Rock Exposure-Driven Ecological Evolution: Multidimensional Spatiotemporal Analysis and Driving Path Quantification in Karst Strategic Areas of Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
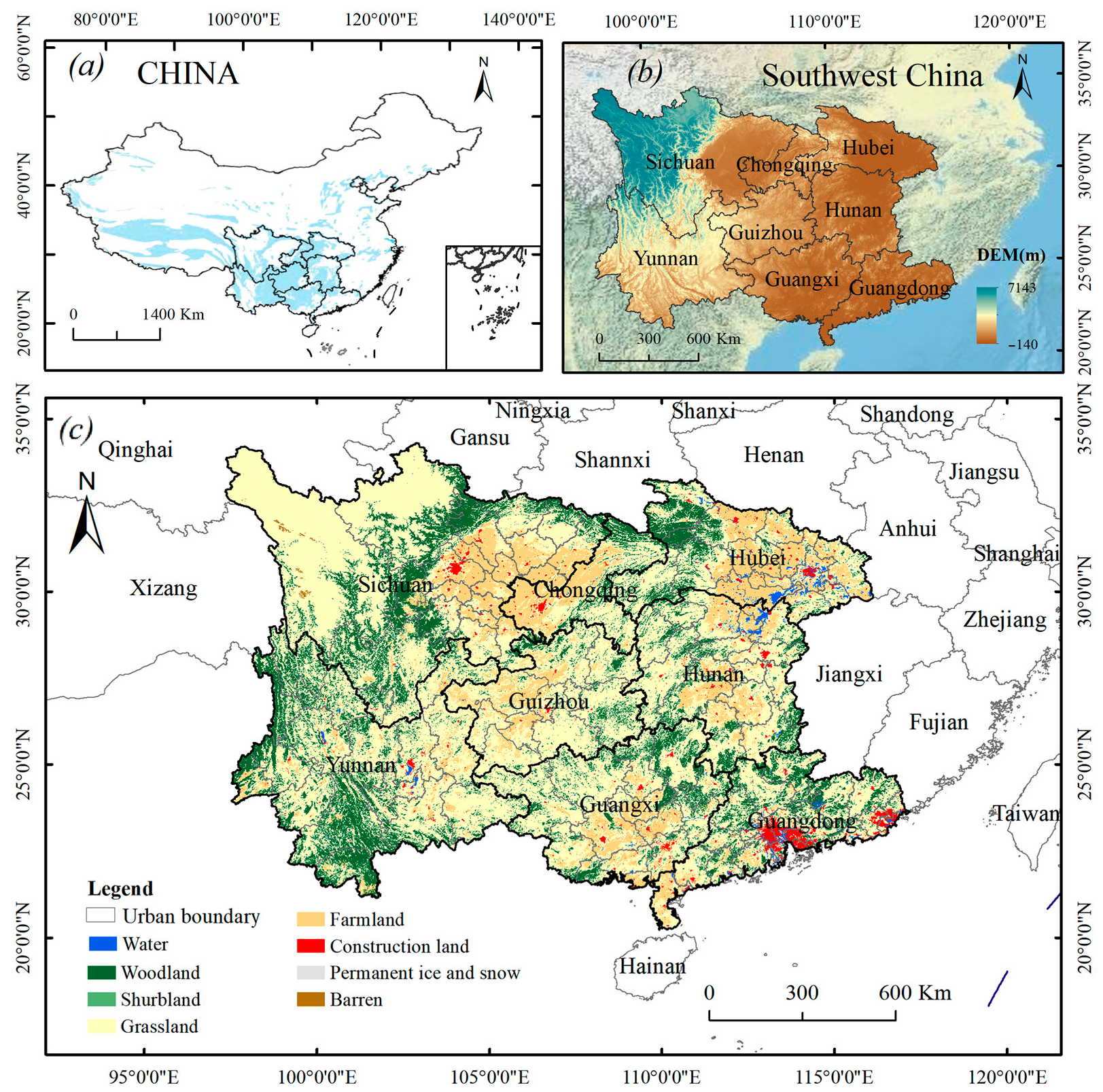
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Methods
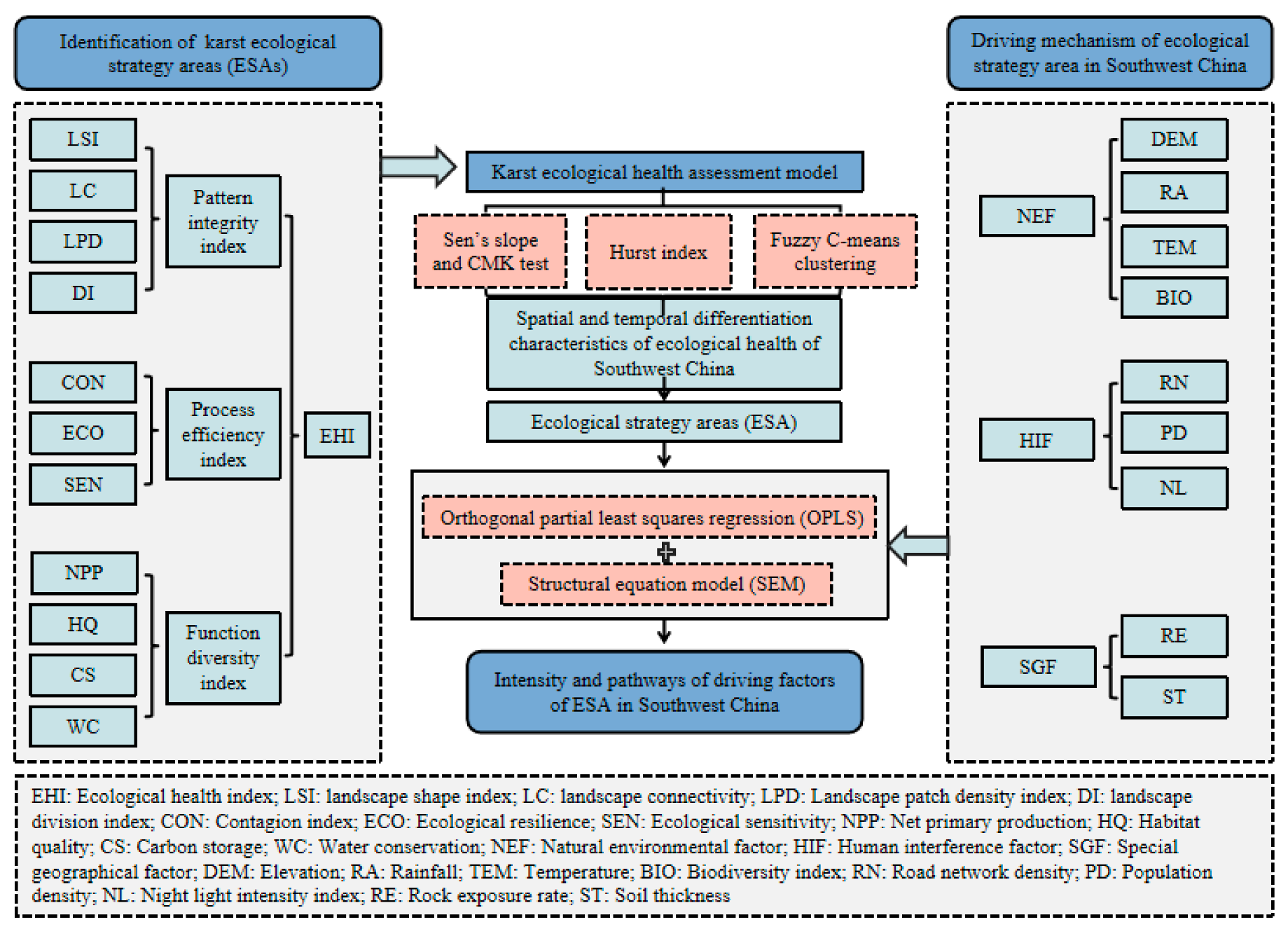
2.3.1. Ecological Health Assessment
- (1)
- Pattern integrity
- (2)
- Process efficiency
- (3)
- Function diversity
2.3.2. Identification of ESAs
2.3.3. Temporal Evolution Pattern Recognition
- (1)
- Sen’s slope and Correlated Mann–Kendall (CMK) test
- (2)
- Hurst index
- (3)
- Fuzzy C-means (FCM) clustering
2.3.4. Driving Factor Analysis Model
- (1)
- Orthogonal partial least squares (OPLS) regression
- (2)
- Structural equation modeling
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of Ecological Health
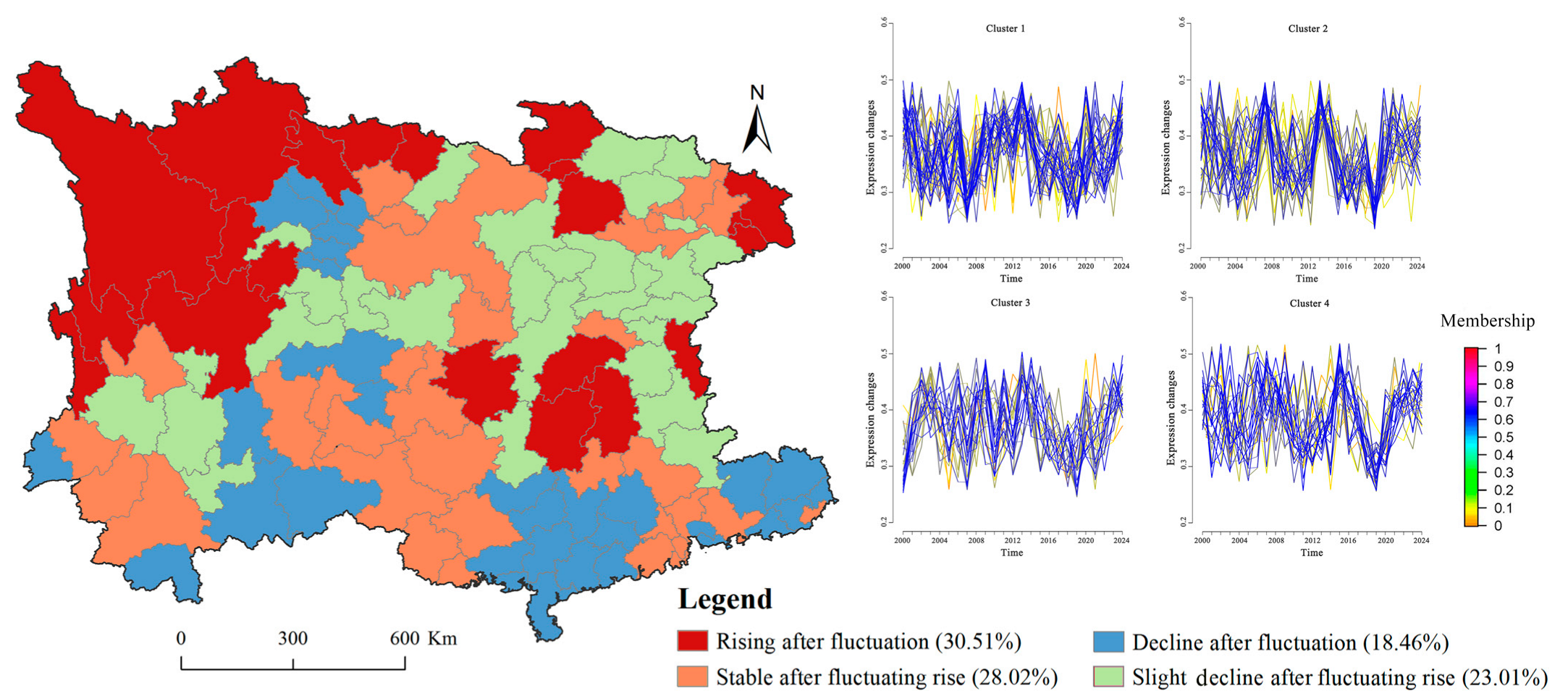
3.2. Temporal Evolution Pattern
3.3. Identification and Classification of ESAs
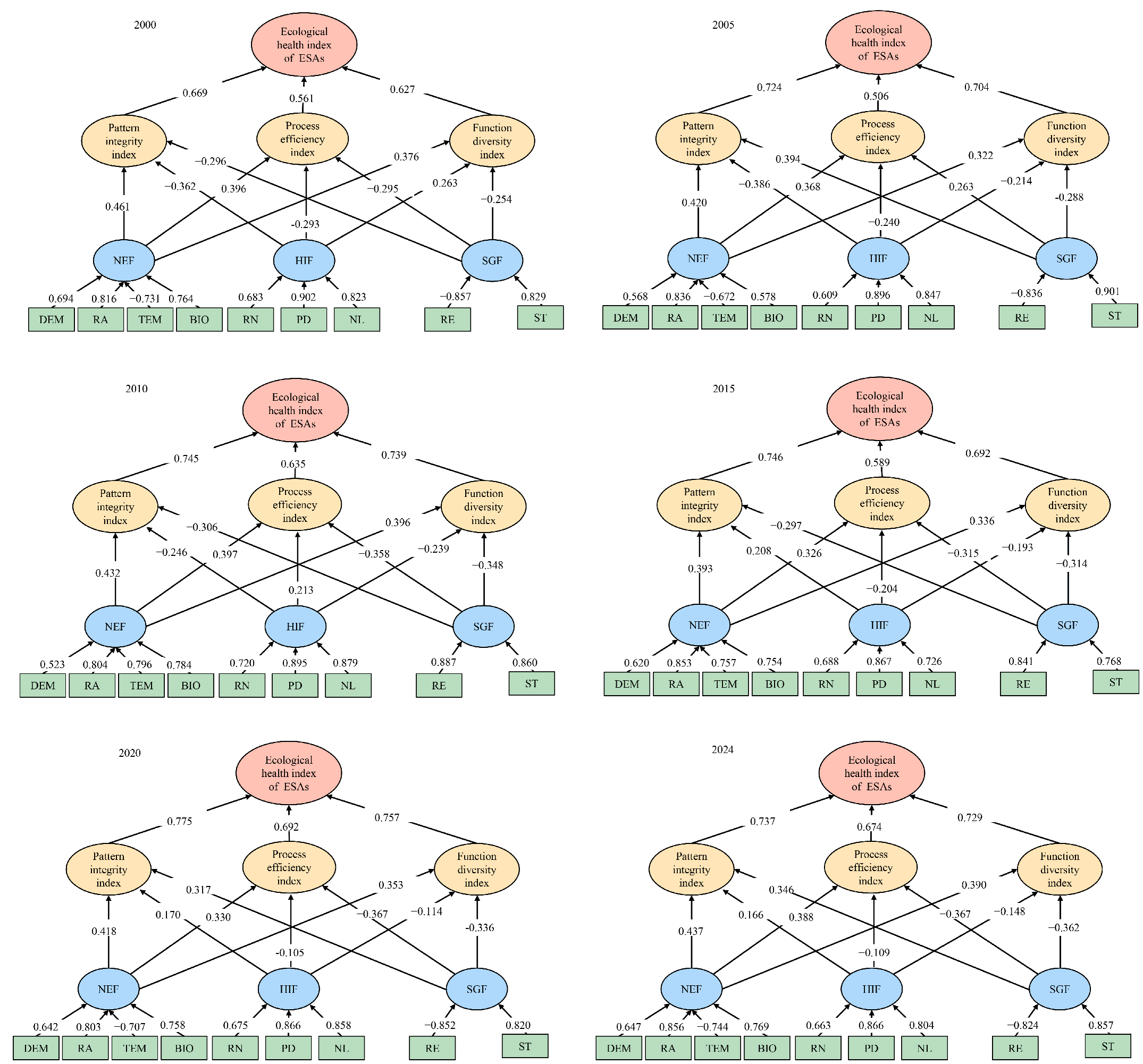
3.4. The Intensity and Pathways of the Driving Factors of the ESA Patterns
4. Discussion
4.1. The Advantages of the Multi-Dimensional Ecological Health Assessment Framework Constructed
4.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecological Health Based on Long-Term Assessment
4.3. Drivers of ESAs in Karst Landscapes: Natural Benefits, Mitigating Human Impact, and Intensifying Geographic Challenges
4.4. Management Recommendations for Ecological Conservation in Southwestern China
4.5. Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, C.-Y.; Shi, X.; Shi, J.; Gan, X.; Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Jackson, M.V.; Fuller, R.A.; Gibson, L. China’s Ecological Conservation Redline policy is a new opportunity to meet post-2020 protected area targets. Conserv. Lett. 2022, 15, e12853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Wei, J.; Wu, T.; Guo, M.; Han, Q.; Zhang, M. Mapping and assessing ecosystem service supply-demand to identify critical areas: A case study of a waterside area in Shanghai metropolitan area. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 943910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Huai, H.; Tang, X. Evaluation of the Potential for Territorial Ecological Restoration: A Case Study of Zhaoping County, China. Land 2023, 12, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xing, L.; Mao, X.; Huang, S.; Duan, K. Biomass burning in Peninsular Southeast Asia intensifies meteorological drought in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Tian, J.; Fu, S.; Liang, Q.; Li, J. Geological Environment and Controlling Factors of Panlongdong Karst Cave in Northeastern Sichuan Basin. Energies 2023, 16, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, L.; Yin, R. A multidisciplinary approach in cover-collapse sinkhole analyses in the mantle karst from Guangzhou City (SE China). Nat. Hazard. 2021, 108, 1389–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yan, S. Evaluating the Implementation of Ecological Control Line Planning (ECLP): A Case Study of Wuhan Metropolitan Development Zone. Land 2024, 13, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, X.; Ding, H. Identification and stability analysis of critical ecological land: Case study of a hilly county in southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Gani, A.A.; Wu, J.; Dai, Y. Identification of Ecological Security Patterns for the Qiandongnan Ecotourism Area in Southwest China Using InVEST and Circuit Theory. Forests 2023, 14, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Mohapatra, G.; Arora, R. Groundwater quality, human health risks and major driving factors in arid and semi-arid regions of Rajasthan, India. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 427, 139149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahfahad; Naikoo, M.W.; Talukdar, S.; Das, T.; Rahman, A. Identification of homogenous rainfall regions with trend analysis using fuzzy logic and clustering approach coupled with advanced trend analysis techniques in Mumbai city. Urban. Clim. 2022, 46, 101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, R. A groundwater conceptual model and karst-related carbon sink for a glacierized alpine karst aquifer, Southwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Deng, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Tuo, Y.; Nie, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal evolution of runoff and sediment and their dominant driving factors in the Lower Jinsha River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Chen, W.; Cai, Q.; Dong, Z.; Wang, L.; Hu, P.; Gao, L.; Garfinkel, C.I. Attribution analysis of the persistent and extreme drought in southwest China during 2022–2023. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 114056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Yu, T.; Liu, X.; Xia, X.; Hou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L. Annual net input fluxes of cadmium in paddy soils in karst and non-karst areas of Guangxi, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 241, 107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Y.; Shao, H.; Du, C.; Guo, Y.; Dai, X. Comparison of the Distribution of Evapotranspiration on Shady and Sunny Slopes in Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Gan, W.; Chen, J.; Ren, K. An Integrated Model for Constructing Urban Ecological Networks and Identifying the Ecological Protection Priority: A Case Study of Wujiang District, Suzhou. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Fu, T.; Qi, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, L. Study on the Characteristics of Ecological Network and Critical Areas of Ecological Restoration in Hebei-Tianjin Coastal Wetlands. Wetlands 2024, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Fu, B.; Lue, Y.; Jiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X. The dynamic patterns of critical ecological areas in the Yellow River Basin are driven primarily by climate factors but threatened by human activities. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, A.; Sinha, N.K.; Jyoti, B.; Kumar, J.; Kumar, D.; Mishra, R.; Singh, P.; Mohanty, M.; Jayaraman, S.; Chaudhary, R.S.; et al. Spatiotemporal Variations in Near-Surface Soil Water Content across Agroecological Regions of Mainland India: 1979–2022 (44 Years). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Fu, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F. A modeling framework for the dynamic correlation between agricultural sustainability and the water-land nexus under uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 131270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zou, L.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, F. Decomposing the impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff changes in the Yangtze River Basin: Insights from regional differences and spatial correlations of multiple factors. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y. Integrating ecosystem services supply-demand balance into landscape ecological risk and its driving forces assessment in Southwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 475, 143671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Jia, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, R.; Luo, H. Evaluation of karst collapse risks induced by over-pumping and karst groundwater resource protection in Zaozhuang region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3443–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhao, X.; Pu, J.; Huang, P.; Gu, Z.; Chen, Y. Evolution Modes, Types, and Social-Ecological Drivers of Ecologically Critical Areas in the Sichuan-Yunnan Ecological Barrier in the Last 15 Years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R. Ecological Environment Problems of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area and countermeasures. In Proceedings of the 2011 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology ESIAT, Beijing, China, 18–19 June 2011; pp. 1431–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, X.F.; Yu, S.; Wei, K.X. Analysis of the influence of stratum on karst development features: Taking Longtan river basin in Youyang County as an example. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Water Resource and Environment, Tokyo, Japan, 23–26 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Dan, Y.; Liang, J.; Liang, B.; Nie, G.; Ji, S. A Hypogene Karst Development Pattern Controlled by the Deep-Cycle of Groundwater in the Syncline in Huanjiang, Guangxi, China. Water 2021, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeana-Pizana, J.M.; Morales-Martinez, G.; Perevochtchikova, M. Forest fates: Unraveling the peri-urban social-ecological trajectories in Mexico City’s conservation land. Ambio 2024, 53, 1768–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Su, Z.; Wei, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, C.; Fu, S.; Han, Y.; Ren, J.; Chen, H. Residual carbonate karst reservoir reconstructed by karst planation: A case study of Ordovician paleokarst reservoir characterization in Ordos Basin, North China. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 233, 212508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, J.; Liu, Q.; Song, J.; Tysklind, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Qu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, F. Comparison and application of SOFM, fuzzy c-means and k-means clustering algorithms for natural soil environment regionalization in China. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Lu, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, R.; Yan, S.; Wu, X. Identification of critical ecological areas using the ecosystem multifunctionality-stability-integrity framework: A case study in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Huang, X.; Shi, L.; Yang, H.; Sun, W. The identification and efficiency evaluation of industrial parcels by integrating multi-source spatial data in Shenzhen, South China. GISci. Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lei, M.; Zhao, H. Review of the advanced monitoring technology of groundwater-air pressure (enclosed potentiometric) for karst collapse studies. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Weng, Q. Impacts of 2D/3D building morphology on vegetation greening trends in Hong Kong: An urban-rural contrast perspective. Urban. For. Urban. Green. 2025, 104, 128624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, L.; Jiao, L.; Zhu, H.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Li, P. Identifying Ecological Security Patterns Considering the Stability of Ecological Sources in Ecologically Fragile Areas. Land 2024, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Yang, Y. Identification of ecological improvement zones in different ecological functional zones in northwest Hubei, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Das, S.; Vrana, V.G. Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Achieving a Net Zero Carbon Economy in Emerging Economies: A Combination of PLS-SEM and fsQCA Approaches to Digital Inclusion and Climate Resilience. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Lin, T.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhu, W. Spatial-temporal characteristics and transfer modes of rural homestead in China. Habitat Int. 2025, 155, 103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xie, C.; Liu, H.; Zhou, T.; Shan, B.; Chen, J. Ecological conservation redline delineation in flood detention areas: A case study in Anxiang County, Yangtze River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 462, 142662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, S.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S. Source-specific ecological risks and critical source identification of PPCPs in surface water: Comparing urban and rural areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Lou, J. Activation of Ms 6.9 Milin Earthquake on Sedongpu Disaster Chain, China with Multi-Temporal Optical Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Unirrigated extensive green roofs in humid subtropics-Plant selection and substrate design for low maintenance and climate resilience. Urban. For. Urban. Green. 2024, 101, 128554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Date Type | Source | Remark |
|---|---|---|
| Land use remote sensing data from 2000 to 2024 | Geospatial Data Cloud | https://www.gscloud.cn/ |
| Digital elevation model (DEM) | ||
| Boundaries of administrative districts | Resource and Environmental Science Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences | http://www.resdc.cn |
| Net primary productivity of vegetation (NPP) from 2000 to 2024 | ||
| Population density data from 2000 to 2024 | ||
| DMSP-OLS night light data | ||
| Rock exposure rate | Guizhou Province Stone Desertification Survey Database | Guizhou Provincial Forestry Bureau |
| Soil data | Harmonized World Soil Database (HWSD) | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/ (accessed on 1 August 2024) |
| Hydrological data from 2000 to 2024 | National Meteorological Science Data Center | https://data.cma.cn/ |
| Road data | Open Street Map | http://www.Openstreetmap.org/ |
| Biodiversity data | Provincial biodiversity assessment reports and Bentai Wan et al. | http://www.biodiversity-science.net |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, X. Rock Exposure-Driven Ecological Evolution: Multidimensional Spatiotemporal Analysis and Driving Path Quantification in Karst Strategic Areas of Southwest China. Land 2025, 14, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14071487
Gong Y, Song S, Zhang X. Rock Exposure-Driven Ecological Evolution: Multidimensional Spatiotemporal Analysis and Driving Path Quantification in Karst Strategic Areas of Southwest China. Land. 2025; 14(7):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14071487
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Yue, Shuang Song, and Xuanhe Zhang. 2025. "Rock Exposure-Driven Ecological Evolution: Multidimensional Spatiotemporal Analysis and Driving Path Quantification in Karst Strategic Areas of Southwest China" Land 14, no. 7: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14071487
APA StyleGong, Y., Song, S., & Zhang, X. (2025). Rock Exposure-Driven Ecological Evolution: Multidimensional Spatiotemporal Analysis and Driving Path Quantification in Karst Strategic Areas of Southwest China. Land, 14(7), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14071487





