Study of Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Net Carbon Emissions in Hubei Province Based on Interpretable Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Areas and Methods
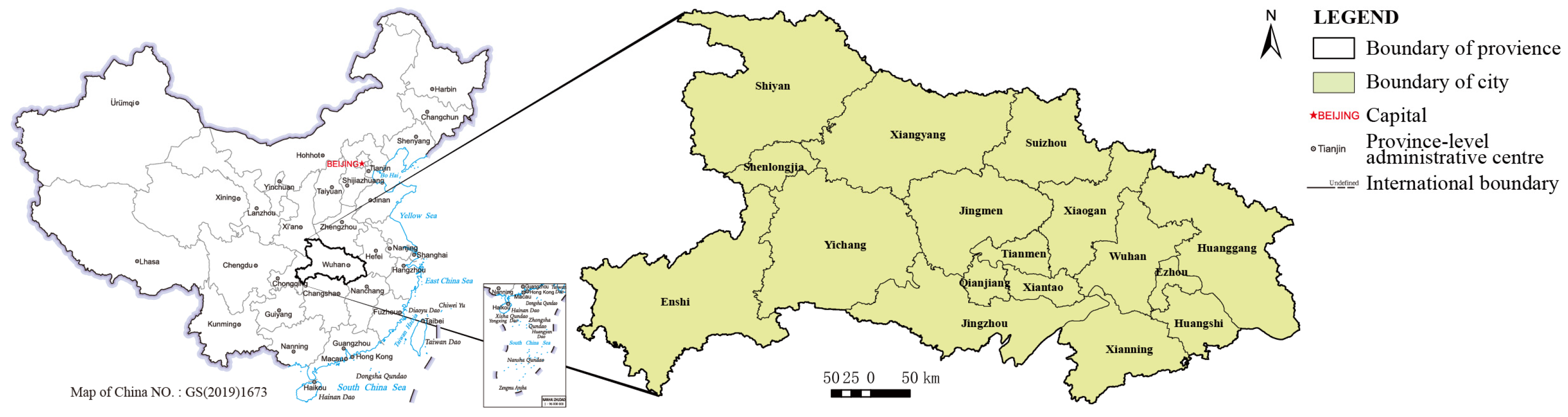
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Net Carbon Emissions Calculation
2.2.1. Calculation of Carbon Sinks
2.2.2. Calculation of Carbon Emissions
2.2.3. Calculation of Net Carbon Emissions
2.3. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Net Carbon Emissions
2.4. Assessment of Net Carbon Emissions with Influencing Factors
3. Results and Analysis
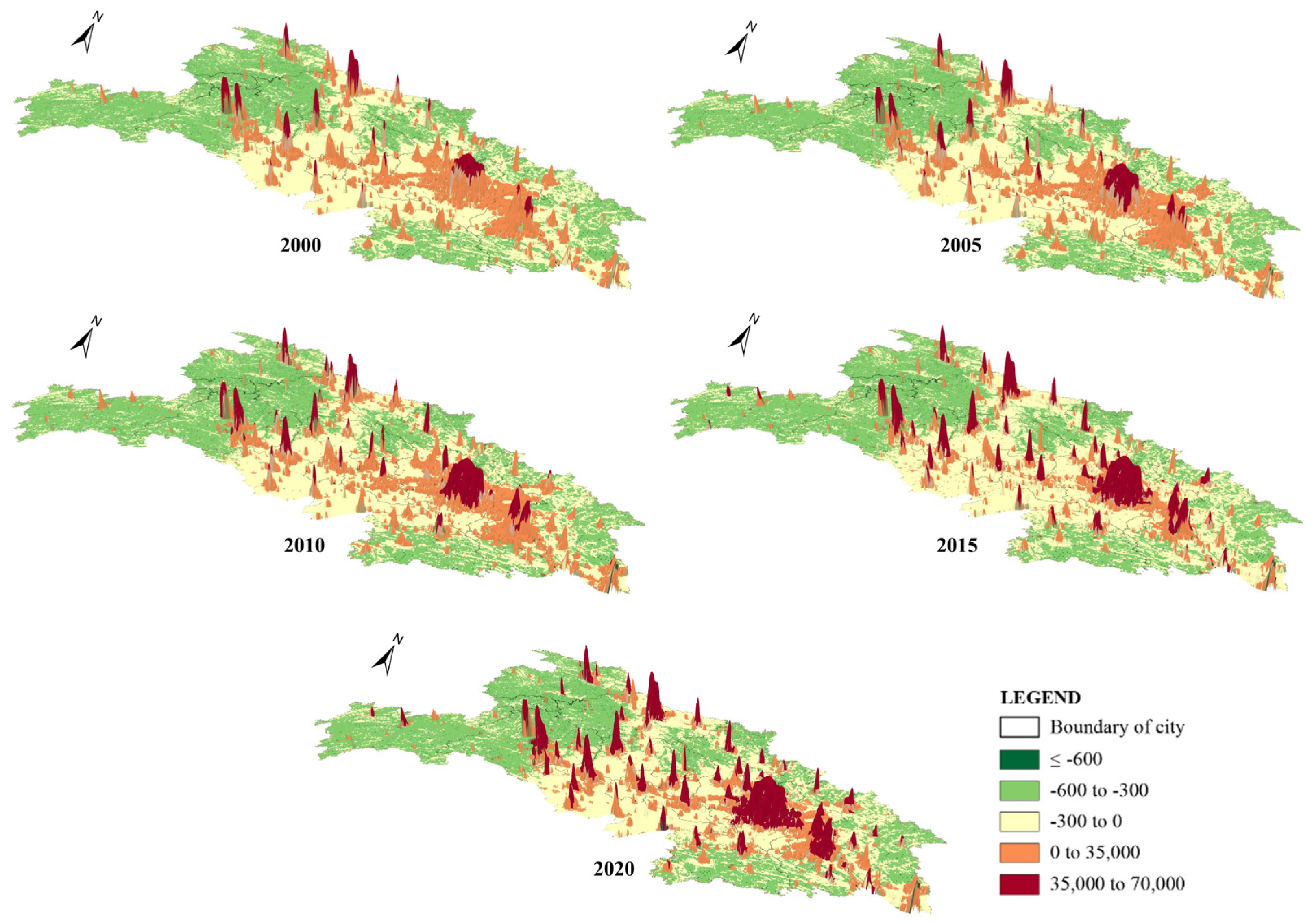
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Land Use Patterns and Net Carbon Emissions
3.2. Assessment of Net Carbon Emissions
3.2.1. Performance Comparison of Different Machine Learning Models
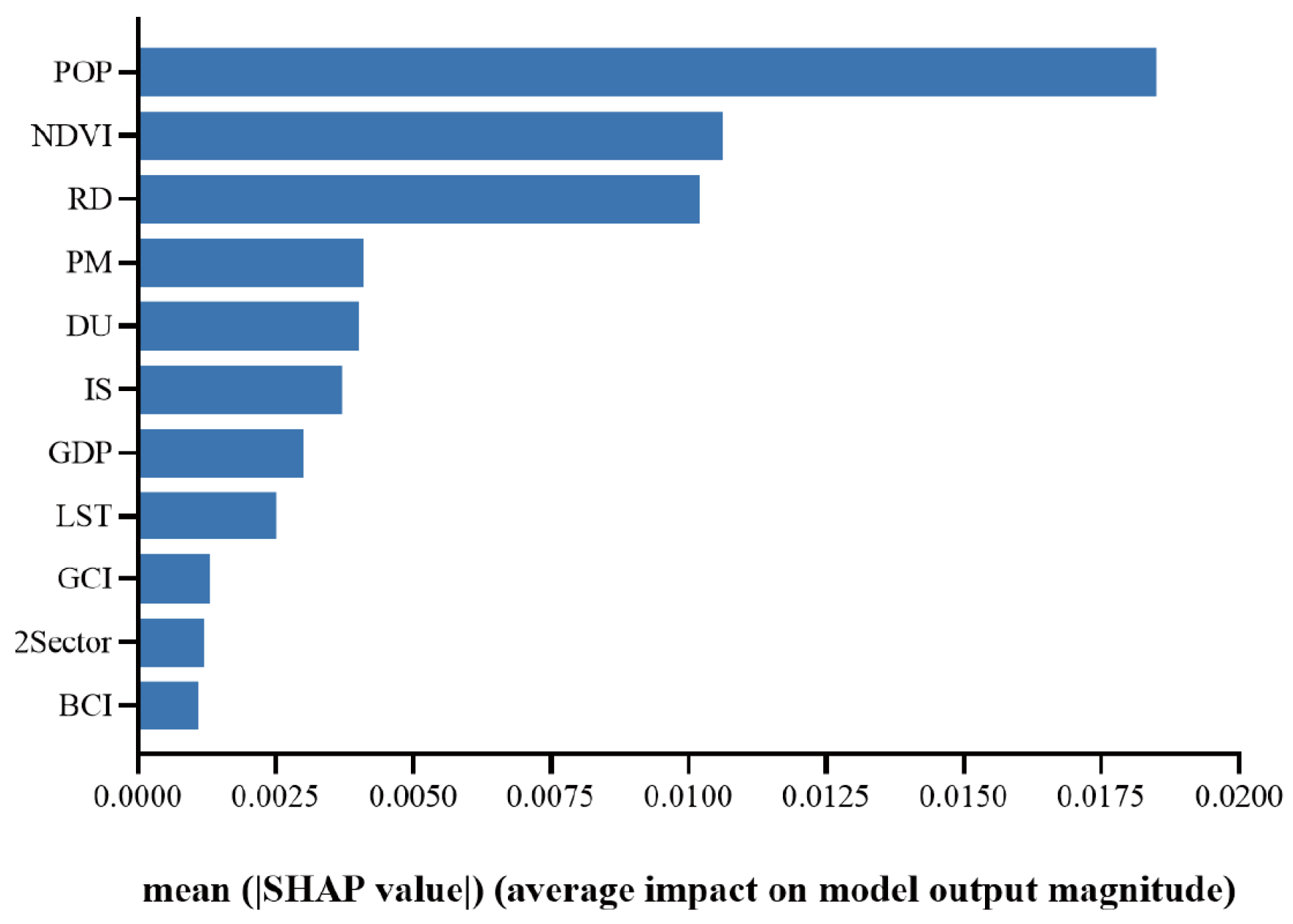
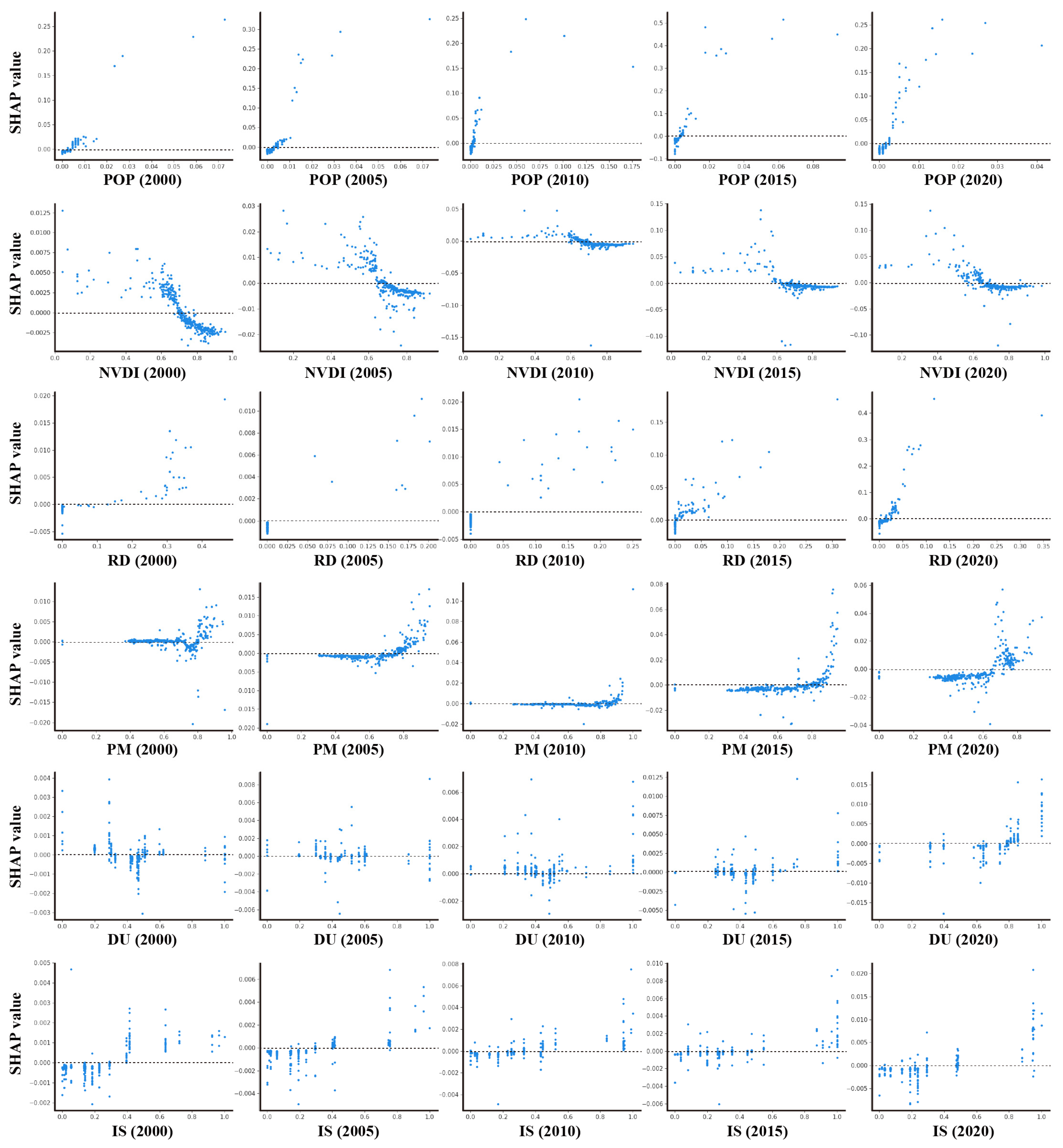
3.2.2. SHAP Interpretation Based on RFR Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Yan, X.; Fan, J.; Deng, X. An Overview of the Progress and Research Framework on the Effects of Land Use Change upon Global Climate. Adv. Earth Sci. 2011, 26, 1015. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Goldewijk, K.K.; Ramankutty, N. Land cover change over the last three centuries due to human activities: The availability of new global data sets. GeoJournal 2004, 61, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A. The annual net flux of carbon to the atmosphere from changes in land use 1850–1990. Tellus Ser. B-Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 1999, 51, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P.; Hutyra, L.R. Spatiotemporal assessment of land use/land cover change and associated carbon emissions and uptake in the Mekong River Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkegren, A.; Grimmond, C.S.B. Net carbon dioxide emissions from central London. Urban Clim. 2018, 23, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, Q.; Guan, D.; Zhu, K.; Yang, C. Revisiting the global net carbon dioxide emission transfers by international trade: The impact of trade heterogeneity of China. J. Ind. Ecol. 2016, 20, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; House, J.I.; Pongratz, J.; Van Der Werf, G.R.; Defries, R.S.; Hansen, M.C.; Ramankutty, N. Carbon emissions from land use and land-cover change. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 5125–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, H. Quantifying the relationship between urban development intensity and carbon dioxide emissions using a panel data analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 49, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Yuan, K.Q. Carbon emission from land use and its efficiency in hubei province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 337–342+348. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Mao, D.; Jiang, Z.; Li, K. Research on factors decomposition and decoupling effects of land use carbon emissions in Chang-Zhu-Tan Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Econ 2019, 35, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.; Guo, Y.; Yao, M.; Cai, W.; Wang, M.; Wei, W. Carbon emissions and driving forces of China’s power sector: Input-output model based on the disaggregated power sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.G.; Li, Z.J.; Song, W.X.; Ma, Z. Spatial differentiation influence factors of residential rent in Nanjing based on geographical detector. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 20, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. Factor decomposition of carbon productivity chang in china’s main industries: Based on the laspeyres decomposition method. Energy Procedia 2014, 61, 1893–1896. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadneh, T.; Batiha, B.; Gharib, G.M.; Montazeri, Z.; Dehghani, M.; Aribowo, W.; Eguchi, K. Candle Flame Optimization: A Physics-Based Metaheuristic for Global Optimization. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2025, 18, 826–837. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadneh, T.; Batiha, B.; Gharib, G.M.; Montazeri, Z.; Dehghani, M.; Aribowo, W.; Eguchi, K. Perfumer Optimization Algorithm: A Novel Human-Inspired Metaheuristic for Solving Optimization Tasks. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2025, 18, 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadneh, T.; Batiha, B.; Gharib, G.M.; Montazeri, Z.; Dehghani, M.; Aribowo, W.; Eguchi, K. Makeup Artist Optimization Algorithm: A Novel Approach for Engineering Design Challenges. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2025, 18, 484–493. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadneh, T.; Batiha, B.; Gharib, G.M.; Montazeri, Z.; Dehghani, M.; Aribowo, W.; Ibraheem, I.K. Revolution Optimization Algorithm: A New Human-based Metaheuristic Algorithm for Solving Optimization Problems. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2025, 18, 520–531. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadneh, T.; Batiha, B.; Gharib, G.M.; Montazeri, Z.; Werner, F.; Dhiman, G.; Eguchi, K. Orangutan optimization algorithm: An innovative bio-inspired metaheuristic approach for solving engineering optimization problems. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2025, 18, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Liu, R.; Chen, D. Distribution characteristics of carbon emission by energy consumption in China as judged by spatial clustering analysis. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2013, 49, 529–533. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.G.; Shen, R.J. Analysis on China’s carbon emission division and reduction path: Based on multivariate panel data clustering analysis method. J. China Univ. Geosci. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 12, 7–13, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, X.; Cai, C. Spatial temporal differences of carbon emissions and carbon compensation in China based on land use change. Sci. Geogr. Sin 2019, 39, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y. Study on spatiotemporal characteristics and decoupling effect of carbon emission from cultivated land resource utilization in China. Land Sci. 2019, 33, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Ota, K.; Dong, M.; Yu, C.; Jin, H. Predicting transportation carbon emission with urban big data. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2017, 2, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K. A Multiscale Analysis on Spatiotemporal Pattern of Carbon Emissions and Its Impact Factors in China Using DMSPOLS Data. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Guan, X.; Pang, B.; Ma, H. Urbanisation, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A panel data analysis of China’s provinces. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Guo, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, H. Variation of net carbon emissions from land use change in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during 1990–2020. Land 2022, 11, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.I. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Xie, Y.; Wu, L.; Jiang, L. Quantifying and comparing the effects of key risk factors on various types of roadway segment crashes with LightGBM and SHAP. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 159, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Energy Statistical Yearbook 2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Lai, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Chuai, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, T.; Thompson, J.R. Carbon emissions from land-use change and management in China between 1990 and 2010. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; Goodale, C.L. Effects of land-use change on the carbon balance of terrestrial ecosystems. Ecosyst. Land Use Change 2004, 153, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, R.A.; Nassikas, A.A. Global and regional fluxes of carbon from land use and land cover change 1850–2015. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Peng, J.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, P. Research progress on carbon sources and sinks of farmland ecosystems. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 11, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Zhang, H.; Miao, J.; Song, M.W.; Zeng, Y.Q. Greenhouse gas emission characteristics and source/sink analysis of farmland ecosystem in Hubei Province. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2021, 38, 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.Y.; Guo, Z.D.; Piao, S.L.; Chen, A.P. Terrestrial vegetation carbon sink in China from 1981–2000. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 37, 804–812. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.N.; Wang, X.K.; Lu, F.; Duan, X.N.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Carbon sequestration and its potential by wetland ecosystem in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, L. Carbon Emission Effect of Land Use in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Lai, L.; Huang, X.J.; Chuai, X.W.; Tan, J.Z. The carbon emission intensity of land use conversion in different regions of China. Resour. Sci. 2013, 35, 792–799. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, A.L.; Dong, J. Carbon emission effect of land use and influencing factors decomposition of carbon emission in Wuhan Urban Agglomeration. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2014, 23, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Xing, H.; Hou, D. Analysis of carbon emissions from land cover change during 2000 to 2020 in Shandong Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B. Reducing carbon dioxide emissions in China’s manufacturing industry: A dynamic vector autoregression approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cao, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, D. Spatial–Temporal Pattern and Influence Factors of Land Used for Transportation at the County Level since the Implementation of the Reform and Opening-Up Policy in China. Land 2021, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, S.; Shi, H.; Wu, S.; Bao, S.; Xiao, T. Research on the Nonlinear Relationship Between Carbon Emissions from Residential Land and the Built Environment: A Case Study of Susong County, Anhui Province Using the XGBoost-SHAP Model. Land 2025, 14, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, T.; Sun, Z. Spatial-temporal pattern and driving factors of carbon emission intensity of main crops in Henan province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y. Toward low-carbon agriculture: Measurement and driver analysis of agricultural carbon emissions in Sichuan province, China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1565776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Hussain, A.; Amir, S.B.; Ahmed, S.H.; Aslam, S.M.H. XGBoost and random forest algorithms: An in depth analysis. Pak. J. Sci. Res. 2023, 3, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, L.C.; Kaneko, S. Decomposing the decoupling of CO2 emissions and economic growth in Brazil. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Du, E.; Li, Z. Low-carbon transition model for power generation companies in China: A case study. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Meng, F.; Li, B. Spatial effects of innovation ecosystem development on low-carbon transition. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Deng, R. Spatial-temporal evolution and influencing factors of net carbon sink efficiency in Chinese cities under the background of carbon neutrality. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Fan, M.; Yao, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, S. Spatial-temporal characteristics of carbon emissions corrected by socio-economic driving factors under land use changes in Sichuan Province, southwestern China. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Li, K. Spatiotemporal dynamic evolution and influencing factors of land use carbon emissions: Evidence from Jiangsu Province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1368205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ren, W.; Hao, Y.; Ke, S. Impact of compact development of urban transportation on green land use efficiency:an empirical analysis based on spatial measurement. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 33, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Tang, L.; Hupy, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Shao, G. A commentary review on the use of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in the era of popular remote sensing. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath, B.D.; Fiscus, D. Water, Land, and Forest Susceptibility and Sustainability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- WFEsystem in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 8568–8580.
- Shu, Y.; Lam, N.S. Spatial disaggregation of carbon dioxide emissions from road traffic based on multiple linear regression model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Che, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hsu, S.C. PM2.5 pollution in a megacity of southwest China: Source apportionment and implication. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8679–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.S.; Marques, A.C. How do energy forms impact energy poverty? An analysis of European degrees of urbanisation. Energy Policy 2023, 173, 113346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubei Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Hubei Statistical Yearbook 2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]

| Data (Accuracy) | Data Sources | |
|---|---|---|
| LUCC (30 m) | Population (1 km) | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 18 January 2025)) |
| GDP (1 km) | VIIRS (500 m) | |
| NDVI (30 m) | National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) (https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/ (accessed on 25 January 2025)) | |
| LST (1 km) | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/ (accessed on 27 January 2025)) | |
| Road (30 m) | Open Street Map (https://www.openstreetmap.org/ (accessed on 02 February 2025)) | |
| PM2.5 (1 km) | The ChinaHighAirPollutants (CHAP) dataset (https://weijing-rs.github.io/product.html (accessed on 27 January 2025)) | |
| Fuel Types | Conversion Coefficient of Standard Coal | Carbon Emission Coefficient | Fuel Types | Conversion Coefficient of Standard Coal | Carbon Emission Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw coal | 0.7143 | 0.7559 | Diesel | 1.4571 | 0.5921 |
| Coke | 0.9714 | 0.8550 | Fuel oil | 1.4286 | 0.6185 |
| Crude oil | 1.4286 | 0.5857 | Natural gas | 1.3300 | 0.4483 |
| Gasoline | 1.4714 | 0.5583 | Electricity | 0.1229 | 0.2132 |
| Kerosene | 1.4714 | 0.5714 |
| City | Fitting Equation | R2 | City | Fitting Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan | y = 2 × 10−12x3 − 1 × 10−6x2 + 0.1542x − 5066.6 | 0.8334 | Huanggang | y = 1 × 10−11x3 − 2 × 10−6x2 + 0.0992x − 719.58 | 0.9228 |
| Huangshi | y = 5 × 10−11x3 − 4 × 10−6x2 + 0.1226x − 628.91 | 0.8199 | Xianning | y = 4 × 10−11x3 − 3 × 10−6x2 + 0.0826x − 307.51 | 0.894 |
| Shiyan | y = 4 × 10−11x3 − 4 × 10−6x2 + 0.1057x − 401.39 | 0.8428 | Suizhou | y = 4 × 10−11x3 − 3 × 10−6x2 + 0.0738x − 158.37 | 0.9171 |
| Yichang | y = 2 × 10−11x3 − 3 × 10−6x2 + 0.1395x − 1148.3 | 0.6659 | Enshi | y = 1 × 10−10x3 − 5 × 10−6x2 + 0.092x − 228.12 | 0.8263 |
| Xiangyang | y = 2 × 10−11x3 − 3 × 10−6x2 + 0.1261x − 918.45 | 0.7678 | Xiantao | y = 4 × 10−10x3 − 1 × 10−5x2 + 0.109x − 162.15 | 0.8146 |
| Ezhou | y = 7 × 10−11x3 − 5 × 10−6x2 + 0.1035x − 366.94 | 0.8858 | Qianjiang | y = 5 × 10−10x3 − 2 × 10−5x2 + 0.1461x − 254.58 | 0.7501 |
| Jingmen | y = 7 × 10−11x3 − 5 × 10−6x2 + 0.1075x − 304.93 | 0.7481 | Tianmen | y = 5 × 10−10x3 − 1 × 10−5x2 + 0.0856x − 49.559 | 0.826 |
| Xiaogan | y = 1 × 10−11x3 − 2 × 10−6x2 + 0.1036x − 823.85 | 0.9038 | Shennongjia | y = 2 × 10−9x3 − 2 × 10−5x2 + 0.0314x + 5.2347 | 0.406 |
| Jingzhou | y = 2 × 10−11x3 − 3 × 10−6x2 + 0.0972x − 392.73 | 0.6959 | Hubei Province | y = 1 × 10−13x3 − 2 × 10−7x2 + 0.1337x − 13,507 | 0.8554 |
| Criterion | Indicator | Criterion | Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental conditions | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | Economic conditions | Secondary Sector Level (2Sector) |
| Blue Cover Impacts (BCI) | Population (POP) | ||
| Green Cover Impacts (GCI) | Degree of Urbanization (DU) | ||
| PM2.5 (PM) | Road Density (RD) | ||
| Land Surface Temperature (LST) | Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | ||
| Industrial Scale (IS) |
| 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon emissions | Industry land | 1559.97 | 2300.71 | 5211.14 | 11,812.09 | 13,351.25 |
| Construction land | 12,225.77 | 14,201.33 | 16,403.55 | 16,747.56 | 17,132.97 | |
| Total | 13,785.74 | 16,502.04 | 21,614.70 | 28,559.65 | 30,484.21 | |
| Carbon sinks | Woodland | −5348.55 | −5340.82 | −5341.29 | −5324.54 | −5313.44 |
| Grassland | −1.55 | −1.54 | −1.52 | −1.51 | −1.53 | |
| Farmland | −90.55 | −89.45 | −86.72 | −85.60 | −87.01 | |
| Water | −32.04 | −34.11 | −36.65 | −36.72 | −34.65 | |
| Unused land | −0.02 | −0.02 | −0.02 | −0.02 | −0.02 | |
| Total | −5472.72 | −5465.94 | −5466.20 | −5448.39 | −5436.64 | |
| Net carbon emissions | 8313.02 | 11,036.10 | 16,148.50 | 23,111.27 | 25,047.57 |
| Models | RMSE Training | RMSE Testing | MAE Training | MAE Testing | Models | RMSE Training | RMSE Testing | MAE Training | MAE Testing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DTR | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.014 | 6 | Ridge | 0.055 | 0.054 | 0.024 | 0.024 |
| 2 | RFR | 0.013 | 0.035 | 0.004 | 0.012 | 7 | Lasso | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.029 | 0.029 |
| 3 | KN | 0.038 | 0.046 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 8 | EN | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.029 | 0.029 |
| 4 | PLR | 0.048 | 0.047 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 9 | SVR | 0.094 | 0.094 | 0.088 | 0.088 |
| 5 | LR | 0.055 | 0.054 | 0.024 | 0.024 | 10 | XGB | 0.576 | 1.171 | 0.418 | 0.686 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Jia, B.; Wu, J.; Wu, X. Study of Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Net Carbon Emissions in Hubei Province Based on Interpretable Machine Learning. Land 2025, 14, 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061255
Zhao J, Jia B, Wu J, Wu X. Study of Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Net Carbon Emissions in Hubei Province Based on Interpretable Machine Learning. Land. 2025; 14(6):1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061255
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Junyi, Bingyao Jia, Jing Wu, and Xiaolu Wu. 2025. "Study of Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Net Carbon Emissions in Hubei Province Based on Interpretable Machine Learning" Land 14, no. 6: 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061255
APA StyleZhao, J., Jia, B., Wu, J., & Wu, X. (2025). Study of Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Net Carbon Emissions in Hubei Province Based on Interpretable Machine Learning. Land, 14(6), 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061255






