Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Copper in Soil Using Bacteria: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
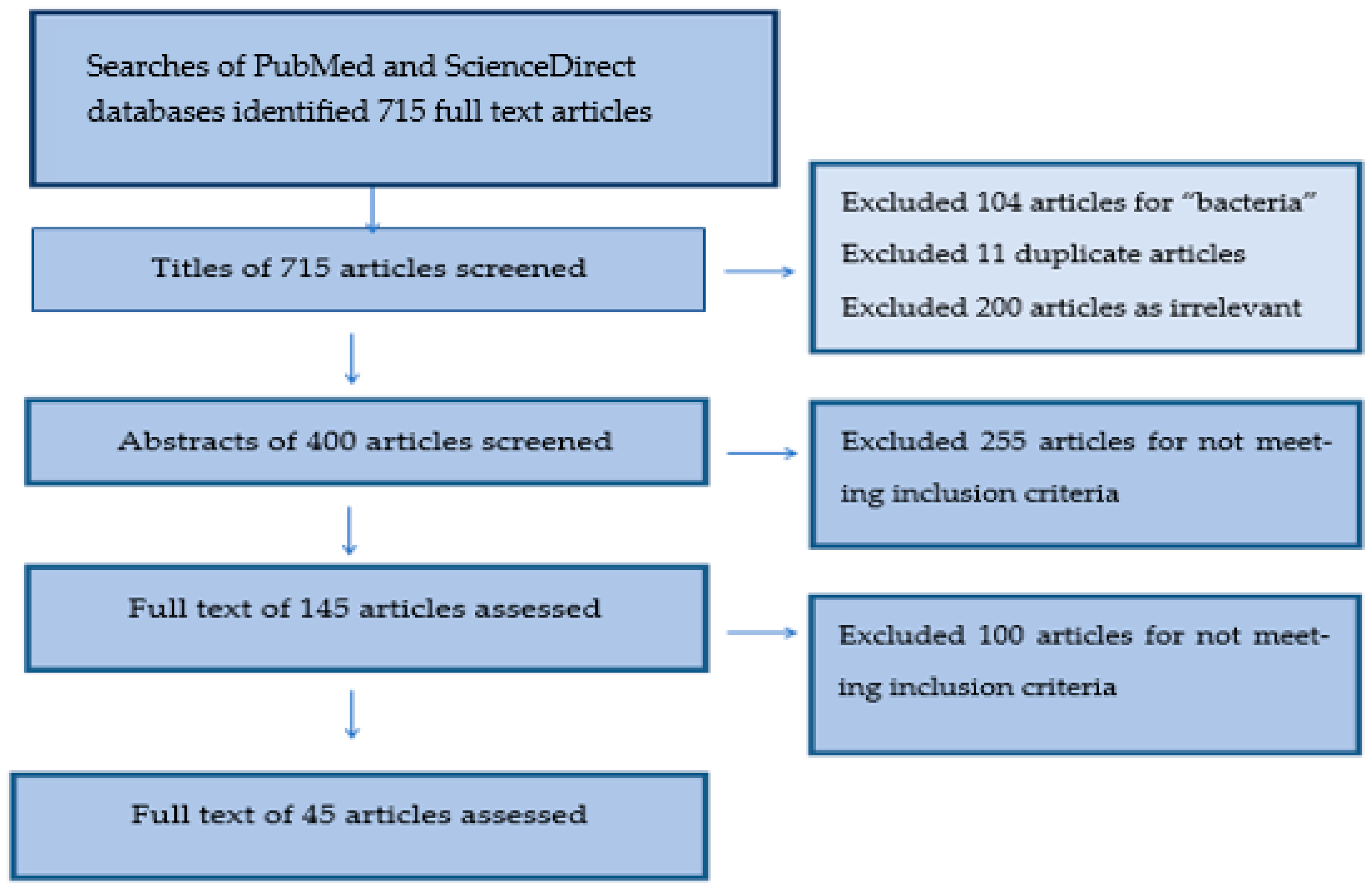
2. Materials and Methods
- Scientific articles investigating the use of bacteria for the immobilization of cadmium, lead, and copper in contaminated soils.
- Articles that presented data on the concentrations of these heavy metals before and after treatment with bacteria.
- Studies describing the bacterial strains or consortia used for heavy metal immobilization.
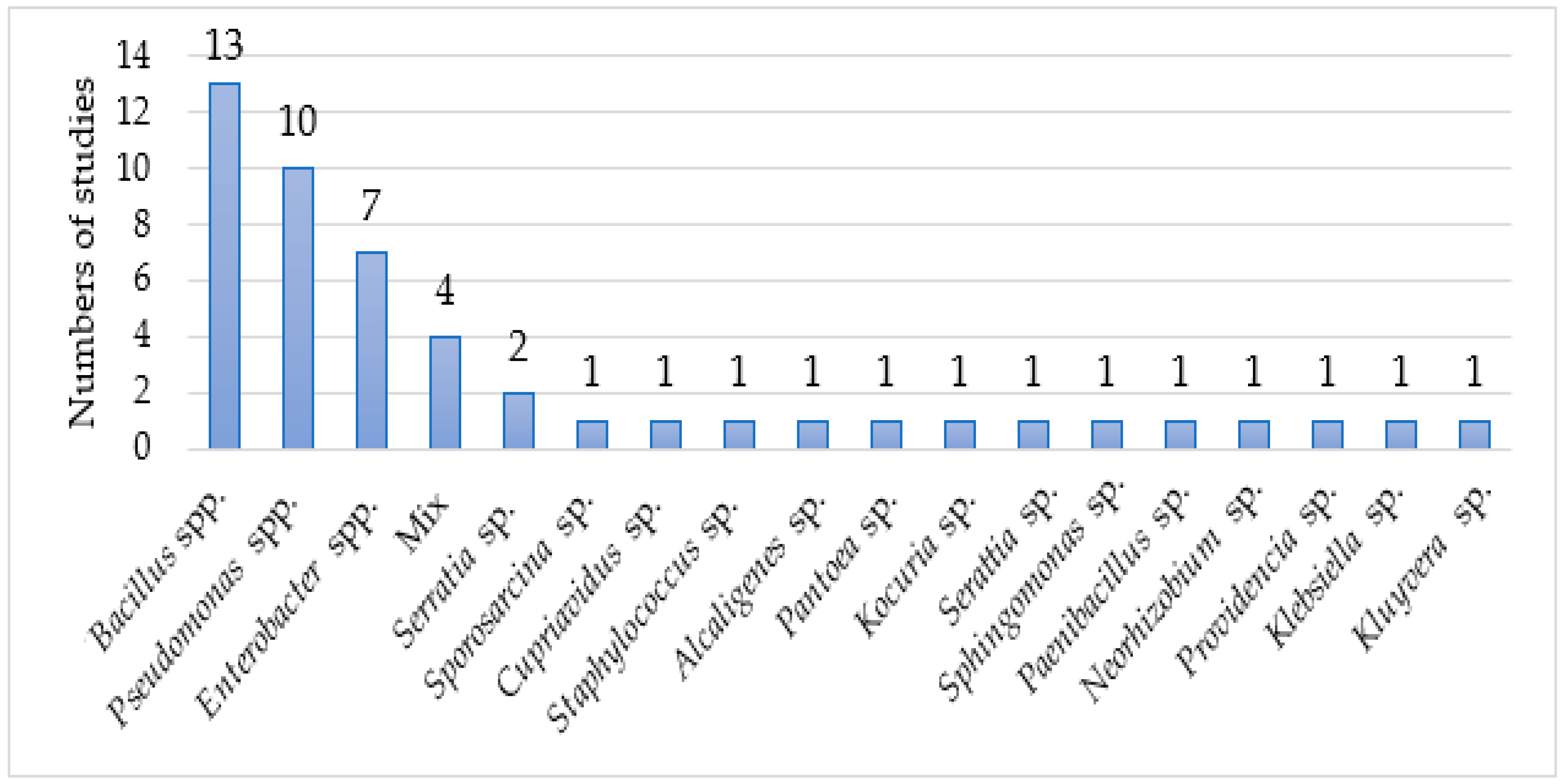
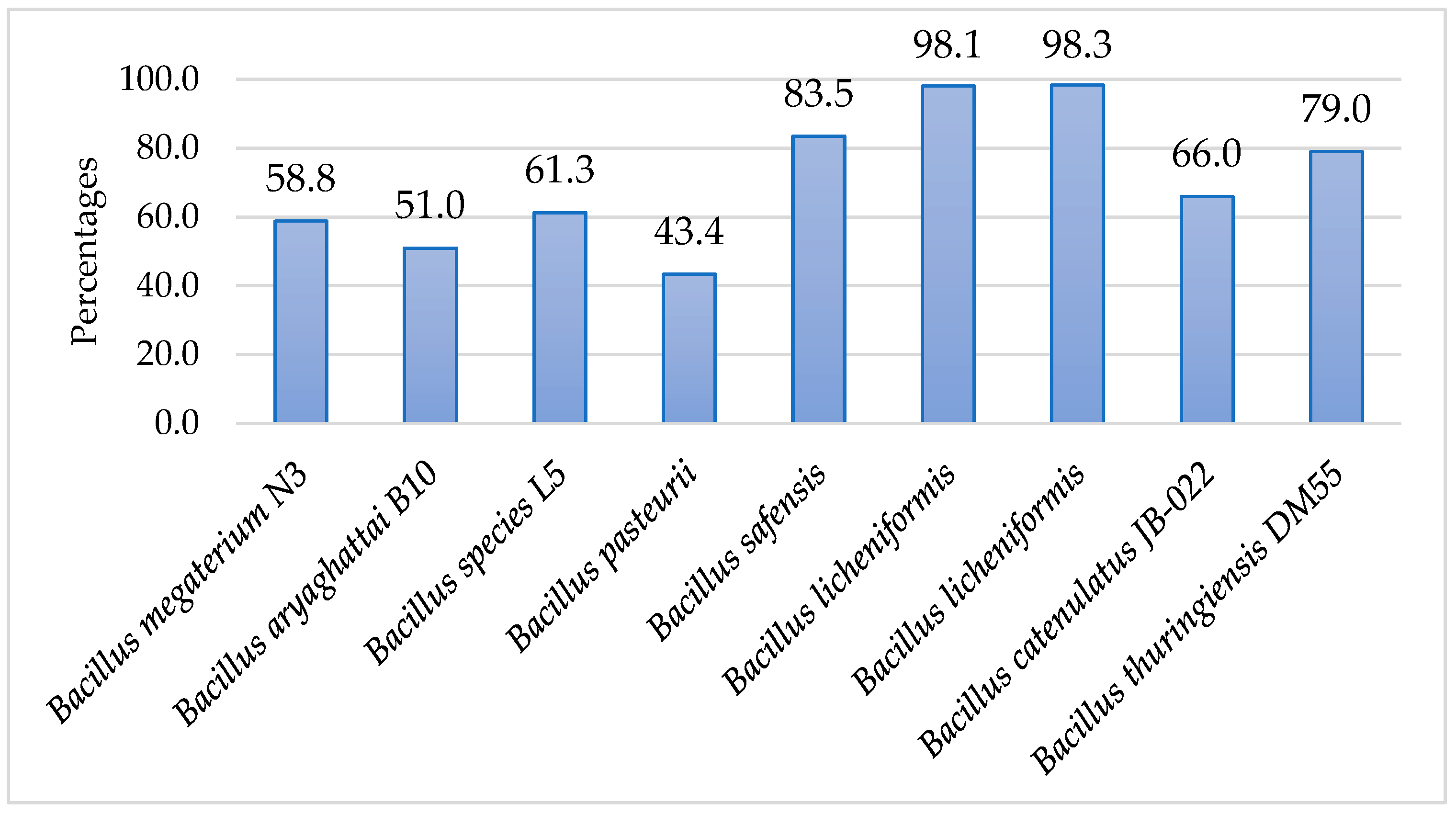
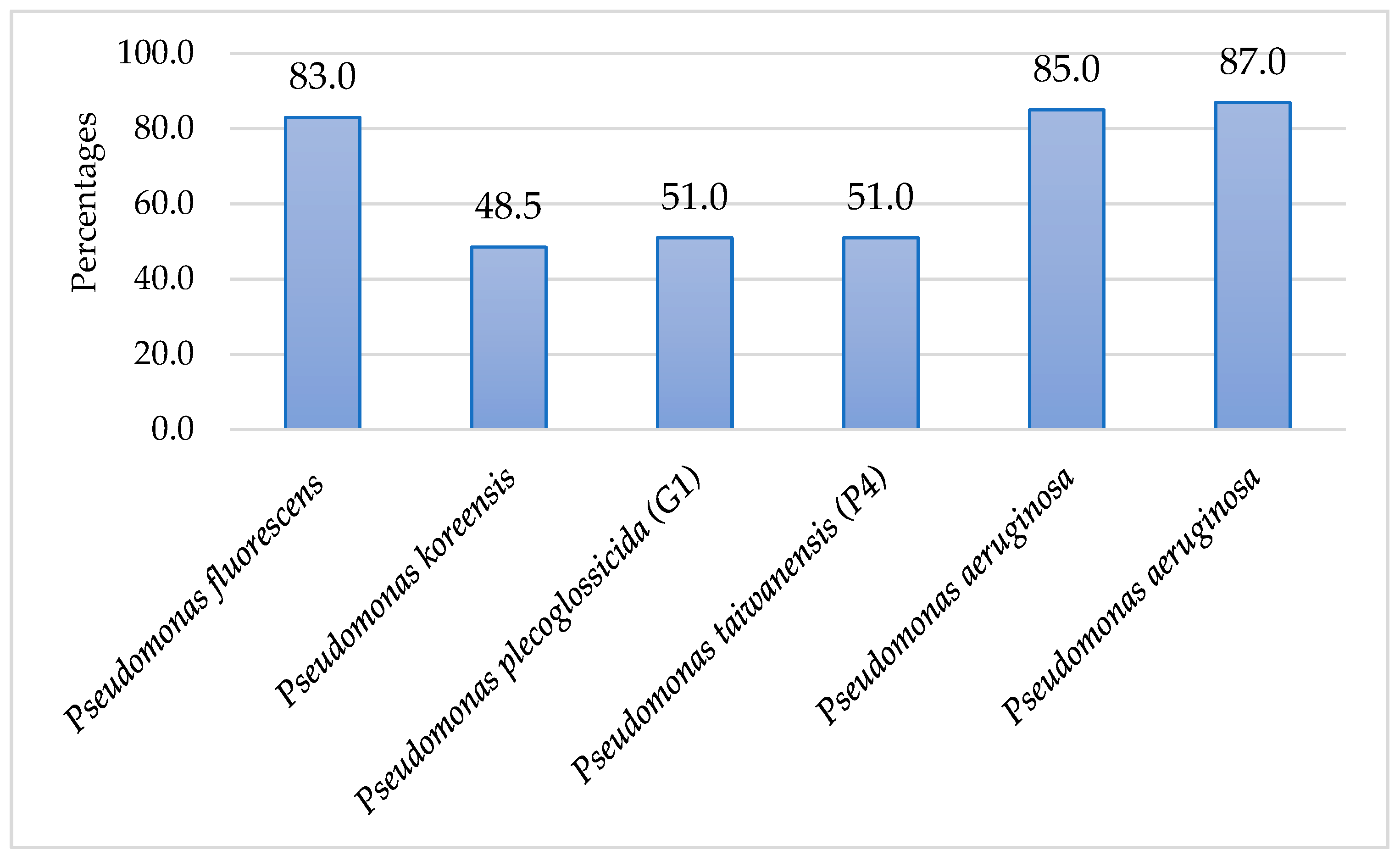
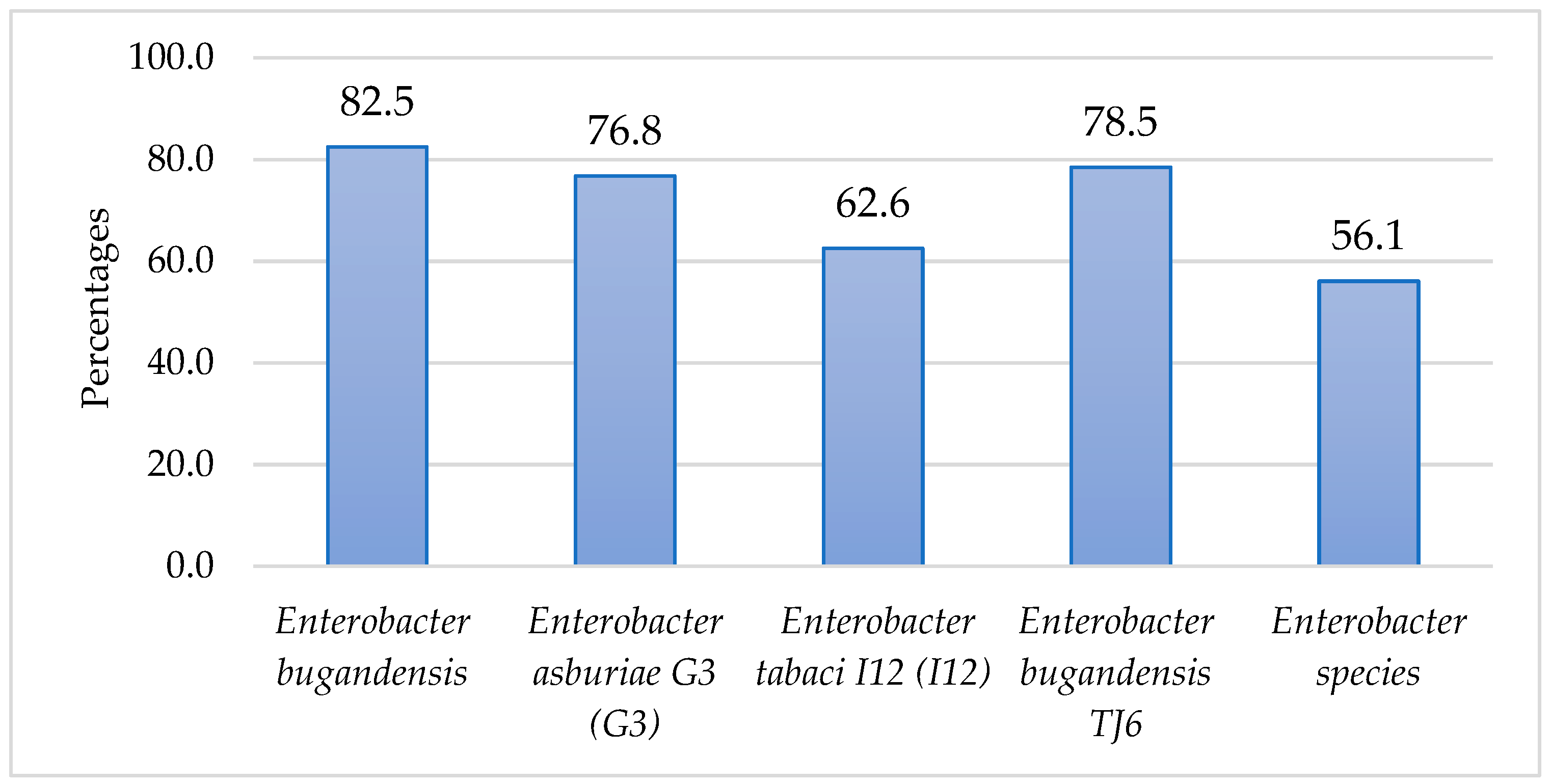
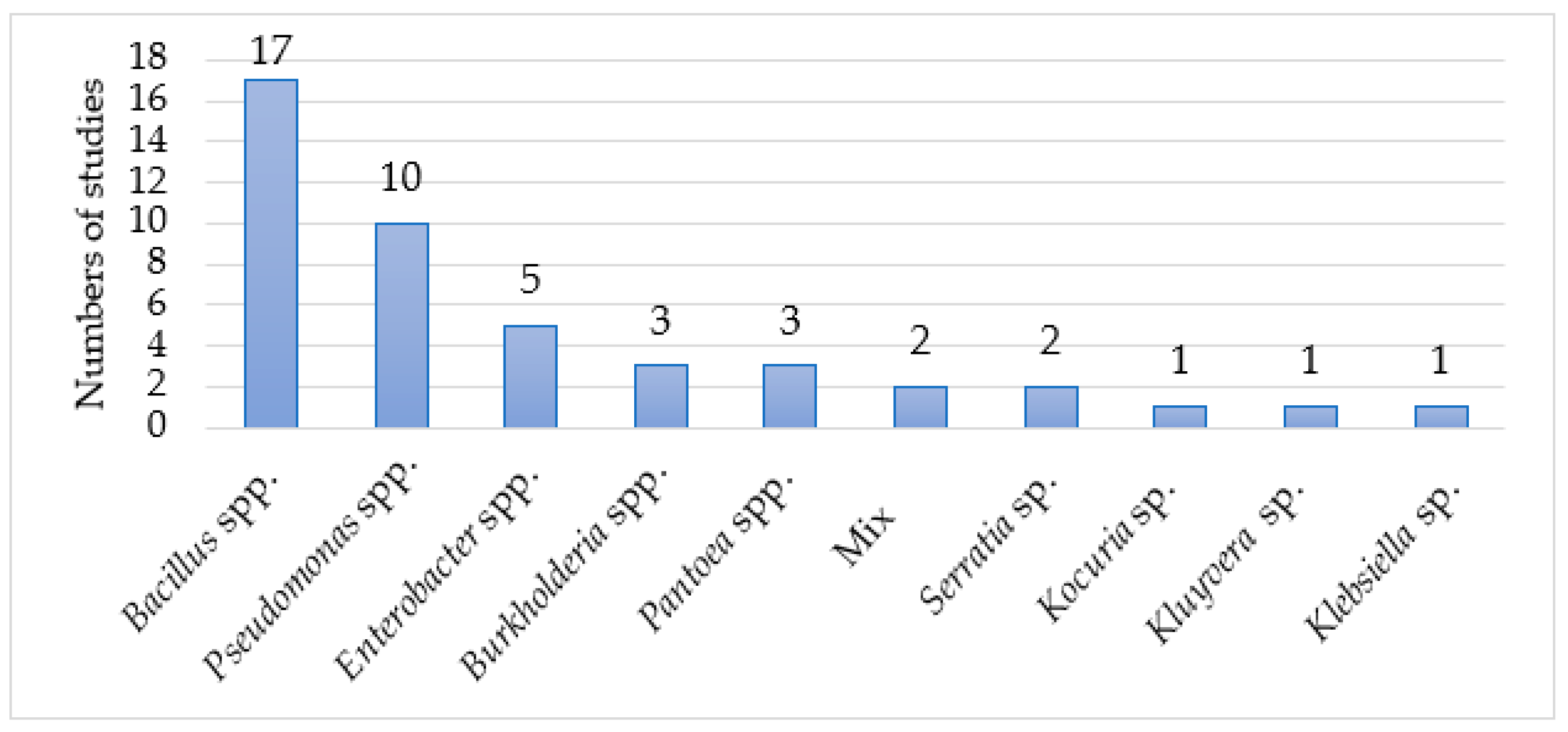
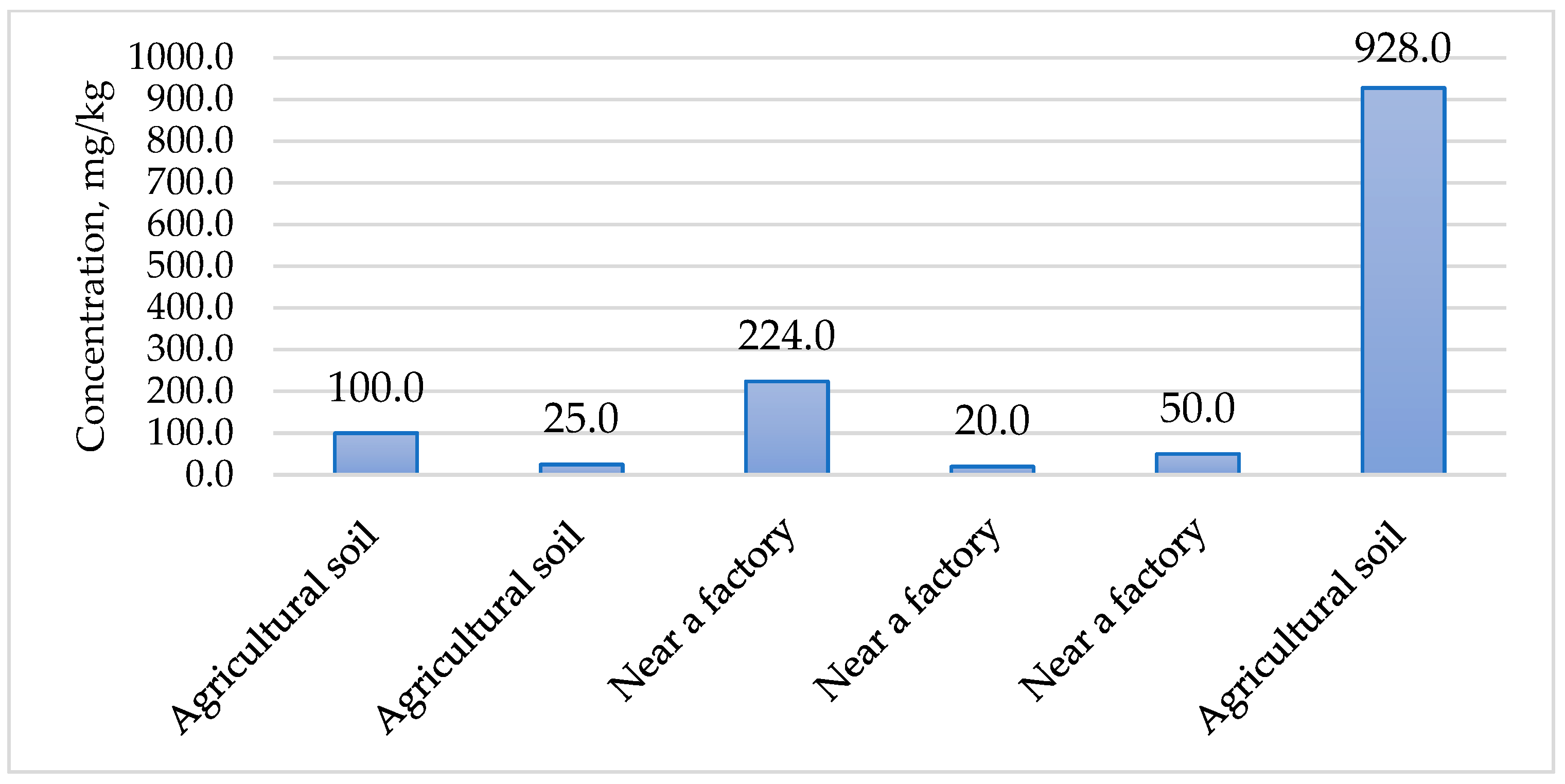
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MICP | Microbially induced carbonate precipitation |
| Spp. | Species (plural) |
| Sp. | Species (singular) |
References
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kumar, V. Heavy metal toxicity: An update of chelating therapeutic strategies. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 54, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Y.; Wu, H.S.; Ma, X.L.; Tang, Y.J.; Li, J.; Chai, Y.; Wang, C.M.; Yang, H.C. Review on the Effects of Combined Pollution of Lead and Chromium on Soil Microorganisms and Treatment Methods. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2020, 8, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; He, L.; Niazi, K.N.; Wang, H.; Gustave, W.; Vithanage, M.; Geng, K.; Shang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Nanobiochar for the remediation of contaminated soil and water: Challenges and opportunities. Biochar 2023, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O. Metal(loid) bioremediation: Strategies employed by microbial polymers. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotaniya, M.L.; Kumar, K.; Dotaniya, C.K.; Doutaniya, R.K. Type of Soil Pollutant and Their Degradation: Methods and Challenges. In Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Hao, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Ye, Y.; Lu, A. Microbial remediation mechanisms and applications for lead-contaminated environments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, S.; Dhanjal, S.D.; Datta, S.; Sharma, D.; Singh, N.K.; Singh, R. Biosurfactant-based bioremediation. In Bioremediation of Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, S.; Sahid, M.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Al-Kahtani, A.; Muztaza, B.; Dumat, C. Predicting chemical speciation of metals in soil using Visual Minteq. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2023, 5, 220162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, B.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qu, C.; Tang, J.; Wu, Y.; Tan, W.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, T. The relationships between heavy metals and bacterial communities in a coal gangue site. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzel, T.; Hahad, O.; Daiber, A.; Landrigan, P.J. Soil and water pollution and human health: What should cardiologists worry about? Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, V.; Pandey, S.C.; Sati, D.; Bhatt, P.; Samant, M. Microbial Interventions in Bioremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminants in Agroecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 824084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Zhang, Y. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater and fixation of heavy metals in soil by manganese dioxide nanosorbents with tailored hollow mesoporous structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandali, M.V.; Safarzadeh, S.; Ghasemi-Fasaei, R.; Zeinali, S. Heavy metals immobilization and bioavailability in multimetal contaminated soil under ryegrass cultivation as affected by ZnO and MnO2 nanoparticle-modified biochar. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, D.K. Multimetal resistance and potential of Alcaligenes sp. MMA for the removal of heavy metals. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Deb, B.; Sharma, I.; Pandey, P. Role of Cadmium and Lead Tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Seedling Germination of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Xiao, X.; Wan, Y.; An, H.; Luo, X.; Luo, S. Exceptional anti-toxic growth of water spinach in arsenic and cadmium co-contaminated soil remediated using biochar loaded with Bacillus aryabhattai. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratush, A.; Kumar, A.; Hu, Z. Adverse effect of heavy metals (As, Pb, Hg, and Cr) on health and their bioremediation strategies: A review. Int. Microbiol. 2018, 21, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Huang, S.; Xu, T.; Lin, Z.; Wu, J. Competitive adsorption, immobilization, and desorption risks of Cd, Ni, and Cu in saturated-unsaturated soils by biochar under combined aging. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, P.; Shukla, A.; Goswami, D.; Gaur, S.; Patel, B.; Saraf, M. Comprehensive depiction of novel heavy metal tolerant and EPS producing bioluminescent Vibrio alginolyticus PBR1 and V. rotiferianus PBL1 confined from marine organisms. Microbiol. Rec. 2020, 238, 126526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, D.; Magotra, S.; Negi, R.; Kumar, S. Bacillus species for sustainable management of heavy metals in soil: Current research and future challenges. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2023, 202, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desoky, E.M.; Merwadb, A.R.M.; Semidac, W.M.; Ibrahima, S.A.; El-Saadonyd, M.T.; Rady, M.M. Heavy metals-resistant bacteria (HM-RB): Potential bioremediators of heavy metals-stressed Spinacia oleracea plant. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocca, V.F.B.; Corrêa, G.G.; Lins, M.R.D.C.R.; de Jesus, V.N.; Tavares, L.F.; Amorim, L.A.D.S.; Kundlatsch, G.E.; Pedrolli, D.B. The CRISPR toolbox for the gram-positive model bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, O.P.; Oyewole, O.A.; Oyeleke, S.B.; Adeyemi, M.O.; Orukotan, A.A. Biosorption of lead, chromium and cadmium in tannery effluent using indigenous microorganisms. Braz. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 5, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapahi, M.; Sachdeva, S. Bioremediation options for heavy metal pollution. J. Health Pollut. 2019, 9, 191203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarekegn, M.M.; Salilih, F.Z.; Ishetu, A.I. Microbes used as a tool for bioremediation of heavy metal from the environment. Cog. Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1783174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wu, X.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Xu, H. Characteristics and in situ remediation effects of heavy metal immobilizing bacteria on cadmium and nickel co-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.F.; Recalde, A.; Orell, A.; Albers, S.-V.; Paradela, A.; Navarro, C.A. Global effect of the lack of inorganic polyphosphate in the extremophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus: A proteomic approach. J. Proteom. 2019, 191, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, F.; Jin, Z.; Yang, Y. Acidic leaching of potentially toxic metals cadmium, cobalt, chromium, copper, nickel, lead, and zinc from two Zn smelting slag materials incubated in an acidic soil. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Cai, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yao, L. Heavy metal immobilizing bacteria increase the biomass and reduce the Cd and Pb uptake by pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) in heavy metal-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cai, D.; Ji, M.; Chen, Z.; Yao, L.; Han, H. Isolation of heavy metal immobilizing and plant growth-promoting bacteria and their potential in reducing Cd and Pb uptake in water spinach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Gao, H.; An, F.; Ma, X.; Hua, L.; Guo, J. Performance of heavy metal-immobilizing bacteria combined with biochar on remediation of cadmium and lead co-contaminated soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6009–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pang, H.D.; He, L.Y.; Wang, Q.; Sheng, X.F. Cd immobilization and reduced tissue Cd accumulation of rice (Oryza sativa wuyun-23) in the presence of heavy metal-resistant bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Dai, C.; Sheng, M.; Chen, Q.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Multiple heavy metals immobilization based on microbially induced carbonate precipitation by ureolytic bacteria and the precipitation patterns exploration. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wu, X.; Yao, L.; Chen, Z. Heavy metal-immobilizing bacteria combined with calcium polypeptides reduced the uptake of Cd in wheat and shifted the rhizosphere bacterial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, H.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q.J.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Tang, J.; Ma, L. The Immobilization of Soil Cadmium by the Combined Amendment of Bacteria and Hydroxyapatite. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, Q.; Achal, V. Heavy Metals Immobilization in Soil with Plant-growthpromoting Precipitation in Support of Radish Growth. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 48, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didi, Z.A.; Attia, E.; Ahmad, M.I.; Zouari, N. Immobilization of heavy metals by microbially induced carbonate precipitation using hydrocarbon-degrading ureolytic bacteria. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 35, e00747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Gou, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, S.; Ali, I.; Shang, R.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Han, M.; Luo, X. Application of mixed bacteria-loaded biochar to enhance uranium and cadmium immobilization in a co-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaun, Z.; Yi, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yao, J. Application of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in immobilization of Pb and Cd in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21877–21884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yao, L.; Han, H. Improving radish phosphorus utilization efficiency and inhibiting Cd and Pb uptake by using heavy metal-immobilizing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Qiao, S.; Luo, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, L.; Hou, S.; Wu, B.; Xu, H. Performance of microbial induced carbonate precipitation for immobilizing Cd in water and soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Lin, L.; Feng, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Z. Screening of cadmium-chromium-tolerant strains and synergistic remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil using king grass combined with highly efficient microbial strains. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, P.; Sanaeizade, S.; Mazloomi, F. Removal of nickel, copper, lead and cad-mium by new strains of Sphingomonas melonis e8 and Entero-bacter hormaechei WW28. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 7, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zuo, H.; Wei, Z. Roles of different humin and heavy-metal resistant bacteria from composting on heavy metal removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 296, 122375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O.; Aremu, O.S. Bioflocculant production and heavy metal sorption by metal resistant bacterial isolates from gold mining soil. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atuchin, V.V.; Asyakina, L.K.; Serazetdinova, Y.R.; Frolova, A.S.; Velichkovich, S.N.; Prosekov, A.U. Microorganisms for Bioremediation of Soils Contaminated with Heavy Metals. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Yue, C.; Si, Y. Biogenic calcium improved Cd2+ and Pb2+ immobilization in soil using the ureolytic bacteria Bacillus pasteurii. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Zang, F.; Ilga, D.; Wu, Y.; Wangas, Y.; Nan, Z. Simultaneous immobilization of multiple heavy metal(loid)s in contaminated water and alkaline soil inoculated Fe/Mn oxidizing bacterium. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, B.S.; Khan, M.; Shamim, S. Unraveling the underlying heavy metal detoxi fication mechanisms of Bacillus species. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaima, K.K.; Mohamed, A.I.; Meshhdany, W.A.Y.; Abdulhassan, A.A. Resistance and bioadsorption of cadmium by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from agricultural soil. IJAES 2017, 12, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Karimpour, M.; Ashrafi, S.D.; Taghavi, K.; Mojtahedi, A.; Roohbakhsh, E.; Naghipour, D. Adsorption of cadmium and lead onto live and dead cell mass of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A dataset. Data Brief 2018, 18, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aka, R.J.N.; Babalola, O.O. Effect of bacterial inoculation of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Alcaligenes feacalis and Bacillus subtilis on germination, growth and heavy metal (Cd, Cr, and Ni) uptake of Brassica juncea. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2016, 18, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Wei, J.; Guan, F.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, Y. Biochar and bacteria inoculated biochar enhanced Cd and Cu immobilization and enzymatic activity in a polluted soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lv, B.; Shang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Yu, X. The immobilization effects on Pb, Cd and Cu by the inoculation of organic phosphorus-degrading bacteria (OPDB) with rapeseed dregs in acidic soil. Geoderma 2019, 350, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, M.S.; Hamme, J.V.; Bundschuh, J.B.; Khan, N.M.; Salam, A.; Waqar, M.; Munis, H.F.M.; Chaudhary, H.J. Biotechnological approaches in agriculture and environmental management—Bacterium Kocuria rhizophila 14ASP as heavy metal and salt- tolerant plant growth- promoting strain. Biologia 2021, 76, 3091–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Jung, A.-J.; Joo, J.H. Biosorptive Capacity of Cd(II) and Cu(II) by Lyophilized Cells of Pseudomonas stutzeri. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyalaxmi, R.; Murugan, A.; Raja, P.; Raj, K.D. Bioremediation of cadmium by Bacillus safensis (JX126862), a marine bacteriumisolated from mangrove sediments. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 326–335. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, S.A.; Rajaganesh, K. Microbial bioremediation of heavy metals from textile industry dye effluents using isolated bacterialstrains. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jin, M.R.; Chung, C.H.; Yun, Y.-S.; Jahng, K.Y.; Yu, K.-Y. Biosorption of cationic basic dye and cadmium by the novelbiosorbent Bacillus catenulatus JB-022 strain. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basitas, A.; Andleeb, S.; Liaqatas, I.; Ali, A.Š.; Naseer, A.; Nazir, A.; Kiyani, F. Characterization of heavy metal-associated bacteria from petroleum-contaminated soil and their resistogram and antibiogram analysis. Folia Microbiol. 2024, 69, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashola, M.O.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Babalola, O.O. Heavy Metal Immobilization Potential of Indigenous Bacteria Isolated from Gold Mine Tailings. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2020, 14, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Bolan, N.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Isolation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their potential for lead immobilization in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, C.; Shi, J.; He, B.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z. Biomineralization mechanism and remediation of Cu, Pb and Zn by indigenous ureolytic bacteria B. intermedia TSBOI. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Rane, R.N.; Xing, C.; Patil, M.S.; Roh, H.S.; Jeon, B.H.; Li, X. Integrative chemical and omics analyses reveal copper biosorption and tolerance mechanisms of Bacillus cereus strain T6. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Goli, D. Bioremediation of lead by a halophilic bacteria Bacillus pumilus isolated from the mangrove regions of Karnataka. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 9, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, H.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, W. Bioimmobilization of lead by Bacillus subtilis X3 biomass isolatedfrom lead mine soil under promotion of multiple adsorption mechanisms. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.-H.; Liu, R.-X.; Tang, H.-X. Surface reaction of Bacillus cereus biomass and its biosorption for lead and copper ions. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifiyanto, A.; Apriyanti, F.D.; Purwaningsih, P.; Kalqutny, S.H.; Agustina, D.; Surtiningdih, T.; Shovitri, M.; Zulaika, E. Lead (Pb)bioaccumulation; genera Bacillus isolated S1 and SS19 as a case study. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1854, 020003. [Google Scholar]
- Cephidian, A.; Makhdoumi, A.; Mashreghi, M.; Mahmudy Gharaie, M.H. Removal of anthropogenic lead pollutions by a potent Bacillus species AS2 isolated from geogenic contaminated site. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, T.M.; Sivakumar, N.; Al-Ansari, A.; Victor, R. Bioremediation of copper by active cells of Pseudomonas stutzeri LA3 isolated from an abandoned copper mine soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y. Tolerance and biosorption of copper and zinc by Pseudomonas putida CZ1 isolated from metal-polluted soil. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohini, B.; Jayalakshmi, S. Bioremediation potential of Bacillus cereus against copper and other heavy metals. Int. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Sci. 2015, 2, 200–209. [Google Scholar]
- Karakagh, R.M.; Chorom, M.; Motamedi, H.; Kalkhajeh, Y.K.Y.; Oustan, S. Biosorption of Cd and Ni by inactivated bacteriaisolated from agricultural soil treated with sewage sludge. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2012, 12, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tirado, V.; Green-Ruiz, C.; Gómez-Gil, B. Cu and Pb biosorption on Bacillus thioparans strain u3 in aqueous solution: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oves, M.; Khan, M.S.; Zaidi, A. Biosorption of heavy metals by Bacillus thuringiensis strain OSM29 originating from industrial effluent contaminated north Indian soil. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

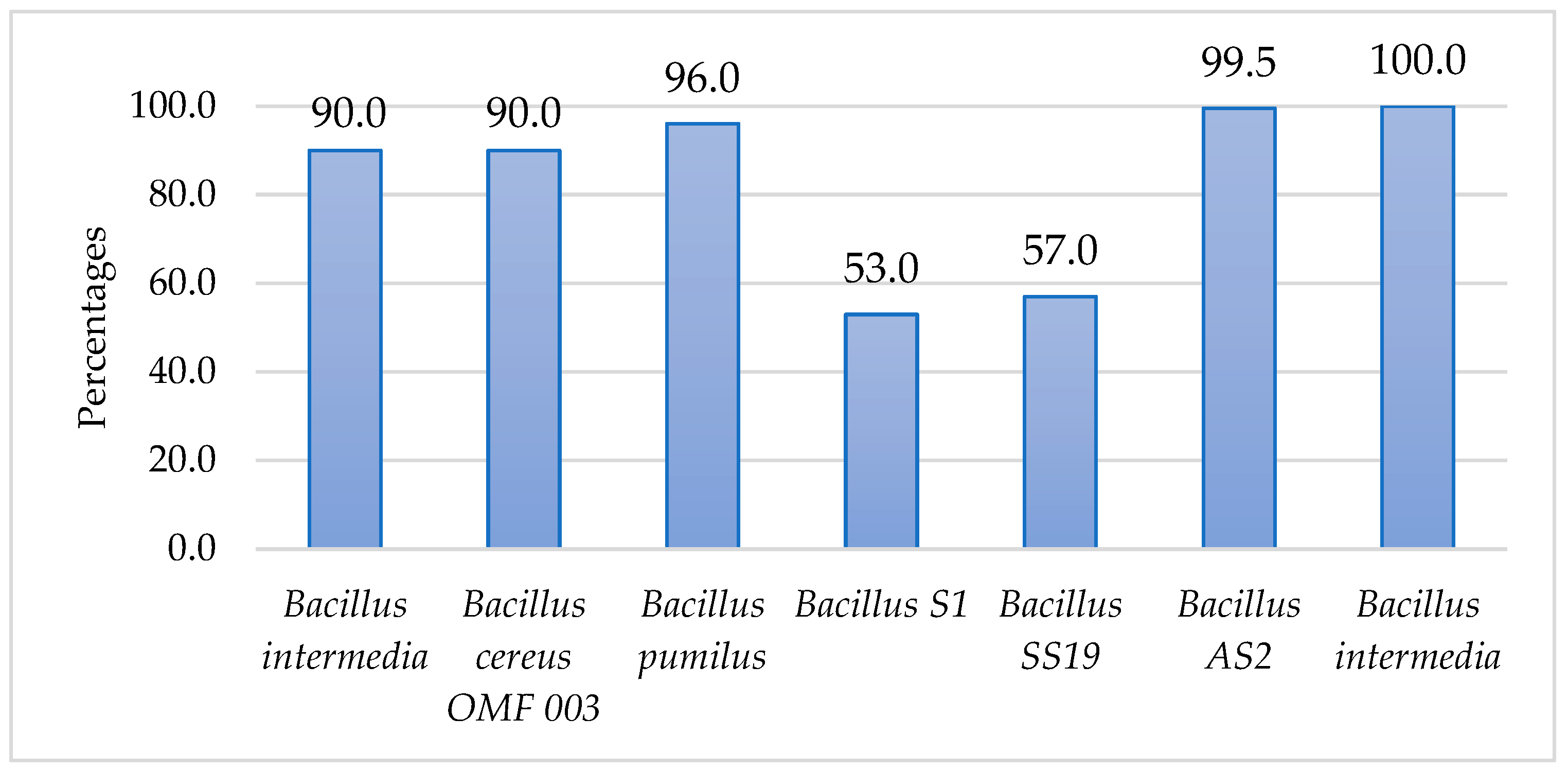

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasarevičius, S.; Paliulienė, V. Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Copper in Soil Using Bacteria: A Literature Review. Land 2025, 14, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081547
Vasarevičius S, Paliulienė V. Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Copper in Soil Using Bacteria: A Literature Review. Land. 2025; 14(8):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081547
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasarevičius, Saulius, and Vaida Paliulienė. 2025. "Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Copper in Soil Using Bacteria: A Literature Review" Land 14, no. 8: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081547
APA StyleVasarevičius, S., & Paliulienė, V. (2025). Immobilization of Cadmium, Lead, and Copper in Soil Using Bacteria: A Literature Review. Land, 14(8), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14081547





