Soil Inorganic Carbon Content and Its Environmental Controls in the Weibei Loess Region: A Random Forest-Based Spatial Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
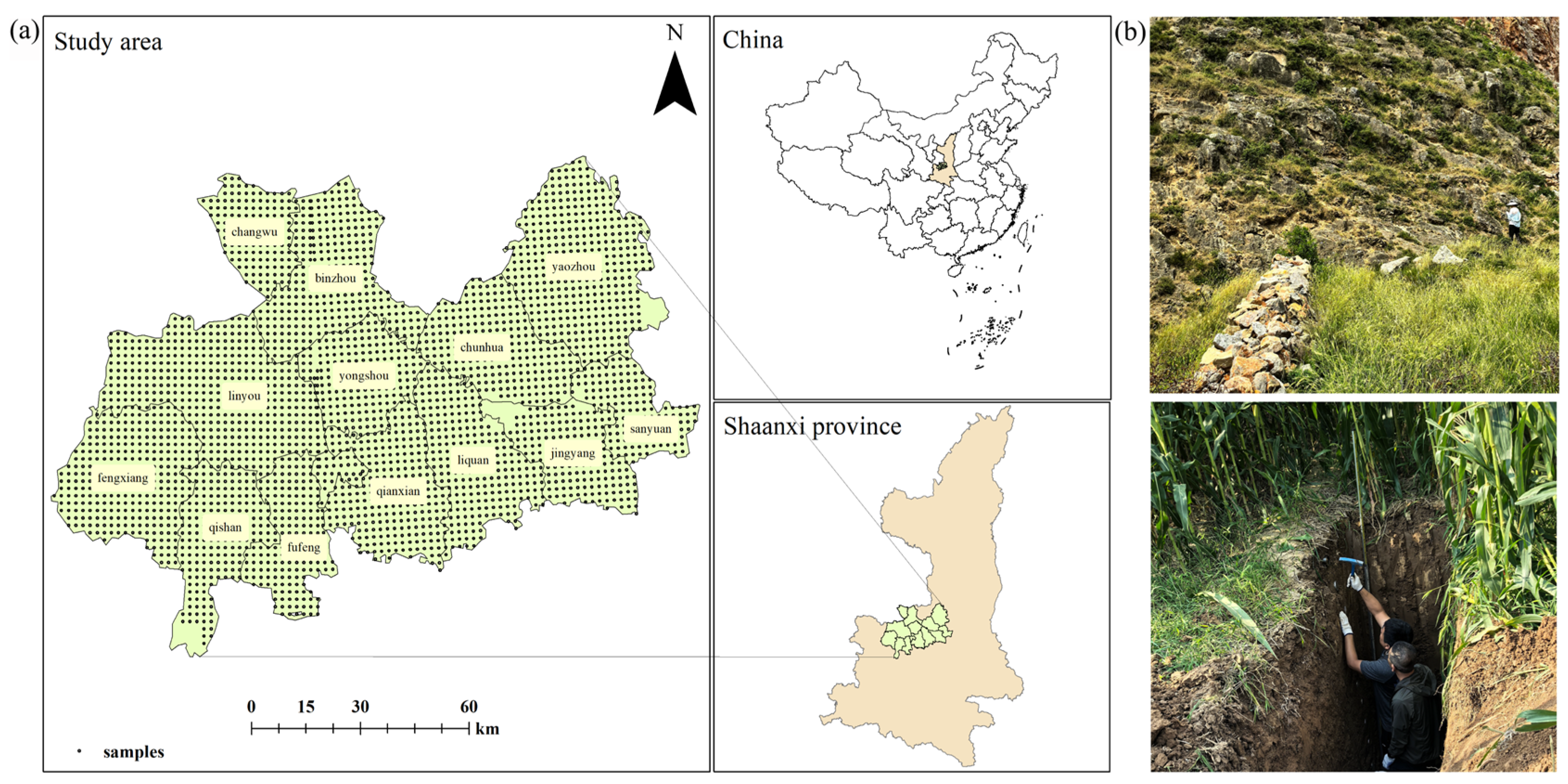
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Environmental Data
2.4. Statistical Modeling and Key Covariates Selection
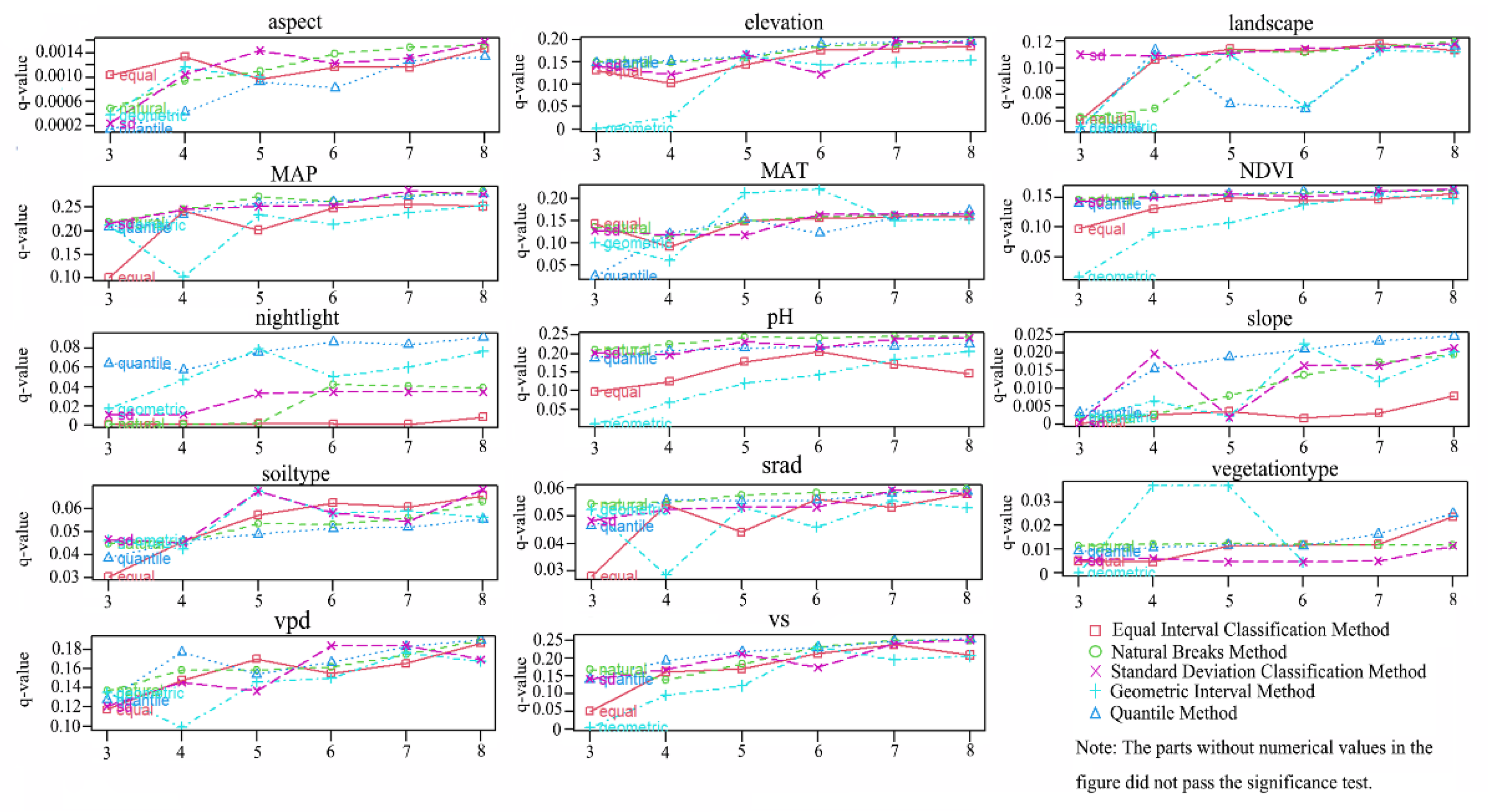
2.5. Geographical Detector Model with Optimal Parameters (OPGD)
3. Results
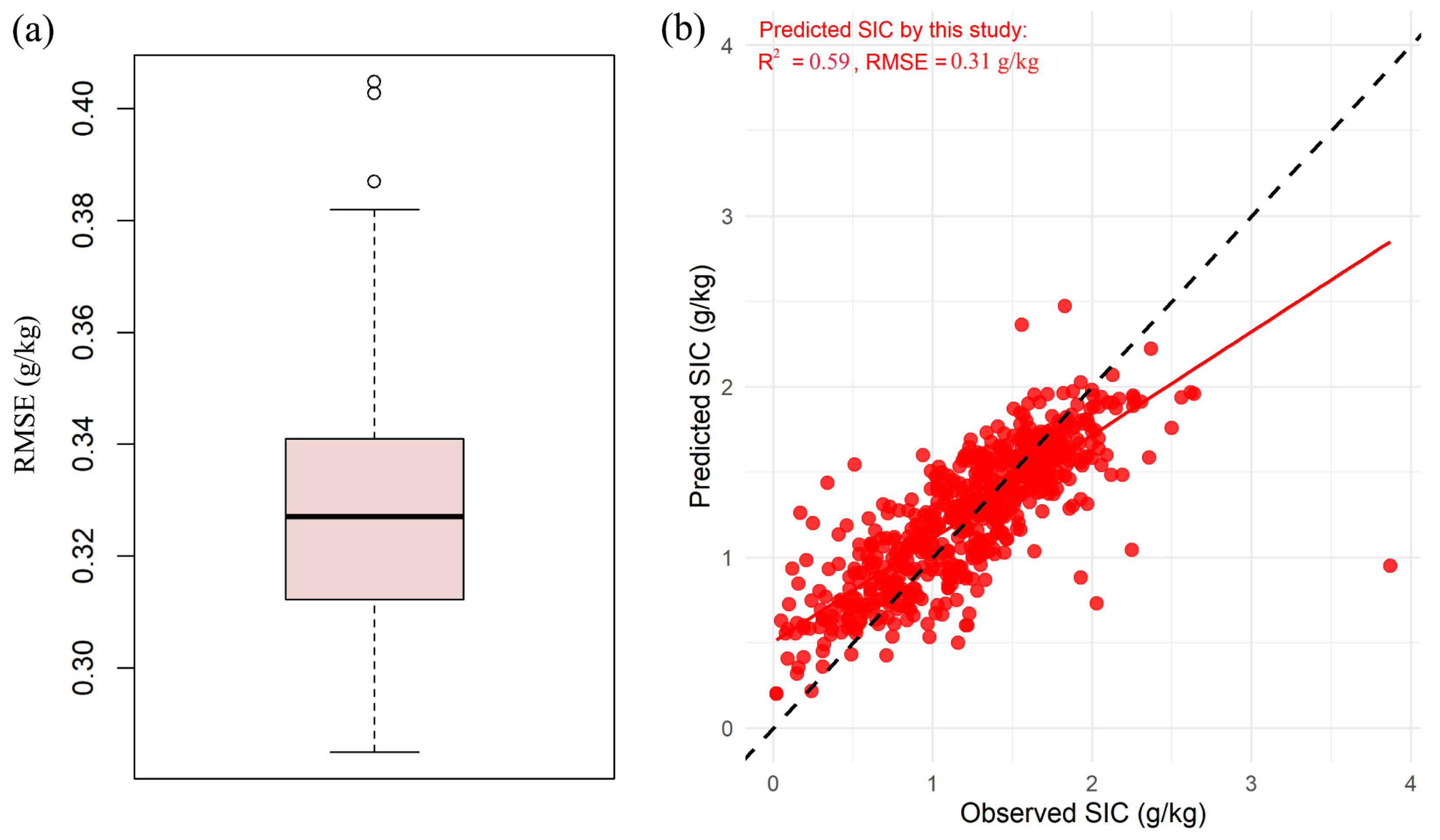
3.1. Model Performance
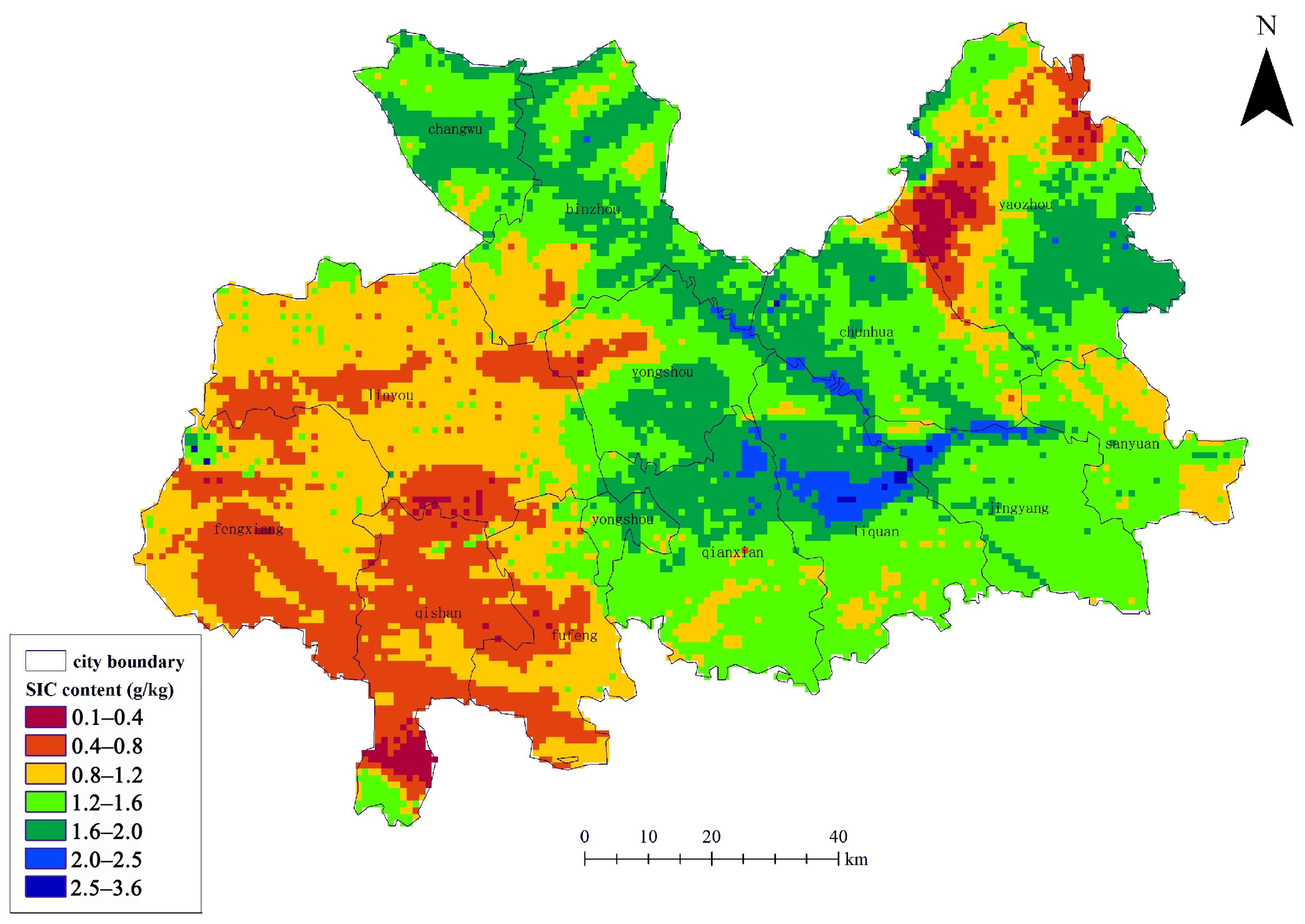
3.2. Spatial Variation and Distribution of SIC Content
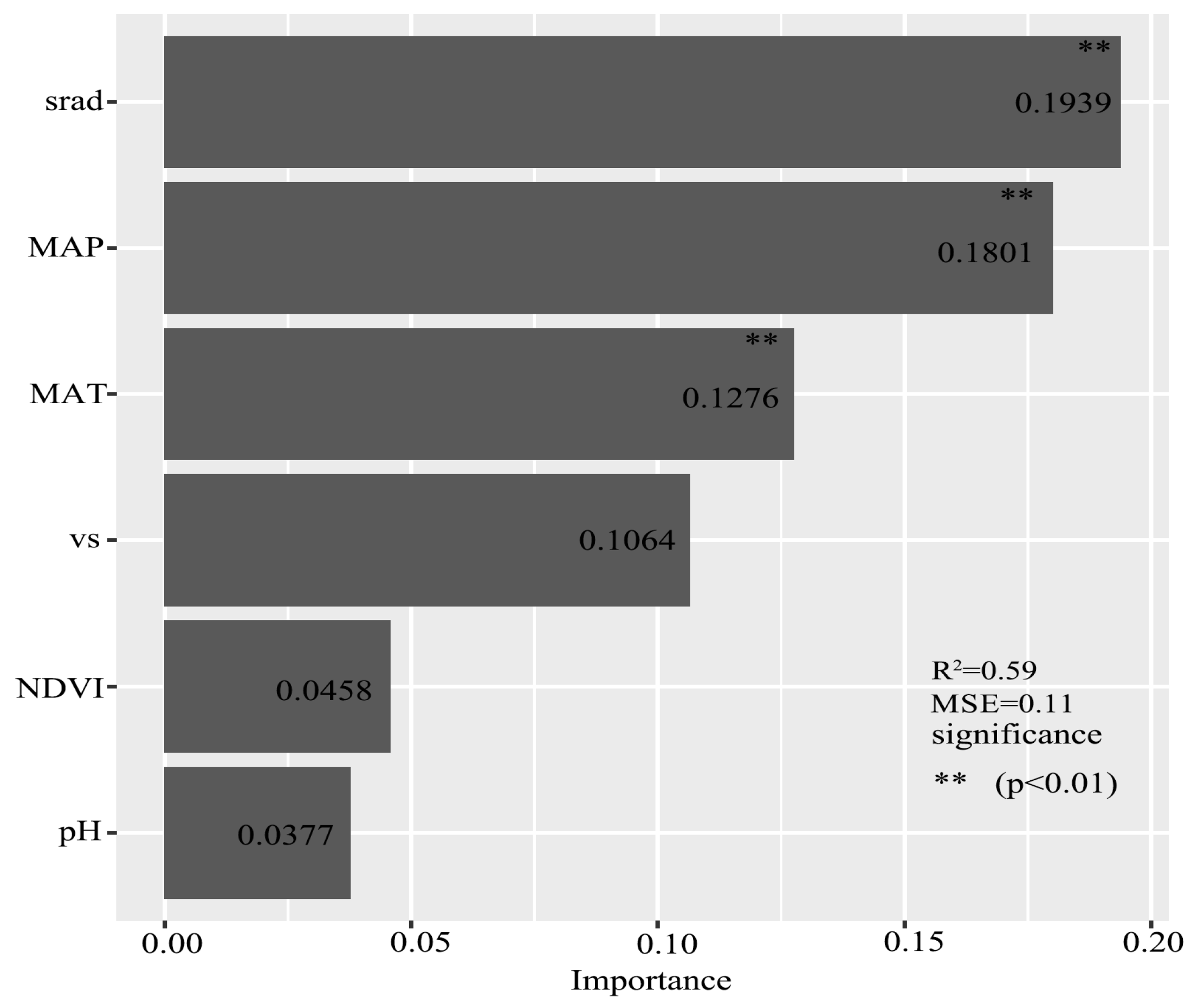
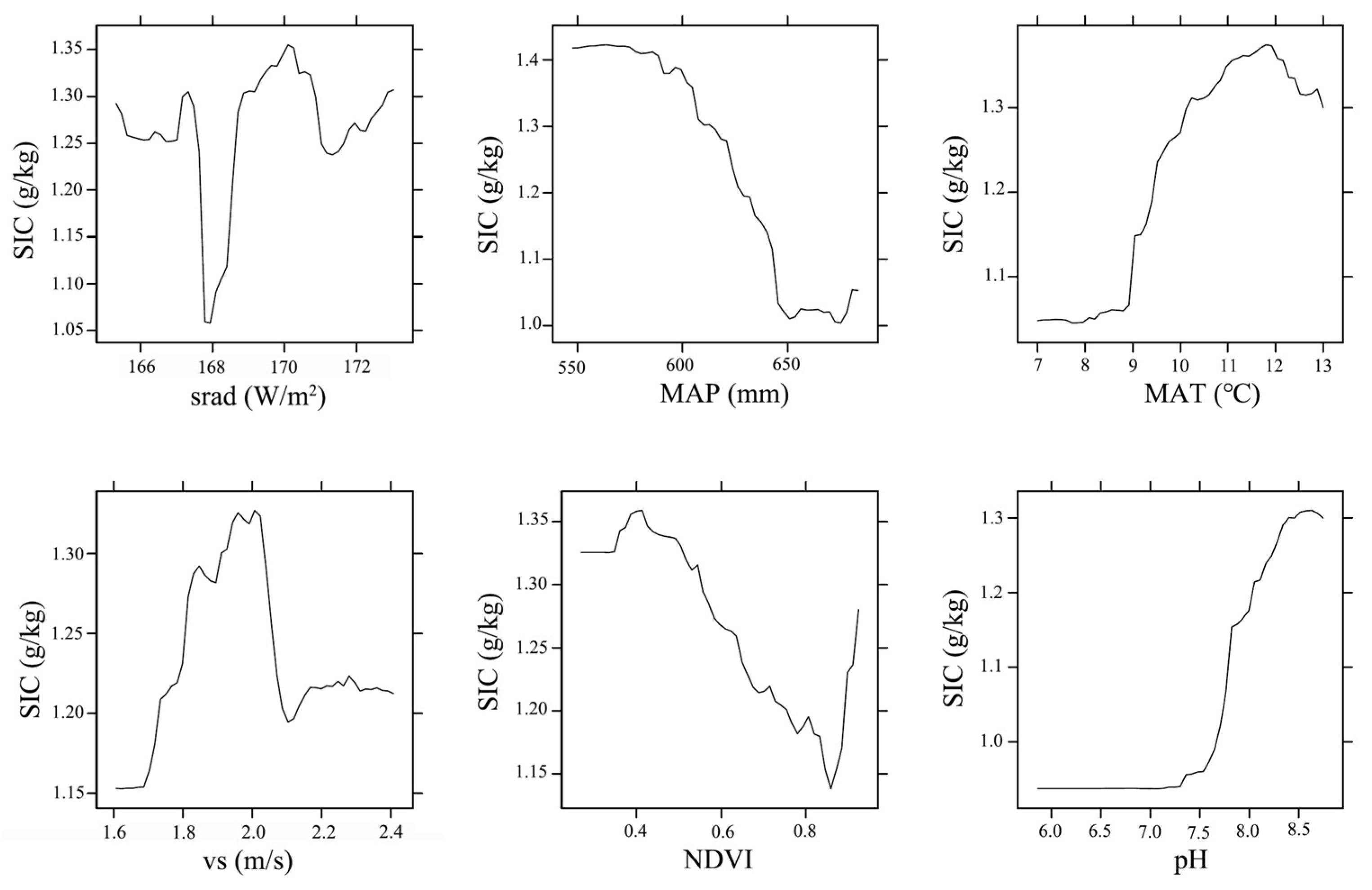
3.3. The Independent Driving Effect of Key Covariates on SIC
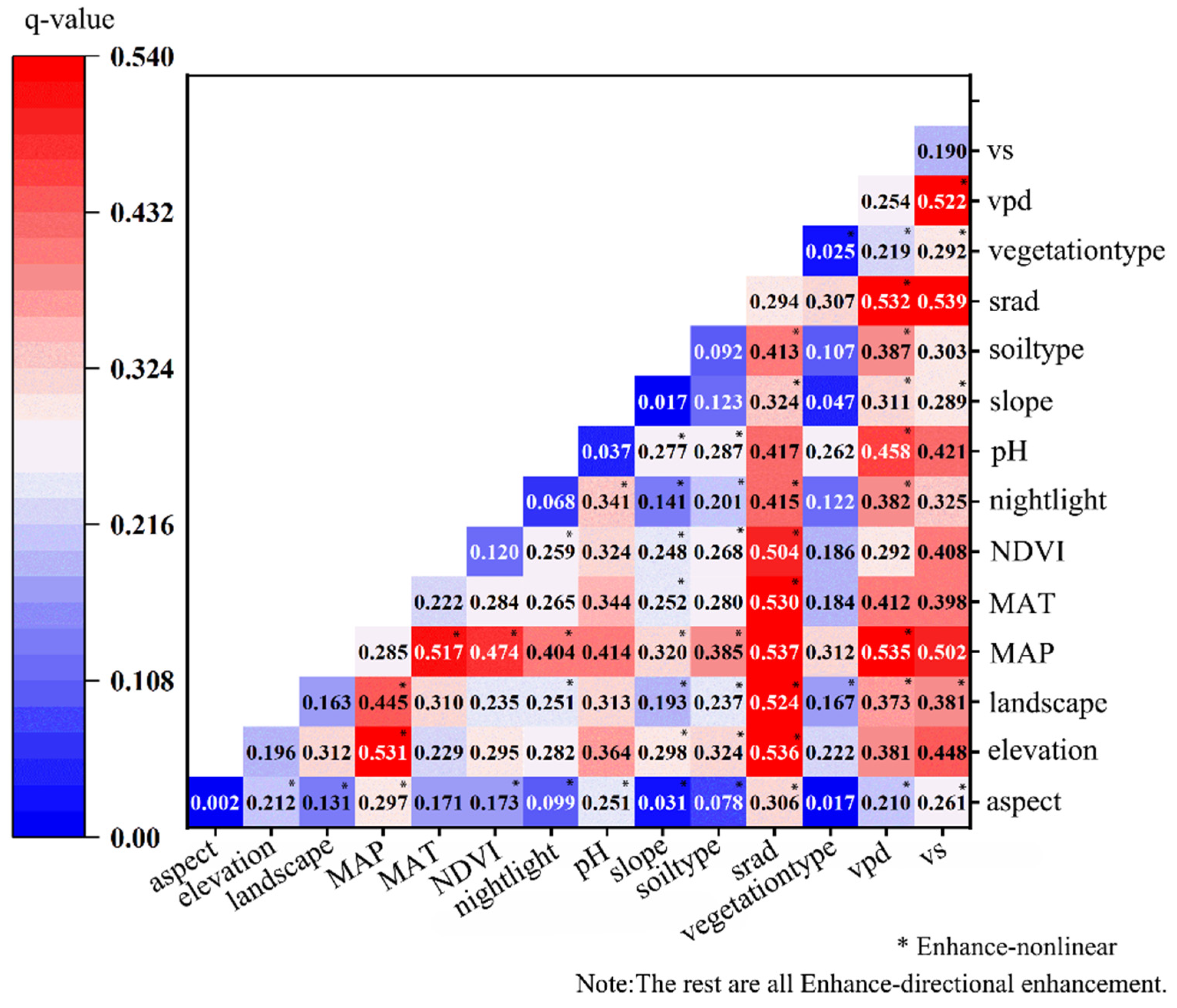
3.4. Nonlinear Enhancement Effect of Two-Factor Interaction
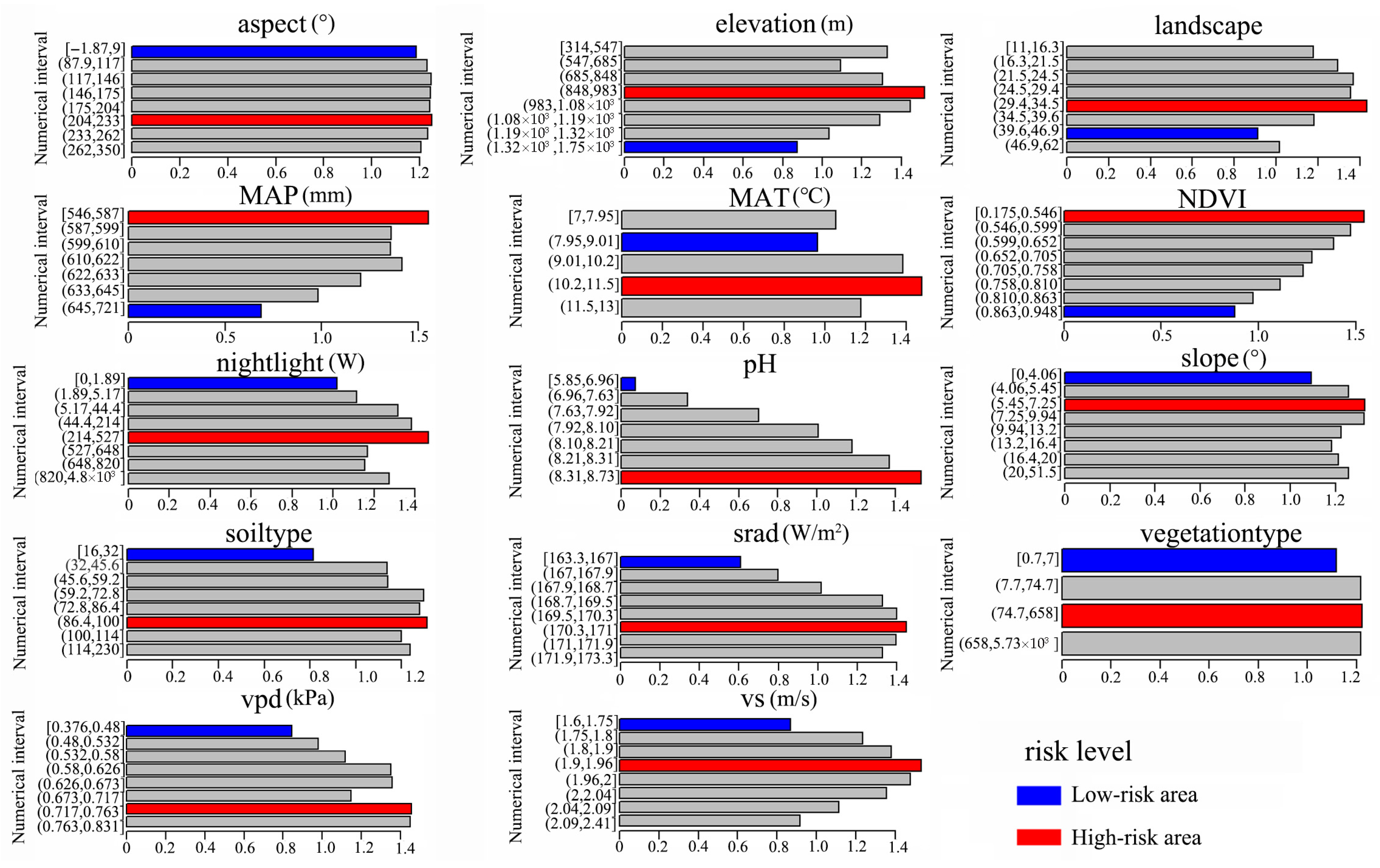
3.5. Optimal Environmental Conditions Accumulated by SIC
4. Discussion
4.1. Regional Heterogeneity and Significance of SIC Patterns in the Weibei Loess Region
4.2. Mechanistic Insights into Dominant and Interactive Environmental Drivers of SIC
4.3. Integrated Implications and Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Fu, Y.; Hou, Q.; Xia, X.; Yan, B.; Yang, Z. Soil organic carbon increase in semi-arid regions of China from 1980s to 2010s. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 116, 104575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenchouni, H.; Neffar, S. Soil organic carbon stock in arid and semi-arid steppe rangelands of North Africa. Catena 2022, 211, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.-P.; Canadell, J.G.; Luo, Y.; Ciais, P.; Chen, A.; Hong, S.; Wang, Y.; Tao, F. Size, distribution, and vulnerability of the global soil inorganic carbon. Science 2024, 384, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Shen, Y. Leguminous forage introduction and returning reduced soil inorganic carbon loss on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2024, 242, 108061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Keppens, E.; Liu, T.; Paepe, R.; Jiang, W. Stable isotope composition of the carbonate concretion in loess and climate change. Quat. Int. 1997, 37, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, J. Soil inorganic carbon storage and spatial distribution in irrigated farmland on the North China Plain. Geoderma 2024, 445, 116887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, D.; Guo, Y. Relationship between soil inorganic carbon and organic carbon in the wheat-maize cropland of the North China Plain. Plant Soil 2017, 418, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, N.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Yu, G.; Zhang, W.; Jobbágy, E. Soil inorganic carbon storage pattern in China. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, R.; Cao, H.; Tan, W. Profile distribution of soil organic and inorganic carbon following revegetation on the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30301–30314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalidy, R.; Arnaud, E.; Santos, R.M. Natural and human-induced factors on the accumulation and migration of pedogenic carbonate in soil: A review. Land 2022, 11, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J. Collapsibility Mechanisms and Water Diffusion Morphologies of Loess in Weibei Area. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Fang, N.; Xiao, H.; Shi, Z. Sediment deposition changes the relationship between soil organic and inorganic carbon: Evidence from the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wei, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, W. Profile distribution of soil inorganic carbon along a chronosequence of grassland restoration on a 22-year scale in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2014, 121, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z. Effects of land-use change on soil inorganic carbon: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2019, 353, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.B.; Mendonça Santos, M.L.; Minasny, B. On digital soil mapping. Geoderma 2003, 117, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Hu, B.; Luo, D.; Peng, J.; Shi, Z. Estimation of soil inorganic carbon with visible near-infrared spectroscopy coupling of variable selection and deep learning in arid region of China. Geoderma 2023, 437, 116589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, R.; Cao, H.; Tan, W. Factor contribution to soil organic and inorganic carbon accumulation in the Loess Plateau: Structural equation modeling. Geoderma 2019, 352, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, Y. Afforestation on cropland promotes pedogenic inorganic carbon accumulation in deep soil layers on the Chinese loess plateau. Plant Soil 2022, 478, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Bai, L.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, J.; Li, Z.; Min, Z.; Cui, L.; Li, P. Vegetation position impacts soil carbon losses on the slope of the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2023, 222, 106875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, B.; Yan, J.; Cheng, X.; Yi, P.; Kang, F.; Han, H. Mixed plantation regulates forest floor water retention and temperature sensitivity in restored ecosystems on the Loess Plateau China. Catena 2023, 222, 106838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Gao, S.; Lu, C.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Wang, T. Effects of different tillage and fertilization management practices on soil organic carbon and aggregates under the rice–wheat rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, T.; Jia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, S. Optimizing Low-Efficiency Robinia pseudoacacia Forests on the Loess Plateau Based on an Evaluation of the Ecological Functions of Soil and Water Conservation. Forests 2024, 15, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianmo, Z.; Yushan, L.; Xianglin, P.; Shuguang, Z. Soils of the loess region in China. Geoderma 1983, 29, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, R.; Vitti, C.; Castellini, M.; Mastrangelo, M.; Pedrero, F.; Vivaldi, G.A.; Stellacci, A.M. Comparison of two methods for total inorganic carbon estimation in three soil types in mediterranean area. Land 2021, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, Q.; Leppäranta, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q. Estimating Winter Arctic Sea Ice Motion Based on Random Forest Models. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.N.; Ziegler, A. ranger: A fast implementation of random forests for high dimensional data in C++ and R. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grömping, U. R package DoE. base for factorial experiments. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 85, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jinfeng, W.; Yong, G.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, C.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yang, G.; Tian, J.; et al. The impacts of climate change and human activities on biogeochemical cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 2940–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Tang, B.; Kong, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Shao, M.; Wei, X. Soil organic and inorganic carbon distribution driven by erosion at various spatial scales on the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 389, 109708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Xu, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Csikós, N. Divergent contribution of environmental factors to soil organic and inorganic carbon in different land use types in a forest-grassland ecotone of Inner Mongolia, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Hao, Q.; Cui, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Gielen, G.; et al. Soil organic carbon in particle-size fractions under three grassland types in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Baumann, F.; Ma, Y.; Song, C.; Kühn, P.; Scholten, T.; He, J.S. Organic and inorganic carbon in the topsoil of the Mongolian and Tibetan grasslands: Pattern, control and implications. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 2287–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Duan, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhong, R.; Zheng, H.; Xie, Y.; Rong, L.; Zhao, H.; Wei, S. Soil inorganic carbon stock and its changes across the Tibetan Plateau during the 1980s–2020s. Glob. Planet. Change 2024, 236, 104433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, O.J.; Jiang, Y. Altitudinal distribution of soil organic and inorganic carbon in a dry alpine rangeland of northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. EGUsphere 2025, 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; He, J.; Lü, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, B.; Mao, H.; Song, W.; Zhao, W.; Hou, D.; Wang, J. Organic carbon fractions and estimation of organic carbon storage in the lake sediments in Inner Mongolia Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.-L.; Yan, M.-J.; Hou, H.; Guan, J.-H.; Shi, W.-Y.; Li, G.-Q.; Du, S. Distribution of soil carbon and nitrogen in two typical forests in the semiarid region of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2016, 143, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Si, J.; He, X.; Jia, B.; Zhou, D.; Wang, C.; Qin, J.; Liu, Z.; Ndayambaza, B.; Bai, X. The distribution and driving mechanism of soil inorganic carbon in semi-arid and arid areas: A case study of Alxa region in China. Catena 2024, 247, 108475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozukara, G.; Hartemink, A.E.; Zhang, Y. Factors driving inorganic carbon levels in the soils of the conterminous USA. Catena 2025, 252, 108841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Keenan, T.; Fu, B. Soil moisture-atmosphere interactions drive terrestrial carbon-water trade-offs. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shao, G.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Zamanian, K.; Alharbi, S.A.; Filimonenko, E.; Liu, E.; Mei, X.; Kuzyakov, Y. The over-estimation of long-term mineral fertilizer on CO2 release from soil carbonates. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 392, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, S.; Olariu, C.; Kerans, C.; Ogiesoba, O.C.; Steel, R.; Palacios, F. Icehouse mixed carbonate and siliciclastic sequence evolution based on 3D seismic analysis: Insights from the Eastern Shelf of the Permian Basin, Texas. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 170, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xing, D.; Wagai, R.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Fan, B.; Feng, W. Divergent effects of soil organic matter and carbonate on soil aggregation and structure in arid regions. Catena 2025, 257, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Liu, Z.; Kaufmann, G. Sensitivity of the global carbonate weathering carbon-sink flux to climate and land-use changes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdush, J.; Paul, V. A review on the possible factors influencing soil inorganic carbon under elevated CO2. CATENA 2021, 204, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihacek, L.; Ulmer, M. Effects of tillage on inorganic carbon storage in soils of the northern Great Plains of the US. In Agricultural Practices and Policies for Carbon Sequestration in Soil; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Ren, K.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, L.; Huo, S.; Liu, J. Changes in soil inorganic carbon following vegetation restoration in the cropland on the Loess Plateau in China: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 372, 123412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Feng, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X. Analysis of spatial and temporal changes in vegetation cover and its drivers in the Aksu River Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharififar, A.; Minasny, B.; Arrouays, D.; Boulonne, L.; Chevallier, T.; Van Deventer, P.; Field, D.J.; Gomez, C.; Jang, H.-J.; Jeon, S.-H. Soil inorganic carbon, the other and equally important soil carbon pool: Distribution, controlling factors, and the impact of climate change. Adv. Agron. 2023, 178, 165–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsia, A.; Moinet, A.; Vazquez, C.; Creamer, R.E.; Moinet, G.Y. The challenge of selecting an appropriate soil organic carbon simulation model: A comprehensive global review and validation assessment. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 5760–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yu, Y.; Nan, S.; Chai, Y.; Xu, W.; Qin, Y.; Li, X.; Bodner, G. Conversion of SIC to SOC enhances soil carbon sequestration and soil structural stability in alpine ecosystems of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 195, 109452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Environmental Factor | Covariates | Description/Unit | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climatic | srad, MAP, MAT, vpd, vs (continuous variable) | Shortwave radiation (W/m2), annual precipitation (mm), mean temperature (°C), vapor pressure deficit (kPa), wind speed (m/s) | TerraClimate dataset, via Google Earth Engine (raster format, ~4 km resolution) |
| Topographic | elevation, slope, aspect (continuous variable) | Elevation (m), slope (°), slope direction | https://www.gscloud.cn, accessed on 4 January 2025 (raster format, 90 m resolution) |
| Vegetation-related | NDVI (continuous variable) | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index | https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov, accessed on 4 January 2025 (raster format, 1 km resolution) |
| vegetation type (categorical variable) | Vegetation classification | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mcd12q1v006, accessed on 4 January 2025 (raster format, 500 m resolution) | |
| Landscape (categorical variable) | Broad landscape classification (e.g., loess hills, river valley, plateau) | https://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=124, accessed on 4 January 2025 (vector format) | |
| Soil Properties | pH (continuous variable) | Field-measured soil acidity | Measured in field/lab then interpolated to study area by kriging |
| soil type (categorical variable) | Soil classification | https://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=145, accessed on 4 January 2025 (vector format) | |
| Anthropogenic | Nightlight (continuous variable) | Nighttime light intensity (proxy for human activity) | https://www.resdc.cn/DOI/DOI.aspx?DOIID=105, accessed on 4 January 2025 (raster format, 500 m resolution) |
| Covariates | VIF # (Round 1) | VIF (Round 2) | VIF (Round 3) | VI * (Round 1) | VI (Round 2) | VI (Round 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aspect | 1.004 | 1.004 | 1.001 | 0.001 | removed | removed |
| elevation | 24.583 | removed & | removed | removed | removed | removed |
| landscape | 2.210 | 2.202 | 2.188 | 0.017 | 0.020 | removed |
| MAP | 6.403 | 6.366 | 5.566 | 0.118 | 0.158 | 0.180 |
| MAT | 31.585 | 27.141 | 8.305 | 0.103 | 0.114 | 0.127 |
| NDVI | 2.158 | 2.079 | 1.835 | 0.043 | 0.046 | 0.045 |
| nightlight | 1.722 | 1.681 | 1.671 | 0.023 | 0.026 | removed |
| pH | 1.320 | 1.319 | 1.319 | 0.025 | 0.026 | 0.037 |
| slope | 1.356 | 1.355 | 1.354 | 0.006 | removed | removed |
| soiltype | 1.308 | 1.299 | 1.298 | 0.024 | 0.025 | removed |
| srad | 11.751 | 11.183 | 7.631 | 0.132 | 0.171 | 0.193 |
| vegetationtype | 1.344 | 1.313 | 1.273 | 0.010 | removed | removed |
| vpd | 20.944 | 20.325 | removed | removed | removed | removed |
| vs | 15.688 | 10.401 | 10.317 | 0.065 | 0.075 | 0.106 |
| R2 † | 0.621 | 0.615 | 0.603 | 0.603 | 0.597 | 0.590 |
| MSE (g2/kg2) † | 0.106 | 0.107 | 0.110 | 0.110 | 0.110 | 0.111 |
| Criterion Interval | Interaction |
|---|---|
| q(X1 ∩ X2) < Min[q(X1), q(X2)] | Nonlinear Weakening |
| Min[q(X1), q(X2)] < q(X1 ∩ X2) < Max[q(X1), q(X2)] | Single-factor Nonlinear Weakening |
| q(X1 ∩ X2) > Max[q(X1), q(X2)] | Two-factor Enhancement |
| q(X1 ∩ X2) = q(X1) + q(X2) | Independent |
| q(X1 ∩ X2) > q(X1) + q(X2) | Nonlinear Enhancement |
| County (Administrative Unit) | SIC Content (g/kg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Range | Mean | Std | |
| Yaozhou | 0.15 | 2.34 | 2.19 | 1.24 | 0.46 |
| Fengxiang | 0.26 | 2.91 | 2.64 | 0.84 | 0.22 |
| Linyou | 0.30 | 1.75 | 1.45 | 0.95 | 0.22 |
| Fufeng | 0.34 | 1.87 | 1.53 | 0.90 | 0.22 |
| Qishan | 0.10 | 1.59 | 1.49 | 0.71 | 0.25 |
| Binzhou | 0.51 | 2.28 | 1.77 | 1.45 | 0.28 |
| Chunhua | 0.30 | 2.72 | 2.42 | 1.49 | 0.30 |
| Changwu | 0.93 | 1.88 | 0.95 | 1.53 | 0.17 |
| Liquan | 0.98 | 3.56 | 2.58 | 1.58 | 0.35 |
| Yongshou | 0.34 | 2.13 | 1.79 | 1.44 | 0.32 |
| Jingyang | 1.07 | 2.74 | 1.68 | 1.51 | 0.22 |
| Qianxian | 0.79 | 2.23 | 1.44 | 1.48 | 0.25 |
| Sanyuan | 0.84 | 1.86 | 1.02 | 1.29 | 0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, D.; Ding, Y.; Yan, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhao, Q.; Xia, A. Soil Inorganic Carbon Content and Its Environmental Controls in the Weibei Loess Region: A Random Forest-Based Spatial Analysis. Land 2025, 14, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081609
Xu D, Ding Y, Yan Y, Qian J, Zhao Q, Xia A. Soil Inorganic Carbon Content and Its Environmental Controls in the Weibei Loess Region: A Random Forest-Based Spatial Analysis. Land. 2025; 14(8):1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081609
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Duoxun, Yongkang Ding, Yuchen Yan, Jianli Qian, Qianzhuo Zhao, and Anquan Xia. 2025. "Soil Inorganic Carbon Content and Its Environmental Controls in the Weibei Loess Region: A Random Forest-Based Spatial Analysis" Land 14, no. 8: 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081609
APA StyleXu, D., Ding, Y., Yan, Y., Qian, J., Zhao, Q., & Xia, A. (2025). Soil Inorganic Carbon Content and Its Environmental Controls in the Weibei Loess Region: A Random Forest-Based Spatial Analysis. Land, 14(8), 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081609




