1. Introduction
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, drones, geoinformation systems (GISs), wireless sensor networks (WSNs), robotics, and autonomous systems are completing the digital transformation of agriculture in the European Union. These technologies work together to increase agricultural practices’ resilience, efficiency, and sustainability, which helps to renew rural communities on all levels—economically, socially, and environmentally [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5].
According to studies [
6,
7], smart agriculture uses analytics and data-driven decision-making (also known as “data-driven farming”) to substantially improve risk management in addition to enabling higher yields and lower resource consumption. This raises the accuracy of all agro-technical procedures while lowering production uncertainty.
These effects can be quantified using specific metrics, such as increase in yield per hectare, water savings per irrigation cycle, reduction in fertiliser and fuel consumption per product unit, as well as the number of precisely optimised agro-technical operations based on sensor and satellite data. Such indicators enable objective monitoring of the effectiveness of digital solutions at the farm and regional levels.
The European Union’s initiatives and policies are a powerful force behind the technological revolution in rural areas. The Common Agricultural Policy strategic plans, digital innovation hubs like SmartAgriHubs and AgDataHubs, and knowledge and innovation initiatives under the AKIS (Agricultural Knowledge and Innovation Systems) are some of the most important. Although these programs have a common goal of accelerating digital transformation, their implementation varies significantly among member states. While some countries, such as the Netherlands and Germany, have made notable progress thanks to well-developed infrastructure and technical support, others—especially in Southern and Eastern Europe—face challenges such as weaker digital connectivity, lack of trained staff, and slower institutional integration. Such differences point to the need for more flexible approaches in planning digital agriculture at the EU level. The Horizon Europe initiative provides funding for research and innovation, allowing the implementation of digital solutions at the farm and regional levels [
8,
9,
10,
11]. These programs aim to increase farmers’ knowledge of technology, build data infrastructure, and develop accessible platforms for current information usage and exchange. The growing digital integration of rural areas into broader European technological and commercial flows is made practical by technology. This approach also creates new jobs in the agricultural technology sector, reduces rural depopulation, and increases the competitiveness of regional production systems [
12].
Digital agriculture is at the basis of a strategy for a stronger and more sustainable rural development because of the urgent need to address issues like food security, rural depopulation, and environmental stresses. While smart technologies’ technical potential is well known, less is known about their broader social and institutional effects, especially with regard to territorial cohesion, community revitalisation, and youth employment. By examining how digital agriculture is influencing rural development routes and promoting inclusive, sustainable change, this article attempts to narrow that gap.
It is believed that in the following stage, models that are just partially digitalised will give access to highly autonomous production systems. By combining robotics, sensor networks, and real-time data processing, these technologies make agricultural production more responsive to environmental changes and local conditions, drastically cut down on the need for human labour, maximise efficiency and cost savings, and open up new job opportunities in the smart agriculture sector. The younger generation, particularly those with skills in IT, engineering, and biotechnology, can now be included in the agricultural industry thanks to this advancement [
9,
13]. The article is based on the following research questions: How do digital technologies in agriculture affect indicators of rural development, such as employment, sustainability, and productivity? What are the key obstacles and factors that enable the wider application of digital solutions in rural areas of the EU? How can the integration of geoinformation systems, IoT technologies, and analytical tools improve the adoption of data-based policies for rural development, adapted to specific agro-ecological conditions?
2. Theoretical and Conceptual Framework
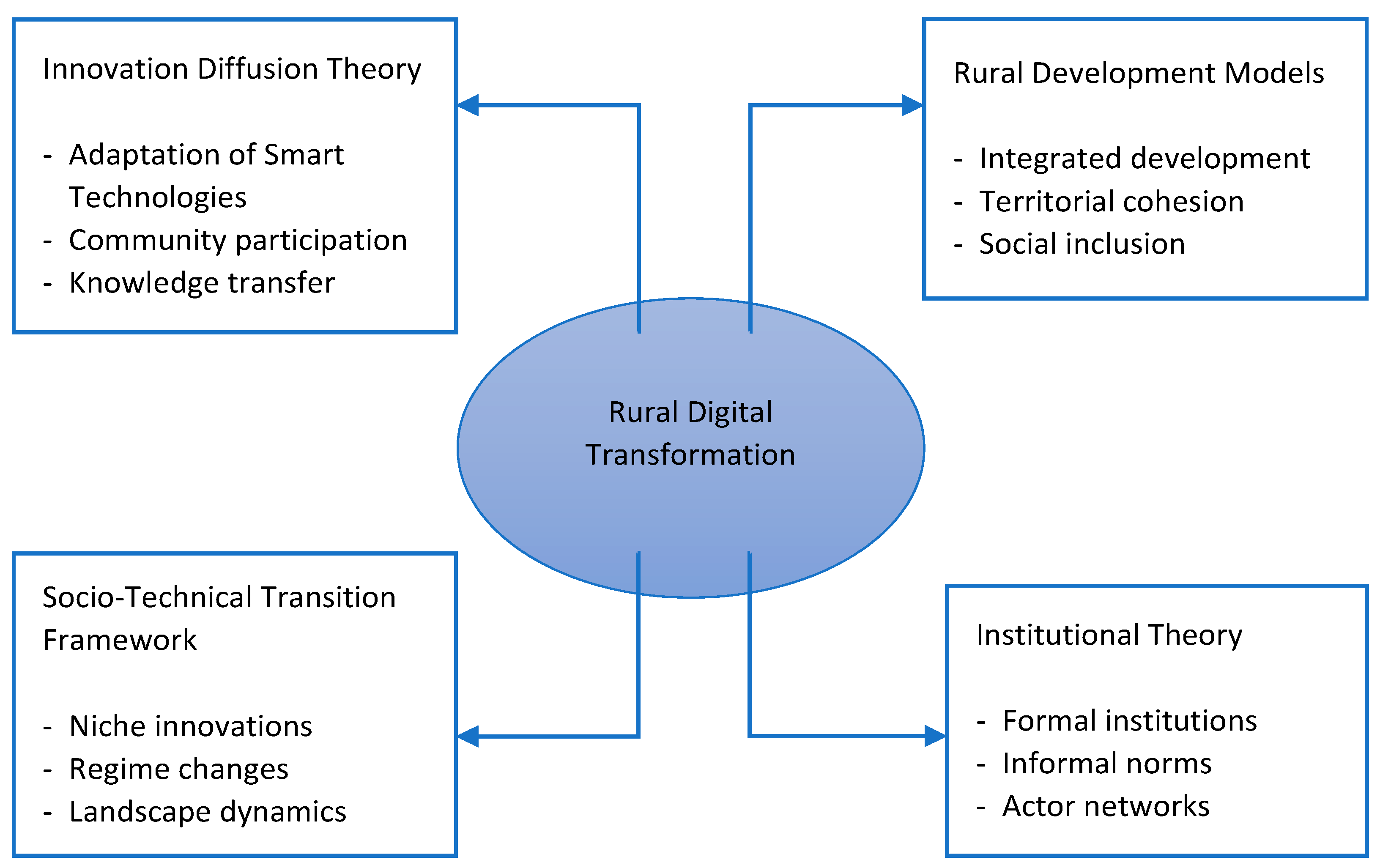
Drawing from innovation diffusion theory, rural development models, institutional theory, and the idea of a multi-level approach to transitions (MLP), this chapter lays out the key theoretical bases that inform the study in this work.
A framework for the integrated development of rural regions is provided by the “smart village” concept created by the European Network for Rural Development (ENRD). This approach suggests employing digital, social, and natural resources to improve living standards in rural areas. Public–private partnerships, investments in digital infrastructure, and community involvement are all encouraged, per [
14,
15]. The notion of territorial cohesion offers an additional foundation, highlighting the necessity of each EU region developing in a balanced manner. This means promoting information exchange, reducing the digital gap, and giving everyone in the agricultural sector equal access to smart technologies [
16,
17,
18].
According to the multi-level perspective (MLP), the digital change in rural areas includes three connected levels: niche (innovation), system (current practices), and landscape (wider sociopolitical context). IoT networks, satellite imaging, and machine learning are examples of precision innovations that act as specific improvements enabling new practices to develop and gradually challenge old regimes [
19,
20]. The effectiveness of these changes depends on the ability of communities to adapt, the flexibility of stakeholders, and institutional support. According to research, digital integration develops more quickly in places with an open local government, effective knowledge base, and high levels of digital literacy [
21,
22,
23]. Institutional theory makes it achievable to understand how informal norms—like collaborative culture and technological trust—and formal processes—like CAP and National Recovery and Resilience Plans, or RRF—influence behaviour during the innovation adoption process. The innovation ecosystem, which includes research facilities, local government organisations, academic institutions, and technology businesses, has a significant impact on rural transformation [
24,
25,
26,
27]. The topics of an inclusive government and power must also be discussed. All stakeholders, especially women, small farmers, and marginalised communities, must be involved for digital reforms to be sustainable. The policy design of EU member states considers the various capacities and limitations of the actors involved [
28,
29,
30]. When combined, these concepts provide an extensive overview of the connections between rural development, institutions, and technology.
Figure 1 illustrates the theoretical–conceptual framework of this study and offers insight into the digital transformation processes of rural areas in the European Union, based on four linked theoretical bases. The term “rural digital transformation,” which is central to the topic, represents a complex series of institutional, social, and technological changes. Four theoretical perspectives are based on this concept.
The first pillar is the innovation diffusion theory, which focuses on how smart technology adoption occurs in rural regions. This concept highlights how important community involvement, information networks, and local leaders are to the adoption of new technology and how quickly and completely it is integrated into daily life. In an effort to reduce regional disparities and improve local system resilience, the second theoretical block focuses on rural development models that integrate the concepts of social diversity, territorial connection, and integrated development.
The third theoretical framework reflects a multi-level approach to sociotechnical transitions (MLP), which interprets digital transformation as a complex process that collaborates at the levels of innovations (niches), dominant practices (regimes), and broader political and economic frameworks (landscapes). In this context, niche developments in digital technology such as drones, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things are gradually transforming traditional agricultural systems. The fourth pillar of institutional theory stresses the significance of legal frameworks, informal standards, and networks of participants that influence how communities accept and use technological advances. The significance of innovative ecosystems and institutional adaptability for a smooth change are given particular attention. When taken together, these theoretical components allow a greater comprehension of the factors influencing the success of digital transformation in rural areas and provide an overview of the situations when new technologies effectively encourage sustainable development and territorial balance.
2.1. Technological Pillars of Rural Digital Transformation and Precision Farming
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs), which allow for continuous, high-precision data collection and processing from the field, are one of the critical foundations of precision and smart agriculture. The use of these networks also opens up new technical and security issues. Maintaining the sensor under conditions of high humidity, temperature fluctuations and physical damage requires reliable service support and spare parts. In addition, protecting the data generated by the sensors becomes crucial—both for farm privacy and the risk of misuse of market-sensitive information. These challenges must be taken into account when planning for wider digitisation.
Monitoring microclimatic and agro-chemical factors such temperature, soil moisture, nutrient concentration, plant photosynthetic activity, light, and pH levels reflects their crucial significance [
3,
31].
Modern systems employ territorially divided sensor nodes in place of isolated measuring stations. These nodes use multimodal sensors (optics, acoustics, and electromagnetics) to provide a more thorough and complex analysis of agro-ecological conditions. This strategy is especially crucial in isolated and climate-sensitive regions with high variability in soil and agro-climatic conditions, where changes in soil composition, temperature, and humidity during the growing season can significantly affect crop quality and yield [
3]. Real-time data processing is made possible through the integration of these networks with edge and cloud infrastructures. The main advance in this field is the use of Edge AI technology, allowing local analysis and decision-making at the sensor node. This minimises the need to constantly transfer large amounts of data to a central computer, saving energy and improving crucial procedures like ventilation control, watering, and autonomous feeding [
32,
33].
The application of LPWAN communication protocols, such as LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, and Sigfox, which allow for a reliable and energy-efficient connection between devices even in remote areas lacking existing infrastructure, further supports technological advancement. When paired with 5G networks, NB-IoT allows for greater coverage and a notable decrease in data transmission costs, whereas LoRaWAN sensors, for instance, can function independently for up to five years due to their low energy consumption [
4,
34,
35].
These techniques significantly boost production efficiency on agricultural fields that vary greatly by geography and have an extensive variety of cultivation conditions. They increase the competitiveness of rural production systems through suitable production, variety, and production technology selection by utilising local characteristics as advantages. Instead of simply being instruments for operational efficiency, they accordingly turn into an important strategic resource for rural development. Wireless sensor network (WSN) installation encourages more sustainable use of natural resources, increases agricultural resistance to climate change, and improves the environment. The profession of digital agronomy generates new employment opportunities and facilitates the return of young professionals to rural regions [
9,
36].
2.1.1. Robotics and Autonomous Systems in Agriculture
Agriculture’s rapid automation is changing laborious, repetitive, and dangerous jobs. Sensor-equipped air and ground robots with computer vision and artificial intelligence are gradually taking the place of humans in tasks including planting, weeding, chemical treatment, and harvesting. Along with increasing efficiency, these robots allow for targeting the usage of pesticides and fertilisers, reducing chemical use and their negative impacts on the environment [
4,
12].
Modern agro-robots utilise machine learning algorithms to analyse plant morphology, assess fruit development, and distinguish between dangerous and helpful species. They are therefore very helpful in viticulture, fruit and vegetable cultivation, and other fields where production quality is strongly correlated with precision [
37,
38,
39].
Parallel guidance systems are being utilised more and more in practice for navigation, allowing robotic platforms, self-propelled equipment, and tractors to drive autonomously along predetermined paths [
40,
41]. Furthermore, algorithms for group control of robots are being developed, allowing several robots to operate in harmony, without collisions, and with the best possible task distribution. These methods are especially important when handling large, culturally sensitive areas [
33,
42,
43].
But human oversight and maintenance are still required. Creating systems that allow a single operator to oversee and manage several robotic units is currently a challenge. This is achieved by developing service systems that autonomously replace batteries, refill insecticides, and transport drones and robots to the next work location [
13].
Autonomy increases as a result of these trends. The next evolutionary stage in this regard is the creation of completely self-sufficient farms, greenhouses, and aqua-systems. These systems offer round-the-clock production management without a continual human presence by combining IoT, sensor networks, robots, and artificial intelligence into a unique architecture [
2,
3,
9]. In addition to improving productivity, this paradigm reinterprets the agricultural industry and creates new opportunities in the biotechnological, engineering, and information technology sectors.
There are two potential development paths that show up. In the first scenario, highly industrialised agricultural production systems that maintain conventional production sizes and are still tailored to local environmental conditions are made more efficient. This route helps to preserve the rural way of life, encourage more equitable regional development across various agro-ecological zones, lessen environmental stressors, and encourage the expansion of organic farming. The European Union actively supports this model and should receive even more focused and systematic support in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The second option, which is more effective for producing immediate advantages but not as helpful for long-term sustainability, is the development of broad, highly protected agricultural facilities that are protected from external environmental impacts. The efficiency of highly intensive conveyor-style farming is improved by automation and digital technologies in such systems. Since the early 2000s, when an unequal specialisation of production among the largest producers and specific regions caused a significant increase in total agricultural output, this pattern has dominated Russia. It has also caused a decrease in arable land in several areas, the closure of many small and medium-sized farms, increased environmental expenses, and serious harm to Russia’s Non-Chernozem zone, which includes parts of Central Russia, the Northeast, and the Northwest [
44,
45,
46,
47].
Major demographic issues facing the European agricultural sector today include the aging of the rural population, youth migration to urban areas, and a lack of seasonal labour, especially in sectors that rely on manual labour-intensive tasks like harvesting, weeding, and plant treatment [
9,
12]. This situation represents an important risk to both the continuation of production and the financial stability of small and medium-sized farms.
Automation and robotisation are becoming increasingly utilised as solutions to these issues since they allow frequent and physically difficult tasks to be performed without the need for a large staff. For example, the impact of a labour shortage can be reduced and farm operational flexibility increased by employing robotic devices for planting, harvesting, and weeding in place of dozens of seasonal labourers [
38].
Autonomous systems offer long-term economic advantages alongside immediate relief. Despite the relatively high initial investment, robotics and automation are becoming less expensive to operate and maintain, and the benefits accrue over many years of use [
12,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52]. Simultaneously, software updates enable the adaptation of new features without requiring more material expenditures.
These developments are also impacting the structure of the rural labour market. It is becoming more and more necessary to replace traditional workers with technicians, operators, analysts, and digital agronomists who can supervise and manage complex systems. This makes it possible for young professionals to move into industries that they had previously avoided due to a lack of perspective [
10,
11].
Especially crucial are platforms like SmartAgriHubs and ATLAS, which provide training and resources for the digital transformation of villages, as well as educational and innovation hubs like DIHs (digital innovation hubs). Especially in places that have seen decades of depopulation, such initiatives can serve as a catalyst for population retention in rural areas and lessen the pressure of migration [
2,
8].
By enabling labour without physical exertion through digital interfaces and automated systems, smart technologies also build a more inclusive atmosphere for elderly farmers and women. This makes rural communities more inclusive and socially cohesive.
Agricultural robotisation is a strategic tool for the socioeconomic revitalisation of rural Europe as well as a technical solution to the labour problem.
2.1.2. Precision Agriculture with Drones and Aerial Mapping
Drones (unmanned aerial vehicles, or UAVs) are a vital component of modern precision agriculture systems because they allow rapid, extensive, and cost-effective gathering of information from the air [
53]. Drones can more accurately identify problems like drought stress, nutritional deficiencies, or pathogen infections in the earliest stages of plant development since they have a significantly higher temporal and spatial resolution than satellite photos [
8,
48].
Using multispectral and thermal cameras, drones can give measurements of vegetation, such as the Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), SAVI, or GNDVI, which provide data on photosynthetic activity and crop health. Production may reduce its ecological impact and maximise input use by using these indices to guide exact decisions about irrigation, fertilisation, and plant protection [
2,
49]. Drones are also utilised for mapping soil variability, classifying terrain, monitoring erosion, and organising seeding activities in several areas. Farmers can utilise the maps of management zones created by integrating drone data with GIS platforms and image processing software to apply pesticides, fertilisers, and water locally [
50,
51].
Drones for agriculture are currently being developed for active jobs like precision spraying and seed distribution. These devices have GPS and artificial intelligence (AI) plant recognition algorithms, which further minimises chemical use and improves operator safety, though they can only treat sick parts of the plot [
4].
Drones have been demonstrated to be especially helpful for small and medium-sized farmers who do not have access to expensive satellite data or large equipment. Because of its reasonable price, flexibility, and simple use, precision agriculture is now becoming increasingly accessible, especially in isolated regions with poor infrastructure [
52]. In addition to its technical advantages, the use of drones in agriculture has strategic importance for sustainable rural development since it encourages young people to look into professions in agronomy, technical support, and data analytics [
9,
11,
54]. Conventional agriculture may now be modified into climate-resistant, productive systems because of these technological advancements.
2.1.3. Data Integration and Analytics Software
In smart agriculture, data gathered by IoT sensors, drones, tools, and robots is not fully beneficial until it is properly analysed and linked. Analytics and data monitoring systems are a crucial part of the digital architecture because they make it easier to convert raw data into insights and operational decisions [
1,
6,
55].
With the use of current precision agriculture software, data from many sources, including satellite imaging, tractors, robots, and field sensors, may be integrated. Technology like machine learning, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics are used in these systems to help with identifying patterns and agronomic forecasting [
7,
56,
57,
58,
59].
One of these solutions’ primary advantages is the development of variable management maps, which are used to organise plots based on variables such as yield potential, humidity, and fertility. Then, these maps are used to automatically run machinery that applies fertiliser, pesticides, or water in precisely measured quantities [
10,
11]. Many platforms have visual interfaces and smartphone apps that enable farmers to send instructions to self-governing systems, provide recommendations based on weather and pesticide conditions, and monitor crop health in real time. Additional functions include disease prediction algorithms, market platform integration, and real-time resource management [
2,
60].
Data exchange between various software and hardware systems is facilitated at the European level through the adoption of so-called AgData standards and compatible formats. From small farms to software experts, projects like DEMETER and ATLAS seek to establish open ecosystems where data can be shared in a safe and useful way [
10].
Applying such solutions not only improves operational efficiency but also fosters transparency, cost savings, and climate change resilience. For this reason, digital analytics is an essential part of the larger rural economy’s transition to intelligent, data-driven systems.
2.1.4. Precision Agriculture’s Foundation: Geoinformation Technologies
Geoinformation technologies (GIS) allow the synthesis of geographically directed data with economic, ecological, and agronomic properties. These technologies are growing rapidly as a crucial tool in modern rural development. GIS is used in smart agriculture for precise land mapping, resource usage planning, risk assessment, and agro-climatic zone classification [
49,
50].
GIS technologies integrate data from satellites, drones, and Internet of Things sensors to build soil variation maps that provide farmers and planners with information on soil structure, terrain, slope, water saturation, and erosion zones. These maps are used to plan for the conservation of streams and biodiversity, to identify areas of intensive and broad production, and to strategically place irrigation systems [
8,
51].
When it comes to rural spatial planning, GIS makes it easier to make decisions about agro-industrial development zones, traffic, infrastructure, and land distribution. For instance, the identification of land suitable for conversion to organic or multifunctional agriculture, surface runoff prediction, and climate change scenario simulation are all performed using GIS models [
2,
61].
The integration of socioeconomic data with the physical features of the terrain is made possible by GIS, which is essential for creating policies that balance environmental preservation and economic development. Roads, schools, and distribution centres are among the rural infrastructural projects that are planned in this environment based on demographic trends and the spatial distribution of production [
10].
Thanks to open-source software and smartphone apps that enable straightforward mapping and analysis at the farm level, GIS technologies are becoming more widely available. This transforms GIS from a specialised instrument to a platform for local power, especially in places where complex infrastructure systems are not available [
52]. GIS provides the basis for localised decision-making, agro-ecological zoning, digital land registries, and precise subsidy zone identification through integration with smart sensors and analytical tools. This method allows geoinformation technology to enhance the multifaceted management of rural development in addition to improving agricultural practices.
Precision farming is undergoing a revolution thanks to the use of satellite mapping and geographic information systems (GIS). While satellite imagery offers a dynamic depiction of biomass, moisture, plant stress, and changes in land use, GIS allows farming activities to be precisely localised [
8,
55].
Farmers and researchers can use multispectral and hyperspectral data from Sentinel satellites obtained through the EU’s Copernicus program to
- -
Map crop health using NDVI and SAVI indices;
- -
Track changes in vegetation and soil over time (2015–2025);
- -
Identify erosion, flooding, and other environmental factors in real time [
62].
Tsiligiridis and Ainali (2023) demonstrated in Greece that using machine learning techniques in conjunction with Sentinel-2 data may facilitate crop classification even in plots smaller than 5 ha [
63]. The EO4AGRI project also integrates agro-software and EO data to make recommendations about planting, fertilisation, and harvesting based on weather patterns and geolocation, according to the European Space Agency [
64].
AgroDIH Net and Horizon Europe-NIVA are two EU programs that promote the use of GIS for monitoring CAP sustainability indicators and digitising administrative procedures (such as e-parcel management and inspections) [
65,
66,
67]. Through the creation of visual maps by NUTS2 areas, GIS also makes it possible to analyse regional performance disparities and more accurately tailor policies to local requirements [
4].
A move towards more precise and efficient management of agricultural land can be seen by
Table 1’s significant increase in the use of digital technologies in agriculture, which includes a rise in the percentage of farms using NDVI and SAVI for plant monitoring, an increase in the number of users of Sentinel satellite data, and the growth of CAP programs with GIS components. This enables farmers to improve yields, optimise resource use, and better monitor plant health [
68,
69,
70,
71].
The patterns demonstrate the EU agriculture sector’s rapid adoption of geodigital tools, demonstrating their strategic importance in policy formation, monitoring, and decision-making. By 2025, GIS and EO systems should be nearly fully integrated into CAP processes and modern farms’ routine operations. Using this integrated approach that combines digital technologies and spatial planning, the next step is to build unique decision-making platforms based on continuous and real-time geo-data.
2.1.5. Integrated Technological Layers in Smart Agriculture
Following an outline of the use of geoinformation technologies in rural spatial planning, the following section describes the important digital elements and their relationships within the larger framework of smart agriculture. This tiered structure makes it possible to move from discrete digital solutions to a system that relies on automated decision-making and constant data flow.
The way that important technologies work with the digital agricultural functional architecture is demonstrated in this section. More effective data collection, processing, and utilisation are made possible by the integration of several levels, resulting in a system of data-driven agriculture and decision-making. It is feasible to achieve the ideas of autonomous logistics and microclimate adaptation in rural areas by integrating sensors, machinery, and algorithms into a single functional unit [
55,
67,
68,
71,
72].
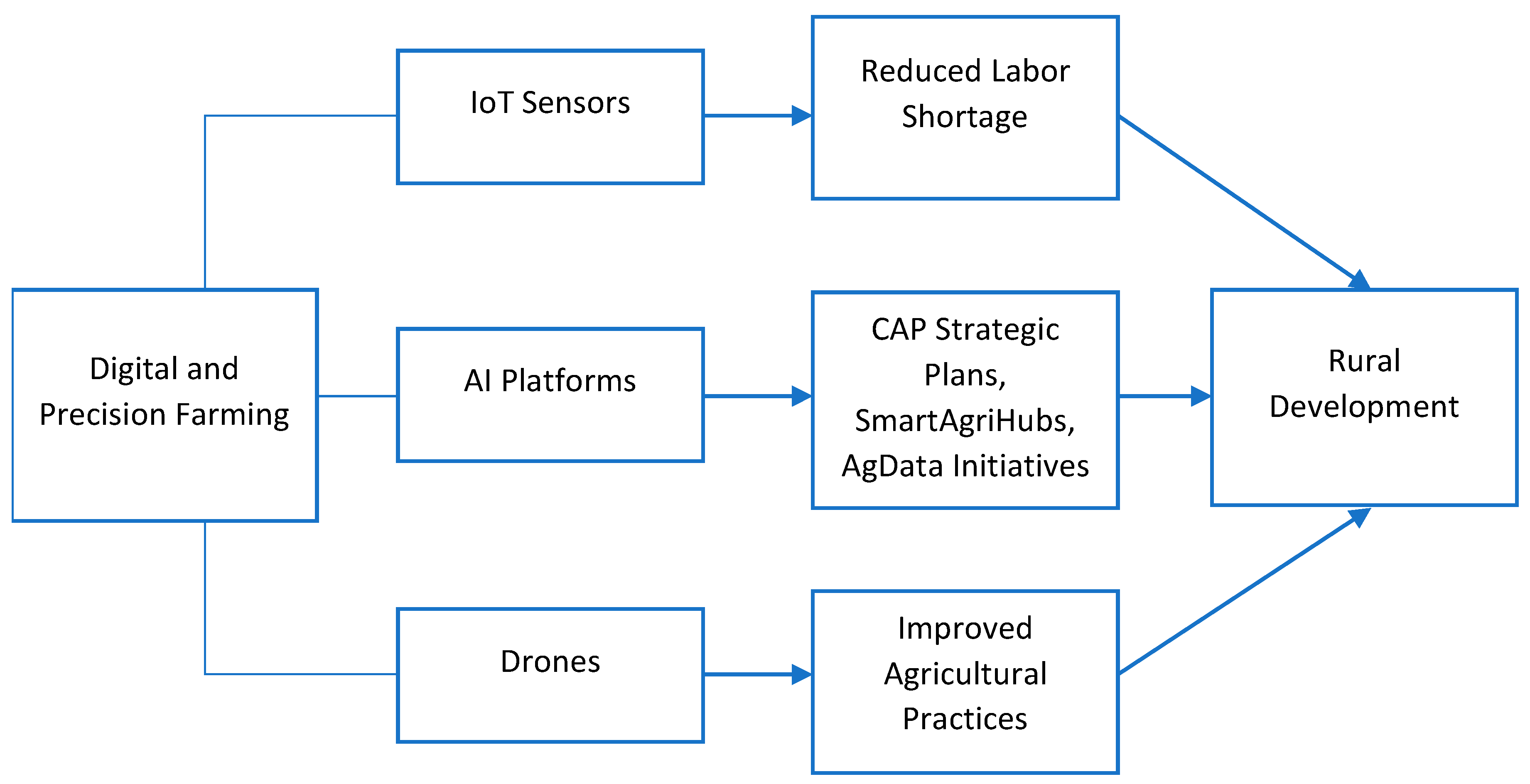
Figure 2 illustrates how the many technology tiers of smart agriculture are interrelated and collectively constitute an integrated ecosystem, encompassing data collection, particular agronomic choices, and the impact of growth in rural regions.
Soil moisture, temperature, insect presence, and other physical or biological indications can all be continuously collected from the field thanks to the Internet of Things’ sensors, which make up the system’s core layer. Their compatibility with LPWANs (such as LoRaWAN and NB-IoT) and low energy consumption make them especially well-suited to widespread deployment in rural regions.
With Edge AI/ML, data may be processed locally on the device without requiring continuous Internet access or transferring massive volumes of data to the cloud. Higher system resilience, reduced costs, and quicker reaction are made possible in remote areas.
GIS and satellite mapping offer the broad picture, including crop mapping, soil categorisation, weather monitoring, and land cover changes. It is feasible to automate change tracking and guide local actions when combined with machine learning.
The “muscles” of the system are intelligent robots and drones, which increase efficiency and decrease reliance on manual labour by enabling autonomous seeding, harvesting, watering, pesticide application, and other operations.
Using algorithms and analytics, Decision Support Systems (DSSs) compile all incoming data and then provide suggestions through dashboards, mobile apps, and automated alerts.
In addition to technical development, EU programs like Horizon Europe, SmartAgriHubs, and AgData provide institutional and political support by funding innovation, educating farmers, setting up data-sharing platforms, and developing regulatory frameworks.
This technological synergy’s ultimate goal is represented by precision agriculture’s results, which include higher yields, less resource use, environmental protection, and enhanced youth involvement. This is how digital agriculture transcends efficiency and enters the larger framework of rural development that is sustainable.
By combining several technological layers, such as sensors and algorithms, modern agriculture moves past the traditional digitisation stage and into the intelligent system optimisation phase. In rural areas, this strategy not only boosts productivity and profitability but also fosters local autonomy, youth employability, and environmental resilience [
73,
74].
3. Materials and Methods
The article uses a mixed methodological approach that combines qualitative analysis of strategy documents, secondary data analysis from European databases, and a thorough literature review. With an emphasis on sustainability, resilience, and demographic revitalisation, the goal is to illuminate the institutional, technological, and socioeconomic aspects of the digital revolution of rural agriculture in the EU. Patterns pertaining to the integration of smart technology and indices of rural development were found using an interdisciplinary framework that included quantitative analysis and GIS techniques.
The research aims to visualise geographic disparities in access to VHCN and digital innovations, analyse correlations between the availability of digital infrastructure and rural economic indicators, evaluate the role of robots and AI technologies in addressing the workforce shortage in the agricultural sector, and implement a qualitative synthesis of EU strategies and tools to support the rural digital transition.
This study used data from a number of sources (
Table 2): the EU Open Database offered data on poverty, productivity, and employment, the European Drought Observatory supplied satellite data on drought and stress, Copernicus Land Monitoring shed light on changes in crop coverage and land use, Harmonised Crop Statistics or Eurostat was utilised for area and yield analysis, and EuroCrops (LPIS) was used for geo-data pertaining to crop classification. Additionally, data from GlobeNewswire’s Smart Agriculture market analysis was incorporated. EU reports (Digital Compass, RRF Reports, SmartAgriHubs) and scientific sources like CORDIS, the Joint Research Centre (JRC), and FAO are used to augment these data [
81,
82,
83,
84,
85,
86,
87,
88,
89,
90].
The Digital Europe and Data Spaces Support Centre databases provide data infrastructure metrics, while Eurostat FAO and OECD are secondary sources for policy and digitisation penetration into the agricultural sector.
Strategic papers including the CAP strategic plans for 2023–2027 and important political frameworks like the EU Green Deal, the Digital Decade, and the EU Data Act were included in this qualitative study. In order to find institutional obstacles, thematic policy clusters, and areas of overlap between the digital and rural agendas, the DEMETER, ATLAS, and AgriDataSpace programs were also examined. The European Commission, Copernicus, CORDIS, and the UNDP were among the sources used in the quantitative analysis of technologies.
In addition to the analysis of strategic documents and data sources, the research also relies on a number of quantitative and spatial indicators that enable a multidimensional assessment of the impact of digital agriculture on the development of rural areas. Among the most important indicators are demographic indicators, such as the participation of young people in agriculture and migration flows from and to villages; then, the coverage of digital infrastructure, including the availability of broadband Internet, the number of digital innovation hubs (DIHs), and functional IoT systems; as well as the degree of use of smart technologies, including geoinformation platforms (GIS), NDVI analysis, IoT sensors, and automated systems. In particular, the percentage of land under digital surveillance, expressed by the number and area of plots included in digital pilot projects, is monitored.
The goal of this approach is to show how digital and precision agriculture can contribute to reducing dependence on physical labour, more efficient use of resources, increased yields, environmental protection, and strengthening of local capacities in rural areas. By combining numerical indicators and geospatial analyses, the research contributes to shaping rural development policies that are both territorially adapted and strategically oriented.
4. Results
According to the goals outlined in the approach, this section provides both quantitative and qualitative findings regarding the integration of digital technology into rural agriculture in the EU. In addition to a comparison of the performance of important technologies, primary indicators of technology penetration, infrastructural capacity, geographic disparities, and institutional support are presented.
Over the last decade, the EU’s rural agriculture has undergone a digital transformation that has seen an exponential increase in the use of smart technology, particularly in the areas of precision agriculture, geoinformation systems (GIS), unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and Edge AI solutions. This study is illustrated in
Table 3. In 2024, over 75% of EU farms will employ NDVI/SAVI data for vegetation monitoring, up from 15% in 2015, according to data from multiple European databases and market evaluations. By 2024, there were over 25,000 users of Sentinel satellite data, up from 3000 in 2015, and over 30,000 users are expected in 2025. Simultaneously, there were 24 CAP initiatives with integrated GIS components in 2024, up from 2 in 2015, suggesting a significant institutional drive towards digitisation.
These metrics attest to the high rate of digital adoption among European farmers, which has been bolstered by calculated investments made through the Digital Europe, CAP, and Horizon projects. Digital technologies are becoming important players in integrated rural development as a result of the expansion of educational platforms, the expansion of DIH networks, and the increasing availability of open satellite data (Copernicus). A complex structure of technical layers is identified in the digital transformation of European agriculture, where various digital systems are integrated to maximise sustainability, output, and decision-making. Every technological layer has a distinct purpose, and when combined, they allow for the development of accurate, effective, and ecologically friendly solutions. When using LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, optical, and acoustic sensors, IoT sensors allow for continuous data collection on the soil, microclimate, humidity, nutrient levels, and insect presence. After that, the data is processed locally using Edge AI systems like CNN, RNN, and TinyML models, which eliminate the requirement for a cloud connection and improve responsiveness and latency.
Soil categorisation, vegetation index monitoring (NDVI, SAVI), erosion and evapotranspiration mapping, and increasingly accurate spatial analysis are made possible by GIS and satellite systems like Copernicus. Deep learning also helps with these tasks. Planting, spraying, disease monitoring, and harvesting are being handled by autonomous robots and drones; nevertheless, their use is still constrained by cost and the requirement for technical user training, particularly on smaller farms.
Decision Support Platforms (DSS) combine all input data and employ recommendation algorithms to identify hazards, prescribe the best agro-technical measures, and sound alerts instantly. These platforms are becoming essential for overseeing intricate farms that depend on fluctuating circumstances.
Simultaneously, EU programs and laws like SmartAgriHubs, Horizon Europe, the AI Act, and the Data Act offer ethical, educational, and infrastructural support, establishing a uniform framework for the sharing and application of agricultural data.
Ultimately, all of these layers result in tangible outcomes, such as raising yields, cutting input costs, lessening the adverse effects on the environment, and possibly most importantly, keeping young people in rural regions by making the sector more appealing to them digitally.
While satellite data provides the broadest coverage and long-term analytical value, the combination of IoT sensors and Edge AI systems demonstrated the highest level of efficiency. Costs and the digital divide between big and small manufacturers continue to be obstacles, which is a major problem for the upcoming stage of digital inclusion.
In nations that have made investments in LoRaWAN and 5G infrastructure, the integration of IoT sensors with Edge AI solutions is expanding quickly. For instance, in Germany, over 60% of pilot farms employ local analytics for irrigation [
73].
In the Netherlands and Denmark, over 15% of commercial farms currently employ DSS platforms like FarmNet, AgriSens, and AgroDataCube; by 2027, that number is expected to rise to 40% [
65].
The degree of technology integration in EU agriculture can be measured by the technical layer using the data that is currently available from the Copernicus program, Eurostat, Digital Europe, and EPRS sources, which is shown in
Table 4.
The digital layers in EU agriculture exhibit distinct growth trends between 2015 and 2025, but at varying rates and levels of technological integration. Less than 10% of farms had IoT sensors in 2015. By 2024, that number had risen to 42%, and by the end of 2025, it is expected to surpass 50%. This expansion demonstrates the increasing accessibility and affordability of sensor networks as well as the growing demand for precise, up-to-date data to maximise agricultural monitoring, plant nutrition, and watering.
With less than 3% usage in 2015, Edge AI and machine learning are now in the experimental stage but are predicted to rise significantly to 18% in 2024 and 30–35% in 2025. This section illustrates how energy-efficient models like TinyML are developing more quickly and how farms are beginning to trust local, decentralised data processing.
One of the most often used layers, GIS and satellite data, saw a rise from 15% to 75% penetration, with an anticipated 85% by 2025. This demonstrates how important vegetation and geolocation data have become for yield forecasting, soil categorisation, and strategic planning.
The beginning rate of less than 2% in 2015 had risen to 12% in 2024 with regard to smart robots and drones. The rise is consistent and indicates a rising application in specialised production, particularly in fruit growing and viticulture, where automated activities are highly valued, even though the total number of users is still relatively low.
The move towards data-driven management is supported by the rise of Decision Support Platforms (DSS), which went from 5% to 25% and is expected to reach 40% by the end of 2025. For small and medium-sized farms seeking integrated, reasonably priced analytics, these platforms are quickly emerging as a key resource.
Lastly, the number of digital measures covered by the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) grew from just two programs in 2015 to twenty-four in 2024, with a propensity to surpass twenty-eight programs in 2025. This indicates a definite institutional change in favour of digitalising rural Europe and a political willingness to use CAP tools to promote digital inclusion.
These quantitative data show the EU’s gradual but complicated shift to digital agriculture, with IoT and GIS leading the way in terms of penetration and AI and robotics advancing due to market and institutional incentives. The infographic in
Figure 3 shows the key actors, technologies, and objectives in the digital transformation of rural development, based on AI, IoT, and participatory planning.
4.1. Digital Agriculture Technologies in the EU
Worth more than EUR 660 million in 2023 and with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18–20% until 2030, drones have emerged as one of the agritechnology markets with the quickest rate of growth [
98], as shown in
Table 5. Their increasing use in mapping, spraying, and monitoring is shown in this growth.
In the IoT sensor market, over 1.2 million farms in the EU utilise devices to evaluate crop health, climate, and soil moisture—a 35% increase over prior years [
90]. The shift from experimental to standardised smart monitoring procedures is supported by this figure.
In 2023, the use of Edge AI and predictive analytics had increased by 28% [
36,
62]. These technologies make it possible to process data quickly on-site without requiring a continuous Internet connection, which is particularly advantageous for rural areas that are distant and lack adequate infrastructure.
At the NUTS2 regional level, crops were classified with an accuracy of over 80% thanks to GIS technologies and satellite observation via the Copernicus system [
62]. This makes it possible to plan production as well as allocate resources more effectively and manage land in an environmentally conscious manner.
The main infrastructural foundation for all of the previously stated digital layers is the Internet of Things (IoT) networks, which cover 98% of rural areas in the EU thanks to the combination of 5G and satellite connectivity [
99].
The information provided clearly demonstrates that digital technologies are now viewed as fundamental cornerstones of the EU’s contemporary agricultural strategy rather than as supplemental tools. The strategic significance of institutional assistance through the CAP and Horizon Europe initiatives is further supported by their beneficial effects on accuracy, coverage, productivity, and sustainability.
4.2. Comparative Analysis of the Performance of Technologies
A comparative study of the technical and economic features of digital solutions was carried out in order to more accurately assess their practical usefulness in agriculture.
Table 6 compares the performance in terms of accuracy, battery life, energy efficiency, data-processing techniques, and implementation costs.
The analysis’s findings demonstrate distinct variations in each technology’s economics and practical usability. Due to their low cost and extensive open data availability, GIS tools and the Copernicus system are especially well-suited for small and medium-sized companies. Edge AI-enabled WSN systems are very energy-efficient and have local data-processing capabilities, making them highly adjustable to various agro-climatic situations.
Autonomous robots are only available on larger farms with stronger infrastructure since they require a significant initial investment and subsequent training, despite being technologically superior in terms of automation and precision. Although drones and AI provide a high degree of accuracy and flexibility, their greater costs and reliance on cloud computing make wider implementation difficult.
All things considered, the information demonstrates that digital transformation is not consistent and is contingent upon regional elements including network infrastructure accessibility, educational attainment, and financial resources. The inclusion of smaller producers in the digital value chain is made possible by these distinctions, which also create room for focused institutional support in the form of training, subsidies, and standardisation of interoperable systems.
4.3. Obstacles and Success Factors of Digital Transition in Rural EU Areas
There are difficulties associated with rural agriculture’s digital transition in the EU. Numerous barriers are preventing broader adoption in various places, despite the data showing an increasing integration of smart technologies. The high initial costs of sophisticated equipment, rural producers’ lack of technical know-how, the lack of infrastructure in less developed areas (particularly high-speed Internet access), and institutional barriers pertaining to administrative processes and unequal CAP policy implementation are some of the main obstacles.
One other issue is digital literacy; many farmers, particularly those over 55, exhibit a poor desire to adopt new tools, which has a direct impact on the rate at which technology is used. Eurostat data from 2023 shows that less than 30% of Southeast European agricultural holdings have the fundamental digital skills required to operate smart technologies.
The existence of pilot projects that show tangible benefits, local hubs for digital training and networking, access to subsidies and funding (such as EAFRD and Horizon Europe), and well-defined national digital strategies are, on the other hand, critical success factors for the digital transition. Because of well-coordinated state policy, Internet infrastructure, and the active participation of young farmers in innovation flows, nations like the Netherlands, Denmark, and Estonia have already achieved a rate of agricultural digitisation of over 70%.
An effective digital transformation thus requires a mix of institutional, educational, and infrastructural assistance. For digital agriculture to be integrated evenly throughout the EU, it must be a top priority to remove the obstacles that have been identified.
In order to overcome this gap, it is necessary to invest in the development of basic digital infrastructure in remote rural areas, as well as in the education of farmers through targeted training and practical workshops. A key role can be played by digital innovation hubs (DIHs) and local cooperatives that would serve as centres for access to technology and knowledge. Also, subsidising digital equipment for small and medium-sized farms can contribute to a more equal participation of all farmers in the digital transformation.
4.4. Demography, Productivity, and Digital Infrastructure
The inclusion of factors linking digital infrastructure to demographic and agronomic changes in EU member states improves the quantitative analysis section of the results, which is shown in
Table 7.
Between 2015 and 2025, the eight EU nations under observation showed a distinct trend of improving their digital infrastructure, with a notable rise in the number of DIH centres [
107]. While Central and Eastern European nations like Poland and the Czech Republic are quickly embracing the digital revolution, Germany and the Netherlands now control the majority of this market.
The majority of rural areas may now use smart technologies thanks to the expansion of broadband Internet coverage, which has nearly universal availability (85–97%) [
110]. This removes obstacles pertaining to data availability and digital tool access.
The rise in yields across the board suggests the increasing importance of input optimisation and digital precision [
109]. With the largest yields, the Netherlands continues to lead, while Hungary and Poland have advanced the most in comparison.
Indicators of demographics are also important; all nations report a rise in the number of young farmers [
108], confirming that digitisation can inspire a new generation to engage in agriculture. In contrast to nations with a smaller beginning proportion, such Hungary and the Czech Republic, this trend is more noticeable in Germany, the Netherlands, and France.
The findings support the link between digital investments, infrastructural growth, higher productivity, and favourable demographic trends, supporting the strategic significance of the digital revolution for rural Europe’s future.
Recent data on the usage of important digital technologies in European agriculture also shows how their deployment affects markets, users, and accuracy. According to data gathered from pertinent sources [
36,
62,
90,
98,
99], quantifiable outcomes are expected in 2023–2024.
A market worth approximately EUR 660 million in 2023, drones are expected to develop at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18–20% until 2030, making them one of the agritechnology sectors with the quickest rate of growth [
98]. This expansion is a result of their increasing application in mapping, spraying, and monitoring.
According to the UNDP [
90], over 1.2 million farms in the EU utilise IoT sensors to evaluate crop health, climate, and soil moisture, a 35% increase over the previous year. This graph validates the shift from trial-and-error to routine smart monitoring procedures.
Deployment of Edge AI and predictive analytics had increased by 28% in 2023 [
36,
62]. Without requiring a continuous Internet connection, these technologies allow for quick data processing on-site, which is particularly advantageous for rural locations that are distant and lack adequate infrastructure.
Crop classification at the NUTS2 regional level was made possible using GIS tools and satellite observation via the Copernicus system, with an accuracy of above 80% [
62]. This makes it possible to plan for production as well as more ecologically conscious land management and resource allocation.
Thanks to the integration of 5G and satellite connectivity, 98% of rural areas in the EU are now connected to IoT networks, forming the core infrastructure for the previously discussed digital layers [
99]. This near-universal coverage eliminates one of the key barriers to digital inclusion: limited connectivity, particularly in remote or underserved regions.
Digital technologies are now viewed as fundamental cornerstones of the EU’s modern agricultural strategy rather than as auxiliary tools, as the evidence presented amply demonstrates. Their beneficial effects on productivity, sustainability, accuracy, and coverage further validate the strategic significance of institutional support provided by the CAP and Horizon Europe programs.
4.5. Case Study: GIS and EO Technologies in Digital Agriculture in Cyprus
Over the past ten years, Cyprus has realised the value of integrating GIS tools and data from European satellite initiatives like Copernicus and Sentinel-2 to digitise agriculture. Despite its small size and limited water resources—factors that heighten the urgency of innovation—Cyprus has developed advanced models for irrigation management, monitoring of olive and vine cultivation, and planning of agro-tourism zones in rural areas [
112,
113,
114].
The Regional GIS Centre in Agros, which optimises groundwater use by using maps of soil moisture change, is one such example:
- -
To evaluate the condition of olive trees and stop the spread of disease, the NDVI is used in the regions of Paphos and Limassol.
- -
“SmartVinesCy” is a Horizon Europe-funded project that uses drones, IoT, and GIS to monitor vineyards digitally and anticipate the yield based on microclimatic parameters.
By connecting administrative e-parcels with agro-ecological zones, the Cyprus Ministry of Agriculture generates geo-referenced subsidy maps using the EO4AGRI platform.
During 2020–2024, the number of farms utilising GIS applications rose by more than 70% [
115], and Copernicus data and local IoT stations helped increase yield prediction accuracy in pilot regions from 62% to 85% [
113].
Cyprus serves as evidence that intelligent, highly precise geotechnologies can be applied in agriculture, especially in small nations with unique agro-climatic problems. The country’s experiences can be used as a template to integrate digital tools in other island and Mediterranean nations aiming to improve rural areas in a sustainable way.
Analysis of the GIS graphic for Cyprus’s agriculture in 2024 (
Table 8): Digital agriculture in Cyprus has developed unevenly, as shown by regional variations in the use of GIS technologies. Paphos and Limassol are at the forefront of geodigital tool use because of their robust wine and citrus industries, improved infrastructure, and participation in EU initiatives like DigiFarmCy and AgriDataValue [
72,
99,
116]. Additionally, these regions have more research and educational resources available, which speeds up the digital shift even more [
117].
Conversely, areas such as Famagusta and Larnaca encounter difficulties such as limited access to IoT infrastructure, a shortage of local GIS specialists, and a lesser degree of digital literacy among the rural populace [
118,
119]. These disparities necessitate focused expenditures on broadband expansion, farmer training, and the establishment of regional centres for digital innovation [
73].
This kind of spatial map is a tool for developing tailored policies that, by means of careful planning and digital resource management, both address agro-economic issues and increase rural communities’ resilience [
120,
121,
122].
An excellent illustration of digital opportunities and disparities is Cyprus: An examination of the use of GIS technologies in Cypriot agriculture reveals considerable geographical inequalities in the rural areas’ digital transformation. Due to sectoral specialisation, infrastructure availability, and involvement in EU innovation projects, areas like as Paphos and Limassol are able to successfully adopt geoinformation tools; nonetheless, the eastern and central sections of the island continue to exhibit a low degree of digital integration. This circumstance emphasises the need for locally specific strategies, such as focused farmer education, the growth of local GIS capabilities, and institutional support via new initiatives like SmartAgriHubs-CY Node and AgriDataValue.
Cyprus offers a prime example of how a small Mediterranean nation can overcome digital disparities and become a model of smart rural transformation in Southeastern Europe through the appropriate use of data, locally tailored solutions, and strategic investments, according to trends and institutional interventions.
Table 8.
Comparative performance indicators—EU vs. Cyprus.
Table 8.
Comparative performance indicators—EU vs. Cyprus.
| Indicator | Value in EU | Value in Cyprus | Source |
|---|
| Increase in farms using GIS/EO technologies | +52% | +70% | CYSTAT, 2024 [115]; Eurostat, 2023 [122] |
| Yield prediction accuracy via EO and IoT | 75–88% | 85% | Kallergis et al., 2025 [123]. |
| Rural areas with access to VHCNs | 68% | 42% | Digital Economy and Society Index, 2024 [110] |
| Drone usage in precision crop monitoring | 36% | 51% | Tsouros et al., 2021 [124] |
| Agricultural subsidies based on geospatial data | 54% | 100% | Ministry of Agriculture Cyprus, 2024 [119] |
| Public and private IoT stations per 1000 ha | 7.2 | 5.1 | Copernicus Reports, 2024 [113] |
| Use of NDVI for crop health monitoring | 47% | 63% | Papadopoulos et al., 2024 [112] |
The selection of Cyprus as a case study in this paper is based on several factors. As the smallest EU member state with limited resources, but pronounced regional differences and challenges in rural development, Cyprus provides an insight into how digital transformation can work even in the context of a small territory and specific agro-ecological conditions. Cyprus is among the first countries that have established operational projects based on the use of geospatial data, IoT sensors, and NDVI analysis, which opens up space for a concrete evaluation of the impact of smart technologies on agricultural practices, but also on broader rural dynamics. Digitisation enables the smaller agricultural economy to increase competitiveness, adapt to climate change, and create new forms of employment, especially for educated youth in STEM fields.
4.6. Influence of Institutional Policies and EU Funds
The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP 2023–2027), the Horizon Europe program, the Digital Europe Fund, and the Recovery and Resilience Mechanism (RRF) are examples of multi-level tools that validate the role of European policies in the digital transformation of rural agriculture. Higher levels of money absorption and more successful AgriTech solution implementation are observed in nations like Italy, Cyprus, and Spain, which have clearly aligned digital and rural agendas [
99,
107,
122]. A network of over 300 digital innovation hubs throughout the EU and over 3200 users in nine regional clusters are part of the SmartAgriHubs initiative, one of the main platforms. This network, which has nodes in Cyprus, Greece, Bulgaria, Romania, and Serbia, conducts regional experiments in Southeast Europe that include blockchain, drones, and artificial intelligence in practical agricultural processes [
73].
Robotic systems and digital twin models can be tested in real-world settings according to the AgrifoodTEF (Testing and Experimentation Facilities for AI) project, which was funded with EUR 60 million through Digital Europe. The infrastructure for verifying technological solutions is supplied by national and satellite centres in Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, and Sweden in accordance with EU regulations on compatibility and cyber security [
125].
CAP and national policy are supported by the Copernicus EO program, which makes satellite data and algorithms like Sen2Agri publicly available. Copernicus has previously been used in countries such as Poland, Spain, and Italy for crop classification, disease detection, and input optimisation, with low costs for small and medium farmers [
62].
4.6.1. Socioeconomic Effects: Migration, Employment, and Revitalisation
Digital technology adoption in rural agriculture has a number of socioeconomic ramifications, including increased employment, community revitalisation, and a decrease in young migration. Jobs in the digital agronomy, the Internet of Things, and geoinformatics engineering, for instance, increased in Cypriot municipalities that took part in EU digital projects [
126,
127]. Between 2020 and 2024, the Agros region saw a 23% rise in jobs in digitally orientated agriculture and a 12% increase in overall local employment as a result of the execution of local pilot programs and the withdrawal of EU funds [
115].
According to demographic trends, youth emigration is declining in digitalised areas: emigration rates in Agros and Omodos fell by 14%, while the number of AgriTech firms rose by 31% [
117,
128]. The development of technology also helps rural communities develop their identities, bolster local initiative, and establish a contemporary workplace that blends digital and agricultural expertise. Villages regain strategic relevance as a result of this technological and community integration, which positions them as catalysts for innovation and sustainable growth.
A well-organised institutional framework that blends strategic planning, regulatory backing, and targeted finance is the driving force behind digital change in agriculture rather than the outcome of market fluctuations. This framework positions the EU as a pioneer in developing a competitive, resilient, and technologically integrated agro-ecosystem in accordance with the Farm to Fork Strategy, the Green Deal, and the Digital Decade [
65,
129,
130]). Technology is no longer viewed as a means of assistance but rather as a structural component that is required to attain digital sovereignty, climate neutrality, and rural revitalisation [
131].
This institutional approach’s main benefits are the advancement of open platforms, interoperable standards, ethical AI use, and enhancing local communities’ ability to employ digital tools to implement sustainable policies [
132]. An inclusive digital ecosystem is created by EU institutions that promote horizontal collaboration between research institutes, industries, entrepreneurs, and government agencies.
AgriDataSpace, ATLAS, AgDataHub, IoF2020, NIVA, DEMETER, and SmartAgriHubs are some of the top projects assisting in the digital shift. These initiatives make it possible to create systems for the electronic management of CAP money, interoperable software tools, and experimental environments. While platforms like AgDataHub and IoF2020 concentrate on building safe and open databases, ATLAS and DEMETER create common standards and APIs for small producers’ digital integration [
133,
134].
4.6.2. Geospatial Distribution of Digital Infrastructure (GIS/EO, IoT, VHCN)
Regional disparities in access to digital infrastructure in agriculture were found using data from the Cyprus Statistical Service, Eurostat, and Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. Because of increased infrastructural availability, increased involvement in EU projects (e.g., AgriDataValue, SmartAgriHubs), and local GIS centres, regions like Limassol and Paphos record a higher degree of introduction of the NDVI, installation of IoT sensors, and implementation of VHCNs [
135,
136,
137]. However, due to a lack of institutional support, poorer digital literacy, and poor connectivity, areas like Famagusta and the area north of Larnaca are falling behind.
Predicting Yield and Technological Efficiency
A far more accurate study of biomass activity and water stress in Cyprus’s vineyards and olive groves was made possible by the combination of satellite imagery (such as Sentinel-2), meteorological data, and data from nearby IoT sensors. According to the Ministry of Agriculture’s report and the evaluation of the Horizon Project SmartVinesCy, the accuracy of yield forecast rose from 62% to 85% between 2020 and 2024 [
123].
Digital robots is emerging as a significant option in agriculture due to the growing labour scarcity. By 2027, 38% of European farms plan to implement automation in some or all of their processes, according to data from the FAO and CORDIS. Autonomous cutting and spraying equipment has been employed in Cyprus, mostly in Limassol’s vineyards, with the assistance of the ATLAS and Horizon initiatives [
138,
139]. More widespread deployment is back by the scarcity of technical staff and financial incentives.
Automation and Robotics as a Solution to the Labour Deficit
The EU invests in technological solutions to address the structural labour shortfall in agriculture as part of its digital and rural development strategies, particularly through initiatives like CAP, Digital Europe, and Horizon Europe. In addition to being a technological advancement, automation and robotisation are a calculated reaction to the ageing population, the industry’s limited appeal to young people, and the seasonal instability of the rural workforce.
Less than 12% of farm managers are under 40 years old, and the EU’s agricultural labour force is expected to shrink by 2024, according to Eurostat data [
139,
140]. Projects centred on precise machinery, driverless cars, and smart machines become strategically significant in this setting.
Examples of robotics initiatives financed by the EU include the following (
Table 9):
- -
ROBS4CROPS: Using GNSS-guided vehicles and intelligent software for operation planning, this EUR 7.9 million project offers integrated solutions for mechanical weeding and spraying. Workload and chemical usage have been reduced by 30% in pilot projects in France, Spain, and Greece [
138,
141].
- -
WINBOT: This project focusses on automating grape harvesting by using robots to determine when the grapes are ripe and the best time to harvest them. Research indicates that small winemakers can boost their profitability and see a return on investment in as little as two to three years [
141,
142].
- -
Robotics for Microfarms (ROMI): This company creates low-cost robotic solutions for tiny farms, such as modular robots for weeding and planting, which are appropriate for areas with tight budgets and particular agro-ecological circumstances [
143].
- -
JRC Robot Trials: According to research conducted by the Joint Research Centre (JRC), automation in greenhouses can result in significant energy and input savings while increasing work efficiency by up to 60% [
144,
145].
AGROBOT, GRAPE, and VINEYARD are viticulture and mechanical harvesting initiatives that could yield a return on investment in three to four years [
146,
147].
Table 9.
Key robotics projects in EU agriculture.
Table 9.
Key robotics projects in EU agriculture.
| Technology/Project | Application | Characteristics | Impact/Savings | Sources |
|---|
| ROBS4CROPS | Mechanical weeding | GNSS navigation, smart software | −30% chemical use, ↑ productivity | CORDIS (2024), ROBS4CROPS.eu [137,140] |
| VINBOT | Grape harvesting | Maturity sensors, robotic harvesting | +20–30% profitability | Vinbot EU Report (2024) [141] |
| ROMI | Microfarms | Modular robots for sowing and weeding | Affordable for small farms | ROMI Project (2023) [143] |
| JRC Robot Trials | Greenhouse fruit and vegetables | Automated harvesting in closed environments | +60% efficiency | JRC (2023), ScienceDirect (2024) [144] |
| AGROBOT, GRAPE, VINEYARD | Vineyard automation | Precision mechanical harvesting | ROI within 3–4 years | Batistatos et al. (2025) [4] |
4.6.3. Strategic Relevance of Digital Agriculture for EU Rural Development
Beyond the actual process of producing food, the digital transformation of agriculture has strategic implications. In the framework of rural development in the EU, it serves as a systemic force behind population retention, rural modernisation, and the creation of new educational and commercial opportunities [
148]. This section examines how rural areas’ socioeconomic flows, demographics, employment, and environmental changes are impacted by digital technologies.
Digitalisation’s Socioeconomic Effects on Remote Communities
Agriculture’s digital revolution has a significant impact on rural communities’ social and economic structures in addition to raising production’s technical capabilities. Precision farming and digital agriculture create jobs, change educational needs, bring young people back to rural areas, and empower small producers by giving them access to markets and data [
149,
150].
According to studies, smart system implementation in rural areas has been associated with up to a 25% decrease in input costs and a rise in agricultural revenue [
151]. In addition to microfinance based on digital risk assessment, digital solutions allow micro-entrepreneurs to access markets through e-platforms [
152].
According to SmartAgriHubs.eu [
153], digital technology not only offers economic advantages but also promotes social inclusion, particularly for women and young people who can now access digital tools, education, and mentorship through digital innovation hubs.
According to the European Commission [
154], the implementation of digital services led to a 12% decrease in migration towards urban areas in places like the NUTS2 regions of Spain, Greece, and Romania between 2015 and 2022. These developments suggest that smart agriculture can be a significant lever for the long-term sustainability and revitalisation of rural communities through inclusive digital development, in addition to being a tool for more efficient production.
For rural communities to survive and thrive in the twenty-first century, digital transformation is now a necessary innovation rather than an optional one. Production, knowledge, and community are all mutually reinforcing in this new paradigm of rural smart autonomy made possible by the combination of digital technologies and local potential.
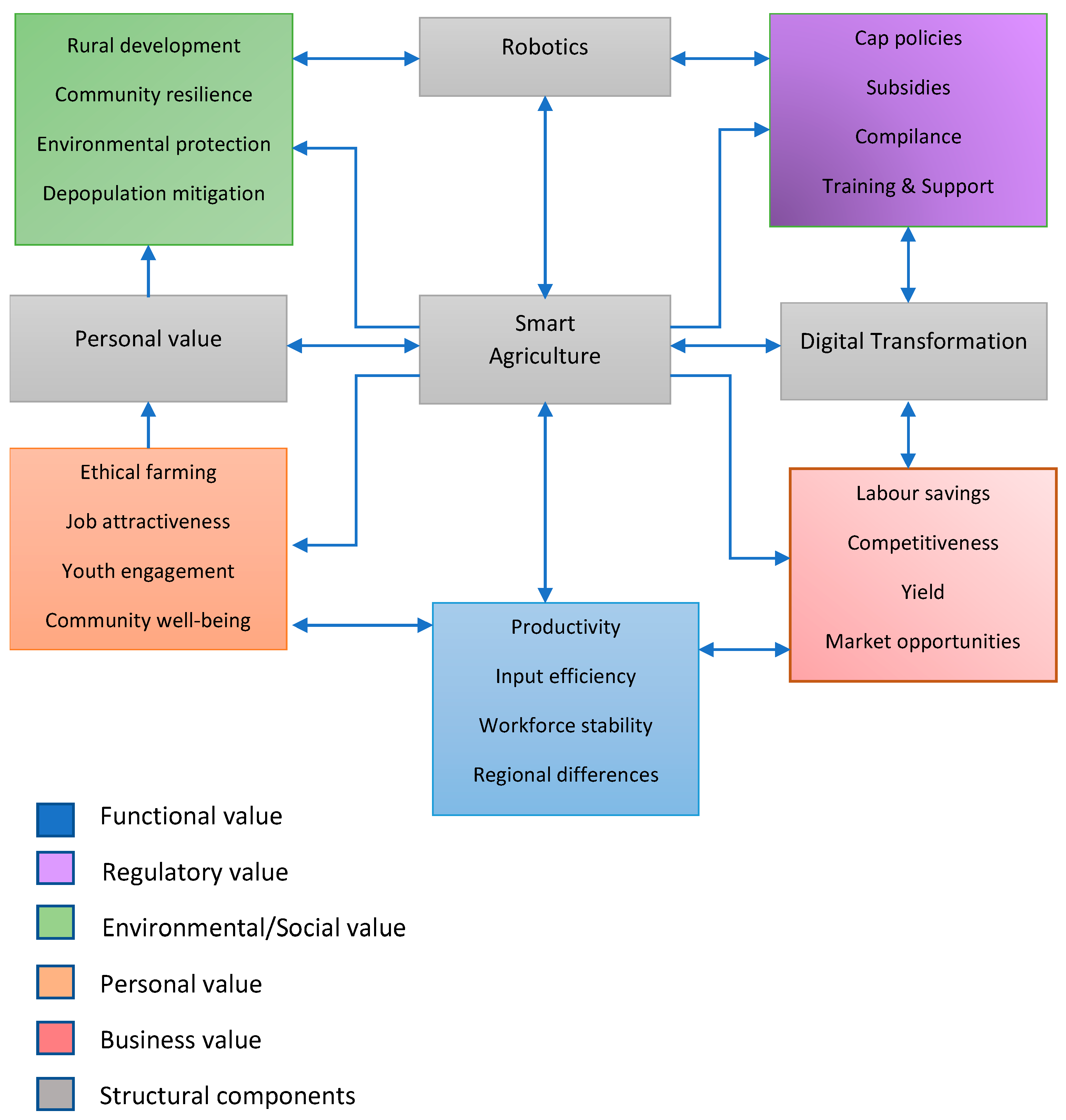
Figure 4 presents a framework of factors influencing agricultural productivity. It is divided into several groups of key blocks (functional, regulatory, personal, business values and structural components), each of which describes different aspects that can facilitate or hinder productivity improvement. The framework shows how different aspects, such as rural development, community sustainability, environmental protection, population management, robotics, agricultural policy, subsidies, compliance, training and support, personal meaning, ethical farming, attractiveness of work, youth engagement, community well-being, smart farming, and digital transformation, influence productivity through the functional, regulatory, personal value, and structural components.
The way that many actors—such as farmers, regulators, DIHs, and academia—cooperate to realise important ideals in the digital revolution of agriculture is illustrated in
Figure 4. The value categories—functional, social, personal, regulatory, and market—indicate a complex structure of advantages and difficulties brought forth by the advent of technology.
Effect on Work and Involvement Among Young
The adoption of smart technologies in agriculture creates new job opportunities, particularly for young professionals with expertise in biology, ecology, engineering, and information technology. Automation, data analytics, and digital platforms are driving the need for professionals with expertise in agriculture, including software engineers, drone operators, sensor technicians, and data analysts [
149,
151]
Youth engagement is actively encouraged by programs such as SmartAgriHubs and EIT Food, which use innovation challenges, incubators, and digital learning environments [
155]. Initiatives like AgROBOfood and StartLife pair together young entrepreneurs with mentors and investors to build AgriTech businesses around Europe [
156].
Research shows that digital revolution is changing the nature of work roles and creating new jobs in rural areas [
157]. Young people are more inclined to remain in the agricultural industry when technology is available, according to [
158]. While the UNDP [
149] observes a rise in youth employability in digital agri-projects in Eastern Europe, the ILO [
159] indicates that young people involved in smart agriculture are less likely to leave villages.
More than 60% of users of educational modules in rural areas stated that they intended to launch AgriTech projects within the next five years, and the 2024 EIT Food report states that over 70 businesses established under their programs are run by individuals under the age of 35.
Young people in rural communities can access new employment opportunities without relocating to urban areas through training and rural digital hubs, improving rural population retention and preventing depopulation. Thus, in addition to being a technical resource, digital infrastructure also serves as a social catalyst for village revitalisation.
According to the European Rural Development Goals, digital agriculture is essential for reviving local economies and lowering youth unemployment, particularly in areas where access to conventional jobs is restricted.
The Role of Digital Competences and Education
One of the most important requirements for participation in contemporary agro-technical operations is digital literacy. Developing digital skills in educational institutions is crucial, especially in rural areas, according to EU plans like the “Digital Education Action Plan” [
160]. Young and adult farmers can now learn how to use AI, GIS, and IoT systems practically thanks to the development of digital agriculture courses like those provided by EIT Food, Wageningen UR, and Erasmus+ AgriTech programs [
155].
Informal learning pathways are equally as vital as formal schooling. Small farmers and young people in rural areas can receive technical assistance, training, and seminars via SmartAgriHubs platforms and digital innovation hubs (DIHs) [
153]. In countries like Poland, Romania, and Italy, the number of young farmers with medium or high levels of digital skills has grown by more than 20% over the past four years, according to [
161]. While the FAO [
162] highlights the importance of contextualising educational content in accordance with agro-ecological and cultural specificities, research by [
158] shows a clear correlation between the availability of digital tools and the level of digital participation in rural areas.
The promotion of “digital literacy for agriculture” is encouraged by programs such as DESIRA (H2020) and ATLAS, which emphasise participatory education including all stakeholders in the rural economy [
163]. For instance, almost 1500 farmers from throughout the EU took part in the direct testing and development of digital teaching modules through the DESIRA Living Labs network.
In this way, digital competencies become a socially transformational element in addition to being technical. As a result, education and digital literacy stop being passive elements and start acting as catalysts for local community empowerment and rural revitalisation. Work positions in rural areas are fundamentally changing as a result of digital agriculture. Agro-technical operators are replacing traditional farmers, and a wide range of new jobs are developing at the nexus of automation, IT, and agronomy. AI agronomists, sensor systems engineers, drone operators, and agricultural data management professionals are a few examples [
157]. While Eurostat [
161] reported a 38% growth in the employment of young IT experts in the agricultural sector between 2019 and 2023, the FAO [
162] reports that over 65% of smart farms in the EU currently employ personnel with digital and technical profiles. The deployment of farm management platforms in initiatives such as ATLAS (Horizon 2020) and DEMETER suggests the function of a so-called “digital agriculture intermediary” that assists farmers in selecting and using solutions [
163]. The shift from manual to high-tech jobs is being ensured by the emergence of educational programs for youth training and adult retraining in rural areas, which are made possible by EIP-AGRI and local digital innovation hubs.
5. Discussion
A comprehensive set of proposals is presented in this study to accelerate the sustainable digital transformation of rural agriculture in the European Union, based on empirical findings and theoretical ideas. The recommendations can be implemented in smaller member states as well as other institutional and geographic situations.
In order to achieve more equitable digital growth, rural areas with poor Internet connectivity and few hubs for digital innovation must first receive infrastructural support. Digital literacy initiatives for farmers and local governments, as well as the establishment of local digital-rural centres, are based on investments in the broadband network, particularly in the areas of 5G and VHCN. Over 5000 rural towns throughout Europe have benefited from funding from the EU’s WiFi4EU and Digital Connectivity Infrastructure Support initiatives [
164,
165,
166]. Encouragement of increased youth participation in agriculture should go hand in hand with infrastructural developments. Tax incentives for digital technologies, the establishment of educational platforms and mentorship programs, and the provision of startup funds for AgriTech ventures can all help achieve this. Numerous Erasmus+ initiatives, such “AgroNext” and EIT Food RisingFoodStars, offer education and startup assistance to thousands of youth around the European Union [
164,
165,
166,
167,
168].
The restricted nature of digital systems and data fragmentation continue to be two of the biggest obstacles. Establishing regional training centres for GIS and AI technologies, standardising data formats, and creating open APIs that allow local datasets to be integrated with EU platforms like Copernicus and EuroCrops are also advised. Such interoperability and connection are already being worked on by projects like AgriDataSpace and ATLAS. Sustainability in the environment must be a key component of the digital transformation. Supporting technology that allows for accurate irrigation, less pesticide use, and biodiversity preservation is essential. Italian researchers are creating artificial intelligence (AI) systems to protect the soil microbiome, while the “SmartWater2025” project [
168] in Greece has demonstrated that sensor networks can cut water use by up to 30%.
Without the establishment of a multi-layered management system that involves collaboration between national governments, local communities, and European institutions, effective digital transformation is impossible. In order to combine goals in the domains of infrastructure, innovation, and agriculture, coordinating organisations must be established. The AgriTech working groups in Finland, Estonia, and Ireland are examples from Europe. Funding needs to be more specifically allocated to the sectors with the biggest promise for digital transformation. Priorities like using AI in agriculture, making datasets publicly available, and fostering the growth of human capital through certification initiatives should be part of EU initiatives like Horizon Europe, Digital Europe, RRF, and EAFRD. Nearly EUR 30 million in digital agricultural grants has already been allocated to pilot projects in the EU [
151]. Measurement indicators that offer a clear evaluation of the impacts of digital technologies need to be established. These indicators should cover the level of technological use, socioeconomic changes, and sustainable development. As with the “Rural Digital Indicators Dashboard” [
169], it is advised that a centralised EU platform be established to track development by NUTS2 regions.
Digital tools for women’s empowerment in rural areas should receive particular attention. Inclusive change requires participation in innovation platforms, mentoring, online education programs, and the growth of digital companies like agro-blogging. Programs like “SheAgriDigital” in Spain and “Women4AgTech” in France, for instance, have already successfully taught over 2000 women to use digital technologies in agriculture [
170,
171]. The creation of a “Policy Impact Map” as a last step shows how different strategic inputs, such as financing, education, and technology, result in tangible outcomes like improved employability, climate resilience, and rural communities’ sustainability. When developing the upcoming generation of strategies under the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy, this tool can provide a helpful framework. The entire flow of how EU policies affect the digital and sustainable transformation of agriculture is depicted in the “Policy Impact Map” diagram in
Figure 5. It links input components to results in rural areas, acting as a strategic synthesis of the ideas made across the entire study. Five levels of interdependence are depicted in the diagram: political inputs (e.g., Horizon Europe, CAP strategic plans, RRF funds, SmartAgriHubs); institutional support (VHCN, 5G, DIH centres, interoperable platforms); technological activation (IoT, AI, drones, GIS); socioeconomic and environmental effects (yield increase, youth retention, biodiversity conservation); and strategic impacts (climate resilience, digital inclusion, rural revitalisation).
In order to more fully understand the effects of digital technologies in rural development, it is necessary to pay attention to their long-term social consequences. The introduction of new digital tools changes the patterns of education, work, and mutual communication in villages, which can contribute to the return of young people and professionals. At the same time, there is a risk that certain groups, especially older and less technologically capable populations, will be excluded from these processes. These aspects require careful monitoring and the development of inclusive strategies that will allow equal access to digital benefits.
Despite the clearly recognised benefits that digital agriculture brings, its implementation in European rural areas faces numerous structural and institutional challenges. One of the key problems is the pronounced digital inequality between regions—especially in remote and mountainous areas, where the availability of broadband Internet is still limited. This infrastructural gap directly affects the ability to access smart technologies, IoT systems, and analytical platforms that form the backbone of modern precision agriculture.
In addition to technical limitations, a significant challenge is the lack of digital skills among existing farmers. In many environments, there is strong resistance to the introduction of new tools, often accompanied by a sense of insecurity and a lack of capacity to implement them. This indicates the need for systematic education and the establishment of advisory support, as well as the creation of local knowledge centres that would function as a bridge between innovation and practical application in the field.
An additional challenge is reflected in institutional fragmentation and the absence of a single regulatory framework that would enable full interoperability, data protection, and standardised information exchange. Without stable institutional support, digital systems remain limited to partial applications and isolated projects, instead of becoming part of integrated development strategies.
There are concrete levers that can accelerate this transition. Among them, the strengthening of local digital innovation centres, improvement of public–private partnerships, as well as targeted investments from European funds for rural development stand out. The introduction of digital components into formal educational programs for young farmers is also of particular importance, thus creating a new generation of actors ready to work in a digital environment.
6. Conclusions
In modern Europe, smart and digital agriculture represents a revolution in how we see and manage space, resources, and communities, in addition to being a technological advancement in the rural setting. With an emphasis on the structural implications for rural development, this study thoroughly examined the opportunities and difficulties associated with the adoption of digital and precision technology in the EU’s agricultural sector. The most important finding is that, when properly planned and used, digitisation may be a potent force for village demographic revitalisation, economic diversification, and climatic resilience. Meanwhile, “bad planning” and institutional failures can lead to the opposite results—hypertrophied growth in the scale and monopolisation of production, polarisation of the level of development of farmers and rural areas.
It was confirmed through the examination of pertinent EU policies, current programs like “SmartAgriHubs,” “Horizon Europe,” “Green Deal,” and the “Farm to Fork” strategy, as well as insights from secondary sources and creative examples from practice, that the digital transformation of agriculture not only facilitates more accurate land and water management, lowers emissions, and increases efficiency but also opens up new markets and generates employment for young, educated workers.
A clear disparity in capacities across various member states and regions is also indicated by the results, nevertheless. Disparities in infrastructural availability, particularly for 5G and VHCN networks, the digital divide, and a lack of institutional support and training in rural areas are major barriers to consistent development. Smart agriculture runs the potential of further marginalising outlying areas rather than promoting inclusiveness if these disparities are not aggressively addressed.
Smart agriculture should not be viewed as merely a technological advancement but also as a component of a larger agricultural, political, and social endeavour. Open access to data must be encouraged, local communities must be involved in the development of digital solutions, and farmers of all generations must be empowered through assistance and training. The concepts of sustainability, equity, and territorial cohesion must serve as the foundation for the European smart agricultural model.
Particular attention should be paid to the part that youth play in this process. In addition to technical advancements, their desire to labour in the field is influenced by the quality of life that is available in rural areas, including access to digital tools, healthcare, and education. One framework that can support a new generation of rural entrepreneurs is smart villages combines digital agriculture with sustainable transportation, digital public services, and participatory governance.
The goal of rural development through 2035 needs to be expansive and comprehensive. Precision and digital agriculture are the cornerstones of that vision, but it also suggests a paradigm change: from isolated projects to systemic solutions, from reactive policies to proactive plans, and from technological excitement to social and environmental security. The only way to make European villages more resilient, competitive, and appealing places to live and work for present and future generations is to pursue this strategy.