Effects of Three Fertilizers on Improving Soil Characteristics and Growth Performance of Mahonia fortunei (Lindl.) Fedde in Rocky Desertification Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Bio-organic fertilizers will outperform NPK and slow-release types in improving karst soil parameters (organic matter and microbial diversity).
- Fertilizer-induced soil improvements will positively correlate with Mahonia fortunei (Lindl.) Fedde growth parameters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Introduction of the Research Region
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Measurements of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities
2.5. Detection of Soil Bacterial Diversity
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results
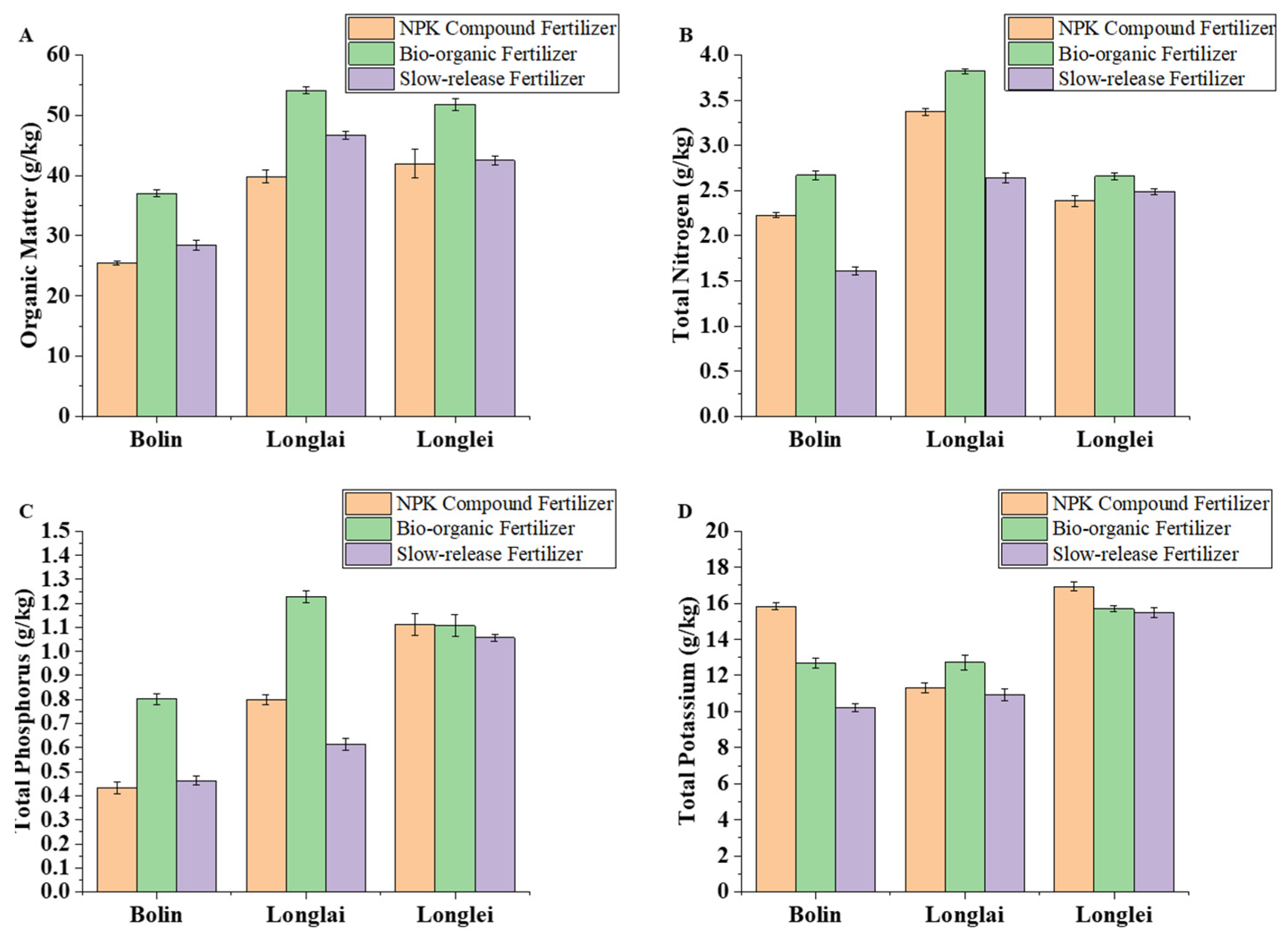
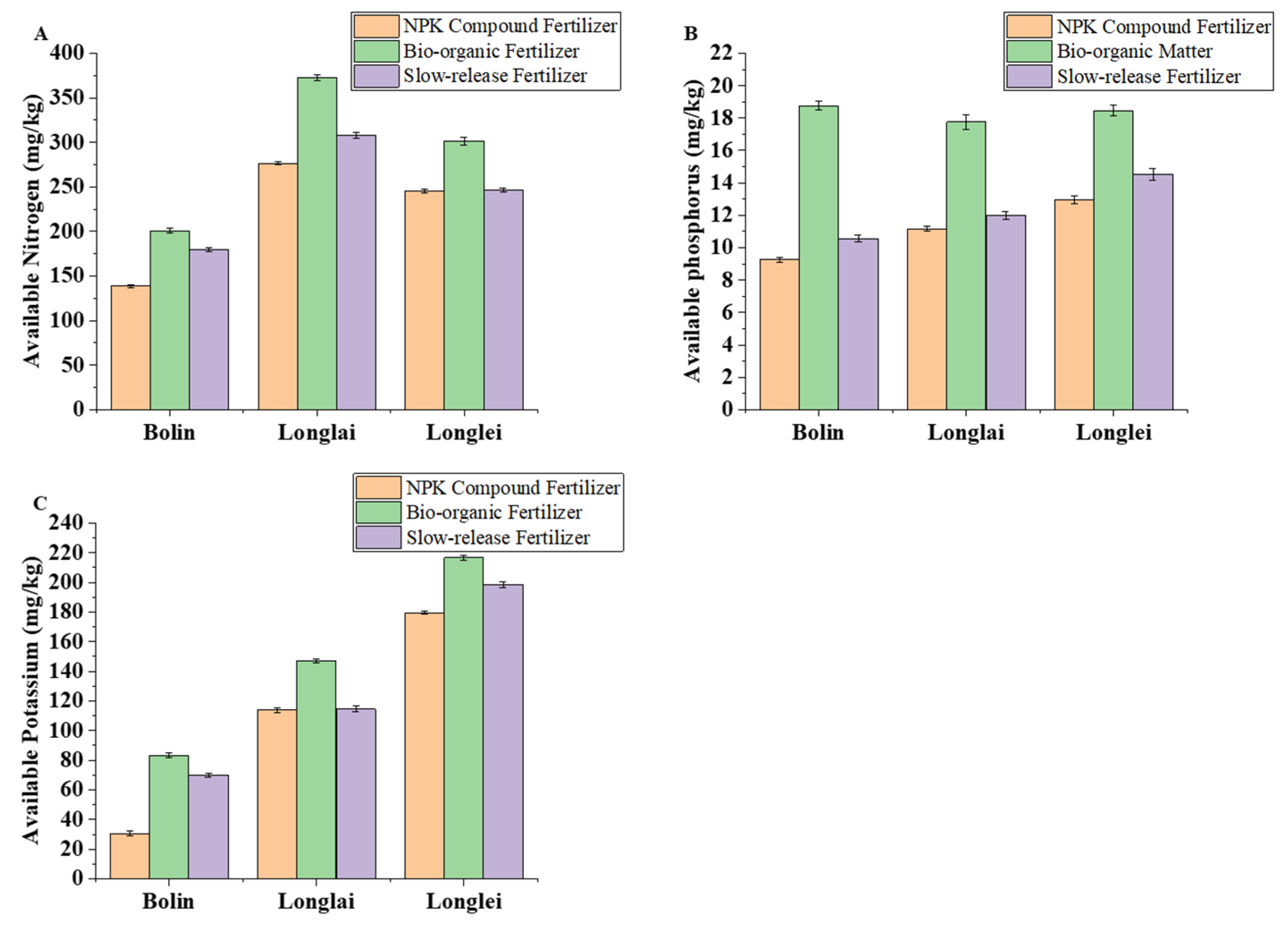
3.1. Effects of Different Fertilizer Applications on Soil Organic Matter and Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Contents of Soil
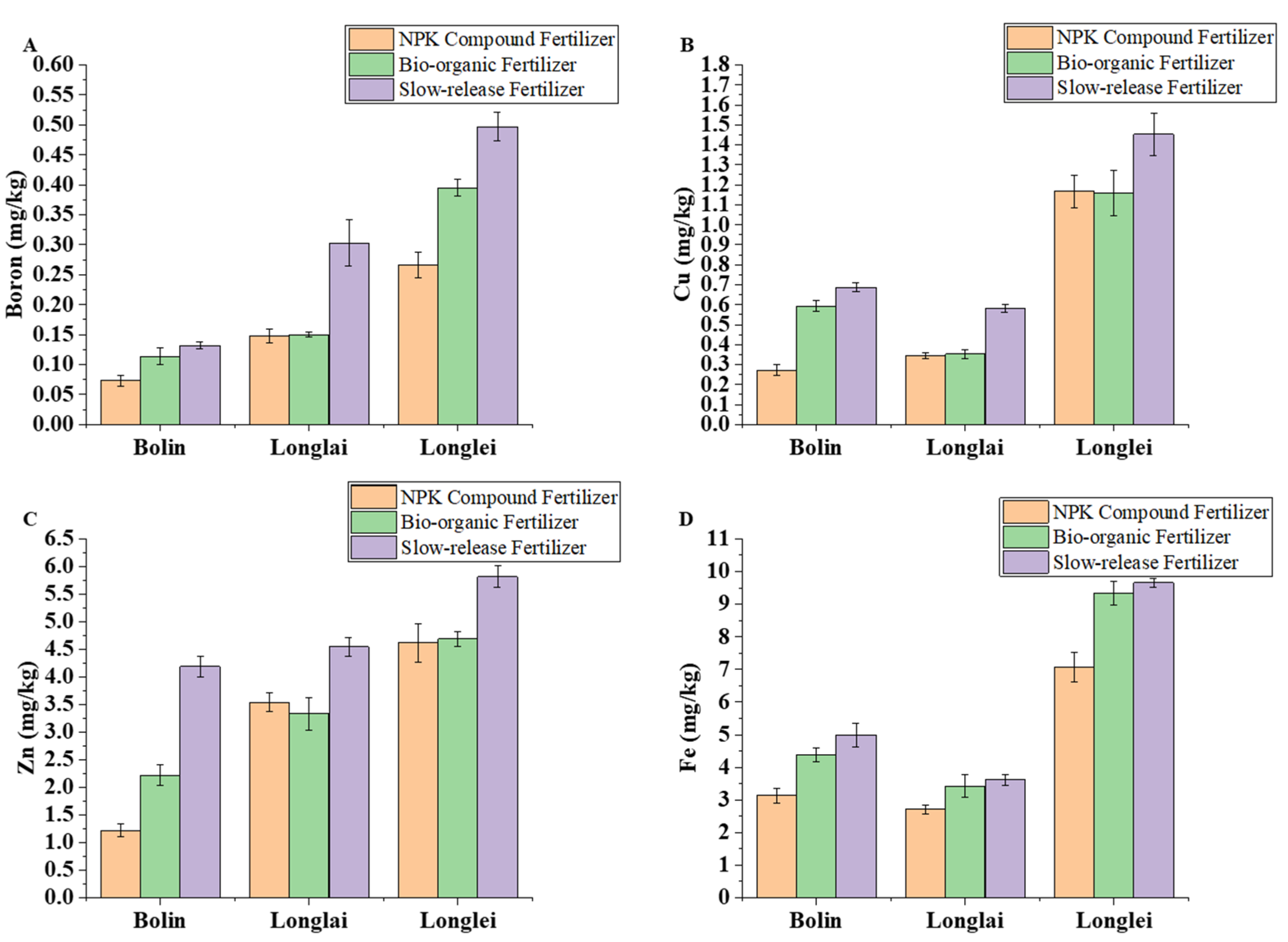
3.2. Effects of Different Fertilizer Applications on Soil Micronutrient Content
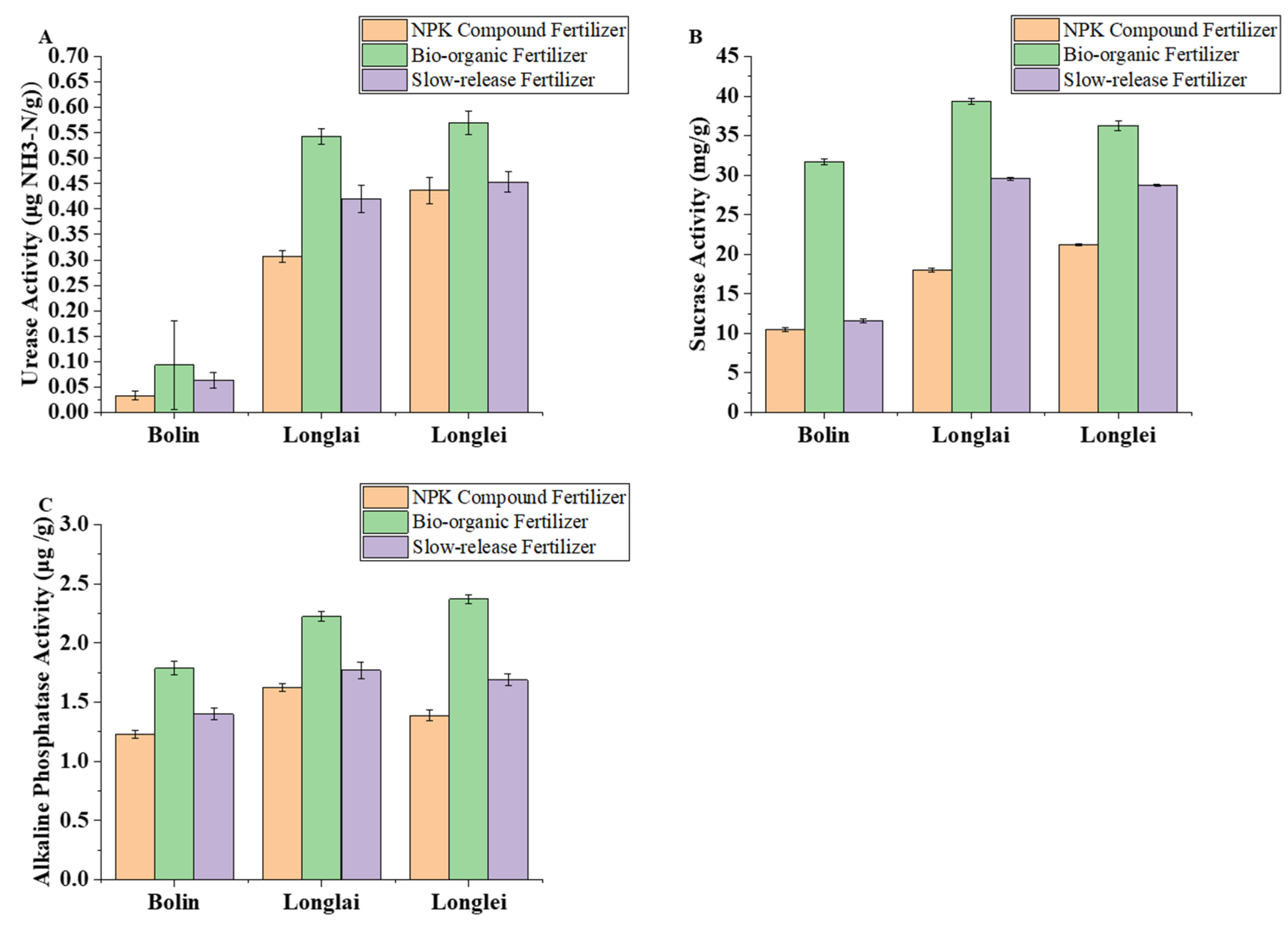
3.3. Effects of Different Fertilizer Applications on Soil Enzyme Activities
3.4. Effects of Different Fertilizer Applications on the Growth of Mahonia fortunei (Lindl.) Fedde
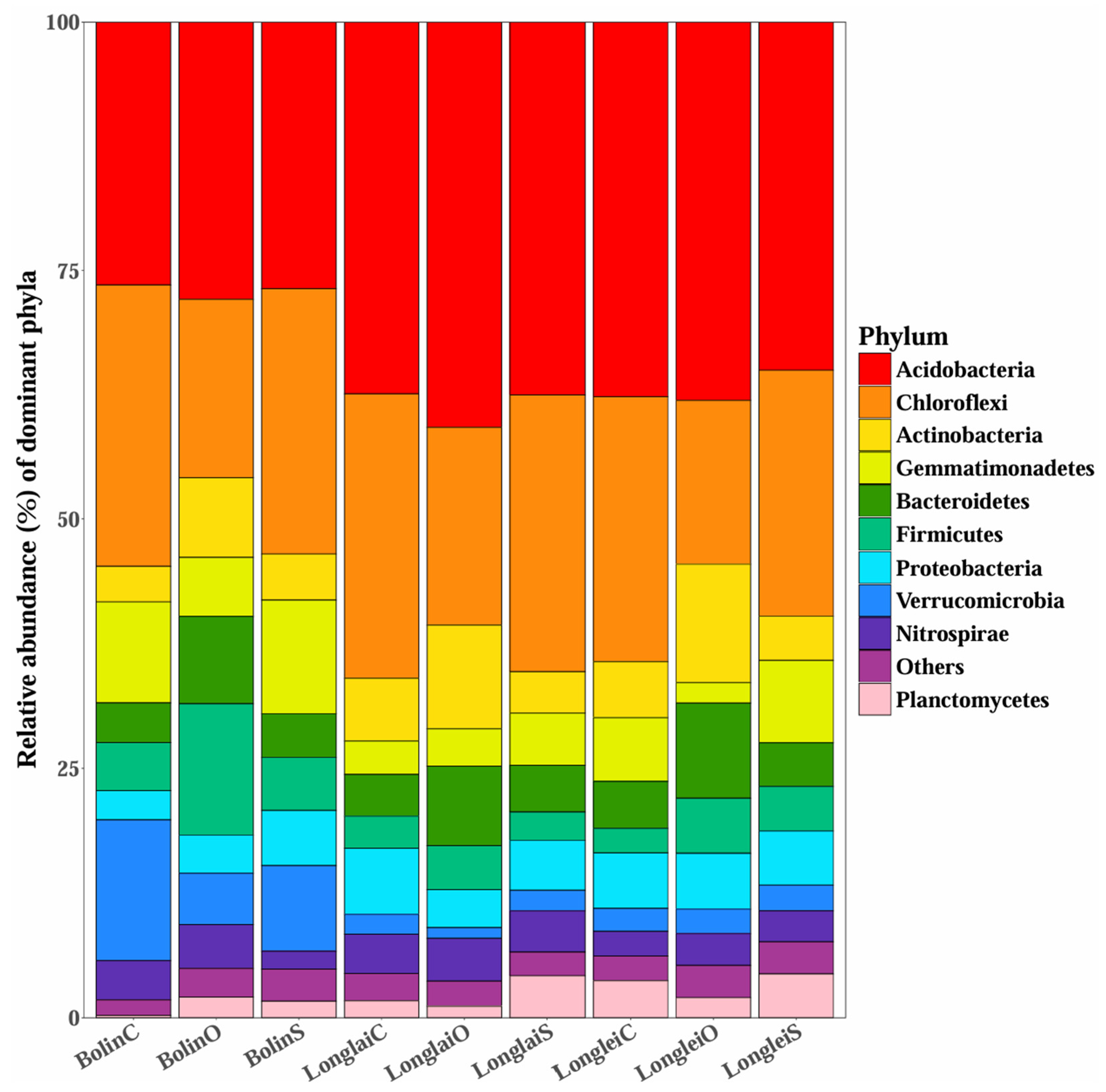
3.5. Effects of Different Fertilizer Applications on the Soil Bacterial Communities in Different Regions
3.6. Correlation Analysis of Soil Nutrients with Enzyme Activities and Plant Growth
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Application of Different Fertilizers on Soil Fertility in Different Regions
4.2. Effects of Application of Different Fertilizers on Soil Micronutrient Content and the Growth of Mahonia fortunei (Lindl.) Fedde in Different Regions
4.3. Effects of Application of Different Fertilizers on Soil Enzyme Activities in Different Regions
4.4. Effects of Applying Different Fertilizers on the Abundance, Diversity, and Structure of Soil Bacteria in Different Regions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, L.; Liu, W.D.; Su, S.; Chen, Z. The rocky desertification management in Guizhou province under the localized governance system. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1065663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Liu, Q.M.; Zhang, D.F. Karst rocky desertification in southwestern China: Geomorphology, landuse, impact and rehabilitation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xiong, K.N. Assessing spatial-temporal evolution processes of kaest rocky desertification land: Indications for restoration strategies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.B.; Yan, Y.J.; Wang, K.; Hu, G.; Ling, Z.H. Effects of control measures on soil quality evolution in the Karst rocky desertification area in southwestern China. Res. Soil Water 2021, 28, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.L.; Sheppard, S.R.J.; Jia, B.Q.; Wang, C. Planning to Practice: Impacts of Large-Scale and Rapid Urban Afforestation on Greenspace Patterns in the Beijing Plain Area. Forests 2021, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, S.R.; Sui, M.Z.; Zhang, G.Q.; Liu, Q.F.; Chen, D.M.; He, Y.J.; Zang, L.P. Does the universal adaptive strategy theory apply to natural regeneration in heterogeneous subtropical karst forests? Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, G.Q.; Chen, D.M.; Zang, L.P.; Liu, Q.F.; Guo, Y.; Xie, P.Y.; Chen, H.C.; He, Y.J. Variability of soil enzyme activities and nutrients with forest gap renewal interacting with soil depths in degraded karst forests. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, K.N.; Lan, A.J. Soil erosion monitoring and its implication in a limestone land suffering from rocky desertification in the Huajiang Canyon, Guizhou, Southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L. The origin, development and propspect of non-timber forest-based economics. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 46, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Somarriba, E. Revisiting the past-an essay on agroforestry definition. Agrofor. Syst. 1992, 19, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.Q.; Gao, L.; Liu, F.Y.; Liu, Y.J. Effects of different management measures of cultivation Panax notoginseng under forest on runoff and sediment yield and soil characteristics on slope. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.Q. The interplanting patterns of economic crops with young Chinese firplantations. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2005, 2, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.S. Research and demonstration of planting grain crops under forest. Agric. Eng. 2020, 10, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.L.; Huang, D.A.; Teng, W.C.; Luo, X.H. Effects of Interplanting of Mahonia fortunei and Different Plants on Chemical Properties of Soil. Guangxi For. Sci. 2021, 50, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, K.; Huang, D.A.; Teng, W.C.; Luo, X.H. Effects of Different Interplanting Models on Soil Chemical Properties. Guangxi For. Sci. 2021, 50, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.S.; Deng, X.W.; Chen, L.; Xiang, W.H. The soil properties and their effects on plant diversity in different degrees of rocky desertification. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T. Soil degradation, land scarcity and food security: Reviewing a complex challenge. Sustainability 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.; Khan, K.S.; Khalid, R.; Shabaan, M.; Alghamdi, A.G.; Alasmary, Z.; Majrashi, M.A. Integrated application of biochar and chemical fertilizers improves wheat (Triticum aestivum) productivity by enhancing soil microbial activities. Plant Soil 2024, 502, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, E.E.; Bradford, M.A.; Wood, S.A. Global meta-analysis of the relationship between soil organic matter and crop yields. Soil 2019, 5, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Abler, D.; Lin, G.; Sher, A.; Quan, Q. Substituting Organic Fertilizer for Chemical Fertilizer: Evidence from Apple Growers in China. Land 2021, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, I.; Ablouh, E.; El Bouchtaoui, F.Z.; Jaouahar, M.; El Achaby, M. Polymer coated slow/controlled release granular fertilizers: Fundamentals and research trends. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 144, 101269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mi, W.H.; Su, L.J.; Shan, Y.Y.; Wu, L.H. Controlled-release fertilizer enhances rice grain yield and N recovery efficiency in continuous non-flooding plastic film mulching cultivation system. Field Crops Res. 2019, 231, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Fan, J.L.; Zhang, F.C.; Yan, S.C.; Zheng, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.Q.; et al. Blending urea and slow-release nitrogen fertilizer increases dryland maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency while mitigating ammonia volatilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Cui, S.; Wu, L.; Qi, W.; Chen, J.; Ye, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, D. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil fertility, yield, and quality of tea. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5109–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naher, U.A.; Biswas, J.C.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Khan, F.H.; Sarkar, M.I.U.; Jahan, A.; Hera, M.H.R.; Hossain, M.B.; Islam, A.; Islam, M.R. Bio-organic fertilizer: A green technology to reduce synthetic N and P fertilizer for rice production. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 602052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.Y.; Hu, Y.C.; Liu, Y.S.; Wu, P.L.; Zhou, X.P. Rocky desertification in Guangxi karst mountainous area: Its tendency, formation causes and rehabilitation. Trans. CSAE 2008, 24, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.C.; Deng, X.W.; Xiang, W.H.; Lei, P.F.; Ouyang, S.; Wen, H.F.; Chen, L. Calcium content and high calcium adaptation of plants in karst areas of southwestern Hunan, China. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2991–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.H.; Li, J.W.; Shen, Z.Q.; Wang, X.W.; Jin, M. High-throughput identification of clinical pathogenic fungi by hybridization to an oligonucleotide microarray. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, T.; Merckx, R.; Elsen, A.; Vandendriessche, H. Impact of long-term compost amendments on soil fertility, soil organic matter fractions and nitrogen mineralization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Organic Matter Management and Compost Use in Horticulture, Murcia, Spain, 20–24 April 2015; pp. 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ernest, B.; Eltigani, A.; Yanda, P.Z.; Hansson, A.; Fridahl, M. Evaluation of selected organic fertilizers on conditioning soil health of smallholder households in Karagwe, Northwestern Tanzania. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Qiu, S.M.; Zhou, R.Y.; Li, L.W.; Xing, W.; Yuan, Y.D. Urban forest soil properties and microbial characteristics: Seasonal and stand-specific variations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 209, 105995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, X.W.; Laipan, M.; Wei, T.; Guo, J.K. Soil health improvement by inoculation of indigenous microalgae in saline soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, R.G. Enzyme-activity in soil-location and a possibile role in microbial ecology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, A.; Sauzet, O.; Matter, A.; Boivin, P. Soil organic carbon content and soil structure quality of clayey cropland soils: A large-scale study in the Swiss Jura region. Soil Use Manag. 2023, 39, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, D.W. The role of soil organic matter in maintaining soil quality in continuous cropping systems. Soil Tillage Res. 1997, 43, 131–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiao, X.M.; Lyu, J.; Gao, C.F.; Ali, M.; Zhang, G.B.; Feng, Z.; Yu, J.H. Integrating bio-organic fertilization increases twice-yearly cabbage crop production by modulating soil microbial community and biochemical properties in Northwest Plateau. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, E.G.; O’Sullivan, C.A.; Roper, M.M.; Palta, J.; Whisson, K.; Peoples, M.B. Yield and nitrogen use efficiency of wheat increased with root length and biomass due to nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium interactions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, D.; Menossi, M.; Mattiello, L. Nitrogen supply influences photosynthesis establishment along the sugarcane leaf. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xucheng, Z.; Zhouping, S. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on photosynthetic pigment and fluorescence characteristics in leaves of winter wheat cultivars on dryland. Acta Agric. Nucleatae Sin. 2007, 21, 299. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Dai, Q.; Kong, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Effects of the mutant with low chlorophyll content on photosynthesis and yield in rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2016, 42, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, S.; Morari, F.; Berti, A.; Tosoni, M.; Giardini, L. Soil organic matter properties after 40 years of different use of organic and mineral fertilisers. Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 21, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Liu, X.L.; Yang, W.P.; Li, W.G.; Chen, J.; Qiao, Y.J.; Gao, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.P. Impact of Bio-Organic Fertilizer Incorporation on Soil Nutrients, Enzymatic Activity, and Microbial Community in Wheat-Maize Rotation System. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, P.; Sheng, M.Y.; Tian, J. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, southwest China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, D.Q.; Bai, X.Y.; Zeng, C.; Xiao, J.Y.; Qian, Q.H.; Luo, G.J. Responses of soil physical and chemical properties to karst rocky desertification evolution in typical karst valley area. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Material Application (ESMA), Chongqing, China, 25–26 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Warman, P.R.; Termeer, W.C. Evaluation of sewage sludge, septic waste and sludge compost applications to corn and forage: Ca, Mg, S, Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn and B content of crops and soils. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, F.S.; Farran, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Kharitonova, G.V.; Kochva, M.; Shaviv, A.; Sugo, T. On boron turnover in plant-litter-soil system. Geoderma 2016, 268, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, J.; Miwa, K.; Fujiwara, T. Boron transport mechanisms: Collaboration of channels and transporters. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhead, J.L.; Reynolds, K.A.G.; Abdel-Ghany, S.E.; Cohu, C.M.; Pilon, M. Copper homeostasis. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravet, K.; Pilon, M. Copper and Iron Homeostasis in Plants: The Challenges of Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, S.A.; Krämer, U. The zinc homeostasis network of land plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmgren, M.G.; Clemens, S.; Williams, L.E.; Kraemer, U.; Borg, S.; Schjorring, J.K.; Sanders, D. Zinc biofortification of cereals: Problems and solutions. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.A.; Lee, J.; Guerinot, M.L.; An, G. Zinc Deficiency-Inducible OsZIP8 Encodes a Plasma Membrane-Localized Zinc Transporter in Rice. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, F.; Abbas, S.; Waseem, F.; Ali, N.; Mahmood, R.; Bibi, S.; Deng, L.F.; Wang, R.F.; Zhong, Y.T.; Li, X.X. Phosphorus (P) and Zinc (Zn) nutrition constraints: A perspective of linking soil application with plant regulations. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 226, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G. Iron uptake, signaling, and sensing in plants. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finazzi, G.; Petroutsos, D.; Tomizioli, M.; Flori, S.; Sautron, E.; Villanova, V.; Rolland, N.; Seigneurin-Berny, D. Ions channels/transporters and chloroplast regulation. Cell Calcium 2015, 58, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.S. Soil enzyme activities with greenhouse subsurface irrigation. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demisie, W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, M.K. Effect of biochar on carbon fractions and enzyme activity of red soil. Catena 2014, 121, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.P.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Q.L.; Zhang, S.R.; Wei, W.L.; Ding, X.D. Changes in soil bacterial community and enzyme activity under five years straw returning in paddy soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 100, 103215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tian, J.; Fang, H.J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, M.G.; Lou, Y.L.; Zhou, B.K.; Kuzyakov, Y. Functional soil organic matter fractions, microbial community, and enzyme activities in a Mollisol under 35 years manure and mineral fertilization. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; van der Putten, W.H. Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 2014, 515, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Bååth, E. Contrasting Soil pH Effects on Fungal and Bacterial Growth Suggest Functional Redundancy in Carbon Mineralization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Si, L.L.; Zhang, X.; Cao, K.; Wang, J.H. Various green manure-fertilizer combinations affect the soil microbial community and function in immature red soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1255056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Knight, R.; Bradford, M.A.; Fierer, N. Consistent effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial communities in contrasting systems. Ecology 2010, 91, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coolon, J.D.; Jones, K.L.; Todd, T.C.; Blair, J.M.; Herman, M.A. Long-term nitrogen amendment alters the diversity and assemblage of soil bacterial communities in tallgrass prairie. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.Y.; Deng, S.P.; Raun, W.R. Bacterial community structure and diversity in a century-old manure-treated agroecosystem. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5868–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Qi, X.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Effects of fertilization on bacterial community structure and function in a black soil of Dehui region estimated by Biolog and PCR-DGGE methods. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, V.; Rehman, A.; Mishra, A.; Chauhan, P.S.; Nautiyal, C.S. Changes in bacterial community structure of agricultural land due to long-term organic and chemical amendments. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.H.; Song, J.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Joa, J.H.; Weon, H.Y. Characterization of the Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in Rice Field Soils Subjected to Long-Term Fertilization Practices. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.B.; Li, Z.W.; Chang, X.F.; Huang, J.Q.; Nie, X.D.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.Y.; Dong, Y.T.; Jiang, J.Y. Soil erosion-related dynamics of soil bacterial communities and microbial respiration. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.J.; Dou, Y.X.; Yang, X.; An, S.S. Soil microbial community and their functional genes during grassland restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampelotto, P.H.; Ferreira, A.D.; Barboza, A.D.M.; Roesch, L.F.W. Changes in Diversity, Abundance, and Structure of Soil Bacterial Communities in Brazilian Savanna Under Different Land Use Systems. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.C.; An, S.S.; Liu, Y. Soil bacterial community response to vegetation succession after fencing in the grassland of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, H.; Moyer, C.L. Comparative Single-Cell Genomics of Chloroflexi from the Okinawa Trough Deep-Subsurface Biosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3000–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.J.; Liu, W.B.; Zhu, C.; Luo, G.W.; Kong, Y.L.; Ling, N.; Wang, M.; Dai, J.Y.; Shen, Q.R.; Guo, S.W. Bacterial rather than fungal community composition is associated with microbial activities and nutrient-use efficiencies in a paddy soil with short-term organic amendments. Plant Soil 2018, 424, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Xie, J.H.; Li, L.L.; Effah, Z.; Xie, L.H.; Luo, Z.Z.; Zhou, Y.J.; Jiang, Y.J. Fertilization treatments affect soil CO2 emission through regulating soil bacterial community composition in the semiarid Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.H.; Xie, J.M.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.D.; Ma, H.Y.; Wang, C. Response of rhizosphere microbial community of Chinese chives under different fertilization treatments. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1031624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | Chao1 | ACE | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BolinC | 2479.75 ± 98.46 | 2903.83 ± 184.02 | 6.97 ± 0.19 | 0.9952 ± 0.0022 |
| BolinO | 6242.78 ± 551.51 | 7681.87 ± 733.17 | 7.32 ± 0.10 | 0.9982 ± 0.0003 |
| BolinS | 2714.07 ± 357.17 | 3227.64 ± 348.53 | 7.11 ± 0.16 | 0.9984 ± 0.0005 |
| LonglaiC | 4836.93 ± 220.27 | 5270.23 ± 253.01 | 7.00 ± 6.86 | 0.9974 ± 0.0002 |
| LonglaiO | 12,054.50 ± 740.03 | 14,476.99 ± 1075.97 | 7.43 ± 0.02 | 0.9987 ± 0.0001 |
| LonglaiS | 6276.02 ± 66.94 | 7220.52 ± 25.25 | 7.31 ± 0.01 | 0.9982 ± 0.0003 |
| LongleiC | 3363.22 ± 439.94 | 4007.23 ± 597.46 | 7.21 ± 0.14 | 0.9977 ± 0.0007 |
| LongleiO | 6126.36 ± 140.22 | 7054.35 ± 158.76 | 7.26 ± 0.03 | 0.9968 ± 0.0004 |
| LongleiS | 4034.46 ± 225.71 | 4629.97 ± 328.63 | 6.91 ± 0.13 | 0.9962 ± 0.0013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; Pan, B.; Gao, H.; Liang, Z. Effects of Three Fertilizers on Improving Soil Characteristics and Growth Performance of Mahonia fortunei (Lindl.) Fedde in Rocky Desertification Areas. Land 2025, 14, 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051090
Fang X, Sun Y, Huang X, Pan B, Gao H, Liang Z. Effects of Three Fertilizers on Improving Soil Characteristics and Growth Performance of Mahonia fortunei (Lindl.) Fedde in Rocky Desertification Areas. Land. 2025; 14(5):1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051090
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Xiuwen, Yue Sun, Xiangxiang Huang, Bo Pan, Haiying Gao, and Zhishui Liang. 2025. "Effects of Three Fertilizers on Improving Soil Characteristics and Growth Performance of Mahonia fortunei (Lindl.) Fedde in Rocky Desertification Areas" Land 14, no. 5: 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051090
APA StyleFang, X., Sun, Y., Huang, X., Pan, B., Gao, H., & Liang, Z. (2025). Effects of Three Fertilizers on Improving Soil Characteristics and Growth Performance of Mahonia fortunei (Lindl.) Fedde in Rocky Desertification Areas. Land, 14(5), 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051090







