Comparative Performance Analysis of Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Models for Multi-Satellite Fusion GNSS-IR Soil Moisture Retrieval
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
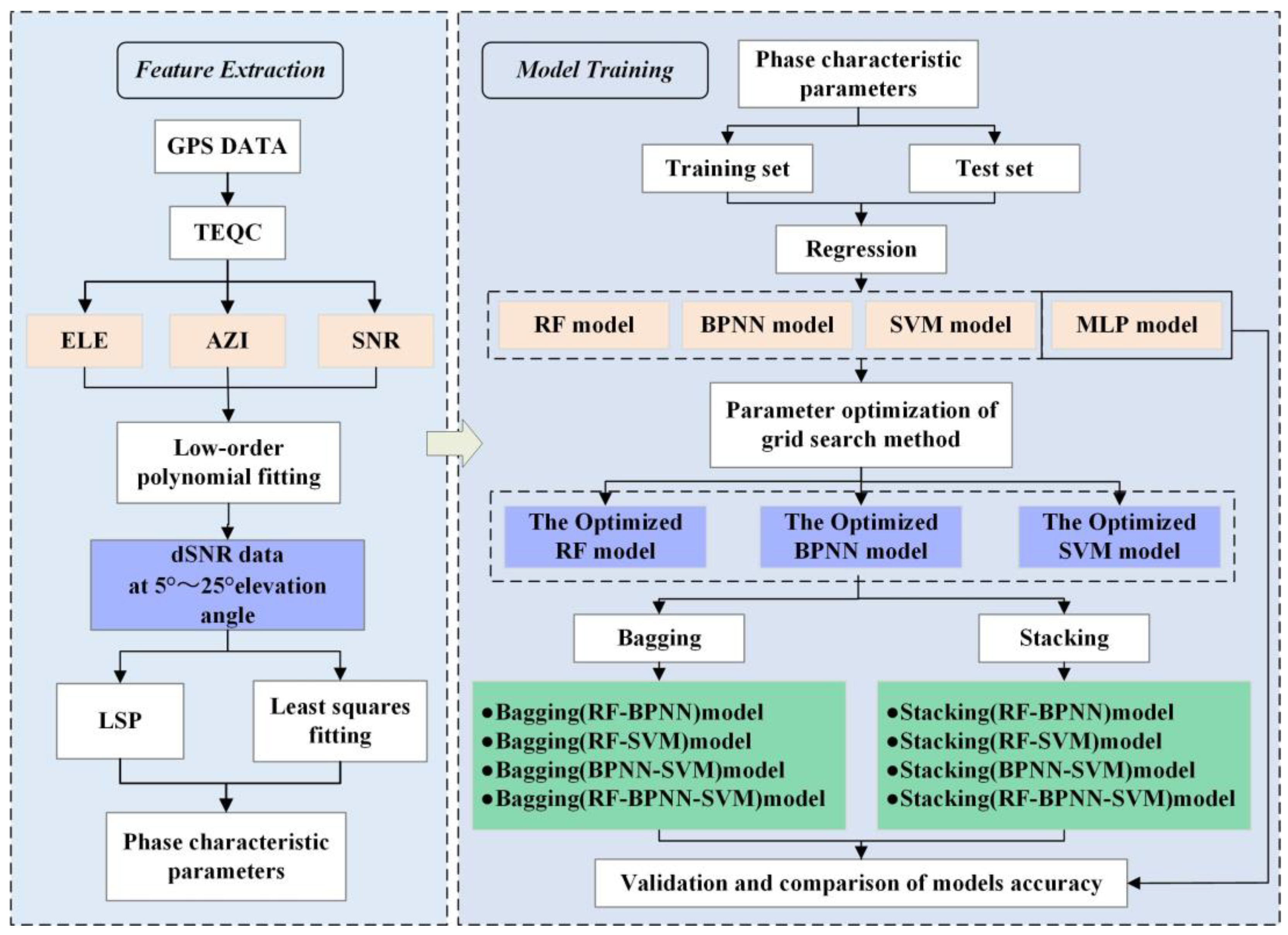
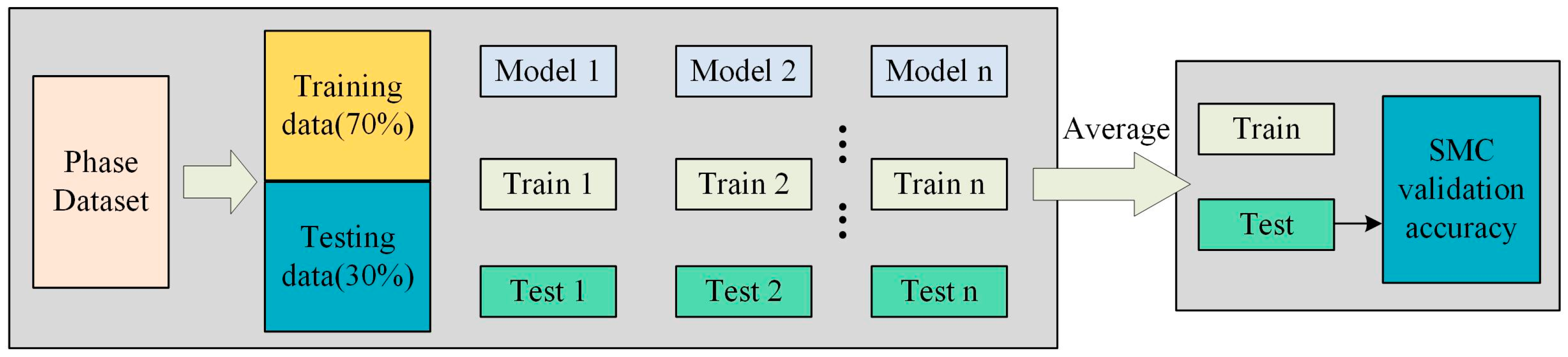
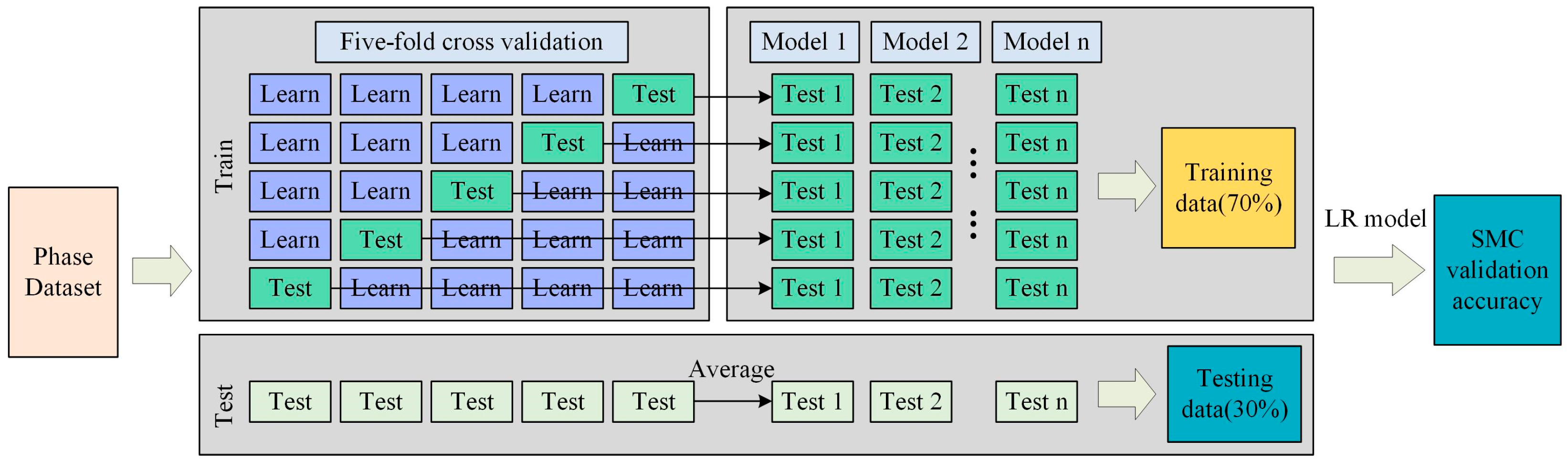
2.1. Technical Processes
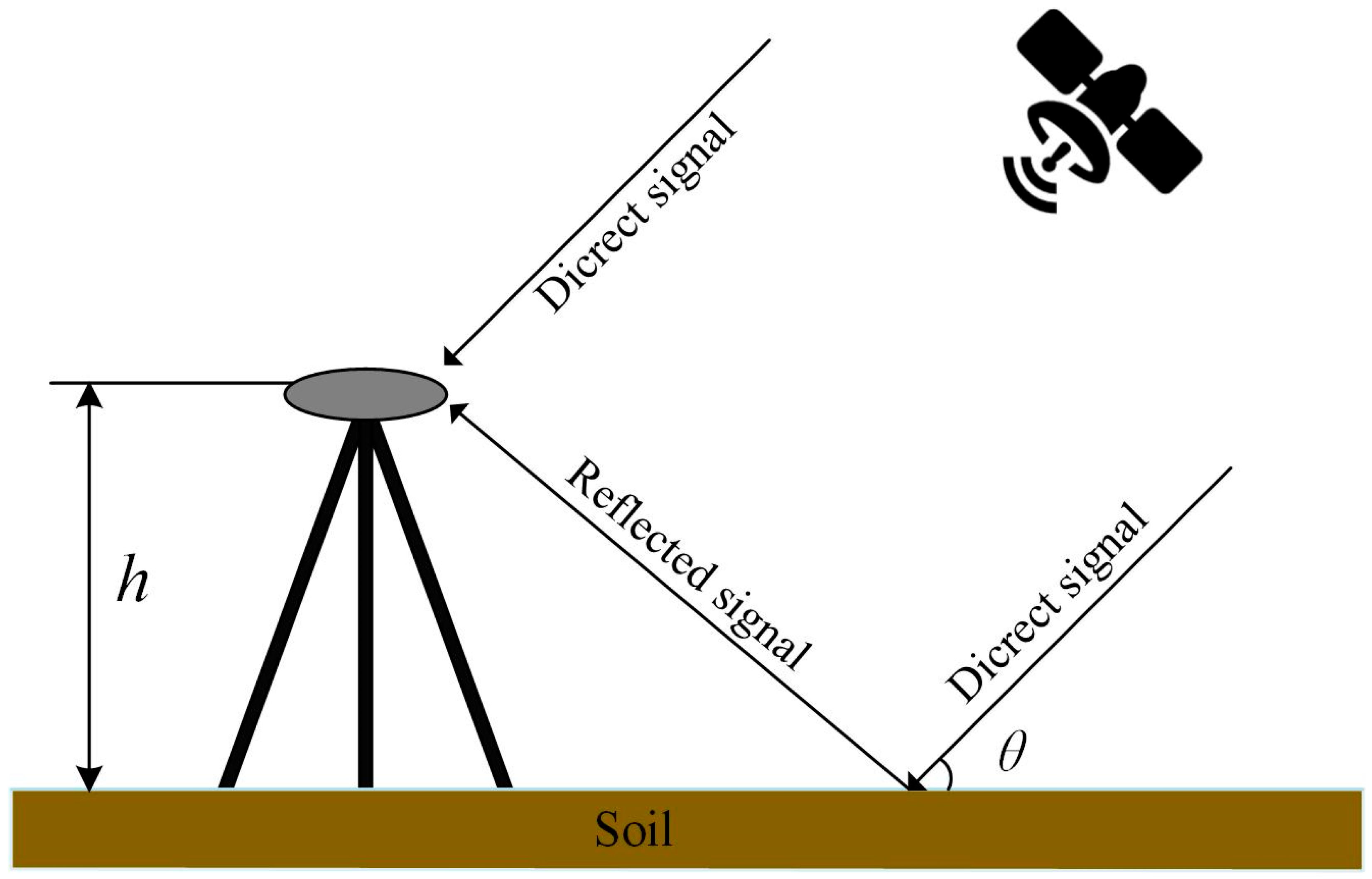
2.2. GNSS-IR Soil Moisture Retrieval Principle
2.3. Heterogeneous Integrated Learning Model Foundation Learner
2.3.1. Back Propagation Neural Network
2.3.2. Random Forest
2.3.3. Support Vector Machine
2.3.4. Multilayer Perceptron
2.4. Heterogeneous Integrated Learning Algorithms
2.4.1. Bagging Integrated Learning Algorithm
2.4.2. Stacking Integrated Learning Algorithm
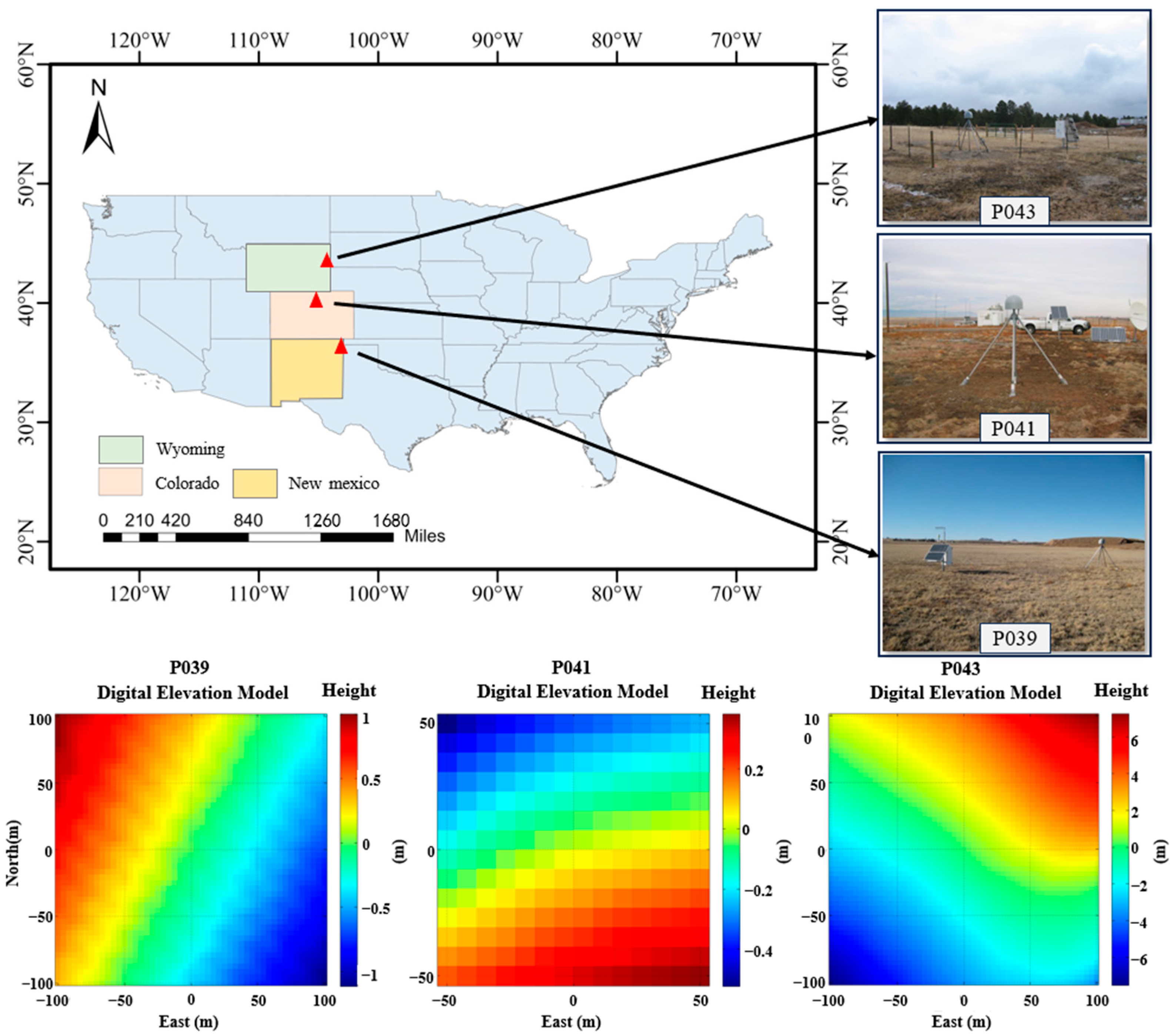
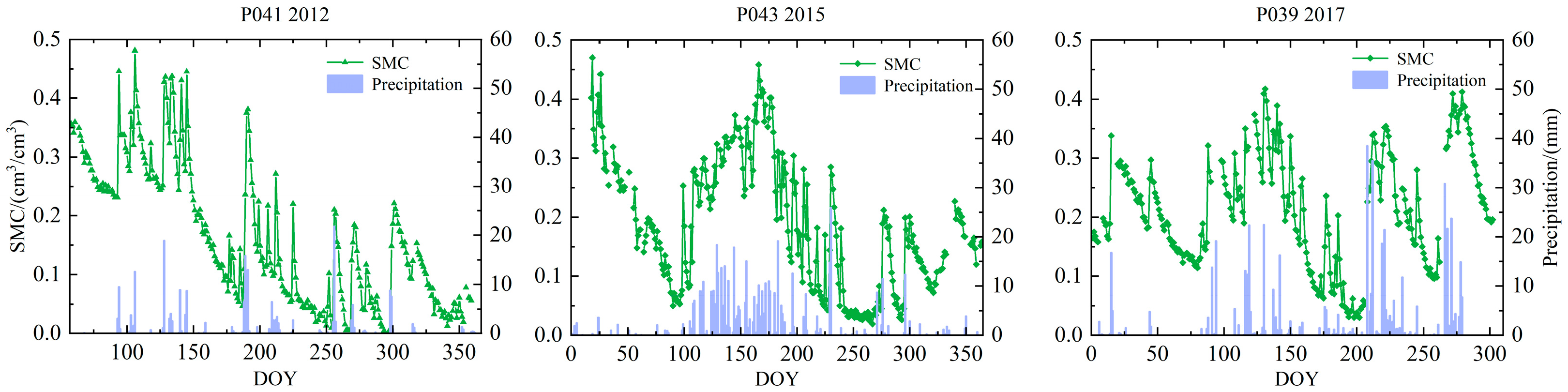
3. Study Area and Data
4. Results
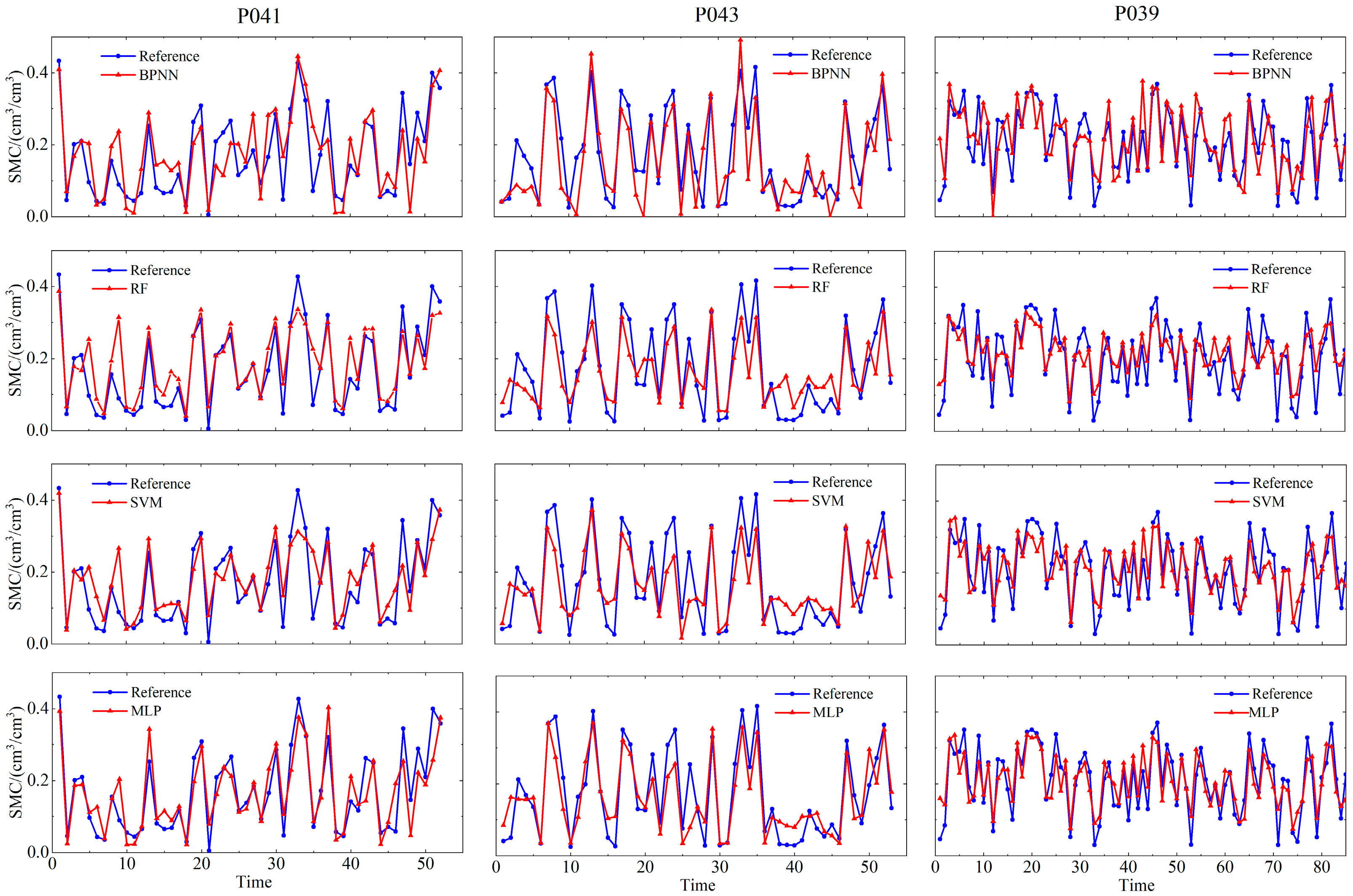
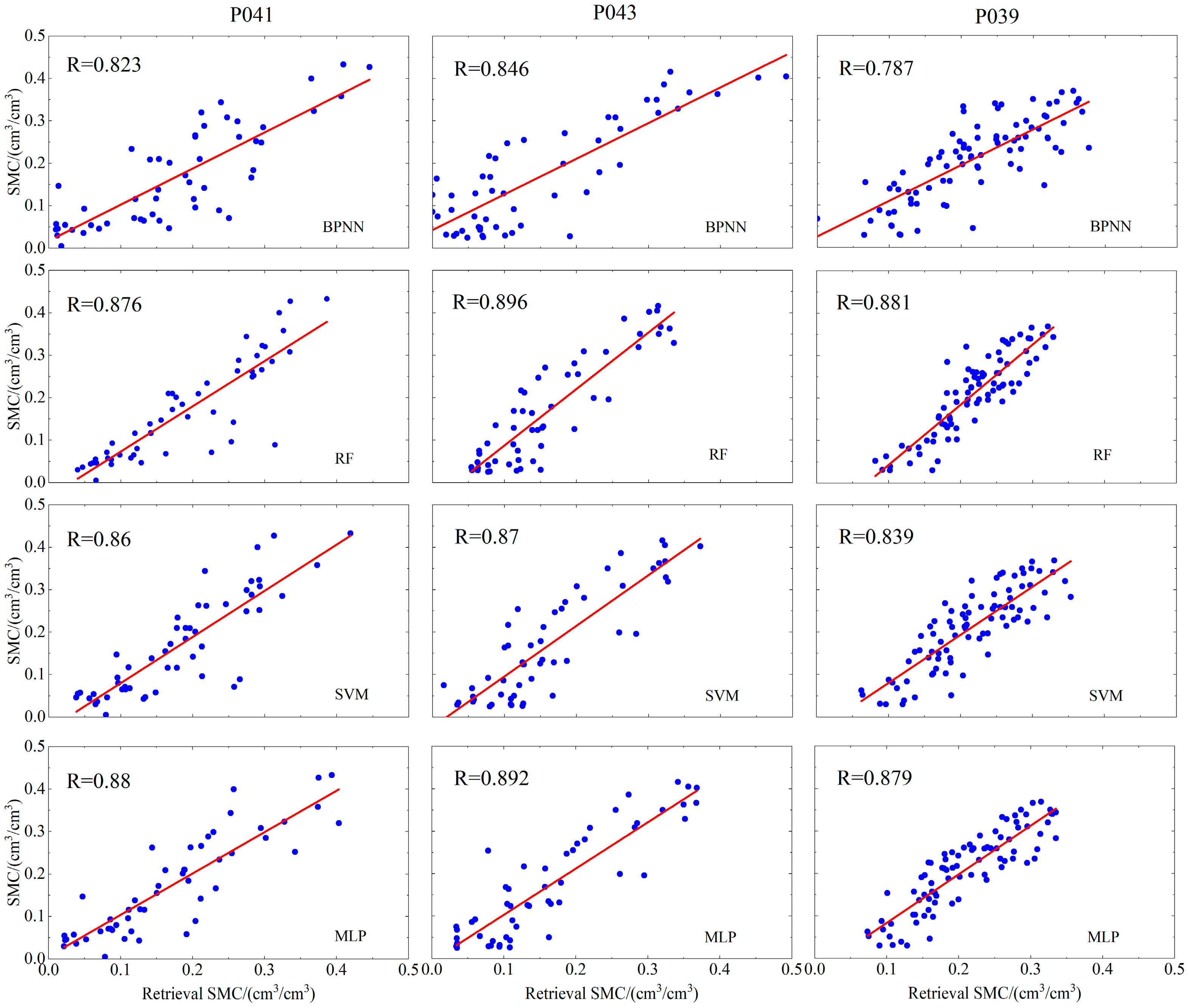
4.1. Soil Moisture Retrieval Results of Baseline Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models
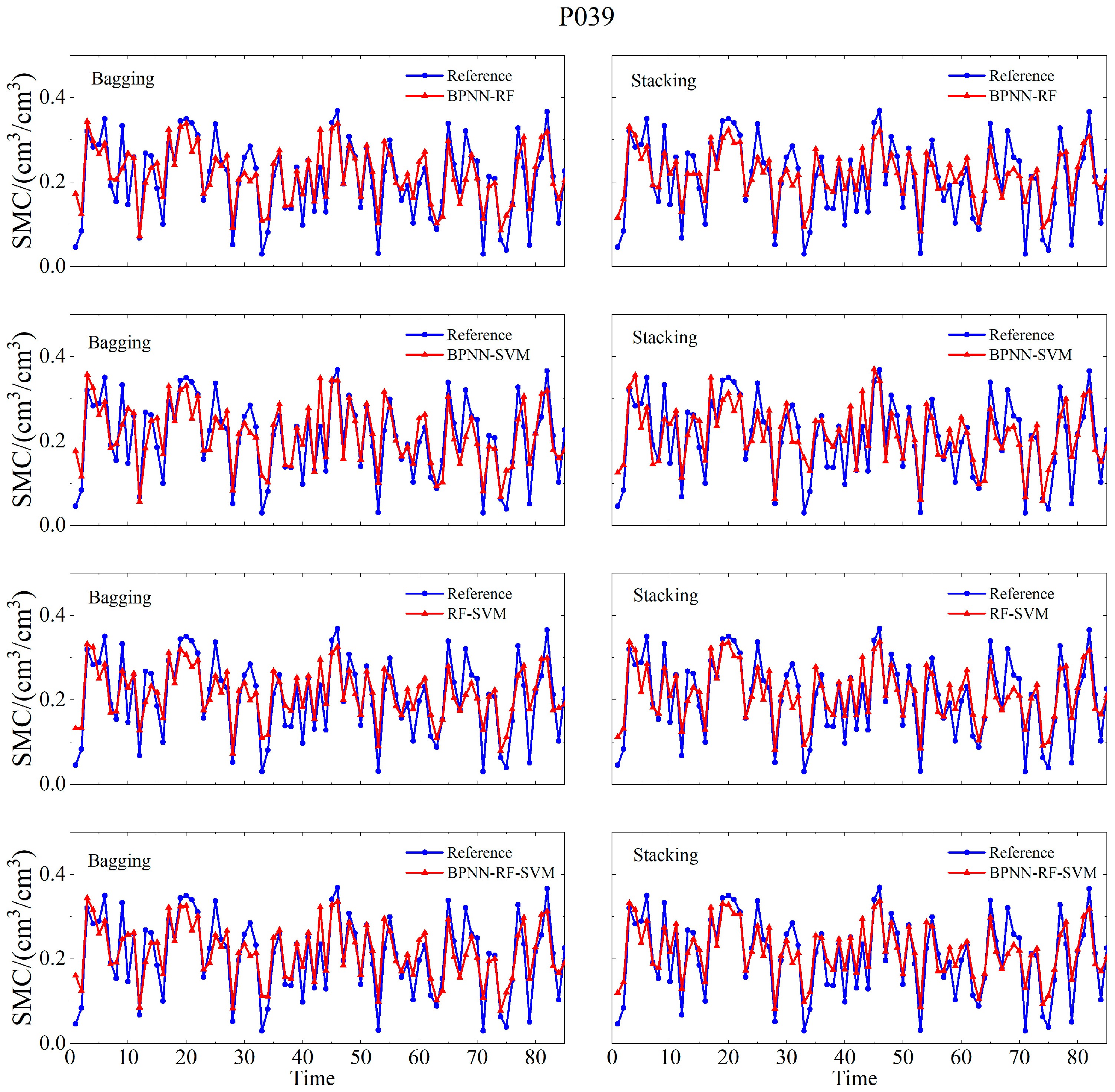
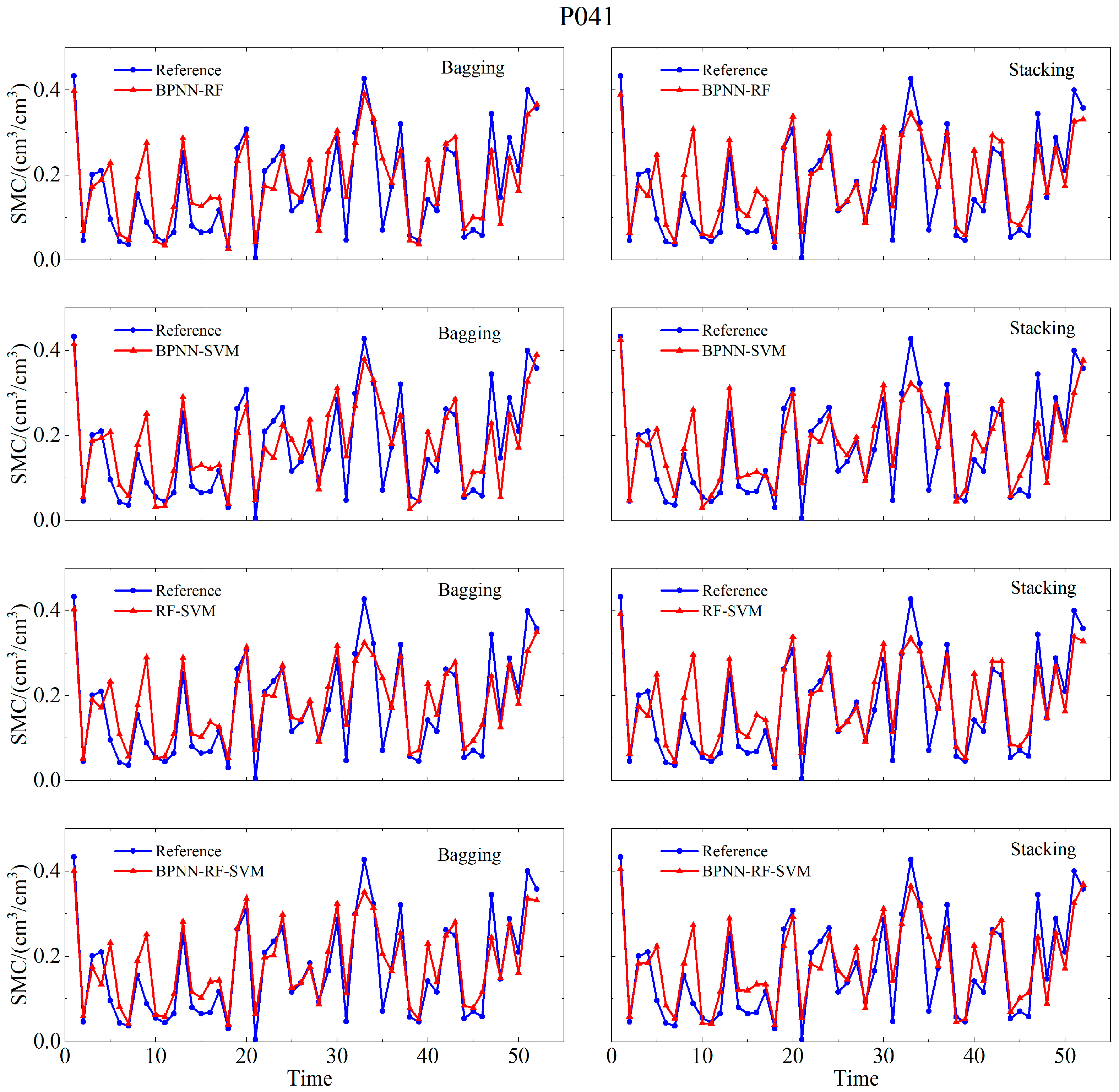
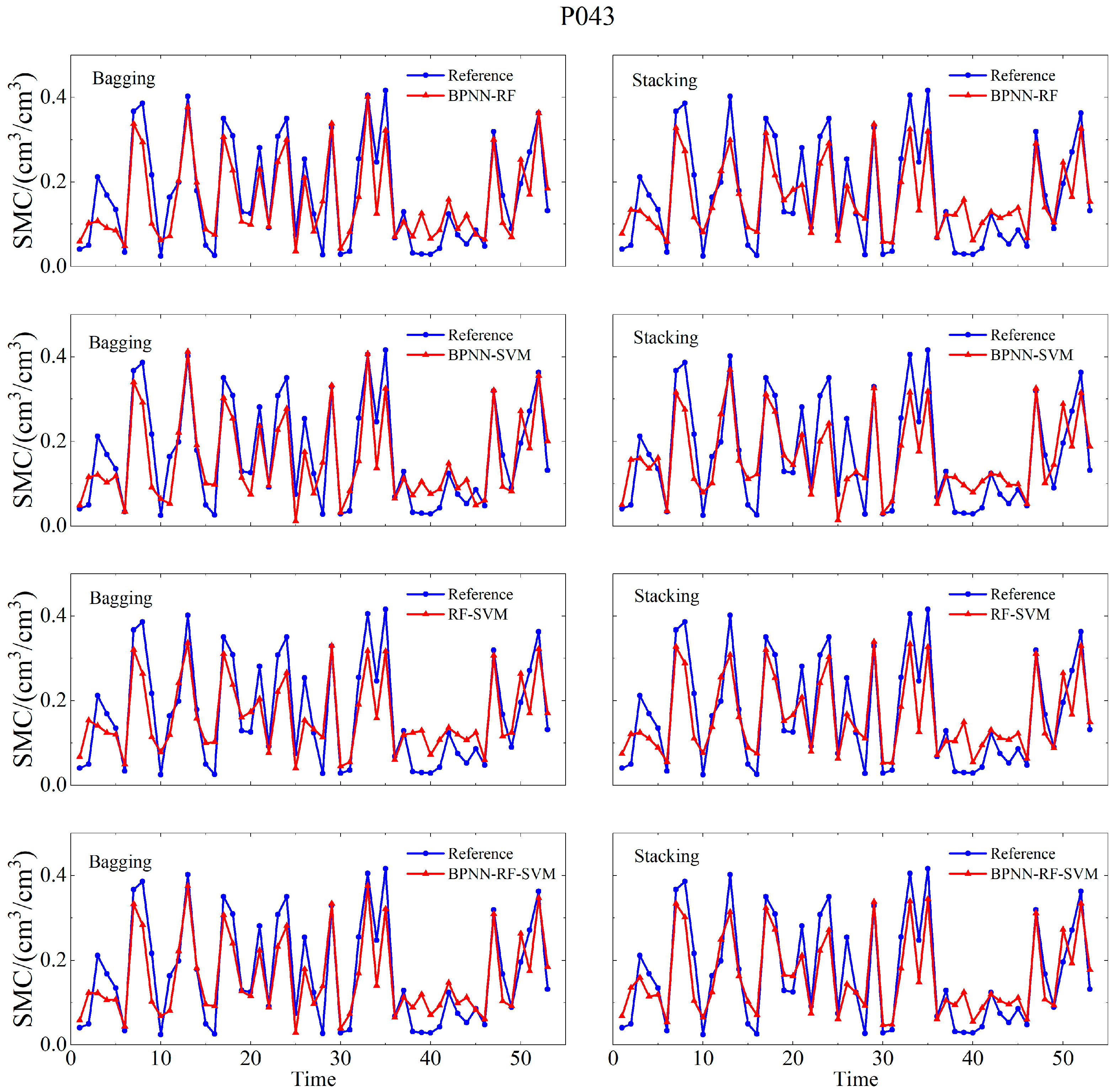
4.2. Integrated Machine Learning Model Soil Moisture Retrieval Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Evaluation of Retrieval Accuracy for Soil Moisture Results Across Different Models
5.2. Computational Cost Control of the Stacking Ensemble Algorithm
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jackson, T.J.; Schmugge, J.; Engman, E.T. Remote Sensing Applications to Hydrology: Soil Moisture. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1996, 41, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, R.; Tu, J.; Liao, M.; Pang, J.; Yu, B.; Li, K.; Xiang, W.; Fu, Y.; Liu, G. A GNSS-IR Method for Retrieving Soil Moisture Content from Integrated Multi-Satellite Data That Accounts for the Impact of Vegetation Moisture Content. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Martin, J.F.; Onrubia, R.; Pascual, D.; Park, H.; Pablos, M.; Camps, A.; Rüdiger, C.; Walker, J.; Monerris, A. Single-Pass Soil Moisture Retrieval Using GNSS-R at L1 and L5 Bands: Results from Airborne Experiment. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavak, A.; Vogel, W.J.; Xu, G. Using GPS to Measure Ground Complex Permittivity. Electron. Lett. 1998, 34, 254–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Voronovich, A.G. Bistatic GPS Signal Reflections at Various Polarizations from Rough Land Surface with Moisture Content. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2000. IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Taking the Pulse of the Planet: The Role of Remote Sensing in Managing the Environment. Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37120), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; Volume 7, pp. 2852–2854. [Google Scholar]
- Zavorotny, V.; Masters, D.; Gasiewski, A.; Bartram, B.; Katzberg, S.; Axelrad, P.; Zamora, R. Seasonal Polarimetric Measurements of Soil Moisture Using Tower-Based GPS Bistatic Radar. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 2, pp. 781–783. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, D.; Katzberg, S.; Axelrad, P. Airborne GPS Bistatic Radar Soil Moisture Measurements during SMEX02. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 2, pp. 896–898. [Google Scholar]
- Katzberg, S.J.; Torres, O.; Grant, M.S.; Masters, D. Utilizing Calibrated GPS Reflected Signals to Estimate Soil Reflectivity and Dielectric Constant: Results from SMEX02. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, H. Near-Surface Soil Moisture Content Measurement by GNSS Reflectometry: An Estimation Model Using Calibrated GNSS Signals. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 7523–7526. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Arroyo, A.; Forte, G.; Camps, A.; Park, H.; Pascual, D.; Onrubia, R.; Jove-Casulleras, R. Soil Moisture Mapping Using Forward Scattered GPS L1 Signals. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium —IGARSS, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 354–357. [Google Scholar]
- Egido, A.; Caparrini, M.; Ruffini, G.; Paloscia, S.; Santi, E.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Floury, N. Global Navigation Satellite Systems Reflectometry as a Remote Sensing Tool for Agriculture. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2356–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egido, A.; Paloscia, S.; Motte, E.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Caparrini, M.; Santi, E.; Fontanelli, G.; Floury, N. Airborne GNSS-R Polarimetric Measurements for Soil Moisture and Above-Ground Biomass Estimation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, O.; Kurum, M.; Boyd, D.; Gurbuz, A.C. High Spatio-Temporal Resolution CYGNSS Soil Moisture Estimates Using Artificial Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreno-Luengo, H.; Luzi, G.; Crosetto, M. Impact of the Elevation Angle on CYGNSS GNSS-R Bistatic Reflectivity as a Function of Effective Surface Roughness over Land Surfaces. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, S.; O’Brien, A.; Russel, A.; Al-Khaldi, M.M.; Johnson, J.T. Geolocation, Calibration and Surface Resolution of CYGNSS GNSS-R Land Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W.; Jin, S.; Jia, Y. Pan-Tropical Soil Moisture Mapping Based on a Three-Layer Model from CYGNSS GNSS-R Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, R.; Yu, B.; Pang, J.; Liao, M.; Liu, G. A GPS-IR Method for Retrieving NDVI From Integrated Dual-Frequency Observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.; Bilich, A.; Axelrad, P.; Braun, J. Using GPS Multipath to Measure Soil Moisture Fluctuations: Initial Results. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, R.; Liu, A.; Yang, Y.; Lv, J.; Jiang, Y. A Novel Snow Depth Retrieving Approach Using Time-Series Clustering in GPS-IR Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 2503505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Larson, K.M.; Braun, J.J.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.D.; Bilich, A.L. A Physical Model for GPS Multipath Caused by Land Reflections: Toward Bare Soil Moisture Retrievals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E.; Larson, K.M.; Zavorotny, V.U. Effects of Near-Surface Soil Moisture on GPS SNR Data: Development of a Retrieval Algorithm for Soil Moisture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Hu, X. GNSS-IR Dual-Frequency Data Fusion for Soil Moisture Inversion Based on Helmert Variance Component Estimation. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ren, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Z. Research on Soil Moisture Inversion Method Based on GA-BP Neural Network Model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2087–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Yong, L.; Mutian, H.; Lei, Y.; Lili, J.; Yongqing, Y. GNSS-IR Soil Moisture Inversion Method Based on GA-SVM. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2019, 45, 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.; Liang, Y.-J.; Lu, X.-J.; Yan, H.-B. Research on the Soil Moisture Sliding Estimation Method Using the LS-SVM Based on Multi-Satellite Fusion. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 2104–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, H.; Shen, F.; Guan, Z.; Zhou, F.; Cao, X.; Ge, Y. A GNSS-IR Soil Moisture Retrieval Method via Multi-Layer Perceptron with Consideration of Precipitation and Environmental Factors. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pourtaghi, Z.S.; Al-Katheeri, M.M. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using Random Forest, Boosted Regression Tree, Classification and Regression Tree, and General Linear Models and Comparison of Their Performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Landslides 2016, 13, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Y. Stacking Ensemble of Deep Learning Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 2207–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.D.; Bilich, A.L.; Braun, J.J.; Zavorotny, V.U. Use of GPS Receivers as a Soil Moisture Network for Water Cycle Studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L24405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Chew, C.C.; Braun, J.J. Using Geodetic GPS Receivers to Measure Vegetation Water Content. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, E.F.; Chen, J.; Mushegian, A.R. Detecting Periodic Patterns in Unevenly Spaced Gene Expression Time Series Using Lomb-Scargle Periodograms. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Cao, Z.; Guo, J.; Jiang, S.-H.; Li, S.; Guo, Z. Comparisons of Heuristic, General Statistical and Machine Learning Models for Landslide Susceptibility Prediction and Mapping. CATENA 2020, 191, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, R.; Shama, A.; Hong, R.; He, X.; Wu, R.; Bao, X.; Liu, G. Exploring the Spatial Patterns of Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Using Interpretable Shapley Method: Mechanisms of Landslide Formation in the Sichuan-Tibet Region. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, S.R. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. Technometrics 1996, 38, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model for Information Storage and Organization in the Brain. Psychol. Rev. 1958, 65, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Bui, D.T.; Dholakia, M.B.; Prakash, I.; Pham, H.V.; Mehmood, K.; Le, H.Q. A Novel Ensemble Classifier of Rotation Forest and Naïve Bayer for Landslide Susceptibility Assessment at the Luc Yen District, Yen Bai Province (Viet Nam) Using GIS. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Tien Bui, D.; Prakash, I. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Using Bagging Ensemble Based Alternating Decision Trees, Logistic Regression and J48 Decision Trees Methods: A Comparative Study. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 2597–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Liu, J.; Bui, D.T.; Pradhan, B.; Acharya, T.D.; Pham, B.T.; Zhu, A.-X.; Chen, W.; Ahmad, B.B. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping Using J48 Decision Tree with AdaBoost, Bagging and Rotation Forest Ensembles in the Guangchang Area (China). CATENA 2018, 163, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, P. Research Progress of Coarse-Grained Slip Zone Soil in China. Nat. Hazards 2023, 118, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Hong, H. A Comparative Study of Heterogeneous Ensemble-Learning Techniques for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, P.; Wolpert, D. Linearly Combining Density Estimators via Stacking. Mach. Learn. 1999, 36, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, K.M.; Witten, I.H. Issues in Stacked Generalization. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1105.5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lai, J.; Ren, C.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Hu, X. GNSS-IR Multisatellite Combination for Soil Moisture Retrieval Based on Wavelet Analysis Considering Detection and Repair of Abnormal Phases. Measurement 2022, 203, 111881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Braun, J.J.; Small, E.E.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Gutmann, E.D.; Bilich, A.L. GPS Multipath and Its Relation to Near-Surface Soil Moisture Content. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Models | Optimization Methods | Hyper-Parameters | Optimal Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPNN | Grid search method | epochs | 1500 |
| goal | 1 × 10−6 | ||
| lr | 0.005 | ||
| RF | Grid search method | trees | 300 |
| leaf | 3 | ||
| Split Criterion | MSE | ||
| SVM | Grid search method | Kernel Function | RBF |
| Kernel Scale | 0.4 | ||
| Box Constraint | 1 | ||
| Layer1Size | 123 | ||
| MLP | Grid search method | Layer2Size | 124 |
| Initial Learn Rate | 1 × 10−4 | ||
| L2Regularization | 6 × 10−4 |
| Station | Model | R | RMSE cm3/cm3 | MAE cm3/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P039 | BPNN | 0.787 | 0.0588 | 0.0449 |
| RF | 0.881 | 0.0501 | 0.0421 | |
| SVM | 0.839 | 0.051 | 0.0421 | |
| MLP | 0.879 | 0.045 | 0.0384 | |
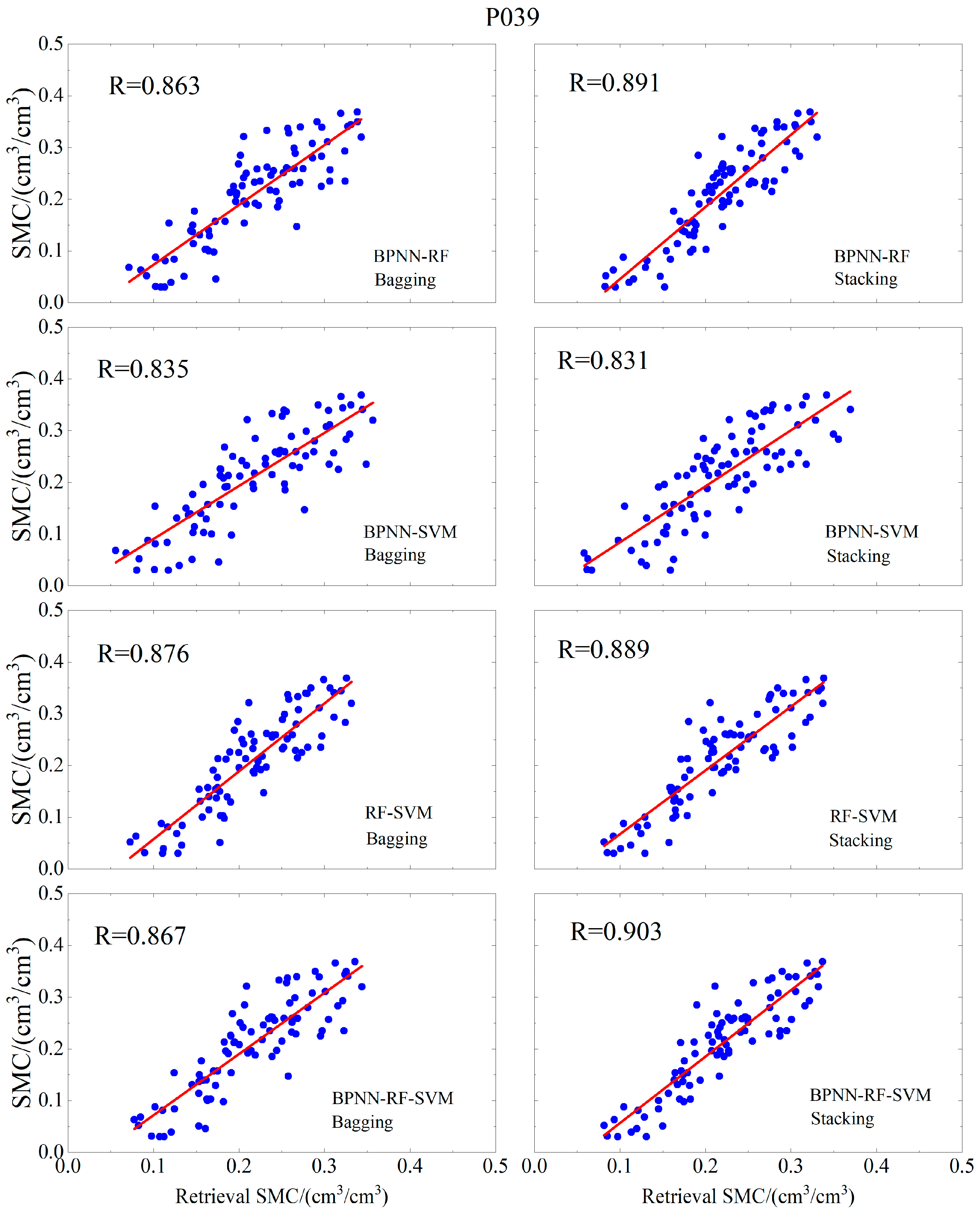
| (Bagging) BPNN-RF | 0.863 | 0.0484 | 0.0383 | |
| (Bagging) BPNN-SVM | 0.835 | 0.051 | 0.0397 | |
| (Bagging) RF-SVM | 0.876 | 0.0486 | 0.0408 | |
| (Bagging) BPNN-RF-SVM | 0.867 | 0.0479 | 0.0386 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-RF | 0.891 | 0.0484 | 0.0417 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-SVM | 0.831 | 0.0518 | 0.0439 | |
| (Stacking) RF-SVM | 0.889 | 0.0452 | 0.0378 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-RF-SVM | 0.903 | 0.0446 | 0.0371 | |
| P041 | BPNN | 0.823 | 0.0683 | 0.0547 |
| RF | 0.876 | 0.0598 | 0.0409 | |
| SVM | 0.86 | 0.061 | 0.0441 | |
| MLP | 0.88 | 0.055 | 0.041 | |
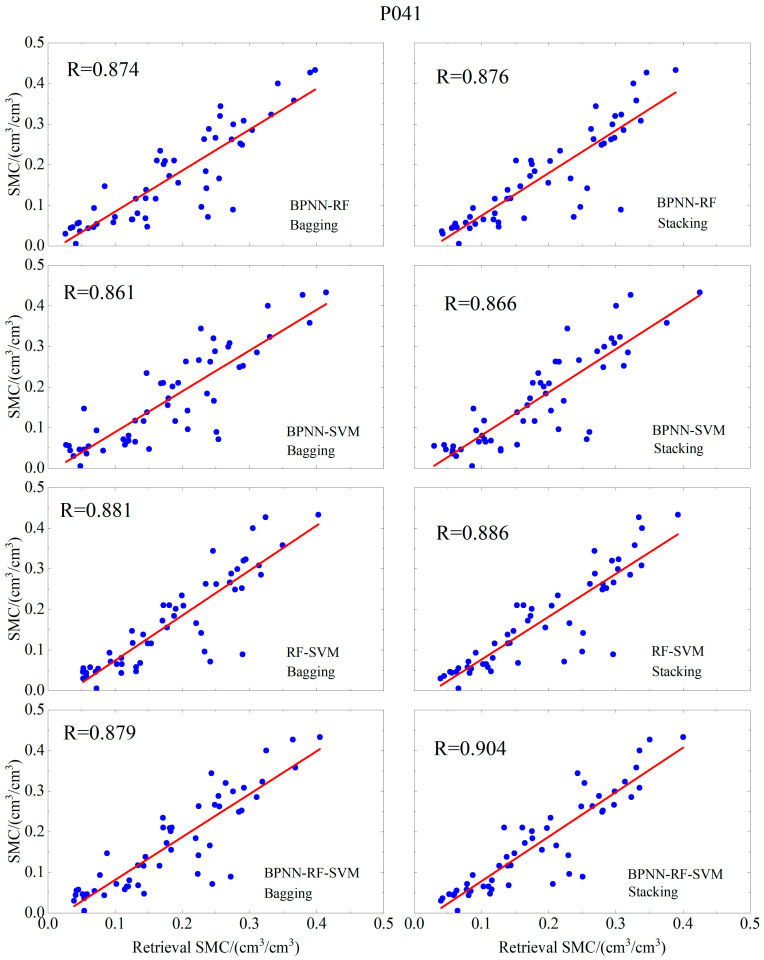
| (Bagging) BPNN-RF | 0.874 | 0.058 | 0.0435 | |
| (Bagging) BPNN-SVM | 0.861 | 0.0599 | 0.0465 | |
| (Bagging) RF-SVM | 0.881 | 0.0582 | 0.0402 | |
| (Bagging) BPNN-RF-SVM | 0.879 | 0.0572 | 0.0424 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-RF | 0.876 | 0.0598 | 0.0411 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-SVM | 0.866 | 0.0598 | 0.0436 | |
| (Stacking) RF-SVM | 0.886 | 0.0572 | 0.0395 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-RF-SVM | 0.904 | 0.0522 | 0.0379 | |
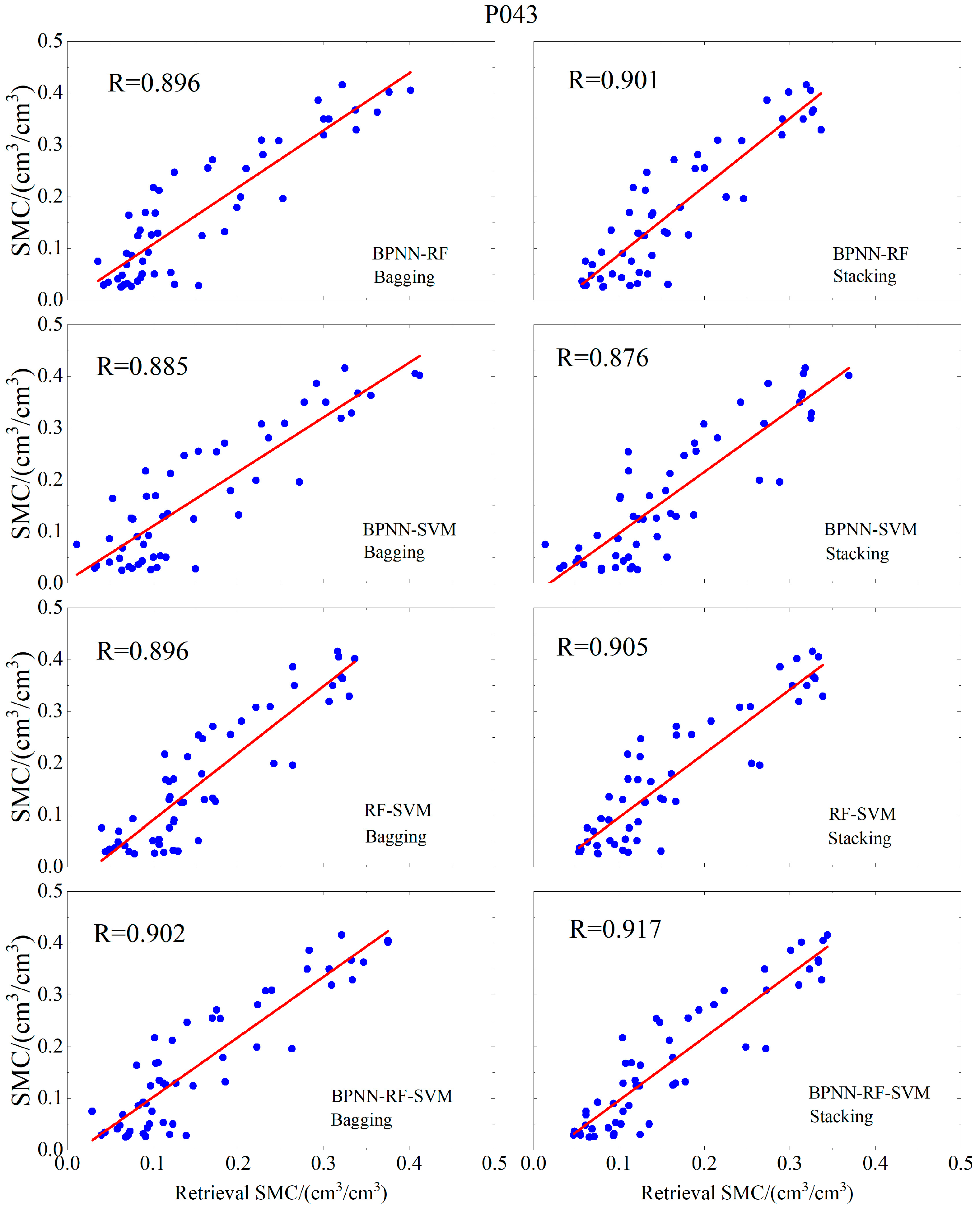
| P043 | BPNN | 0.846 | 0.0717 | 0.0577 |
| RF | 0.896 | 0.0621 | 0.0529 | |
| SVM | 0.87 | 0.0643 | 0.0534 | |
| MLP | 0.892 | 0.0576 | 0.0462 | |
| (Bagging) BPNN-RF | 0.896 | 0.0577 | 0.0469 | |
| (Bagging) BPNN-SVM | 0.885 | 0.0596 | 0.0481 | |
| (Bagging) RF-SVM | 0.896 | 0.0613 | 0.0526 | |
| (Bagging) BPNN-RF-SVM | 0.902 | 0.0572 | 0.0467 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-RF | 0.901 | 0.0608 | 0.0509 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-SVM | 0.876 | 0.063 | 0.0524 | |
| (Stacking) RF-SVM | 0.905 | 0.0577 | 0.0483 | |
| (Stacking) BPNN-RF-SVM | 0.917 | 0.0545 | 0.0457 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, K.; Lv, J.; Chen, J.; Song, Y. Comparative Performance Analysis of Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Models for Multi-Satellite Fusion GNSS-IR Soil Moisture Retrieval. Land 2025, 14, 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091716
Jiang Y, Zhang R, Jiang H, Zhang B, Chen K, Lv J, Chen J, Song Y. Comparative Performance Analysis of Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Models for Multi-Satellite Fusion GNSS-IR Soil Moisture Retrieval. Land. 2025; 14(9):1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091716
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yao, Rui Zhang, Hang Jiang, Bo Zhang, Kangyi Chen, Jichao Lv, Jie Chen, and Yunfan Song. 2025. "Comparative Performance Analysis of Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Models for Multi-Satellite Fusion GNSS-IR Soil Moisture Retrieval" Land 14, no. 9: 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091716
APA StyleJiang, Y., Zhang, R., Jiang, H., Zhang, B., Chen, K., Lv, J., Chen, J., & Song, Y. (2025). Comparative Performance Analysis of Heterogeneous Ensemble Learning Models for Multi-Satellite Fusion GNSS-IR Soil Moisture Retrieval. Land, 14(9), 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14091716






