Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Forces of Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Area
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Land Use Changes
2.3.2. Assessment of ESV
2.3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
2.3.4. Analysis of ES Trade-Offs and Synergies
2.3.5. Spatial Clustering Analysis
2.3.6. Optimal Parameters-Based Geographical Detector (OPGD) Model
3. Results and Analysis
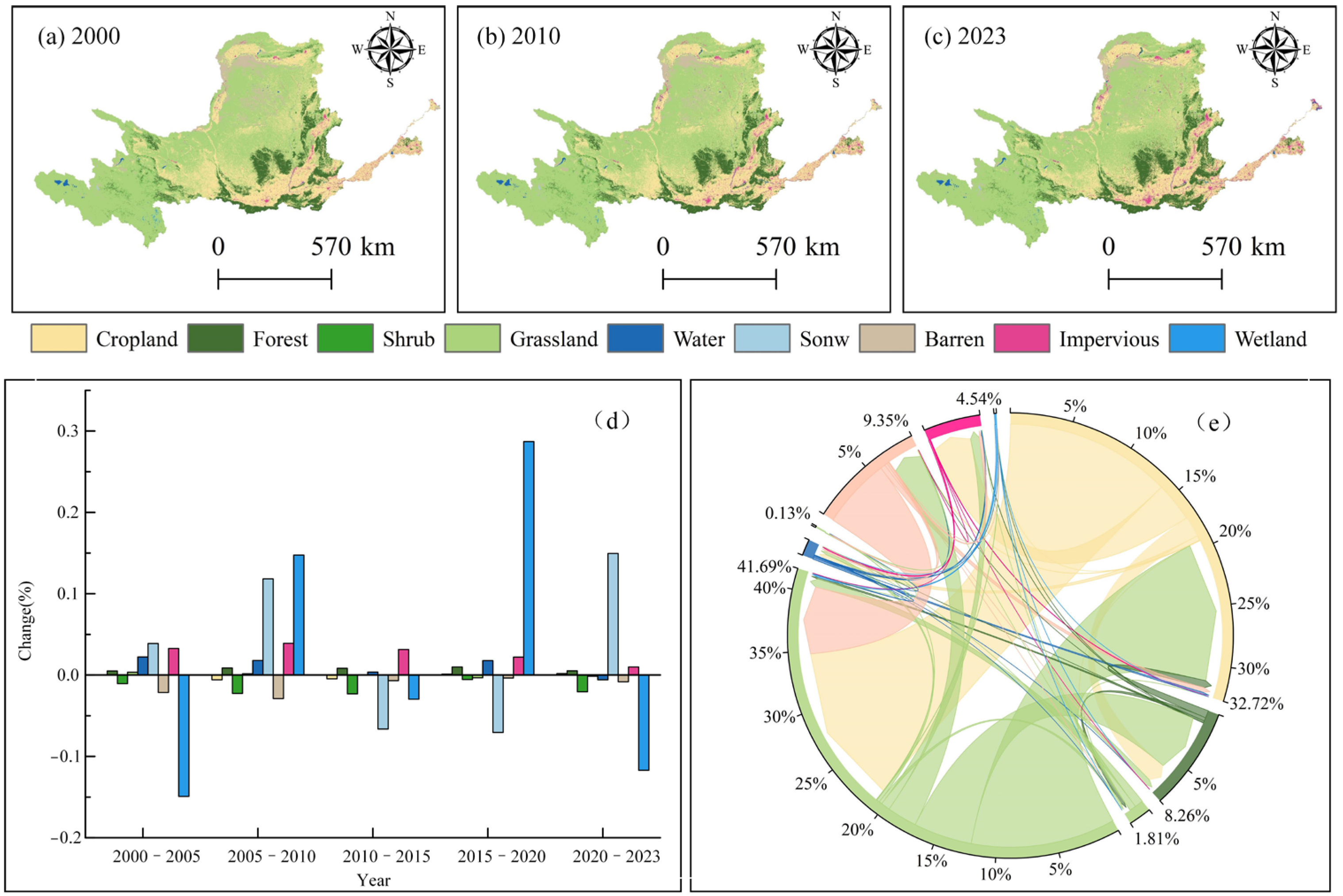
3.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Land Use Changes
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of ESV Changes
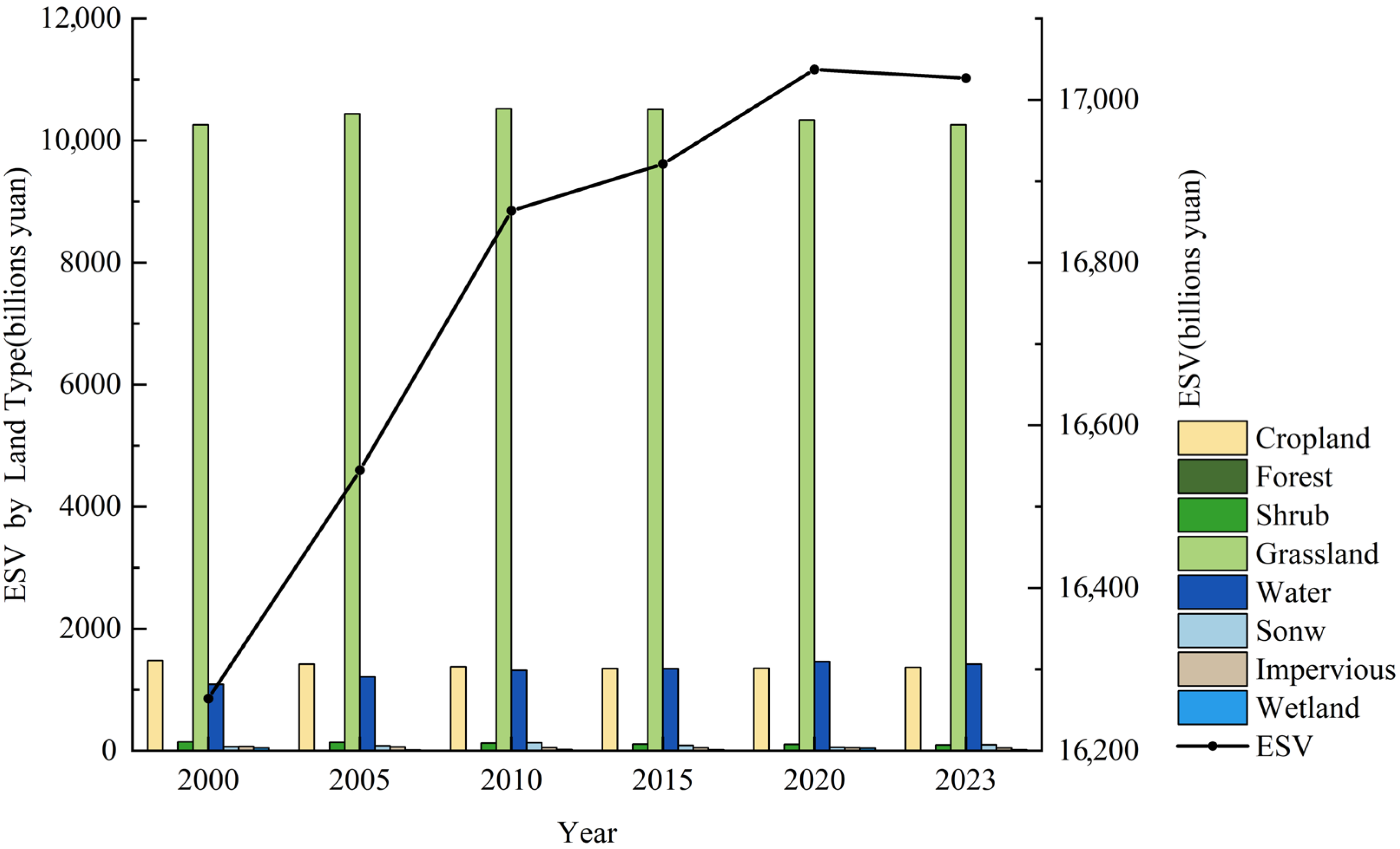
3.2.1. Temporal Evolution of ESV
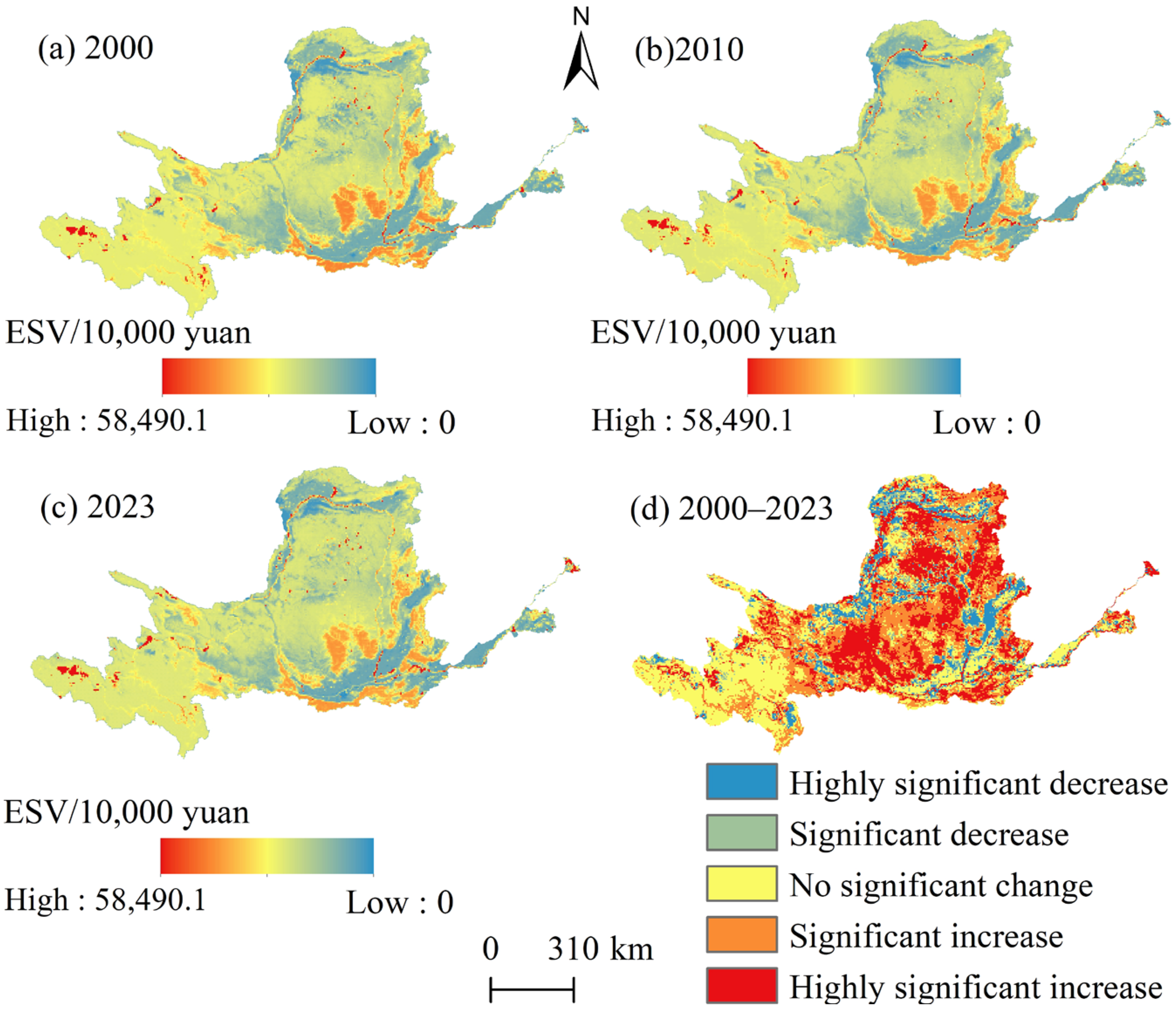
3.2.2. Spatial Dynamics of ESV
3.2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis of ESV
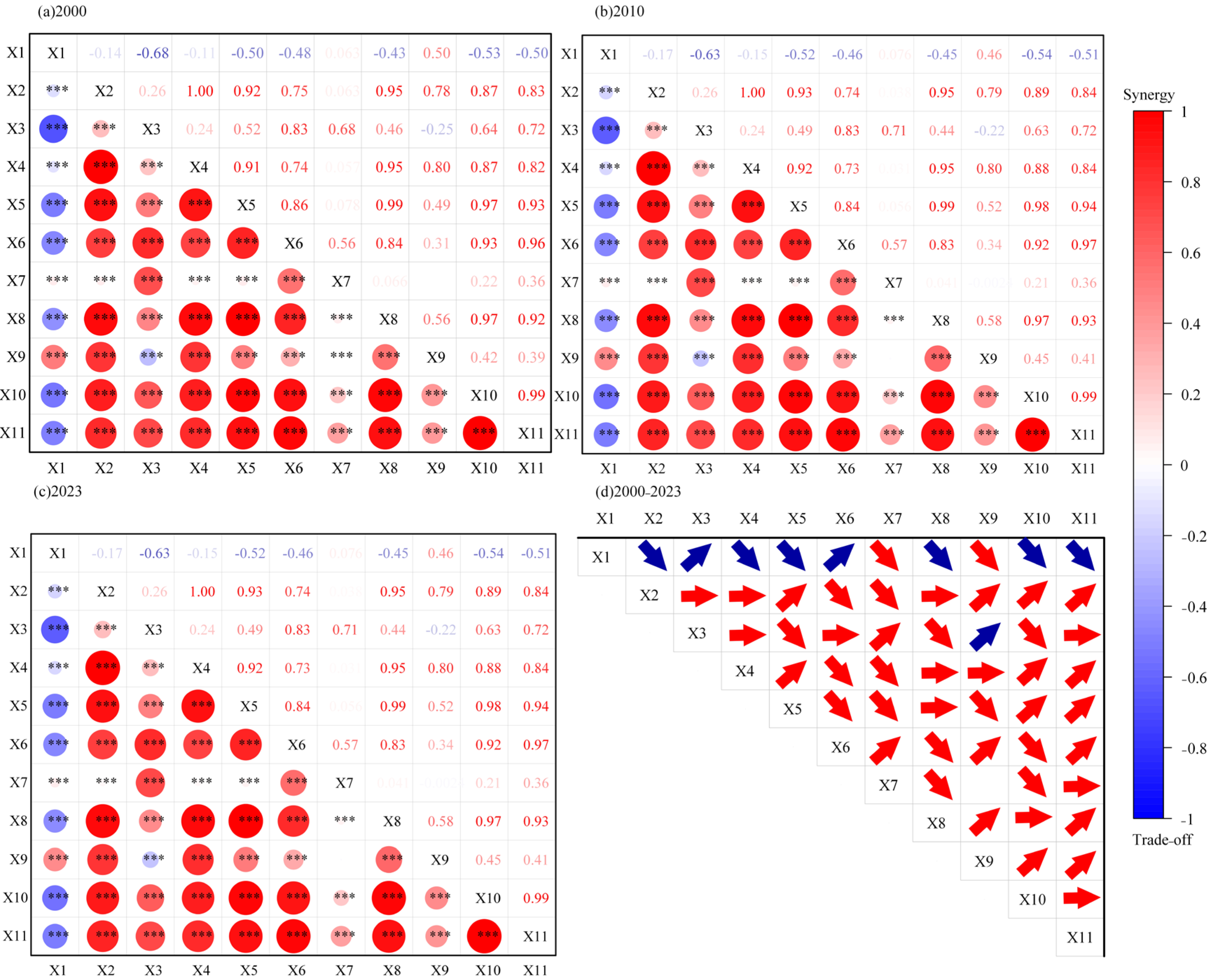
3.3. Trade-Offs and Synergies Among Ecosystem Services
3.4. Geographic Detector Analysis of Spatial Differentiation in ESV
3.4.1. Factor Detection
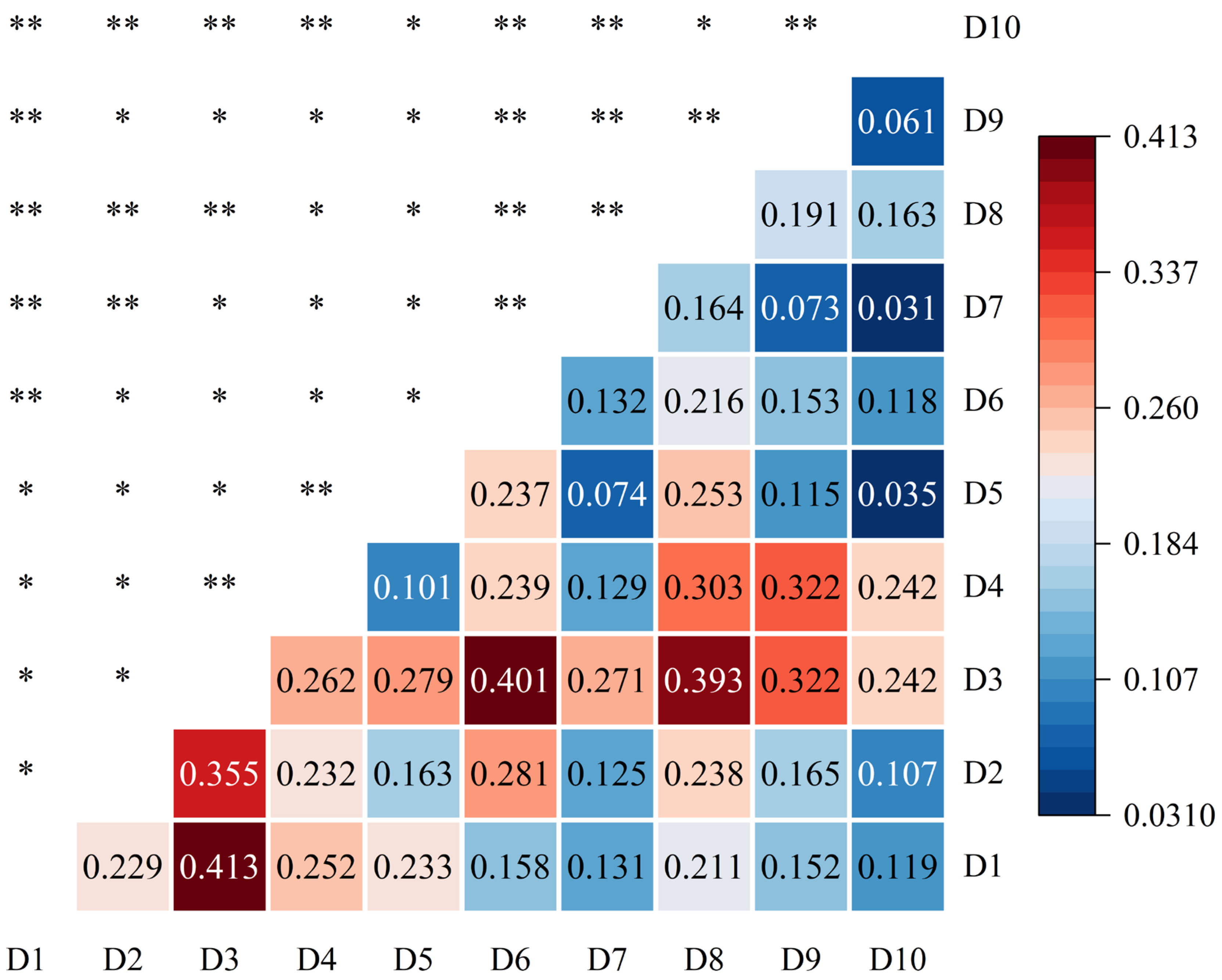
3.4.2. Interaction Detection Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Evolution of ESV
4.2. Driving Factors of ESV
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
4.4. Targeted Measures for Enhancing Ecosystem Service Value
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.C.; Groot, R.D.; Farber, S.B.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.M.; Limburg, K.E.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.M.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Fu, B. Achieving a fit between social and ecological systems in drylands for sustainability. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 48, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assessment, M.E. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Wetlands and Water; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Taffarello, D.; Bittar, M.S.; Sass, K.S.; Calijuri, M.D.C.; Cunha, D.G.F.; Mendiondo, E.M. Ecosystem service valuation method through grey water footprint in partially-monitored subtropical watersheds. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Inter-regional ecological compensation in the Yellow River Basin based on the value of ecosystem services. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yin, S.; Zhu, H.; Xing, Z. Evaluation of ecosystem service value of riparian zone using land use data from 1986 to 2012. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, D.R. Valuation of wildlife resources. Reg. Stud. 1969, 3, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westman, W.E. How Much Are Nature’s Services Worth? Science 1977, 197, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.; Postel, S.; Bawa, K.; Kaufman, L. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Bibliovault OAI Repository, the University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, S.; Liu, C. Sustainability Status and Trends of China’s Development: An Assessment based on the Natural Resource Base. Resour. Sci. 2008, 30, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, S. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Guan, Q.; Lin, J.; Yang, L.; Luo, H.; Ma, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, N. The response and simulation of ecosystem services value to land use/land cover in an oasis, Northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Pei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Revegetation projects significantly improved ecosystem service values in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China in recent 20 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Guan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, Y. Spatial Differentiation and Driving Mechanisms in Ecosystem Service Value of Arid Region: A case study in the middle and lower reaches of Shule River Basin, NW China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Barton, D.N. Classifying and valuing ecosystem services for urban planning. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 86, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trégarot, E.; Touron-Gardic, G.; Cornet, C.C.; Failler, P. Valuation of coastal ecosystem services in the Large Marine Ecosystems of Africa. Environ. Dev. 2020, 36, 100584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.; Bagstad, K.; Johnson, G.; Voigt, B. Scientific instruments for climate change adaptation: Estimating and optimizing the efficiency of ecosystem service provision. Econ. Agrar. Recur. Nat. 2011, 11, 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sherrouse, B.C.; Semmens, D.J.; Ancona, Z.H. Social Values for Ecosystem Services (SolVES): Open-source spatial modeling of cultural services. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 148, 105259. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Rao, E.; Jiang, L.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Yin, L.; Zhang, B. Global occupation of wetland by artificial impervious surface area expansion and its impact on ecosystem service value for 2001–2018. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Yin, J.; Xu, G. Evaluating human-nature relationships at a grid scale in China, 2000–2020. Habitat Int. 2025, 156, 103282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åhlén, I.; Hambäck, P.A.; Thorslund, J.; Frampton, A.; Destouni, G.; Jarsjö, J. Wetlandscape size thresholds for ecosystem service delivery: Evidence from the Norrström drainage basin, Sweden. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 704, 135452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, H. A new method to classify cultural ecosystem services and visualize their economic value: A case study of Guilin, a famous tourist destination in China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2025, 72, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Luan, X.; Zhang, Z. Wetland ecosystem service values in Beijing significantly increased from 1984 to 2020: Trend changes, type evolution, and driving factor. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Comparison of various models for multi-scenario simulation of land use/land cover to predict ecosystem service value: A case study of Harbin-Changchun Urban Agglomeration, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 144012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Jiang, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, E.; Guo, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J. Understanding scale effects and differentiation mechanisms of ecosystem services tradeoffs and synergies relationship: A case study of the Lishui River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanusa, T.; Garratt, M.; Cathcart-James, M.; Hunt, L.; Cameron, R. Urban hedges: A review of plant species and cultivars for ecosystem service delivery in north-west Europe. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 44, 126391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Mao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Liu, T.; Wei, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, L.; et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics and multi-scenario simulation analysis of ecosystem service value in coastal wetland: A case study of the coastal zone of Hainan Island, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lü, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, T. The thresholds of forest-to-grassland ratios can be critical for harmonizing ecosystem service relationships spatiotemporally in dryland regions. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 169, 103334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, X.; An, J.; Su, Q.; Chen, B. Drivers of ecosystem services and their trade-offs and synergies in different land use policy zones of Shaanxi Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Z. Multi-scenario simulation and evaluation of the impacts of land use change on ecosystem service values in the Chishui River Basin of Guizhou Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xing, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H. Sustainability assessment of coupled human and natural systems from the perspective of the supply and demand of ecosystem services. Frontiers in Earth Science. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 1025787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hong, W.; Qiu, R.; Hong, T.; Chen, C.; Wu, C. Geographic variations of ecosystem service intensity in Fuzhou City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. What are the dominant factors and optimal driving threshold for the synergy and tradeoff between ecosystem services, from a nonlinear coupling perspective? J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, R.; Yan, S.; Wu, X. Identification of critical ecological areas using the ecosystem multifunctionality-stability-integrity framework: A case study in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhu, H.; Tan, C.; Ji, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecological vulnerability in the Yellow River Basin under ecological restoration initiatives. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, T.; Yan, D.; Liu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Gao, H. Analysis of the evolution of ecosystem service value and its driving factors in the Yellow River Source Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, S.; Han, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, T.; Fan, C. Study on urban economic resilience of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei based on night light remote sensing data during COVID-19. Sci. Remote Sens. 2024, 9, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Tian, G.; He, Y.; Wang, M. Spatial and temporal differentiation and coupling analysis of land use change and ecosystem service value in Jiangsu Province. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Cai, C.; Tang, J.; Shi, J.; Yang, R. Analysis of coupling coordination and obstacle factors between tourism development and ecosystem services value: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; And Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Q.; Feng, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Fu, B. Cross-scale coupling of ecosystem service flows and socio-ecological interactions in the Yellow River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, C.; Li, X.; Song, M. The spatial–temporal evolution and influencing factors of the coupling coordination of new-type urbanization and ecosystem services value in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Du, M.; Yan, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Kou, Y. Coupling coordination degree analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between water ecosystem service value and water system in Yellow River Basin cities. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Yuan, R.; Singh, V.P.; Wu, W.; Wang, D. Dynamic responses of ecological vulnerability to land cover shifts over the Yellow river Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Fu, B. Evolution of ecosystem services in the Chinese Loess Plateau under climatic and land use changes. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 101, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Jiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X. The dynamic patterns of critical ecological areas in the Yellow River Basin are driven primarily by climate factors but threatened by human activities. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data | Resolution (m) | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| DEM | 30 | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn) (accessed on 20 May 2024) |
| Land use | 30 | Wuhan University (https://zenodo.org/records/12779975) (accessed on 18 June 2024) |
| Precipitation | 1000 | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn) (accessed on 9 July 2024) |
| NDVI | 1000 | Resource and Environment Science Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/) (accessed on 26 August 2024) |
| NPP | 500 | Net Primary Productivity (NPP) product MOD17A3H from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), US Geological Survey (https://lpdaac.usgs.gov) (accessed on 15 October 2024) |
| Population | 1000 | The LandScan dataset, Oak Ridge National Laboratory (https://landscan.ornl.gov/) (accessed on 30 November 2024) |
| Nighttime light | 1000 | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn) (accessed on 12 January 2025) |
| Road network | Vector | OpenHistoricalMap (https://www.openhistoricalmap.org/) (accessed on 8 April 2025) |
| Statistical data | - | Provincial and municipal statistical yearbooks, national agricultural cost–benefit compilations |
| Primary Category | Secondary Category | Variable | Cropland | Forest | Shrub | Grassland | Water | Snow | Wetland | Barren |
| Provisioning services | Food supply | X1 | 2049.96 | 507.07 | 352.48 | 432.87 | 1484.13 | 1484.13 | 946.13 | 18.55 |
| Raw material supply | X2 | 454.51 | 1168.75 | 797.72 | 636.94 | 426.68 | 426.68 | 927.58 | 55.65 | |
| Water supply | X3 | −2420.99 | 606.02 | 408.13 | 352.48 | 15,379.33 | 15,379.33 | 4804.88 | 37.10 | |
| Regulating services | Gas regulation | X4 | 1651.09 | 3846.38 | 2615.78 | 2238.56 | 1428.47 | 1428.47 | 3524.81 | 204.06 |
| Climate regulation | X5 | 862.65 | 11,502.04 | 7847.35 | 5917.98 | 4248.33 | 4248.33 | 6678.60 | 185.51 | |
| Environmental purification | X6 | 250.44 | 3345.48 | 2374.61 | 1954.10 | 10,296.18 | 10,296.18 | 6678.60 | 575.10 | |
| Hydrological regulation | X7 | 2773.47 | 7167.12 | 6214.81 | 4334.90 | 189,672.30 | 189,672.3 | 44,950.7 | 389.58 | |
| Supporting services | Soil conservation | X8 | 964.68 | 4681.20 | 3190.88 | 2727.09 | 1725.30 | 1725.30 | 4285.43 | 241.17 |
| Nutrient cycling | X9 | 287.55 | 358.66 | 241.17 | 210.25 | 129.86 | 129.86 | 333.93 | 18.55 | |
| Maintaining biodiversity | X10 | 315.37 | 4260.72 | 2912.61 | 2479.74 | 4730.67 | 4730.67 | 14,600.16 | 222.62 | |
| Cultural services | Providing an aesthetic landscape | X11 | 139.13 | 1867.53 | 1280.06 | 1094.54 | 3506.26 | 3506.26 | 8774.94 | 92.75 |
| Total | / | 7327.91 | 39,310.99 | 28,235.64 | 22,379.53 | 233,027.54 | 233,027.51 | 96,505.79 | 2040.68 |
| 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.4798 | 0.3894 | 0.4895 | 0.3731 | 0.4859 | 0.4103 |
| Forest | 0.1906 | 0.1921 | 0.1967 | 0.2041 | 0.2128 | 0.2184 |
| Shrub | 0.0091 | 0.0084 | 0.0073 | 0.0065 | 0.0063 | 0.0056 |
| Grassland | 0.6307 | 0.6309 | 0.6238 | 0.6211 | 0.6067 | 0.6025 |
| Water | 0.0670 | 0.0732 | 0.0782 | 0.0793 | 0.0858 | 0.0833 |
| Snow | 0.0043 | 0.0050 | 0.0078 | 0.0052 | 0.0033 | 0.0058 |
| Barren | 0.0030 | 0.0007 | 0.0013 | 0.0011 | 0.0026 | 0.0011 |
| Wetland | 0.0044 | 0.0038 | 0.0032 | 0.0031 | 0.0030 | 0.0029 |
| Primary Classification | Secondary Classification | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2023 | Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESV | ESV | ESV | ESV | ESV | ESV | 2000–2023 | ||
| Provisioning services | Food supply | 662.6844 | 650.5023 | 643.0673 | 635.5617 | 637.444 | 640.1825 | −3.40% |
| Raw material supply | 484.5945 | 487.7621 | 491.2848 | 492.6368 | 493.5889 | 494.3131 | 2.01% | |
| Water supply | −197.147 | −166.196 | −138.681 | −128.077 | −123.793 | −129.128 | −34.50% | |
| Regulating services | Gas regulation | 1692.461 | 1702.507 | 1713.706 | 1717.406 | 1719.735 | 1721.741 | 1.73% |
| Climate regulation | 3865.854 | 3926.471 | 3981.725 | 4010.981 | 4018.604 | 4021.925 | 4.04% | |
| Environmental purification | 1297.07 | 1318.057 | 1339.123 | 1346.102 | 1350.973 | 1349.272 | 4.02% | |
| Hydrological regulation | 4124.411 | 4239.82 | 4391.862 | 4382.258 | 4465.855 | 4457.616 | 8.08% | |
| Supporting services | Soil conservation | 1849.776 | 1870.715 | 1890.28 | 1899.245 | 1900.903 | 1901.587 | 2.80% |
| Nutrient cycling | 185.4406 | 185.2791 | 185.5755 | 185.3518 | 185.7053 | 186.1114 | 0.36% | |
| Maintaining biodiversity | 1590.175 | 1611.667 | 1635.767 | 1645.702 | 1650.709 | 1647.498 | 3.60% | |
| Cultural services | Providing an aesthetic landscape | 708.8584 | 718.2812 | 730.0765 | 734.2279 | 737.5522 | 735.4823 | 3.76% |
| Total | 16,075.31 | 16,386.43 | 16,656.43 | 16,762.83 | 16,884.5 | 16,859.41 | 4.88% | |
| Driving Factor | q Value | p Value | Order | Driving Factor | q Value | p Value | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 0.1176 | 0.0000 | 3 | D6 | 0.1160 | 0.0000 | 4 |
| D2 | 0.1051 | 0.0000 | 5 | D7 | 0.0300 | 0.0000 | 9 |
| D3 | 0.2397 | 0.0000 | 1 | D8 | 0.1608 | 0.0000 | 2 |
| D4 | 0.0946 | 0.0000 | 6 | D9 | 0.0599 | 0.0000 | 7 |
| D5 | 0.0326 | 0.0000 | 8 | D10 | 0.0027 | 0.5132 | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.; Wei, L.; Jin, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C. Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Forces of Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Land 2025, 14, 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091907
Yu W, Wei L, Jin Z, Lin Y, Wang C. Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Forces of Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Land. 2025; 14(9):1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091907
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Wensheng, Lijie Wei, Zhenxing Jin, Yuzhen Lin, and Chengxin Wang. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Forces of Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin" Land 14, no. 9: 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091907
APA StyleYu, W., Wei, L., Jin, Z., Lin, Y., & Wang, C. (2025). Spatiotemporal Variations and Driving Forces of Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Land, 14(9), 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091907






