Abstract
Optimizing the ecological network is an urgent need to enhance the stability of the ecosystem and maintain regional ecological security. We utilized the PLUS (Patch-generating Land Use Simulation) model to simulate the land use patterns of the Loess Plateau of China under four different development scenarios in 2030, constructed the corresponding ecological network, and evaluated the network structure. The results indicate the following: (1) By 2030, the spatial pattern of ecological network under the four scenarios will be concentrated in the east and west, in the north and south, and the middle of the Loess Plateau. (2) The change of land use pattern driven by a single policy has a trade-off effect on the ecological network and is prone to form the phenomenon of “ecological increase–functional lag”. (3) The regional ecological network layout of “four cores, multiple corridors and multiple sources” was proposed. The results reveal the development trends of land-use change and ecological protection construction under different future development scenarios in the Loess Plateau, which is helpful for decision-makers to balance the relationship between ecological protection and economic development and realize regional sustainable development.
1. Introduction
The rapid urbanization process, high intensity of land use, and human activities are encroaching on the natural ecosystem. Unreasonable land use reduces natural landscape elements, and ecological patch fragmentation becomes more and more obvious [1,2], which seriously affects the balance and coordination relationship inside the “three-life space” (production space, living space, and ecological space) [3]. This has resulted in biodiversity, soil, and water degradation, declining human well-being, and a series of serious ecological and environmental problems [4,5]. The ecological network is a network system of continuous spatial structure formed by ecological sources (an area with important ecological functions in the ecosystem), ecological corridors (the passage with the least resistance between two adjacent “sources”) and ecological nodes (the space that connects two adjacent ecological sources) [6]. It is a key link between natural ecosystems and human activity space and has far-reaching significance for the coordinated symbiosis and balanced development of regional production space, living space, and ecological space. [7,8,9]. A well-structured ecological network plays an important role in habitat conservation and landscape connectivity. High landscape connectivity can promote material circulation, energy flow, and information exchange among landscape patches and enhance population vitality and species richness at the local and regional scales [10]. It is an effective measure to reduce ecological resistance (the impedance imposed by non-habitat landscapes on species movement) and ensure economic development [11] and has positive significance for promoting high-quality regional development.
At present, the construction of the ecological network is mostly based on the spatial configuration of existing biological resources. Although this static protection mode has positive significance in maintaining the integrity of existing ecological patches, it is difficult to adapt to the dynamic balance and collaborative evolution of the regional ecosystem and ignores the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of landscape patterns caused by land-use evolution. There is an absence of adaptive response mechanisms to future changes in ecosystem service supply and demand [12], which necessitates systematic assessment of future scenarios. Consequently, assessing the impacts of future land-use changes on ecological network structures will enhance our understanding of ecosystem dynamics [13]. The Markov model and the System Dynamics (SD) model are the early products of land-use simulation models. However, they can only predict the quantitative changes of various land types and cannot predict the spatial distribution law of the land, which limits the spatial compatibility between ecological corridors and habitats [14,15,16]. With the proposal of improved models such as the CA–Markov model [17], CLUE-S model (Conversion of Land Use and its Effects at Small Region Extent) [18], SLEUTH model (Slope, Land use, Exclusion, Urban, Transportation, Hill shade) [19], FLUS model (Future Land Use Simulation) [20], and PLUS model (Patch-generating Land Use Simulation) [21], the accuracy of land-use simulation has been continuously improved. Among them, the PLUS model retains the adaptive inertia and roulette mechanism of the FLUS model and the RF (random forest) algorithm is used to obtain the expansion probability of each class, which improves the future simulation accuracy [21]. At the same time, the PLUS model fills the demand of land-use-change simulation under the guidance of spatial planning policy in urban development, which can better support the implementation of spatial planning policy and multi-scenario assessment of the ecological network [22]. Therefore, considering the dynamic evolution of future land-use patterns in the process of ecological network construction can optimize the collaborative relationship between ecological sources and corridors and enhance the understanding of the dynamic evolution of the ecosystem. Meanwhile, it helps mitigate the negative impacts of urbanization on the ecological environment and facilitates the development of effective measures for sustainable long-term landscape protection [13,23].
“Source identification-resistance surface construction-corridor extraction” is the basic mode of current ecological network construction [24]. At present, the identification of ecological source areas primarily employs two approaches. One is to directly select protected and important ecological conservation zones as sources [25,26]. The other is to conducting assessments such as ecological function importance, ecological suitability, and eco-environment sensitivity to identify suitable source areas [27,28]. However, among the above methods, the former does not consider the internal differences of the same land-use type, and the latter is too dependent on the regional environment [29]. Therefore, this paper adopts the Morphological Spatial Pattern (MSPA) method to determine the ecological source area [20,30,31]. Compared with the previous two methods, this method can objectively define landscape characteristics and quantitatively identify ecological source areas [32]. It has been widely applied in recent years [33,34]. The resistance surface is usually obtained by weighting regional characteristics, with appropriate weights given to factors such as land use and altitude [35]. An ecological corridor is a linear corridor that serves ecological service functions such as biodiversity conservation, pollutants filtration, soil and water conservation, windbreak and sand fixation, and flood regulation [36]. It can be constructed using models like the Minimum Cumulative Resistance (MCR), the gravity, and the circuit theory models. Among these, the MCR model demonstrates greater advantages in coupling both natural and anthropogenic disturbance factors [12,37,38,39,40,41].
To explore the simulation and prediction of the priority orientation for future ecological networks under different policies, this paper takes the Loess Plateau of China as an example. We use the PLUS model to construct and evaluate multi-scale ecological networks for four different land development scenarios in 2030 and identify the most suitable regional development scenario. This approach enables the construction of an ecological network for the Loess Plateau that balances ecological protection, economic development, and cultivated land conservation needs, thus ensuring the region’s stable ecological development.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Loess Plateau is located in the middle and upper reaches of the Yellow River in China, spanning approximately 33°41′ N to 41°16′ N and 100°52′ E to 114°33′ E (Figure 1). It is one of the regions with the largest loess coverage in the world, covering a total area of about 625,900 km2. The plateau spans three ecological zones: the Tibetan Plateau, the Northwest Arid, and the East Asian Monsoon. Characterized by complex topography and variable climate, it is a key ecological conservation area in China [42]. Due to long-term over-cultivation, deforestation, and unsustainable land-use practices, natural vegetation on the Loess Plateau has been significantly reduced, remaining only in scattered patches, leading to severe soil erosion [43].
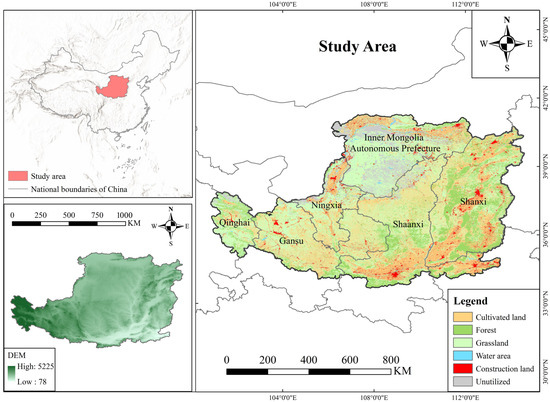
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the study area.
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Land-Use Change and Simulation
- (1)
- Scenario setting
To accommodate diverse development needs and comprehensively consider the land-use changes in the study area from 2000 to 2020, as well as the future territorial spatial development plan, we have established four scenarios: the natural development scenario (Q1), the ecological protection scenario (Q2), the urban development scenario (Q3), and the cropland protection scenario (Q4) [44,45,46].
The Q1 scenario is to continue the development trend of the study area from 2000 to 2020, maintaining the probability of cluster transfer and neighborhood weight. With the protections as the premise, the Q2 scenario limits urbanization development. It increases the probability of transfer to forest and grassland while designating water body as the restricted expansion area. The goal is to achieve forest and grassland land coverage exceeding 60% in 2030. Under scenario Q3 and scenario Q4, construction land and arable land with a slope of less than 5° are introduced as limiting conversion factors, respectively. Scenario Q3 introduces construction land as a conversion constraints, accelerates built-up area growth (ensuring >5% total coverage), enhances utilization efficiency of unused land, and counters food security risks through cropland expansion. The Q4 scenario focuses on cultivated-land protection. By prohibiting the conversion of cultivated land, it strengthens the transition from forest and grassland to cultivated land, ensuring that the cultivated land area increases by more than 10,000 km2 compared with the baseline in 2020. This is consistent with the national goal of protecting cultivated land.
- (2)
- The PLUS model
The PLUS model significantly improves upon the FLUS model, providing a land-use prediction framework that can incorporate policy-driven guidance and perform refined patch-level simulations [47]. It primarily consists of three sub-models: the Markov model, the Land Expansion Analysis Strategy (LEAS) model, and the Cellular Automata model, which is based on the Multi-type Random Patch Seeds (CARS) model [21]. Among them, the Markov model derives a land-use-transition probability matrix from multi-period historical land-use data to predict future land demand. The LEAS model identifies areas of land-use change and applies the RF algorithm to generate development probabilities for each land type. The CARS model, based on the development probabilities and conversion constraints for each land use type, simulates land-use evolution by establishing a land-use transition matrix and neighborhood coefficients. In the transfer matrix, 0 means that the conversion between different classes is not allowed, and 1 means that the conversion is allowed (Table 1). The neighborhood weight parameter indicates a land type’s expansion intensity, reflecting its ability to expand when driven by external factors. Its value ranges from 0 to 1. Building upon previous research, this study utilizes historical changes in the area of each land-use type to characterize land expansion intensity, and then calculates neighborhood weight parameters based on this characterization [21,48,49]. The neighborhood rights of each class are shown in Table 2. The PLUS model incorporates an accuracy validation model, which evaluates prediction performance using the Kappa coefficient and Figure of Merit (FOM) coefficient. The closer the Kappa and FOM coefficients are to 1, the better the simulation effect is; when the value is greater than 0.85, the simulation accuracy is high [50]. This study employed the Kappa coefficient for model accuracy validation.

Table 1.
Land-use transfer matrix under different scenarios (Note: 1 = transition permitted; 0 = transition prohibited).

Table 2.
Class neighborhood coefficients.
2.2.2. Ecological Network Construction
- (1)
- Selection of the ecological source areas
The Morphological Spatial Pattern (MSPA) method leverages the advantages of strong spatial scale compatibility and well-defined ecological significance of landscape elements [51,52]. The method is based on morphological principles and classifies the landscape types of the study area into foreground and background. Typically, the ecosystem service of forest land surpasses that of other land types, followed by grassland, cultivated land, water areas, and unused land [53]. Therefore, forest and grassland were designated prospect classes, while other categories served as background. Using MSPA analysis, we screened a core patch with an area exceeding 20 km2 [54]. Hotspot analysis, a local statistical method widely applied to identify regional high-value accumulation zones, can effectively pinpoint areas of significant ecological importance [55]. Thus, conducting hotspot analysis on selected patches by land type aids in identifying forest and grassland accumulation zones, thereby enhancing the objectivity of the ecological source identification.
- (2)
- Construction of the resistance surface
A resistance surface characterizes the spatial flow trends of ecological processes. It reflects the behavioral preferences of species during migration, with its core function being the quantification of resistance intensity encountered during species dispersal [56]. Building upon an integrated consideration of the natural environmental context, socio-economic development status, and established research findings [57,58], we selected five indicators: slope, elevation, land-use type, distance from a road, and distance from construction land. By combining the weighting factors, the integrated resistance face value is obtained. According to relevant studies and the characteristics of the study area, the assignment and weighting of each resistance factor are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Assignment and weighting of each resistance factor.
- (3)
- Extraction of the ecological corridors
The Least-cost path method (LCP) can be used to calculate the cumulative resistance values of species migrating between source areas through different resistance landscape surfaces. We used the Linkage Mapper (LM) tool to identify the minimum cost path for species migration and diffusion in ArcGIS and obtained the minimum cost distance channel, namely an ecological corridor. In this study, the cost-weighted distance threshold for truncating ecological corridors was set at 2 km [59].
- (4)
- Extraction of the ecological pinches
An ecological pinch is an important part of the ecological security network, which is often used to characterize the quality of a habitat [60]. They are typically situated at key points along ecological corridors, serving as crucial hubs for species, material, and gene flow. Identifying ecological pinch points based on circuit theory is a common method in current research. In this paper, we used the Circuit-scape 4.0.7 software and Linkage Mapper 3.0.0 toolbox to identify ecological pinch points based on the ecological source and resistance surface [61].
2.2.3. Ecological Network Evaluation
The ecological network is composed of landscape elements such as source areas, corridors, and nodes, which jointly maintain the ecological continuity of the ecological process [62]. Network stability and complexity are commonly used to evaluate the ability of the network to resist external interference and the strength of the internal interaction between the network [63]. Based on the calculation data of each landscape element and the theory of complex networks, we quantitatively describe the layout of the network and the spatial relationships among each element. The average clustering coefficient (the degree of aggregation of the network) and the average path length (the connectivity and diffusion efficiency of the network) are respectively used to characterize the aggregation and transmissibility of the network. Network density, average degree, and average weighting degree measure connectivity. The three together constitute the stability of the network [64,65]. The indicators α (loop closure), β (connectivity), and γ (connectivity rate) are used to represent the network complexity [66,67]. The meanings and calculation methods of each indicator are shown in the Table 4.

Table 4.
Explanation and calculation method of the ecological network evaluation indicators.
The gravity model is used to determine the relative importance of ecological sites by constructing the interaction matrix between ecological sites. The greater the interaction force, the greater the importance of the source and the closer the connection between the corridors [29,68]. We used this model to evaluate the strength of the interaction force between source areas, thereby judging the importance of ecological corridors, and took the calculated gravitational force between corridors as the edge weight of corridors in the ecological network [28].The gravity model formula is as follows:
where represents the gravitational force between two sources, that is the edge weight, refers to the maximum resistance value of the ecological corridor, and represent the areas of sources and , respectively, represent the areas of sources and , respectively, and represent the resistance value between the sources and .
The workflow is shown in Figure 2.
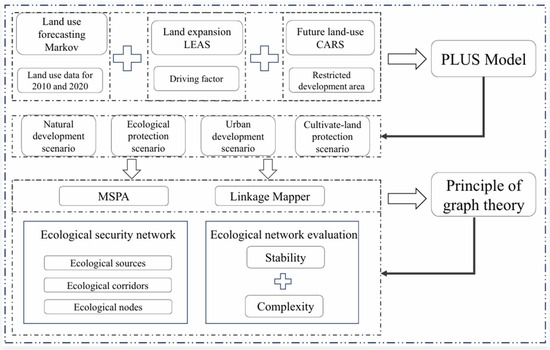
Figure 2.
Technical roadmap for land-use simulation and ecological network construction based on the PLUS model.
2.2.4. Data Source
The data involved in this study mainly include four types: land use, social economy (population, road), meteorology (precipitation, temperature, etc.), and topography and its derivative products (DEM, slope). All the above data are uniformly reprojected to CGCS2000_GK_Zone_36 with a spatial resolution of 250 m and time range from 2000 to 2020. The complete data list and sources are detailed in Table 5.

Table 5.
Data types, names, and sources.
3. Results
3.1. Simulation of Land-Use Change and Pattern
Based on the LUCC data of 2010 and 2020, we generated the development probability of each class in the LEAS model of the PLUS model, used the CAES model to simulate the LUCC of 2020, and compared it with the actual LUCC of 2020. The Kappa coefficient was 0.907 for accuracy verification. It shows that the PLUS model has high precision in simulating future LUCC in the study area and can be used to predict future land-use change in the study area. The land-use changes in the Loess Plateau under different scenarios in 2030 are shown in Figure 3.
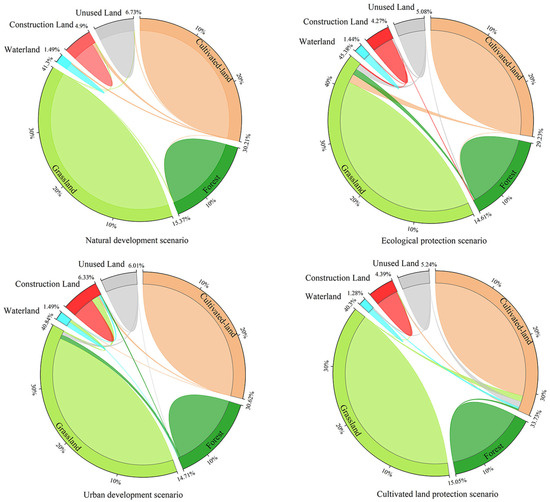
Figure 3.
Transfer the string diagrams for the different scenarios.
As can be seen from Table 6, the area of cultivated land and grassland area decreased by 5211.25 km2 and 1240.5 km2, respectively, from 2010 to 2020, while the area of construction land increased by 4807.75 km2, which is in line with the urban development law in recent ten years. During the early 2010s, the unrestrained expansion of urban areas, accompanied by a massive shift of rural populations to cities, led to a sharp increase in construction land, resulting in significant encroachment on cultivated land and grassland. Concurrently, due to the unique importance of the Yellow River and its severe ecological challenges, the implementation of converting cropland to forest and grassland to combat soil erosion and desertification further reduced the area of cultivated land.

Table 6.
Land-use change from 2010 to 2020 (note: the area is in km2).
Under the Q1 scenario, the area of cultivated land and grassland showed a downward trend, while the forest, water area, construction land, and unused land increased, which was consistent with the change trend of different regions from 2010 to 2020. It shows that, under this scenario, a large amount of land is converted into construction land. Compared with 2020, under the Q2 scenario, grassland area increased by 9.4%, while construction land area saw a minimal increase of only 0.8%. The vast majority of land conversion was directed towards grassland, resulting in an expansion of ecological land by 20,810.2 km2, which aligns well with ecological protection objectives. In the Q3 and Q4 scenarios, aiming at urban development and cultivated-land protection, respectively, the changes of land-use pattern are quite different. In the Q3 scenario, with economic development as the goal, construction land expanded rapidly, with an area increase of 33.12% compared to that in the Q1 scenario. Except for water area, all other land-use types showed a downward trend, showing a significant urban expansion trend. Under the Q4 scenario, affected by the cultivated-land protection policy, the change trend of cultivated land is contrary to other scenarios, with an increase of 17,244 km2. The vast majority of it is transferred from unused land and grassland, which conforms to the development characteristics of the land-use landscape pattern driven by the cultivated-land protection policy. The land-use changes under different scenarios in 2030 are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Land-use change under different scenarios in 2030 (note: the area is in km2 and the rate of change is in %).
3.2. Construction of the Ecological Network
- (1)
- Ecological Source Identification
The ecological source areas identified under the four different development scenarios in 2020 and 2030 are shown in Figure 4. In 2020, we identified 133 source areas, accounting for 10.54% of the total area, showing the spatial characteristics of “large dispersion and small aggregation”. Most of them are located in the northern Inner Mongolia Plateau and the eastern region. In the Q1 scenario, a total of 125 ecological source areas were identified, with a total area of approximately 55,972 km2. In the Q2 scenario, on the premise of ecological protection, we identified 136 ecological sources with a total area of 68,257 km2. It increased by 12,285 km2 compared with the Q1 scenario, and the increased area was mainly located in the southern and central parts of the study area. In Q3 scenario, the construction land expanded rapidly and occupied a large amount of cultivated land and grassland. The scale of the source areas was significantly reduced, and only 109 sources were generated, with a total area of 46,490 km2. In the Q4 scenario, due to the conversion of some grassland and other land into cultivated land, the overall fragmentation degree of the source area is high, and the area is also reduced. Comparing the sources under the four different scenarios, it can be found that the integration and fragmentation of ecological sources occur at the same time driven by different policies. For example, in scenario Q3, the number of source areas decreased compared with scenario Q4, but the area of the source areas increased by 5201 km2. The reason is that under the protection of cultivated land, the scattered increase of cultivated land aggravates the fragmentation degree of source areas and reduces the connectivity between source areas. Coupled with the demand for ecological civilization under urban development, the number of “policy-oriented” sources has increased.
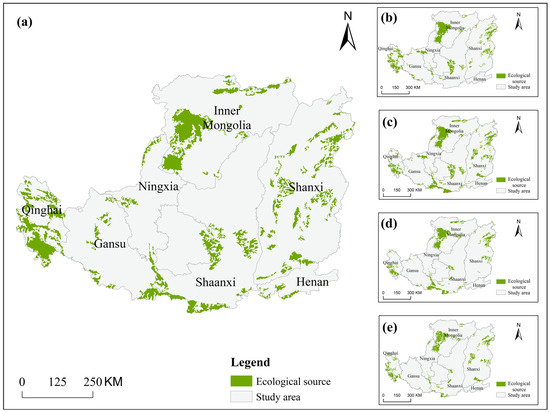
Figure 4.
Comparison of ecological sources in different scenarios ((a–e) are 2020, the natural development scenario, the ecological protection scenario, the urban development scenario, and the cultivated-land protection scenario, respectively).
- (2)
- Extraction of the Ecological Corridors
Based on the ecological resistance surfaces constructed in various scenarios, we have determined the eastern part of the study area and the Yellow River Basin as the key areas for the construction of ecological corridors. In the baseline scenario of 2020, 312 main ecological corridors were identified, showing the spatial distribution characteristics of eastern dense and western sparse. Through comparative analysis, it is found that there are obvious differences in the number of corridors under the four different development scenarios in 2030, which are 289, 307, 234, and 257, respectively. Although the distribution of the corridors in each scenario was affected by the distribution of ecological sources, they formed an interconnected network structure as a whole.
Under the Q1 scenario, the number of corridors has decreased by 23 compared to 2020. This is related to the expansion of construction land in 2030, which results in encroachment on the source area space and increases the fragmentation of the source area. In the Q2 scenario, driven by the policy goal of ecological protection, the ecological protection was strong. This has effectively restored and protected the source areas in the central and eastern regions, and the area of the source areas has increased. Therefore, the increased number of corridors in this scenario exactly responds to the positive effect of ecological protection measures on maintaining and increasing landscape connectivity. In the Q3 and Q4 scenarios, economic development and cultivated-land protection are targeted, respectively. Against this backdrop, large-scale urban construction and agricultural expansion activities have exerted considerable pressure on ecological space, with a large amount of forest, grassland, and cultivated land being encroached upon or transformed. This change directly led to a reduction in the source area, which was ultimately reflected in a decrease in the number of corridors, to a value significantly lower than that in 2020.
- (3)
- Ecological Network Structure
Based on the identification results of the source area and corridors, the ecological intersection point results under different scenarios were identified by using the Circuit scape and Linkage Mapper toolboxes. It was found that the ecological nodes under the four development scenarios in 2030 were 111, 116, 99, and 108, respectively. These identified ecological sources, corridors, and nodes together constitute a complete ecological network under the different development scenarios. The ecological network pattern under the four scenarios had a great relationship with the distribution of land use, showing the spatial characteristics of dense in the east and west, concentrated in the south and north, and hollow in the middle. The high-resistance areas appeared in the areas with high elevation and dense construction land, and the low-resistance areas were mainly located in the central low-altitude areas. The sources, corridors, and intersections identified under the different scenarios also show significant differences. The ecological networks in the different scenarios are shown in Figure 5.
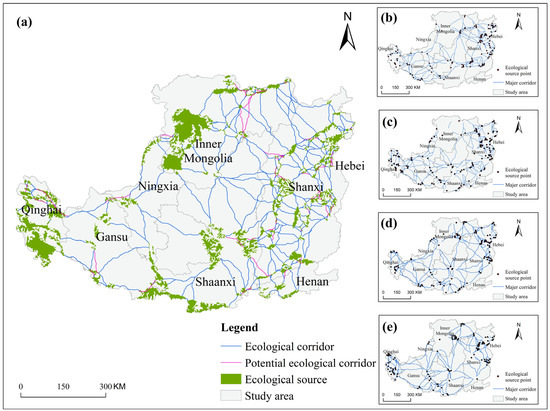
Figure 5.
The ecological network under the different scenarios ((a–e) are 2020, the natural development scenario, the ecological protection scenario, the urban development scenario, and the cultivated-land protection scenario, respectively).
3.3. Evaluation of the Ecological Network Structure and Analysis of the Scenario Differences
Based on the complex network theory, we determined the weight of the corridors by combining the gravity model, taking the ecological source as the node and the ecological corridor as the edge. Subsequently, topological analysis was conducted on the ecological networks under the four scenarios in the Loess Plateau from three dimensions of “point–edge–network”. At the same time, we selected the average clustering coefficient, average path length, network density, average degree, and average weighting degree to compare the transmission, aggregation, and connectivity of the different ecological networks, and then calculated the α, β, and γ indexes of the network to reflect the complexity and stability of the network structure.
The results show (Table 8) that the different development scenarios in 2030 have a significant impact on the network structure. Compared with the Q1 scenario in 2020, as the Q1 scenario continued the development trend of the previous decade, there was no significant difference in network stability and complexity in 2030. The average clustering coefficient characterizes the degree of clustering within a network. The coefficient reaches a maximum value of 0.485 under the Q2 scenario, which indicates that the increase of the central and eastern source areas promotes the aggregation effect of ecological patches under this scenario. Meanwhile, in this scenario, the complexity index is 0.738, which is the highest among the four scenarios. It also shows that the topological structure of the ecological network is diverse and stable. This result is in line with the ecological protection goal. In the Q3 and Q4 scenarios, the stability index is 0.402 and 0.416, respectively. In addition, the average path length is reduced compared with 2020 and the other scenarios, while the γ index decreases. This change indicates that there are vulnerable points in the network structure and that it is susceptible to interference from external factors. It also precisely indicates that while economic development and the expansion of cultivated land squeeze the ecological space and affect the network structure, both are unsustainable.

Table 8.
Comparison of the ecological network indicators in the different scenarios.
In summary, we find that there is a sensitive response between ecological network topology and development policies. The Q2 scenario enhances the complexity and stability by optimizing the source area structure. The network density of scenarios Q3 and Q4 remained unchanged compared with that in 2020, but their complexity index decreased significantly, exposing the unsustainability of the two scenarios in future development. This also highlights the limitations of ecological networks driven solely by single-policy approaches, providing a reliable basis for the Loess Plateau region to synergistically advance ecological conservation, agricultural development, and economic growth.
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Land-Use-Pattern Change on the Ecological Network
Land-use patterns exert a significant influence on the construction of ecological networks [13], especially in the context of urbanization, considering that the impact of land-use-pattern change on the ecological network can help mitigate conflicts between land use and ecological development. This is of great significance for realizing the dynamic and balanced regional, economic, and ecological development [12]. To further investigate the impact of land-use-pattern changes on ecological networks, we integrated multi-scenario future land-use simulation with an ecological network model. This integration enabled the evaluation of spatiotemporal variations in ecological network structure across four development scenarios projected for 2030. Furthermore, by comparing these results with the 2020 ecological network, we quantitatively assessed the constraining effects of key land-use transformations on the ecological network structure.
The results show (Table 9), that compared with 2020, the changes in land-use patterns under different scenarios have significant differences in the integrity of the ecological source areas and the connectivity of the corridors. In scenario Q2, the area of the ecological source areas increased by 0.37% by restricting human development activities and promoting the restoration and expansion of source areas in the Inner Mongolia Plateau by the “Grain for Green” project. However, the network density decreased to 0.03 compared with 2020, and the average degree dropped to 4.50. This contrast indicates that the newly added source area may be located in the ecological edge zone and fails to effectively connect with the core migration path, resulting in a low overall network connectivity efficiency. Compared with 2020, the Q3 and Q4 scenarios showed a strong ecological space squeezing effect, and by 2030, the area of ecological source areas decreased by 3.31% and 3.94%, respectively. Especially in scenario Q4, where cultivated-land-protection policies dominate, there is potential risk that agricultural expansion may occur through the encroachment on substantial areas of wetland, forest, and grassland. This expansion, in turn, leads to a spatial pattern of the ecological sources characterized by the contraction of core areas and fragmentation at the edges. The decline in the average weighted degree to 15.20 indicates that while farmland corridors enhance connectivity among local patches, they are insufficient to sustain biological exchange between the ecological sources.

Table 9.
Comparison of the ecological sources in the different scenarios.
In summary, the impact of land-use-pattern change driven by different policies on the ecological network exhibit significant variations. Sole reliance on land-use regulation measures is insufficient to ensure the stability and complexity of ecological networks. Therefore, future ecological planning must adopt a coordinated development path that integrates multiple objectives, such as “ecological protection, urban development, and cultivated-land conservation”.
4.2. Tradeoff Synergistic Effect Analysis Between Ecological Network Structure and Land-Use Pattern
Different land-use patterns have different contribution degrees to the ecosystem, and the ecological network structure generated based on the land-use pattern is also significantly different [20]. In this paper, we construct four future scenarios to reveal the differentiated impact of land-use-pattern evolution on ecological network structure. The result shows that land-use changes under different policy orientations mainly drove ecological network changes by reshaping the distribution of ecological source areas.
The dynamic change of the ecological source area is the direct manifestation of the change of land-use pattern. From the perspective of land-use pattern, compared with 2020, under the Q1 scenario, the forestland area increased by 0.35%, and the grassland area decreased by 0.44%. Under the Q2 scenario, the forest area decreased by 4.59% and the grassland area increased by 9.40%, which increased the proportion of ecological source area to 10.91%. However, both the network density and the average degree in scenario Q2 have decreased compared with those in 2020, indicating that there is a trade-off effect between the increase in source area and the improvement of functions. In addition, the newly added source areas are mostly distributed in high-altitude areas and economic development areas. Constrained by terrain and conflicting development priorities, establishing ecological source areas proves more challenging and costly. This results in reduced network connectivity, creating a phenomenon where ecological area increases but functional capacity lags. Under the Q3 scenario, construction land increased by 49.76% compared to 2020, encroaching on a large amount of forest and grassland, damaging the ecological matrix and exacerbating local environmental issues, such as soil erosion and grassland degradation. At the same time, the network complexity of this scenario drops to 0.472, indicating that high-intensity development causes damage to the ecological network. Under scenario Q4, the area of cultivated land increased by 17,244.1 km2 compared to 2020. The construction of supporting linear agricultural facilities, such as field ridges, facilitates exchange between source patches. However, the expansion of cultivated land intensifies the fragmentation of source patches, which in turn leads to compromised network stability and complexity.
Comparing the four scenarios, it was found that there were significant differences in the scale, structure, and functional synergy degree of the ecological networks under the different land-use scenarios. Under the two scenarios Q2 and Q4, the area of grassland and cultivated land increased, respectively, and the land-type conversion law was significantly different from that of Q1. However, the Loess Plateau has long-standing problems such as over-reclamation, abandoned land, and vegetation destruction, and the ecological problems are prominent. Whether the land-type conversion can be realized under this scenario is highly dependent on government policies. Under scenario Q3, socioeconomic development generates substantial wealth for the region, which can provide financial support for ecological network construction. However, urban expansion inevitably encroaches upon cultivated land, forests, and grasslands, thereby damaging the ecosystem and conflicting with national ecological civilization goals. The future construction of the ecological network should comprehensively consider the three dimensions of “scale–structure–function” and pay attention to the coupling mechanism between land-use patterns and ecological network structure.
4.3. Ecological Network Building in the Future
Ecological network layout provides guidance for regional ecological protection in the future, and ecological network structure reflects regional network stability and resilience to external shocks, to a certain extent [69]. We proposed four different development scenarios based on the possible future development directions of the study area. In the Q2 scenario, the effectiveness of ecological protection is maximally reflected, but it will limit economic development and agricultural production [22]. This dynamic may indirectly impede ecological advancement, rendering the synergistic development of ecological, agricultural, and economic systems unattainable. In the Q3 scenario, rapid urbanization drove significant expansion of construction land, encroaching upon ecological spaces and degrading ecosystem function. This was particularly evident in the central Shanxi Province and northern Ningxia regions within the study area, where core habitats became fragmented. Extensive surrounding construction land severely constrained ecological development, resulting in low ecosystem service capacity. Therefore, prioritizing urban construction and development as the regional goal necessitates rational land-use planning. This approach is more conducive to overall development and construction, while also generating the economic resources needed to support future ecological network construction. In Q4 scenario, most of the source areas located in the southeast region are transformed into cultivated land, which increases the cultivated-land area and improves the quality of agricultural production. However, on the Ordos Plateau, located in the northwest, the degree of fragmentation in the source area has significantly increased as a result of arable land expansion. Additionally, the area of ecological source regions, such as grasslands and forest lands, has decreased, thereby impacting regional ecological benefits.
To achieve the coordinated development of “ecological protection, urban development and cultivated-land protection”, we spatially superimposed the ecological sources in 2020 and the different future development scenarios and proposed a regional ecological network of “four cores, multiple corridors, and multiple sources” (Figure 6). We also propose corresponding protection and management strategies. The “Four Cores” comprise the Western Wushaoling Conservation Core (development prohibited; ecological relocation zones; degraded grassland restoration); the Northern Inner Mongolia Grassland Core (rotational grazing; grass–livestock balance demonstration zones); the Eastern Fenhe Plain Urban Core (urban growth boundaries; prioritized green infrastructure); and the Western Weihe Plain Agricultural Core (farmland shelterbelts; ecological ditches; non-point pollution control). Furthermore, establishing a hierarchical management system for multiple corridors and a dynamic monitoring framework for diversified sources enables effective monitoring and protection of the corridors and ecological sources. This approach is vital for future ecological development and economic growth in the Loess Plateau.
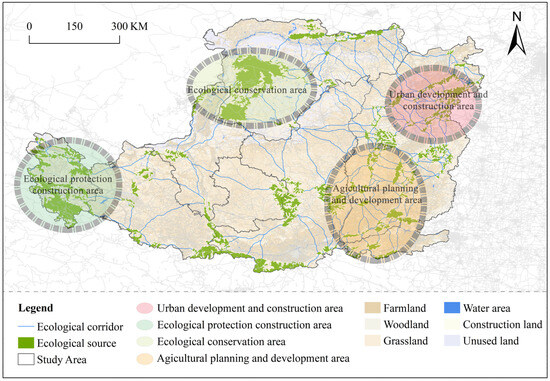
Figure 6.
Future ecological network layout of the Loess Plateau.
The ecological network construction method that coupled the land use pattern with the “source–resistance surface–corridor” model is not only conducive to dividing the territorial space restoration zones, but also can refine the restoration scope and goals by quantifying the ecological vulnerability threshold. It can provide it with a collaborative optimization plan of “protection–restoration–development”, which is consistent with the core requirement of building an ecological security barrier in China’s “National Major Project for the Protection and Restoration of Critical Ecosystems (2021–2035) (NMPPRCE)”. It is an important means for the future division of national space planning and the optimization of ecological development goals in various regions.
5. Conclusions
This study integrates land-use change prediction with ecological security network construction. Using the PLUS model, we simulated land-use patterns under four scenarios for 2030 and established corresponding ecological networks for each. Subsequently, we analyzed the spatial characteristics of the current ecological network and compared them against those projected under the four future scenarios. We found the following: (1) The land-use status of the Loess Plateau was mainly grassland and cultivated land, which accounted for 72.4% of the total area. (2) The change of land-use pattern driven by a single policy has a trade-off effect on the ecological network, under which it is easy to form the phenomenon of “ecological increase and function lag”. (3) Ecological networks show different shortcomings under different scenarios. In Q2 scenario, most of the new sources are located in the ecological economic belt, and the implementation resistance should be reduced through the ecological compensation mechanism. Under Q3 scenario, construction land surges and occupies a large number of sources. To balance the ecological impacts, we should delimit the urban development boundary and compulsively retain the ecological isolation zone. In Q4 scenario, cultivated land expansion increased the fragmentation of grassland in the northwest and increased the resistance of corridor construction.
The results of this study provide the changing trend of land-use pattern under different development goals in the future. By analyzing the comprehensive situation of the different ecological network structures, it is helpful for decision-makers to understand how the land-use patterns affect the ecological network results, which has important guiding significance for improving the ecological environment of the Loess Plateau and realizing the coordinated development of the regional ecological economy.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by X.L. (Xun Luo), J.L., Y.H., X.Y., J.W., Y.D. and Y.Y. The first draft of the manuscript was written by X.L. (Xiaoyan Luo) and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. X.L. (Xiaoyan Luo) and X.L. (Xun Luo) supervised all stages of the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Sichuan Province Ecological Environmental Protection Science and Technology Program, grant number: 2024HB35; the Financial Fund of the Sichuan Institute of Geological Survey grant number: SCIGS-CZDXM-2024014.
Data Availability Statement
The spatial distribution of key datasets is visualized in the Graphical Abstract and Figure 1 and Figure 3, with complete PLUS model parameters provided in Table 1 and Table 2. Original raster/vector datasets and model configuration files will be made available by the corresponding author upon reasonable request, after acceptance, to support research reproducibility.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Chen, X.P.; Chen, W.B. Construction and evaluation of ecological network in Poyang Lake Eco-economic Zone, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.B.; Bo, J.; Li, X.Y.; Fang, F.; Cheng, W.J. Identifying key landscape pattern indices influencing the ecological security of inland river basin: The middle and lower reaches of Shule River Basin as an example. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.H.; Jia, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.F. How can urban expansion and ecological preservation be balanced? A simulation of the spatial dynamics of production-living-ecological spaces in the Huaihe River Eco-Economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, K. Encroachment of agricultural land in urban fringe areas of Aligarh city, India—Process and parameters. Asian Geogr. 2014, 31, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, X.; Wu, K.N.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Y.N.; Li, X.L. Land-use zoning management to protecting the Regional Key Ecosystem Services: A case study in the city belt along the Chaobai River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opdam, P.; Steingröver, E.; Rooij, S.V. Ecological networks: A spatial concept for multi-actor planning of sustainable landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2006, 75, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.H.; Yin, H.W.; Nakagoshi, N.; Zong, Y.G. Urban green space network development for biodiversity conservation: Identification based on graph theory and gravity modeling. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2010, 95, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Hou, X.Y.; Yin, Y.J.; Cheng, F.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.K. Research progress on landscape ecological networks. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3947–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huo, J.G.; Shi, Z.Q.; Zhu, W.B.; Li, T.Q.; Xue, H.; Chen, X.; Yan, Y.H.; Ma, R. Construction and Optimization of an Ecological Network in Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area, China. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.D.; Fahrig, L.; Henein, K.; Merriam, G. Connectivity is a vital element of landscape structure. Oikos 1993, 68, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.B.; Luo, X.Y. Integrating the MCR and DOI models to construct an ecological security network for the urban agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Rong, W.Z. Construction of ecological network in Suzhou based on the PLUS and MSPA models. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.S.; Lourenço-de-Moraes, R.; Ruas, D.S.; Mira-Mendes, C.V.; Franch, M.; Llorente, G.A.; Solé, M.; Cabral, P. Searching for Networks: Ecological Connectivity for Amphibians Under Climate Change. Environ. Manag. 2020, 65, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamusoko, C.; Aniya, M.; Adi, B.; Manjoro, M. Rural sustainability under threat in Zimbabwe—Simulation of future land use/cover changes in the Bindura district based on the Markov-cellular automata model. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Zheng, X.Q.; Fu, M.C. Scenario analysis of sustainable intensive land use based on SD model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 29, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dang, X.W.; Sun, Q.K.; Wang, S.H. Multi-scenario simulation of urban land change in Shanghai by random forest and CA-Markov model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Zhou, Q.G.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, F.H. Simulation and prediction of land use change in Three Gorges Reservoir Area based on MCE-CA-Markov. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2017, 33, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Fu, M.C.; Tao, J.; Hu, L.Z.; Yang, X.L. Scenario simulation of land use change in mining city based on CLUE-S model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2013, 29, 246–256. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.J.; Qian, L.X.; Wu, Z.F.; Cui, H.S.; Yong, H.X. The SLEUTH Model Simulation of High Density Urban Sprawl in Haizhu District of Guangzhou City. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2010, 65, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Hou, X.Y.; Li, X.W.; Song, B.Y.; Wang, C. Assessing and predicting changes in ecosystem service values based on land use/cover change in the Bohai Rim coastal zone. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.F.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.B.; Xu, B.; Ma, S.; Yang, F.; Shi, Y.; Liu, B.T.; Hao, N.Y.; Wu, R.W.; Lin, W.; Bao, Z.Y. Coupling an Ecological Network with Multi-Scenario Land Use Simulation: An Ecological Spatial Constraint Approach. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, C.; Cheng, Y.J. Spatial influence of ecological networks on land use intensity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Guo, X.N.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.X. Constructing ecological security patterns in mountain areas based on geological disaster sensitivity: A case study in Yuxi City, Yunnan Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Aminzadeh, B.; Khansefid, M. A case study of urban ecological networks and a sustainable city: Tehran’s metropolitan area. Urban Ecosyst. 2010, 13, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergnes, A.; Kerbiriou, C.; Clergeau, P. Ecological corridors also operate in an urban matrix: A test case with garden shrews. Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 16, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Xu, W. Assessment and zoning of eco-environmental sensitivity for a typical developing province in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2012, 26, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Z.; Niu, T.; Yu, Q.; Yue, D.P.; Ma, J.; Pei, Y.R. Ecological spatial optimization based on complex network theory: A case study of Songhua River Basin of northeastern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2022, 44, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J. Combining MSPA-MCR Model to Evaluate the Ecological Network in Wuhan, China. Land 2022, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Chon, J.; Ahn, C. Planning Landscape Corridors in Ecological Infrastructure Using Least-Cost Path Methods Based on the Value of Ecosystem Services. Sustainability 2014, 6, 7564–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.W.; Yan, C.Z.; Xiu, L.N.; Feng, K. The impact of mining changes on surrounding lands and ecosystem service value in the Southern Slope of Qilian Mountains. Ecol. Complex. 2018, 36, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; He, P. MSPA-Based Urban Green Infrastructure Planning and Management Approach for Urban Sustainability: Case Study of Longgang in China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2015, 141, A5014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.D.; Riitters, K.H.; Wade, T.G.; Vogt, P. A national assessment of green infrastructure and change for the conterminous United States using morphological image processing. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2010, 94, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X. Ecological Corridors Analysis Based on MSPA and MCR Model—A Case Study of the Tomur World Natural Heritage Region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, A.T.H.; Beier, P.; Gagnon, J.W. Estimating landscape resistance from habitat suitability: Effects of data source and nonlinearities. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 2151–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yu, K.J.; Li, D.H. The width of ecological corridor in landscape planning. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 2406–2412. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J. Establishing archipelagic landscape ecological network with full connectivity at dual spatial scales. Ecol. Model. 2019, 399, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Xu, J.L.; Chu, J.L. The Construction of a Regional Ecological Security Pattern Based on Circuit Theory. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Han, Y. Integrating spatial continuous wavelet transform and kernel density estimation to identify ecological corridors in megacities. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2020, 199, 103815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.H.; Wu, J.S.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.H. Can policy maintain habitat connectivity under landscape fragmentation? A case study of Shenzhen, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Guo, C.X.; Zhao, M.Y.; Yang, Z.G.; Guo, M.Y.; Wu, B.Y.; Chen, Q.L. Integrating morphological spatial pattern analysis and the minimal cumulative resistance model to optimize urban ecological networks: A case study in Shenzhen City, China. Ecol. Process. 2021, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.L.; Li, Z.S. Ecological regionalization and overview of the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7389–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, M.; Han, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L. The Effect of the Human Footprint and Climate Change on Landscape Ecological Risks: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau, China. Land 2022, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Liu, L. Integrated assessment of land-use/land-cover dynamics on carbon storage services in the Loess Plateau of China from 1995 to 2050. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Sang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, K.; Ma, H.; Xu, Y.; Wan, Q. Land-use changes lead to a decrease in carbon storage in arid region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, D.; Cao, L.; Anderson, B. Assessment and Prediction of Carbon Storage Based on Land Use/Land Cover Dynamics in the Tropics: A Case Study of Hainan Island, China. Land 2022, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Huang, M.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Xiao, L.J.; Xu, K.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.M.; Xu, Z.; Shi, Z. Identification and risk prediction of potentially contaminated sites in the Yangtze River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 151982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liao, J.; Zhu, W.; Qiu, Q.; Wagn, L.; Tang, L. The weight of neighborhood setting of the FLUS model based on a historical scenario: A case study of land use simulation of urban agglomeration of the Golden Triangle of Southern Fujian in 2030. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 4284–4298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q.; Cheng, D.; Xu, C.; Chang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, B. Coupling Coordination Analysis and Prediction of Landscape Ecological Risks and Ecosystem Services in the Min River Basin. Land 2022, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.Q.; Hu, X.M.; Sun, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Multi-scenario land use change and its impact on carbon storage based on coupled Plus-Invest model. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2023, 31, 300–314. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Mu, H.K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Tian, Y.; Tang, D.W.; Li, X. Research on construction path optimization of urban-scale green network system based on MSPA analysis method: Taking Zhaoyuan City as an example. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7547–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, C.C.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, C.M.; Lin, S.; Qiu, R.Z.; Hu, X.S. Construction of ecological network in Fujian Province based on Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Lu, C.X.; Leng, Y.F.; Zheng, D.; Li, S.C. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 18, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Shi, X.; He, J.; Yuan, Y.; Qu, L. Identification and optimization strategy of county ecological security pattern: A case study in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Brown, G.; Hockings, M. Methods and participatory approaches for identifying social-ecological hotspots. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Beier, P. Circuit theory predicts gene flow in plant and animal populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19885–19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, J. Scenario-based ecological security patterns to indicate landscape sustainability: A case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y. Study on the Construction of the Ecological Security Pattern of the Lancang River Basin (Yunnan Section) Based on InVEST-MSPA-Circuit Theory. Sustainability 2023, 15, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Su, J.; Yin, H.W.; Kong, F.H. Construction of Xuzhou ecological network based on comprehensive sources identification and multi-scale nesting. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 1986–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Liu, H. Identifying key areas of ecosystem restoration for territorial space based on ecological security pattern: A case study in Hezhou City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.L.; Qin, M.Z. Identification of ecological corridors and its importance by integrating circuit theory. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3344–3352. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Zhu, C.; Fan, X.; Li, M.; Xu, N.; Yuan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Lyu, C.; Bai, Z. Analysis of ecological network evolution in an ecological restoration area with the MSPA-MCR model: A case study from Ningwu County, China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.J.; Zhang, W.J.; He, L.; Miu, J.Y.; Zi, Y.K. Construction and Optimization of Chengdu Ecological Network Based on Linkage Mapper and Complex Network. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2023, 38, 176–184. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Lin, Y.; Gu, C. Evaluation and optimization strategy of city network structural resilience in the middle reaches of Yangtze River. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, F.N.; Yang, Y.C.; Luo, Y.L. A study on the resilience of ecological networks in the Loess Plateau from the perspective of ecological security patterns. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 10471–10485. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Shan, L.; Xiao, F. Constructing and optimizing urban ecological network in the context of rapid urbanization for improving landscape connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Song, X.; Leng, P.; Zhu, X.; Hu, R.; Guo, D.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xue, K. Higher water ecological service values have better network connectivity in the middle Yellow River basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Lindquist, M. Enhancing landscape connectivity through multifunctional green infrastructure corridor modeling and design. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 38, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Chen, H.; Wan, S.L.; Lu, J.G. Spatial Pattern and Stability Measurement of Regional Ecological Space Network Based on Complex Network Theory: A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta. J. Chin. Urban For. 2021, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).