Multiple Paths of Rural Transformation and Its Driving Mechanisms Under the Perspective of Rural–Urban Continuum: Taking Suzhou, China as an Example
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Research Methodology
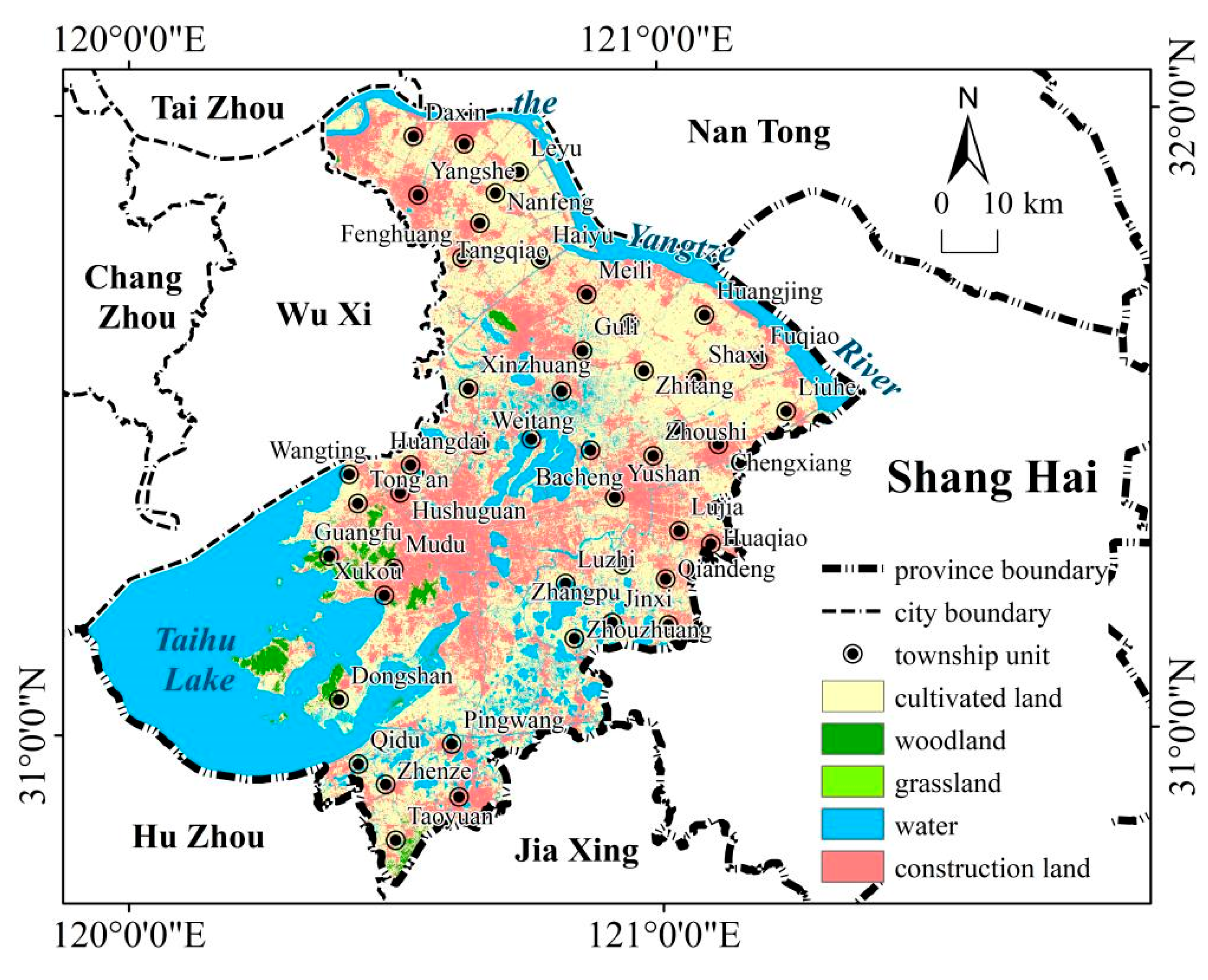
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Research Methods
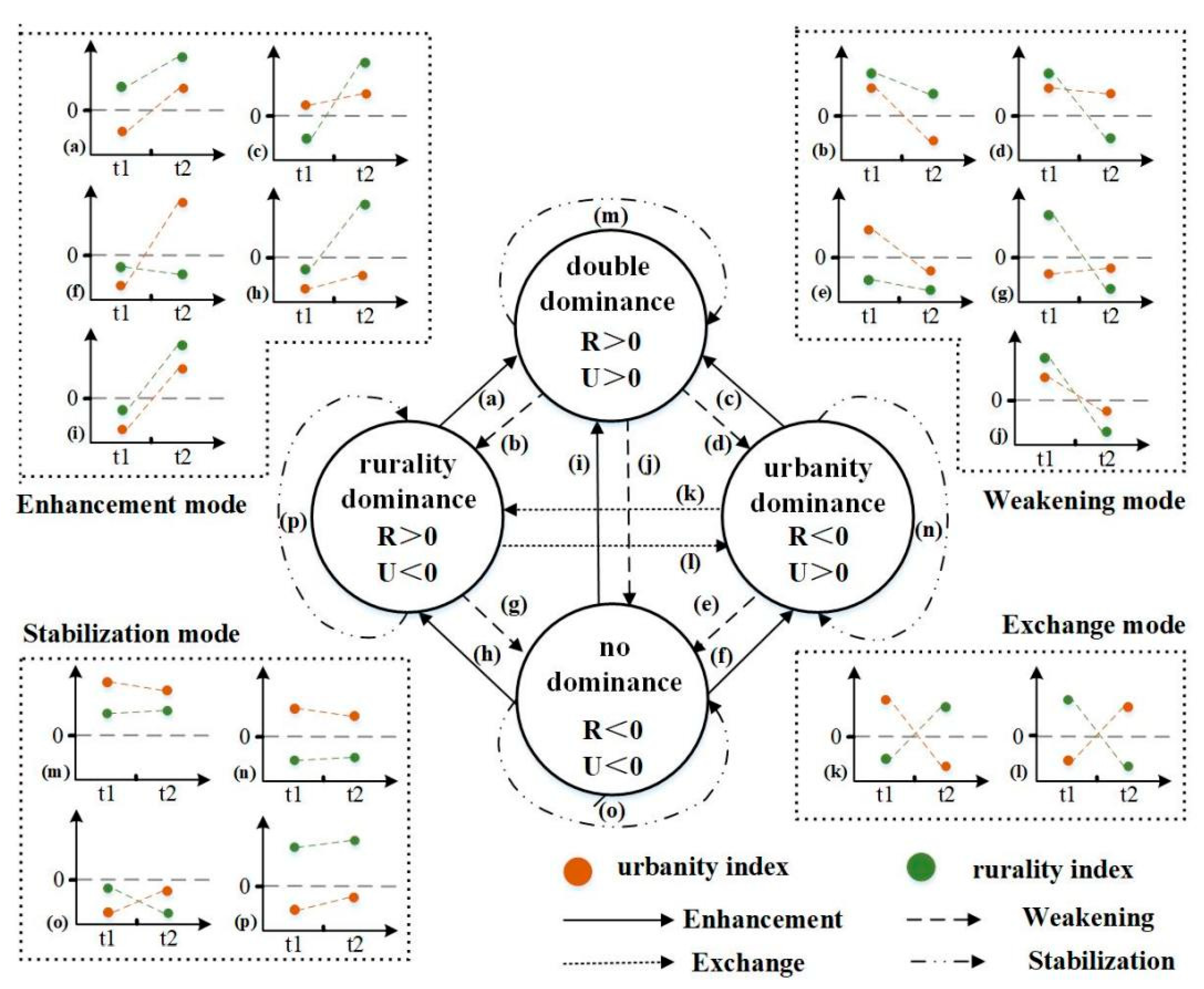
2.2.1. Theoretical Framework Construction
2.2.2. Evaluation Indices System
2.2.3. Driving Factors Measurement
3. Research Results
3.1. Results of the Urban–Rural Dominance Evaluation
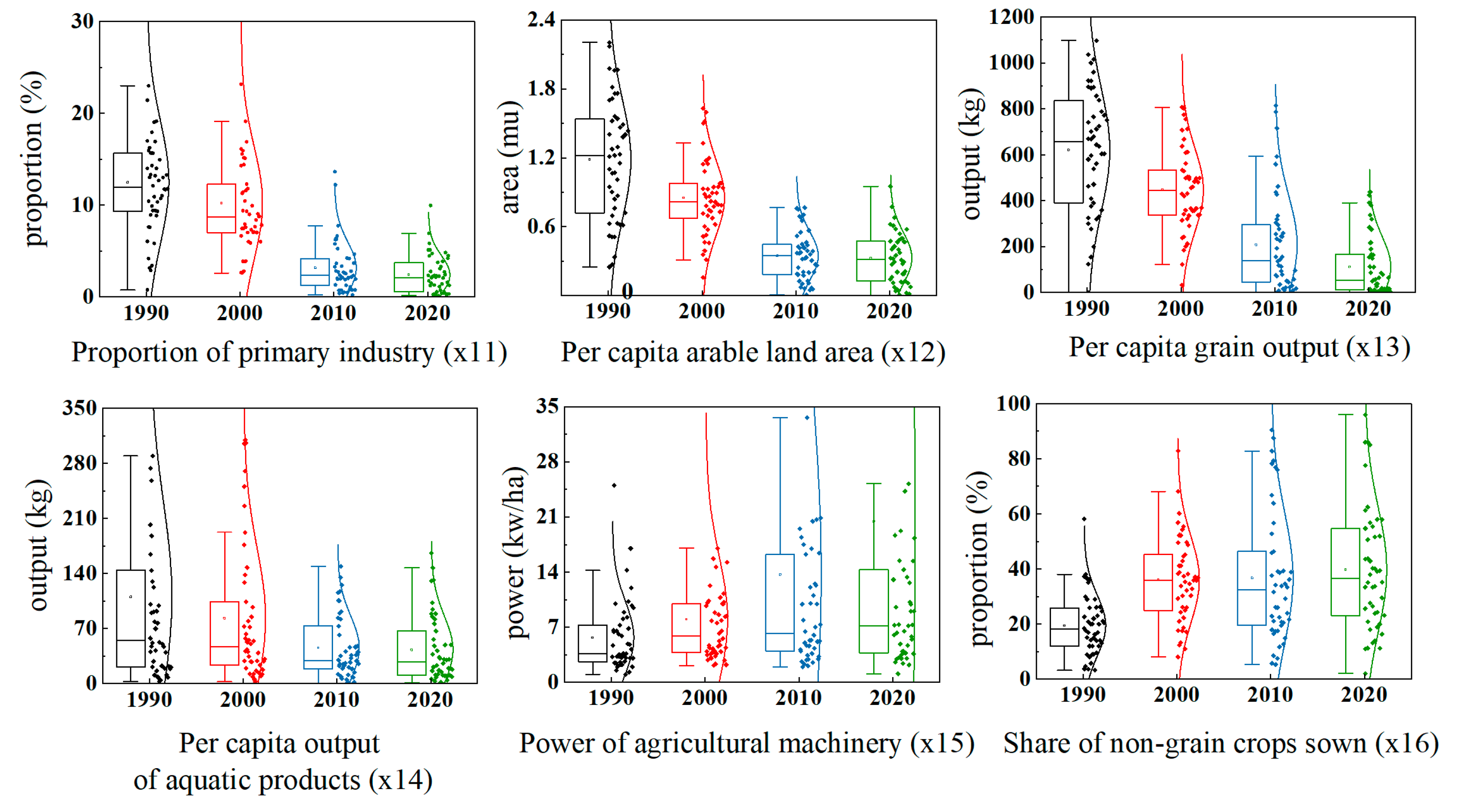
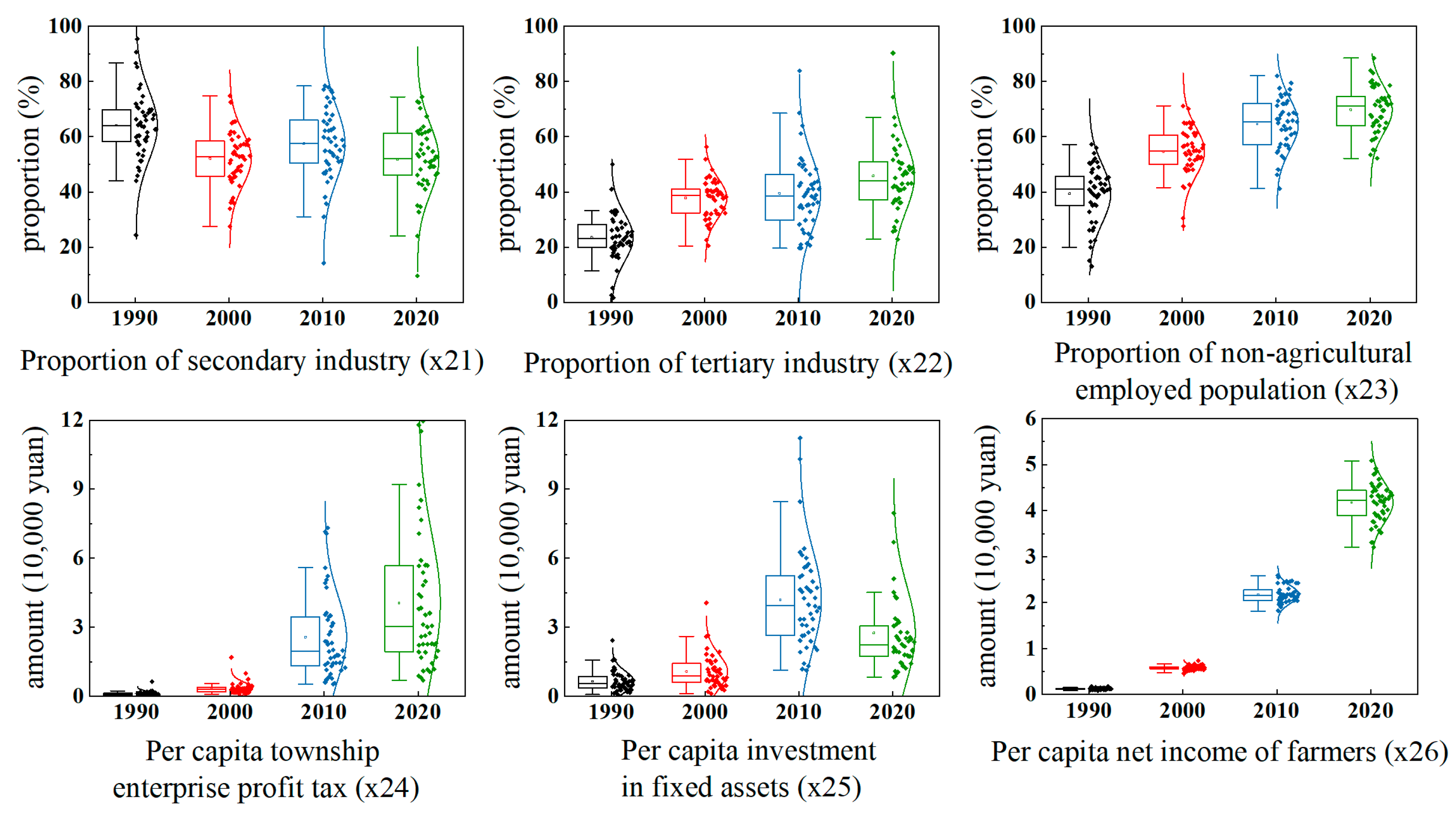
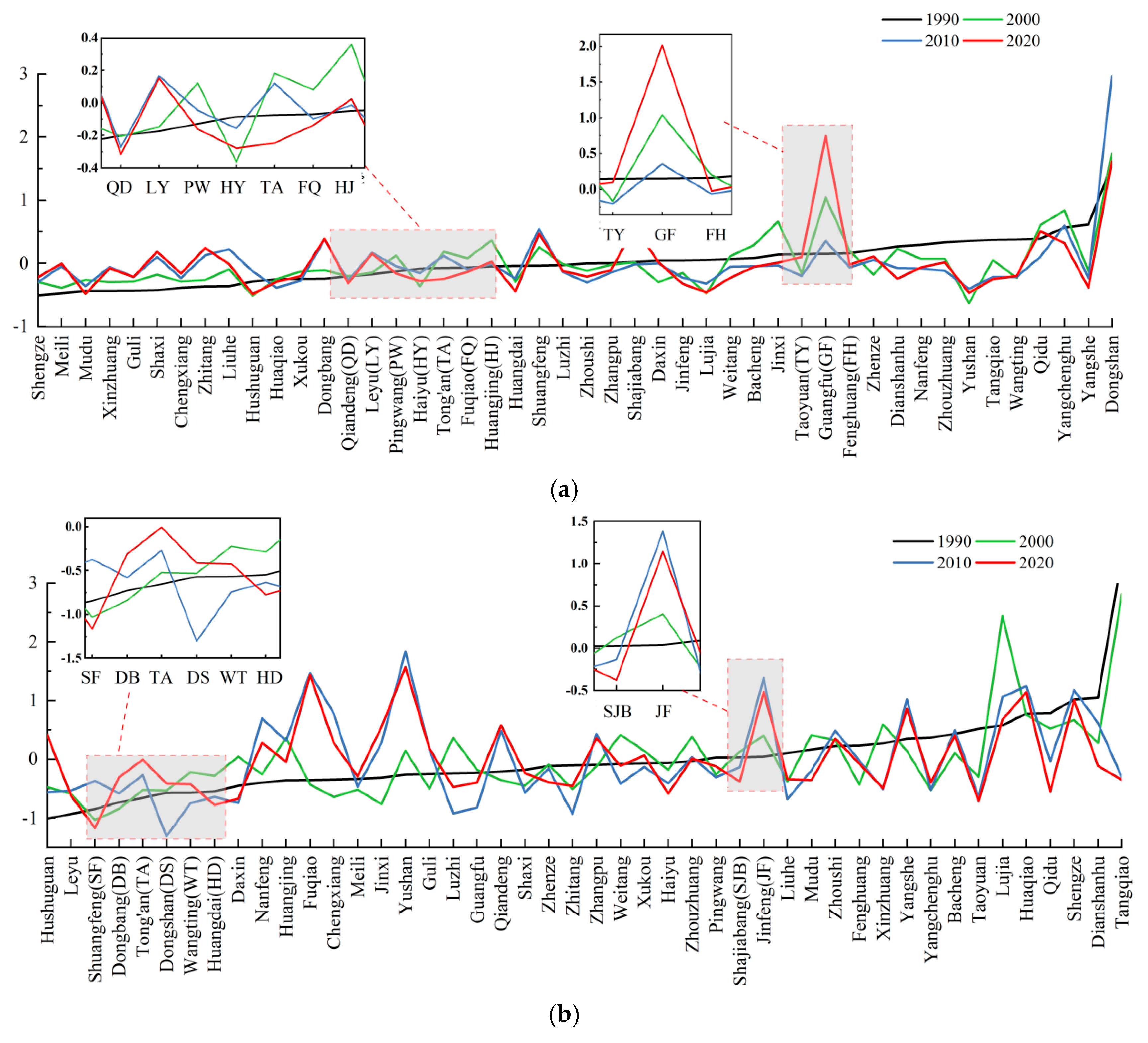
3.1.1. Chronological Change in Evaluation Indices
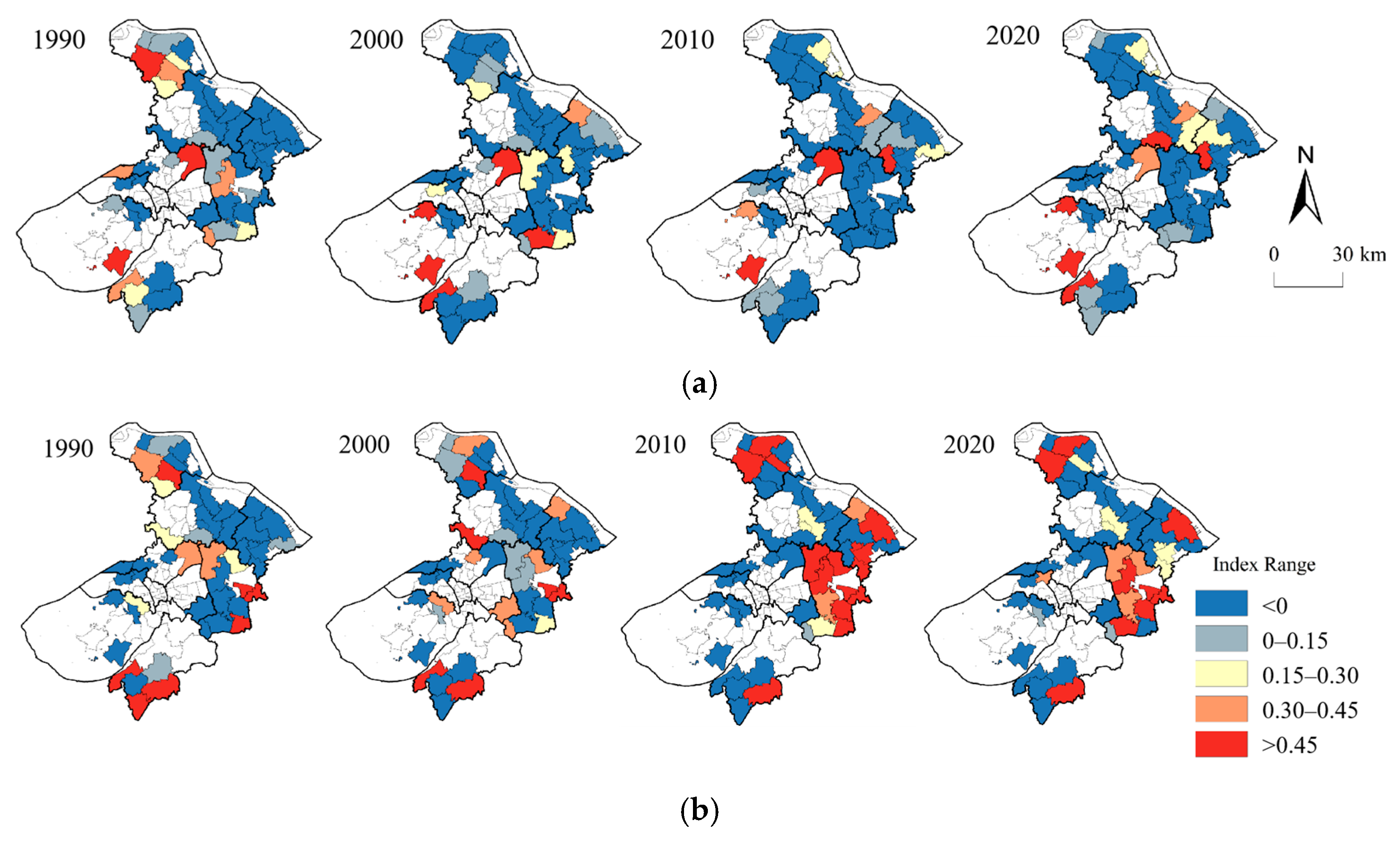
3.1.2. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Urban–Rural Dominance
3.2. Multiple Paths to Rural Transformation
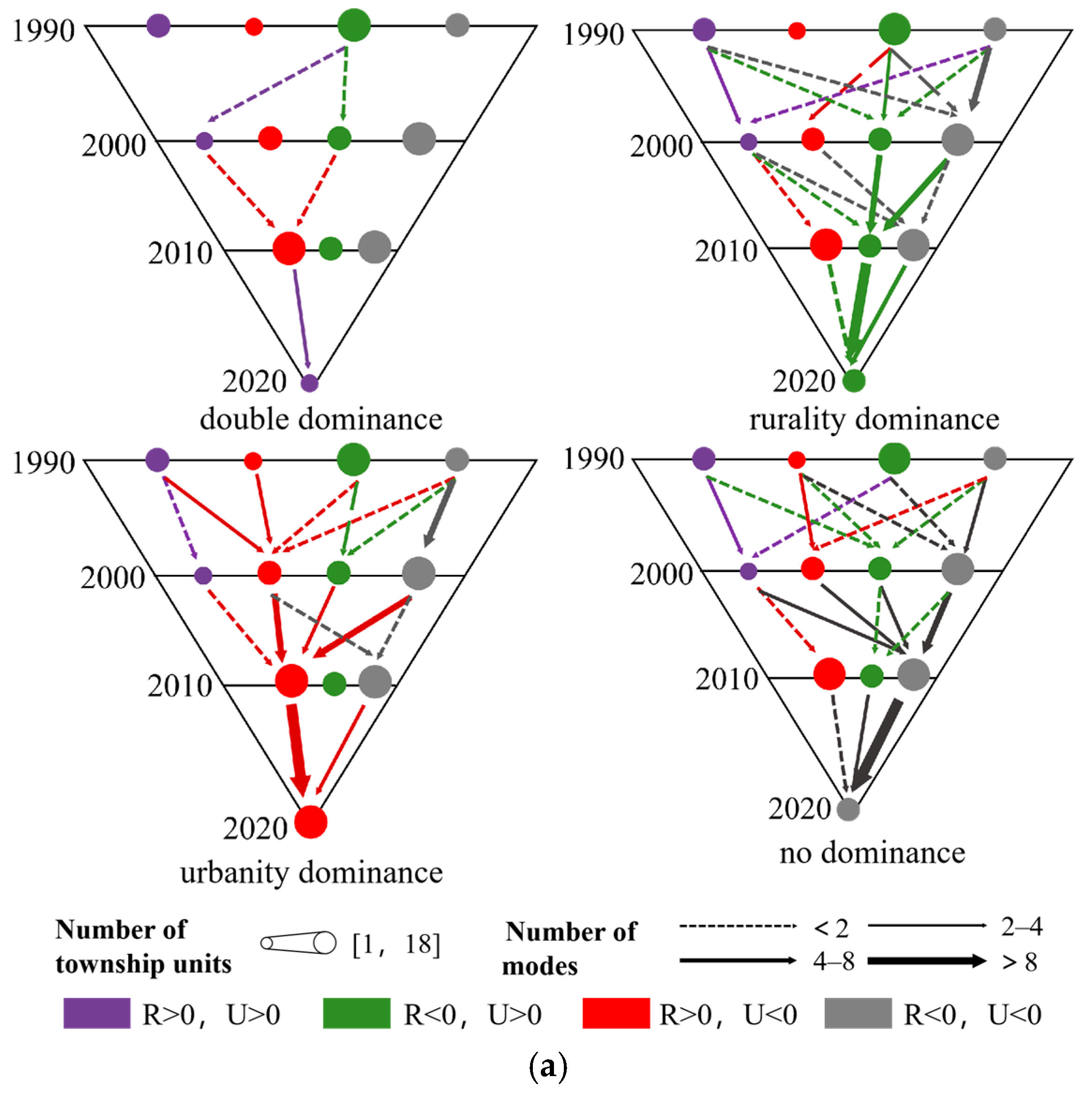
3.2.1. Transformation Patterns at Different Times
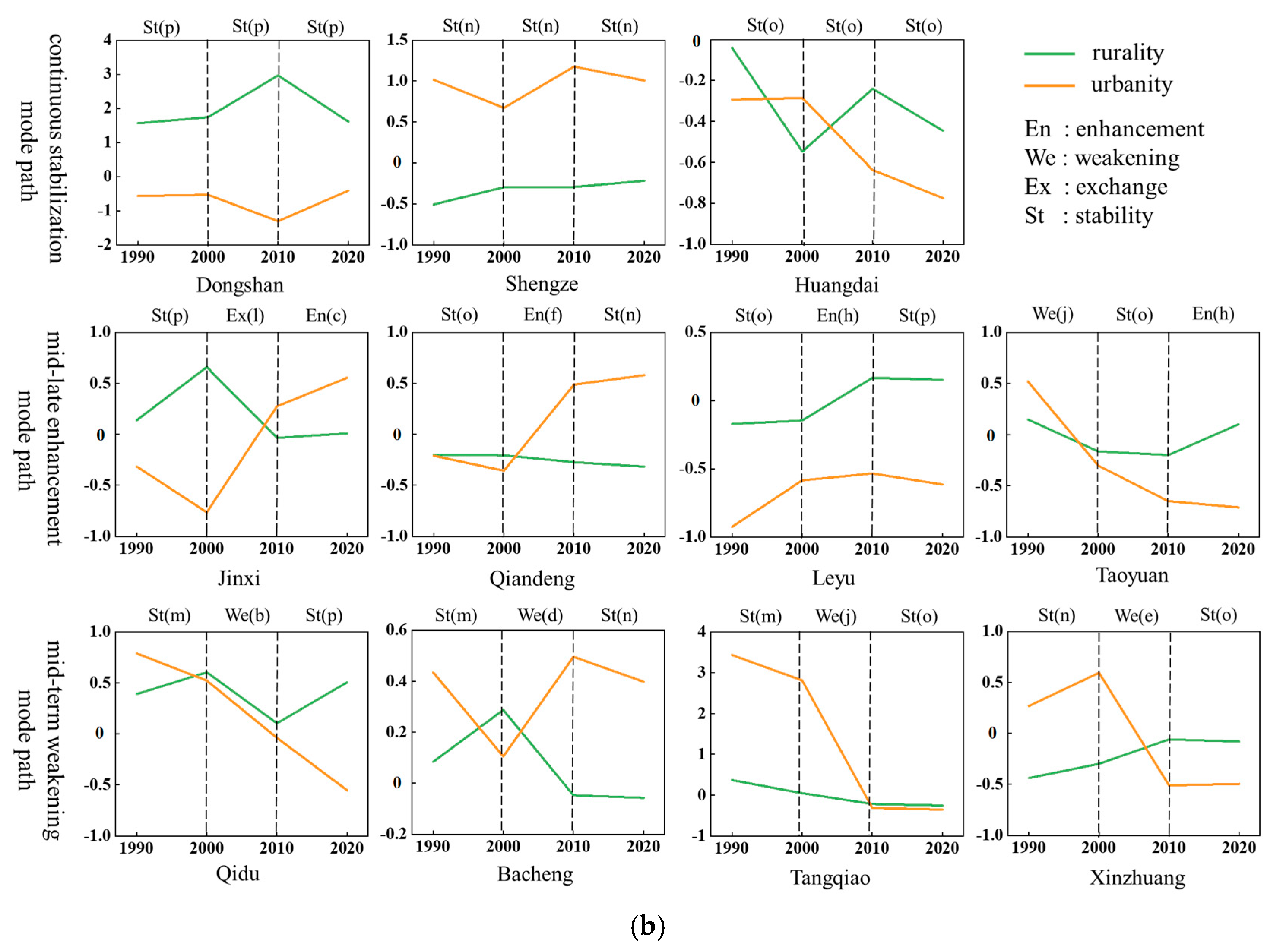
3.2.2. Multiple Transformation Paths
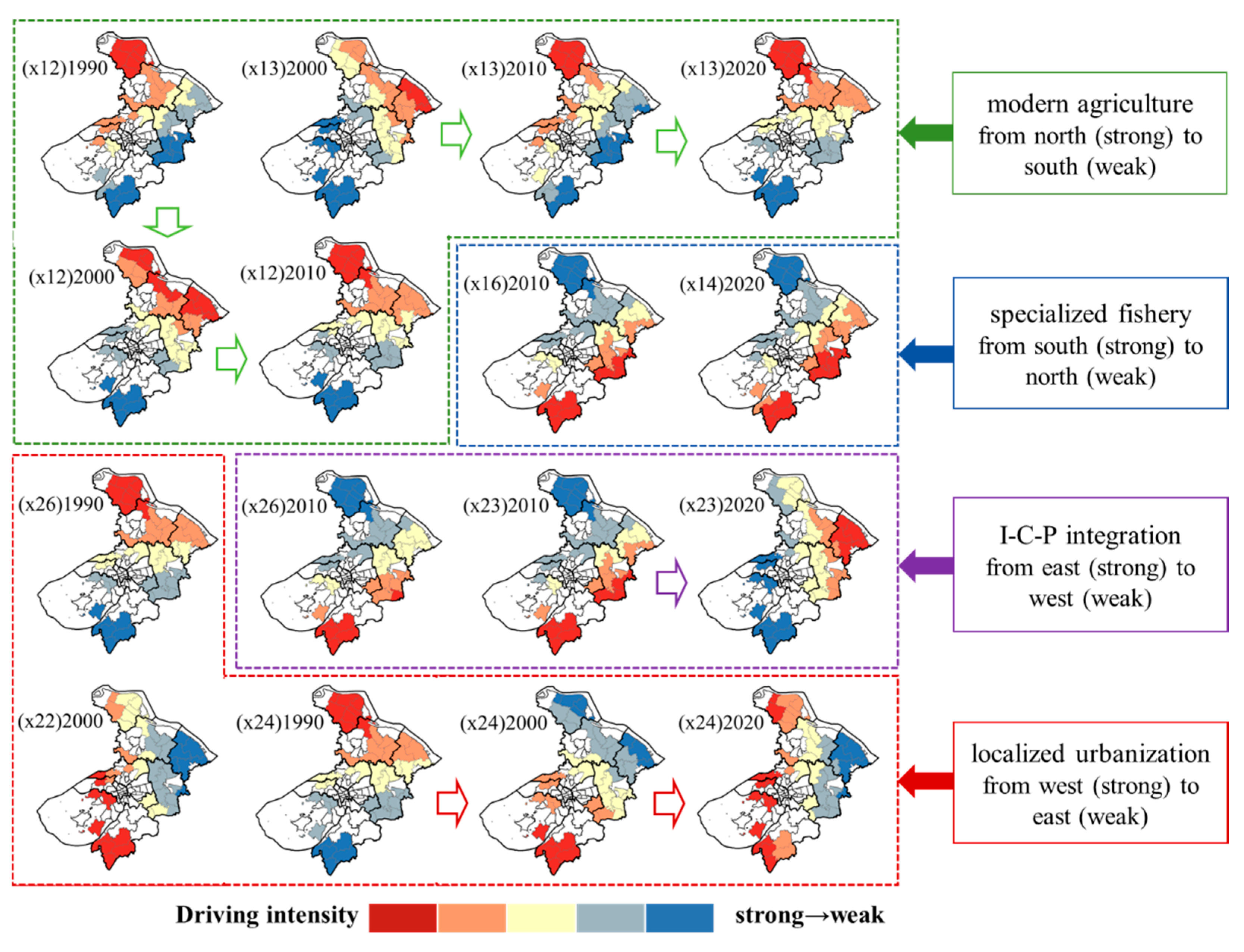
3.3. Driving Mechanisms for Rural Transformation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woods, M. Engaging the global countryside: Globalization, hybridity and the reconstitution of rural place. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2007, 31, 485–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Wang, Y.G. From native rural China to urban-rural China: The rural transition perspective of China transformation. Manag. World 2018, 34, 128–146, 232. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.B.; Zhan, L.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wu, M.J. Unpacking the “supply-utilization-demand” interplay: Keys to multifunctional sustainability in rural China. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K. Rural-Urban Interaction in the Developing World; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Halfacree, K.H. Locality and social representation: Space, discourse and alternative definitions of the rural. J. Rural. Stud. 1993, 9, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, T.; Murdoch, J.; Lowe, P.; Munton, R.C.; Flynn, A. Constructing the Countryside: An Approach to Rural Development; Routledge: London, UK, 1993; pp. 144–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, G. Multifunctional Agriculture. A Transition Theory Perspective; Cromwell Press: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, H.B.; Hu, X.L. Rural space transition in Western countries and its inspiration. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Gao, J.L.; An, F.P. Rural multifunctionality: A comprehensive literature review. Prog. Geogr. 2024, 43, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Li, Y.R.; Chen, Y.F. Approaches to rural transformation and sustainable development in the context of urban-rural integration. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2560–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.B.; Dong, X.Z.; Ma, W.Q.; Zhao, W.Y. New rural community construction or retention development: A comparative analysis of rural settlement transition mechanism in plain agriculture area of China based on actor network theory. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.B.; Tao, T.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Wu, S.S.; Zhang, W.B. Study on spatial divergence of rural resilience and optimal governance paths in oasis: The case of Yongchang County in the Hexi Corridor of China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 4603–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Yang, X.J. Rural transformation adaptation and development path optimization in vulnerable environment areas: A case study of Minqin County, Gansu province. Hum. Geogr. 2024, 39, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.S. The process of rural development and paths for rural revitalization in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 1408–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H. Urban-rural interaction patterns and dynamic land use: Implications for urban-rural integration in China. Reg. Environ. Change 2012, 12, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, W.T.; Li, H.Q.; Mu, H. Analyzing the driving mechanism of rural transition from the perspective of rural-urban continuum: A case study of Suzhou, China. Land 2022, 11, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.Y. A review of the theory and practice of “Sunan Model” for 30 years. Mod. Econ. Res. 2008, 8, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.M. The new Sunan model is on the horizon. Mod. Econ. Res. 2001, 8, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.K.; Shi, J.C. Evolution and sustained development of Sunan model. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2024, 32, 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Q.; Li, G.B.; Wang, Y. Space-time evolution and mechanisms of traditional village hollowing in Suzhou: A case study of Houbu, Tangli and Wengxiang villages. Agric. Econ. 2021, 2, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Shen, J.F.; Chung, C.K.L. City profile: Suzhou-a Chinese city under transformation. Cities 2015, 44, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.C.; Luo, Z.D.; Geng, L. Reopen the path of endogenous development: Rethinking the roles and mechanisms of township and village enterprises in the development of small towns in Sunan. Urban Plan. Forum 2013, 2, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.L.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, X.L.; Yuan, Y. On the recognition of rural definitions. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 398–409. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Z.Y.; Lin, G. Hybridity: Rethinking rurality. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Zou, J. Assessment of rural development types and their rurality in Eastern coastal China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 426–434. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.M.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.G.; Lin, S.N. Spatio-temporal differentiation and driving mechanisms of rurality in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Zhao, Y.X. The Impact of Digital Economy on China’s Energy “Dual Control” Goals. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 34, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Duan, X.J.; Wang, L.; Zou, H.; Yang, Q.K. Spatial and temporal differentiation and driving mechanisms of economic development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Rsour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2020, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.F. The effect of family off-farm work on farmers’ participation in farmland transfer. China Land Sci. 2020, 34, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.F. Exploration of the practice and theory of the leading development of the Southern Jiangsu region: From the “Sunan model”, “New Sunan model” to the “Sunan modernization model”. Nanjing Soc. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, T.J.; Xie, X.; Gao, J.; Dong, X.D. Local government system innovation and industrial transformation and upgrading: A case study on Suzhou’s industrial district. Acad. Res. 2016, 2, 82–89+177–178. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.L.; Tan, Q.M. The new Sunan model: A theoretical framework of rural revitalization. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 2, 18–26+163–164. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, P. Cultivated land use control from the perspective of “non-grain” governance: Response logic and framework construction. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 942–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.T.; Gong, J.W.; Gao, X.W.; Shi, Q.H. The employment effects and mechanisms of the implementation of rural e-commerce development policy in China. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2024, 4, 141–162. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Long, H.L.; Wang, J.Y. Rural development process and driving mechanisms of South Jiangsu: A case study of Suzhou City. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Office of Suzhou Municipal Committee for the Compilation of Local Chronicles. 70 Glorious Years of Wujiang: From the Home of Silk to a City of Joyful Living. Available online: https://dfzb.suzhou.gov.cn (accessed on 26 September 2019).
- Ye, Z.P. Industrial governance capacity and industrial development in China: Based on the case of Kunshan City with a process-tracing approach, Jiangsu Province. Chin. J. Urban Environ. Stud. 2020, 3, 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.L. Does the system in which counties are directly managed by the province reduce regional economic performance? Based on the comparison of typical sample cities and counties in Jiangsu and Zhejiang Provinces. Economist 2022, 4, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, G.Z.; Shi, L.N.; Wen, Q.; Niu, S.D. Coupling and coordination of the multifunction and value of arable land at the regional scale from the perspective of rural hollowing governance. Prog. Geogr. 2024, 43, 587–602. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.Y.; Jiang, G.H.; Xing, Y.Q.; Wu, S.D.; Kong, X.R.; Zhou, T. From process to effects: An approach for integrating dominant and recessive transitions of rural residential land (RRL). Land Use Policy 2025, 148, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.Q.; Hu, S.G.; Yang, R.; Tao, W.; Li, H.B.; Li, B.H.; Liu, P.L.; Wei, F.Q.; Guo, W.; Tang, C.C.; et al. Protection and utilization of the traditional villages of China in the context of rural revitalization: Challenges and prospects. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 1735–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.; Luo, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.H.; Liu, X.Q. Classification and revitalization of Chinese traditional villages based on resource transformation: A perspective of “people-industry-location” elements. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2024, 38, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.B.; Chen, M.M.; Fang, F.; Che, X.L. Research on the spatiotemporal variation of rural-urban transformation and its driving mechanisms in underdeveloped regions: Gansu Province in western China as an example. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Sun, D.; Wang, Z. Exploring the Rural Revitalization Effect under the Interaction of Agro-Tourism Integration and Tourism-Driven Poverty Reduction: Empirical Evidence for China. Land 2024, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.L.; Fan, D.X.F.; Wang, R.; Ou, Y.H.; Ma, X.L. Does Rural Tourism Revitalize the Countryside? An Exploration of the Spatial Reconstruction Through the Lens of Cultural Connotations of Rurality. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2023, 29, 100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Indices | Unit | Weight | Explanation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rurality (R) | x11 | Proportion of primary industry | % | 0.1355 | Proportion of the primary industry in the gross domestic product |
| x12 | Per capita arable land area | mu | 0.0921 | Average amount of cultivated land area to the year-end population | |
| x13 | Per capita grain output | kg | 0.1273 | Average amount of grain output to the year-end population | |
| x14 | Per capita output of aquatic products | kg | 0.1879 | Ratio of the output of aquatic products to the year-end population | |
| x15 | Power of agricultural machinery | Kw/ha | 0.3852 | Average amount of dynamics of farm machinery for sowing areas | |
| x16 | Share of non-grain crops sown | % | 0.0720 | Proportion of non-grain in the sowing area of crops | |
| Urbanity (U) | x21 | Proportion of secondary industry | % | 0.0237 | Proportion of secondary industry in the gross domestic product |
| x22 | Proportion of the tertiary industry | % | 0.0421 | Proportion of the tertiary industry in the gross domestic product | |
| x23 | Proportion of non-agricultural employed population | % | 0.0361 | Ratio of employees in TVEs to year-end population | |
| x24 | Per capita township enterprise profit tax | 10,000 CNY | 0.4000 | Average amount of profits and taxes of TVEs for the year-end population | |
| x25 | Per capita investment in fixed assets | 10,000 CNY | 0.2225 | Total fixed assets investment of the year-end population | |
| x26 | Per capita net income of farmers | 10,000 CNY | 0.2756 | Average amount of income from rural residents | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, P.; Mu, H.; Shao, J.; Yuan, Y. Multiple Paths of Rural Transformation and Its Driving Mechanisms Under the Perspective of Rural–Urban Continuum: Taking Suzhou, China as an Example. Land 2025, 14, 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061145
Xu P, Mu H, Shao J, Yuan Y. Multiple Paths of Rural Transformation and Its Driving Mechanisms Under the Perspective of Rural–Urban Continuum: Taking Suzhou, China as an Example. Land. 2025; 14(6):1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061145
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ping, Han Mu, Jingwei Shao, and Yuan Yuan. 2025. "Multiple Paths of Rural Transformation and Its Driving Mechanisms Under the Perspective of Rural–Urban Continuum: Taking Suzhou, China as an Example" Land 14, no. 6: 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061145
APA StyleXu, P., Mu, H., Shao, J., & Yuan, Y. (2025). Multiple Paths of Rural Transformation and Its Driving Mechanisms Under the Perspective of Rural–Urban Continuum: Taking Suzhou, China as an Example. Land, 14(6), 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061145







