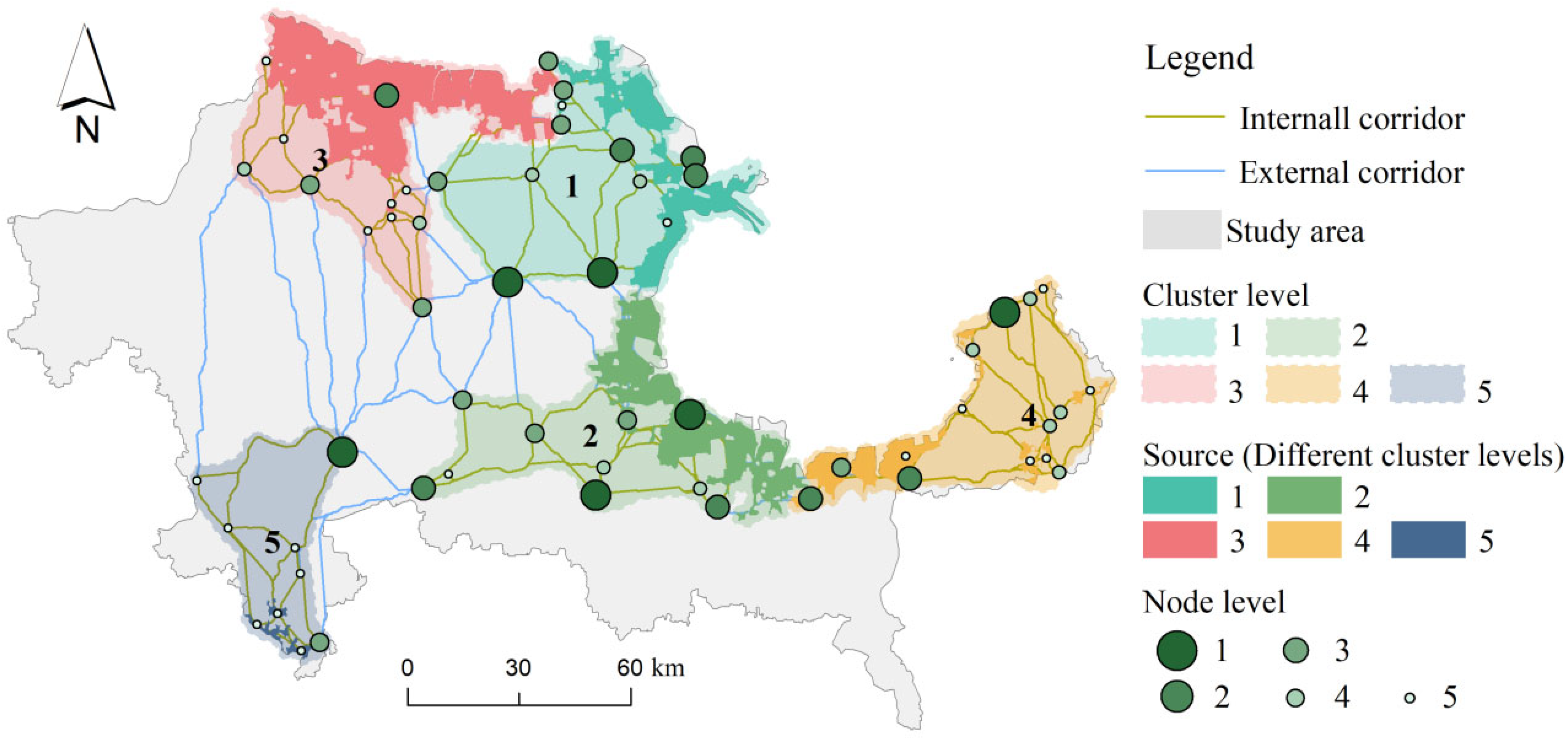
4.4. Community Detection Within the EN
5. Discussion
5.1. Relationship Between Land Use and EN Patterns
5.2. Factors Influencing the Resilience of EN
5.3. Priority Area Management Guided by Clustering
5.4. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EN | Ecological Network |
| NDS | Natural Development Scenario |
| EPS | Ecological Protection Scenario |
| UDS | Urban Development Scenario |
References
- Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Shan, L.; Xiao, F. Constructing and Optimizing Urban Ecological Network in the Context of Rapid Urbanization for Improving Landscape Connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Su, K.; Yu, S.; Jiang, X. Multi-Scenario Ecological Network Conservation Planning Based on Climate and Land Changes: A Multi-Species Study in the Southeast Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Forests 2024, 15, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Huang, L. Linking MSPA and Circuit Theory to Identify the Spatial Range of Ecological Networks and Its Priority Areas for Conservation and Restoration in Urban Agglomeration. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 828979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhai, T. Measuring the Resilience of Mountain City Ecological Network: A Methodological Framework Integrating Real Disaster Shocks and Simulated Disturbance Scenarios. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 384, 125573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A Future Land Use Simulation Model (FLUS) for Simulating Multiple Land Use Scenarios by Coupling Human and Natural Effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, D.; Pan, J. Incorporating Network Topology and Ecosystem Services into the Optimization of Ecological Network: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Huan, Y.; Wang, L.; Lan, Y.; Liang, T.; Shi, B.; Zhang, Q. Linking Ecosystem Services and Circuit Theory to Identify Priority Conservation and Restoration Areas from an Ecological Network Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Cai, J.; Peng, R.; Li, P.; Chen, W.; Xia, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Z. Establishment and Optimization of Urban Ecological Network Based on Ecological Regulation Services Aiming at Stability and Connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Haiwei, Y.; Fanhua, K.; Jiangang, X. Developing Ecological Networks Based on Mspa and the Least-Cost Path Method a Case Study in Bazhong Western New District. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 6425–6434. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. The Complex Ecological Network’s Resilience of the Wuhan Metropolitan Area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Jiao, L.; Lian, X.; Wang, W. Linking Supply-Demand Balance of Ecosystem Services to Identify Ecological Security Patterns in Urban Agglomerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 92, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhang, P. Linking Ecosystem Service and MSPA to Construct Landscape Ecological Network of the Huaiyang Section of the Grand Canal. Land 2021, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jia, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Gao, Q. Application of MSPA-MCR Models to Construct Ecological Security Pattern in the Basin: A Case Study of Dawen River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Min, H. Solving Minimum Constraint Removal (MCR) Problem Using a Social-Force-Model-Based Ant Colony Algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 43, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fu, H. Construct the Future Wetland Ecological Security Pattern with Multi-Scenario Simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Xu, K.; Qian, Y. Ecological Network Resilience Evaluation and Ecological Strategic Space Identification Based on Complex Network Theory: A Case Study of Nanjing City. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation and Optimization of Ecological Spatial Resilience of Yanhe River Basin Based on Complex Network Theory. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tang, F.; Wang, G.; Li, M. Construction of an Ecological Security Network in the Fenhe River Basin and Its Temporal and Spatial Evolution Characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 137961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Li, G.; Li, B. Research on the Resilience of Ecological Networks from the Perspective of Ecological Security Pattern: A Case Study of Wuhan Metropolitan Area. Sci. Rep. 2025, 16, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Du, Q.; Xiao, X.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Mi, J. Simulation of Future Land Use/Cover Change (LUCC) in Typical Watersheds of Arid Regions under Multiple Scenarios. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verburg, P.H.; Soepboer, W.; Veldkamp, A.; Limpiada, R.; Espaldon, V.; Mastura, S.S.A. Modeling the Spatial Dynamics of Regional Land Use: The CLUE-S Model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the Drivers of Sustainable Land Expansion Using a Patch-Generating Land Use Simulation (PLUS) Model: A Case Study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Rong, W. Construction of Ecological Network in Suzhou Based on the PLUS and MSPA Models. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wang, H.; Qin, F.; Miao, C.; Zhang, F. Coupled MOP and PLUS-SA Model Research on Land Use Scenario Simulations in Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area, Central China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Tong, D.; Liu, Z.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Forecasting Urban Land Use Change Based on Cellular Automata and the PLUS Model. Land 2022, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Le, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, J.; Luo, Y. Multi-Scenario Analysis and Optimization Strategy of Ecological Security Pattern in the Weihe River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Cai, X.Q.; Hao, C.S.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ma, Y.N. Ecosystem Service Tradeoff and Synergistic Relationship in the Yellow River Delta High-Efficiency Eco-Economic Zone. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 457–468. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, Y.; Duanmu, Z.; Li, M. Exploring Habitat Patch Clus-ters Based on Network Community Detection to Identify Restored Priority Areas of Ecological Networks in Urban Areas. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 78, 127771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yan, D.; Li, K.; Zhou, C.; Chen, X. Ecological Network Construction and Community Resilience Analysis of Nocturnal Birds: A Case Study of Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 175, 113613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor Rollan, A.; Berlow, E.L.; Williams, R.; Treml, E.A. Managing the Fuzzy Boundaries and Partitions of Marine Ecological Systems Using Network Theory. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Chang, M.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, L. Exploring the Changes and Driving Mechanisms in the Production-Transport-Consumption Process of Ecosystem Services Flow in the Yellow River Basin under the Background of Policy Changes. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gou, Y.; et al. Dynamic Landscapes and the Influence of Human Activities in the Yellow River Delta Wetland Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 166239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Kong, F.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, W.; Han, M. Assessment of Coastal Landscape Fragmentation and Its Driving Factors Based on Optimal Scale: A Case Study of the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, C. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation and Policy Optimization of Ecological Well-Being in the Yellow River Delta High-Efficiency Eco-Economic Zone. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ren, J.; Hou, C.; Ren, M. Meaning of Space Balance and Assessing the State of the Coastal Ecological Regions: A Case of the Yellow River Delta Efficient Ecological Economic Zone. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 37, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chuai, X. Study on the Optimization of Territory Spatial “Urban–Agricultural–Ecological” Pattern Based on the Improvement of “Production–Living–Ecological” Function under Carbon Constraint. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, S. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Urban Land Change in Shanghai by Random Forest and CA-Markov Model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wu, J. Land-Use and Habitat Quality Prediction in the Fen River Basin Based on PLUS and InVEST Models. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1386549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Y. Study on the Measurement of High-Quality Development Efficiency and Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Wetlands and Their Future Multi-Scenario Simulation in the Yellow River Delta, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Suo, M.; Gao, S.; Jiao, H. Construction of an Ecological Network Based on an Integrated Approach and Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Panzhou in Guizhou Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, L. The spatial-temporal patterns of bird diversity and its determinants in the small wetlands in Hefei City. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 21445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Exploring the Optimization and Management Methods of Ecological Networks Based on the Cluster Mode: A Case Study of Wuhan Metropolis, China. Land Use Policy 2024, 137, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Fazlali, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M. Accelerating Louvain Community Detection Algorithm on Graphic Processing Unit. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 6056–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pu, P.; Han, D.; Tang, M. Self-Adaptive Louvain Algorithm: Fast and Stable Community Detection Algorithm Based on the Principle of Small Probability Event. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 506, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.P.; Garcia-Callejas, D.; Lai, H.R.; Wootton, K.L.; Tylianakis, J.M. The Propagation of Disturbances in Ecological Networks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2024, 39, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B. Identifying Priority Areas for Conservation in the Lower Yellow River Basin from an Ecological Network Perspective. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2022, 8, 2105751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, F.; Qin, L. Construction and Stability Evaluation of Ecological Networks in the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Dong, B.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z. Study on Habitat Quality of Chongming Dongtan Based on InVEST Model in Shanghai, China. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2025, 53, 3237–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Data Sources | Related Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Land use | http://www.resdc.cn/DOl,2018.https://doi.org/10.12078/2018070201 (accessed on 24 November 2025) | LULC simulation and Resistance factor |
| MSPA | Generated from land use (http://www.resdc.cn/DOl,2018.https://doi.org/10.12078/2018070201 (accessed on 24 November 2025)) using Guidos Toolbox 3.3 | Resistance factor |
| DEM | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 24 November 2025)) | Resistance factor and driving factor |
| Slope | ||
| Distance from highway | Open Street Map (https://www.openstreetmap.org/ (accessed on 24 November 2025)) | Resistance factor and driving factor |
| Distance from railway | ||
| Distance from provincial road | ||
| Distance from national road | ||
| Distance from water area | driving factor | |
| Distribution data of soil types | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform (https://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 24 November 2025)) | driving factor |
| Annual average precipitation | ||
| Annual average temperature | ||
| Gross domestic product | ||
| Population distribution data |
| Land Classification and Code | Secondary Classification of Land Use Classification System | Neighborhood Weight Values |
|---|---|---|
| Agricultural production land (A) | Dryland and paddy fields | 0.5 |
| Industrial production land (B) | Other construction land | 1 |
| Forest ecological land (C) | Forest land, shrubland, sparse forest land, other forest land | 0.5 |
| Grassland Ecosystem Land (D) | High coverage grassland, medium coverage grassland, low coverage grassland | 0.8 |
| Aquatic Ecological Land (E) | Rivers, canals, reservoirs, and ponds | 0.6 |
| Other ecological land (F) | Beach land, swamp land | 0.3 |
| Urban residential land (G) | Urban land | 1 |
| Rural residential land (H) | Rural residential areas | 1 |
| Land Type | NDS | EPS | UDS | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | |
| A | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| B | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| C | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| D | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| E | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| F | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| G | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| H | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Resistance | Classification/Grading of Factors | Resistance Value | Weight | Resistance | Classification/Grading of Factors | Resistance Value | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSPA | Core | 10 | 0.35 | Land type | Agricultural production land | 50 | 0.25 |
| Bridge | 10 | Industrial production land | 90 | ||||
| Edge | 20 | Forest ecological land | 10 | ||||
| Islet | 20 | Grassland Ecosystem Land | 20 | ||||
| Branch | 30 | Aquatic Ecological Land | 40 | ||||
| Loop | 30 | Other ecological land | 50 | ||||
| Perforation | 40 | Urban residential land | 90 | ||||
| Background | 90 | Rural residential land | 70 | ||||
| DEM | 0–100 | 0.1 | Slope | 0–100 | 0.1 | ||
| Distance from highway | 0–100 | 0.05 | Distance from railway | 0–100 | 0.05 | ||
| Distance from provincial road | 0–100 | 0.05 | Distance from national road | 0–100 | 0.05 | ||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 15,904.54 | 405.48 | 258.00 | 1773.05 | 2584.31 | 1652.22 | 270.48 | 2076.75 |
| 63.81% | 1.63% | 1.04% | 7.11% | 10.37% | 6.63% | 1.09% | 8.33% | |
| 2010 | 16,329.62 | 591.35 | 187.40 | 355.73 | 3749.87 | 401.43 | 1232.01 | 2077.41 |
| 65.52% | 2.37% | 0.75% | 1.43% | 15.04% | 1.61% | 4.94% | 8.33% | |
| 2020 | 15,981.00 | 605.66 | 199.23 | 342.10 | 3971.88 | 341.57 | 1378.62 | 2104.76 |
| 64.12% | 2.43% | 0.80% | 1.37% | 15.94% | 1.37% | 5.53% | 8.44% | |
| NDS | 15,322.48 | 630.34 | 177.77 | 318.47 | 4364.81 | 295.03 | 1664.33 | 2151.59 |
| 61.47% | 2.53% | 0.71% | 1.28% | 17.51% | 1.18% | 6.68% | 8.63% | |
| UDS | 15,194.04 | 629.96 | 172.46 | 316.49 | 4364.02 | 303.44 | 1737.61 | 2206.79 |
| 60.96% | 2.53% | 0.69% | 1.27% | 17.51% | 1.22% | 6.97% | 8.85% | |
| EPS | 15,470.41 | 582.83 | 189.11 | 318.59 | 4357.24 | 314.02 | 1591.54 | 2101.06 |
| 62.07% | 2.34% | 0.76% | 1.28% | 17.48% | 1.26% | 6.39% | 8.43% |
| Source Amount | Source Area/km2 | Corridor Amount | Corridor Total Length/km | Corridor Area/km2 | Source and Corridor Area/km2 | Proportion of EN Area in the Study Area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 82 | 3593.11 | 232 | 4226.76 | 1773.55 | 5366.67 | 21.53% |
| 2020 | 70 | 3036.90 | 195 | 3550.78 | 1580.36 | 4617.26 | 18.52% |
| NDS in 2040 | 60 | 3327.74 | 157 | 3483.57 | 1337.83 | 4665.57 | 18.72% |
| UDS in 2040 | 58 | 3338.29 | 161 | 3457.30 | 1666.48 | 5004.78 | 20.08% |
| EPS in 2040 | 62 | 3401.04 | 174 | 3436.54 | 1543.04 | 4944.08 | 19.84% |
| Cluster Level | Source Amount | Internal Corridor Amount | External Corridor Amount | Connect Clusters Amount | Degree Centrality | Eigenvector Centrality | Comprehensive Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13 | 29 | 17 | 3 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.72 |
| 2 | 10 | 21 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0.54 | 0.60 |
| 3 | 11 | 25 | 8 | 3 | 0.75 | 0.43 | 0.46 |
| 4 | 15 | 35 | 2 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.26 | 0.34 |
| 5 | 9 | 17 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.36 | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, Y.; Yong, C.; Yang, J.; Guan, B.; Qu, F.; Wang, Z. Multi-Scenario Assessment of Ecological Network Resilience and Community Clustering in the Yellow River Delta. Land 2026, 15, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010170
Zhu Y, Du Z, Li Y, Yong C, Yang J, Guan B, Qu F, Wang Z. Multi-Scenario Assessment of Ecological Network Resilience and Community Clustering in the Yellow River Delta. Land. 2026; 15(1):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010170
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yajie, Zhaohong Du, Yunzhao Li, Chienzheng Yong, Jisong Yang, Bo Guan, Fanzhu Qu, and Zhikang Wang. 2026. "Multi-Scenario Assessment of Ecological Network Resilience and Community Clustering in the Yellow River Delta" Land 15, no. 1: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010170
APA StyleZhu, Y., Du, Z., Li, Y., Yong, C., Yang, J., Guan, B., Qu, F., & Wang, Z. (2026). Multi-Scenario Assessment of Ecological Network Resilience and Community Clustering in the Yellow River Delta. Land, 15(1), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/land15010170








