Effect of Rotational Grazing on Soil Quality and Animal Behavior in an Integrated Crop–Livestock (ICL) System on Small Subtropical Farms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
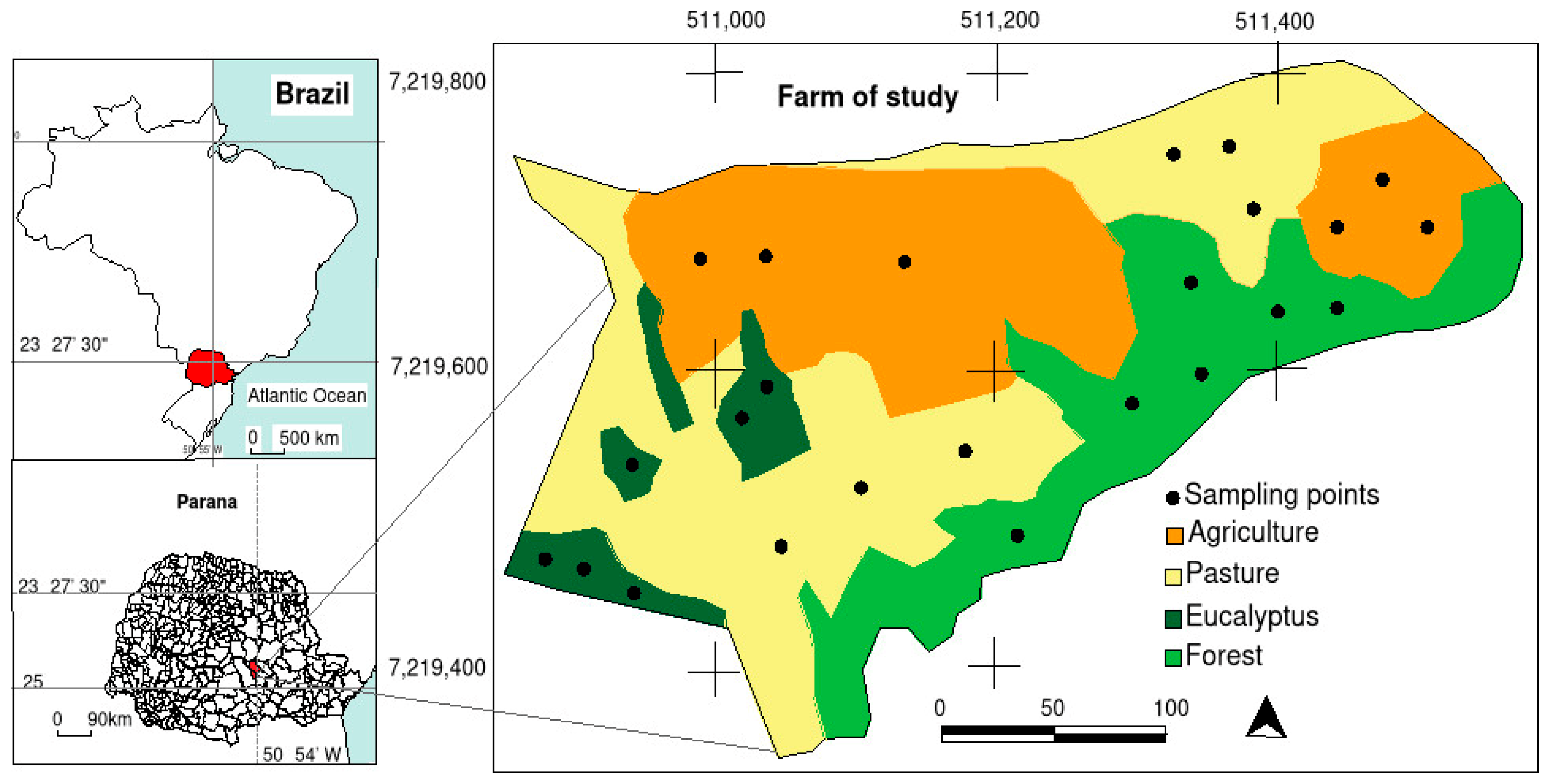
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Animal Daily Behavior
2.4. Forage Availability
2.5. Soil Bulk Density
2.6. Water Infiltration and Antecedent Moisture
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
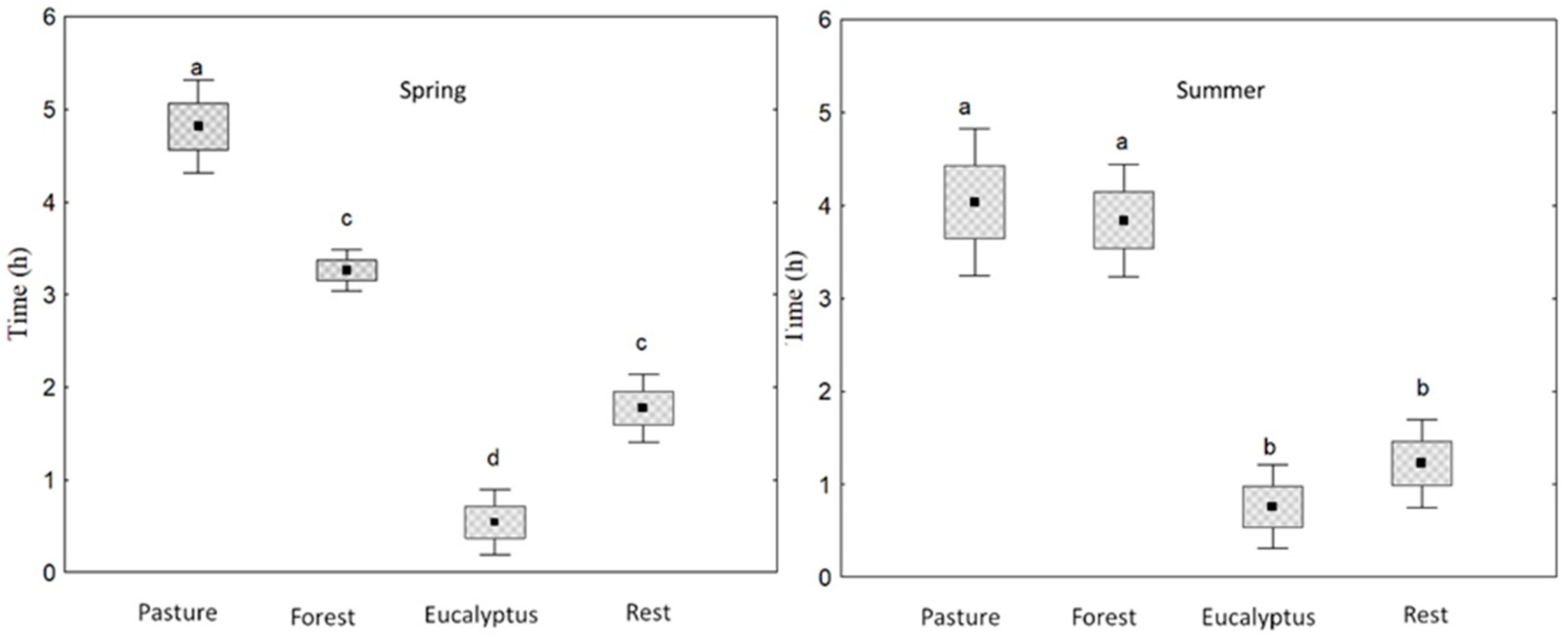
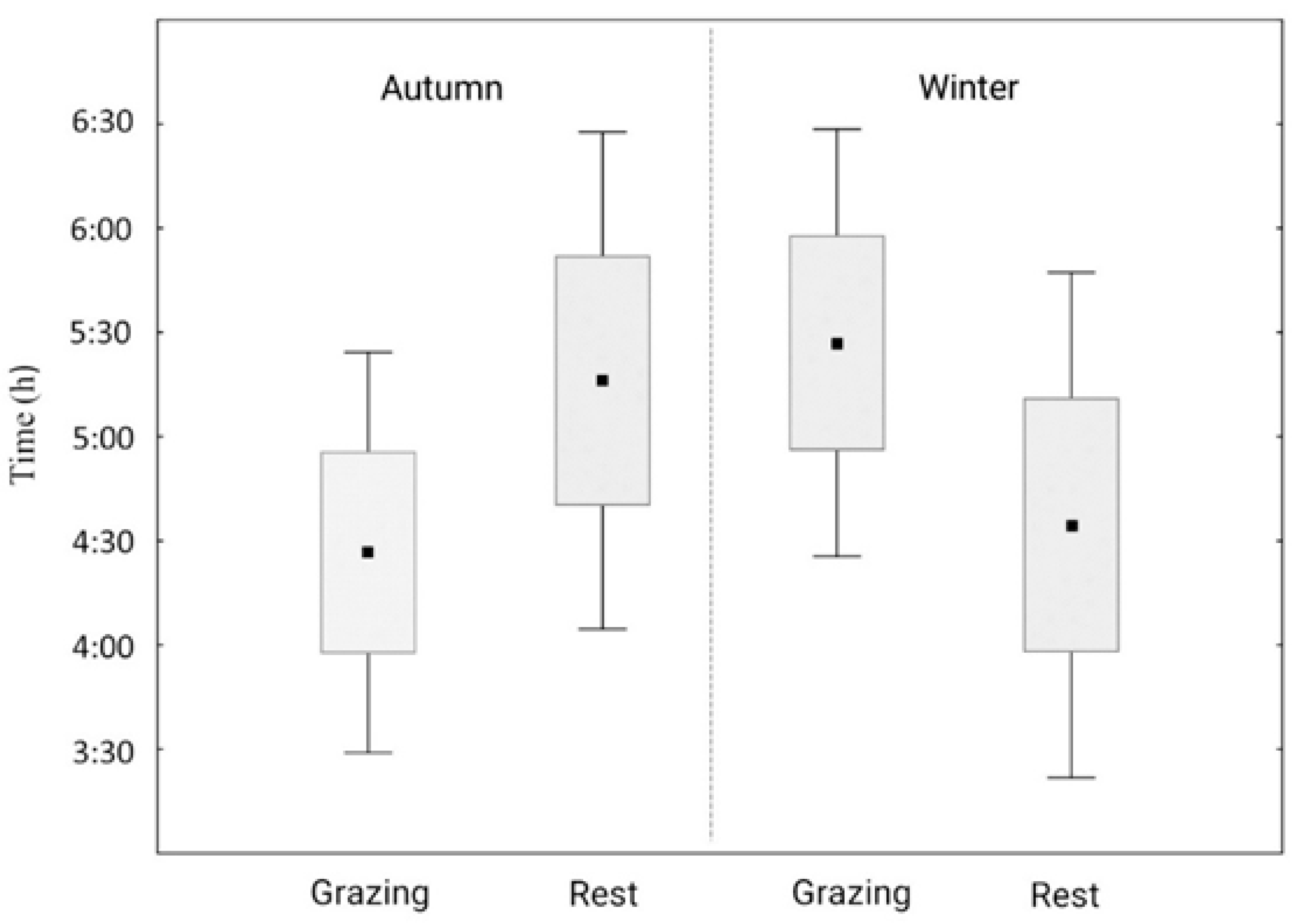
3.1. Animal Grazing Dynamics
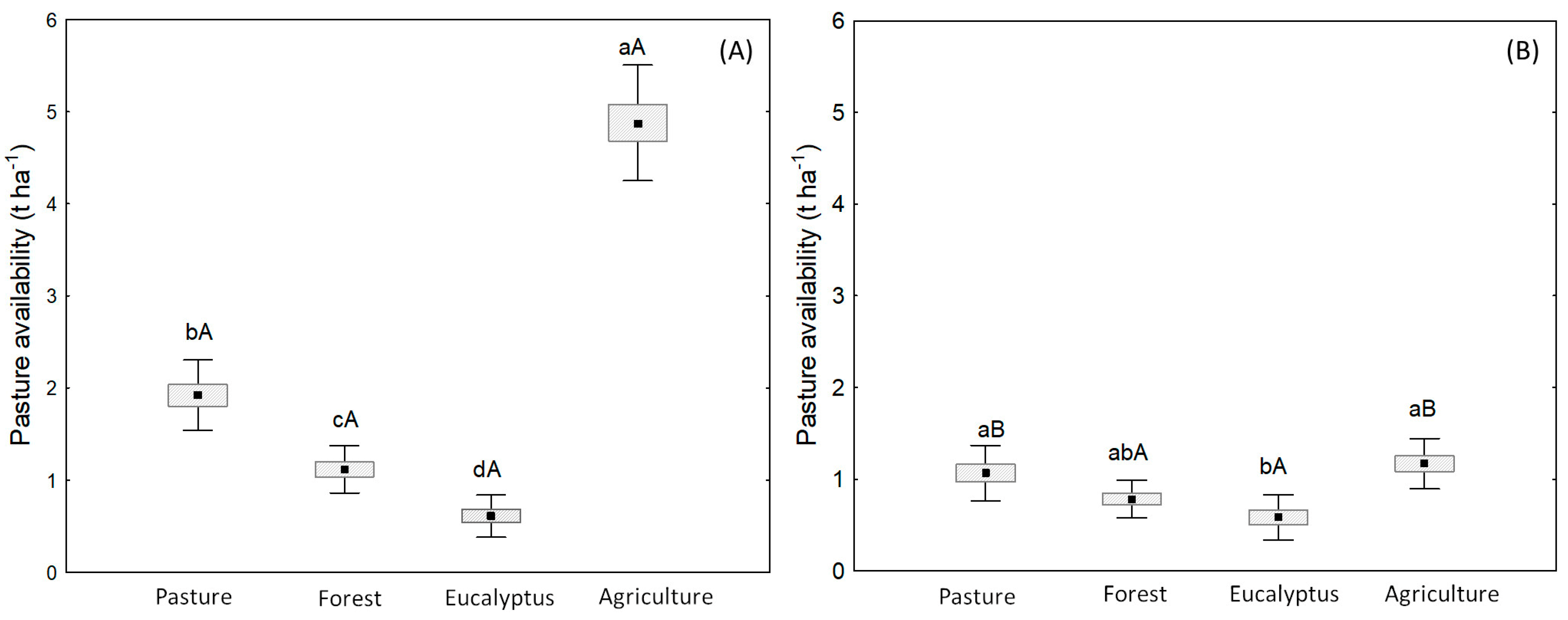
3.2. Forage Availability
3.3. Soil Bulk Density
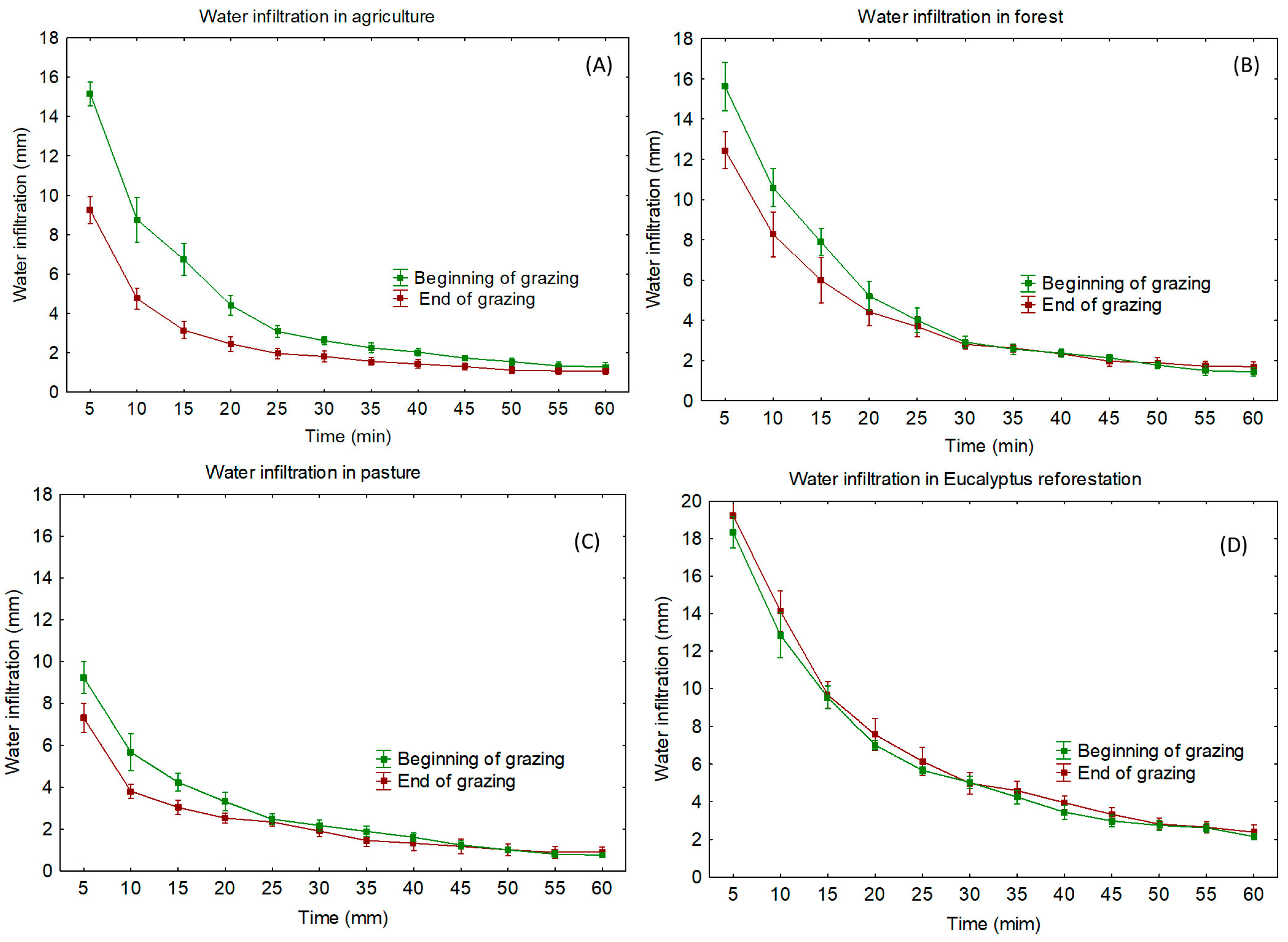
3.4. Water Infiltration and Antecedent Moisture
3.5. Relationships Between Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirkman, K.P.; Fynn, R.W.S.; McGranahan, D.; O’Reagain, P.J.; Dugmore, T. Future-proofing extensive livestock production in subtropical grasslands and savannas. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, T.C.; Mizik, T. Comparative economics of conventional, organic, and alternative agricultural production systems. Economies 2021, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocchi, C.; Orsi, L.; Ferrazzi, G.; Corsi, S. The dimensions of agricultural diversification: A spatial analysis of Italian municipalities. Rural. Sociol. 2020, 85, 316–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkora, M.I.; Vrahnakis, M.; Kleftoyanni, V. Soil quality characteristics of traditional agroforestry systems in Mouzaki area, central Greece. Agrofor. Syst. 2022, 96, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiakiris, R.; Stara, K.; Kazoglou, Y.; Kakouros, P.; Bousbouras, D.; Dimalexis, A.; Dimopoulos, P.; Fotiadis, G.; Gianniris, I.; Kokkoris, I.P.; et al. Agroforestry and the climate crisis: Prioritizing biodiversity restoration for resilient and productive Mediterranean landscapes. Forests 2024, 15, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoneli, V.; Bednarz, J.A.; Thomaz, E.L. Tobacco harvest phase is critical to runoff and soil loss in conventional tillage system. Soil Use Manag. 2023, 1, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, A.d.; Carvalho, P.C.d.F.; Lustosa, S.B.C.; Lang, C.R.; Deiss, L. Research on Integrated Crop-Livestock Systems in Brazil. Rev. Ciência Agronômica 2014, 45, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Moraine, M.; Ryschawy, J.; Magne, M.A.; Asai, M.; Sarthou, J.P.; Duru, M.; Therond, O. Crop–livestock integration beyond the farm level: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tey, Y.S.; Brindal, M. Factors Influencing Farm Profitability. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.K.; Epper, C.A.; Tschopp, D.J.; Long, C.T.M.; Tungani, V.; Burra, D.; Hok, L.; Phengsavanh, P.; Douxchamps, S. Crop-livestock integration provides opportunities to mitigate environmental trade-offs in transitioning smallholder agricultural systems of the Greater Mekong Subregion. Agric. Syst. 2022, 195, 103285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, K.M.; Gaudin, A.C.M. Potential of crop-livestock integration to enhance carbon sequestration and agroecosystem functioning in semi-arid croplands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, J.M.; Anghinoni, I.; Martins, A.P.; Costa, S.E.V.G.D.A.; Cecagno, D.; Carlos, F.S.; Carvalho, P.C.D.F. Soil carbon and nitrogen stocks and fractions in a long-term integrated crop–livestock system under no-tillage in southern Brazil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 190, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.Z.; Han, H.; Ning, T. Crop–Livestock integration via maize straw recycling increased carbon sequestration and crop production in China. Agric. Syst. 2023, 210, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Chakraborty, P.; Kumar, S. Crop–livestock integration enhanced soil aggregate-associated carbon and nitrogen, and phospholipid fatty acid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, J.C.; Rodrigues, G.S.; de Barros, I.; Rodrigues, R.d.A.R.; Garrett, R.D.; Valentim, J.F.; Kamoi, M.Y.T.; Michetti, M.; Wruck, F.J.; Rodrigues-Filho, S.; et al. Integrated crop-livestock systems: A sustainable land-use alternative for food production in the Brazilian Cerrado and Amazon. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, L.S.; Bergier, I.; Ortega, R.; Moraes, A.; Bayma-Silva, G.; Zanetti, M.R. Soil improvement and mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions for integrated crop–livestock systems: Case study assessment in the Pantanal savanna highland, Brazil. Agric. Syst. 2015, 137, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, V.J.L.P.; de Souza, E.S.; Martins, A.P.; Tiecher, T.; Bremm, C.; da Silva Ramos, J.; Duarte Farias, G.; de Faccio Carvalho, P.C. Structural soil quality and system fertilization efficiency in integrated crop-livestock system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 349, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanolli, B.d.S.; Dias, H.B.; da Luz, F.B.; Lamparelli, R.A.C.; Magalhães, P.S.G.; Cherubin, M.R. Crop–Livestock Integrated Systems Improve Soil Health in Tropical Sandy Soils. Agronomy 2025, 15, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogado, R.F.; de Souza, H.A.; Sagrilo, E.; de Brito, L.D.C.R.; Matias, S.S.R.; Neto, M.L.T.; de Oliveira Junior, J.O.L.; de Andrade, H.A.F.; Leite, L.F.C. Soil organic carbon stocks and fractions under integrated systems and pasture in the cerrado of Northeast Brazil. Catena 2024, 243, 108196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, G.; Franzluebbers, A.; Carvalho, P.C.d.F.; Dedieu, B. Integrated crop–livestock systems: Strategies to achieve synergy between agricultural production and environmental quality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 190, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderkamp, L.M.; van Zandbrink, R.M.E.; Meulman, F.; van Middelaar, C.E.; de Olde, E.M.; Hoes, A.; de Roo, N. Social aspects of integrated crop-livestock systems: Key for future policy. Animal 2025, 19, 101564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Mostafa, M. Impact Assessment of Tobacco Cultivation on Soil Ecosystem Using Multi-Evaluation Techniques. Asian J. Environ. Res. 2024, 1, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, E.; Antoneli, V. Long-term soil quality decline due to the conventional tobacco tillage in Southern Brazil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoneli, V.; Pulido Fernández, M.; de Oliveira, T.; Lozano-Parra, J.; Bednarz, J.A.; Vrahnakis, M.; García-Marín, R. Partial grazing exclusion as strategy to reduce land degradation in the traditional Brazilian faxinal system: Field data and farmers’ perceptions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMBRAPA. Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solo, 2nd ed.; Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1997. (In Portugues) [Google Scholar]
- Chang-Fung-Martel, J.; Harrison, M.; Rawnsley, R.; Smith, A.; Meinke, H. The impact of extreme climatic events on pasture-based dairy systems: A review. Crop Pasture Sci. 2017, 68, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridhar, K.; Samireddypalle, A. Impact of Climate Change on Forage Availability for Livestock. In Climate Change Impact on Livestock: Adaptation and Mitigation; Sejian, V., Gaughan, J., Baumgard, L., Prasad, C., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Churchill, A.C.; Zhang, H.; Fuller, K.J.; Amiji, B.; Anderson, I.C.; Barton, C.V.M.; Carrillo, Y.; Catunda, K.L.M.; Chandregowda, M.H.; Igwenagu, C.; et al. Pastures and climate extremes: Impacts of cool season warming and drought on the productivity of key pasture species in a field experiment. Front Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 836968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.K.; Scharf, B.; Eichen, P.A.; Spiers, D.E. Relationships between ambient conditions, thermal status, and feed intake of cattle during summer heat stress with access to shade. J. Therm. Biol. 2017, 63, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geremia, E.V.; Crestani, S.; Mascheroni, J.D.C.; Carnevalli, R.A.; Mourão, G.B.; da Silva, S.C. Sward structure and herbage intake of Brachiaria brizantha cv. Piatã in a crop-livestock-forestry integration area. Livest. Sci. 2018, 212, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, J.R.; Cangiano, C.A.; Pece, M.A.; Larripa, M.; Milone, D.; Utsumi, S.; Laca, E. Monitoring and assessment of ingestive chewing sounds for prediction of herbage intake rate in grazing cattle. Animal 2018, 12, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.D.; Schlecht, E. Livestock mobility in sub-Saharan Africa: A critical review. Pastoralism 2019, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbut, P.; Hoffmann, G.; Angrecka, S.; Godyń, D.; Corrêa Vieira, F.M.; Adamczyk, K.; Kupczyński, R. The effects of heat stress on the behaviour of dairy cows—A review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2021, 21, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, M.; Schmitt Filho, A.L.; Hötzel, M.J.; de Sousa, K.T.; Pinheiro Machado Filho, L.C.; Sinisgalli, P.A. Microclimate and pasture area preferences by dairy cows under high biodiversity silvopastoral system in Southern Brazil. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, K.T.; Deniz, M.; Vale, M.M.d.; Dittrich, J.R.; Hötzel, M.J. Influence of microclimate on dairy cows’ behavior in three pasture systems during the winter in south Brazil. J. Therm. Biol. 2021, 97, 102873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, C.A.; Zolin, C.A.; Lulu, J.; Lopes, L.B.; Furtini, I.V.; Vendrusculo, L.G.; Zaiatz, A.P.S.R.; Pedreira, B.C.; Pezzopane, J.R. Improvement of thermal comfort indices in agroforestry systems in the southern Brazilian Amazon. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 91, 102636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzopane, J.R.M.; Bosi, C.; Nicodemo, M.L.F.; Santos, P.M.; Gomes da Cruz, P.; Parmejiani, R.S. Microclimate and soil moisture in a silvopastoral system in southeastern Brazil. Bragantia 2015, 74, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.F.; Person, J.A.; Cosgrove, G.P.; Barker, D.J.; Marotti, D.M.; Venning, K.J.; Rutter, S.M.; Hill, J.; Thompson, A.N. Impacts of spatial patterns in pasture on animal grazing behavior. Intake Perform 2007, 47, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launchbaugh, K.L. Grazing animal behavior. Forages 2020, 2, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciullo, D.S.C.; Fernandes, P.B.; Carvalho, C.A.B.; Morenz, M.J.F.; Lima, M.A.; Maurício, R.M.; Gomide, C.A.M. Pasture and animal production in silvopastoral and open pasture systems managed with crossbred dairy heifers. Livest. Sci. 2021, 245, 104426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, B.G.; Adams, R.; Branco, S.; Powers, J.S. Scale-dependent variation in nitrogen cycling and soil fungal communities along gradients of forest composition and age in regenerating tropical dry forests. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzech, K.; Wanic, M.; Załuski, D. The effects of soil compaction and different tillage systems on the bulk density and moisture content of soil and the yields of winter oilseed rape and cereals. Agriculture 2021, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R. Time dependence of soil mechanical properties and pore functions for arable soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J.M.; Suzuki, L.E.A.S.; Reinert, D.J.; Horn, R.; Håkansson, I. Reference bulk density and critical degree-of-compactness for no-till crop production in subtropical highly weathered soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 102, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufekcioglu, M.; Schultz, R.C.; Zaimes, G.N.; Isenhart, T.M.; Tufekcioglu, A. Riparian Grazing Impacts on Streambank Erosion and Phosphorus Loss Via Surface Runoff. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, M.; Monaghan, R. Impacts of grazing on ground cover, soil physical properties and soil loss via surface erosion: A novel geospatial modelling approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, M.T.; Tonin, T.; Stegemann, J.; Zerbe, S.; Geitner, C.; Mayr, A.; Wellstein, C. Towards a better understanding of shallow erosion resistance of subalpine grasslands. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, C.; Moore, P.A.; Pote, D.H.; Pennington, J.H.; Martin, J.W.; Brauer, D.K.; Raper, R.L.; Dabney, S.M.; Lee, J. Long-term effects of grazing management and buffer strips on soil erosion from pastures. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoneli, V.; Rebinski, E.A.; Bednarz, J.A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Keesstra, S.D.; Cerdà, A.; Pulido Fernández, M. Soil erosion induced by the introduction of new pasture species in a faxinal farm of Southern Brazil. Geosciences 2018, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, G.S.; Brazier, R.E.; Haygarth, P.M. The impacts of grazing animals on the quality of soils, vegetation, and surface waters in intensively managed grasslands. Adv. Agron. 2007, 94, 237–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivation | |||||||||||||
| Tabacco | |||||||||||||
| Avena | |||||||||||||
| Land type used by grazing animals | |||||||||||||
| Pasture | |||||||||||||
| Forest | |||||||||||||
| Agriculture | |||||||||||||
| Variables | Land Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native Forest | Pasture | Agriculture | Eucalyptus Reforestation | |
| Slope (%) | 10 | 13 | 9 | 10 |
| Soil type | Cambisol haplic | Cambisol haplic | Cambisol haplic | Cambisol haplic |
| Sand (%) | 25 ± 0.19 | 26 ± 0.21 | 26 ± 0.23 | 28 ± 0.21 |
| Silt (%) | 37 ± 0.11 | 30 ± 0.16 | 29 ± 0.19 | 32 ± 0.17 |
| Clay (%) | 38 ± 0.34 | 44 ± 0.29 | 45 ± 0.18 | 40 ± 0.15 |
| Soil pH | 5.6 ± 0.02 | 5.9 ± 0.01 | 6.1 ± 0.01 | 5.8 ± 0.01 |
| Soil OM (g/kg−1) (%) | 42.1 ± 0.38 | 30.4 ± 0.12 | 31.6 ± 0.09 | 33.6 ± 0.1 |
| Native Pasture | ||||||
| Forage (t ha−1) | Animals Grazing (h) | Animals Rest (h) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Soil Moisture (%) | Infiltration Rate (mm h−1) | |
| Forage | 1.00 | |||||
| Animals grazing | 0.867 *** | 1.00 | ||||
| Animals rest | 0.821 *** | 0.721 ** | 1.00 | |||
| Bulk density | 0.621 ** | 0.792 *** | 0.532 * | 1.00 | ||
| Soil moisture | 0.761 *** | 0.442 * | 0.232 | 0.749 ** | 1.00 | |
| Infiltration rate | 0.739 *** | 0.721 ** | 0.314 | 0.813 *** | 0.843 *** | 1.00 |
| Native Forest | ||||||
| Forage (t ha−1) | Animals Grazing (h) | Animals Rest (h) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Soil Moisture (%) | Infiltration Rate (mm h−1) | |
| Forage | 1.00 | |||||
| Animals grazing | 0.567 ** | 1.00 | ||||
| Animals rest | 0.801 *** | 0.581 ** | 1.00 | |||
| Bulk density | 0.438 * | 0.492 * | 0.682 ** | 1.00 | ||
| Soil moisture | 0.259 | 0.029 | 0.309 | 0.891 *** | 1.00 | |
| Infiltration rate | 0.426* | 0.293 | 0.207 | 0.828 *** | 0.813 *** | 1.00 |
| Agricultural Land | ||||||
| Forage (t ha−1) | Animals Grazing (h) | Animals Rest (h) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Soil Moisture (%) | Infiltration Rate (mm h−1) | |
| Forage | 1.00 | |||||
| Animals grazing | 0.906 *** | 1.00 | ||||
| Animals rest | 0.873 *** | 0.688 ** | 1.00 | |||
| Bulk density | 0.647 ** | 0.725 ** | 0.482 * | 1.00 | ||
| Soil moisture | 0.259 | 0.289 | 0.349 | 0.821 *** | 1.00 | |
| Infiltration rate | 0.426 * | 0.293 | 0.207 | 0.801 *** | 0.792 ** | 1.00 |
| Eucalyptus Reforestation | ||||||
| Forage (t ha−1) | Animals Grazing (h) | Animals Rest (h) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Soil Moisture (%) | Infiltration Rate (mm h−1) | |
| Forage | 1.00 | |||||
| Animals grazing | 0.867 *** | 1.00 | ||||
| Animals rest | 0.259 | 0.341 * | 1.00 | |||
| Bulk density | 0.349 * | 0.738 ** | 0.355 * | 1.00 | ||
| Soil moisture | 0.638 ** | 0.281 | 0.241 | 0.409 * | 1.00 | |
| Infiltration rate | 0.406 * | 0.590** | 0.228 | 0.372 * | 0.898 *** | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antoneli, V.; Martini Gamba, L.; Bednarz, J.A.; Corrales Marmol, M.P.; Vrahnakis, M.; Kastridis, A.; Zaimes, G.N. Effect of Rotational Grazing on Soil Quality and Animal Behavior in an Integrated Crop–Livestock (ICL) System on Small Subtropical Farms. Land 2025, 14, 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081617
Antoneli V, Martini Gamba L, Bednarz JA, Corrales Marmol MP, Vrahnakis M, Kastridis A, Zaimes GN. Effect of Rotational Grazing on Soil Quality and Animal Behavior in an Integrated Crop–Livestock (ICL) System on Small Subtropical Farms. Land. 2025; 14(8):1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081617
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntoneli, Valdemir, Leticia Martini Gamba, Joao Anésio Bednarz, Maria Paz Corrales Marmol, Michael Vrahnakis, Aristeidis Kastridis, and George N. Zaimes. 2025. "Effect of Rotational Grazing on Soil Quality and Animal Behavior in an Integrated Crop–Livestock (ICL) System on Small Subtropical Farms" Land 14, no. 8: 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081617
APA StyleAntoneli, V., Martini Gamba, L., Bednarz, J. A., Corrales Marmol, M. P., Vrahnakis, M., Kastridis, A., & Zaimes, G. N. (2025). Effect of Rotational Grazing on Soil Quality and Animal Behavior in an Integrated Crop–Livestock (ICL) System on Small Subtropical Farms. Land, 14(8), 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081617








