Effect of Visual Quality of Street Space on Tourists’ Stay Willingness in Traditional Villages—Empirical Evidence from Huangcun Village Based on Street View Images and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Evaluation of the Visual Quality of Street Space (vQoSS)
2.2. The Relationship Between the vQoSS and Walking Behavior
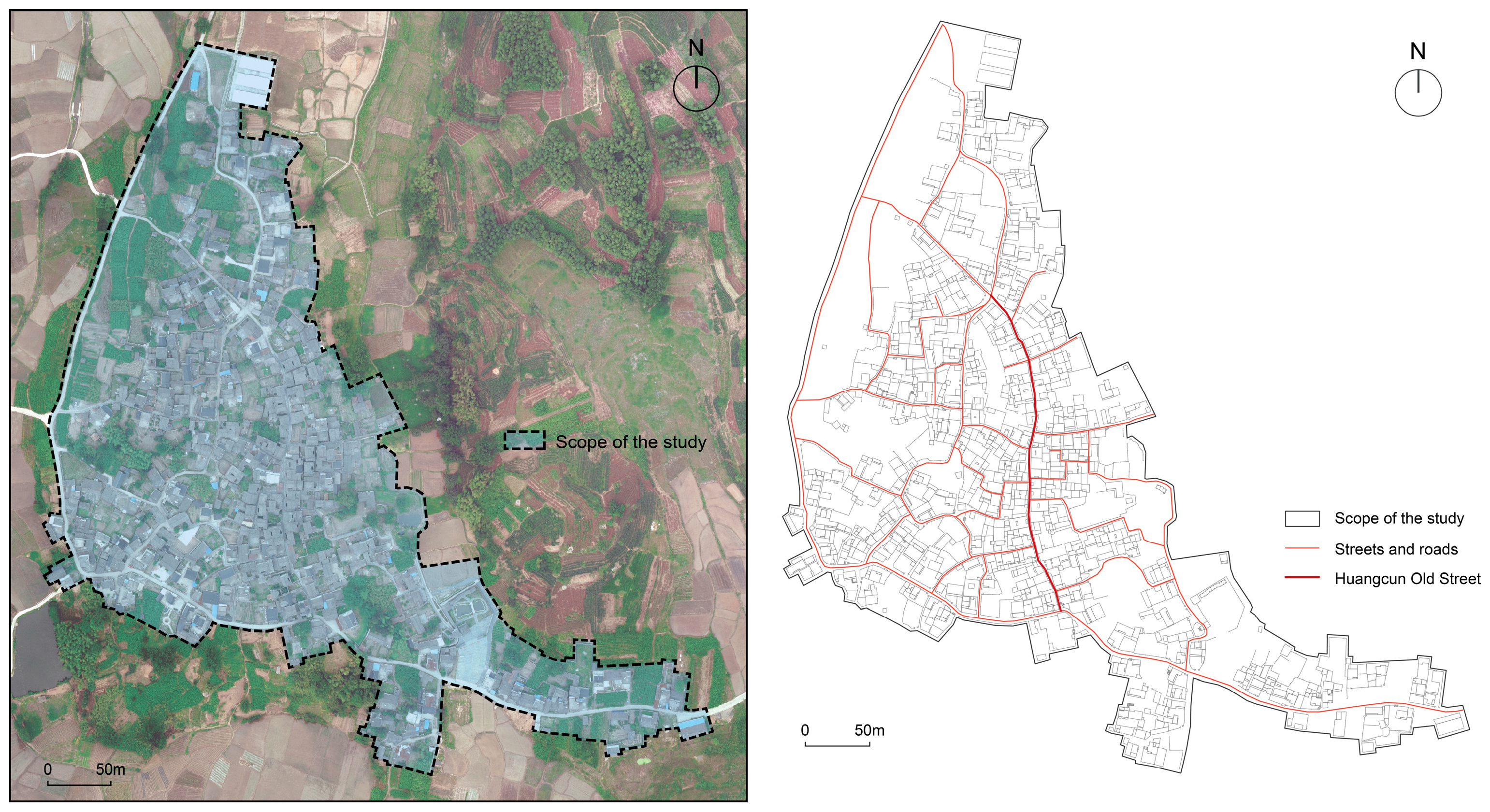
3. Study Area and Data Sources
3.1. Study Area
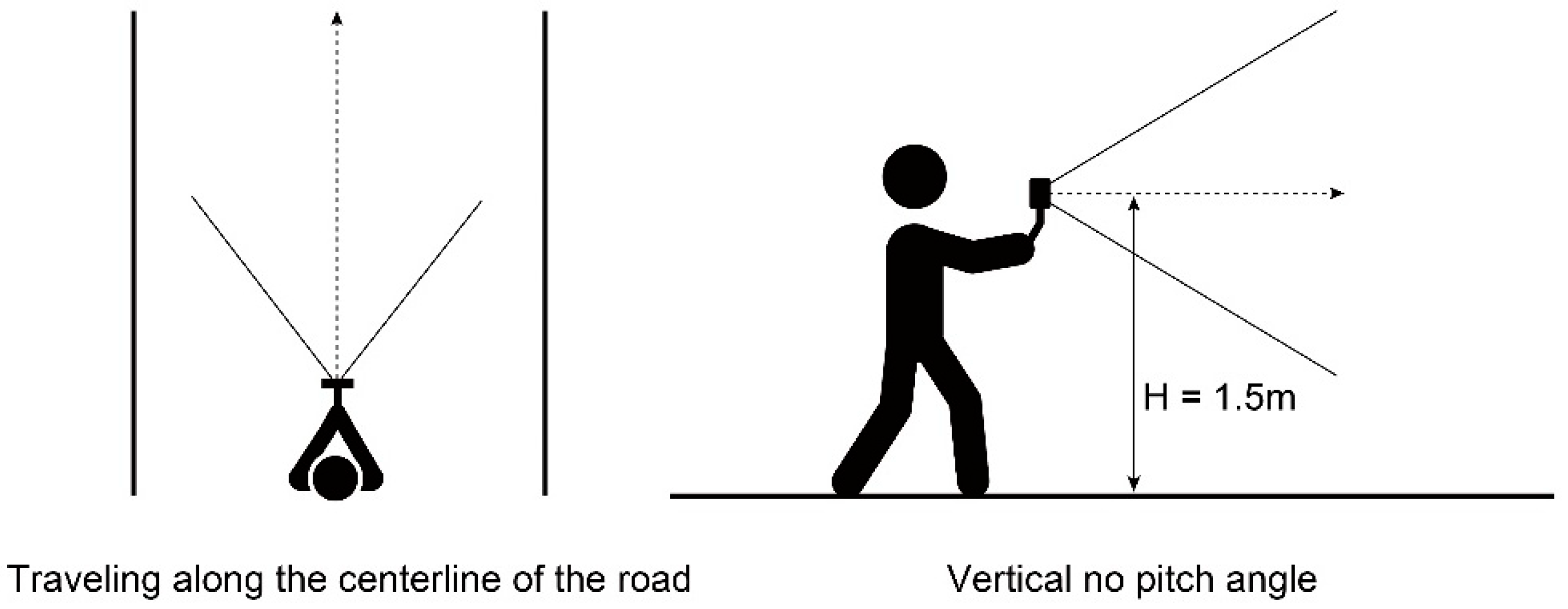
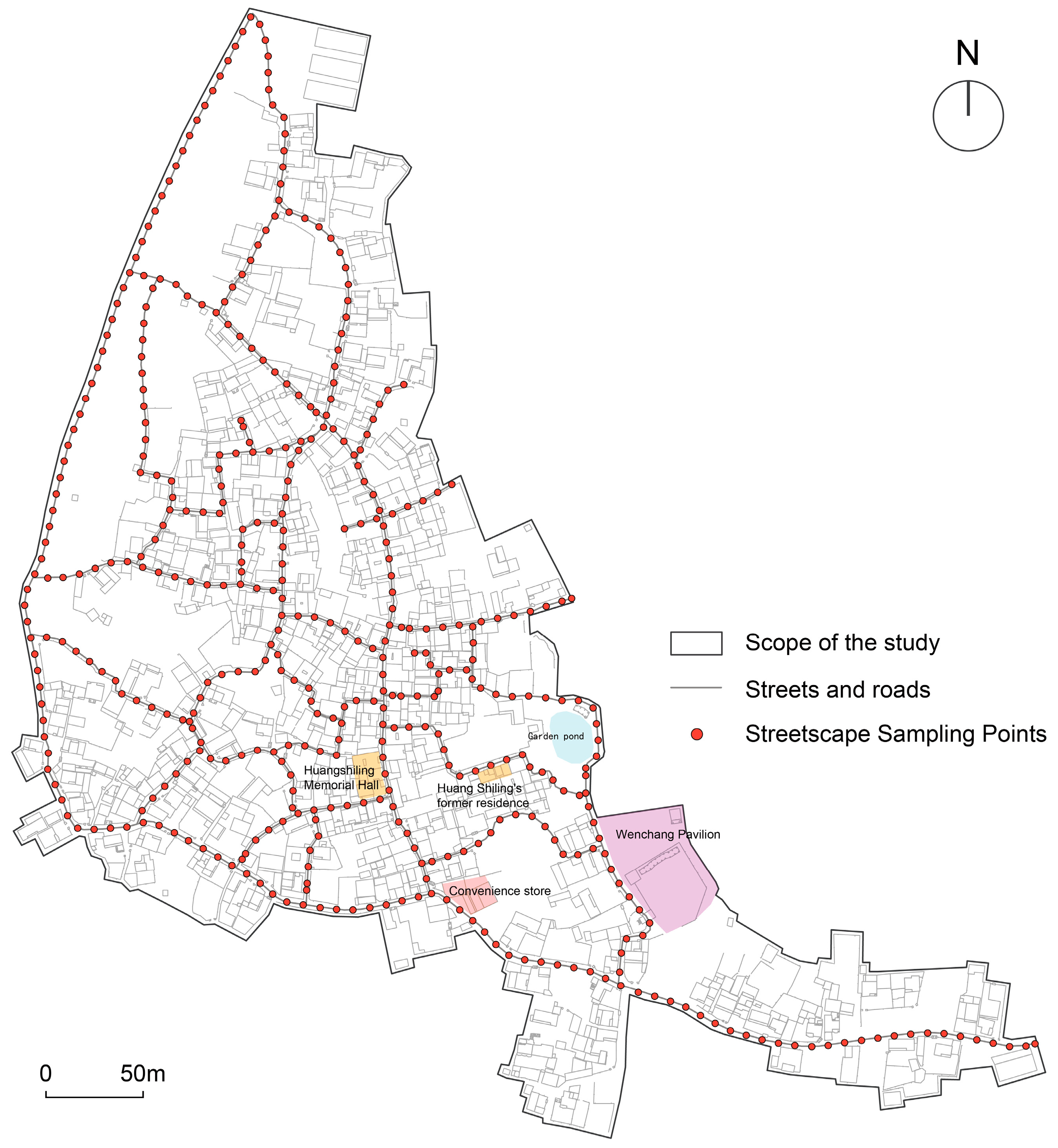
3.2. Street View Image Data Collection and Screening
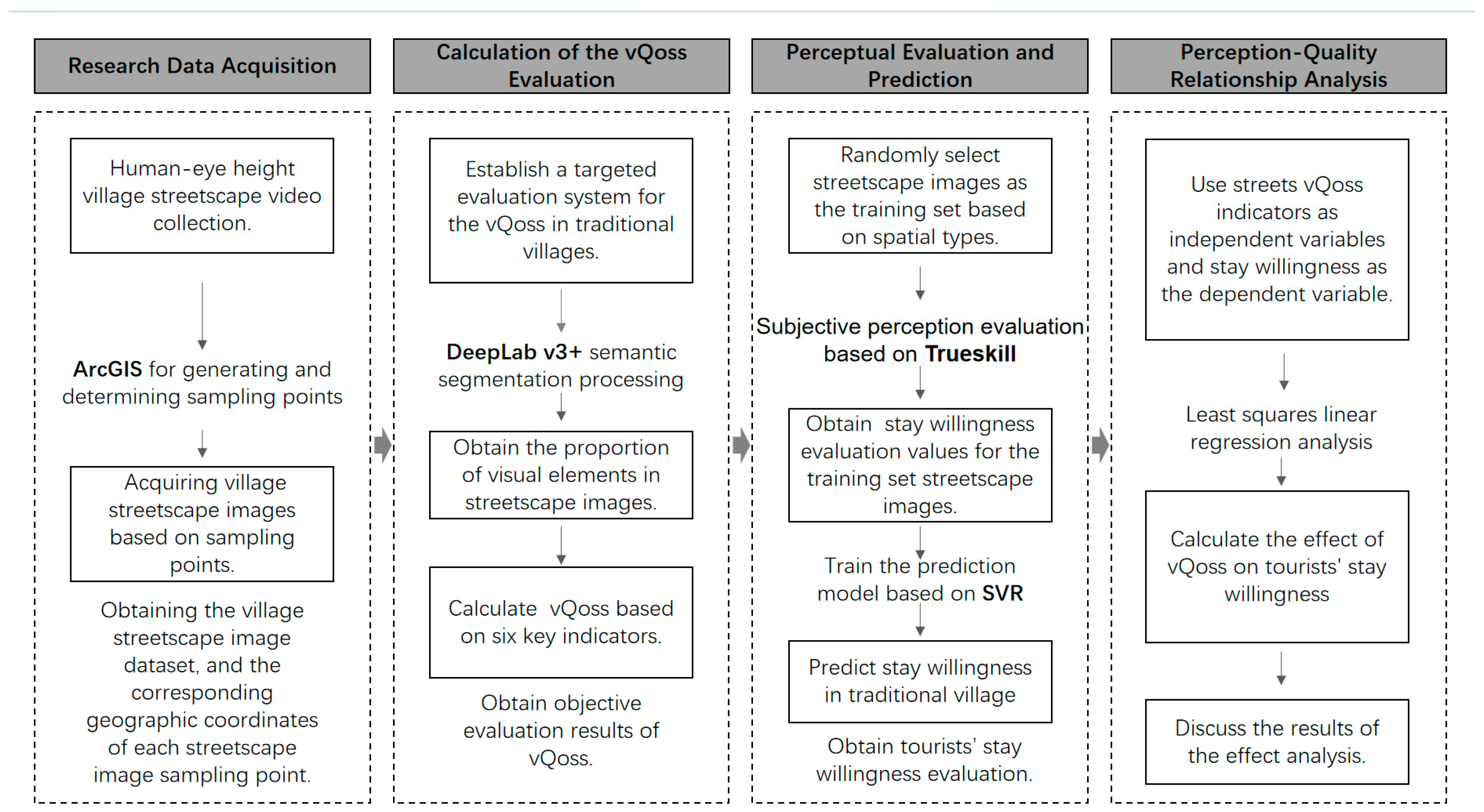
4. Research Methods
4.1. Research Framework
4.2. Construction of Objective Evaluation Index System
4.3. Tourists’ Subjective Stay Willingness Evaluation Based on Trueskill Algorithm
5. Empirical Study
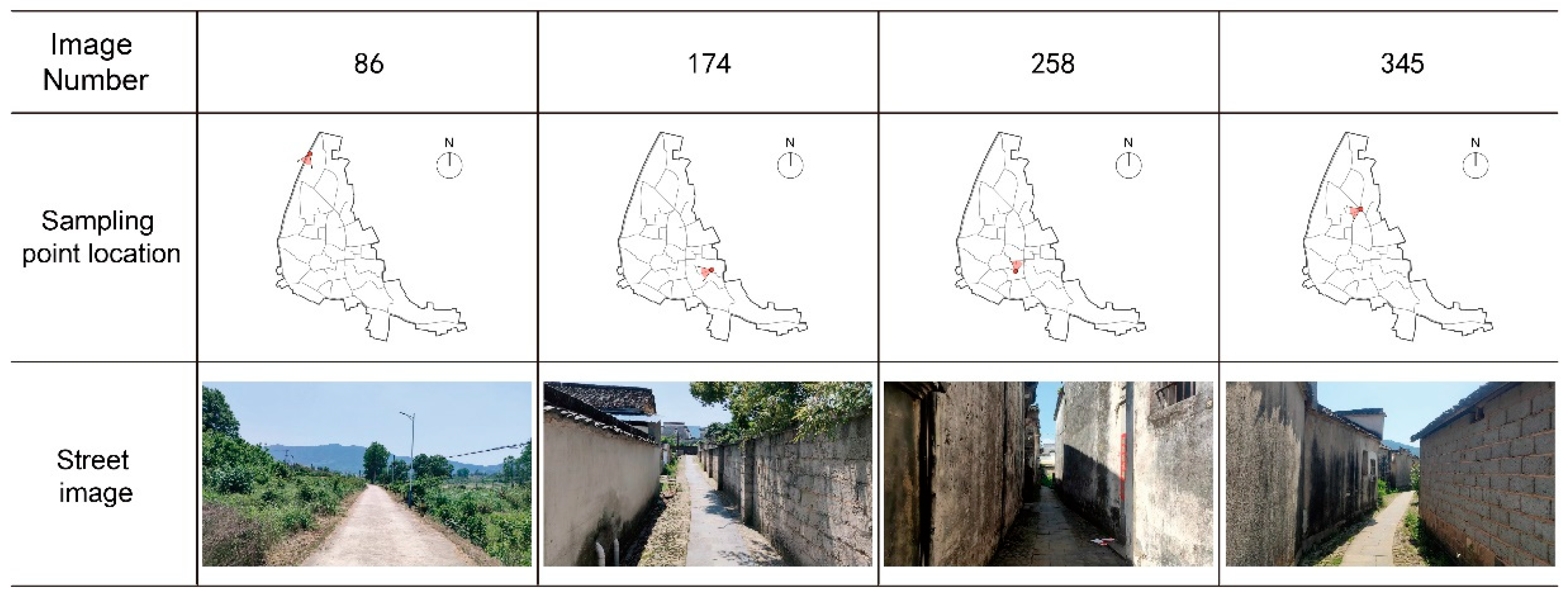
5.1. Acquisition of Spatial Descriptive Indicators
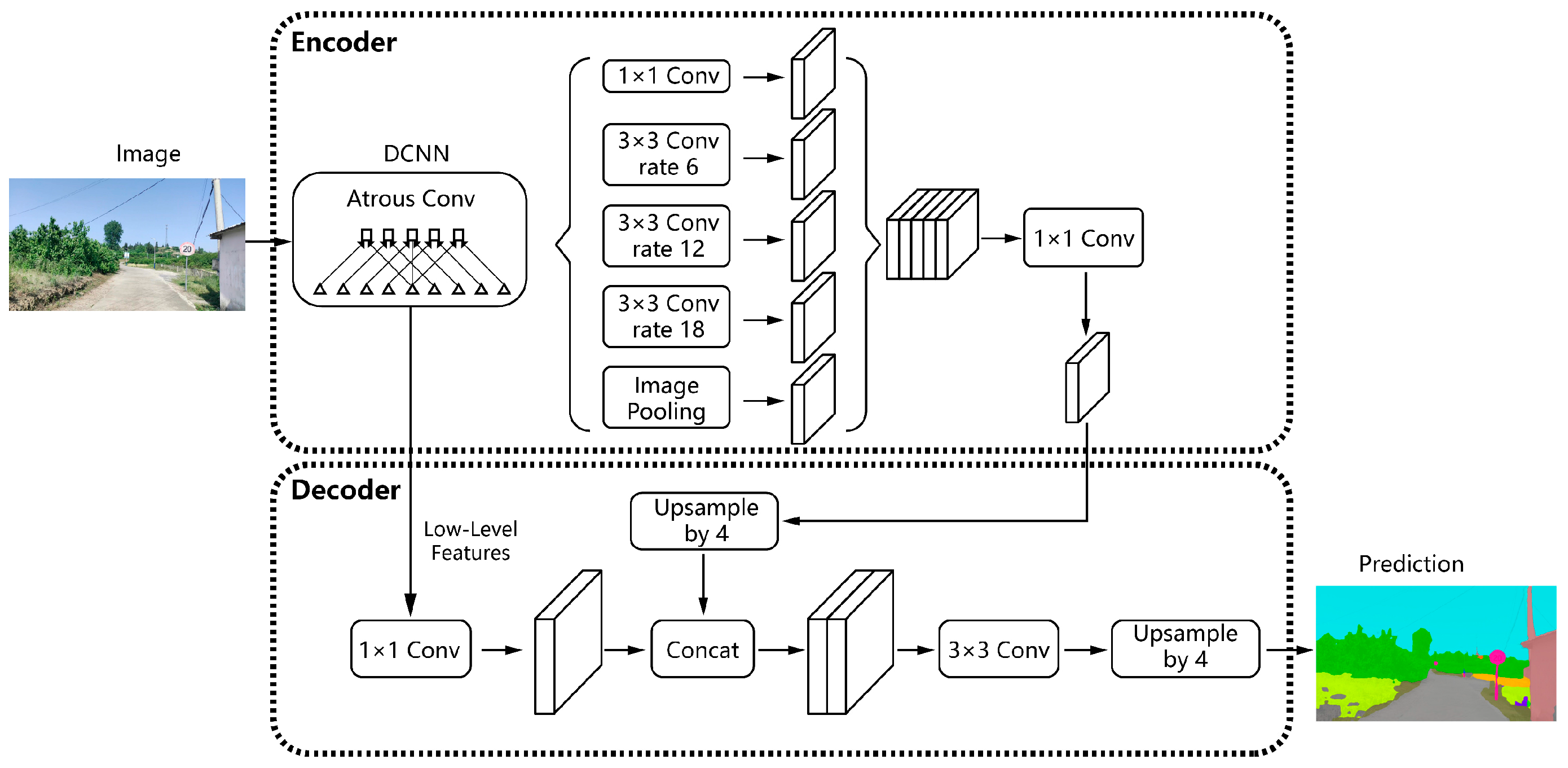
5.1.1. Segmentation and Extraction of Image Features
5.1.2. Calculation of Visual Quality Evaluation Indicators
5.2. Subjective Evaluation and Prediction of Tourists’ Stay Willingness
5.2.1. Subjective Perception Evaluation of Images Based on the Trueskill Algorithm
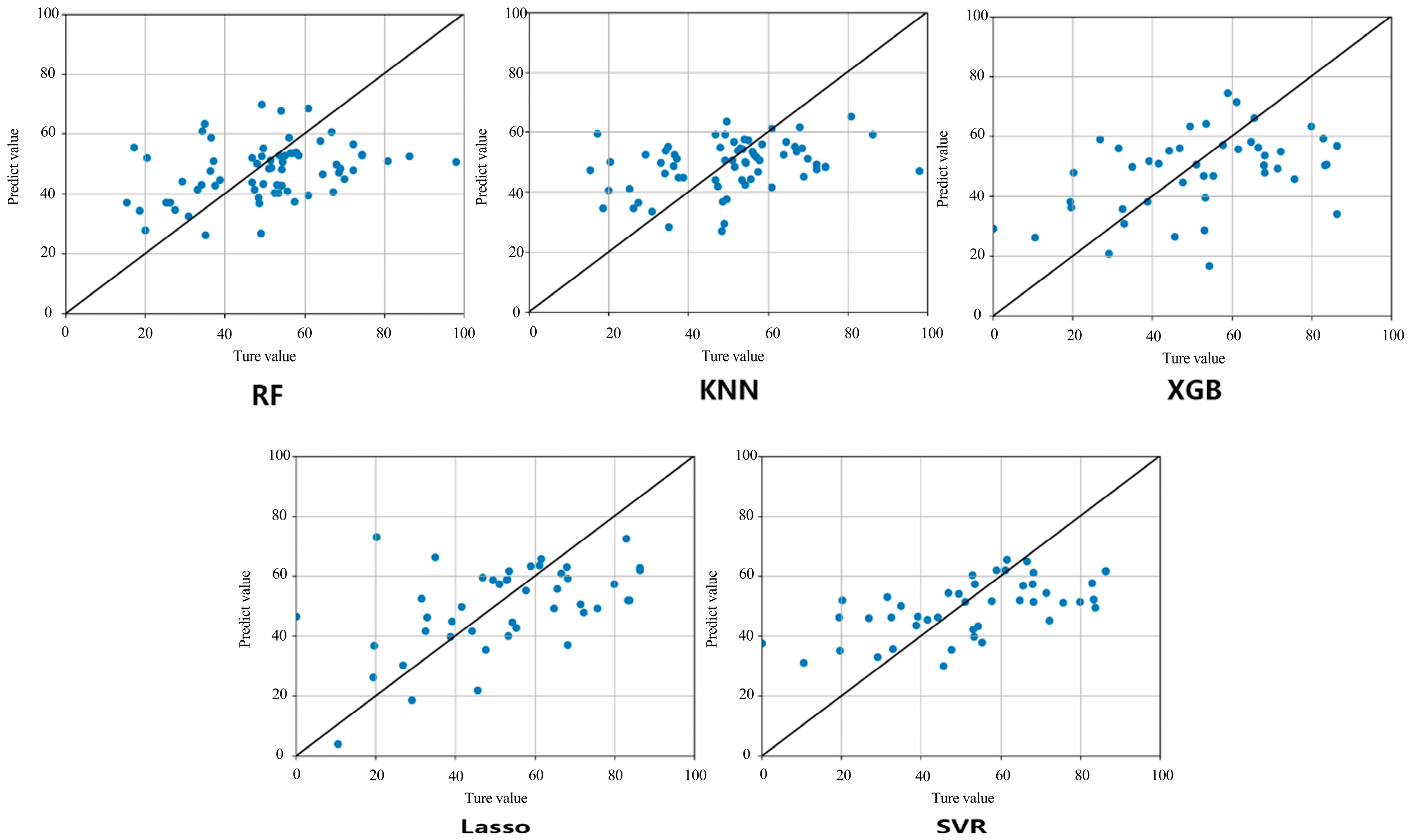
5.2.2. Prediction of Tourists’ Stay Willingness Evaluation
6. Experimental Results and Analysis
6.1. Analysis of Visual Quality of Street Space
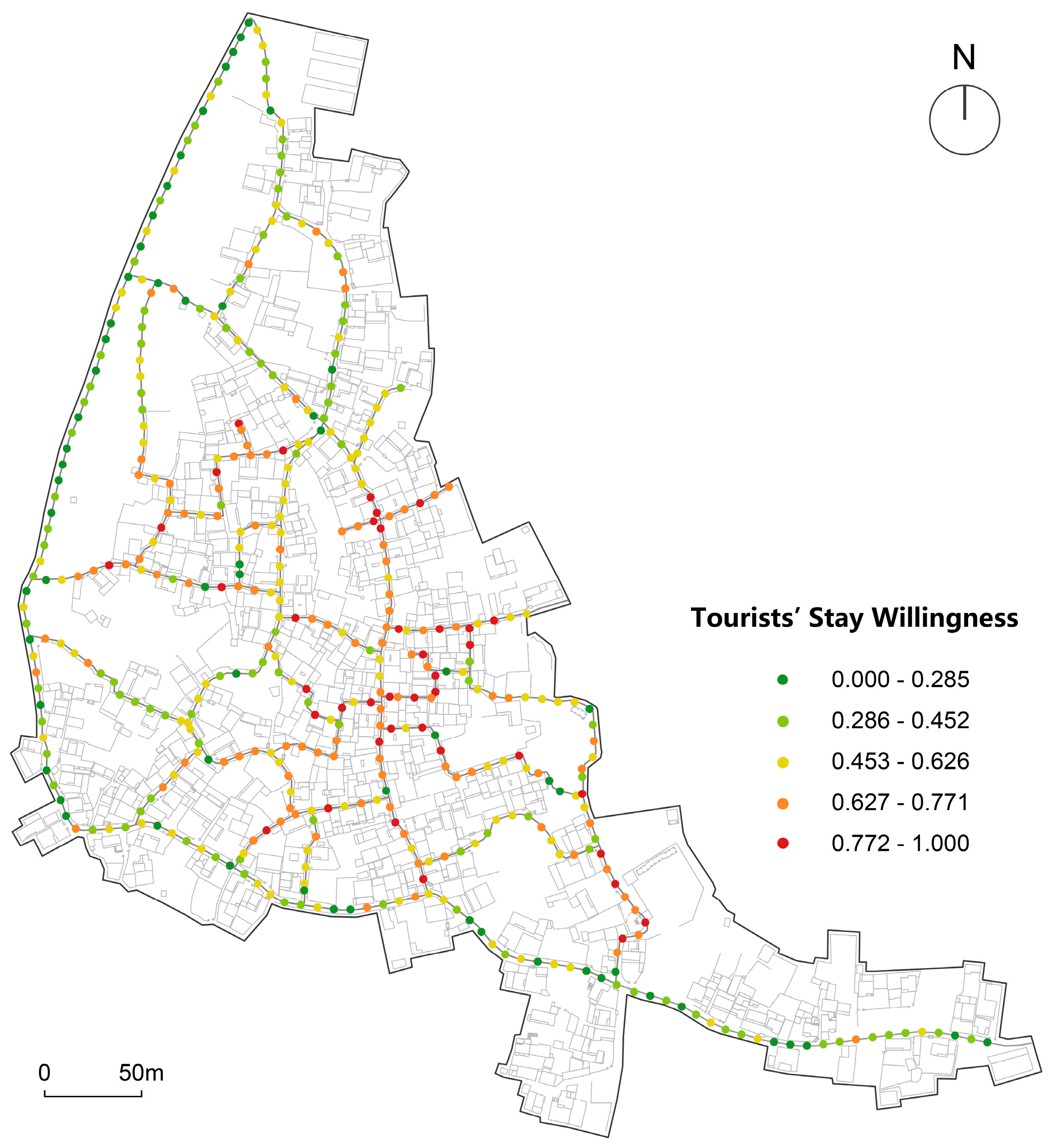
6.2. Analysis of Tourists’ Subjective Stay Willingness in Streets
6.3. Discussion on Influence Mechanisms
6.4. Limitations of the Study
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, J.; Long, Y. Measuring visual quality of street space and its temporal variation: Methodology and its application in the Hutong area in Beijing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 191, 103436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.; Aultman-Hall, L.; Hurley, S.E.; Troy, A. Effects of skeletal streetscape design on perceived safety. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 142, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qiu, W.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Luo, D. Associations between Street-View Perceptions and Housing Prices:Subjective vs. Objective Measures Using Computer Vision and Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Assessment of street space quality and subjective well-being mismatch and its impact, using multi-source big data. Cities 2024, 147, 104797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Bai, M.; Bai, Y. Evaluation of Street Space Renovation in Historic Areas Using Deep Learning Based on Street View Imagery in the Human Visual Field. China City Plan. Review. 2024, 33, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Natural Resource Defense Council. Evaluation of Walkability in Chinese Cities (Periodic Reports). 2014. Available online: http://www.nrdc.cn/Public/uploads/2016-12-02/58416c0a65c05.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Natural Resource Defense Council. Evaluation of Walkability in Chinese Cities:Research on Promoting Walking Based on Street Functions. 2017. Available online: http://www.nrdc.cn/Public/uploads/2017-12-15/5a336e65f0aba.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Natural Resource Defense Council. Evaluation of Walkability in Chinese Cities:Research on the Walkability of Urban Vitality Centers. 2019. Available online: http://www.nrdc.cn/Public/uploads/2019-10-23/5db00acc2661c.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Natural Resource Defense Council. Evaluation of Walkability in Chinese Cities: A Study on the Improvement Status of Sidewalk Facilities. 2021. Available online: http://www.nrdc.cn/Public/uploads/2021-09-22/614aae8cc54f7.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Easteal, M.; Bannister, S.; Kang, J.; Aletta, F.; Lavia, L.R.; Witchel, H.J. Urban sound planning in Brighton and Hove. In Proceedings of the Forum Acusticum, Krakow, Poland, 7–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Aletta, F.; Lepore, F.; Kostara-Konstantinou, E.; Kang, J.; Astolfi, A. An Experimental Study on the Influence of Soundscapes on People’s Behaviour in an Open Public Space. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, L.M.; Schifanella, R.; Quercia, D.; Aletta, F. Chatty maps: Constructing sound maps of urban areas from social media data. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 150690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, B.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Fung, H.H.; Lin, H.; Ratti, C. Measuring human perceptions of a large-scale urban region using machine learning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 180, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, Y.; Qian, C.; Guan, Q.; Liang, X.; Dai, L.; Zhang, J. Discovering the homogeneous geographic domain of human perceptions from street view images. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 212, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ma, C.; Wu, C.; Xi, Y.; Yang, R.; Peng, N.; Zhang, C.; Ren, F. Measuring human perceptions of streetscapes to better inform urban renewal: A perspective of scene semantic parsing. Cities 2021, 110, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yue, W.; Li, M.; Gao, J. Mapping human perception of urban landscape from street-view images: A deep-learning approach. Int. J. Appiled Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Q.; Cheng, H. Quantifying the spatial quality of urban streets with open street view images: A case study of the main urban area of Fuzhou. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, J. Measuring streetscape perceptions from driveways and sidewalks to inform pedestrian-oriented street renewal in Düsseldorf. Cities 2023, 141, 104472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K. Research on the Factors Influencing the Spatial Quality of High-Density Urban Streets: A Framework Using Deep Learning, Street Scene Images, and Principal Component Analysis. Land 2024, 13, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, H.; Sun, H. Spatial Patterns and Multi-Dimensional Impact Analysis of Urban Street Quality Perception under Multi-Source Data: A Case Study of Wuchang District in Wuhan, China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Liu, A. Evaluation and Optimization of Urban Street Spatial Quality Based on Street View Images and Machine Learning: A Case Study of the Jinan Old City. Buildings 2025, 15, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Duolihong, W. Diagnosis and Planning Strategies for Quality of Urban Street Space Based on Street View Images. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pang, C. A Spatial Visual Quality Evaluation Method for an Urban Commercial Pedestrian Street Based on Streetscape Images—Taking Tianjin Binjiang Road as an Example. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liao, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, X.; Shang, A.; Huang, Z. Evaluating the Spatial Quality of Urban Living Streets: A Case Study of Hengyang City in Central South China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, J. Automatic Estimation for Visual Quality Changes of Street Space via Street-View Images and Multimodal Large Language Models. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 87713–87727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Zhang, C.; Li, W. Does the Visibility of Greenery Increase Perceived Safety in Urban Areas? Evidence from the Place Pulse 1.0 Dataset. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 1166–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, A. Analyzing green view index and green view index best path using Google street view and deep learning. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2022, 9, 2010–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, C.; Ye, Y. Measuring Street Quality: A Human-Centered Exploration Based on Multi-Sourced Data and Classical Urban Design Theories. Buildings 2024, 14, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Xu, Y.; Sun, L.; Liao, P.; Wang, J. Application of Machine Learning and Multi-Dimensional Perception in Urban Spatial Quality Evaluation: A Case Study of Shanghai Underground Pedestrian Street. Land 2024, 13, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, C.; Webster, C.; Pryor, M.; Tang, D.; Melbourne, S.; Zhang, X.; Jianzheng, L. Exploring associations between urban green, street design and walking: Results from the Greater London boroughs. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 143, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sarkar, C.; Xiao, Y. The effect of street-level greenery on walking behavior: Evidence from Hong Kong. Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 208, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, D.; Gou, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. Association between Street Greenery and Walking Behavior in Older Adults in Hong Kong. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 51, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, N. Study on the Evaluation of Security Perception in Tourist Street Space and its Influencing Factors Based on Machine Learning: Taking Gulangyu Island in Xiamen as an Example. China Anc. City 2025, 39, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; He, S.Y. Decoding the spatial effects of walkability on walking behavior among older adults by integrating big data and small data. Cities 2025, 156, 105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, S.; Moazzeni, S. Moazzeni. Examining the Relationship between Urban Design Qualities and Walking Behavior: Empirical Evidence from Dallas, TX. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, Z. Measuring visual enclosure for street walkability: Using machine learning algorithms and Google Street View imagery. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 76, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.W.; Guhathakurta, S.; Botchwey, N. How are Neighborhood and Street-Level Walkability Factors Associated with Walking Behaviors? A Big Data Approach Using Street View Images. Environ. Behav. 2022, 54, 211–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Kang, Q. The Relationship between Pedestrian Behaviors and the Spatial Features along the Ground-floor Commercial Street: The case of West Nanjing Road in Shanghai. Urban Plan. Forum 2014, 3, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann-Lunecke, M.G.; Mora, R.; Vejares, P. Perception of the built environment and walking in pericentral neighbourhoods in Santiago, Chile. Travel Behav. Soc. 2021, 23, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrate, A.-L. Street Vitality: What Predicts Pedestrian Flows and Stationary Activities on Predominantly Residential Chinese Streets, at the Mesoscale? J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2025, 45, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conservation and Utilization Plan for the Historic Village of Huang, Yi County; People’s Government of Biyang Town: Huangshan, China, 2011.
- Ye, Y.; Zeng, W.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. The visual quality of streets: A human-centred continuous measurement based on machine learning algorithms and street view images. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2019, 46, 1439–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbrich, R.; Minka, T.; Graepel, Y. Trueskill: A bayesian skill rating system. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Spatial Structure Characteristics of Huizhou Ancient Villages from the Perspective of Crime Prevention. Urban Plan. 2020, 44, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Lin, S.; Jiao, H.; Wang, L. A Study on the Landscape Characteristics and Mechanism of Ancient Villages in Huizhou. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2004, 24, 660–665. [Google Scholar]
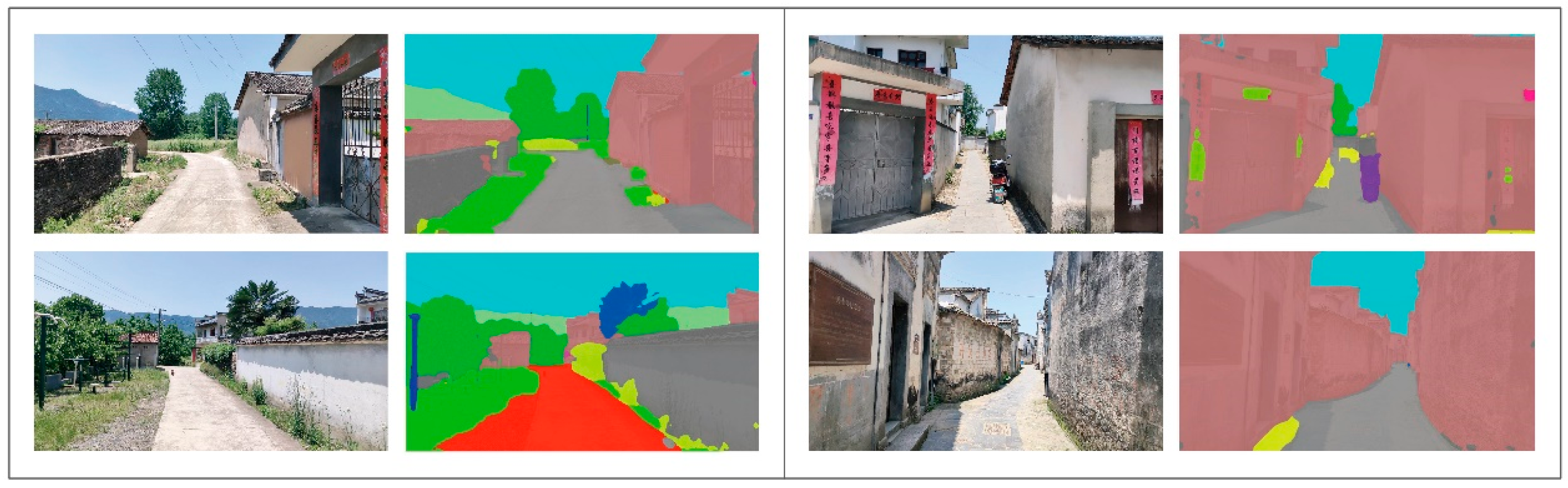

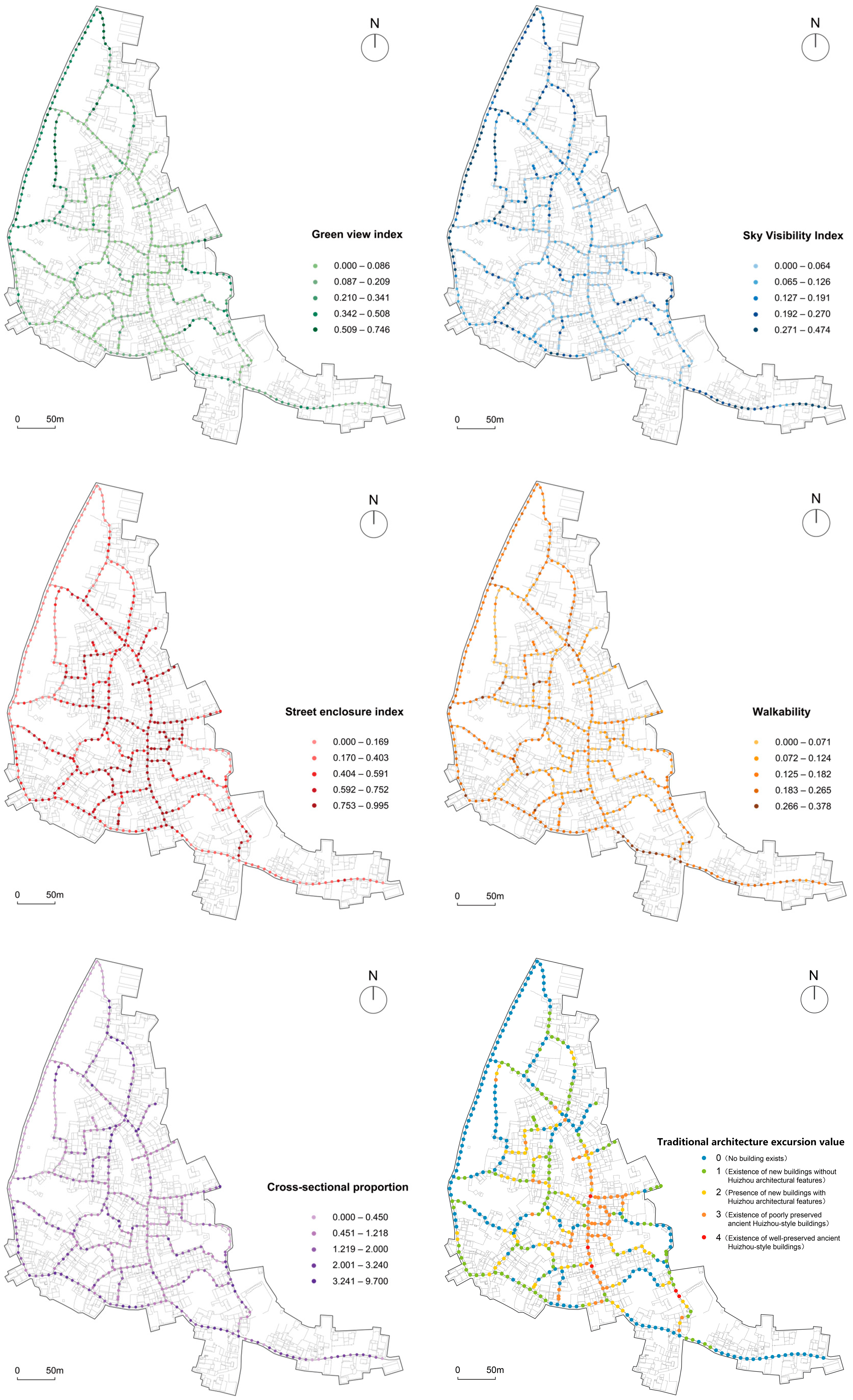
| Evaluation Indicators | Visual Elements | Calculation Formula | Formula Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green view index Gi | greenery, crops | (1) | |
| Street enclosure index Ei | buildings, fences, roads, greenery | (2) | |
| Sky Visibility Index Oi | sky | (3) | |
| Walkability Wi | road | (4) | |
| Cross-sectional proportion Ri | buildings, fences, roads | (5) | |
| Traditional architecture excursion value | buildings | 0 points–There are no buildings in the field of view. 1 point–New buildings with no Hui architectural features in the field of view. 2 points–There are new buildings with Hui architectural characteristics within the field of view. 3 points–There are poorly preserved ancient buildings of the Hui school within the field of view. 4 points–There are well-preserved ancient buildings of the Hui school within the field of view. |
| Image Number | Green Rating | Openness of the Sky | Enclosure | Walkability | DH Ratio | Traditional Architectural Excursion Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1494 | 0.0718 | 0.3769 | 0.3777 | 3.75 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.249 | 0.0668 | 0.3352 | 0.3041 | 1.9 | 0 |
| 3 | 0.4167 | 0.0597 | 0.2241 | 0.2624 | 2.55 | 0 |
| 4 | 0.4313 | 0.0556 | 0.2038 | 0.2649 | 4.4 | 0 |
| 5 | 0.3162 | 0.011 | 0.3346 | 0.3157 | 4.4 | 0 |
| 6 | 0.2935 | 0.0262 | 0.2634 | 0.3037 | 2.75 | 0 |
| 7 | 0.36 | 0.0621 | 0.2615 | 0.2911 | 2.1667 | 0 |
| 8 | 0.4442 | 0.0815 | 0.0962 | 0.3669 | 2 | 0 |
| 9 | 0.3084 | 0.1125 | 0.1685 | 0.3525 | 2.9 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.2574 | 0.1951 | 0.3162 | 0.2216 | 1 | 0 |
| Model | Lasso | XGB | KNN | RF | SVR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | ||||||
| R2 | 0.203 | 0.109 | 0.092 | 0.042 | 0.314 | |
| Beta | Adjusted R2 | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green view index | −0.402 | 0.158 | −6.354 | 0.000 *** |
| Street enclosure index | −0.662 | 0.435 | −8.495 | 0.000 *** |
| Sky Visibility Index | 0.69 | 0.474 | 10.778 | 0.000 *** |
| Walkability | −0.59 | 0.345 | −7.025 | 0.000 *** |
| Cross-sectional proportion | −0.34 | 0.112 | −5.235 | 0.000 *** |
| Traditional architecture excursion value | 0.413 | 0.167 | 6.563 | 0.000 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, L.; Jiang, X.; Guo, Y.; Qin, Q. Effect of Visual Quality of Street Space on Tourists’ Stay Willingness in Traditional Villages—Empirical Evidence from Huangcun Village Based on Street View Images and Machine Learning. Land 2025, 14, 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081631
Tu L, Jiang X, Guo Y, Qin Q. Effect of Visual Quality of Street Space on Tourists’ Stay Willingness in Traditional Villages—Empirical Evidence from Huangcun Village Based on Street View Images and Machine Learning. Land. 2025; 14(8):1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081631
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Li, Xiao Jiang, Yixing Guo, and Qi Qin. 2025. "Effect of Visual Quality of Street Space on Tourists’ Stay Willingness in Traditional Villages—Empirical Evidence from Huangcun Village Based on Street View Images and Machine Learning" Land 14, no. 8: 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081631
APA StyleTu, L., Jiang, X., Guo, Y., & Qin, Q. (2025). Effect of Visual Quality of Street Space on Tourists’ Stay Willingness in Traditional Villages—Empirical Evidence from Huangcun Village Based on Street View Images and Machine Learning. Land, 14(8), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081631






