Evaluating Future Water Resource Risks in the Driftless Midwest from Climate and Land Use Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
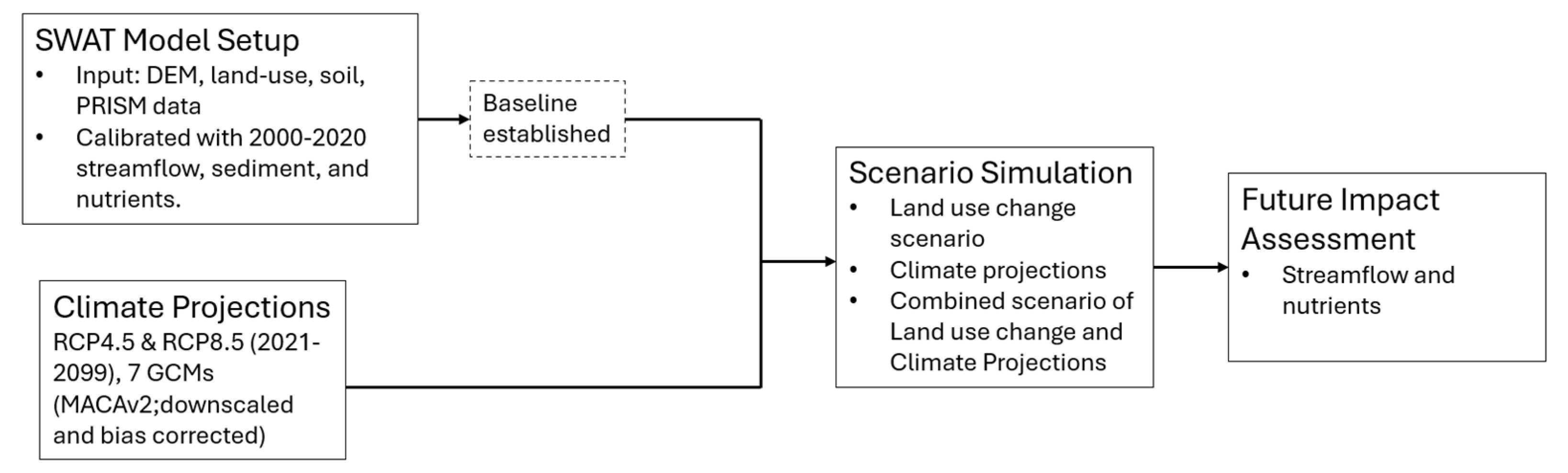
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
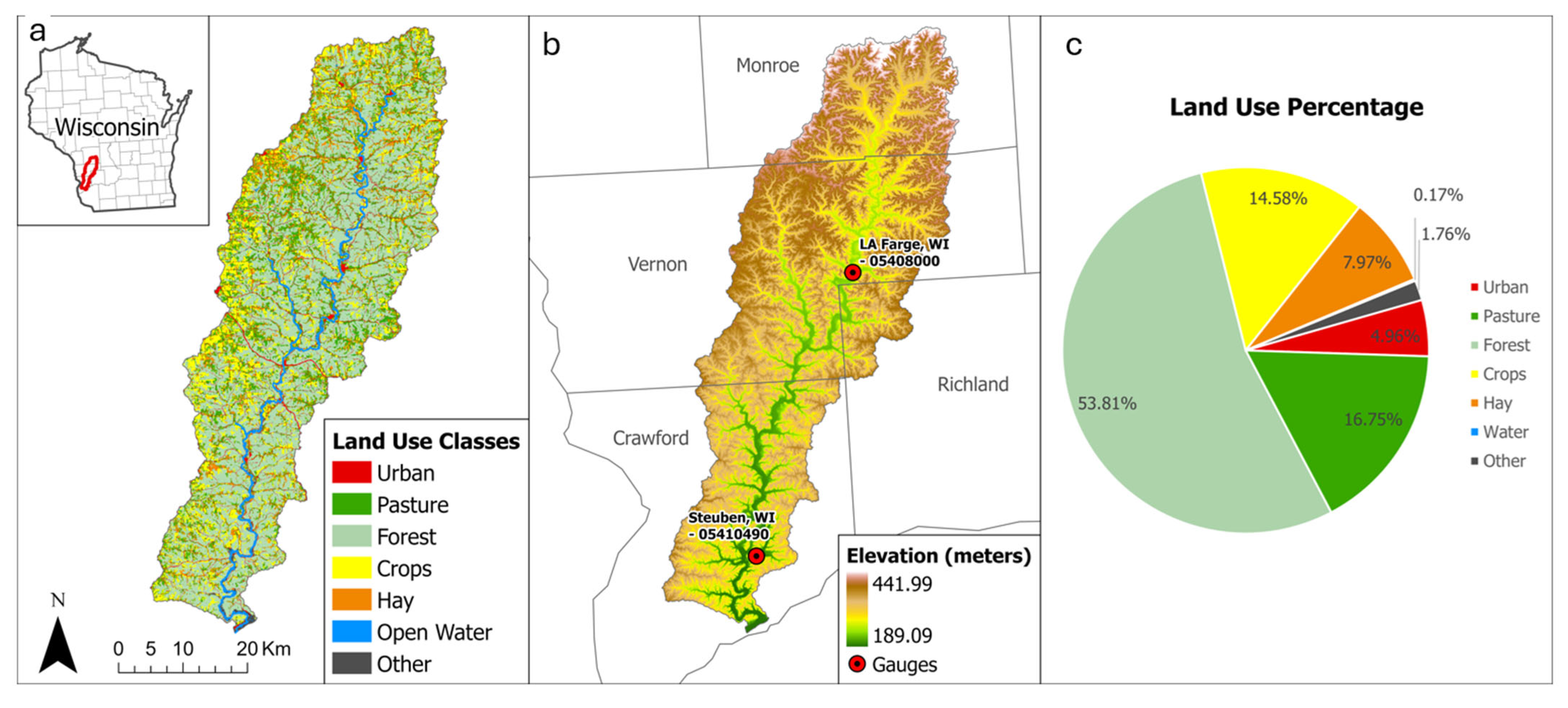
2.2. Methods
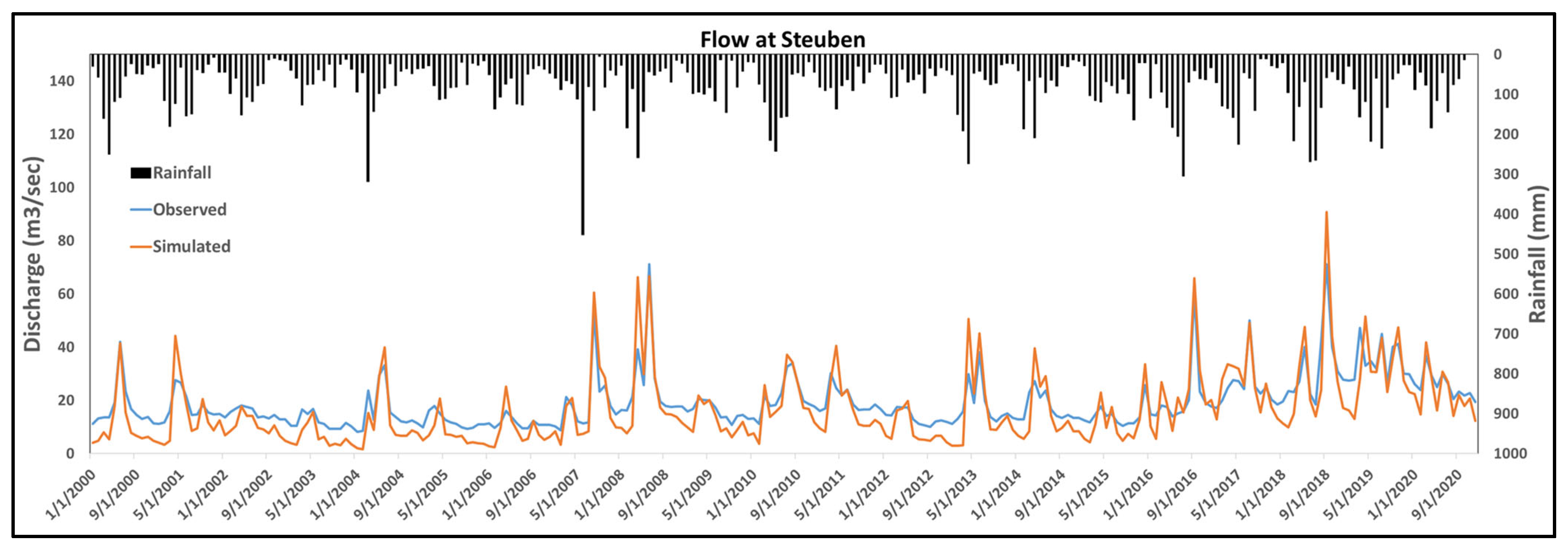
2.2.1. Model Setup and Calibration
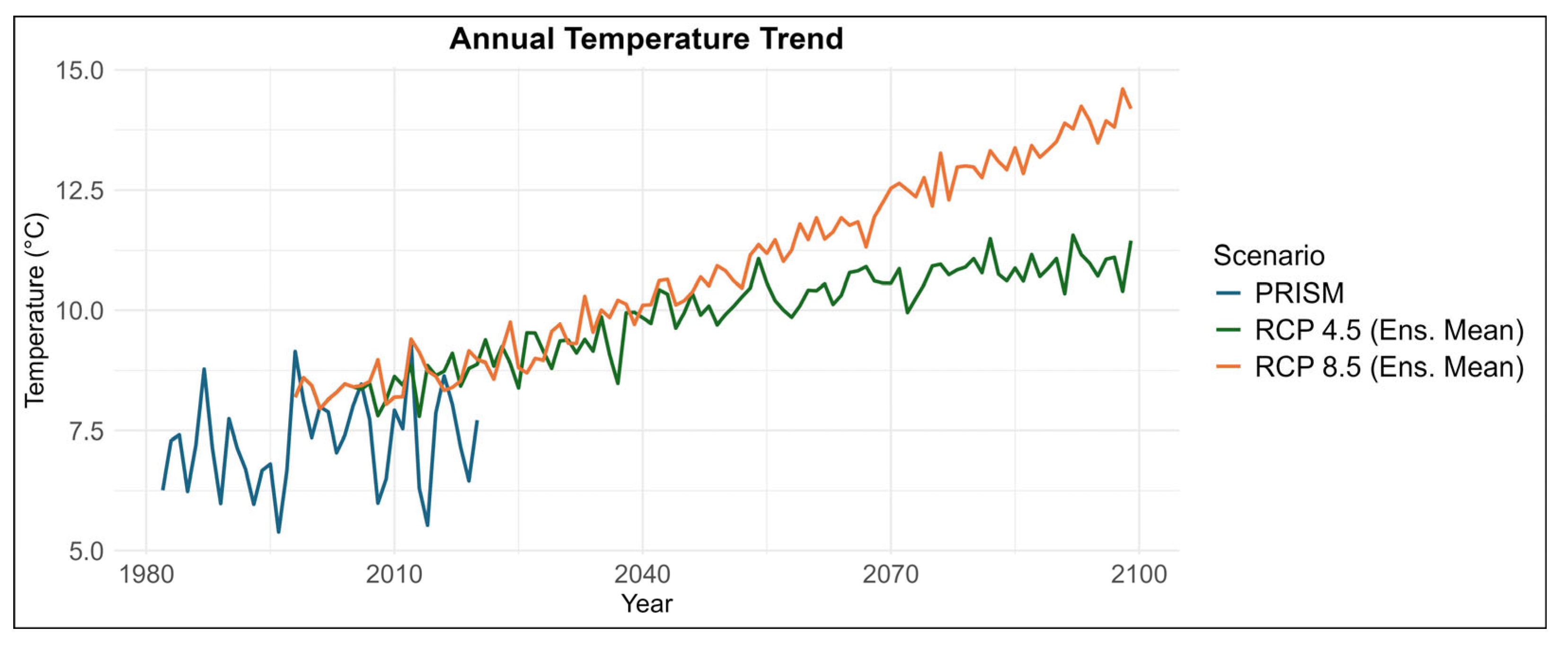
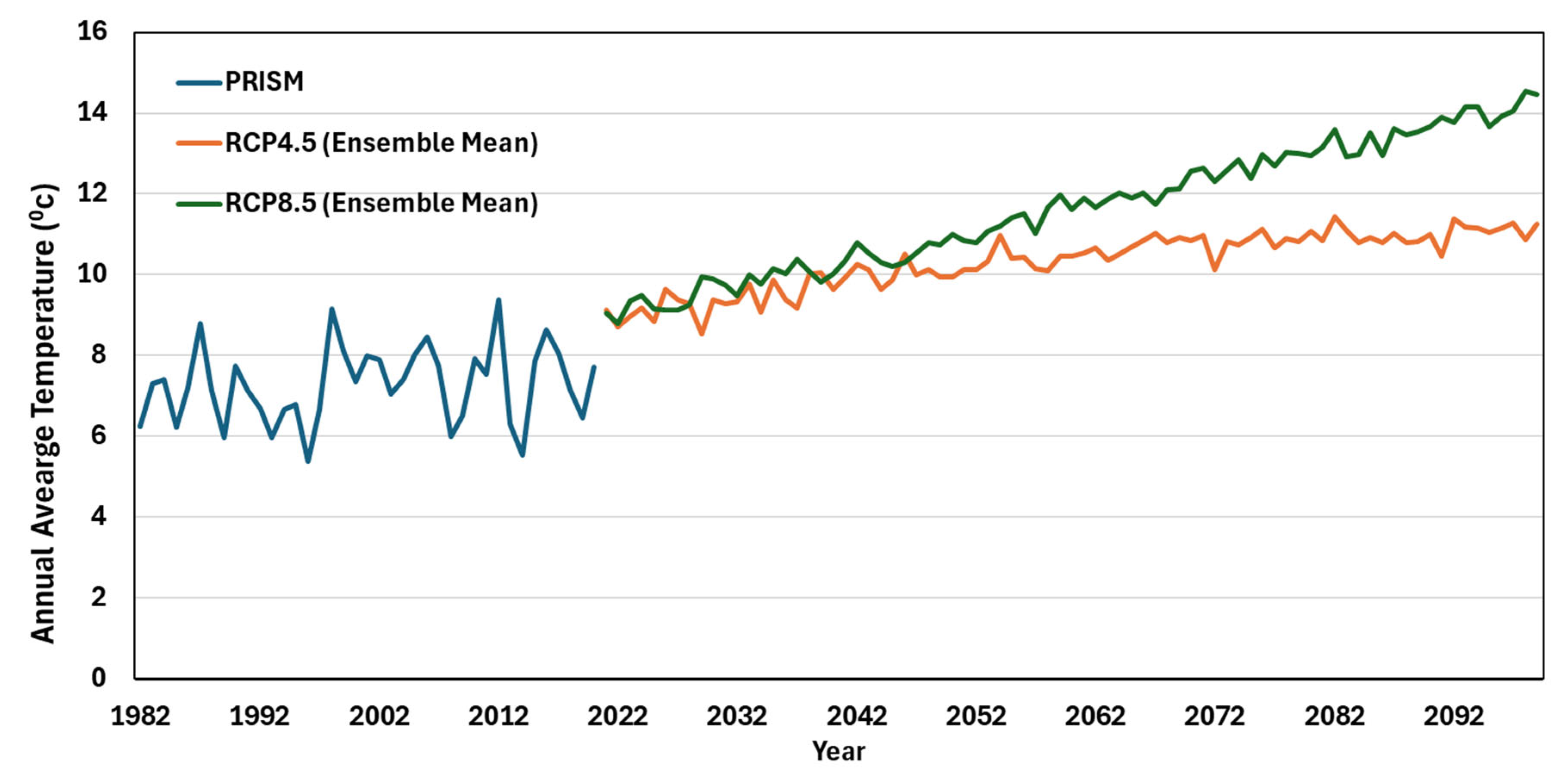
2.2.2. Future Climate Projections
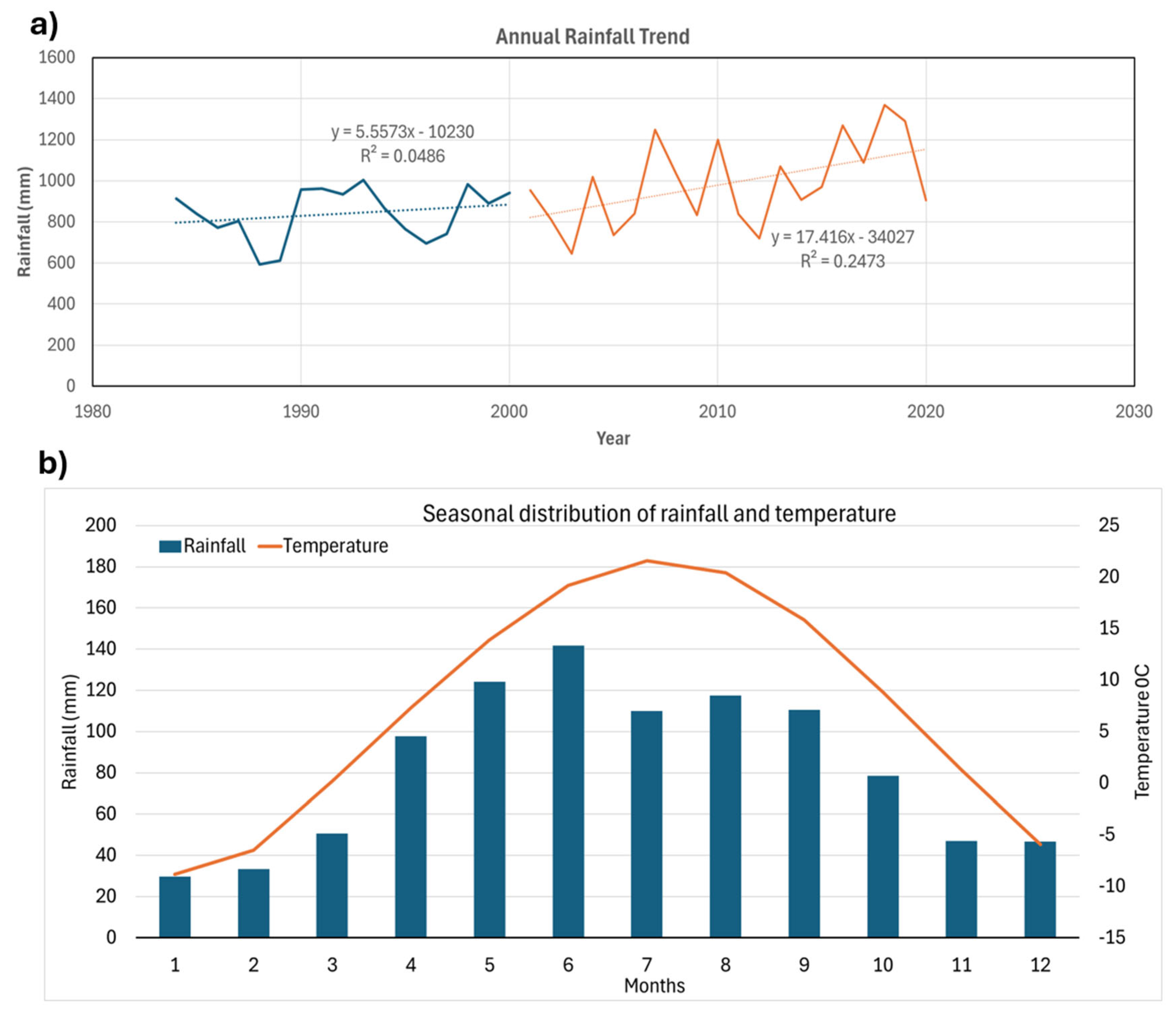
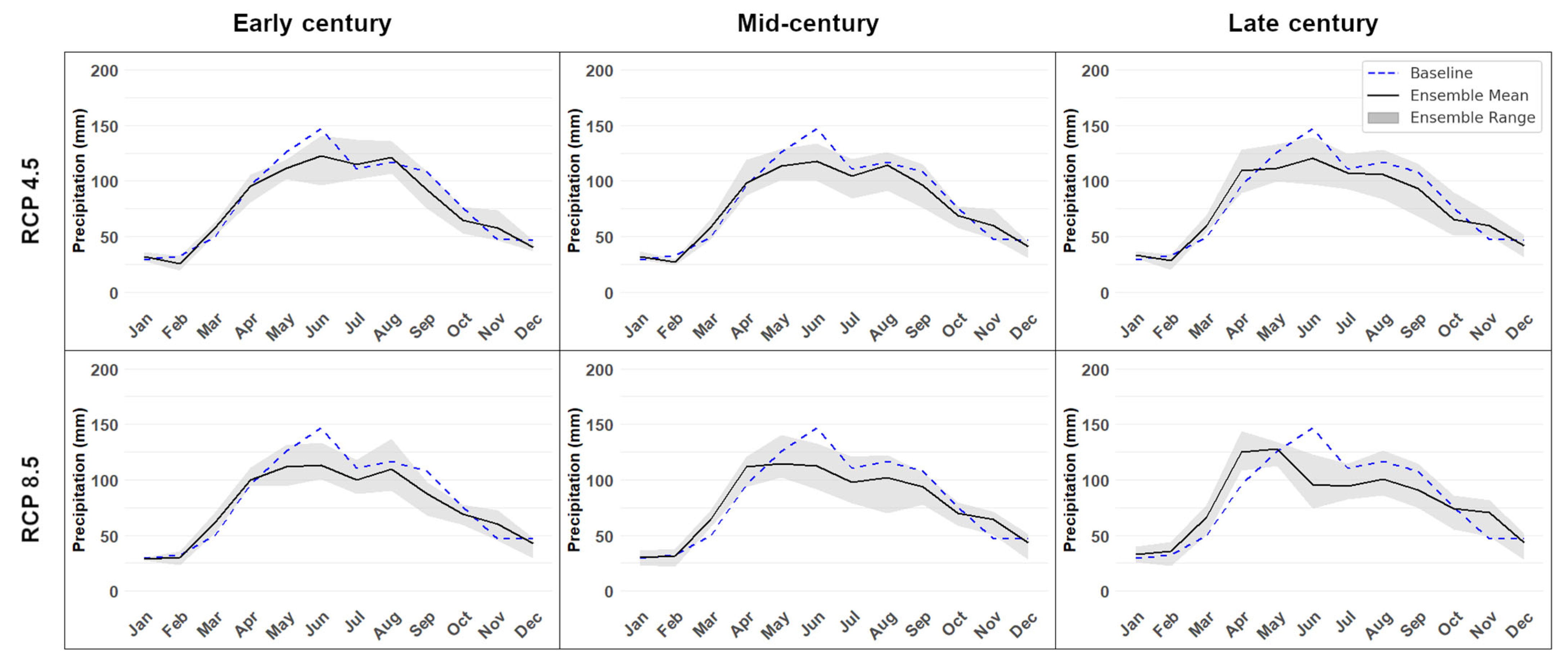
2.2.3. Projected Rainfall and Temperature
2.3. Scenarios
3. Results
3.1. Climate Change Scenario (CC) Impacts on the Entire Watershed
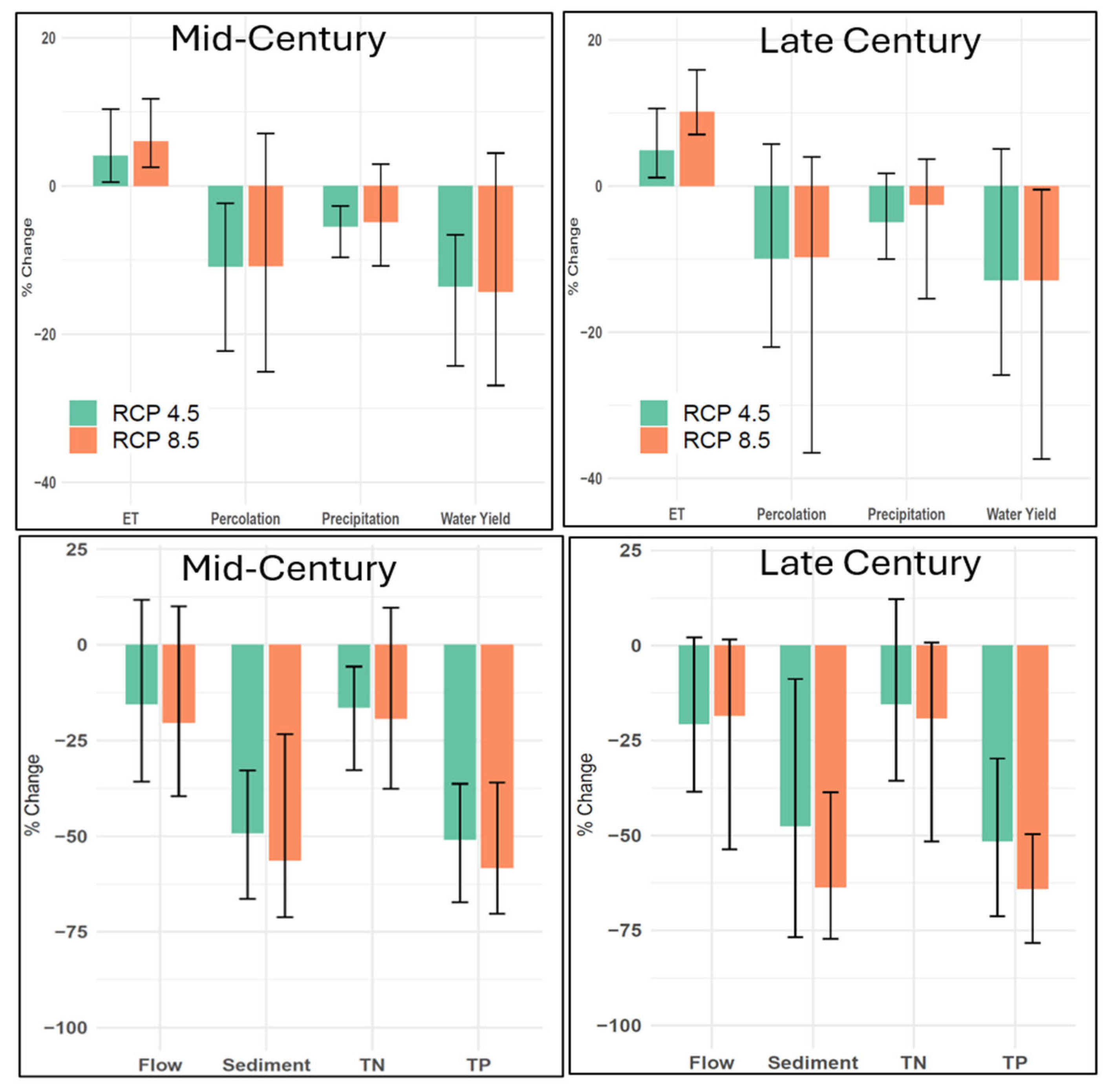
3.1.1. Impact on Water Balance
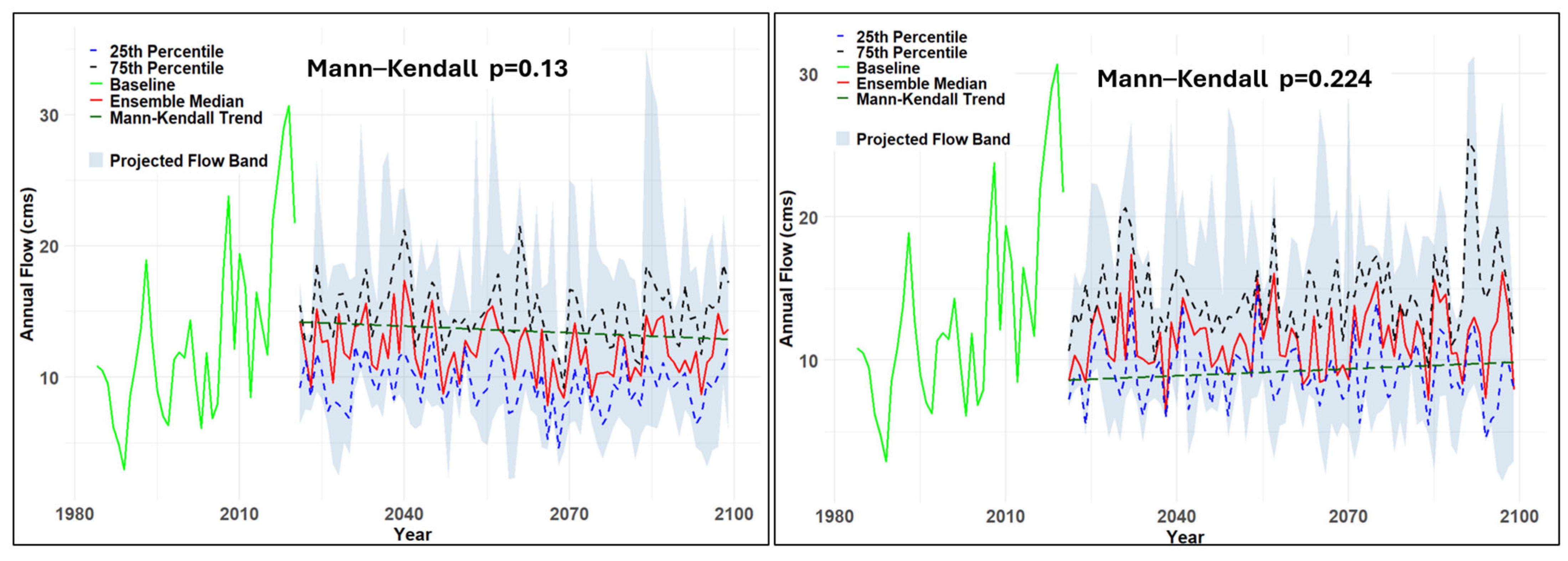
3.1.2. Impact on Stream Flow
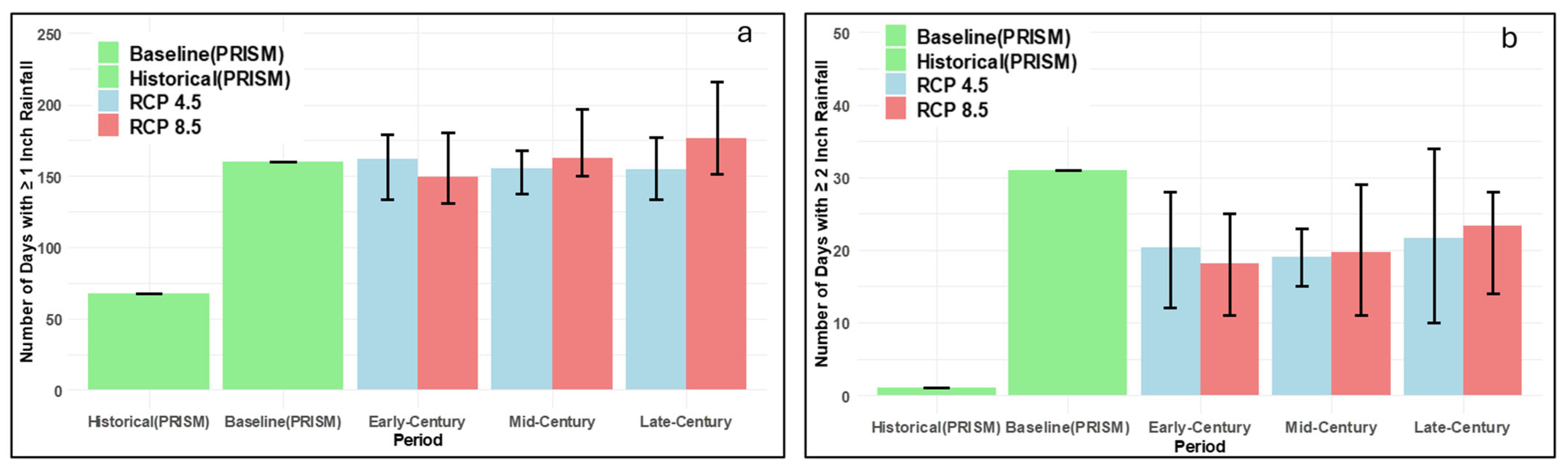
3.1.3. Impact on Sediment and Nutrient Load
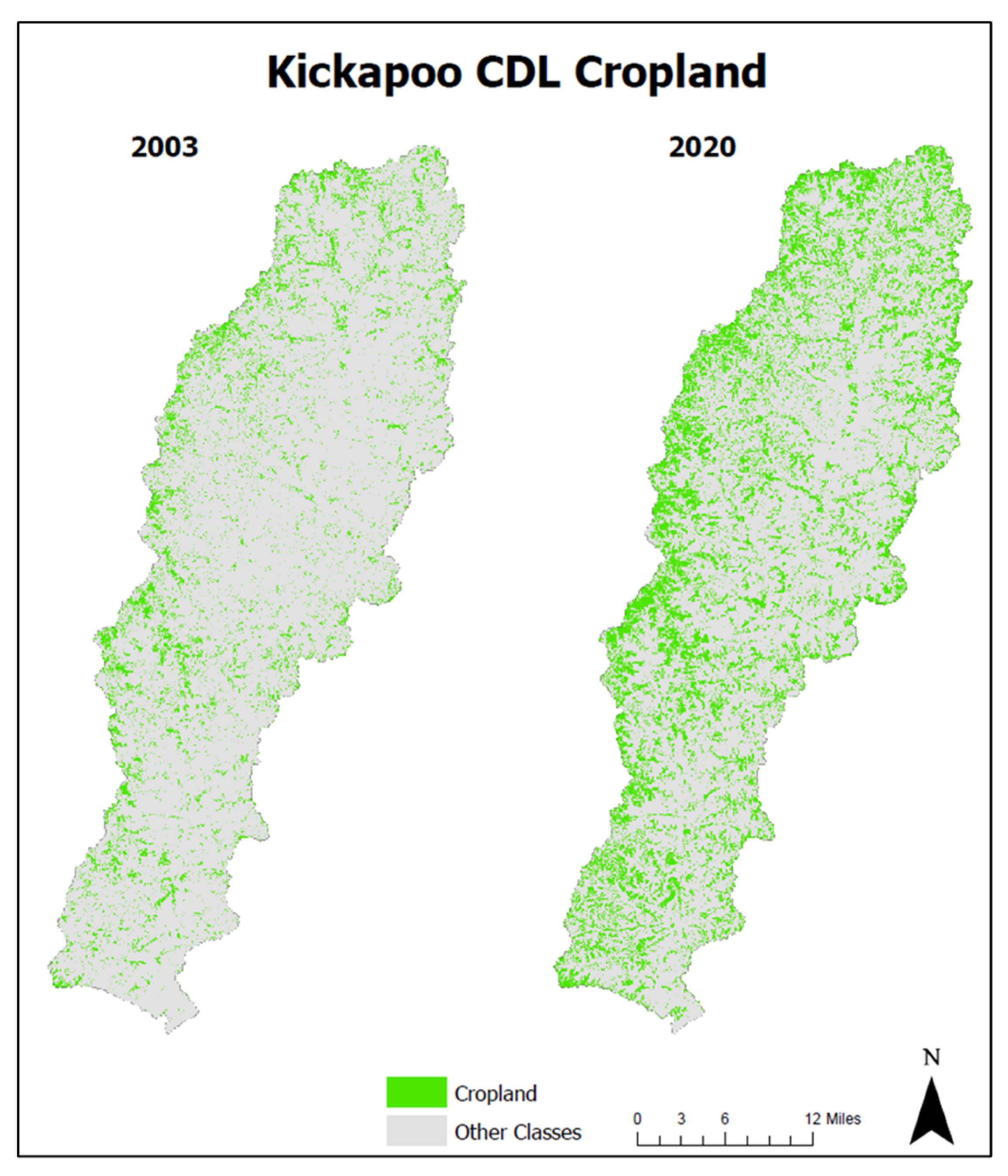
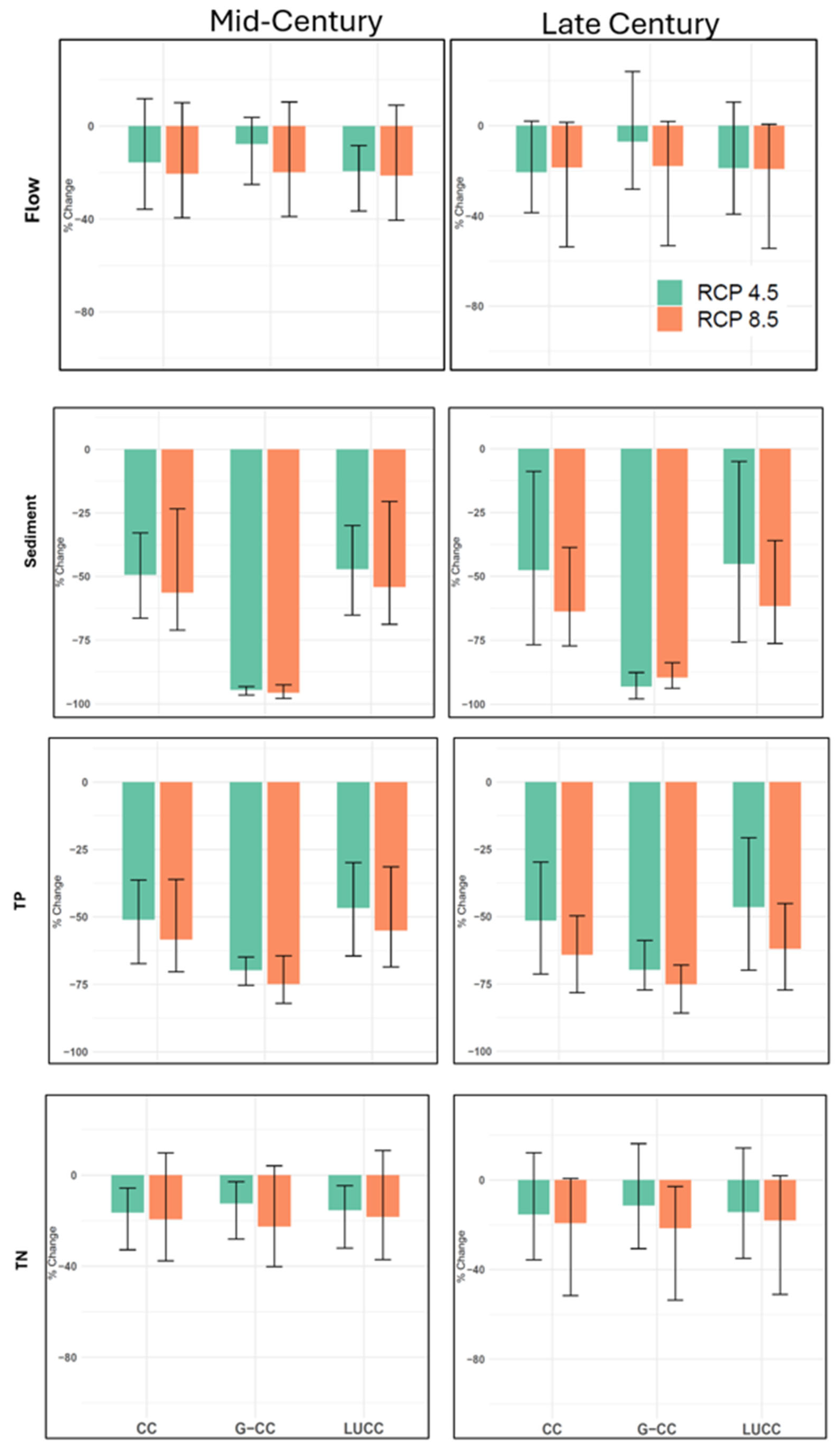
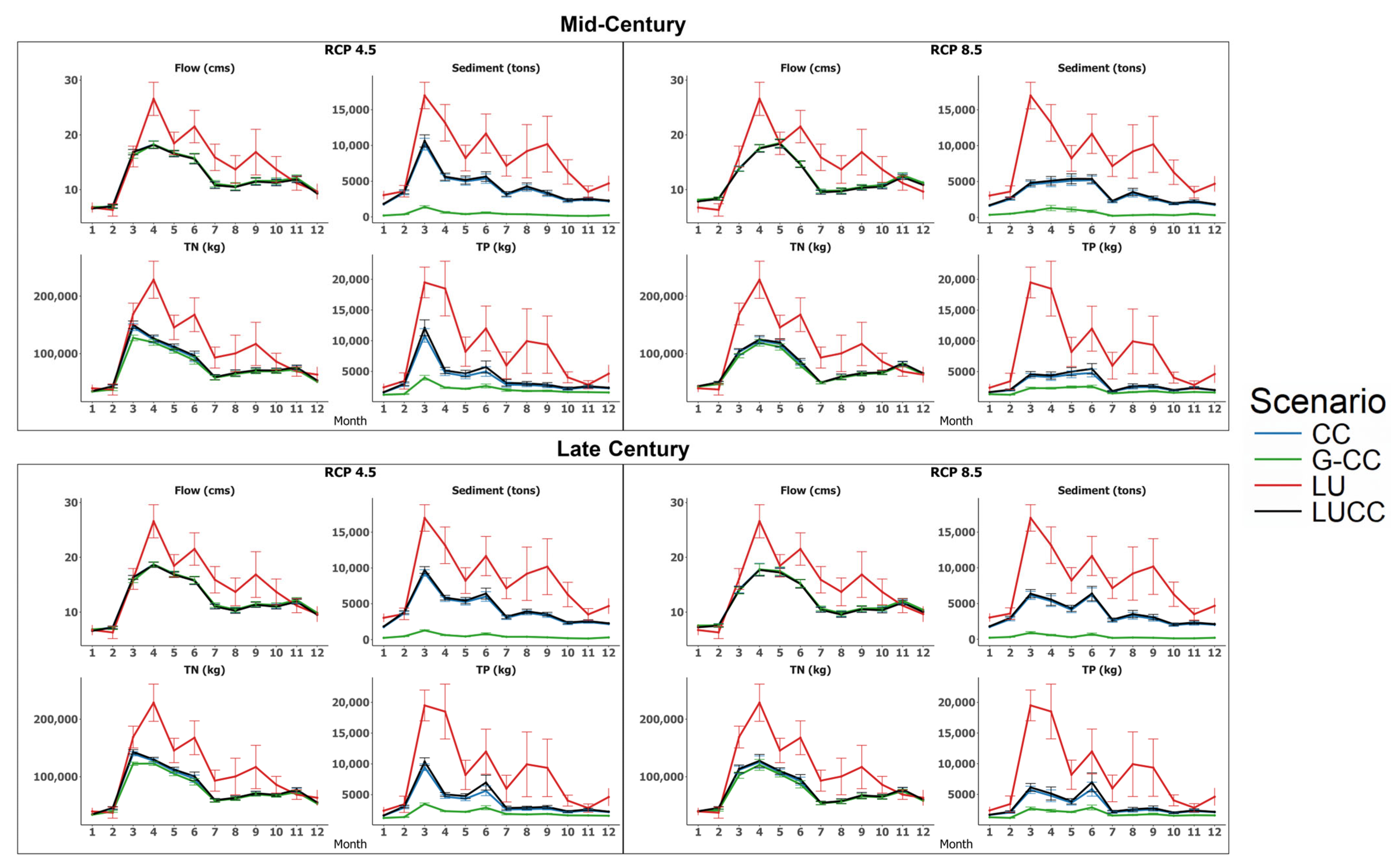
3.2. Land Use and Climate Change Compounding Impacts on the Entire Watershed
4. Discussion
Research Limitations and Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Villarini, G.; Smith, J.A.; Baeck, M.L.; Krajewski, W.F. Examining Flood Frequency Distributions in the Midwest U.S. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 47, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpa, D.; Nunes, J.P.; Santos, J.; Sampaio, E.; Jacinto, R.; Veiga, S.; Lima, J.C.; Moreira, M.; Corte-Real, J.; Keizer, J.J.; et al. Impacts of climate and land use changes on the hydrological and erosion processes of two contrasting Mediterranean catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Gold, A.J.; Mayer, P.M. Land Use, Climate, and Water Resources—Global Stages of Interaction. Water 2017, 9, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.S.; Ramachandran, R.M.; Paul, O.; Thakur, P.K.; Ravan, S.; Behera, M.D.; Sarangi, C.; Kanawade, V.P. Anthropogenic Land Use and Land Cover Changes—A Review on Its Environmental Consequences and Climate Change. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2022, 50, 1615–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perring, M.P.; De Frenne, P.; Baeten, L.; Maes, S.L.; Depauw, L.; Blondeel, H.; Carón, M.M.; Verheyen, K. Global environmental change effects on ecosystems: The importance of land-use legacies. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D.; Islam, S.; Vogel, R.M. Trends in precipitation and streamflow in the eastern U.S.: Paradox or perception? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L03403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficklin, D.L.; Stewart, I.T.; Maurer, E.P. Effects of projected climate change on the hydrology in the Mono Lake Basin, California. Clim. Change 2013, 116, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zwiers, F.W.; Groisman, P.Y. The Influence of Large-Scale Climate Variability on Winter Maximum Daily Precipitation over North America. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2902–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.J.; Miller, S.N. Using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to assess land use impact on water resources in an East African watershed. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, C.; Yin, F. Impacts of land use and land cover changes on surface energy and water balance in the Heihe River Basin of China, 2000–2010. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2015, 79-82, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Ren, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Shi, P.; Zhu, Y. Hydrologic Response to Land Use and Land Cover Changes within the Context of Catchment-Scale Spatial Information. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.-Z.; Zhang, X.-C.; Zheng, F.-L. Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarian, H.; Balasundram, S.K.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Talib, J.B.; Boon Sung, C.T.; Sood, A.M. SWAT-based hydrological modelling of tropical land-use scenarios. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1808–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, C.M.; Spoehr, J. The acceptability of climate change in agricultural communities: Comparing responses across variability and change. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 115, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Balarezo, J.J.; Sucozhañay-Calle, A.E.; Crespo-Sánchez, P.J.; Timbe-Castro, L.M. Applying hydrological modeling to unravel the effects of land use change on the runoff of a paramo ecosystem. DYNA 2022, 89, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Libra, R.D. Increased baseflow in iowa over the second half of the 20th century. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 39, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomer, M.D.; Schilling, K.E. A simple approach to distinguish land-use and climate-change effects on watershed hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillon, S.; Booth, E.G.; Rissman, A.R. Shifting drivers and static baselines in environmental governance: Challenges for improving and proving water quality outcomes. Reg. Environ. Change 2016, 16, 759–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E. Relation of baseflow to row crop intensity in Iowa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Schilling, K.E. Increasing streamflow and baseflow in Mississippi River since the 1940s: Effect of land use change. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, P.Y.; Knight, R.W.; Karl, T.R. Changes in Intense Precipitation over the Central United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, E.V.; Stefan, H.G. Stream flow in Minnesota: Indicator of climate change. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G.; Scoccimarro, E.; White, K.D.; Arnold, J.R.; Schilling, K.E.; Ghosh, J. Projected Changes in Discharge in an Agricultural Watershed in Iowa. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.; Arnold, J.G.; Gassman, P.W.; Giorgi, F.; Gu, R.R. Climate chhange sensitivity assessment on upper mississippi river basin streamflows using swat. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 997–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauldin, L. Official Recognized Boundary of Driftless Area Restoration Effort, 2013; D.A.R.E. United States Geological Survey, National Fish Habitat Partnership, Eds.; National Fish Habitat Partnership Science and Data Committee. 2013. Available online: https://www.sciencebase.gov/catalog/item/52274d4ce4b01904cf5a81e0 (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- Knox, J.C. Geology of the Driftless Area. In The Physical Geography and Geology of the Driftless Area: The Career and Contributions of James C. Knox; Carson, E.C., Rawling, J.E., III, Daniels, J.M., Attig, J.W., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gebert, W.A.; Krug, W.R. Streamflow trends in Wisconsin’s driftless area. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1996, 32, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juckem, P.F.; Hunt, R.J.; Anderson, M.P.; Robertson, D.M. Effects of climate and land management change on streamflow in the driftless area of Wisconsin. J. Hydrol. 2008, 355, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.C. Agricultural influence on landscape sensitivity in the Upper Mississippi River Valley. CATENA 2001, 42, 193–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, L. Analysis of the Driftless Area. In Regional and Property Analysis for the Development of a Master Plan for Department of Natural Resources’ Properties Along Trout and Smallmouth Bass Streams in the Driftless Area; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bendorf, J.; Hubbard, S.; Kucharik, C.J.; VanLoocke, A. Rapid changes in agricultural land use and hydrology in the Driftless Region. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2021, 4, e20214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, L.W.; Hobbs, J.; Arbuckle, J.G.; Loy, A. Upper Midwest Climate Variations: Farmer Responses to Excess Water Risks. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Jha, M.K.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Gassman, P.W.; Wolter, C.F. Impact of land use and land cover change on the water balance of a large agricultural watershed: Historical effects and future directions. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00A09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, A.; Markham, L.; McFarlane, D.; Olson, E.; Roberts, R.; Stoll, L. Wisconsin Land Use Megatrends: Agriculture; University of Wisconsin Extension: Madison, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jodar-Abellan, A.; Ruiz, M.; Melgarejo, J. Climate change impact assessment on a hydrologic basin under natural regime (SE, Spain) using a SWAT model. Rev. Mex. De Cienc. Geológicas 2018, 35, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes-Abellan, J.; Pardo, M.A.; Jodar-Abellan, A.; Pla, C.; Fernandez-Mejuto, M. Climate change impact on karstic aquifer hydrodynamics in southern Europe semi-arid region using the KAGIS model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharik, C.J.; Serbin, S.P.; Vavrus, S.; Hopkins, E.J.; Motew, M.M. Patterns of Climate Change Across Wisconsin From 1950 to 2006. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 31, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwalter, D.C.; Mitro, M.G. Climate Change, Recent Floods, and an Uncertain Future. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Driftless Area Symposium, La Crosse, WI, USA, 5–6 February 2019; Trout Unlimited: Denver, CO, USA, 2019. 8p. [Google Scholar]
- Serbin, S.P.; Kucharik, C.J. Spatiotemporal Mapping of Temperature and Precipitation for the Development of a Multidecadal Climatic Dataset for Wisconsin. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 742–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, R. Perspectives on the eutrophication of the Yahara lakes. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2007, 23, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, S.B. Peak Streamflow Trends in Wisconsin and Their Relation to Changes in Climate, Water Years 1921–2020. In Peak Streamflow Trends and Their Relation to Changes in Climate in Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wisconsin: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2024; 49p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, R.; Herlihey, C.; Parr, J.; Rosner, R.; Sodeman, R.; Wandsnider, K. Flood Resilience in the Coon Creek Watershed-2020 Water Resources Management Practicum Report; Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies, University of Wisconsin–Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Updating the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Water Quality Trading Policy to Promote Market-Based Mechanisms for Improving Water Quality; US EPA, Ed.; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2020-10/documents/trading-policy-memo-2019.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. Water Quality Standards for Wisconsin Surface Waters. In s. 35.93; Wisconsin Legislative Reference Bureau, Ed.; The State of Wisconsin: Wis. Stats.: Madison, WI, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Arden, S.; Morelli, B.; Miller, J.; Rath, S.; Ferrando, J.; Azevedo, G.; Nepal, S.; Demeke, B.; Ma, X. Environmental impacts and cost of a water quality trading approach for NPDES nutrient permit compliance in a rural watershed. Water Res. X 2025, 28, 100363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part i: Model development. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation, Version 2005; USDA Agricultural Research Service and Texas A&M Blackland Research Center: Temple, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation, Version 2009; USDA Agricultural Research Service and Texas A&M Blackland Research Center: Temple, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.; Butcher, J.; Deb, D.; Faizullabhoy, M.; Hummel, P.; Kittle, J.; McGinnis, S.; Mearns, L.O.; Nover, D.; Parker, A.; et al. Modeling Streamflow and Water Quality Sensitivity to Climate Change and Urban Development in 20 U.S. Watersheds. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 1321–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, I.B.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Trolle, D.; Børgesen, C.D.; Olesen, J.E.; Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, K.H. Combined effects of climate models, hydrological model structures and land use scenarios on hydrological impacts of climate change. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffield, S.J.; Bradbury, K.R.; Potter, K.W. Hydrologic Assessment of the Kickapoo Watershed, Southwestern Wisconsin; Wisconsin Geological and Natural History Survey and Department of Geological Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison: Madison, MI, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Trimble, S.W.; Lund, S.W. Soil Conservation and the Reduction of Erosion and Sedimentation in the Coon Creek Basin, Wisconsin; Professional Paper 1234; USGS Publications Warehouse: Virgina, VA, USA, 1982; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Frolking, T.A. The genesis and distribution of upland red clays in Wisconsin’s driftless area. In Quaternary History of the Driftless Area, Proceedings of the 29th Annual Meeting Midwest Friends of the Pleistocene; Ostrom, M.E., Ed.; University of Wisconsin-Extension: Prairie du Chien, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Knox, J.C. Valley Alluviation in Southwestern Wisconsin. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1972, 62, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.J. Geology of La Crosse County, Wisconsin. Wisconsin Geological and Natural History Survey Bulletin 101; Wisconsin Geological and Natural History Survey: Madison, WI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, E.G.; Zipper, S.C.; Loheide, S.P.; Kucharik, C.J. Is groundwater recharge always serving us well? Water supply provisioning, crop production, and flood attenuation in conflict in Wisconsin, USA. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 21, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA); National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS). USDA NASS Cropland Data Layer; USDA, NASS Marketing and Information Services Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P.; Doggett, M.K.; Taylor, G.H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P.P. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 2031–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.A.; Flint, L.E.; Flint, A.L.; Boynton, R.M.; Stewart, J.A.E.; Wright, J.W.; Thorne, J.H. Selecting the Optimal Fine-Scale Historical Climate Data for Assessing Current and Future Hydrological Conditions. J. Hydrometeorol. 2022, 23, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T. Development of gridded surface meteorological data for ecological applications and modelling. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Brown, T.J. A comparison of statistical downscaling methods suited for wildfire applications. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, L.A.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Coulson, D.P. Climate Data for RPA 2020 Assessment: MACAv2 (METDATA) Historical Modeled (1950–2005) and Future (2006–2099) Projections for the Conterminous United States at the 1/24 Degree Grid Scale; Forest Service Research Data Archive: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Wang, G. Heat stress to jeopardize crop production in the US Corn Belt based on downscaled CMIP5 projections. Agric. Syst. 2023, 211, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Long-Term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility Pages 1029 to 1076. In Climate Change 2013—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1029–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, A.; Fant, C.; Strzepek, K.; Lickley, M.; Solomon, S. Climate model uncertainty in impact assessments for agriculture: A multi-ensemble case study on maize in sub-Saharan Africa. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbia, S.S.; Gill, L.; Johnston, P.; Pilla, F. Multi-GCM ensembles performance for climate projection on a GIS platform. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, C.F.; Jones, R.G. How representative is the spread of climate projections from the 5 CMIP5 GCMs used in ISI-MIP? Clim. Serv. 2016, 1, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R. HAWQS User Guide Version 1.1; Office of Water, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- NRCS WI Agronomy. Wisconsin Agronomy Technical Note 7-Cover and Green Manure Crops Benefits to Soil Quality; N.R.C.S. (NRCS), Ed.; Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS); United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.C. SWAT-CUP: SWAT Calibration and Uncertainty Programs; Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Runkel, R.L.; Crawford, C.G.; Cohn, T.A. Load Estimator (LOADEST): A Fortran Program for Estimating Constituent Loads in Streams and Rivers; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Kirchhoff, C.J.; Seth, A.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Livneh, B.; Pierce, D.W.; Fomenko, L.; Ding, T. Projected Changes of Precipitation Characteristics Depend on Downscaling Method and Training Data: MACA versus LOCA Using the U.S. Northeast as an Example. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 2739–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, J. HAWQS 2.0: Hydrologic and Water Quality System Version 2 Technical Documentation; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Agricultural Statistics Service. Cropland Data Layer (Version 2003, 2020) [Data Set]. USDA NASS. 2003. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Research_and_Science/Cropland/Release/index.php (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies. Wisconsin’s changing climate: Impacts and solutions for a warmer climate. In Wisconsin Initiative on Climate Change Impacts; University of Wisconsin-Madison and the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, V.; Cherkauer, K.A.; Niyogi, D.; Lei, M.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Ray, D.K.; Bowling, L.C.; Yang, G. A regional scale assessment of land use/land cover and climatic changes on water and energy cycle in the upper Midwest United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 2025–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Kessler, A.C.; Brown, M.K.; Zvomuya, F. Climate and agricultural land use change impacts on streamflow in the upper midwestern United States. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5301–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubleday, A.; Errett, N.A.; Ebi, K.L.; Hess, J.J. Indicators to Guide and Monitor Climate Change Adaptation in the US Pacific Northwest. Am. J. Public Health 2020, 110, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Climate Change Indicators in the United States Fifth Edition; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampittiello, M.; Marchetto, A.; Boggero, A. Water Resources Management under Climate Change: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.H.; Masroor, M.; Rehman, S.; Singh, R.; Ahmed, R.; Sahana, M.; Sajjad, H. State of Art of Review on Climate Variability and Water Resources: Bridging Knowledge Gaps and the Way Forward. Water Resour. 2022, 49, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Winter, J.M.; Osterberg, E.C.; Horton, R.M.; Beckage, B. Total and Extreme Precipitation Changes over the Northeastern United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1783–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, K.E.; Stevens, L.E.; Stevens, S.E.; Sun, L.; Janssen, E.; Wuebbles, D.J.; Hilberg, S.D.; Timlin, M.S.; Stoecker, L.A.; Westcott, N.E.; et al. Regional Climate Trends and Scenarios for the U.S. National Climate Assessment Part 3: Climate of the Midwest U.S.; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, B.; Gameda, S.; Zhang, X.; De Jong, R. Changing growing season observed in Canada. Clim. Change 2012, 112, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.; Yohe, G.; Easterling, W.; Kates, R.; Ruth, M.; Sussman, E.; Whelchel, A.; Wolfe, D.; Lipschultz, F. Ch. 16: Northeast. Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment. In Global Change Research Program; Melillo, J.M., Richmond, T.T.C., Yohe, G.W., Eds.; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 371–395. [Google Scholar]
- Ryberg, K.R.; Lin, W.; Vecchia, A.V. Impact of Climate Variability on Runoff in the North-Central United States. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Meehl, G.A. An Overview of CMIP5 and the Experiment Design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langousis, A.; Mamalakis, A.; Deidda, R.; Marrocu, M. Assessing the relative effectiveness of statistical downscaling and distribution mapping in reproducing rainfall statistics based on climate model results. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.; Arsenault, R. Uncertainty of gridded precipitation and temperature reference datasets in climate change impact studies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3331–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Quiring, S.M. Identifying the Dominant Drivers of Hydrological Change in the Contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR029738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; A/RES/70/1; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nover, D.M.; Witt, J.W.; Butcher, J.B.; Johnson, T.E.; Weaver, C.P. The effects of downscaling method on the variability of simulated watershed response to climate change in five U.S. basins. Earth Interact 2016, 20, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Krysanova, V.; Benestad, R.E.; Hov, Ø.; Piniewski, M.; Otto, I.M. Uncertainty in climate change impacts on water resources. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 79, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Mejia, A.; Sharma, S.; Zeng, P.; Che, Y. Evaluating the Credibility of Downscaling: Integrating Scale, Trend, Extreme, and Climate Event into a Diagnostic Framework. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 1453–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aven, T. On How to Deal with Deep Uncertainties in a Risk Assessment and Management Context. Risk Anal. 2013, 33, 2082–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Scenario | Acronym | Land Use Data | Temperature and Precipitation Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Baseline | 2016 | 2000–2020 |
| Climate change | CC | 2024–2049 (Early Century) | |
| 2016 | 2050–2074 (Mid-Century) | ||
| 2075–2099 (Late Century) | |||
| Land use change | LU | Hay -> Crop | 2000–2020 |
| Land use and climate change | LUCC | Hay -> Crop | 2050–2074 (Mid-Century) |
| 2075–2099 (Late Century) | |||
| G-CC | Crop -> Grassland | 2050–2074 (Mid-Century) | |
| 2075–2099 (Late Century) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rath, S.; Arden, S.; Brighneti, T.M.; Moore, S.; Srinivasan, R. Evaluating Future Water Resource Risks in the Driftless Midwest from Climate and Land Use Change. Land 2025, 14, 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091919
Rath S, Arden S, Brighneti TM, Moore S, Srinivasan R. Evaluating Future Water Resource Risks in the Driftless Midwest from Climate and Land Use Change. Land. 2025; 14(9):1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091919
Chicago/Turabian StyleRath, Sagarika, Sam Arden, Tassia Mattos Brighneti, Sam Moore, and Raghavan Srinivasan. 2025. "Evaluating Future Water Resource Risks in the Driftless Midwest from Climate and Land Use Change" Land 14, no. 9: 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091919
APA StyleRath, S., Arden, S., Brighneti, T. M., Moore, S., & Srinivasan, R. (2025). Evaluating Future Water Resource Risks in the Driftless Midwest from Climate and Land Use Change. Land, 14(9), 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091919






