Spatiotemporal Distribution of Cultural Heritage in Relation to Population and Agricultural Productivity: Evidence from the Ming-Qing Yangtze River Basin
Abstract
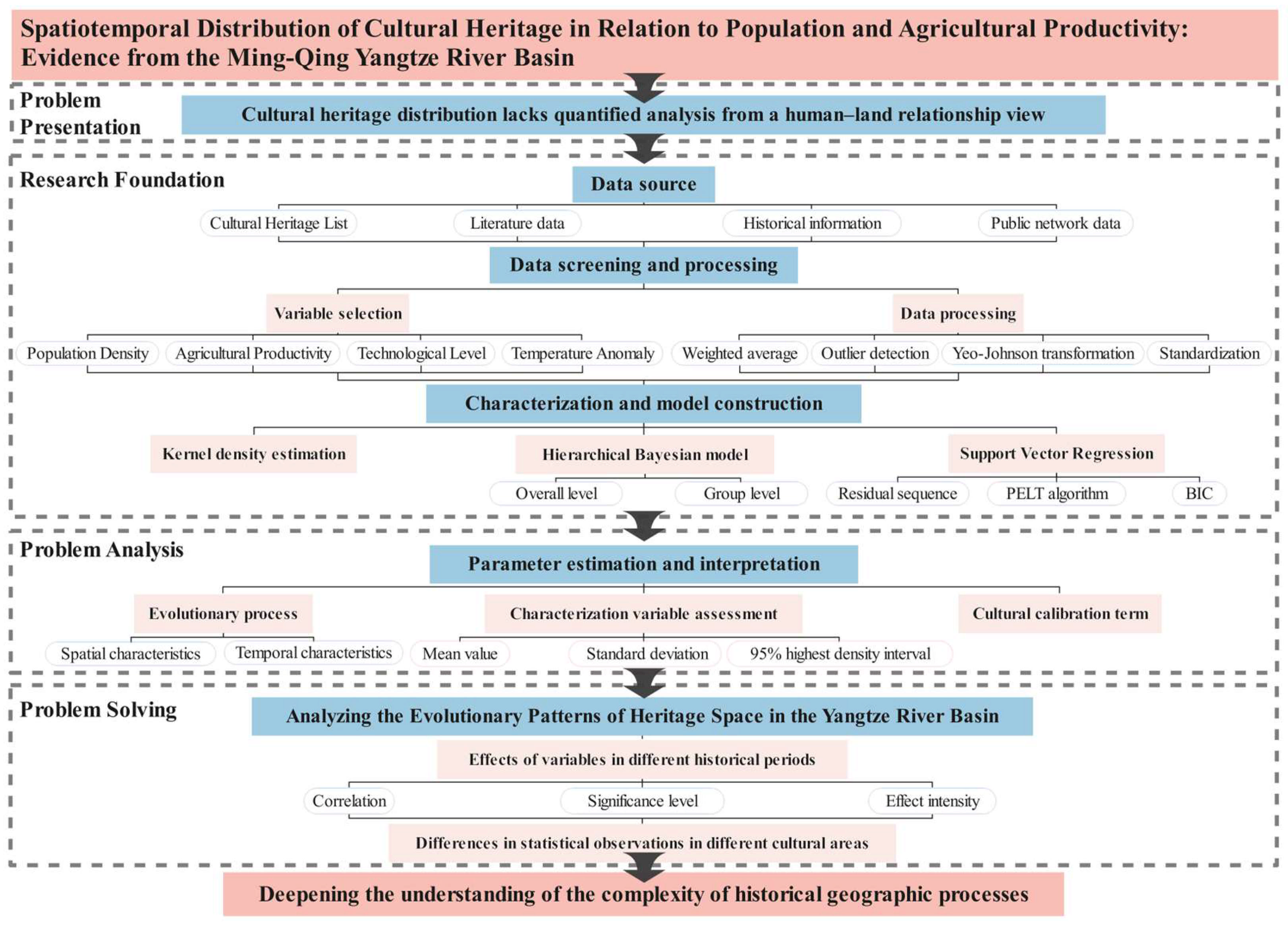
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
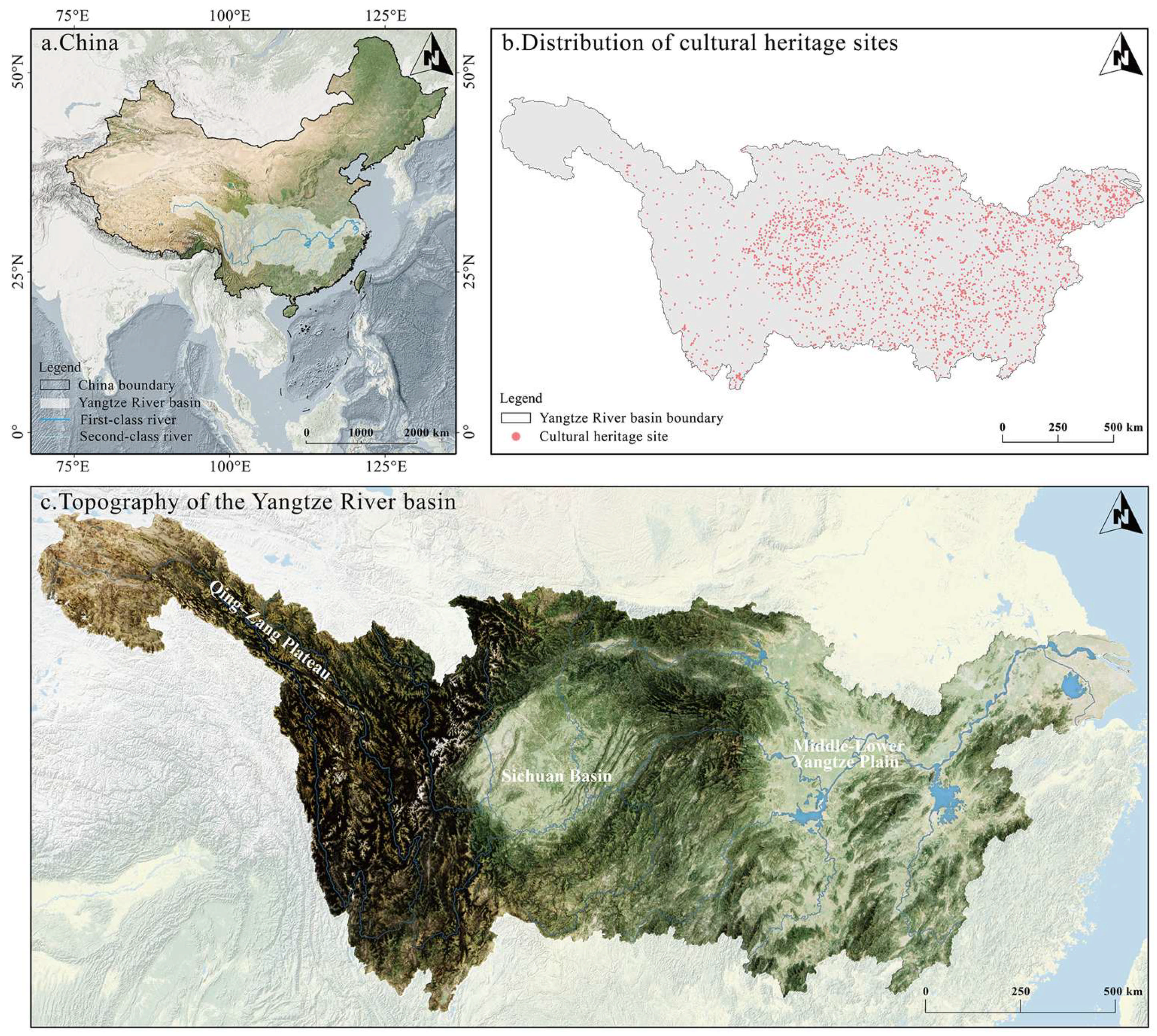
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Data Screening and Processing
- (1)
- Calculation of average annual heritage density
- (2)
- Calculation of agricultural productivity
- (3)
- Calculation of technological level
- (4)
- Weighted average processing of multi-period characteristic variables
- (5)
- Outlier detection and treatment
- (6)
- Yeo–Johnson transformation
- (7)
- Standardization
2.4. Research Methods
- (1)
- Kernel density estimation (KDE)
- (2)
- Hierarchical Bayesian model (HBM)
- (3)
- Change point detection method
2.5. Model Evaluation
3. Results
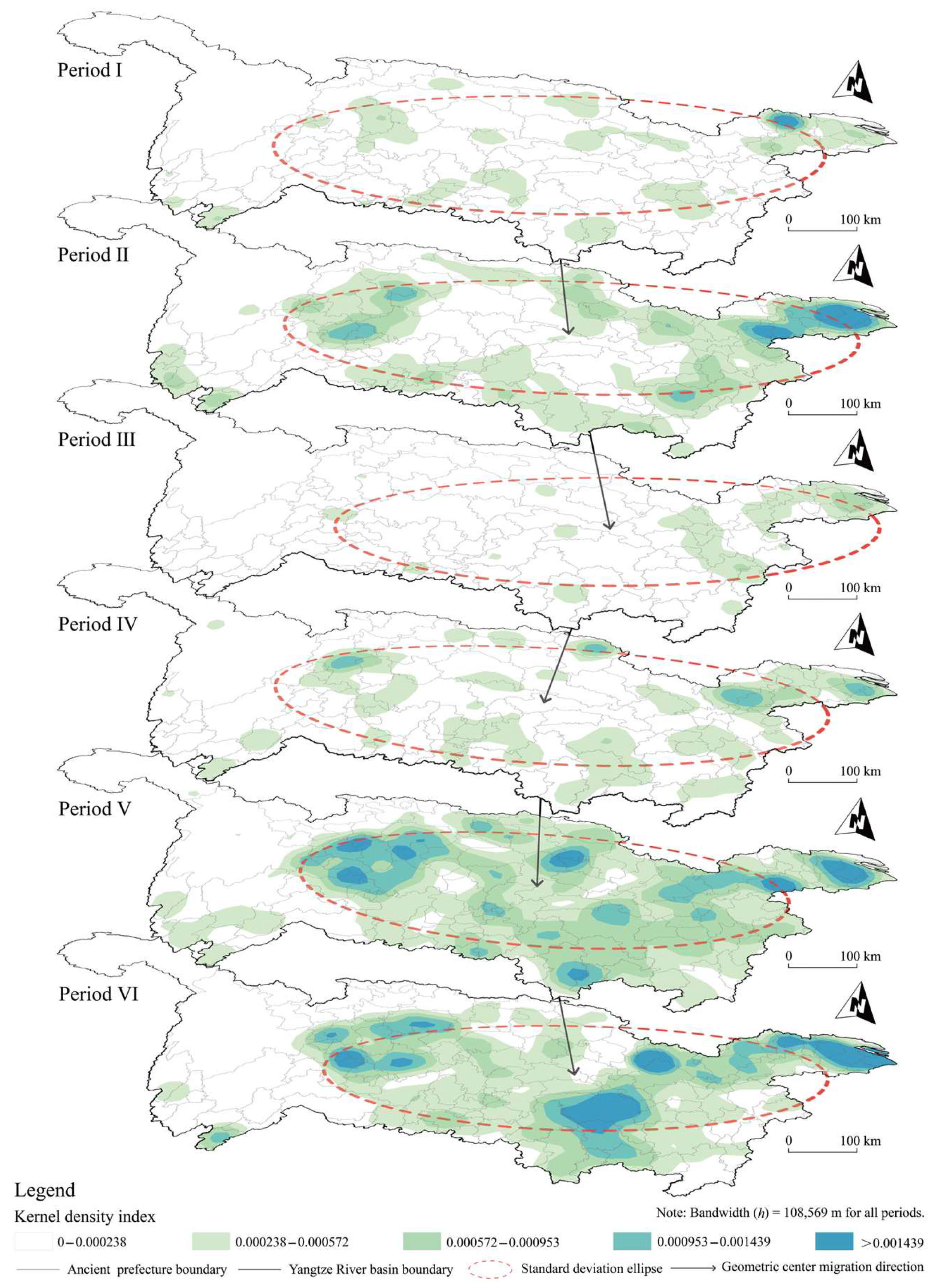
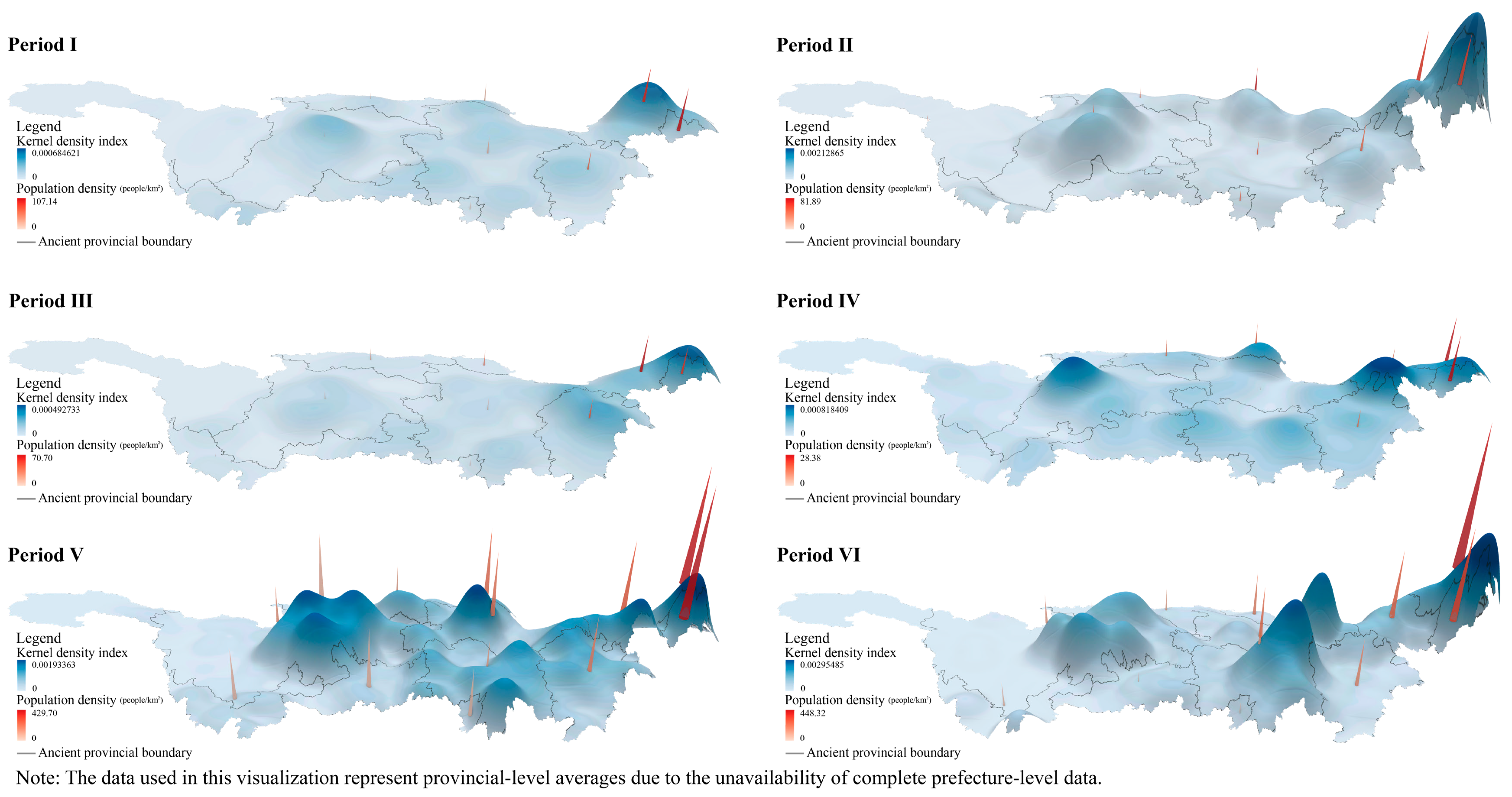
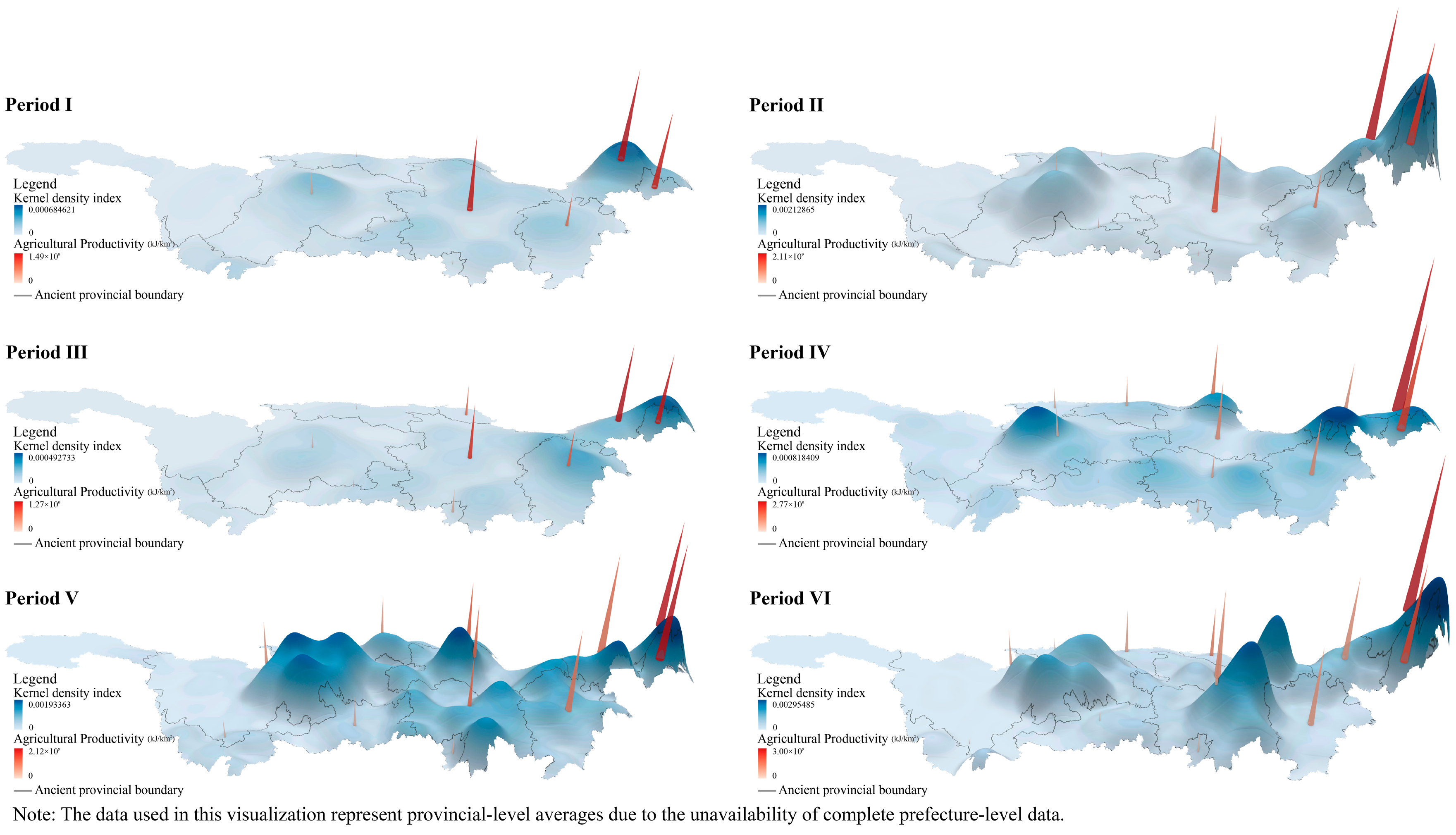
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of Cultural Heritage
3.2. HBM Performance Evaluation
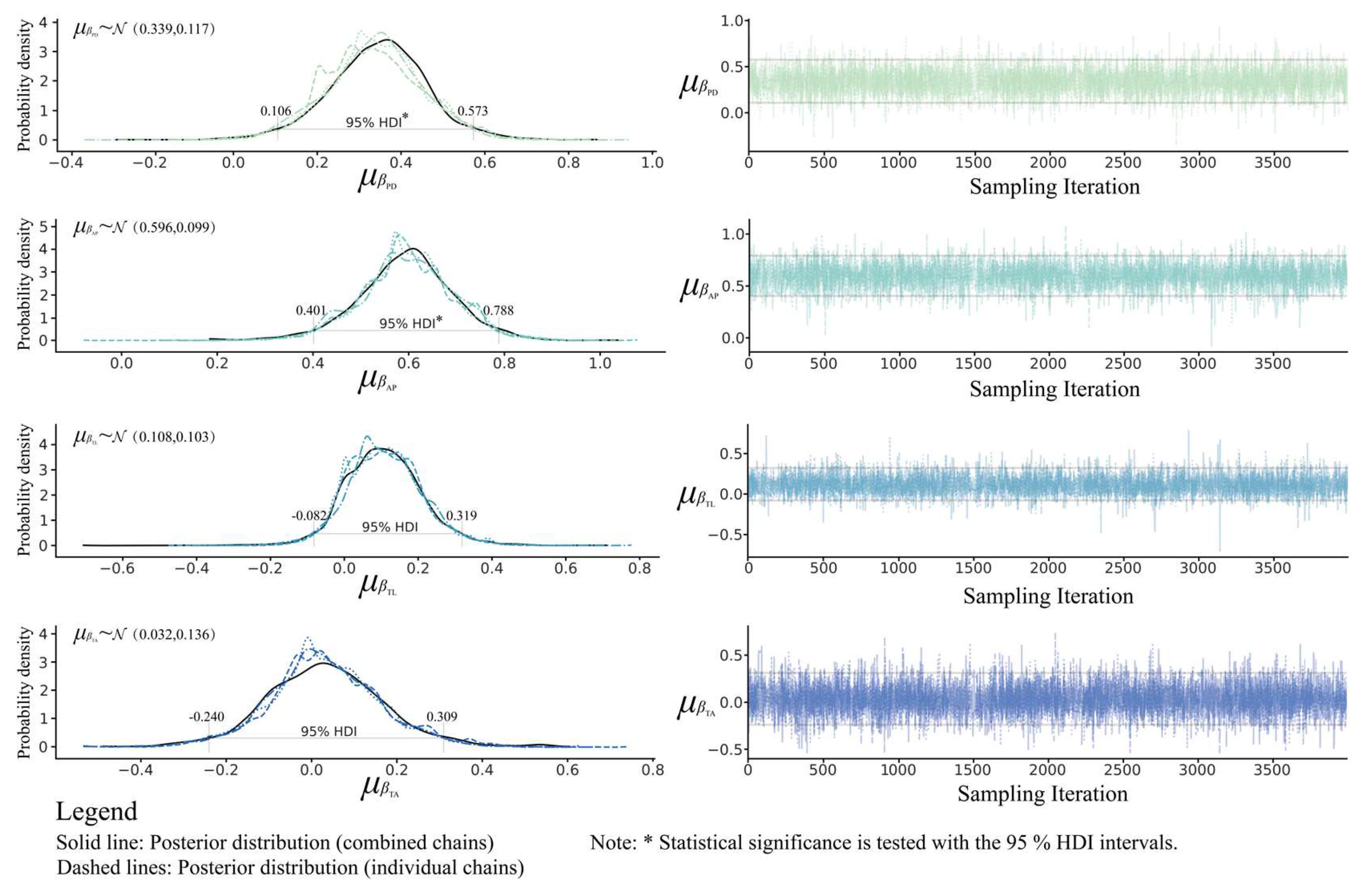
3.3. Posterior Distribution and Sampling Analysis of Regression Coefficients at the Overall Level
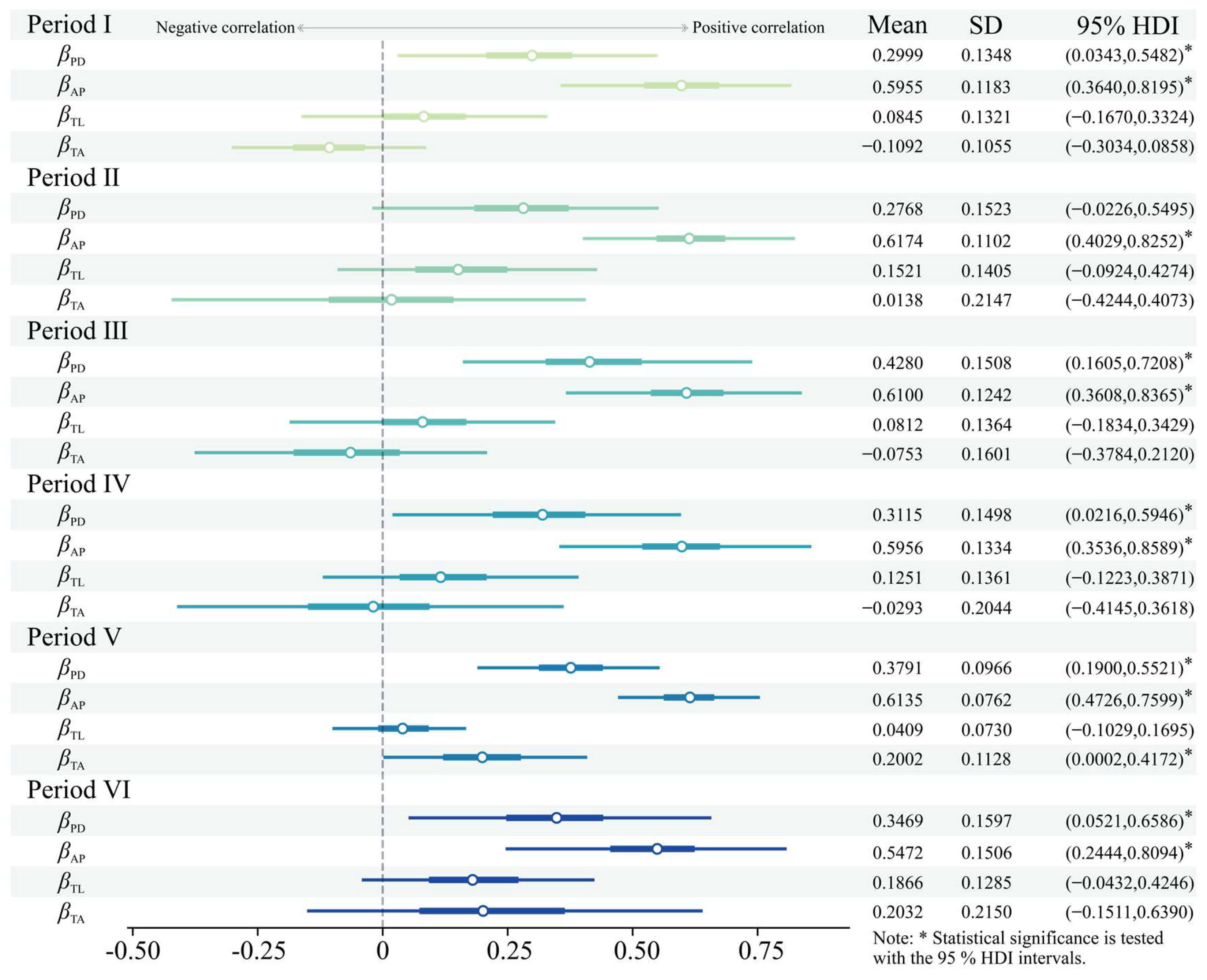
3.4. Posterior Distribution of Regression Coefficients at the Group Level
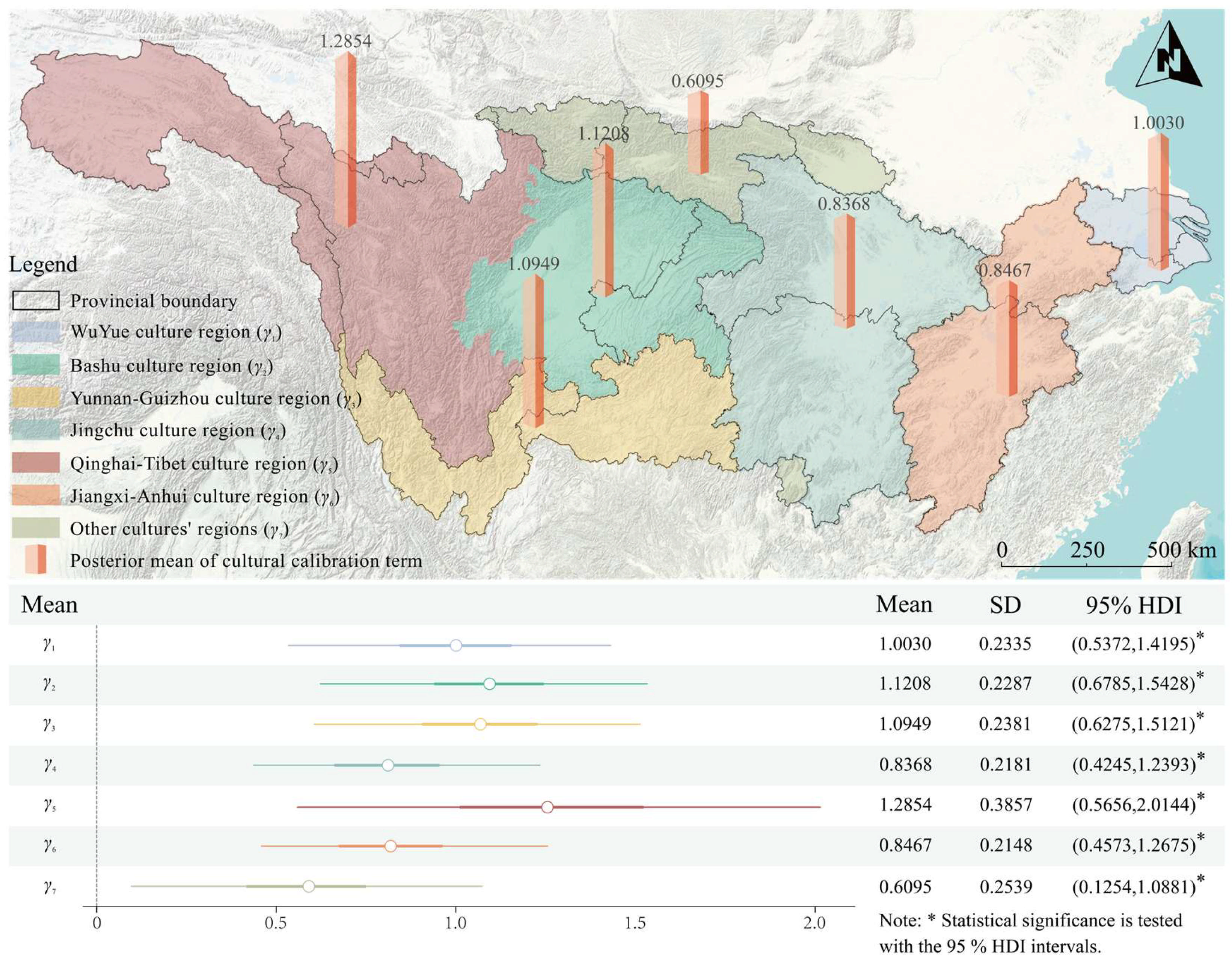
3.5. Posterior Distribution of Cultural Calibration Terms
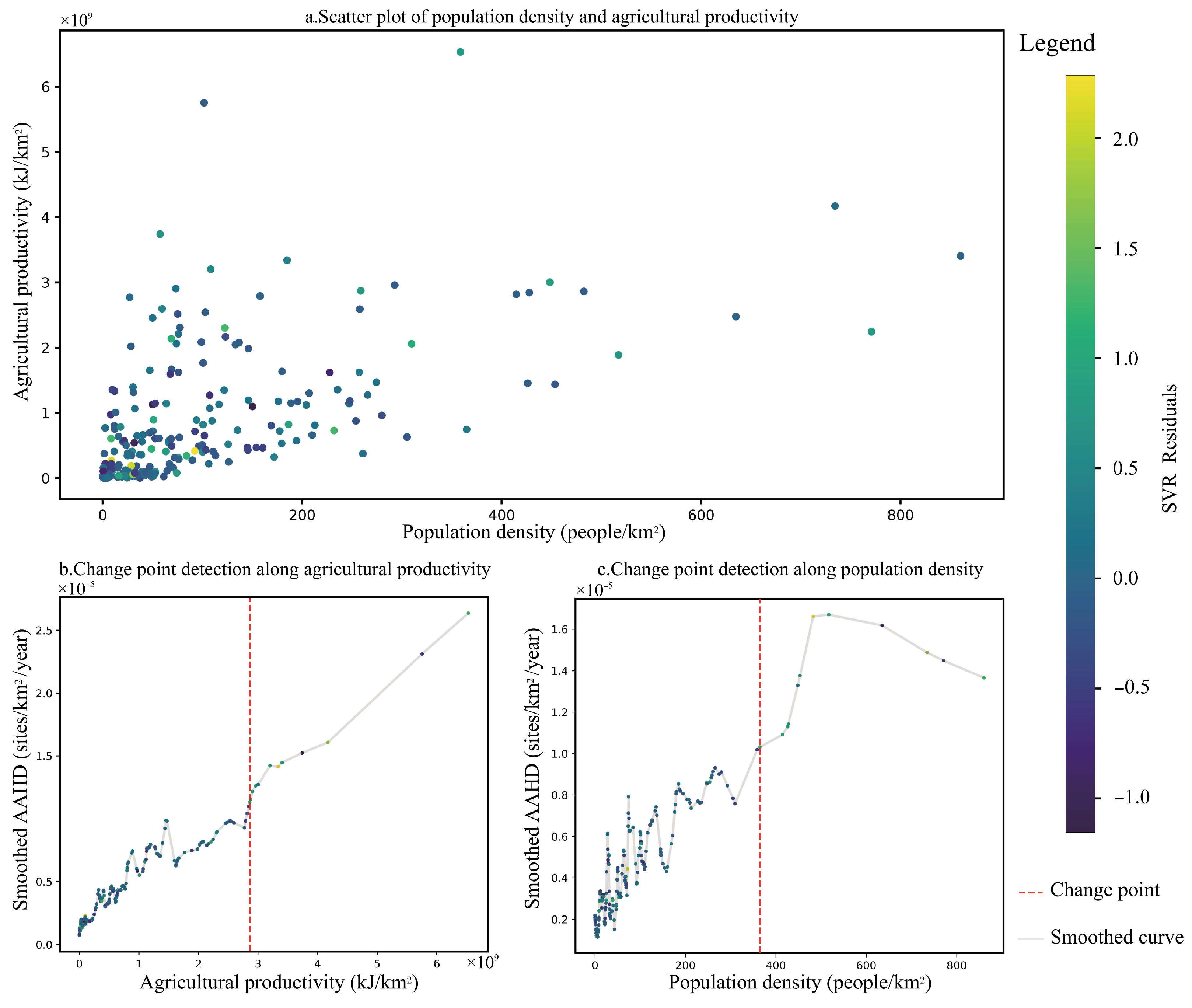
3.6. Change Point Detection Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Relationship Between Population and Cultural Heritage
4.2. The Impact of Agricultural Productivity on the Distribution of Cultural Heritage
4.3. Constraining Role of Physical Geography
4.4. Theoretical Contributions and Practical Significance
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Cultural heritage was primarily concentrated in the lower and middle reaches of the Yangtze River and the Sichuan Basin. During the Ming Dynasty, the density of cultural heritage first increased and then declined. In contrast, during the Qing Dynasty, it exhibited a continuous upward trend. During both dynasties, a clear multipolar pattern emerged in the middle period, followed by the contraction of high-density areas in the late period.
- (2)
- The HBM demonstrated good model fit and generalization capability. Posterior results indicated that PD and AP were statistically significant overall, with AP demonstrating a stronger positive effect. At the group level, AP remained consistently significant. PD had a significant positive effect in all periods except Period II. TL was not significant in any period, while TA was only significant in Period II with a positive effect.
- (3)
- The cultural calibration terms do not imply any value judgment about cultural significance. After controlling for feature variables, the mean values of the cultural calibration terms in the Qinghai–Tibet, Bashu, Yunnan–Guizhou, and WuYue cultural regions were all greater than 1, indicating a higher baseline level of cultural heritage in these areas. In contrast, the JingChu and Jiangxi–Anhui cultural regions showed slightly lower mean values, potentially due to ecological stress or other contextual constraints.
- (4)
- The identified change points were 364.83 people/km2 for PD and 2.86 × 109 kJ/km2 for AP. Once the AP and PD values exceed these thresholds, the state of AAHD tends to shift, indicating threshold-driven transitions in heritage density patterns.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| PD | Population Density |
| AP | Agricultural Productivity |
| TL | Technological Level |
| TA | Temperature Anomaly |
| AAHD | Average Annual Heritage Density |
| C-D | Cobb–Douglas |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Squares |
| MAD | Median Absolute Deviation |
| KDE | Kernel Density Estimation |
| HBM | Hierarchical Bayesian Model |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| PELT | Pruned Exact Linear Time |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| HQC | Hannan–Quinn Criterion |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| BPV | Bayesian p-value |
| MCMC | Markov Chain Monte Carlo |
References
- Choi, Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Sohn, H.G. Resilient cultural heritage through digital cultural heritage cube: Two cases in South Korea. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 48, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage. 1972. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/conventiontext/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- UNESCO. The Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage. 2003. Available online: https://ich.unesco.org/en/convention (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Dippon, P.; Helferich, A. Sharing the documentary heritage of humanity: Disparities in distribution. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2023, 29, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, Q.; Luo, J.; Xu, J.; Pan, Y. Enhancing User Participation in Cultural Heritage through Serious Games: Combining Perspectives from the Experience Economy and SOR Theory. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, N.; Lee, J.H.; Zou, C.; Jeon, W.S. Digital Technology in Cultural Heritage: Construction and Evaluation Methods of AI-Based Ethnic Music Dataset. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Li, J.J.; Wider, W.; Tanucan, J.C.M.; Lobo, J.; Fauzi, M.A.; Hidayat, H.; Zou, R. A bibliometric insight into immersive technologies for cultural heritage preservation. npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.C.; Zheng, X.; Yan, J. Contradictory or aligned? The nexus between authenticity in heritage conservation and heritage tourism, and its impact on satisfaction. Habitat. Int. 2021, 107, 102307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Moon, J.; Choe, Y. Determinants of cultural heritage tourism demands: Learning in cultural heritage tourism destination. J. Hosp. Leis. Sport Tour. Educ. 2024, 35, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Liu, L.; Pan, T.B.; Wu, Z.X. A bibliometric analysis of cultural heritage visualisation based on Web of Science from 1998 to 2023: A literature overview. Hum. Soc. Sci.Commun. 2024, 11, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Jing, B.W.; Yang, L.Y.X.; Zhang, Y.H. AI-based experts’ knowledge visualization of cultural heritage: A case study of Terracotta Warriors. J. Cult. Herit. 2025, 72, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, G.; Farhan, S.L. Reactivating voices of the youth in safeguarding cultural heritage in Iraq: The challenges and tools. J. Soc. Archaeol. 2024, 24, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katapidi, I. The role of conservation policies in local understandings of heritage in living heritage places: A Greek testimony. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2023, 29, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, L.J.; Vadher, A.N.; Teller, J. Disaster risk management and cultural heritage: The perceptions of European world heritage site managers on disaster risk management. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 89, 103625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatorić, S.; Daly, C. Towards a climate-smart cultural heritage management. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2023, 14, e855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.L.; Fu, X.X.; Lin, B.N.; Sun, J.X. Authenticity, identity, self-improvement, and responsibility at heritage sites: The local residents’ perspective. Tour. Manag. 2024, 102, 104875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, M.; de Andrade, B.; Roders, A.P. Capturing public voices: The role of social media in heritage management. Habitat. Int. 2023, 142, 102934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Zhou, X.P.; Weng, F.F.; Ding, F.Z.; Wu, Y.J.; Yi, Z.X. Evolution of cultural landscape heritage layers and value assessment in urban countryside historic districts: The case of Jiufeng Sheshan, Shanghai, China. npj Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaqawy, G.A.; Alnaim, M.M.; Bay, M.A.; Touahmia, M. Assessment of Saudi Arabia’s Classification and Selection Criteria for Heritage Sites: A Case Study of Barzan Heritage Area in Hail City. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qian, Y.Y.; Li, Z.K.; Tong, T. Identifying factors influencing the spatial distribution of minority cultural heritage in Southwest China. npj Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Han, Q.W.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Dai, J. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Evolution of Global World Cultural Heritage, 1972–2024. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, J.; Kearney, M.; Veall, M.A. Direct Inlet Py-GC-MS analysis of cultural heritage materials. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 164, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvagno, E.; Tartaglia, E.; Stratigaki, M.; Tossi, C.; Marasco, L.; Menegazzo, F.; Zanardi, C.; Omenetto, F.; Coletti, C.; Traviglia, A. Present status and perspectives of graphene and graphene-related materials in cultural heritage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2313043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Gelli, R.; Giorgi, R.; Pierigè, M.I.; Ridi, F.; Baglioni, P. Cementitious materials containing nano-carriers and silica for the restoration of damaged concrete-based monuments. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 49, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.K.; Liang, H.E. Digital restoration and reconstruction of heritage clothing: A review. npj Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpina, D.; Casartelli, V.; Marengo, A.; Mysiak, J. Financing strategies for the resilience of cultural landscapes. Lessons learned from a systematic literature and practice review. Cities 2025, 162, 105922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.; Sordini, M.; Berlioz, S.; Vidale, M.; Al-Lyla, R.; Abbo al-Araj, A.; Bianchi, A. Remote sensing and ground survey of archaeological damage and destruction at Nineveh during the ISIS occupation. Antiquity 2022, 96, 436–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Zhu, R.; Shi, C.Y.; Yang, X.K.; Chen, J.Z.; Wei, K.X. Research on the construction of intangible cultural heritage corridors in the Yellow River Basin based on geographic information system (GIS) technology and the minimum cumulative resistance (MCR) model. npj Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, H.Q.; Chen, C.W.; Zhao, G.; Ni, J.H. Deterioration identification of stone cultural heritage based on hyperspectral image texture features. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 69, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, M.; Jiang, Y.J. The inheritance and analysis of colors in Rimpa art: A machine learning perspective. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 276, 127129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Bibliometric analysis of GIS applications in heritage studies based on Web of Science from 1994 to 2023. npj Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Zhang, T.J.; Duan, L.G.; Liritzis, I.; Li, J.S. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of intangible cultural heritage in the Yellow River Basin. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 66, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.Y.; Fan, J.Y. Construction of integrated, contiguous conservation and utilization system for cultural relics protection unit in Qiandongnan based on quantitative analysis. npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.Q.; Chen, Z.H.; Xu, S.B. A Study on the Spatiotemporal Aggregation and Corridor Distribution Characteristics of Cultural Heritage: The Case of Fuzhou, China. Buildings 2024, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Tian, Y. Temporal and spatial patterns and influencing factors of intangible cultural heritage: Ancient Qin-Shu roads, Western China. npj Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, Y.L.; Cao, W.W.; Yu, R.Y.; Rong, P.J.; Cheng, J.L. Spatial pattern and its influencing factors of national-level cultural heritage in China. npj Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Lu, L. Spatiotemporal distribution of toponymic cultural heritage in Jiangsu Province and its historical and geographical influencing factors. npj Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Wu, L. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of Intangible Cultural Heritage in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. npj Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.G. The Broad-Spectrum Revolution at 50: Increasing dietary diversity reflects the heterogeneity of domesticated landscapes. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2022, 68, 101444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, P.; Seekamp, E. Sustainable adaptation planning for cultural heritage in coastal tourism destinations under climate change: A mixed-paradigm of preservation and conservation optimization. J. Travel Res. 2024, 63, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cultural Heritage Administration. The State of Cultural Heritage Preservation in China. The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. 2023. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/guoqing/2012-04/11/content_2584143.htm (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Zhao, Y.L.; Sun, H.J.; Wang, X.D.; Ding, J.; Lu, M.Y.; Pang, J.W.; Zhou, D.P.; Liang, M.; Ren, N.Q.; Yang, S.S. Spatiotemporal drivers of urban water pollution: Assessment of 102 cities across the Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 20, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.Q.; Tian, Y.G.; Geng, B.; Liu, X.B.; Zheng, K. Does ‘living by water’ still exist? A new perspective for quantifying ISA dynamics at different distances from the Yangtze River. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.Z. Statistics of Population, Land and Land Tax in China Throughout the Dynasties; Zhonghua Book Company: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 264–555. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.X. Development History of Population in China; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1991; pp. 227–257. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.S.; Wu, L.; Zhuang, Y.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Ma, C.M.; Li, L.Y.; Guan, H.C.; Lu, S.G.; Luo, W.J.; Xu, Z.Y. Evolution of the historical polder landscape in the ancient Danyang wetland, lower Yangtze River, China, during the last 3000 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 2053–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H. Study on Grain Yield per Mu in Past Dynasties of China (Updated and Reprinted); China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 213–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.L. Historical Agricultural Geography of China; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 461–510. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, Y.C.; Wu, H.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhu, J.F.; Chen, Q.K. Study on Grain Yield Per Mu in Qing Dynasty; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 15–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.W.; Wen, X.Y.; Luo, Y.; Dong, W.J.; Zhao, Z.C.; Yang, B. Reconstruction of temperature series of China for the last 1000 years. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.; Gingrich, S.; MacFadyen, J. Recent advances in social metabolism research: Sources and methods. Hist. Methods 2024, 57, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Cai, Z.M.; Tan, K.H.; Zhang, L.L.; Du, J.T.; Song, M.L. Technological innovation and structural change for economic development in China as an emerging market. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 167, 120671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteska, A.; Sharif, T.; Bhuiyan, F.; Abedin, M.Z. Impacts of the changing climate on agricultural productivity and food security: Evidence from Ethiopia. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 449, 141793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Food Composition Tables. 2001. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/x9892e/X9892e05.htm (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Li, C.X. Climate change impacts on rice production in Japan: A Cobb-Douglas and panel data analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.G.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, C.B.; Yan, P.K.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.T.; Song, M.K.; Aurangzeib, M. Key factors influencing the spatial distribution of soil organic carbon and its fractions in Mollisols. Catena 2024, 247, 108522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchesne, D.; Cazelles, K.; Daigle, R.M.; Gravel, D.; Archambault, P. Ecological interactions amplify cumulative effects in marine ecosystems. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadp9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.M.; Xue, L.Q.; Dong, Z.C.; Zhu, B.L.; Zhang, K.; Wei, Q.; Fu, F.B.; Wei, G.H. Cumulative ecohydrological response to hydrological processes in arid basins. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemifar, S.; Awais, M.; Akbari, A.; Kittler, J. Developing a generic framework for anomaly detection. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 124, 108500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A.C.; Riani, M.; Corbellini, A. The Box–Cox Transformation: Review and Extensions. Stat. Sci. 2021, 36, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Li, T.H.; Liu, S.P.; Xu, X.Y. tanh As a robust feature scaling method in training deep learning models with imbalanced data. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 167, 111746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; De Ceuster, S.; Eremin, K.; Laursen, S.; Degryse, P. A methodological case study of lead resource movements during the Warring States Period and Western Han Dynasty: Applying kernel density estimation to four lead-barium glass Bi Artifacts. J. Cult. Herit. 2025, 71, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, R.R. Introduction to Robust Estimation and Hypothesis Testing; Academic press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Dardeno, T.A.; Worden, K.; Dervilis, N.; Mills, R.S.; Bull, L.A. On the hierarchical Bayesian modelling of frequency response functions. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2024, 208, 111072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, M. Simulation-Based Bayesian Analysis. Annu. Rev. Stat. Appl. 2023, 10, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D. Interdistrict Interaction Study of Ethnic Dance in the Cultural Space of the Yangtze River Basin—An Essay on the Basin Anthropological Paradigm of Ethnic Dance Studies. J. Southeast Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2022, 24, 129–138+14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Suo, W.Y. Research on the Construction and Application of a SVM-Based Quantification Model for Streetscape Visual Complexity. Land 2024, 13, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obour, M.I.; Brian, B.; Conor, C. Assessing change point detection methods to enable robust detection of early stage Artisanal and Small-Scale mining (ASM) in the tropics using Sentinel-1 time series data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 139, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Z.Y.; Xiao, X.; Fang, Y.P.; Rao, J.; Mo, H.D. A Selective Review on Information Criteria in Multiple Change Point Detection. Entropy 2024, 26, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Ding, J. Information criteria for model selection. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2023, 15, e1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, B.; Liu, C.J.; Zhou, Z.L.; Miao, J.X.; Huang, H. Prediction of compression coefficient of Nanjing floodplain soft soil based on explainable artificial intelligence. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2025, 65, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, W.G.; Liu, S.L.; Han, L. Determination of groundwater buoyancy reduction coefficient in clay: Model tests, numerical simulations and machine learning methods. Undergr. Space 2023, 13, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, O. Bayesian Analysis with Python: A Practical Guide to Probabilistic Modeling; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2024; pp. 152–154. [Google Scholar]
- Saadati Nik, A.; Asgharzadeh, A.; Fernández, A.J. Bayesian credible regions for two-parameter exponential distributions under type-II censoring. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2025, 470, 116721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, S.P.; Liu, J.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, X.Y. Entropy Change of Historical and Cultural Heritage in Traditional Tibetan Area of China Based on Spatial-Temporal Distribution Pattern. Buildings 2023, 13, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ou, H.J.; Zhong, Y.J. Political governance and urban systems: A persistent shock on population distribution from capital relocation in ancient China. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2024, 108, 104034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.J.; He, F.N.; Yang, F.; Hao, R.F. Per Capita Cropland Estimations for Traditional Agricultural Areas of China over Past Millennium. Land 2024, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Q.F.; Li, Q.; Song, H.M.; Sun, C.F. The collapse of the Ming Dynasty actually began with the Wanli megadrought: Insights from a hydroclimate reconstruction based on tree-ring δ18O over the past 460 years. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Paleoecol. 2024, 655, 112548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Dong, G.P.; Wu, P.F.; He, F.N. Stylized facts of past 1000-year of China’s cropland changes. Land Use Pol. 2024, 144, 107258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, G.; Hoyer, D.; Zhao, H.J.; Bennett, J.S.; Benam, M.; Kohn, K.; Turchin, P. Structural-demographic analysis of the Qing Dynasty (1644–1912) collapse in China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.C.; Jiang, M. Migration and Land Exploitation from Yuan to Qing Dynasties: Insights from 252 Traditional Villages in Hunan, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jia, X.; Lee, H.F.; Zhao, H.Q.; Cai, S.L.; Huang, X.J. Relationship between ancient bridges and population dynamics in the lower Yangtze River Basin, China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Rodríguez-Pose, A.; Lee, N. The long shadow of history in China: Regional governance reform and Chinese territorial inequality. Appl. Geogr. 2021, 134, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.Q.; Ruan, W.Q.; Zhang, S.N.; Wang, M.Y. Cultural resilience of heritage sites: Dimension exploration and scale development. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2024, 61, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.G.; Wang, Y.H.; Ma, C.; Chi, Y.W. Ensuring the Authenticity of the Conservation and Reuse of Modern Industrial Heritage Architecture: A Case Study of the Large Machine Factory, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derex, M.; Mesoudi, A. Cumulative Cultural Evolution within Evolving Population Structures. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2020, 24, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.B.; Yang, Y.D.; Shi, F.; Hao, Z.X.; Liu, B.T.; Zhang, R.H. The response of agricultural harvest in southern China to climate change during the Ming and Qing dynasties (1368–1911CE). Sci. China Earth Sci. 2025, 68, 1974–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.Y.; Chen, X.D.; Su, Y. Comparative Analysis of Extreme Drought Events and Social Impacts in Henan Province during the Middle Ming Dynasty. Weather Clim. Soc. 2022, 14, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; An, R.; Gao, G.; Li, P.W. The famine of the Ming Dynasty in Shaanxi Province, China. Reg. Envir. Chang. 2024, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward-Hopkins, J.; Steinberger, J.K.; Rao, N.D.; Oswald, Y. Providing decent living with minimum energy: A global scenario. Glob. Environ. Change 2020, 65, 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Feng, C.X.; Xu, W.; Nie, Q.F.; Liu, Q. The effect of environmental changes on locust outbreak dynamics in the downstream area of the Yellow River during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.J. The Sweet Potato: Its Origin and Dispersal. Am. Anthropol. 1972, 74, 342–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Garcia, M. Global History and New Polycentric Approaches; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2018; pp. 53–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.F.; Zhang, D.D. A tale of two population crises in recent Chinese history. Clim. Chang. 2013, 116, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, J.H.; Xu, Z.L.; Li, W.C.; Ji, S.S.; Qiu, R. Quantitative typological analysis applied to the morphology of export mugs and their social factors in the Ming and Qing dynasties from the perspective of East–West trade. npj Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.C.; Fan, J.; Zhou, K.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.P.; Guo, R.; Chen, S.F. Assessing the dynamics of human activity intensity and its natural and socioeconomic determinants in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Geogr. Sustain. 2023, 4, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, J.P.; Hoggarth, J.A.; Ebert, C.E.; Fedick, S.L.; Biggie, M.; Meyer, B.; Shaw-Müller, K.; Qiu, Y.J.; Ran, W.Y.; Ellis, O.P.; et al. Classic Maya Settlement Systems Reveal Differential Land Use Patterns in the Upper Belize River Valley. Land 2023, 12, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goggins, G.; Rau, H.; Moran, P.; Fahy, F.; Goggins, J. The role of culture in advancing sustainable energy policy and practice. Energy Policy 2022, 167, 113055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
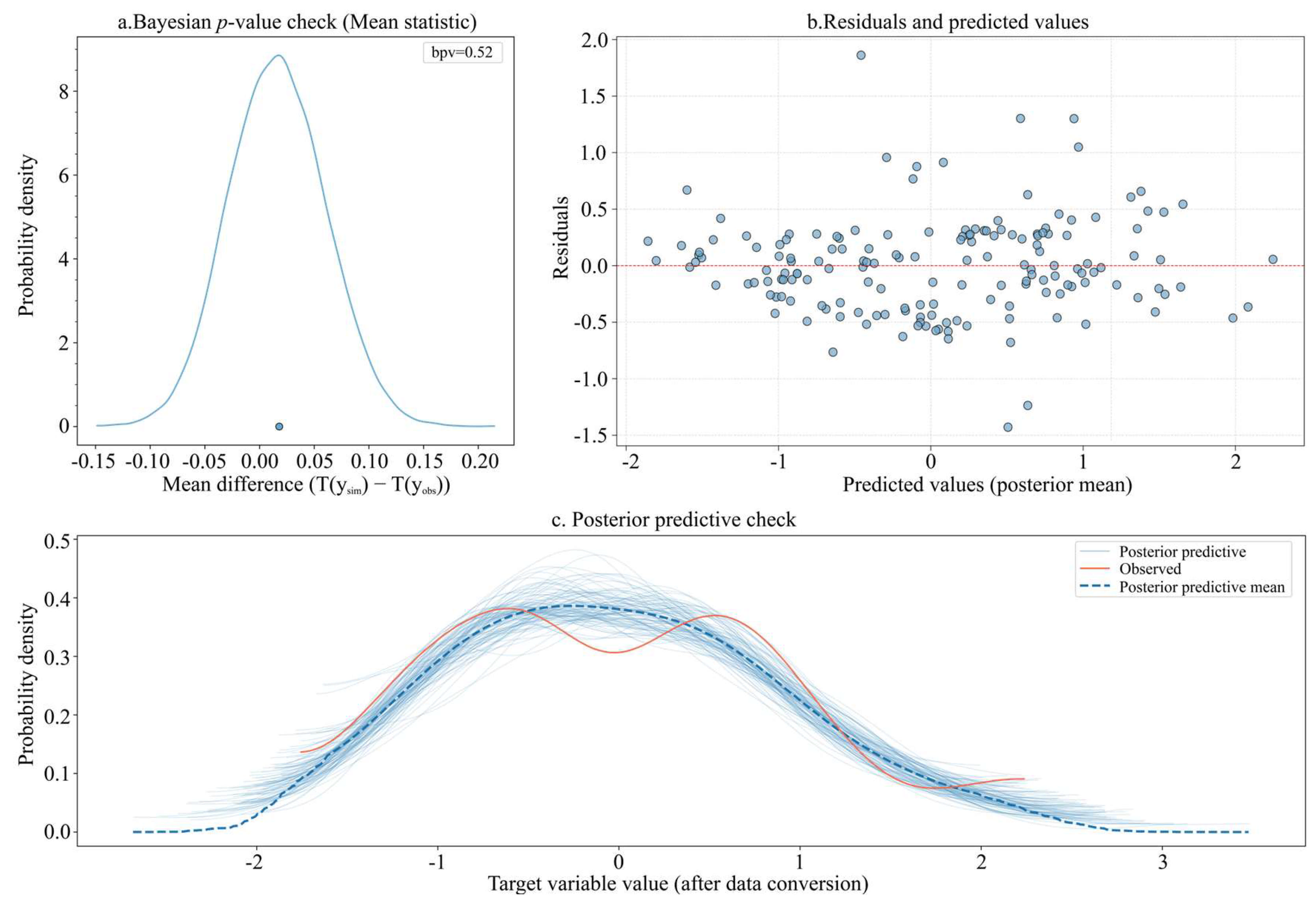
| Evaluation Metrics | Training Dataset | Testing Dataset |
|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.81 | 0.72 |
| RMSE | 0.44 | 0.51 |
| BPV | 0.52 | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Q.; Du, X. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Cultural Heritage in Relation to Population and Agricultural Productivity: Evidence from the Ming-Qing Yangtze River Basin. Land 2025, 14, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14071416
Liu Y, Bai Y, Li W, Chen Q, Du X. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Cultural Heritage in Relation to Population and Agricultural Productivity: Evidence from the Ming-Qing Yangtze River Basin. Land. 2025; 14(7):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14071416
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuxi, Yu Bai, Wushuang Li, Qibing Chen, and Xinyu Du. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Distribution of Cultural Heritage in Relation to Population and Agricultural Productivity: Evidence from the Ming-Qing Yangtze River Basin" Land 14, no. 7: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14071416
APA StyleLiu, Y., Bai, Y., Li, W., Chen, Q., & Du, X. (2025). Spatiotemporal Distribution of Cultural Heritage in Relation to Population and Agricultural Productivity: Evidence from the Ming-Qing Yangtze River Basin. Land, 14(7), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14071416







