Abstract
In recent decades there has been a deterioration of wetlands with severe implications for human health, particularly through its effects on food, water, and climate security. Thus, there is an increasing interest in addressing the adverse effects of wetland degradation, particularly in relation to public health. Despite the necessity to comprehend the economic value associated with wetland degradation, there is still a paucity of research on the subject in many areas of the world, such as Latin American countries. The objective of this work is to determine the economic impacts of wetland degradation through its health impacts on local communities to achieve sustainable wetland management. To this end, a contingent valuation method has been applied selecting Lake Cuitzeo (Mexico) as an emblematic case study where there is a process of ecological degradation that has a negative impact on both the well-being and health of the population. Based on contingent valuation surveys of the population, respondents were directly asked to express their willingness to accept (WTA) by considering changes in well-being resulting from the loss of a benefit or their willingness to pay (WTP) for the improvement of goods/services. The findings indicated a willingness to accept economic compensation of 47.86 USD/household/month for health-related damages and a willingness to pay 2.77 USD/household/month for the environmental management measures to improve lake conditions. In addition, a multivariate analysis was carried out to determine the influence of socio-economic and environmental factors on the economic valuation exercise. The results can serve as a guide for policymakers in the implementation of socially accepted measures to solve the environmental and public health problems in degraded water bodies.
1. Introduction
Wetlands are defined as valuable ecosystems that include various types of water bodies, such as marshes, peatlands, swamps and lakes [1]. These ecosystems are of paramount importance to the planet, playing a fundamental role in maintaining ecological functions [2]. However, wetlands have experienced widespread decline and deterioration due to various factors, including changes in land use, pollution from agriculture and industry, overgrazing, droughts, urbanization, groundwater overexploitation, and the proliferation of invasive species [1,2,3,4].
The degradation of wetlands has a detrimental impact on the provision of ecosystem services, such as water purification, climate regulation, or recreation, as well as biodiversity and human health [4,5]. It is therefore necessary to restore degraded wetlands to prevent the reduction in these benefits for nature and society. Accordingly, many governments have increased their interest in addressing this problem, especially in developing countries where wetlands are deteriorating rapidly [6,7].
In many countries, particularly across Latin America, Asia, and Africa, the adverse environmental impacts of wetland degradation are compounded by a decline in public health [7,8,9]. The consequences of this phenomenon are wide-ranging, directly affecting human health through impacts on food, water, and climate security [5]. Moreover, the spread of water-borne diseases and vulnerability to natural disasters are further exacerbated [10].
To address the challenges of environmental degradation and its impact on public health, various conservation and management measures have been implemented. These focus on optimizing resource use and management, promoting sustainable development, utilizing green technologies, and engaging the public in achieving positive outcomes [11,12,13,14].
Despite growing interest in promoting management measures to reduce wetland degradation and its impact on public health, only a few studies have conducted economic valuations of these impacts [15,16,17]. Most existing studies have applied stated preference methods, such as contingent valuation [18], to assess the economic value of conservation and management measures in protected natural areas [19], river restoration projects [20], high-value agricultural ecosystems [21], or selected wetlands [15,16,17]. However, there is still a scarcity of studies addressing the economic valuation of sustainable wetland management in regions such as Latin America [17,22], particularly regarding the direct effects of wetland degradation on public health. To date, no such studies have been conducted in Central or South America [18].
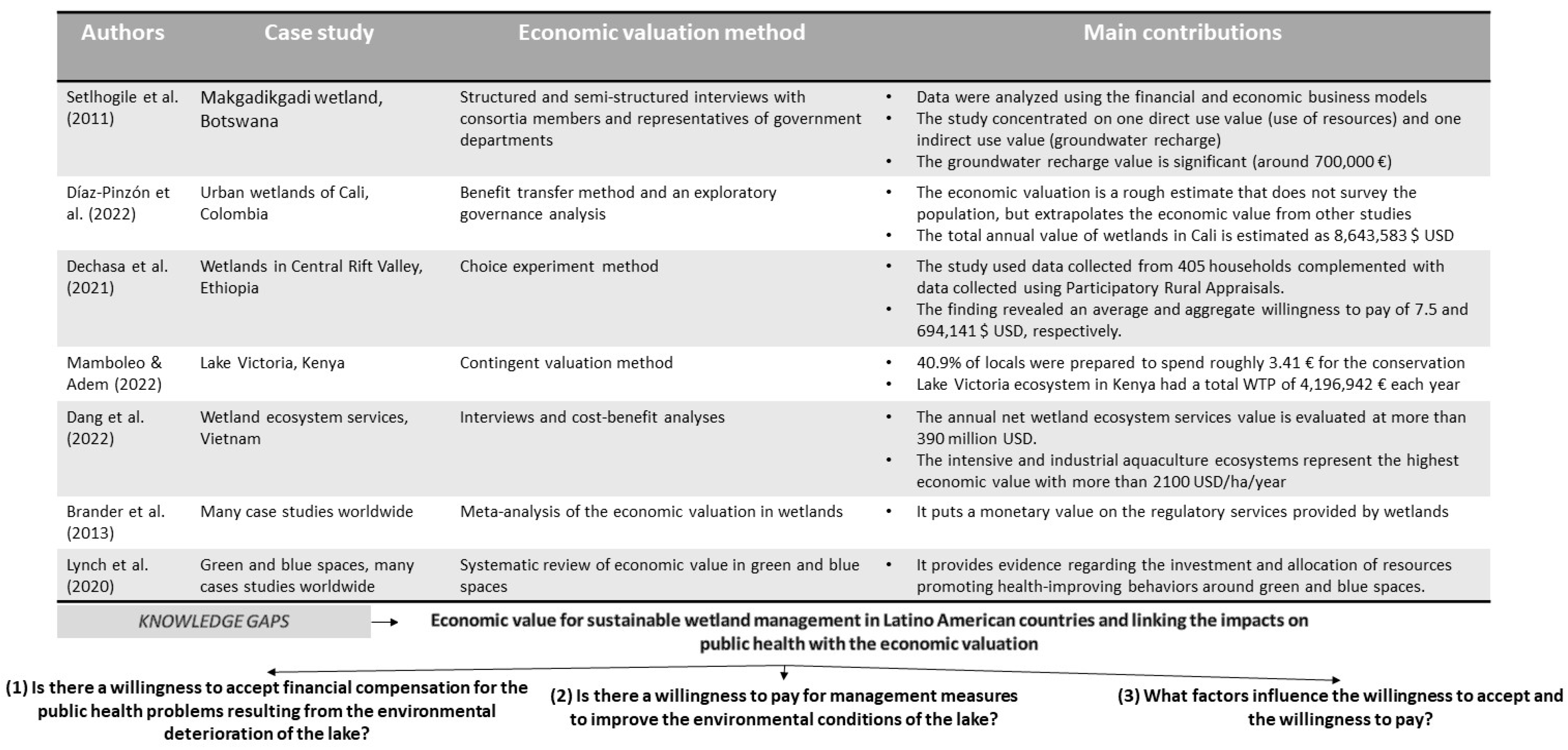
The development of action plans that integrate and promote environmental conservation and strategies for preventing health impacts require an understanding of the economic value and factors that may influence the demand for wetland management measures. It is essential to understand the social perception of wetland mismanagement and the influence of socioeconomic factors on this behavior, as well as the temporal variation in social perception. Figure 1 presents case studies that demonstrate analogous characteristics to those observed in Latin American countries, particularly regarding social and economic indicators, with a focus on Africa and Asia.
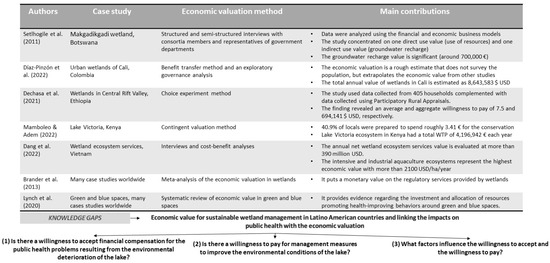
Figure 1.
Background and knowledge gaps on the economic value of wetlands in Latin American countries [23,24,25,26,27,28,29].
All these wetland studies [23,24,25,26,27], together with others conducted on other continents [15] and around the world [28], have focused on the economic importance of both use and non-use values, and the beneficial and adverse effects on human health and well-being. However, while wetlands provide essential ecosystem services, such as water purification and flood regulation, they can also pose risks to public health by serving as breeding grounds for mosquitoes and other disease-carrying insects [28]. In this regard, several studies in the literature [29] provide evidence of the relationship between public health and economic valuation. Economically, wetlands can reduce water treatment costs, but their influence on the economic value of surrounding land must also be considered.
The objective of this work is to determine the economic impacts of wetland degradation as a basis for achieving sustainable wetland management in México [22] through a contingent valuation survey. Furthermore, this work seeks to analyze the socioeconomic and temporal factors that influence the demand for improved management. For this work, Lake Cuitzeo in México has been selected as a case study. This lake is an emblematic wetland that is undergoing a process of ecological deterioration in both water quantity and quality. This has had a direct negative effect on the health of the population living around the wetland. Thus, the economic impact valuation of degraded wetlands allows us to quantify the economic impact of environmental degradation and justify investments in conservation/restoration. This has a direct relationship with the promotion of measures/policies that promote public health and favors disease prevention at the collective level, while also influencing the quality of life and well-being of people within their living environment.
In this work the extent to how it can determine the economic impact value for wetland degradation to answer the following research questions: (1) Is there a willingness to accept financial compensation for the public health problems resulting from the environmental deterioration of the lake? (2) Is there a willingness to pay for management measures to improve the environmental conditions of the lake? (3) What factors influence the willingness to accept and the willingness to pay?
The use of the contingent valuation method makes a valuable contribution to the existing literature, offering insight into the prevailing economic value of sustainable wetland management. Therefore, this work seeks to generate scientific knowledge through three key contributions: (I) test the economic value of the population health of inhabitants living near the wetland, (II) test the economic value of management measures that promote sustainable development in the wetland area, and (III) test the factors influencing the behavior of individuals towards the economic impacts valuation of the lake. It should be emphasized that the novelty of this work does not lie in the method itself, but in its application to a case study that has rarely been examined from the perspective of wetland environmental economics. Furthermore, its novelty lies not only in the scarcity of Latin American studies, but also in the explicit link it establishes between public health impacts and the economic valuation of wetland degradation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study
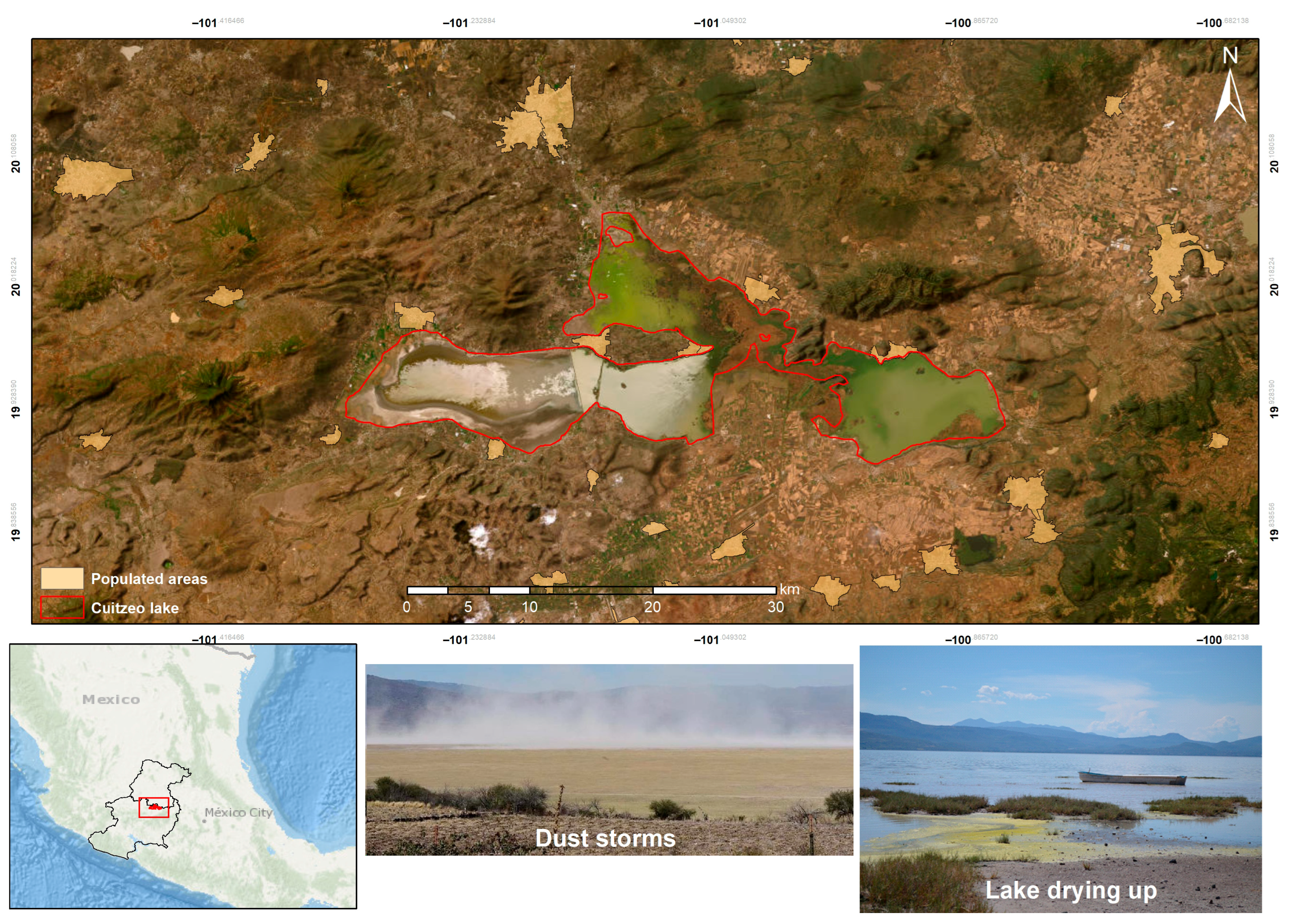
Lake Cuitzeo (Figure 2), situated in the northern region of the Mexican state of Michoacán, was selected as a case study. This wetland illustrates a process of ecological deterioration, which is evident in the drying up of the western part of the ecosystem. Environmental deterioration is primarily attributed to socioeconomic activities in the surrounding area, including the rapid urbanization process associated with population growth, which exacerbates the problems of water availability and quality in the lake. Additionally, wastewater discharges from urban areas, groundwater exploitation to meet demand for agricultural and urban uses, and deforestation contribute to the issue [30].
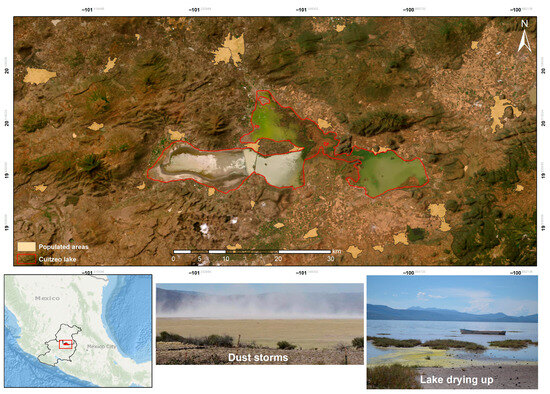
Figure 2.
Study area. Lake Cuitzeo, Michoacán (Mexico).
Given its topographical characteristics, the lake is shallow, with an average depth of about 30 cm, and undergoes a period of low water levels during the early months of the year (average monthly precipitation of 5.7 mm until the end of March). This period is accompanied by high evaporation, which causes pollutants to accumulate in the sediments and subsequently become incorporated into the dry soil. Strong prevailing winds further contribute to the formation of “tolvaneras” or dust storms, which take the form of dust or sand swirls [31]. These storms frequently affect communities along the western shore of Lake Cuitzeo, posing a harmful effect on public health. Their frequency has increased over time: between 2010 and 2020 they lasted about four months per year, whereas today they extend for more than six months [32]. As a result, dust storms have worsened health conditions in the riparian areas west of the lake, where cases of respiratory, gastrointestinal, and dermatological diseases have recently increased [30,31].
With regard to dust storms, in the past decade there have been 97,026 cases of acute respiratory infections and 11,288 cases of intestinal infections [33]. Thus, the socioeconomic activities of the population around the lake have caused not only an environmental problem but also a public health issue for nearby communities. The record of infections associated with the ecological deterioration of Lake Cuitzeo provides evidence to justify the existence of a public health problem in the study area, which has not yet been consistently addressed due to the lack of knowledge regarding its economic value for the population.
2.2. Methods
The contingent valuation method [18,34,35] was the main methodology used in this study. This stated preference approach directly asks respondents to express either their willingness to accept (WTA) compensation for changes in well-being resulting from the loss of a benefit, or their willingness to pay (WTP) for improvements in goods and services. In this way, the monetary value of an environmental asset can be estimated by creating a hypothetical market and calculating its Total Economic Value. This value encompasses both use and non-use components, including the public health costs of wetland degradation as well as the benefits derived from management measures.
For the univariate analyses of the WTA and WTP, the Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test was used to assess differences between two samples collected at different time periods.
Furthermore, multivariate analyses using logit and tobit models were conducted to identify the factors influencing WTA and WTP among the population [20].
2.3. Data Collection
The primary data were collected through a structured questionnaire consisting of 25 questions divided into three sections.
The first section focused on issues related to the context and the existing problem at Lake Cuitzeo. Here, respondents were informed of both the beneficial and adverse effects of the lake from an environmental and economic point of view.
The second section focused on the economic valuation of the wetland. For this purpose, two different types of questions were asked.
On the one hand, the WTA was asked for compensation for the damage caused by the degradation of the lake on the public health of the population near the wetland. The payment vehicle selected in the pilot survey is a voucher for medical or pharmaceutical expenses damage caused by the environmental deterioration of the lake. The WTA binary question was formulated as follows: Would you be willing to accept monthly financial compensation in the form of a medical or pharmaceutical voucher in exchange for the damage caused by the environmental deterioration of the lake due to the “tolvaneras”? In the case of an affirmative answer the respondents had to state the minimum amount of money they would be willing to receive for their household (WTAT). Four starting points were proposed (USD 27, 54, 81, and 108), and respondents were asked to indicate their minimum WTA using these reference payments. Regardless of their answer, they were also asked an open-ended question about the minimum amount they would be willing to accept as compensation for wetland degradation. For those who refused compensation in the WTA binary question, their motivations were recorded and categorized as either protest or non-protest responses.
On the other hand, respondents were asked to show their WTP for management measures that would promote lake remediation and the reduction in dust storms. The binary WTP question was formulated as follows: To carry out management measures to improve the environmental conditions of the lake, would you be willing to make a payment through the monthly water bill? If they answered affirmatively, respondents had to state the maximum amount they would be willing to pay for their household (WTPT). A specific amount of 5.40 USD/household/month was proposed as a reference, and respondents were asked to indicate their maximum WTP based on this figure. They were also asked to rank on a Likert scale from 1 to 5, which management measures they would be willing to support financially. For those who refused payment in the binary WTP question, their motivations were recorded and categorized as either protest or non-protest responses.
The third section included the socio-economic information and environmental behavior of the respondents, which was measured by ecological commitment indices with Likert scales 1–5.
Following a pilot survey of 30 respondents in October 2017, the final survey was conducted between February and April 2018. For the WTA question, 846 households around Lake Cuitzeo were considered, while for the WTP question, 13,542 households across the region were included. Based on these household numbers, a sample of 272 respondents was obtained. At a 95% confidence level for a dichotomous variable, this yielded a sampling error of 5.9% for intermediate proportions and 3.6% for extreme proportions, which is standard in economic valuation studies. To examine whether there was variation in the economic valuation over time, given that Lake Cuitzeo has not experienced any improvement in its environmental status, a second survey was conducted in March 2025 with 35 respondents. This resulted in a pooled sample of 306 respondents. To test significant differences between the samples, a binary time variable (Year 2025 = 1) was created to capture the period effect in the univariate and multivariate analyses of WTA and WTP. Monetary variables for WTA and WTP, as well as household and personal incomes, were adjusted to constant 2025 prices for comparability.
2.4. Sample Description
The descriptive data collected from the survey has enabled the composition of a profile of the average respondent to be determined. A Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test was performed on all respondent descriptive and socioeconomic variables, and the results showed that there were no significant differences between the 2018 and 2025 respondents.
It has been found that the average respondent is a man (78% of cases) aged 50, hasn’t received a university education (completed or in progress) and is employed in 94% of cases. The most prevalent household size is four, with an average monthly family income of 159 USD (see Table A1). It has been established that the characteristics of the surveys are largely consistent with the census values for the target population [36].
More than 90% of respondents are concerned that the wetland will disappear in the future and become a source of infection for the population. Respondents also rated on a scale of 1–5 which actors should solve the environmental deterioration of the lake and address the “tolvaneras”, expressing a desire for collaboration between the federal government (4.95 out of 5), state government (4.82), municipal government (4.69), private companies (4.71), NGOs (4.83) and citizens (4.94). The respondents also indicated a high level of affective ecological commitment (4.89 out of 5), a medium level of verbal commitment to willingness to act (3.89), and a low level of real commitment (1.34) (see Table A1).
3. Results
3.1. Willingness to Accept Analysis
For the willingness to accept (WTA) analysis, both samples from 2018 and 2025 were considered, and a Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test was performed to verify the existence of significant differences in the total WTA values. As no significant differences were observed during this period, all respondents who participated in the hypothetical market were considered jointly in the analysis (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of the willingness to accept (USD/household/month).
From the WTA question, 89.54% of the sample (274 respondents) showed their willingness to receive financial compensation (WTA > 27/54/81/108 USD/household/month), while the remaining 10.46% (32 respondents) were not willing to accept. Furthermore, respondents who declined to accept remuneration for the damage caused to the lake were invited to justify their decision, being able to point out more than one reason. Practically all of them (31 respondents) stated that the reason for their non-participation was their belief that the measure was ineffective in addressing the underlying issue. More than half (18 respondents) cited the perceived inadequacy of the payment method as a reason for non-participation, and one third (10 respondents) cited a lack of credibility. These final two responses were categorized as protest zeros. This finding suggests that 22 of the 32 respondents with a null WTA corresponded to protesting zeros, while the remaining 10 corresponded to real zeros. The hypothetical market comprises respondents with WTA > 0 and real zeros and is therefore composed of 284 households.
The mean WTA is 47.86 USD/household/month, with a maximum of 135 USD/household/month and a minimum of 0 USD/household/month (corresponding to real zeros) (Table 1).
From the mean individual WTA, it is possible to estimate the aggregate total WTA for the population living near Lake Cuitzeo (846 households), which would be the total economic value, a proxy of the social benefit derived from the public health problems caused by the degradation of the lake. This gives a total economic value of 40,490 USD/household/month (around 485,875 USD/year).
After demonstrating that there are no significant differences in WTA values for two different samples over time, multivariate analyses were performed for binary and total WTA considering pooled samples.
The factors explaining the WTA voucher for medical or pharmaceutical expenses in exchange for the damage caused by lake degradation, through multivariate analysis, were measured using variables grouped into socioeconomic characteristics and the environmental commitment index (Table A1). The interactions of these variables were also included as possible explanatory factors.
The factors to explain willingness or not to accept, so called binary WTA (WTAB), were identified with a logit model (Table 2), where WTAB takes a value of 1 if the respondent’s response is positive (89.54%) and 0 null (10.46%). The logit model presents a good fit (96.5% of Correct Classification—CPC) and shows no collinearity problems (VIF < 10).

Table 2.
Logit estimation of WTAB.
Two significant variables were found in the logit model (Table 2). Given their marginal effects, the probability of WTA voucher increases by 0.1% for every one-year increase in age. Additionally, if the respondent is a woman, it reduces the probability of WTA by 4.3%.
As for the total willingness to accept (WTAT), modeling was performed with tobit estimation censored at 0 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Tobit estimation of WTAT (USD/household/month).
The explanatory variables for the medical voucher were different from those of the previously estimated logit model. The fact of being active workers or considering the importance of private companies in solving the problem of Lake Cuitzeo reduces this economic compensation. Thus, given the marginal effects evaluated for the sample means, being an active worker reduces WTA by 42.62 USD/household/month), while giving one more unit of importance to private companies reduces WTA by 3.67 USD/household/month.
Finally, it should be noted that in both models (logit and tobit) the time variable Year 2025 did not appear significant, corroborating the univariate analyses of the WTA, which show that there are no significant differences between the samples of both years.
3.2. Willingness to Pay Analysis
For the willingness to pay (WTP) analysis, respondents were first presented with eight measures that could be implemented to solve the problem of Lake Cuitzeo, previously selected in the pilot questionnaire. Respondents assessed from 1 to 5 the level of urgency for the implementation of management measures, which has an outstanding global average (4.76 out of 5) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Assessment of the level of urgency to implement management measures (1–5).
Respondents considered the planting of vegetation in key areas of the lake shore (4.94) and reforestation in strategic areas of the watershed (4.91), followed by the implementation of efficient water catchment systems (4.87) and the expansion of wastewater treatment plant infrastructure (4.86).
Once respondents assessed the level of urgency of the management measures, they were asked about WTP for their implementation. The payment vehicle, selected in the pilot survey, was a surcharge on their household water bill. As in the WTA analysis, a comparison was made between the two samples, demonstrating through the Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test that there are also no significant differences between 2018 and 2025, so the pooled sample was considered.
Half of the full sample (155 respondents) demonstrated a willingness to pay for the implementation of management measures, while the remaining 49.35% (151 respondents) were not willing to pay. Furthermore, respondents who refused to pay were invited to justify their decision. In the survey, 80.13% of respondents who did not show a WTP stated that the reason was that “My income level would not allow me to contribute” and 78.15% said that the government is responsible for providing funds to improve the lake. This last response was categorized as protest zeros. This finding suggests that 118 of the 151 respondents with a null WTP corresponded to protesting zeros, with the remaining 33 being real zeros. The hypothetical market comprises respondents with WTP > 0 and real zeros and is therefore composed of 188 households.
The mean amount of WTP is 2.77 USD/household/month, with a maximum of 26.98 USD/household/month and a minimum of 0 USD/household/month (corresponding to real zeros) (Table 5).

Table 5.
Descriptive statistics of the willingness to pay (USD/household/month).
From the mean individual WTP, it is possible to estimate the aggregate total WTP for the region surrounding Lake Cuitzeo (13,542 households), which represents the total economic value, a proxy for the social benefit derived from implementing management measures to address the lake’s degradation. This gives a total economic value of 37,503 USD/household/month (around 450,032 USD/year).
As in the WTA analysis, a multivariate analysis of WTP was performed considering socioeconomic and environmental commitment variables (Table A1), as well as the interaction between these variables.
Willingness to pay binary (WTPB) factors were identified with a logit model (Table 6), where WTPB takes a value of 1 if the respondent’s response is WTP for the implementation of management measures (50.65%) and 0 if it is a WTP = 0 (49.35%). The logit model presents a good fit (87.8% of Correct Classification—CPC) and shows no collinearity problems (VIF < 10).

Table 6.
Logit estimation of WTPB.
Three significant variables were found in the logit model (Table 6). Given their marginal effects, the probability of WTP for the implementation of management measures in Lake Cuitzeo increases by 72.1% when the respondent is an active worker. Furthermore, each additional point of the verbal ecological index increases the probability of payment by 9.3%, which rises to 12.4% for each point of concern that respondents have towards the lake issue.
To model the amount of the willingness to pay (WTPT) a tobit estimation censored at 0 was carried out (Table 7).

Table 7.
Tobit estimation of WTPT (USD/household/month).
Five explanatory variables are significant in this model. It is observed that being a woman reduces the amount of payment for management measures, while having a university education, being an active worker, having a higher family income and a higher affective commitment index increase the willingness to pay. Thus, given the marginal effects evaluated for the sample means, being a woman reduces WTPT by 0.97 USD/household/month, while the amount of payment increases by 8.52 USD/household/month if the respondent has university studies, by 4.26 USD/household/month if the respondent is an active worker, 0.27 USD/household/month for every 54 USD of family income, and by 2 USD/household/month for each additional affective ecological commitment index point. It should also be noted that the time variable (Year 2025) was not significant in either of the two estimations, demonstrating, as in the WTA analysis, the absence of significant differences between samples.
4. Discussion
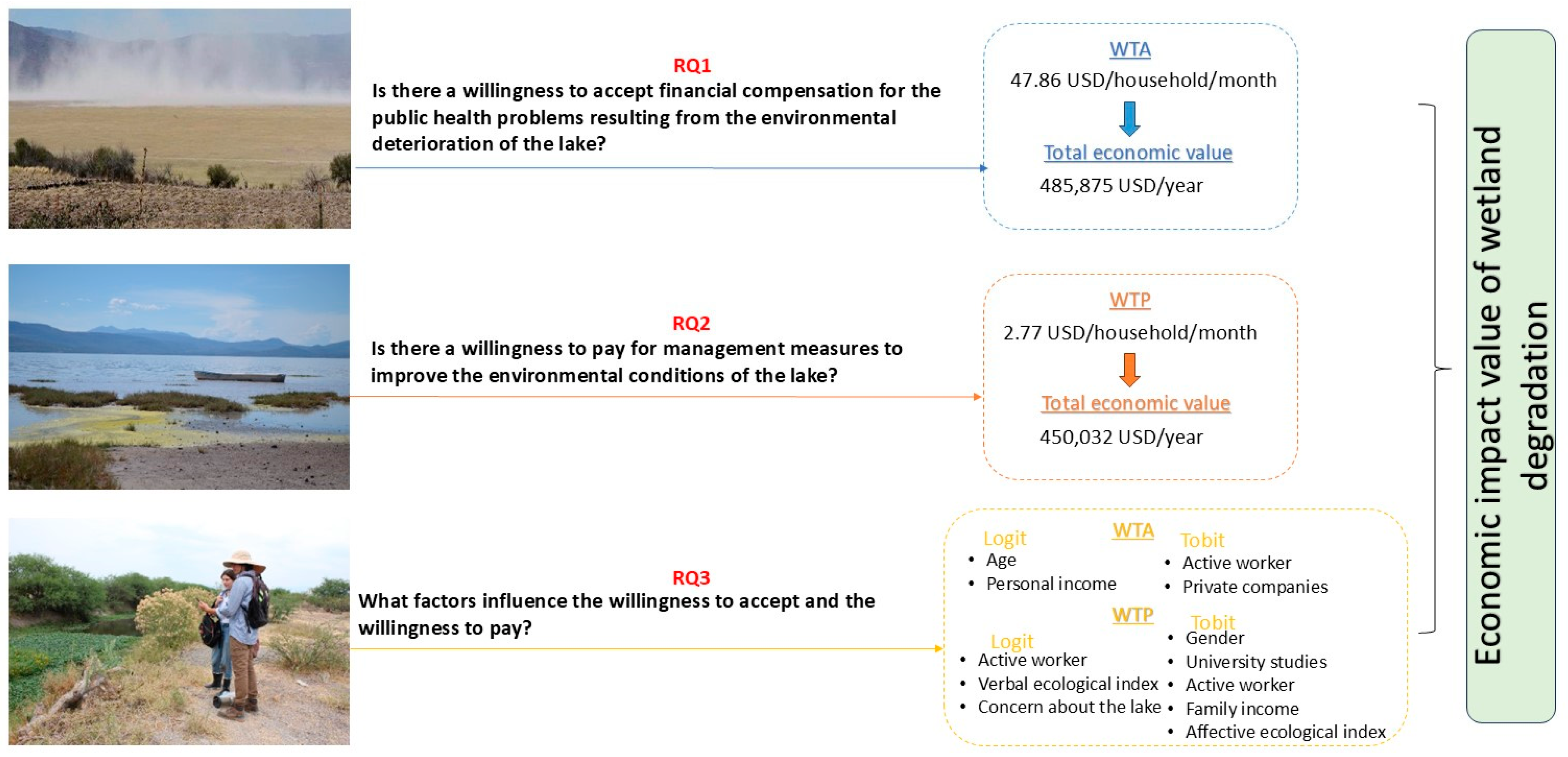
This work addresses the economic valuation of wetland degradation in Mexico, a country where research on this issue remains scarce despite the critical role of its lakes. Lake Cuitzeo was chosen as a case study due to its severe ecological deterioration and its direct impacts on public health in surrounding communities. By applying a contingent valuation survey, the study successfully answered the three research questions formulated (Figure 3).
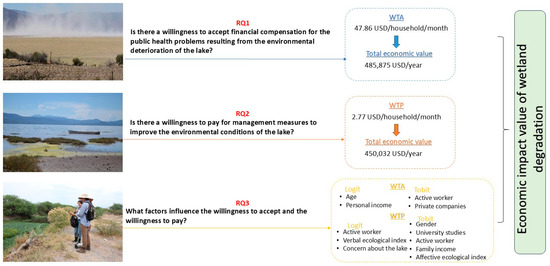
Figure 3.
Summary of the main results.
(1) Is there a willingness to accept financial compensation for the public health problems resulting from the environmental deterioration of the lake?
Approximately 90% of respondents expressed a willingness to accept compensation, with an average WTA of 47.86 USD/household/month. This finding confirms the existence of a serious public health issue associated with Lake Cuitzeo. The estimated health cost of the tolvaneras (around 500,000 USD annually) highlights an externality that markets alone cannot address.
To our knowledge, this is the first study in Latin America to quantify the economic cost of direct health impacts from wetland degradation. These results are consistent with findings in European [37,38] and Asian wetlands [39,40], where increased health expenditures have underscored the urgency of implementing sustainable management measures.
It is imperative that a public policy is formulated to allocate vouchers for medical expenses, encompassing the amount of the WTA, to reduce defensive health costs. The responsibility for overseeing this process should be entrusted to the policy makers of the region, to enhance the well-being of the inhabitants of the lake area.
(2) Is there a willingness to pay for management measures to improve the environmental conditions of the lake?
This work showed the existence of a social demand for improving the environmental conditions of Lake Cuitzeo where approximately 50% of the sample, with an average WTP of 2.77 USD/household/month, were willing to finance the implementation of a series of management measures.
The total economic value obtained from WTP, which amounted to 450,000 USD/year, could be used to calculate the budget that would have to be spent annually for the implementation of the management measures assessed by the respondents. The high social valuation assigned to all management measures proposed for implementation in the area suggests a relatively equal distribution of the budget among all measures, with a higher budget allocation towards reforestation and the planting of riparian vegetation in key areas of the wetland. These economic values can be compared with those obtained in wetlands in Spain [15], the United States [41], Bangladesh [42], and China [43] where there is a clear social preference for measures to promote wetland support services such as revegetation of wetland environments.
The values obtained in this work should be used by policy makers as an indicator of the well-being that would be generated by the implementation of management measures in Lake Cuitzeo. It could be suggested that tax collection through a fee on the water bill as a basis for the WTP incentivizes the implementation of actions to improve the conditions of the lake. Furthermore, as reflected in the survey, beyond the collection of taxes from the population, there must be greater involvement from the state, federal and municipal administrations. It is incumbent upon these policy makers to promote public investment in innovation and nature-based solutions [44], to support the most sustainable sectors and the most environmentally vulnerable regions. Furthermore, there is a need to focus on identifying novel models of agricultural production that exhibit reduced water consumption and erosive capacity [20]. This should be accompanied by a reduction in the exploitation of aquifers, the planning of urban development outside floodplains, and respect for the biodiversity associated with the wetland.
(3) What factors influence the willingness to accept and the willingness to pay?
The findings of the multivariate analyses demonstrated, firstly, that there was no significant influence between the two samples employed in this work, as the time variable used was not significant. Secondly, they demonstrated that it was the socio-economic and environmental perception characteristics that determined WTA and WTP. In this sense, significant evidence was found that older people, those who are economically inactive and have a lower personal income, are those who show a higher WTA. Conversely, being a man, an active worker, having a university education and a higher ecological commitment (affective and verbal) show a higher WTP. These results are consistent with those reported in the existing literature on the economic valuation of environmental assets [15,19,20,21], which highlights the influence of socio-economic and environmental factors on the valuation exercise.
Thus, it is imperative that the knowledge produced is disseminated through appropriate channels, such as forums and workshops. These initiatives are instrumental in promoting awareness and education in environmental terms. By doing so, the population of the area can be encouraged to align their daily actions with the principles of environmental sustainability. Furthermore, it is essential to cultivate behaviors that are conducive to enhancing the condition of the lake. In this manner, the efficient allocation of monetary resources for environmental improvements is imperative, a matter of even greater urgency in the present context of global change, which casts doubt on the spatio-temporal availability of water resources.
The economic valuation method employed in this work provides a foundation for determining the allocation of economic resources in the pursuit of public policies aimed at addressing the environmental challenges posed by Lake Cuitzeo. Consequently, valuation methods should be utilized in conjunction with the results obtained, employing cost–benefit analyses to assess the socio-economic profitability of implementing environmental restoration initiatives. This would enable the authorities responsible for overseeing public health, environmental issues in water bodies, and the wider environment to guide the analysis for decision-making.
5. Conclusions
This work has demonstrated the economic impacts associated with the degradation of a wetland in Mexico, using Lake Cuitzeo in the state of Michoacan as a representative case study. A significant proportion of the population is willing to accept economic compensation for damage to public health, also willing to pay for the implementation of management measures to improve the environmental status of the wetland.
The findings of this work have practical implications that may be of use to governmental institutions charged with the management of the water resources of Lake Cuitzeo, given the direct impact of wetland degradation on public health and on the socio-economic and environmental development of the area. It can thus be concluded that the transition towards sustainable wetland management requires the involvement of public participatory processes, including surveys such as those carried out in this work, to support and encourage the implementation of regional policies with the aim of reducing the negative effects on the well-being of the population. It is therefore important to highlight the need for multidisciplinary research that integrates socio-ecological and economic perspectives and comprehensively examines both the degradation and restoration of wetlands, to better inform management decisions. Consequently, economic valuation analyses constitute a pivotal component in the formulation of public policies. However, although an economic assessment was carried out here to obtain results that would serve as an indicator of the well-being generated by addressing the problem of lake degradation, it would be advisable to conduct complementary studies that include both environmental and health analyses.
Finally, the implications of this work extend beyond conventional economic valuation by emphasizing not only the benefits of environmental improvement, but also the costs of public health damage. In summary, the population has a strong interest in resolving the degradation of Lake Cuitzeo, which provides a foundation for designing socially acceptable, efficient, and sustainable policies, particularly in under-studied regions such as Latin America.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.T.-R., J.A.A.-G., A.C.-T., C.F.O.-P. and J.M.M.-P.; methodology, R.T.-R. and J.M.M.-P.; software, R.T.-R., J.A.A.-G. and J.M.M.-P.; validation, R.T.-R., J.A.A.-G., A.C.-T., C.F.O.-P. and J.M.M.-P.; formal analysis, R.T.-R., J.A.A.-G., A.C.-T., C.F.O.-P. and J.M.M.-P.; investigation, R.T.-R., J.A.A.-G., C.F.O.-P. and J.M.M.-P.; resources, R.T.-R., J.A.A.-G., C.F.O.-P. and J.M.M.-P.; data curation, R.T.-R. and J.A.A.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, R.T.-R. and J.A.A.-G.; writing—review and editing, R.T.-R., J.A.A.-G. and J.M.M.-P.; visualization, R.T.-R., J.A.A.-G., A.C.-T., C.F.O.-P. and J.M.M.-P.; supervision, C.F.O.-P. and J.M.M.-P.; project administration, R.T.-R.; funding acquisition, R.T.-R., C.F.O.-P. and J.M.M.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received funding through a doctoral scholarship by the National Council of Humanities, Science, Technology and Innovation (CONAHCYT), now known as the Secretariat of Science, Humanities, Technology and Innovation (SECIHTI) of the Government of Mexico.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the interviewees from the municipalities of Cuitzeo (Jeruco and Miguel Silva) and Huandacareo (Capacho), Michoacan. Without their valuable contributions this work would not have been possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Contingent valuation sample description (n = 306).
Table A1.
Contingent valuation sample description (n = 306).
| Description | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Household size (people) | 4.01 | 1.62 | 1 | 13 |
| Age (years) | 50.13 | 12.70 | 27 | 85 |
| Family income (USD/household/month) | 159.05 | 122.90 | 53.95 | 1349 |
| Personal income (USD/person/month) | 127.65 | 124.20 | 53.95 | 1349 |
| Active worker (% yes) | 93.79 | |||
| University studies (%) | 6.21 | |||
| Gender (% women) | 21.57 | |||
| Concern about the lake (1–5) | 3.94 | 0.32 | 3 | 5 |
| Federal government (1–5) | 4.95 | 0.24 | 3 | 5 |
| State government (1–5) | 4.82 | 0.40 | 3 | 5 |
| Municipal government (1–5) | 4.69 | 0.61 | 3 | 5 |
| Private companies (1–5) | 4.71 | 0.62 | 2 | 5 |
| NGOs (1–5) | 4.83 | 0.44 | 3 | 5 |
| Citizens (1–5) | 4.94 | 0.27 | 3 | 5 |
| Affective ecological index (1–5) | 4.89 | 0.27 | 3.5 | 5 |
| Verbal ecological index (1–5) | 3.89 | 0.78 | 1 | 5 |
| Real ecological index (1–5) | 1.34 | 0.67 | 1 | 5 |
References
- Kundu, S.; Kundu, B.; Rana, N.K.; Mahato, S. Wetland degradation and its impacts on livelihoods and sustainable development goals: An overview. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 48, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Cui, B.; Cao, H.; Li, A.; Zhang, B. Wetland degradation and ecological restoration. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 523632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, S.; Su, F. Coastal wetland degradation and ecosystem service value change in the Yellow River Delta, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 44, e02501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballut-Dajud, G.A.; Sandoval Herazo, L.C.; Fernández-Lambert, G.; Marín-Muñiz, J.L.; López Méndez, M.C.; Betanzo-Torres, E.A. Factors affecting wetland loss: A review. Land 2022, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, P.E.R.; Connelly, R. Wetlands and human health: An overview. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 20, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltby, E. The wetlands paradigm shift in response to changing societal priorities: A reflective review. Land 2022, 11, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, K.; Zabbey, N. Contaminated land and wetland remediation in Nigeria: Opportunities for sustainable livelihood creation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1560–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebresllassie, H.; Gashaw, T.; Mehari, A. Wetland degradation in Ethiopia: Causes, consequences and remedies. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 4, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Adhya, T.; Banerjee, S. Impact of wetland development and degradation on the livelihoods of wetland-dependent communities: A case study from the lower gangetic floodplains. Wetlands 2022, 42, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A.P.; Jupiter, S. Natural disasters, health and wetlands: A Pacific small island developing state perspective. In Wetlands and Human Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 169–191. [Google Scholar]
- García-Herrero, L.; Lavrnić, S.; Guerrieri, V.; Toscano, A.; Milani, M.; Cirelli, G.L.; Vittuari, M. Cost-benefit of green infrastructures for water management: A sustainability assessment of full-scale constructed wetlands in Northern and Southern Italy. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 185, 106797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hou, Y.; Xue, Y. Water resources carrying capacity of wetlands in Beijing: Analysis of policy optimization for urban wetland water resources management. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Gourevitch, J.D.; Wemple, B.C.; Watson, K.B.; Rizzo, D.M.; Polasky, S.; Ricketts, T.H. Optimizing wetland restoration to improve water quality at a regional scale. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musasa, T.; Muringaniza, K.C.; Manyati, M. The role of stakeholder participation in wetland conservation in urban areas: A case of Monavale Vlei, Harare. Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perni, Á.; Martínez-Paz, J.M. Measuring conflicts in the management of anthropized ecosystems: Evidence from a choice experiment in a human-created Mediterranean wetland. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marre, J.B.; Thebaud, O.; Pascoe, S.; Jennings, S.; Boncoeur, J.; Coglan, L. Is economic valuation of ecosystem services useful to decision-makers? Lessons learned from Australian coastal and marine management. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 178, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.; Fraser, G.; Snowball, J. Economic evaluation of wetland restoration: A systematic review of the literature. Restor. Ecol. 2018, 26, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaladejo-García, J.A.; Alcon, F.; Martínez-Carrasco, F.; Martínez-Paz, J.M. Understanding socio-spatial perceptions and Badlands ecosystem services valuation. Is there any welfare in soil erosion? Land Use Policy 2023, 128, 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, R.; Brough, P.; Hague, L.; Chauvenet, A.; Fleming, C.; Roche, E.; Sofija, E.; Harris, N. Economic value of protected areas via visitor mental health. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Paz, J.M.; Albaladejo-García, J.A.; Barreiro-Hurle, J.; Pleite, F.M.C.; Perni, Á. Spatial effects in the socioeconomic valuation of peri-urban ecosystems restoration. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.F.; Sullivan, C.A. Ecosystem services within agricultural landscapes—Farmers’ perceptions. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 98, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer, J.; Escobar, E. Limnological regionalization of Mexico. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1996, 2, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlhogile, T.; Arntzen, J.; Mabiza, C.; Mano, R. Economic valuation of selected direct and indirect use values of the Makgadikgadi wetland system, Botswana. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Pinzón, L.; Sierra, L.; Trillas, F. The Economic value of wetlands in urban areas: The benefits in a developing country. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechasa, F.; Senbeta, F.; Guta, D.D. Economic value of wetlands services in the Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Environ. Econ. Policy Stud. 2021, 23, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamboleo, M.; Adem, A. Estimating willingness to pay for the conservation of wetland ecosystems, Lake Victoria as a case study. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2022, 423, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, K.B.; Phan, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Pham, T.P.N.; Nguyen, M.H.; Dang, V.B.; Hoang, T.T.H.; Van Liem, N. Economic valuation of wetland ecosystem services in northeastern part of Vietnam. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2022, 423, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brander, L.; Brouwer, R.; Wagtendonk, A. Economic valuation of regulating services provided by wetlands in agricultural landscapes: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 56, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Spencer, L.H.; Tudor Edwards, R. A systematic review exploring the economic valuation of accessing and using green and blue spaces to improve public health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalado, R.T.; Paniagua, C.F.O. Percepción social de medidas de gestión sostenible en el lago de Cuitzeo, México. Papeles Geogr. 2024, 70, 106–122. [Google Scholar]
- Regalado, R.T.; Paniagua, C.F.O. Preferencias socioeconómicas por costos ambientales en la Región Oeste del Lago de Cuitzeo, Michoacán, México. Campos Neutrais-Rev. Lat. Am. Relações Int. 2019, 1, 8–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chacón, A.; Rosas, C.; Trueba, R.; Sauno, F.; Jacobo, A. Lake Cuitzeo, Michoacan, Mexico. Effects of environmental deteroration. In Proceedings of the 18th World Lake Conference, Universidad de Guanajuato, Mexico City, Mexico, 9–11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaria de Salud de Michoacán. Jurisdicción Sanitaria N°1 Morelia. Carpeta Básica. Coordinación y Evaluación y Estadística. 2025. Available online: https://salud.michoacan.gob.mx/jurisdiccion-sanitaria-no-1-morelia/ (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Hoyos, D. The state of the art of environmental valuation with discrete choice experiments. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, R.C.; Heberlein, T.A. The contingent valuation method. In Economic Valuation of Natural Resources; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2019; pp. 81–104. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Censo de Población y Vivienda. 2020. Available online: https://inegi.org.mx/programas/ccpv/2020/ (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Busse, M.; Heitepriem, N.; Siebert, R. The acceptability of land pools for the sustainable revalorisation of wetland meadows in the Spreewald Region, Germany. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzén, F.; Dinnétz, P.; Hammer, M. Factors affecting farmers’ willingness to participate in eutrophication mitigation—A case study of preferences for wetland creation in Sweden. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 130, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Khachatryan, H.; Zhu, H. Poyang lake wetlands restoration in China: An analysis of farmers’ perceptions and willingness to participate. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Kong, F. The analysis of farmers’ willingness to accept and its influencing factors for ecological compensation of Poyang Lake wetland. Procedia Eng. 2017, 174, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, W.A.; Murray, B.C.; Kramer, R.A.; Faulkner, S.P. Valuing ecosystem services from wetlands restoration in the Mississippi Alluvial Valley. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, M.S.I.; Islam, H.N.; Ullah, M.A.; Newaz, K.M.N.; Khan, M.F.A.; Sarker, G.C.; Bhuiyan, M.S.R. Ecological and economic significance of swamp vegetation nursery for successful reforestation program: An insight from Bangladesh. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2024, 9, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Peng, S.; Liu, G.; Ducharne, A.; Ciais, P.; Prigent, C.; Li, X.; Tang, X. Trade-off between tree planting and wetland conservation in China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Solomun, M.K.; Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Zhao, W.; Kalantari, Z. Wetlands as nature-based solutions for water management in different environments. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 33, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).