Abstract
Dark skies, a vital natural and cultural resource, have been increasingly threatened by light pollution due to rapid urbanization, leading to ecological degradation and biodiversity loss. As a key strategy for sustainable regional development, dark sky parks (DSPs) not only preserve nocturnal environments but also enhance livability by balancing urban expansion and ecological conservation. This study develops a novel framework for evaluating DSP suitability, integrating ecological and socio-economic dimensions, including the resource base (e.g., nighttime light levels, meteorological conditions, and air quality) and development conditions (e.g., population density, transportation accessibility, and tourism infrastructure). Using the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) as a case study, we employ Delphi expert consultation, GIS spatial analysis, and multi-criteria decision-making to identify optimal DSP locations and prioritize conservation zones. Our key findings reveal the following: (1) spatial heterogeneity in suitability, with high-potential zones being concentrated in the GBA’s northeastern, central–western, and southern regions; (2) ecosystem advantages of forests, wetlands, and high-elevation areas for minimizing light pollution; (3) coastal and island regions as ideal DSP sites due to the low light interference and high ecotourism potential. By bridging environmental assessments and spatial planning, this study provides a replicable model for DSP site selection, offering policymakers actionable insights to integrate dark sky preservation into sustainable urban–regional development strategies. Our results underscore the importance of DSPs in fostering ecological resilience, nighttime tourism, and regional livability, contributing to the broader discourse on sustainable landscape planning in high-urbanization contexts.
1. Introduction
The influence of artificial light sources on the environment and human activities has become increasingly significant due to the rapid urbanization and technological advancements in lighting caused by the unprecedented rate of global population increase [1,2,3]. Such conditions harm the physiological cycles of animals and plants and disrupt natural ecological processes [4,5,6]. It has previously been shown that 70% of migratory birds are attracted to artificial lights at night. This attraction can draw migratory birds into sub-optimal stopover habitats near urban areas and result in excess mortality [7]. Additionally, the widespread use of artificial lighting is leading to a scarcity of dark night skies, depriving people of the opportunity to appreciate the beauty of the dark sky. Over 80% of the global population lives under light-polluted skies [8]. Therefore, the dark night sky, as a scarce resource, has increasingly attracted the attention of scholars, and studying it is of great value.
In 1916, dark sky protection was first put forward in Article 27 of the Basic Law promulgated by the National Park Service of the United States. In recent decades, communities and resource management agencies worldwide have begun to define the dark sky as a new kind of natural and cultural resource and tourism attraction, efforts which align with the environmental imperatives of DarkSky. DarkSky was established in 1988 and is now active around the world, working to reduce the negative impacts of light pollution and “protect the dark sky” [9]. Based on differences in their location, area availability, usage functions, and land properties, DarkSky’s classification of DSPs includes five types: dark sky sanctuaries, DSPs, dark sky reserves, dark sky communities, and urban night sky locations. Among them, DSPs are the most common type, as this type of protection can easily be achieved within this framework. DarkSky first defined a DSP in 2006 as land with excellent starry sky quality and a night environment that is specially protected because of its scientific, natural, educational, and cultural heritage value and its role in providing public leisure [10].
Current research on the dark sky focuses on these categories. In the relevant research on the site selection and identification of DSPs, the impact of artificial light sources on the dark sky is a crucial factor that cannot be ignored, and scholars have utilized a variety of instruments and test methods to measure the impact of light pollution [11]. For example, existing research has confirmed the extent to which sites are affected by light pollution through surveys of existing lighting installations and sky brightness measurements using photometers [12], “Sky Quality Meters” (SQMs) [13,14,15,16,17], digital single lens reflex (DSLR) [18,19], unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) [20], or macro-analyses of light pollution with remote sensing imagery [21,22]. Meanwhile, several suitable methods are available to plot and analyze huge long-term night sky brightness datasets, such as mean histograms and circa-lunar, annual (“hourglass”), and cumulative (“jellyfish”) plots [23]. Simultaneously, selecting DSPs with reasonable indicators is also a paramount step. Nazım Aksaker classified potential international DSP (IDSP) locations in southwestern Türkiye based on long-term artificial light and cloud cover data in a GIS environment [24]. Ya Wen Nie constructed a Dark-Sky Composite Fit Index (DSCFI) using NPP-VIIRS nighttime lighting images and historical weather data to select the most suitable sites for establishing DSPs [25]. In Greece, a method was proposed for identifying and planning protected dark sky areas. This involved a detailed investigation of existing lighting facilities, measurements of lighting illuminance and sky brightness levels, and an analysis of the sources of light pollution [11].
In addition, several studies have investigated how to protect the dark sky, such as by identifying the appropriate lighting brightness according to the experiences of tourists, providing environmental education (e.g., websites, signage, and programs) about the night sky, determining the appropriate lighting fixtures [26,27], or examining how to formulate a scientific policy on the protection of the dark starry night sky [28,29]. At the same time, some researchers have examined the potential of utilizing the dark sky as a tourism resource [30]. For instance, preserving dark starry skies and astronomy tourism has been proposed in the National Park Muranska Planina (Slovakia) as a new tourism concept for parks [31]. Bryce Canyon National Park has made full use of its dark night skies as a resource through astronomy programs, such as multimedia evening programs, nighttime stargazing with telescopes, and educating visitors about the importance of dark night skies [32]. The Zselic Landscape Protection Area described how to develop a new lighting project based on the need to view the dark, starry night sky [33]. Galloway Forest DSP and the Torrance Barrens Dark Sky Preserve in Muskoka, Ontario, Canada, demonstrate how dark sky resources can be used in existing parks to serve visitors and promote tourism [34].
In summary, current research on DSPs mainly focuses on site selection, establishment, and subsequent protection and development. It can be seen that site selection studies for DSPs exhibit certain geographical limitations: most research focuses on remote areas far from cities or around nature reserves, while urban agglomerations with high population density and intensive urbanization remain underexplored. Meanwhile, most relevant studies on DSP site selection consider background resource conditions such as artificial light intensity and frequency of clear skies, with little attention paid to the tourism potential of DSPs, failing to fully address the contradiction between the protection and utilization of dark night skies in urban areas.
The location of a DSP requires not only consideration of the resource base of the site but also the conditions of development. Accordingly, this study attempts to consider the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) as its research object, adopting a more comprehensive and objective evaluation index system to determine alternative sites with the potential to establish DSPs. By doing this, the study adds to the existing research in this area and provides an important reference for future site selection and the establishment of DSPs in other areas.
2. Study Area
The GBA, located in southern China, includes the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Macao Special Administrative Region, Guangzhou City, Shenzhen City, Zhuhai City, Foshan City, Huizhou City, Dongguan City, Zhongshan City, Jiangmen City, and Zhaoqing City, covering an area of 5.59 × 104 km2. The population in this region is estimated to be 86 million (Figure 1). The GBA has a well-developed economy with a high level of industrialization and urbanization, with a GDP of over CNY 13 trillion in 2022, accounting for about 10% of the total Chinese GDP. This makes it one of the strongest Chinese regions in terms of overall strength and degree of openness. However, the rapid development of the economy has also caused damage to the environment. Light pollution in the GBA has become increasingly serious, and the dark sky is gradually disappearing from this area, which makes its protection urgent. Therefore, establishing a DSP is an appropriate means of conservation to preserve this valuable resource. The GBA is dominated by mountains, hills, and coastal plains. The mountain ranges in the west and north, along with the central hills, form natural geographical barriers, effectively blocking the spread of light from coastal urban agglomerations into the inland areas and creating relatively independent dark sky spaces. Additionally, the region features a high annual average of clear nights (150–200 days), providing strong natural conditions for dark sky stargazing. Meanwhile, its developed economic system supports the establishment of DSPs with comprehensive supporting facilities and systems. As a precious natural resource, DSPs can lead to new possibilities for environmental protection and tourism development in the GBA.
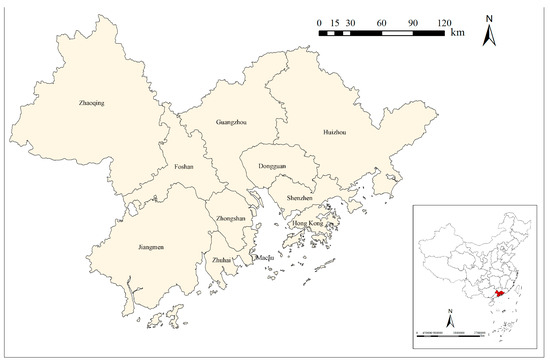
Figure 1.
The Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area.
3. Data and Research Methods
3.1. Data Selection and Sources
DarkSky published criteria for establishing DSPs on its official website [35]. Moreover, as mentioned in the standards designated by the China Biodiversity Conservation and Green Development Foundation (CBCGDF), the dark sky, as a heritage site of scientific, natural, educational, historical, and cultural resources, should be specially protected and opened to the public for sharing [36]. In this study, we combined the definitions of DSPs put forward by two organizations and proposed a site suitability indicator system based on two dimensions (Figure 2). Among them, the resource background comprises indicators that are directly related to the quality of the dark sky environment. Therefore, we ultimately selected the intensity of artificial light, cloud-free days, and PM2.5. The development conditions have an indirect relationship with the quality of the dark sky, which is directly related to the tourism potential of DSPs. Therefore, we selected the population density, Points of Interest (POIs), and the traffic accessibility as the three indicators of the development conditions dimension.
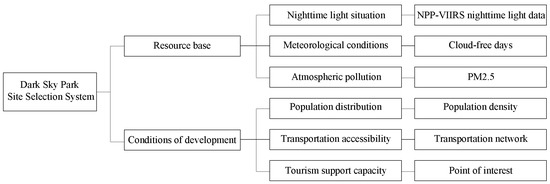
Figure 2.
The DSP site selection index system.
Among these six elements, the nighttime lighting data are based on the NPP-VIIRS nighttime lighting situation, reflecting the extent to which an area is affected by artificial light sources. Cloud-free days reflect the meteorological conditions, indicating the number of days on which people can see the night sky clearly during a certain period. PM2.5 reflects the atmospheric pollution, which indicates extremely fine particulate matter in the atmosphere and affects the ability to recognize distant objects [37]. The population density represents the population distribution, which can reflect the tourism potential of an area. The transportation network impacts transportation accessibility, which indicates the ease of moving around the region. The POI indicates the tourism support capacity, reflecting whether an area can accommodate tourists. By using six indicators divided into two major aspects, the data on the resource base and development conditions are normalized. Next, the Delphi method is applied to perform superposition according to the respective weights of these indicators. The result is used as the evaluation outcome of the suitability of the model for site selection of DSPs in the GBA. Finally, based on the evaluation criteria for DSPs set by DarkSky and CBCGDF and the current situation of nature reserves, the final spatial distribution results for DSPs are obtained.
3.1.1. NPP-VIIRS Data
The nighttime lighting and cloud-free days data are the most important factors influencing the location of DSPs, indicating the night sky quality of a region. In previous studies, the DMSP (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program)-OLS (Operational Linescan System) and NPP (National Polar-orbiting Partnership)-VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) are commonly used sensors for monitoring light pollution [38,39,40,41]. The advantages of NPP-VIIRS data include their ability to block out light from sources other than artificial light, including sunlight, moonlight, and cloudy pixel light sources [5]. NPP-VIIRS data offer substantial improvements from the DMSP-OLS data in terms of spatial resolution, dynamic range, quantization, calibrations, and the availability of suitable spectral bands for discriminating thermal sources of light emissions [42]. This study derived its NPP-VIIRS nighttime light and cloud-free days data from the Earth Observation Group and applied “vcm-orm-ntl” (VIIRS Cloud Mask–Outlier Removed–Nighttime Lights, in the following referred to as “VON data”) [43] to represent the intensity of artificial light at night and the number of cloud-free days (from now on referred to as “CVG data”) to determine the impact of nighttime clearness on dark sky observations.
3.1.2. PM2.5 Data
The atmospheric quality level is also one of the natural factors affecting the observation of the dark sky, in which PM2.5 is the most important factor leading to hazy weather and affecting atmospheric visibility. Research has indicated that among the various air pollutants, particulate matter (PM) has the strongest correlation with night sky brightness [44]. In this paper, we use the raster data on the annual mean PM2.5 [μg/m3] at 0.01° × 0.01°, obtained from the Atmospheric Composition Analysis Group (APAC), and select the data on the GBA to evaluate the atmospheric quality level.
3.1.3. Population Density
Population density is an important indicator of the population distribution in a region. It can also, to a certain extent, reflect the level of development and tourism potential of a region [45,46]. In this paper, population raster data with a spatial resolution of 1 km × 1 km was obtained from the Geographical Information Monitoring Cloud Platform to characterize the population distribution in the GBA.
3.1.4. Transportation Data
An appropriately located DSP requires easy access to the park for people to visit [47]. Therefore, we selected data on the distribution of highways, trunk roads, secondary roads, and expressways on the road network from the Open Street Map.
3.1.5. POI Data
An area’s tourism support capacity is also an important factor affecting the location of a DSP. POIs are a new type of spatial data that contains geographic information, such as name, category, address, latitude, and longitude coordinates [48]. They can represent the spatial distribution of various types of facilities in a city, reflecting the areas with intensive crowd activities, and, to a certain extent, the tourism support capacity of the region [49]. Synthesizing the site selection requirements for DSPs, this study selects the three aspects of catering, shopping, and accommodation services in the POI data from the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research (CAS) as its research object.
3.2. Research Methods
3.2.1. Fishnet
The regional grid is an important tool for applications analyzing raster data. Using the expanded section of the fishnet in ArcGIS10.7, several grids with rows and columns can be generated to resolve a problem more effectively. This offers a more convenient function for overlay analysis and property operations [50]. At the same time, the raster data from various studies usually have different resolutions, which can be harmonized using the fishing net tool [51]. The grid was set to 1 km × 1 km for analysis, covering the entire surface of the GBA.
3.2.2. Transportation Accessibility
Based on the cost–distance method, transportation accessibility is measured by constructing OD cost matrices and calculating the least expensive paths from each grid in the region to other grids [52].
3.2.3. Kernel Density
Kernel density estimation has become a common tool for empirical studies in any research area [53]. Using the kernel density tool in GIS, more than 1 million data points from the POI were analyzed to derive the distribution of infrastructure services in the region.
3.2.4. Normalization
The normalization method is used to eliminate the influence of the units and scales of each element, standardize the data, and unify the thresholds of each element to within the range of [0~1]. Normalization usually has two outcomes: the research objective is positively correlated with the standardized indicator (income-oriented), or the research objective is negatively correlated with the standardized indicator (cost-oriented). The specific formulas for the two types of normalization are as follows:
In the formulas, yi represents the normalized value of each factor, xi represents the initial value of the corresponding factor, max(xi) represents the maximum initial value of the corresponding factor, and min(xi) represents the minimum initial value of the corresponding factor.
3.2.5. Delphi Technique
The Delphi technique is used internationally to investigate a wide variety of issues. The aim was to develop an expert-based judgment regarding an epistemic question [54]. Comprehensive evaluation systems for parks typically encompass multi-dimensional indicators. The weights of these indicators must balance scientific rigor and practicality. The Delphi technique, through its structured expert consultation process, can transform subjective experiences into quantifiable weight values, which strongly aligns with the complex requirements of park evaluation. Therefore, in previous studies, the Delphi technique has often been used to determine the weights of various indicators in comprehensive park evaluation systems [55,56]. The technique is based on a questionnaire that allows experts to evaluate and score the importance of individual indicators; organize, summarize, and count them; and then anonymously feed them back to the experts to seek their opinions until a consensus is established (Figure 3). In this study, we solicited the opinions of nine experts of different age groups, professional backgrounds, and occupations (Table 1). The specific weighting is shown in Table 2, with E representing experts.

Figure 3.
Specific content of the questionnaire.

Table 1.
Basic information of experts.

Table 2.
Weighting of each element.
3.2.6. Quantification of Site Suitability
The site selection evaluation system constructed in this study has six influencing elements after normalization and multiplication, with the weights of each element being obtained using the Delphi technique for superposition analysis to establish the final DSP site suitability index. The formula is as follows:
In the formula, IDSPSSI represents the DSP site suitability index, INL represents the nighttime lighting data, ICVG represents the cloud-free days, IPM represents PM2.5, IPD represents the population distribution, ITA represents the transportation accessibility, ITSC represents the tourism support capacity, and α1–α6 represent the weights of each element.
4. Site Suitability Analysis of DSPs
4.1. Analysis of Single Elements
4.1.1. Nighttime Lighting Data
By combining the literature review above and the weight ratio obtained by means of the Delphi technique, it can be seen that the nighttime lighting situation is the primary factor affecting the site selection of DSPs, and the region with the lowest intensity of artificial light should be selected to the extent possible to avoid the influence of light pollution. As shown in Figure 4a, there are significant spatial differences in the GBA regarding artificial light. The eastern and southern parts of the central region and parts of the southern region are more affected by artificial light sources, while most other areas are slightly influenced. Among them, the areas that are most affected by light pollution are the central region of Guangzhou, the eastern region of Foshan City, Dongguan City, the coastal region of Shenzhen City, Hong Kong, and Macao. These cities are the areas with higher levels of economic development in the GBA. Therefore, light pollution is severe. Zhongshan City and Zhuhai City are less affected by artificial light sources, Zhaoqing City, Jiangmen City, and Huizhou City are the least affected by light pollution, and only small areas have a higher intensity of artificial light, which creates better conditions for the establishment of DSPs.
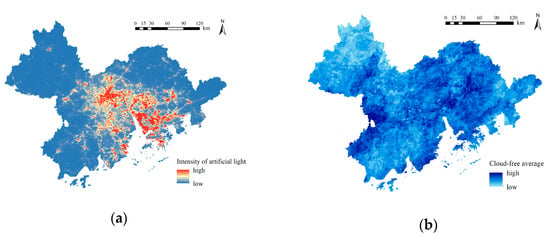
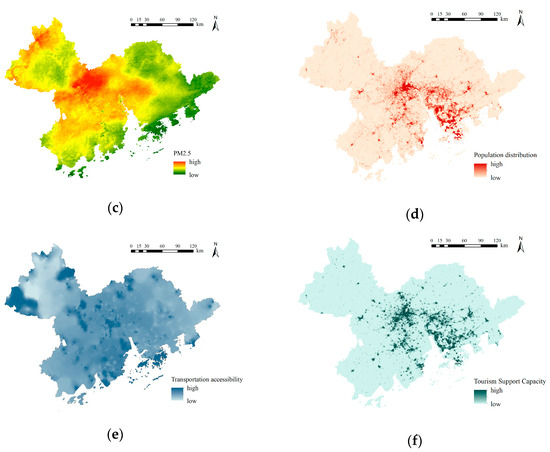
Figure 4.
Single-element site suitability grading: (a) nighttime lighting data; (b) cloud-free days; (c) PM2.5; (d) population distribution; (e) transportation accessibility; (f) tourism support capacity.
4.1.2. Cloud-Free Days
Cloud-free days are also an important factor in the process of evaluating potential DSP sites, reflecting the degree to which an area is obscured by cloud cover. More cloud-free days mean more opportunities to enjoy the night sky. As shown in Figure 4b, areas with many cloud-free days are concentrated in the southeastern coastal, central, and western regions of the GBA, mainly including the eastern central region of Guangzhou, the western region of Jiangmen City, the southeastern region of Zhaoqing City, the western and central regions of Huizhou City, and the western part of Zhuhai City, Shenzhen City, and Hong Kong, which is advantageous for the establishment of DSPs. The northwestern and eastern regions of the GBA are the middle and lower mountainous areas of the Nanling Mountains, mainly including the eastern parts of Zhaoqing City and Huizhou City, which are at a higher elevation than the other cities and more affected by cloudiness, with a poor quality of nighttime observations.
4.1.3. PM2.5
PM2.5 reflects the air quality in an area. Even a high-quality dark sky cannot be observed in an area with high levels of air pollution. As shown in Figure 4c, the region with the highest PM2.5 values is concentrated in the central and northwestern parts of the GBA, showing a clear patchy pattern, with Guangzhou City being the most populous urban area in the GBA. At the same time, Foshan City is more industrialized. Hence, the air pollution in Guangzhou and Foshan City is the most serious, and neighboring cities, including Dongguan City, Zhongshan City, and the northern part of Jiangmen City, are also more seriously affected. The air quality in the eastern and southwestern regions is relatively good, with the best air quality being found in Huizhou City, Shenzhen City, and the southern part of Jiangmen City, where the dark sky can therefore be observed more clearly, with less impact from air pollution.
4.1.4. Population Distribution
The population distribution can also influence the location of DSPs. Attracting more people is an important aim of establishing a park, and high population densities usually mean high levels of park usage. As shown in Figure 4d, the differences in the spatial distributions of populations between the cities in the GBA are relatively obvious, with a significant concentration in the central and southeastern coastal areas, mainly in the western and central parts of Guangzhou, Shenzhen, the eastern part of Foshan City, the central part of Zhongshan City, Dongguan City, Hong Kong, and Macao, which have high tourism potential. In contrast, the population distribution in the northern and southern parts of Zhaoqing City, Jiangmen City, Huizhou City, and Guangzhou City is relatively sparse.
4.1.5. Transportation Accessibility
A suitable site for a DSP should not only have good viewing conditions but also convenient transportation for people to get around. Based on the cost–distance method mentioned in Section 3.2.2, the accessibility of each grid is shown in Figure 4e. Most areas in the GBA have good accessibility, with the central and southeastern areas (such as Hong Kong, Macao, and central Guangzhou City) having good accessibility through convenient transportation, making it easy for people to reach the parks. The areas with worse accessibility are mainly concentrated in the peripheral areas of the GBA, including Zhaoqing City, Huizhou City, and Jiangmen City, whose transportation infrastructures are relatively poor and where further improvements in accessibility are required.
4.1.6. Tourism Support Capacity
A suitable site for a DSP requires good infrastructure and service facilities to enhance the travel experiences of tourists. The extent of shopping, catering, and accommodation services in a POI, as described in Section 3.1.5, could determine the tourism support capacity of a region. As shown in Figure 4f, areas with high tourism support capacities in the GBA are concentrated in the central and southeastern regions, mainly including the western part of Guangzhou City, the eastern part of Foshan City, Dongguan City, Shenzhen City, the central and northwestern parts of Zhongshan City, and the southern parts of Macao and Hong Kong, which have relatively well-developed city infrastructures to serve tourists visiting parks; in contrast, in the western, southern, and eastern parts of the GBA, i.e., Zhaoqing City, Huizhou City, Jiangmen City, and Zhuhai City, there are inadequate infrastructures to serve park visitors.
4.2. Analysis of Multifactor Overlays
4.2.1. DSP Suitability of Sites
The spatial distribution map of the suitability for DSPs of various sites in the GBA was ultimately developed through normalization of the raster data of the above six elements and a superposition analysis according to the weight values of each element, obtained using the Delphi technique. The DSP site suitability assessment was categorized into four zones based on the results: a high-suitability zone [0.54~0.75], medium-suitability zone [0.49~0.54], low-suitability zone [0.45~0.49], and unsuitable zone [0.32~0.45] (Table 3).

Table 3.
Site suitability classification.
As shown in Figure 5, the distribution of suitable sites for DSPs across the GBA is uneven. The highly suitable areas are concentrated in the northeastern, central–western, and southern parts of the GBA, mainly in the northern part of Guangzhou City, the central and northern parts of Huizhou City, the southwestern part of Foshan City, the central part of Shenzhen City, and the southern part of Zhuhai City, Hong Kong, and Macao. The medium-suitability areas are mostly located around the high-suitability areas, mainly in Guangzhou City, Huizhou City, Dongguan City, Shenzhen City, Zhongshan City, and Jiangmen City, as well as the southern part of Zhuhai City and the southwestern part of Zhaoqing City. Most of the western–central and southwestern regions are of low suitability, including the western part of Guangzhou, southeastern part of Zhaoqing City, central part of Foshan City, central and southern parts of Jiangmen City, and central part of Huizhou City. The area of unsuitability is distributed in patches, mainly concentrated in the northwestern part of the GBA, including Zhaoqing City and the northern part of Foshan City.
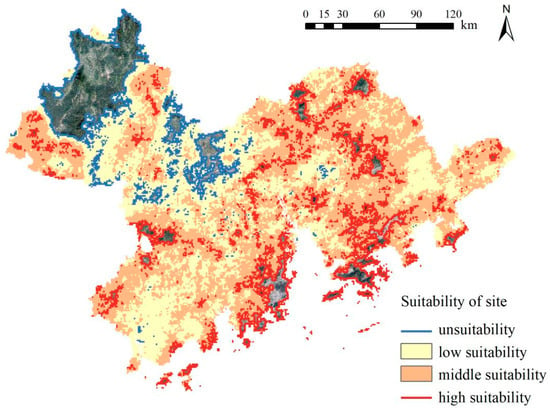
Figure 5.
DSP site suitability.
A comprehensive analysis of highly suitable areas for DSP site selection was combined with remotely sensed satellite imagery. Based on both the resource base and the development conditions, these areas were classified into two broad categories according to the main terrain, geomorphology, and land cover types, which included prominent types of ecological resources and economic development.
As can be seen from Figure 6, the most prominent types of ecological resources are contiguous natural forests, wetlands, and islands, which are located in the north of Guangzhou City, northwest and south of Huizhou City, south of Zhuhai City, and northwest and south of Jiangmen City. They are located a certain distance away from urban agglomerations, meaning that the impact of artificial light sources is lower, and they can also be easily accessible and have basic service facilities. Meanwhile, these areas would not be exposed to too much urban air pollution.
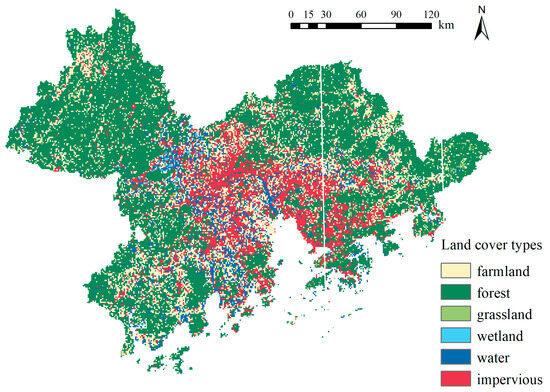
Figure 6.
Land cover types.
Combined with Figure 7, it can be seen that these places have a high altitude, which means that there are longer periods of cloud-free coverage, making it easier to observe dark starry skies. For example, the Guifeng Mountain Tourism Zone in Huizhou City is a highly suitable place for observing the dark starry night sky, as it is a scenic spot with rolling hills, forests, natural greenery, and water, with a favorable light environment and an excellent resource base. In addition, the surrounding cities, such as Dongguan City, Foshan City, and Guangzhou City, can be reached by means of convenient routes. At the same time, as a tourist area, it has existing facilities, which can attract tourists to travel to the area and enjoy the dark starry night sky. In summary, these areas are simultaneously characterized by excellent resource bases and relatively good development conditions, which is consistent with the results presented in Figure 8.
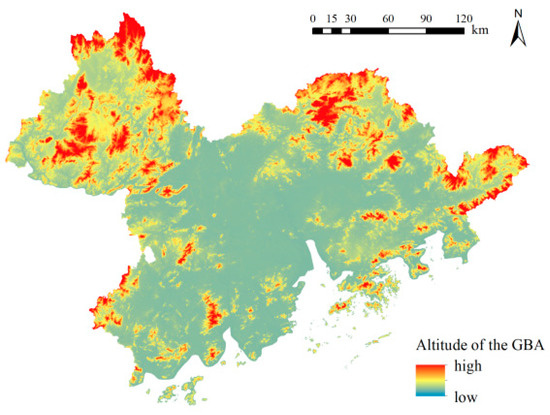
Figure 7.
Altitudes of the GBA.
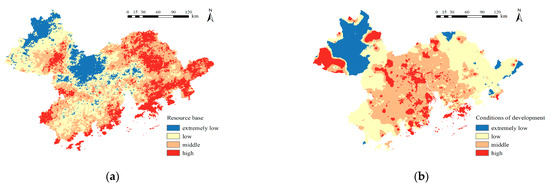
Figure 8.
(a) Resource base; (b) development conditions.
The area with the highest level of economic development is situated at the mouth of the Pearl River in the southern part of the GBA, mainly comprising the eastern–central parts of Zhongshan City, the southern and eastern parts of Zhuhai City, the central parts of Shenzhen City and Dongguan City, and the southern parts of Huizhou City, Guangzhou City, Hong Kong, and Macau. This region is developed economically, with sufficient capacity to support tourism and provide convenient transport services for tourists, while also being less affected by artificial light sources due to its coastal location. At the same time, these areas are mostly developed, with tertiary industries being found there (e.g., modern services, commerce). These areas produce less air pollution, and people can see the dark sky. For example, Jingshan Park in Zhuhai is close to a highly developed urban area with good transport links and sufficient capacity to support tourism. In addition, the industrial development in the vicinity is mostly dominated by tertiary industries, such as information technology and new energy, so air pollution, such as with PM2.5, is relatively low.
Furthermore, its proximity to the Pearl River makes it less affected by artificial light sources. Combining these conditions, Jingshan Park has a significant advantage in terms of establishing a DSP and fully utilizing the dark starry night sky. It can combine the facilities of the park and its coastal location to create a unique astronomical tourist attraction.
Additionally, through the specific analysis of unsuitable areas, we found that this type is mainly located in the central and northwestern parts of Zhaoqing City and the northern part of Foshan City. In terms of their resource base, the light environment in Zhaoqing and Foshan City is impacted by the process of industrial development. This is due to the large number of ceramic factories, coal-fired power plants, and tile factories. The consumption of coal is exceptionally high, and the lack of corresponding pollution control measures results in high PM2.5 levels in the air and severe air pollution. Air pollution also affects cloud cover, resulting in cloudy days, meaning that these areas lack good natural conditions for stargazing. Focusing on development conditions, the population density and tourism support capacity of Foshan City and Zhaoqing City are relatively low compared with the entire GBA. At the same time, the lack of transportation access in Zhaoqing City leads to a lack of an overall tourism service capacity. These two major shortcomings make these areas unsuitable locations of DSPs, since people cannot enjoy the view of the night sky.
4.2.2. Identification of Potential DSPs
In China, nature reserves are areas where long-term protection is implemented for important natural ecosystems, natural relics, and natural landscapes. They are more suitable as sites for dark sky preserves or dark sky sanctuaries in accordance with the DarkSky framework. Meanwhile, neither DarkSky nor CBCGDF has specific restrictions on the areas in which DSPs could be placed. Therefore, based on the results presented in Figure 9, we identified highly adaptable sites and overlaid them with the land use of nature reserves. Eventually, the potential spaces for establishing DSPs in the GBA were obtained. There are a total of 656 candidate sites that can serve as DSPs, accounting for 15.5% of the total area of the GBA. Among them, 13 have an area of over 100 square kilometers, 75 have an area ranging from 10 to 100 square kilometers, and 568 have an area of less than 10 square kilometers.
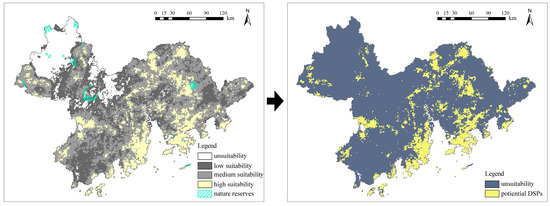
Figure 9.
Distribution of potential DSPs in GBA.
5. Discussion
This study developed a site selection system for DSPs based on six elements and the two aspects of resource base and development conditions. The study also analyzed the suitability of this site selection method for DSPs through a range of research methods, such as fishing nets, accessibility analysis, and the Delphi method. Finally, through an overlay analysis with nature reserves, potential spaces for establishing DSPs were obtained.
The research results indicate that the potential spaces for establishing DSPs are primarily distributed across two types of regions. The first type comprises ecologically prominent areas such as forests, wetlands, and islands, which benefit from their distance from urban light pollution, a high number of cloud-free days due to their high elevation, and basic transportation and tourism infrastructure. The second type includes economically developed coastal regions, which are characterized by low levels of industrial pollution, convenient transportation and good accessibility, and well-developed tourism services. This outcome aligns with the core requirement of DSPs to balance natural conditions and socio-economic support: ecologically prominent areas ensure inherent advantages in terms of their dark sky quality, while economically developed areas enhance the practical usability of parks through mature supporting facilities.
The coastal area and the island have obvious advantages for establishing a dark night park, with a generally excellent resource base and relatively good conditions for developing tours. Shenzhen Xichong, located in the southern coastal area of Shenzhen, is one of the best examples and was certified as the first international dark sky community in China in March 2023. Due to its favorable light environment, the Shenzhen Observatory was established, making this the best stargazing area in Xichong. Based on the observatory, several cultural and tourism projects related to the dark night sky have been established in the surrounding area. Meanwhile, the Xichong international dark sky community is promoting the development of dark sky and tourism economies by redesigning outdoor lighting facilities and restricting the intensity of artificial lighting at night to protect the lighting environment. Seizing this opportunity, the Shenzhen Urban Lighting Special Plan (2021–2035) also states that it will promote the establishment of the Dapeng Dark Sky Park in its surrounding area, publicize and implement the concept of dark sky protection, and create a DSP integrating dark sky protection, stargazing, astrophotography, popular science lectures, and coastal vacation tourism. It is also proposed that light pollution should be strictly controlled in the planned area to reduce the impact of artificial light pollution on stargazing and moon-watching activities.
Most previous studies focusing on the site selection of DSPs were conducted in areas that are located far from cities or around nature reserves [57]. In contrast, this study was carried out in the GBA, which has a high population density and a large urban population. This resulted in some differences in the selection of indicators for this study compared with previous ones. In terms of the selection and data acquisition of indicators along the resource background dimension, by integrating NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data (VON data) with calibrated DMSP-OLS data, this study compensated for the limitations of single data sources, thus reflecting the nighttime brightness at the regional scale more accurately. The PM2.5 indicator addresses the direct impact of air pollutants on dark sky observation, such as the reduced visibility caused by fine particulate matter, rectifying the underemphasis of atmospheric conditions in existing research. Meanwhile, previous studies on the site selection of DSPs mostly focused on resource background conditions and generally paid insufficient attention to socio-economic factors. In their study in southwestern Turkey, Aksaker et al. mainly relied on long-term artificial light data, cloud cover data, and elevation data to construct a site selection system. Although they identified potential areas, they did not analyze the tourism potential of these areas further [24]. The population and POI density, which were used as indicators along the development conditions dimension in this study, effectively reflect the tourism service capacity of a region, thereby mitigating the problem of identifying sites that are suitable in terms of natural conditions but lack operational viability, which often arises when focusing exclusively on natural factors. Transportation accessibility, quantified via the cost–distance method, resolves the limitation of previous studies that only considered geographic distance while neglecting the actual travel difficulty.
Additionally, although regions with favorable development conditions as potential spaces for establishing DSPs in terms of low levels of light pollution, their proximity to urban built-up areas makes them vulnerable to potential light interference. Thus, it is crucial to establish a comprehensive lighting management plan. Specific measures, including implementing time-based lighting management and specifying the types of lighting fixtures that can be used, are important supplementary steps to protect the quality of the dark sky in the subsequent phases.
6. Limitations
The system proposed in this study for evaluating the site selection of protected dark sky areas is a framework for testing and exploring site options, rather than a fixed model. The study used the Delphi method to assign weights to the six elements of the intensity of artificial light, cloud-free days, PM2.5, population density, transportation network, and POIs. However, this method is still partially subjective. Some of the studies of the suitability site selection indicated that the intensity of artificial light should be given a higher proportion in the weighting.
In contrast, the analysis results for population density and POIs have a high degree of similarity, which will cause some interference in the final site selection evaluation. Therefore, an objective and scientific method, such as the entropy value method [58], should be selected to determine the weights of the indicators to exclude the interference of a subjective factor. Moreover, this study evaluated the suitability of the proposed method for selecting DSP sites. Due to the limitations of objective measurements, this study only used remote sensing data and other data to classify the suitability of DSP sites across a large area. The final results are only for reference, rather than a definite and specific site selection plan. Subsequently, it is still necessary to measure the dark sky conditions and light pollution levels in the suitable areas according to the standards of international organizations and through means such as on-site investigations to obtain specific site selection results. In future research, the authors hope to use the Sky Quality Meter, a digital SLR camera [59], and other professional measurement tools to measure the brightness of the night sky in areas of high suitability as DSP sites. Combining local economic development and political conditions will help build a more complete DSP selection system [3].
7. Conclusions
Based on the two aspects of resource base and development conditions, this study constructed a site selection system for DSPs based on six elements. It analyzed the suitability of this site selection method for DSPs through research methods such as fishing nets, accessibility analysis, and the Delphi method. Finally, through an overlay analysis with nature reserves, the potential spaces for establishing DSPs were obtained, with the following conclusions. In most regions, the sites of all suitability classes showed a staggered distribution, with no clear zoning characteristics. Among them, the most suitable areas for DSPs were concentrated in the northeastern, central–western, and southern parts of the GBA. The medium-suitability areas were mostly centered around the high-suitability areas, and most of the western–central and southwestern regions were of low suitability. Additionally, low-suitability sites accounted for half of the area of the GBA, while medium- and high-suitability sites accounted for about one-third of the area. All these conditions indicate the difficulty of forming large-scale DSPs in the GBA, and that the main focus should be the establishment of small- to medium-sized DSPs. Additionally, the high-suitability areas were mostly mountainous and forested, with high elevations and a certain distance from the city, thus ensuring an excellent resource base and convenient transportation accessibility and tourism support systems. Simultaneously, the coastal area and the island had a clear advantage in establishing DSPs. Overall, the establishment of DSPs offers multiple benefits: ecologically, it mitigates light pollution, preserving critical habitats for nocturnal species and maintaining the balance of nighttime ecosystems; scientifically, the pristine dark sky conditions provide ideal environments for astronomical observation and research, fostering scientific exploration; and economically, it promotes ecotourism by attracting astronomy enthusiasts and nature lovers, thereby boosting local revenue, supporting community development, and aligning with the global trend of sustainable development. The GBA has a certain potential for the establishment of DSPs, and different types of DSPs can be established by taking the different topographies and processes of development of each region into account to attract the attention of potential visitors and protect the natural resources of the dark sky.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.; funding acquisition, Y.L. methodology, D.F.; software, Z.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.F. and Z.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.L., Z.H., H.H. and S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No.2022YFB3903405).
Data Availability Statement
The dataset is available on request from the authors: the raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Academic Specialty Group for Urban Sensing in the Chinese Society of Urban Planning for the support.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Deliang Fan, Yang Liu, Ziwen Huo and Huiwen He were employed by the company Guangzhou Urban Planning & Design Survey Research Institute Co., Ltd. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gallaway, T.; Olsen, R.N.; Mitchell, D.M. The economics of global light pollution. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaddle, J.P.; Francis, C.D.; Barber, J.R.; Cooper, C.B.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Dominoni, D.M.; Shannon, G.; Aschehoug, E.; Goodwin, S.E.; Kawahara, A.Y.; et al. A framework to assess evolutionary responses to anthropogenic light and sound. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasole, G.; Raap, T.; Costantini, D.; AbdElgawad, H.; Asard, H.; Pinxten, R.; Eens, M. Neither artificial light at night, anthropogenic noise nor distance from roads are associated with oxidative status of nestlings in an urban population of songbirds. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 210, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raap, T.; Casasole, G.; Pinxten, R.; Eens, M. Early life exposure to artificial light at night affects the physiological condition: An experimental study on the ecophysiology of free-living nestling songbirds. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, H.; Huang, Y. Association between nighttime artificial light pollution and sea turtle nest density along Florida coast: A geospatial study using VIIRS remote sensing data. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, L.F.B.; Davies, T.; Smyth, T.; Rodríguez, A.; Hamann, M.; Duarte, C.; Pendoley, K.; Berge, J.; Maggi, E.; Levy, O. Impacts of artificial light at night in marine ecosystems—A review. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5346–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, K.G.; Buler, J.J.; Anderson, S.J.; Burt, C.S.; Collins, A.C.; Dokter, A.M.; Guo, F.; Sheldon, D.; Tomaszewska, M.A.; Henebry, G.M. Artificial light at night is a top predictor of bird migration stopover density. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Duriscoe, D.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Portnov, B.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Furgoni, R. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.M.; Stokowski, P.A. Discursive constructions of night sky experiences: Imagination and imaginaries in national park visitor narratives. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 85, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, I.D. International Dark Sky Places. 2001. Available online: https://darksky.org/what-we-do/international-dark-sky-places/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Papalambrou, A.; Doulos, L.T. Identifying, Examining, and Planning Areas Protected from Light Pollution. The Case Study of Planning the First National Dark Sky Park in Greece. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamorano, J.; García, C.; Tapia, C.; de Miguel, A.S.; Gallego, J. STARS4ALL Night Sky Brightness Photometer. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 2017, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, T.; Binder, F.; Puschnig, J. Systematic measurements of the night sky brightness at 26 locations in Eastern Austria. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 211, 144–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinzano, P. Night Sky Photometry with Sky Quality Meter. Istil. Int. Rep. 2005, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Bará, S.; Tapia, C.E.; Zamorano, J. Absolute Radiometric Calibration of TESS-W and SQM Night Sky Brightness Sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschnig, J.; Posch, T.; Uttenthaler, S. Night sky photometry and spectroscopy performed at the Vienna University Observatory. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 139, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschnig, J.; Schwope, A.; Posch, T.; Schwarz, R. The night sky brightness at Potsdam-Babelsberg including overcast and moonlit conditions. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 139, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatanu, C.D. Luminance Measurements For Light Pollution Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electromechanical and Power Systems, Iasi, Romania, 11–13 October 2017; pp. 456–461. [Google Scholar]
- Jechow, A.; Ribas, S.J.; Domingo, R.C.; Hölker, F.; Kolláth, Z.; Kyba, C.C. Tracking the dynamics of skyglow with differential photometry using a digital camera with fisheye lens. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 209, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massetti, L.; Paterni, M.; Merlino, S. Monitoring Light Pollution with an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: A Case Study Comparing RGB Images and Night Ground Brightness. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barducci, A.; Marcoionni, P.; Pippi, I.; Poggesi, M.; Ehlers, M. Light pollution observed by MIVIS and VIRS 200 during a nocturnal remote sensing campaign over Italy. Remote Sens. Environ. Monit. Gis Appl. Geol. II 2003, 4886, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Barentine, J.C.; Walczak, K.; Gyuk, G.; Tarr, C.; Longcore, T. A Case for a New Satellite Mission for Remote Sensing of Night Lights. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Haim, A.; Portnov, B.A. Using kernel density function as an urban analysis tool: Investigating the association between nightlight exposure and the incidence of breast cancer in Haifa, Israel. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2009, 33, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksaker, N.I.; Kurt, Z.; Yerli, S.K.; Erdogan, M.A.; Karabacak, A.E.; Yalcin, A.U.; Uluc, K. Investigation of potential dark sky parks in Southwestern Turkiye. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 8486–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.W.; Lan, T.; Yu, M. Scenic Sites Selection in Dark-Sky Park Based on NPP/VIIRS: A Case Study in Fujian Province. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 154, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeco, J.A.; Wilkins, E.J.; Miller, A.B.; Lamborn, C.C.; Anderson, S.J.; Miller, Z.D.; Smith, J.W. Support for management actions to protect night sky quality: Insights from visitors to state and national park units in the U.S. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Hallo, J. Informing good lighting in parks through visitors’ perceptions and experiences. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 2019, 21, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothukuchi, K. Mitigating urban light pollution: A review of municipal regulations and implications for planners. J. Urban Aff. 2023, 47, 1663–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva, A.; Brown, E.; Evans, A.; Morris, D.; Dunning, K. Dark Sky Parks: Public policy that turns off the lights. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2023, 68, 907–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.L.; Rodrigues, A.; Peroff, D.M. The Sky and Sustainable Tourism Development: A Case Study of a Dark Sky Reserve Implementation in Alqueva. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2015, 17, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuda, M.; Pavličková, K.; Števová, J. Dark Sky Parks—New impulse for nature tourism development in protected areas (National Park Muranska Planina, Slovakia). E-Rev. Tour. Res. 2016, 13, 536–549. [Google Scholar]
- Collison, F.M.; Poe, K. “Astronomical Tourism”: The Astronomy and Dark Sky Program at Bryce Canyon National Park. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2013, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollath, Z. The effects of artificial lights at the Zselic Landscape Protection Area. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2008, 84, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, D.A.; Hickey, G.M. Managing light pollution through dark sky areas: Learning from the world’s first dark sky preserve. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2020, 63, 2627–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DarkSky. International Dark Sky Park Program Guideline. Available online: https://darksky.org/app/uploads/bsk-pdf-manager/2018/12/IDSP-Guidelines-2018.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Dark and Starry Sky Conservation Areas and Projects. Standard. Available online: https://www.ttbz.org.cn/StandardManage/Detail/23815/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Xu, N.; Zhang, F.; Xuan, X. Impacts of industrial restructuring and technological progress on PM2. 5 pollution: Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baugh, K.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T.; Ziskin, D. Development of a 2009 Stable Lights Product using DMSP-OLS data. Proc. Asia-Pacific Adv. Netw. 2010, 30, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, T.R.K.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Elvidge, C.D.; Tuttle, B.T. Spatial characterization of electrical power consumption patterns over India using temporal DMSP-OLS night-time satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Straka, W.; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lee, T.F.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.K.; Weiss, S.C. Illuminating the Capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Day/Night Band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.-C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.D.; Molthan, A.; Schultz, L.; Bell, J.; Stokes, E.C.; Pandey, B.; et al. NASA’s Black Marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Su, X. Impact of urban air pollutants on the night sky brightness and color in Hohhot. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 96, 104671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Liu, Y. Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages Distribution in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Xu, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y. Spatial Distribution, Accessibility, and Influencing Factors of the Tourism and Leisure Industry in Qingdao, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Huang, R.H.; Zhang, J.S. US national parks accessibility and visitation. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 2894–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Fang, J. A diverse and personalized POI recommendation approach by integrating geo-social embedding relations. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 226309–226323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zou, C.; Shu, C.; Zhang, M.; Feng, H. Research on Site Selection Planning of Urban Parks Based on POI and Machine Learning—Taking Guangzhou City as an Example. Land 2024, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Dong, X.; Xin, W. Benefit assessment of soil and water conservation from cropland to forest in hilly Loess Plateau at Qinghai. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopeliti, A.; Stamou, L.; Tsoulos, L.; Pe’eri, S. Generalization of soundings across scales: From DTM to harbour and approach nautical charts. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. Bayesian inference for origin-destination matrices of transport networks using the EM algorithm. Technometrics 2005, 47, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, N.B.; Schindler, A.; Sperlich, S. Bandwidth Selection Methods for Kernel Density Estimation—A Review of Performance. SSRN Electron. J. 2010, 97, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niederberger, M.; Spranger, J. Delphi Technique in Health Sciences: A Map. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zheng, G. An Evaluation of National Park System Pilot Area Using the AHP-Delphi Approach: A Case Study of the Qianjiangyuan National Park System Pilot Area, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Oladi, J.; Amirnejad, H. The evaluation of environmental, economic and social services of national parks. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 9052–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, G.; Guebsi, R.; Guessoum, N.; Flamant, C. Search for Best Astronomical Observatory Sites in the MENA Region using Satellite Measurements. Front. Theor. Appl. Phys. UAE 2017, 869, 012070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Y. Complexity quantification for overhead transmission line emergency repair scheme via a graph entropy method improved with petri net and ahp weighting method. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jechow, A.; Hölker, F.; Kolláth, Z.; Gessner, M.O.; Kyba, C.C. Evaluating the summer night sky brightness at a research field site on Lake Stechlin in northeastern Germany. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2016, 181, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).