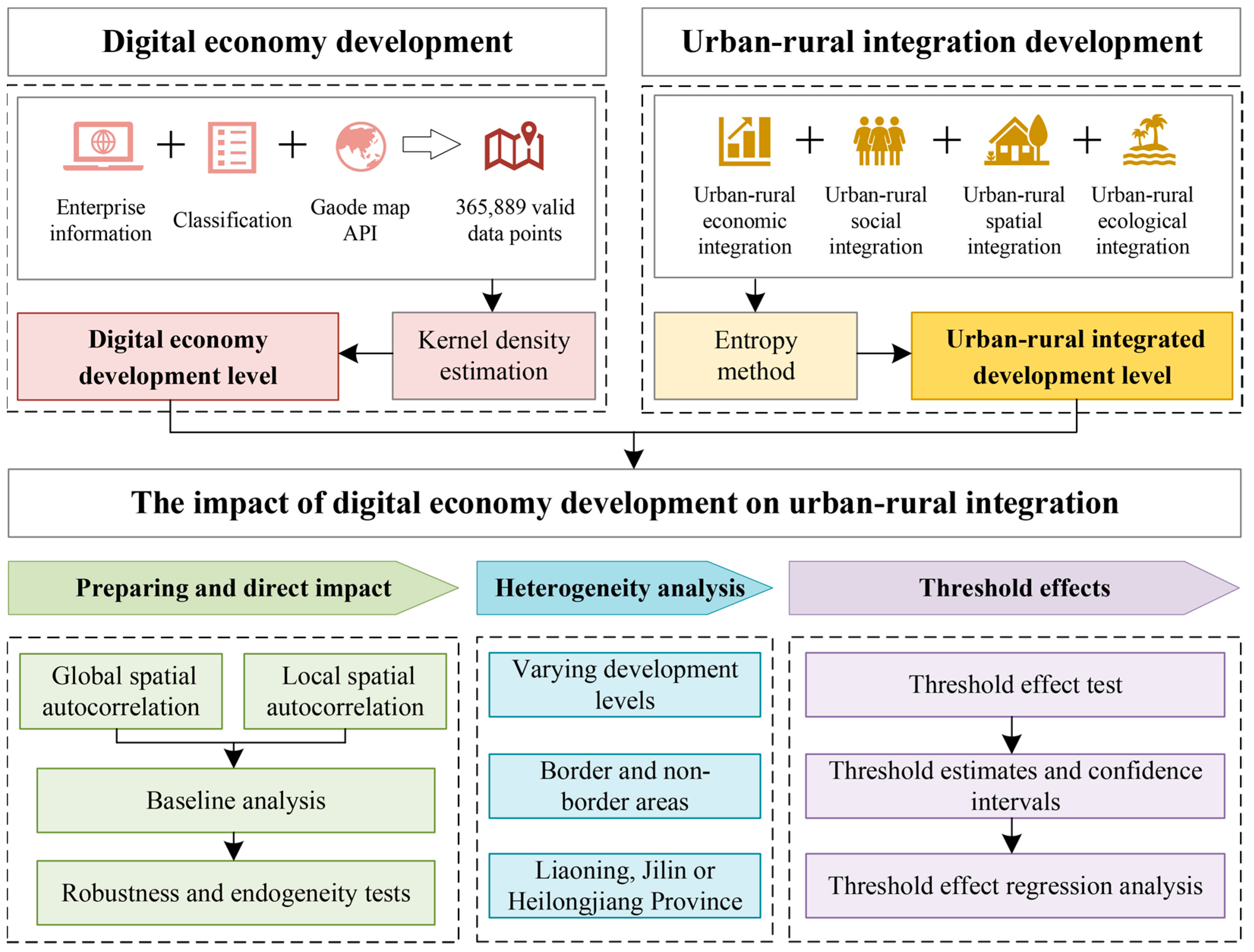
Digital Economy Development and Urban–Rural Integration in Northeast China: An Empirical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
3. Research Design
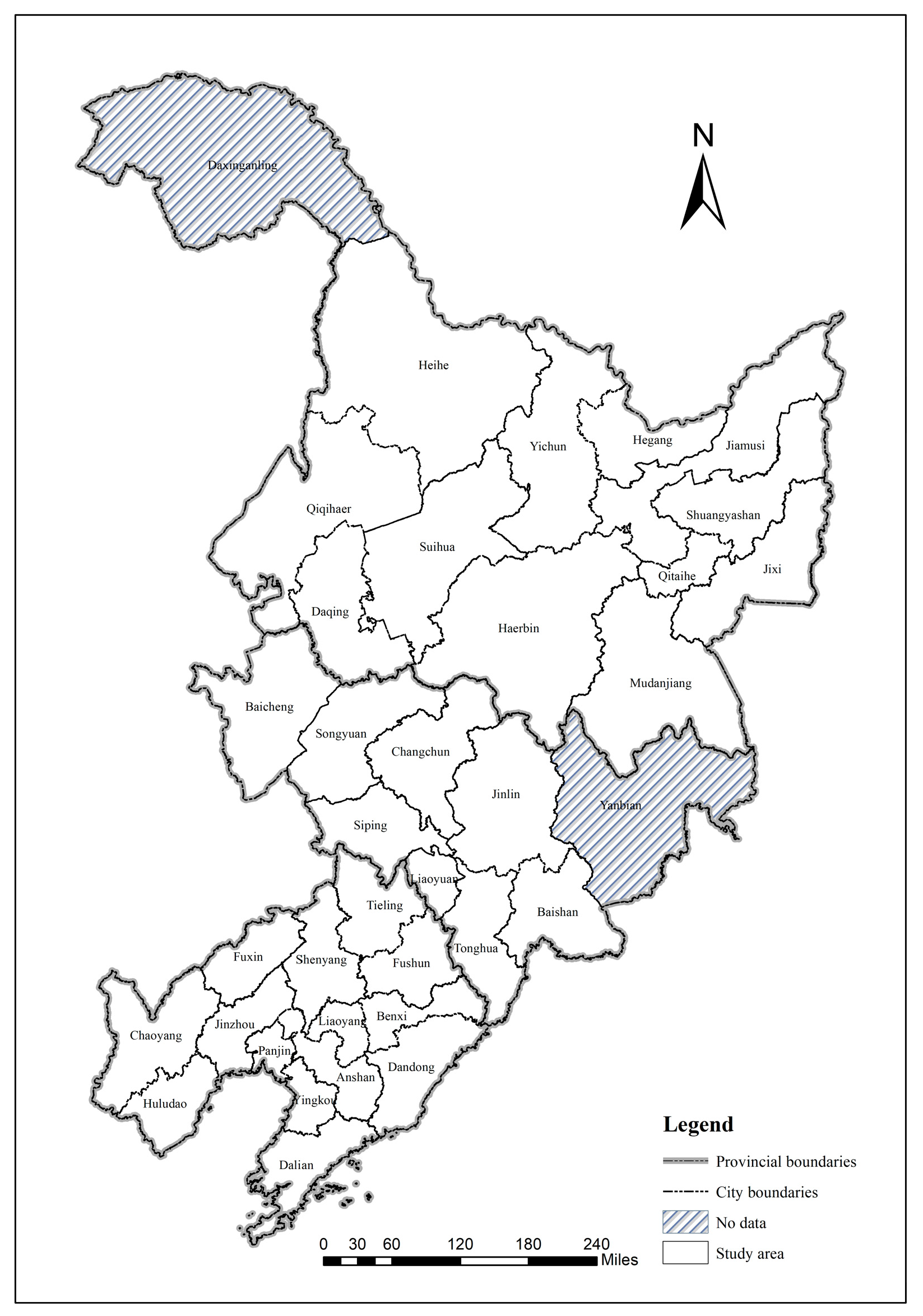
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Measurement of Digital Economy Development Level
3.2.2. Measurement of Rural–Urban Integration Development Level
3.2.3. Research Methods for Impact and Effect Analysis
- 1.
- Spatial autocorrelation analysis
- 2.
- Threshold Effects Model
- (1)
- Government intervention level
- (2)
- Social security level
- (3)
- Employee wage level
- (4)
- Household savings level
- (5)
- Financial development level
3.3. Data Sources
3.3.1. Enterprise Big Data
3.3.2. Socio-Economic Statistical Data
4. Results
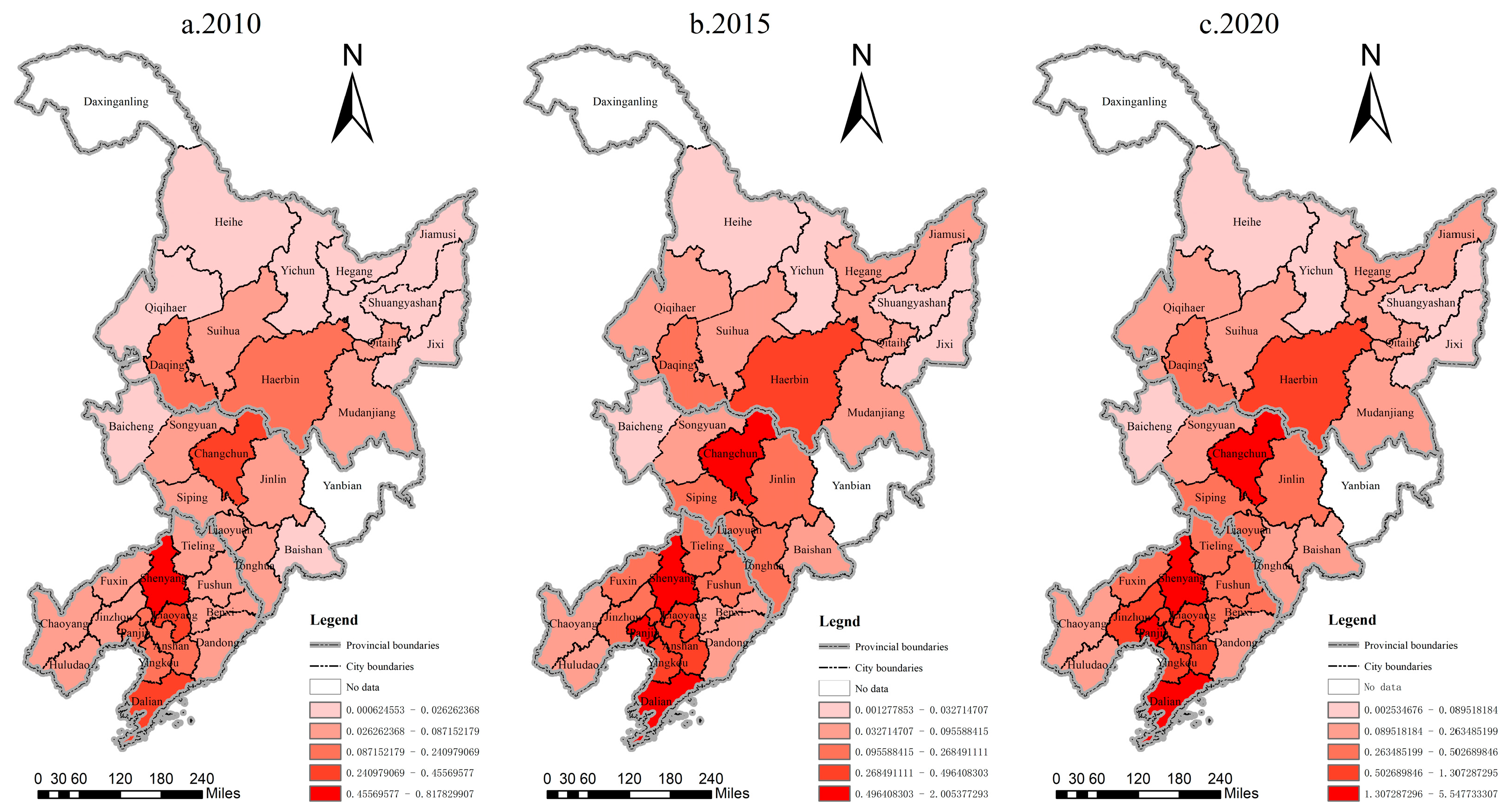
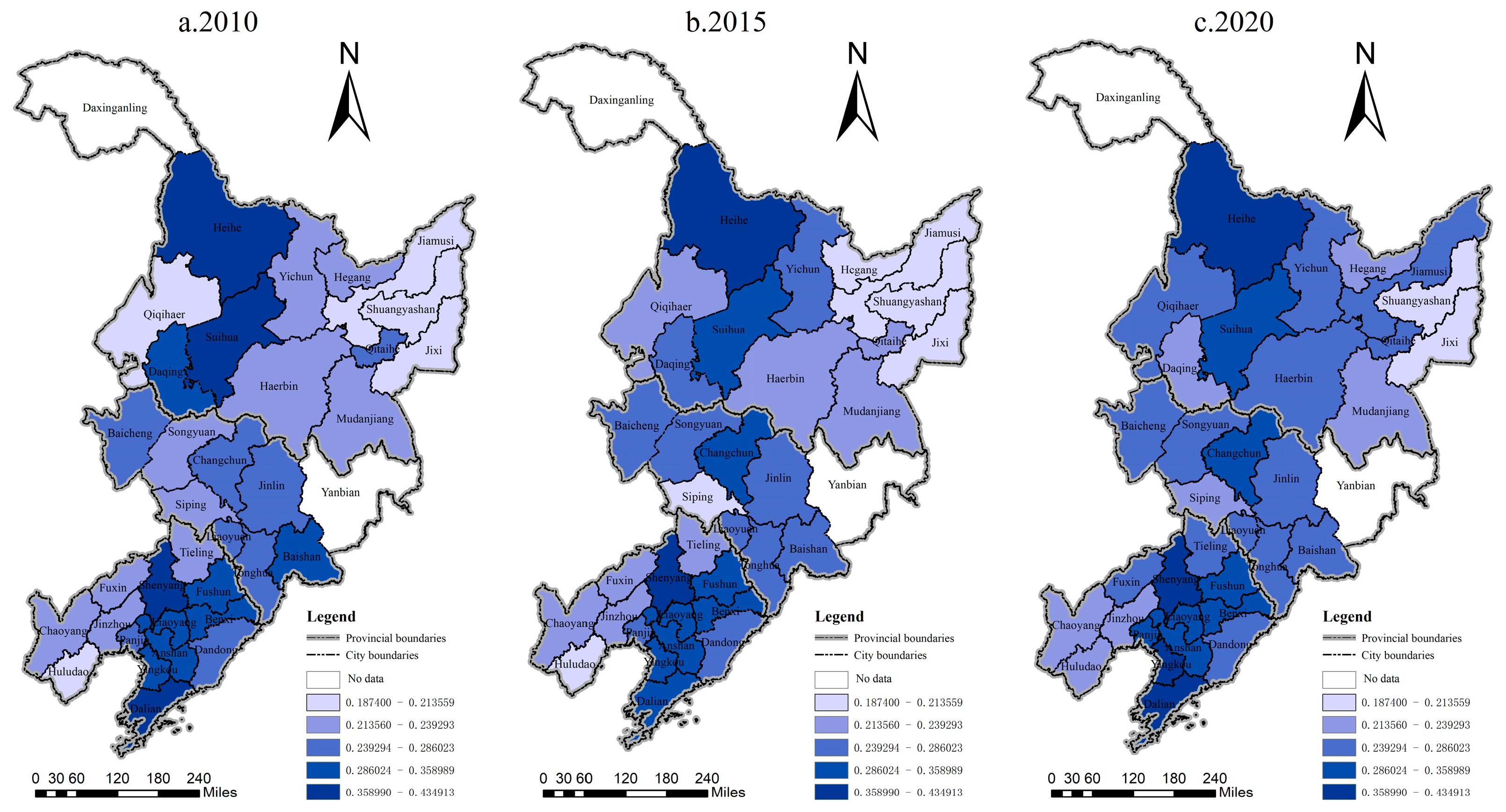
4.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of the Digital Economy Industry and Urban–Rural Integration Development in Northeast China
4.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
4.3. Baseline Analysis
4.4. Robustness and Endogeneity Tests
4.4.1. Replacing the Explained Variable
4.4.2. Excluding Capital Cities
4.4.3. Instrumental Variable Approach
4.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.6. Threshold Effects of the Digital Economy Industry on Urban–Rural Integration in Northeast China
4.6.1. Threshold Effect Test
4.6.2. Threshold Estimates and Confidence Intervals
4.6.3. Threshold Effect Regression Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpretation of Results
5.1.1. Digital Economy Industry and Urban–Rural Integration in Northeast China
5.1.2. Heterogeneity of the Digital Economy Industry’s Impact on Urban–Rural Integration in Northeast China
5.1.3. Threshold Characteristics of the Digital Economy Industry’s Impact Effect on Urban–Rural Integration
5.2. Policy Recommendations
5.3. Limitations and Constraints
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Ma, H.; Hu, X. How Does Digital Economy Affect Urban-Rural Integration? An Empirical Study from China. Habitat Int. 2024, 154, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, F. Study on the influence of factor mismatch on urban-rural integration development—Evidence from Chinese Provincial Panel Data. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2019, 2, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Long, H. Rural spatial governance and urban-rural integration development. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1272–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, T.; Chen, Y. Research on the Digital Economy and Agriculture and Rural Economy Integration:Practice Pattern, Realistic Obstacles and Breakthrough Paths. Issues Agric. Econ. 2020, 7, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, M.W.L. Digital Divide Between Urban and Rural Regions in China. Electron. J. Inf. Syst. Dev. Ctries. 2009, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Impact of Digital Development and Technology Innovation on the Marine Fishery Economy Quality. Fishes 2024, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, X. Power of Digital Economy to Drive Urban-Rural Integration: Intrinsic Mechanism and Spatial Effect, from Perspective of Multidimensional Integration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, F. A Collaborative Evolutionary Model: The Self-Organizing Evolutionary Process of Urban–Rural Digital Sharing System of Social Public Resources. J. Econ. Interact. Coord. 2022, 17, 1115–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, Z. The Impacts of Digital Finance Development on Household Income, Consumption, and Financial Asset Holding: An Extreme Value Analysis of China’s Microdata. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2023, 27, 1607–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.-J.; Zhong, S.-B.; Sun, B.-W.; Song, Y.; Chen, X.-H. Is Internet Penetration Narrowing the Rural–Urban Income Inequality? A Cross-Regional Study of China. Qual. Quant. 2021, 55, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Guo, F.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, X. Promotion or Inhibition? Exploring the Influence of the Digital Economy on Urban-Rural Integration: A Case Study of Yellow River Basin. Sustain. Futures 2024, 8, 100293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, M. Can Rural E-Commerce Narrow the Urban–Rural Income Gap? Evidence from Coverage of Taobao Villages in China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2023, 15, 580–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, G.; Tian, Y.; Dong, Q. Nonlinear Effect of Digital Economy on Urban–Rural Consumption Gap: Evidence from a Dynamic Panel Threshold Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Integrated Urban–Rural Development in Northeast China under the Background of Population Shrinkage. Buildings 2023, 13, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Long, H.; Li, Y. Human geography research based on the new thinking of global rural-urban relationship. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2869–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tu, S.; Ge, D.; Li, T.; Liu, Y. The Allocation and Management of Critical Resources in Rural China under Restructuring: Problems and Prospects. J. Rural. Stud. 2016, 47, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Revitalize the World’s Countryside. Nature 2017, 548, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q. Regional Habitat Units in the Context of Urban-Rural China: Concept, Mechanism and Features. Habitat Int. 2022, 128, 102668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, T.G. Managing the Rural–Urban Transformation in East Asia in the 21st Century. Sustain. Sci. 2008, 3, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysgård, H.K. The Assemblage of Culture-Led Policies in Small Towns and Rural Communities. Geoforum 2019, 101, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Chen, Y. Spatio-Temporal Change of Urban–Rural Equalized Development Patterns in China and Its Driving Factors. J. Rural. Stud. 2013, 32, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Long, H.; Liao, L.; Tu, S.; Li, T. Land Use Transitions and Urban-Rural Integrated Development: Theoretical Framework and China’s Evidence. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cui, P. A Study of the Time–Space Evolution Characteristics of Urban–Rural Integration Development in a Mountainous Area Based on ESDA-GIS: The Case of the Qinling-Daba Mountains in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.Y.; Wan, T. Research on Land Utilization and Cultivated Land Protection in Urban and Rural Planning. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 347–353, 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.; Wilsdon, J. Digital Futures—An Agenda for a Sustainable Digital Economy. Corp. Environ. Strategy 2001, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.K. Assessing the Digital Economy: Aims, Frameworks, Pilots, Results, and Lessons. J. Innov. Entrep. 2020, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Xie, T.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L. Digital Economy: An Innovation Driver for Total Factor Productivity. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 139, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhong, S.; Sun, B. Blessing or Curse? The Effect of Broadband Internet on China’s Inter-City Income Inequality. Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 72, 626–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulturbayevich, M.B.; Jurayevich, M.B. The Impact of the Digital Economy on Economic Growth. Int. J. Bus. Law Educ. 2020, 1, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, B. The Digital Economy: What Is New and What Is Not? Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2004, 15, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.J.M.; Fernandes, C.I.; Ferreira, F.A.F. To Be or Not to Be Digital, That Is the Question: Firm Innovation and Performance. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 101, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancillai, C.; Sabatini, A.; Gatti, M.; Perna, A. Digital Technology and Business Model Innovation: A Systematic Literature Review and Future Research Agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 188, 122307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsmeier, B.; Woerter, M. Is This Time Different? How Digitalization Influences Job Creation and Destruction. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 103765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, T.; Singer, D. Compulsory Admission to Hospital: (Sections 2, 3 and 4 of the Mental Health Act). In Mental Health Law 2EA Practical Guide; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-429-25291-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ofori, I.K.; Osei, D.B.; Alagidede, I.P. Inclusive Growth in Sub-Saharan Africa: Exploring the Interaction between ICT Diffusion, and Financial Development. Telecommun. Policy 2022, 46, 102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignamissi, D. Digital Divide and Financial Development in Africa. Telecommun. Policy 2021, 45, 102199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunje, M.Y.; Abendin, S.; Wang, Y. The Multidimensional Effect of Financial Development on Trade in Africa: The Role of the Digital Economy. Telecommun. Policy 2022, 46, 102444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Gans, J.S.; Goldfarb, A. Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence: Prediction versus Judgment. Inf. Econ. Policy 2019, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brynjolfsson, E.; Rock, D.; Syverson, C. The Productivity J-Curve: How Intangibles Complement General Purpose Technologies. Am. Econ. J. Macroecon. 2021, 13, 333–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresnahan, T.F.; Brynjolfsson, E.; Hitt, L.M. Information Technology, Workplace Organization, and the Demand for Skilled Labor: Firm-Level Evidence. Q. J. Econ. 2002, 117, 339–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Fang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Research on the Impact of the Integration of Digital Economy and Real Economy on Enterprise Green Innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 200, 123097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ma, Y. Effect of Industrial Structure on Urban–Rural Income Inequality in China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2022, 14, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; You, X. Do Digital Inclusive Finance, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship Activities Stimulate Vitality of the Urban Economy? Empirical Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta, China. Technol. Soc. 2023, 72, 102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, Y.; Si, H. Digital Economy Development and the Urban–Rural Income Gap: Intensifying or Reducing. Land 2022, 11, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Jin, C.; Ren, J.; Fu, Y.; Yue, X. Whether the Digital Economy Will Successfully Encourage the Integration of Urban and Rural Development: A Case Study in China. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 21, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Ma, S. Research on the Spatial Spillover and Threshold Effect of the Digital Economy on the Urban-Rural Integration——A Case Study of Zhejiang Province. World Surv. Res. 2022, 2022, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. How Does Digital Economy Affect Green Total Factor Productivity? Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Chen, X. Identification of Urban-Rural Integration Types in China—an Unsupervised Machine Learning Approach. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2022, 15, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wu, X.; Shi, L.; Wan, Y.; Hao, Z.; Ding, J.; Wen, Q. How Does the Digital Economy Affect the Urban–Rural Income Gap? Evidence from Chinese Cities. Habitat Int. 2025, 157, 103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, S.; Fang, C. Spatiotemporal Variation and Spatial Convergence of China’s Digital Economy Industry Development: Based on the Big Data of Enterprise. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Ma, H.; Bao, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Sun, S.; Fan, Y. Urban–Rural Human Settlements in China: Objective Evaluation and Subjective Well-Being. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Measurement of Urban-Rural Integration Level and Its Spatial Differentiation in China in the New Century. Habitat Int. 2021, 117, 102420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, G.; Tang, C.; Fan, S.; Guo, X. The Spatial Organization Pattern of Urban-Rural Integration in Urban Agglomerations in China: An Agglomeration-Diffusion Analysis of the Population and Firms. Habitat Int. 2019, 87, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, S.; Fang, F.; Che, X.; Chen, M. Evaluation of Urban-Rural Difference and Integration Based on Quality of Life. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. The Inner Mechanism and Empirical Testing of Digital Economy Driving Urban-rural Integration Development: Evidence from 275 Prefecture-level Cities in China. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2024, 12, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranos, E.; Kitsos, T.; Ortega-Argilés, R. Digital Economy in the UK: Regional Productivity Effects of Early Adoption. Reg. Stud. 2021, 55, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dian, J.; Song, T.; Li, S. Facilitating or Inhibiting? Spatial Effects of the Digital Economy Affecting Urban Green Technology Innovation. Energy Econ. 2024, 129, 107223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M. The Impact of Entrepreneurship of Farmers on Agriculture and Rural Economic Growth: Innovation-Driven Perspective. Innov. Green Dev. 2024, 3, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Shi, F. New Urbanization and High-Quality Urban and Rural Development: Based on the Interactive Coupling Analysis of Industrial Green Transformation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, T.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M. The Transformation of Peri-Urban Agriculture and Its Implications for Urban–Rural Integration Under the Influence of Digital Technology. Land 2025, 14, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomber, P.; Koch, J.-A.; Siering, M. Digital Finance and FinTech: Current Research and Future Research Directions. J. Bus. Econ. 2017, 87, 537–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.C.; Gleisner, F. Emergence of Financial Intermediaries in Electronic Markets: The Case of Online P2P Lending. Bus. Res. 2009, 2, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesser, M.; Hanly, J.; Cassells, D.; Berrill, J. Fuel Poverty Measurements in Residential America. Who Are the Most Vulnerable? Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 50, 103217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Dan, T. Digital Dividend or Digital Divide? Digital Economy and Urban-Rural Income Inequality in China. Telecommun. Policy 2023, 47, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhu, Q. Innovation in Emerging Economies: Research on the Digital Economy Driving High-Quality Green Development. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 145, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmersson, F.P.; Hilmersson, M. Networking to Accelerate the Pace of SME Innovations. J. Innov. Knowl. 2021, 6, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Korkmaz, A.G.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, H. The Rise of Digital Finance: Financial Inclusion or Debt Trap? Financ. Res. Lett. 2022, 47, 102604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Fan, Y.; Fang, C. When Will China Realize Urban-Rural Integration? A Case Study of 30 Provinces in China. Cities 2024, 153, 105290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, I.N.; Fedorova, M.Y. Digital Economy and Green Economy: Rural Unemployment and Territorial Self-Development in Russia. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 110, 02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L. Digital Economy, Industrial Structure Upgrading, and Residents’ Consumption: Empirical Evidence from Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 92, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Digital Inclusive Finance and Rural Revitalization. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 57, 104157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. The Impact of the Platform Economy on Urban–Rural Integration Development: Evidence from China. Land 2023, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y. Does Digitalization Mitigate Regional Inequalities? Evidence from China. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Guan, J.; Wang, R.; Kong, L.; Dai, Q. How Does Digitalization Affect the Urban-Rural Disparity at Different Disparity Levels: A Bayesian Quantile Regression Approach. Technol. Soc. 2024, 78, 102633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dimension Layer | Indicator Layer | Indicator Description | Unit | Attribute | Weight Coefficients. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban–Rural Economic Integration | Industrial upgrading | Value-added of Secondary and Tertiary Industries/Value-added of Primary Industry | % | + | 13.67% |
| Fiscal Support for Agriculture | Total Fiscal Expenditure on Agriculture/Local Fiscal Expenditure | % | + | 7.36% | |
| Agricultural Modernization Level | Total Agricultural Machinery Power/Total Cultivated Land Area | kw/hm2 | + | 3.53% | |
| Urban–Rural Social Integration | Urbanization Rate | Urban Population/Total Population at Year-End | % | + | 5.20% |
| Urban–Rural Income Disparity | Disposable Income of Urban Residents/Disposable Income of Rural Residents | % | − | 1.08% | |
| Employment Structure | Employment in Primary Industry/Total Employment | % | − | 2.26% | |
| Medical Services | Number of Hospital Beds per 10,000 People in the Downtown/Number of Hospital Beds per 10,000 People in Districts | % | − | 0.77% | |
| Education Services | Student–Teacher Ratio in Primary and Secondary Schools in the Downtown/Student–Teacher Ratio in Districts | % | − | 0.81% | |
| Public Cultural Services | Number of Public Library Collections per 10,000 People in the Downtown/Number of Public Library Collections per 10,000 People in Districts | % | − | 0.21% | |
| Urban–Rural Spatial Integration | Urban Spatial Expansion | Total Sown Area of Crops/Built-up Area | % | + | 26.90% |
| Land Urbanization Level | Built-up Area/Total Downtown Area | % | + | 16.59% | |
| Urban Transportation Network Density | Total Road Mileage/Urban Construction Land Area | km/km2 | + | 3.70% | |
| Urban–Rural Ecological Integration | Forest Coverage Rate | Forest Area/Total Land Area | % | + | 7.70% |
| Investment in Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Control | Agricultural Environmental Protection Expenditure/Local Fiscal Expenditure | % | + | 10.22% |
| Variable | Variable Description | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UrRu | Urban–Rural Integrated Development Level | 0.271691 | 0.058414 | 0.469157 | 0.184543 | 374 |
| digital | Digital Economy Industry Level | 0.304423 | 0.603904 | 5.547733 | 0.002682 | 374 |
| gov | Government Intervention Level | 0.002323 | 0.001088 | 0.006754 | 0.000353 | 374 |
| soc | Social Security Level | 0.000477 | 0.000284 | 0.002069 | 0.00005355 | 374 |
| wag | Employee Wage Level | 48,152.7265 | 15,842.0035 | 100,781 | 15,986.25 | 374 |
| sav | Household Savings Level | 1.035 | 0.5620 | 3.3488 | 0.1322 | 374 |
| fin | Financial Development Level | 1.0188 | 0.5054 | 2.8686 | 0.2469 | 374 |
| Years | Digital Economy Industry | Urban–Rural Integration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | Z | Moran’s I | Z | |
| 2010 | 0.053 * | 1.688 | 0.162 ** | 2.163 |
| 2015 | 0.047 * | 1.845 | 0.172 ** | 2.311 |
| 2020 | 0.042 * | 1.723 | 0.128 * | 1.798 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| digital | 0.049 *** (0.004) | 0.040 *** (0.005) | 0.042 *** (0.005) | 0.043 *** (0.005) | 0.047 *** (0.006) | 0.047 *** (0.006) |
| gov | 0.014 *** (0.005) | 0.029 *** (0.010) | 0.025 ** (0.010) | 0.035 *** (0.012) | 0.037 *** (0.012) | |
| soc | −0.016 * (0.009) | −0.006 (0.010) | −0.004 (0.010) | 0.000 (0.011) | ||
| wag | −0.023 ** (0.011) | −0.022 * (0.011) | −0.020 * (0.011) | |||
| sav | −0.010 (0.006) | −0.006 (0.008) | ||||
| fin | −0.011 (0.011) | |||||
| cons | 0.257 *** (0.003) | 0.123 ** | 0.107 ** (0.050) | 0.308 *** (0.107) | 0.330 *** (0.107) | 0.368 *** (0.114) |
| N | 374 | 374 | 374 | 374 | 374 | 374 |
| R2 | 0.254 | 0.269 | 0.275 | 0.284 | 0.289 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| digital | 0.049 *** (0.006) | 0.059 *** (0.011) | 0.047 *** (0.129) | 0.048 *** (0.006) |
| gov | 0.027 ** (0.013) | 0.044 *** (0.012) | 0.031 ** (0.012) | 0.028 ** (0.013) |
| soc | 0.005 (0.012) | −0.002 (0.012) | 0.003 (0.012) | 0.008 (0.013) |
| wag | −0.024 (0.013) | −0.023 * (0.012) | −0.023 * (0.013) | −0.029 ** (0.015) |
| sav | −0.008 (0.008) | −0.004 (0.008) | −0.005 (0.008) | −0.005 (0.008) |
| fin | −0.006 (0.012) | −0.013 (0.011) | −0.010 (0.012) | −0.012 (0.012) |
| cons | 0.417 *** (0.131) | 0.357 *** (0.125) | 0.409 *** (0.129) | 0.498 *** (0.149) |
| N | 340 | 341 | 340 | 306 |
| R2 | 0.294 | 0.179 | 0.295 | 0.308 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| digital | 0.011 * (0.006) | 0.177 *** (0.042) | 0.129 *** (0.049) |
| gov | −0.009 (0.035) | −0.069 *** (0.037) | 0.068 *** (0.014) |
| soc | 0.065 ** (0.027) | 0.074 ** (0.035) | −0.008 (0.013) |
| wag | −0.123 *** (0.024) | −0.183 *** (0.05) | −0.007 (0.014) |
| sav | −0.053 * (0.029) | −0.035 (0.027) | −0.024 ** (0.009) |
| fin | 0.11 * (0.058) | 0.041 (0.032) | −0.027 ** (0.012) |
| cons | 0.225 (0.348) | 2.154 *** (0.488) | 0.518 *** (0.155) |
| N | 44 | 55 | 275 |
| R2 | 0.875 | 0.459 | 0.113 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| digital | −0.192 (0.161) | 0.044 *** (0.005) | 0.022 *** (0.006) | 0.038 *** (0.008) | 0.072 (0.051) |
| gov | 0.159 *** (0.027) | −0.006 (0.012) | −0.043 ** (0.018) | −0.000 (0.017) | 0.184 *** (0.023) |
| soc | −0.044 ** (0.022) | 0.010 (0.012) | 0.041 ** (0.018) | −0.012 (0.013) | −0.063 *** (0.018) |
| wag | 0.007 (0.783) | −0.035 *** (0.012) | −0.076 *** (0.020) | 0.028 *** (0.010) | 0.022 (0.017) |
| sav | −0.026 * (0.014) | 0.000 (0.010) | 0.046 *** (0.012) | 0.026 ** (0.011) | −0.036 *** (0.012) |
| fin | −0.043 ** (0.019) | 0.011 (0.014) | 0.001 (0.014) | −0.031 ** (0.013) | −0.078 *** (0.026) |
| cons | 0.087 (0.267) | 0.443 *** (0.122) | 0.413 ** (0.189) | 0.133 (0.103) | 0.498 *** (0.237) |
| N | 110 | 264 | 154 | 88 | 132 |
| R2 | 0.288 | 0.387 | 0.560 | 0.582 | 0.363 |
| Threshold Variable | F-Value | p-Value | BS Times | Critical Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% | 5% | 10% | ||||
| Single Threshold | 7.93 | 0.6733 | 300 | 41.821 | 36.4776 | 28.0413 |
| Double Threshold | 20.74 | 0.0633 | 300 | 18.9684 | 23.3904 | 35.0592 |
| Triple Threshold | 7.70 | 0.7433 | 300 | 54.3821 | 34.5187 | 26.6234 |
| Model | Threshold | Threshold Estimate | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double Threshold | First Threshold | 9.9372 | [9.9161, 9.9544] |
| Second Threshold | 11.1578 | [11.1255, 11.2026] |
| Variable | Coefficient Estimate | Standard Error | T-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| gov | 6.120021 ** | 2.727532 | 2.25 |
| soc | −13.09029 | 10.80317 | −1.21 |
| wag | 0.0171868 *** | 0.0052269 | 3.29 |
| sav | −0.0028994 | 0.0037079 | −0.78 |
| fin | −0.0061335 | 0.0043309 | −1.42 |
| Digital × I (eco ≤ 9.9372) | 0.5595292 *** | 0.1985051 | 2.82 |
| Digital × I (9.9372 < eco ≤ 11.1578) | 0.0209711 *** | 0.0047689 | 4.40 |
| Digital × I (eco > 11.1578) | 0.0110146 *** | 0.0026738 | 4.12 |
| Constant | 0.0833433 | 0.527455 | 1.58 |
| N | 374 | ||
| R2 | 0.2590 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, S.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Digital Economy Development and Urban–Rural Integration in Northeast China: An Empirical Analysis. Land 2025, 14, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050993
Gao S, Zhang J, Ma Z, Zhou G, Liu Y, Liu Y. Digital Economy Development and Urban–Rural Integration in Northeast China: An Empirical Analysis. Land. 2025; 14(5):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050993
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Shibo, Jing Zhang, Zuopeng Ma, Guolei Zhou, Yanjun Liu, and Yuliang Liu. 2025. "Digital Economy Development and Urban–Rural Integration in Northeast China: An Empirical Analysis" Land 14, no. 5: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050993
APA StyleGao, S., Zhang, J., Ma, Z., Zhou, G., Liu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2025). Digital Economy Development and Urban–Rural Integration in Northeast China: An Empirical Analysis. Land, 14(5), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14050993





