Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization Based on NSGA-II and PLUS Models: Balancing Economic Development and Carbon Neutrality Goals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Research Framework and Methods
2.3.1. Research Framework
2.3.2. Estimate Ecosystem Carbon Storage
2.3.3. Estimating Carbon Emissions
2.3.4. Optimization of the Quantitative Structure of LULC
- (1)
- Construct the Objective Function
- (2)
- GM (1,1) Model Prediction
- (3)
- Constraint Conditions
2.3.5. Optimization of LULC Spatial Layout
2.3.6. Accuracy Validation of the PLUS
3. Results
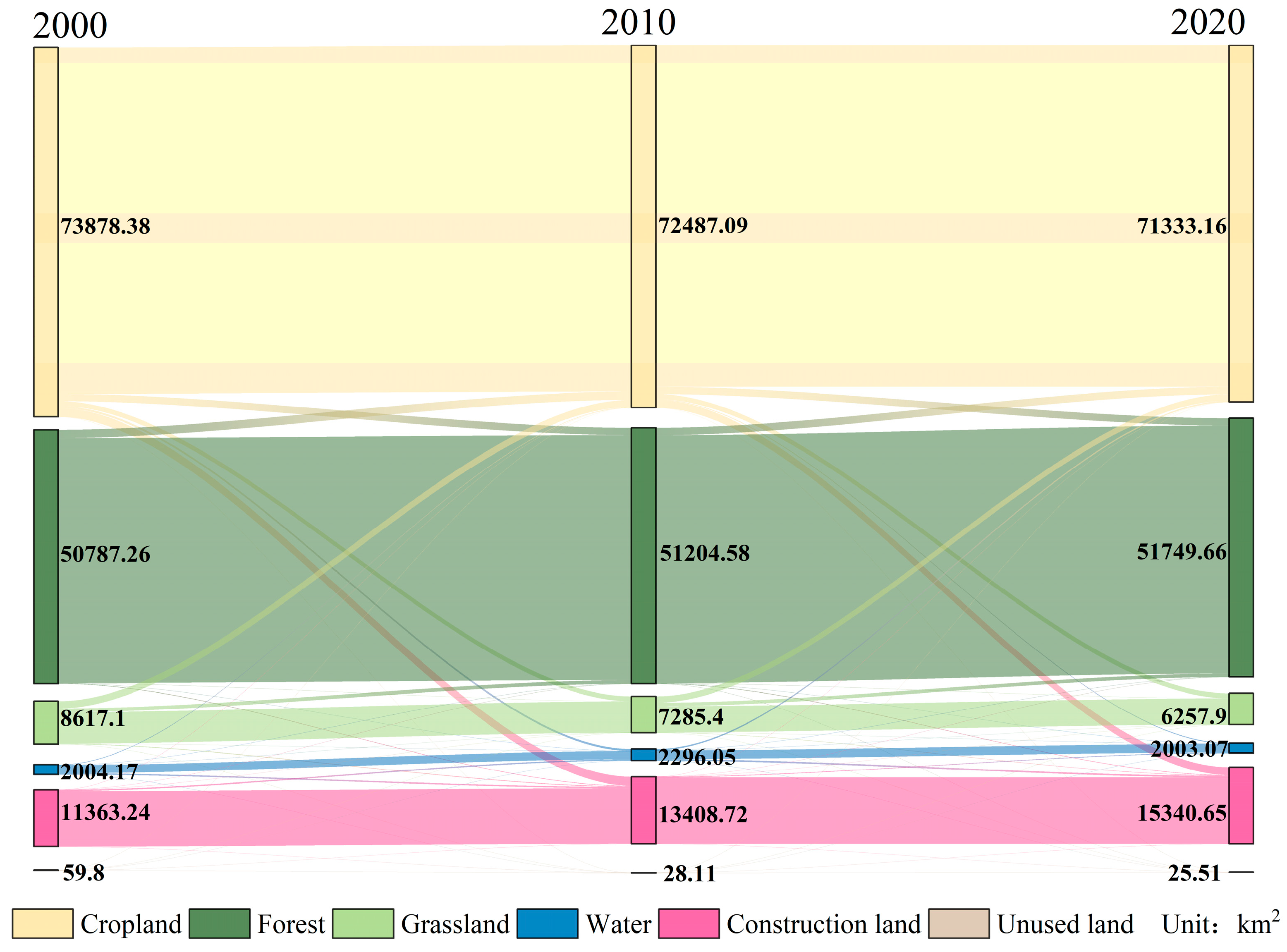
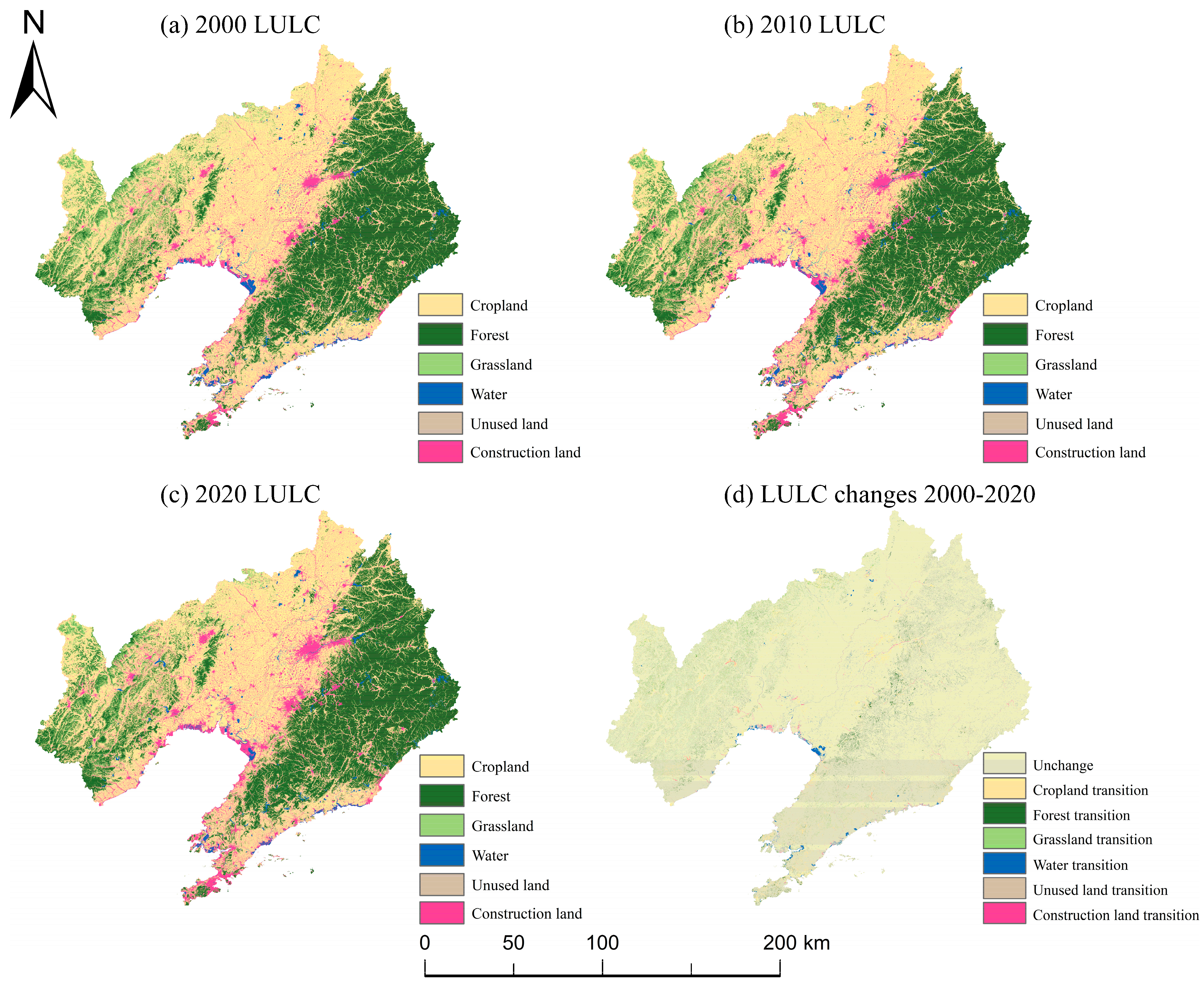
3.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of LULC
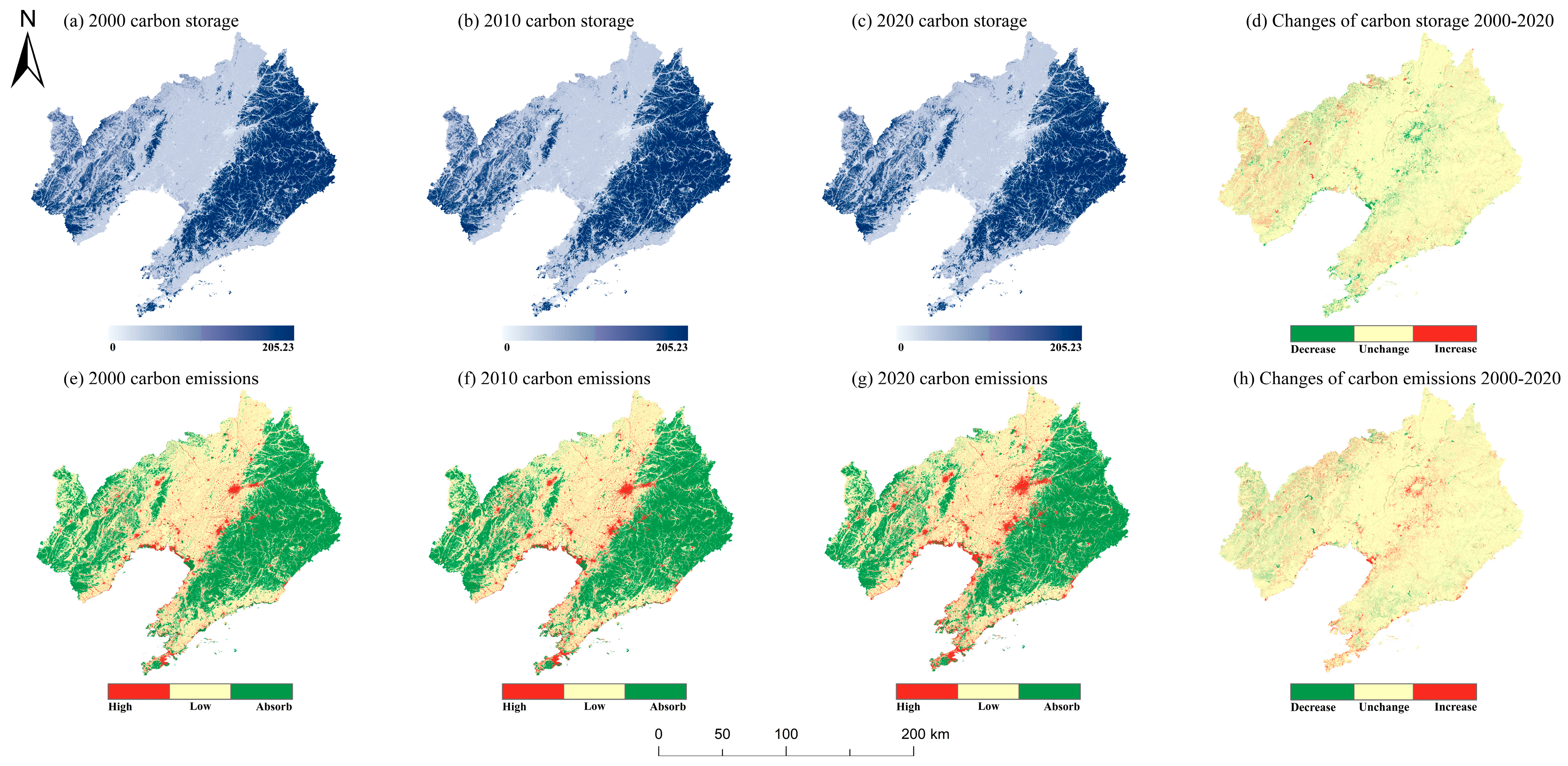
3.2. Dynamic Changes in ECS and LUCE from 2000 to 2020
3.3. Carbon Neutrality Potential of Different LULC Scenarios
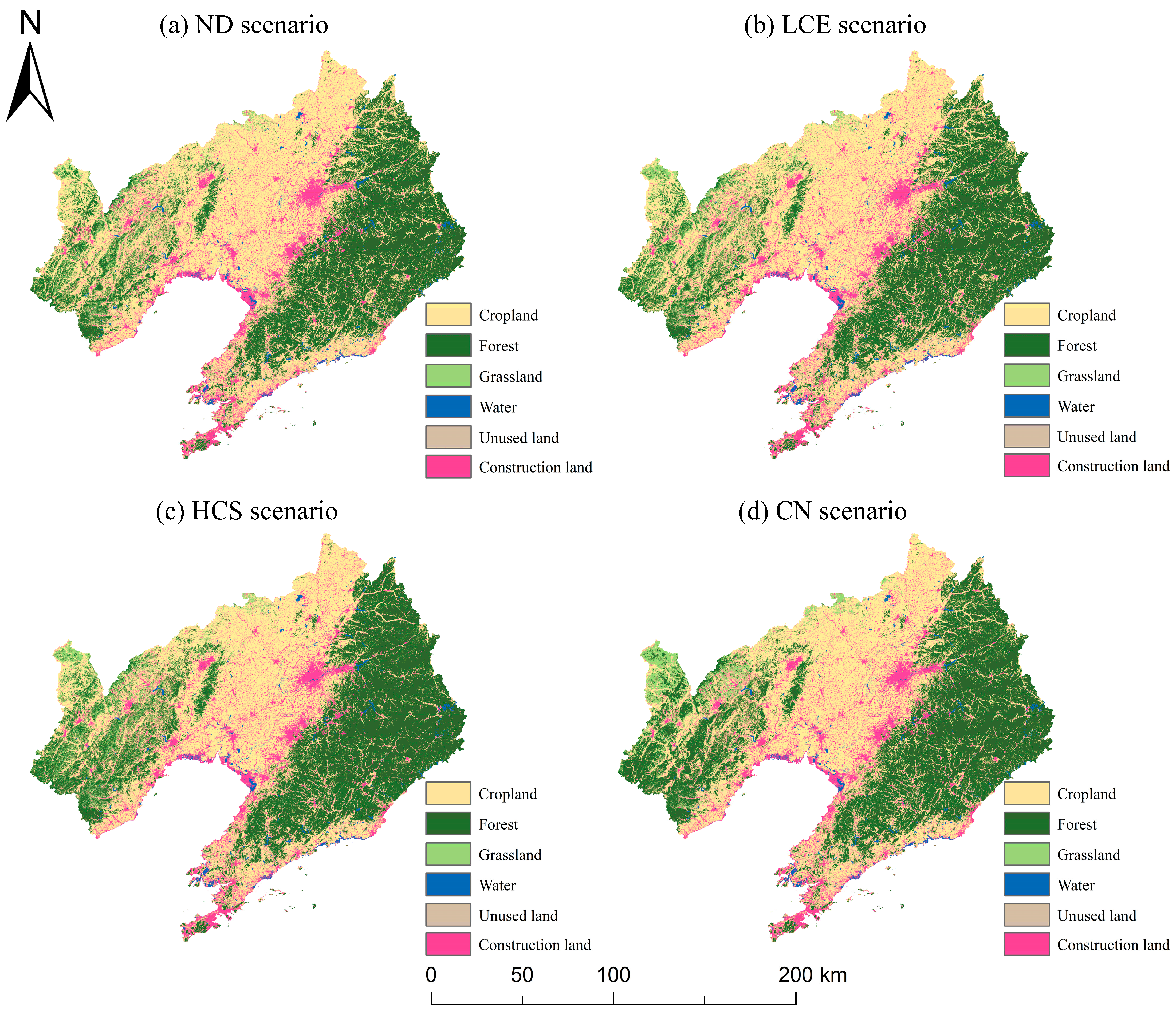
3.3.1. Future LULC Changes Under Different Scenarios
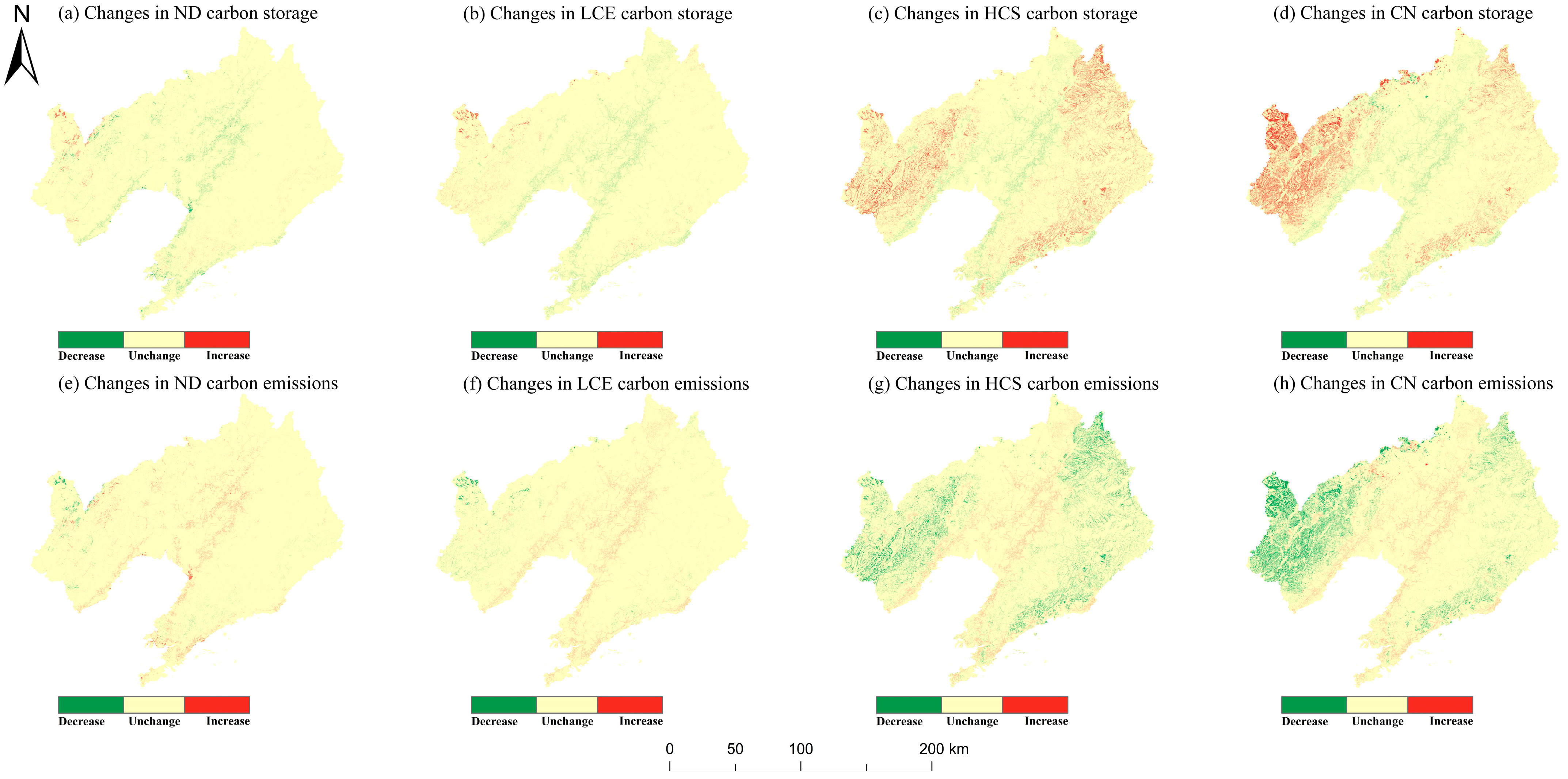
3.3.2. Contribution of Future LULC Scenarios to Carbon Neutrality
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of LULC Dynamics in Liaoning Province on Carbon Cycle
4.2. Impact of Different Future Development Scenarios on ECS and LUCE
4.3. Policy Recommendations
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Ruan, Z.; Du, P. Spatial–Temporal Evolution Analysis of Multi-Scenario Land Use and Carbon Storage Based on PLUS-InVEST Model: A Case Study in Dalian, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Du, C.; Chen, X.; Jia, L.; Guo, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality in China: Goals, Implementation Path, and Prospects. China Geol. 2021, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-Y.; Xu, Y.-F.; Sun, Q.; Liu, W.-J.; Qi, W. Contributing to Carbon Neutrality Targets: A Scenario Simulation and Pattern Optimization of Land Use in Shandong Province Based on the PLUS Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Kasimu, A.; Reheman, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Aizizi, Y.; Liang, H. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Prediction of Carbon Emissions/Absorption from Land Use Change in the Urban Agglomeration on the Northern Slope of the Tianshan Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use/Cover Change and Terrestrial Ecosystem Carbon Reserve Response in Liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z. Effects of Land-Use Change on Carbon Emission and Its Driving Factors in Shaanxi Province from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 68313–68326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Land Use Transitions and the Associated Impacts on Carbon Storage in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhai, G.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Research on Regional Terrestrial Carbon Storage Based on the Pattern-Process-Function. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, X.; Xie, R.; Lin, Y.; Fang, J.; Yuan, J. Response of Carbon Energy Storage to Land Use/Cover Changes in Shanxi Province, China. Energies 2024, 17, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C. Land Use, Total Carbon Emissions Change and Low Carbon Land Management in Coastal Jiangsu, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Shao, X.; Yu, T.; Hou, Q. Spatial Analysis of Land Use Change Effect on Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in the Eastern Regions of China between 1980 and 2000. Geosci. Front. 2017, 8, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Gen, L.; Li, N. Path of Carbon Emission Reduction through Land Use Pattern Optimization under Future Scenario of Multi-Objective Coordination. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1065140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Xue, F.; Li, Q.; Fang, K.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, J. Exploring Potential of Urban Land-Use Management on Carbon Emissions—A Case of Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Chen, S.; Xiao, D. Multi-Scenario Land Cover Changes and Carbon Emissions Prediction for Peak Carbon Emissions in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cui, Z.; Fan, T.; Yin, H. Impacts of Land Use Change on Carbon Storage in the Guangxi Beibu Gulf Economic Zone Based on the PLUS-InVEST Model. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. Does Partition Matter? A New Approach to Modeling Land Use Change. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 106, 102041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Song, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, D. Multi-Scenario Simulation and Spatial-Temporal Analysis of LUCC in China’s Coastal Zone Based on Coupled SD-FLUS Model. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 579–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Hu, M.; Xia, B. Spatiotemporal Dynamic Simulation of Land-Use and Landscape-Pattern in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, J.; Jiang, D.; Lin, G.; Cao, C. Land Use Optimization in Ningbo City with a Coupled GA and PLUS Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, X.; Liu, M.; Deng, S. Modeling Dynamic Urban Growth Using Cellular Automata and Particle Swarm Optimization Rules. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 102, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X. An Improved Simulated Annealing Algorithm for Interactive Multi-Objective Land Resource Spatial Allocation. Ecol. Complex. 2018, 36, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Kang, L. The Contribution of Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization to Reducing Ecological Risk: A Case Study of the Lanzhou-Xining Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Lan, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, P. Optimization of Low-Carbon Land Use in Chengdu Based on Multi-Objective Linear Programming and the Future Land Use Simulation Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 989747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, J. Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization Based on Integrated NSGA–II–PLUS Model: Comprehensive Consideration of Economic Development and Ecosystem Services Value Enhancement. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, F.; Tian, H. Towards Low-Carbon Cities: Patch-Based Multi-Objective Optimization of Land Use Allocation Using an Improved Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xin, C.; Zhang, B.; Xin, S.; Tang, D.; Chen, H.; Ma, X. Contribution of Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization to Carbon Neutrality: A Case Study of Northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Ban, K.; Jin, L.; Wu, D. Balancing Economic Growth, Carbon Emissions, and Sequestration: A Multi-Objective Spatial Optimization in Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area in China. Land 2024, 13, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Zhu, D.; Yun, W. Simulation of Land Use Spatial Pattern of Towns and Villages Based on CA–Markov Model. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 54, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Deng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Lei, X.; Chen, Z. Modelling the Potential Impacts of Urban Ecosystem Changes on Carbon Storage under Different Scenarios by Linking the CLUE-S and the InVEST Models. Ecol. Model. 2017, 345, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A Future Land Use Simulation Model (FLUS) for Simulating Multiple Land Use Scenarios by Coupling Human and Natural Effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the Drivers of Sustainable Land Expansion Using a Patch-Generating Land Use Simulation (PLUS) Model: A Case Study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Ye, C.; Li, X.; Hu, H. Land-Use Optimization Based on Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study of Urban Agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Lai, L.; Wang, W.; Peng, J.; Zhao, R. Land Use Structure Optimization Based on Carbon Storage in Several Regional Terrestrial Ecosystems across China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2013, 25, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Qiao, R.; Ma, X. Optimization of Land-Use Structure Based on the Trade-Off Between Carbon Emission Targets and Economic Development in Shenzhen, China. Sustainability 2018, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, H. Optimizing Land Use Patterns to Improve the Contribution of Land Use Planning to Carbon Neutrality Target. Land Use Policy 2023, 135, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, M.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Gong, J. Compound Optimization of Territorial Spatial Structure and Layout at the City Scale from “Production–Living–Ecological” Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Cai, M.; Jiang, P.; Fei, D.; Liao, C. Spatial Multi-Objective Optimization towards Low-Carbon Transition in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Teng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, W.; Ji, X. Simulation of Land Use and Carbon Storage Evolution in Multi-Scenario: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liu, Y.; Qian, F.; Wang, Q.; Dong, X. An Empirical Analysis of the Factors Affecting Farmer Satisfaction Under the China Link Policy. Sage Open 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Song, F.; Su, F.; Shi, Z.; Song, S. Quantifying the Independent Contributions of Climate and Land Use Change to Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Zhang, J. Multi-Scenario Prediction of Ecosystem Services Value and Mechanism of Its Trade-Offs under the Township Scale—Evidence from Liaoning Province. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y. Impact of LULC in Coastal Cities on Terrestrial Carbon Storage and Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study of Liaoning Province. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, W. Using the InVEST-PLUS Model to Predict and Analyze the Pattern of Ecosystem Carbon Storage in Liaoning Province, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.-F.; Cao, A.-H.; Wang, F.-Y. Response and Multi-Scenario Prediction of Carbon Storage and Habitat Quality to Land Use in Liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Fang, R.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Carbon Emissions from Land Use Change in Yellow River Delta Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, B.; Zheng, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, C. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Service Value for Optimization of Land Use in the Sichuan-Yunnan Ecological Barrier, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; He, J.-M. Generalized GM (1, 1) Model and Its Application in Forecasting of Fuel Production. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 6234–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ming, D.; Yang, J. Optimization of Land Use Structure Based on Ecological GREEN Equivalent. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2002, 5, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, B.; Pei, T.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y. Measurement of Spatial Conflicts and Multi-Scenario Simulation of “production-Living-Ecological” Spaces in the Lanzhou-Xining Urban Agglomeration Based on the MOP-PLUS Model. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, J.; Wu, J. Multi-Scenario Land Use Optimization Analysis of the Hohhot-Baotou-Ordos Urban Agglomeration under Dual Carbon Targets. Geogr. Res. 2025, 44, 656–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Ju, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, J. The Double-Edged Sword Effects of Land Use Optimization Based on Dual Carbon Goals: A Perspective from Landscape Ecological Risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Tong, D.; Liu, Z.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Forecasting Urban Land Use Change Based on Cellular Automata and the PLUS Model. Land 2022, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Cai, T.; Wen, Q.; Han, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Yin, C. Scenario Simulation of Land Use Change and Carbon Storage Response in Henan Province, China: 1990–2050. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global Forecasts of Urban Expansion to 2030 and Direct Impacts on Biodiversity and Carbon Pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Duan, X.; Mao, M.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Qiu, X.; Rao, X.; et al. Assessing the Impact of Land Use and Changes in Land Cover Related to Carbon Storage by Linking Trajectory Analysis and InVEST Models in the Nandu River Basin on Hainan Island in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1038752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Xia, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Urban Expansion Simulation towards Low-Carbon Development: A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Song, R.; Sun, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, K. Land Use/Land Cover Change and Its Impact on Ecosystem Carbon Storage in Coastal Areas of China from 1980 to 2050. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Qi, S.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y. Exploring the Spatiotemporal Variation of Carbon Storage on Hainan Island and Its Driving Factors: Insights from InVEST, FLUS Models, and Machine Learning. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Rong, W. Construction of Ecological Network in Suzhou Based on the PLUS and MSPA Models. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Type | Attribute | Spatial Resolution | Year(s) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LULC data | LULC | Raster 30 m | 2000–2020 | China Land Cover Dataset (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8176941) (accessed on 10 June 2024) |
| Socio-economic factors | Population GDP | Raster 1 km | 2020 | Resource and Environment Science Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn) (accessed on 10 June 2024) |
| Main roads Secondary roads Third-class road Government Railway Highway River | Vector data | 2020 | Open Street Map (https://www.openhistoricalmap.org) (accessed on 17 June 2024) | |
| Climate and environmental factors | DEM Slope | Raster 90 m | 2020 | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn) (accessed on 20 June 2024) |
| Temperature Precipitation | Raster 100 m | 2020 | Resource and Environment Science Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn) (accessed on 10 June 2024) | |
| Statistical Yearbook | GDP | Statistics | 2020–2020 | Liaoning Provincial Bureau of Statistics (https://www.stats.gov.cn) (accessed on 17 June 2024) |
| LULC Type | Aboveground | Belowground | Soil Organic | Dead Organic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 4.75 | 0 | 33.51 | 0 |
| Forest | 49.6 | 24.97 | 128.67 | 1.99 |
| Grassland | 24.38 | 19.59 | 52.29 | 22.74 |
| Water | 2.45 | 0.62 | 80.11 | 0.1 |
| Unused land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Construction land | 4.33 | 2.17 | 6.37 | 0.58 |
| Energy Type | Conversion Coefficient (t/t) | Emission Factor (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|
| Coal | 0.7143 | 0.7559 |
| Coke | 0.9714 | 0.855 |
| Crude oil | 1.4286 | 0.5857 |
| Gasoline | 1.4714 | 0.5538 |
| Kerosene | 1.4714 | 0.5714 |
| Diesel | 1.4571 | 0.5921 |
| Fuel oil | 1.4286 | 0.6185 |
| Nature gas | 1.2143 | 0.4483 |
| Electricity | 0.1229 | 0.2132 |
| LULC Type | Economic Value (104 yuan/hm2) | Carbon Emission (t/hm2) |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 4.51 | 0.422 |
| Forest | 0.28 | −0.613 |
| Grassland | 28.69 | −0.021 |
| Water | 4.95 | −0.253 |
| Construction land | 0.0001 | −0.005 |
| Unused land | 214.89 | 257.753 |
| Cropland | Forest | Grassland | Water | Unused Land | Construction Land | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 actual value | 71,333.16 | 51,749.66 | 6257.90 | 2003.07 | 25.51 | 15,340.65 |
| Proportion | 48.6219% | 35.2734% | 4.2655% | 1.3653% | 0.0174% | 10.4564% |
| 2020 predicted value | 70,983.21 | 51,464.96 | 6295.55 | 2568.95 | 18.64 | 15,378.64 |
| Proportion | 48.3834% | 35.0794% | 4.2912% | 1.7510% | 0.0127% | 10.4823% |
| Error proportion (2020 predicted–actual) | −0.2385% | −0.194% | 0.0257% | 0.3857% | −0.0047% | 0.0259% |
| 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland carbon storage | 282.66 | 277.34 | 272.92 |
| Forest carbon storage | 1042.31 | 1050.87 | 1062.06 |
| Grassland carbon storage | 102.54 | 86.7 | 74.47 |
| Water carbon storage | 16.69 | 19.12 | 16.68 |
| Unused land carbon storage | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Construction land carbon storage | 15.28 | 18.03 | 20.63 |
| Total carbon storage | 1459.48 | 1452.06 | 1446.76 |
| Total carbon emissions | 95.29 | 194.29 | 245.73 |
| 2020 | 2030ND | 2030LCE | 2030HCS | 2030CN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 71,333.16 | 70,049.07 | 68,900.38 | 61,363.26 | 62,289.88 |
| Forest | 51,749.66 | 52,153.93 | 52,155.49 | 59,513.37 | 58,722.57 |
| Grassland | 6257.9 | 5506.06 | 6607.27 | 6607.27 | 6607.27 |
| Water | 2003.07 | 1803.07 | 1979.56 | 2000.67 | 1873.49 |
| Unused land | 25.51 | 22.71 | 18.19 | 18.76 | 20.23 |
| Construction land | 15,340.65 | 17,175.11 | 17,049.06 | 17,206.62 | 17,196.51 |
| Type | Economic Value | Carbon Storage | Carbon Emissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actual value of ND | 418.82 | 1442.00 | 442.40 |
| Increment of LCE value | 200.30 | 10.04 | −3.30 |
| Increment of HCS value | 2230.66 | 132.60 | −0.013 |
| Increment of CN value | 3386.21 | 118.84 | −0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, H.; Liu, S.; Huan, C.; Cheng, M.; Dong, X.; Sun, H. Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization Based on NSGA-II and PLUS Models: Balancing Economic Development and Carbon Neutrality Goals. Land 2025, 14, 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081585
Gu H, Liu S, Huan C, Cheng M, Dong X, Sun H. Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization Based on NSGA-II and PLUS Models: Balancing Economic Development and Carbon Neutrality Goals. Land. 2025; 14(8):1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081585
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Hanlong, Shuoxin Liu, Chongyang Huan, Ming Cheng, Xiuru Dong, and Haohang Sun. 2025. "Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization Based on NSGA-II and PLUS Models: Balancing Economic Development and Carbon Neutrality Goals" Land 14, no. 8: 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081585
APA StyleGu, H., Liu, S., Huan, C., Cheng, M., Dong, X., & Sun, H. (2025). Multi-Objective Land Use Optimization Based on NSGA-II and PLUS Models: Balancing Economic Development and Carbon Neutrality Goals. Land, 14(8), 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081585








