Spatio-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in Xuzhou City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
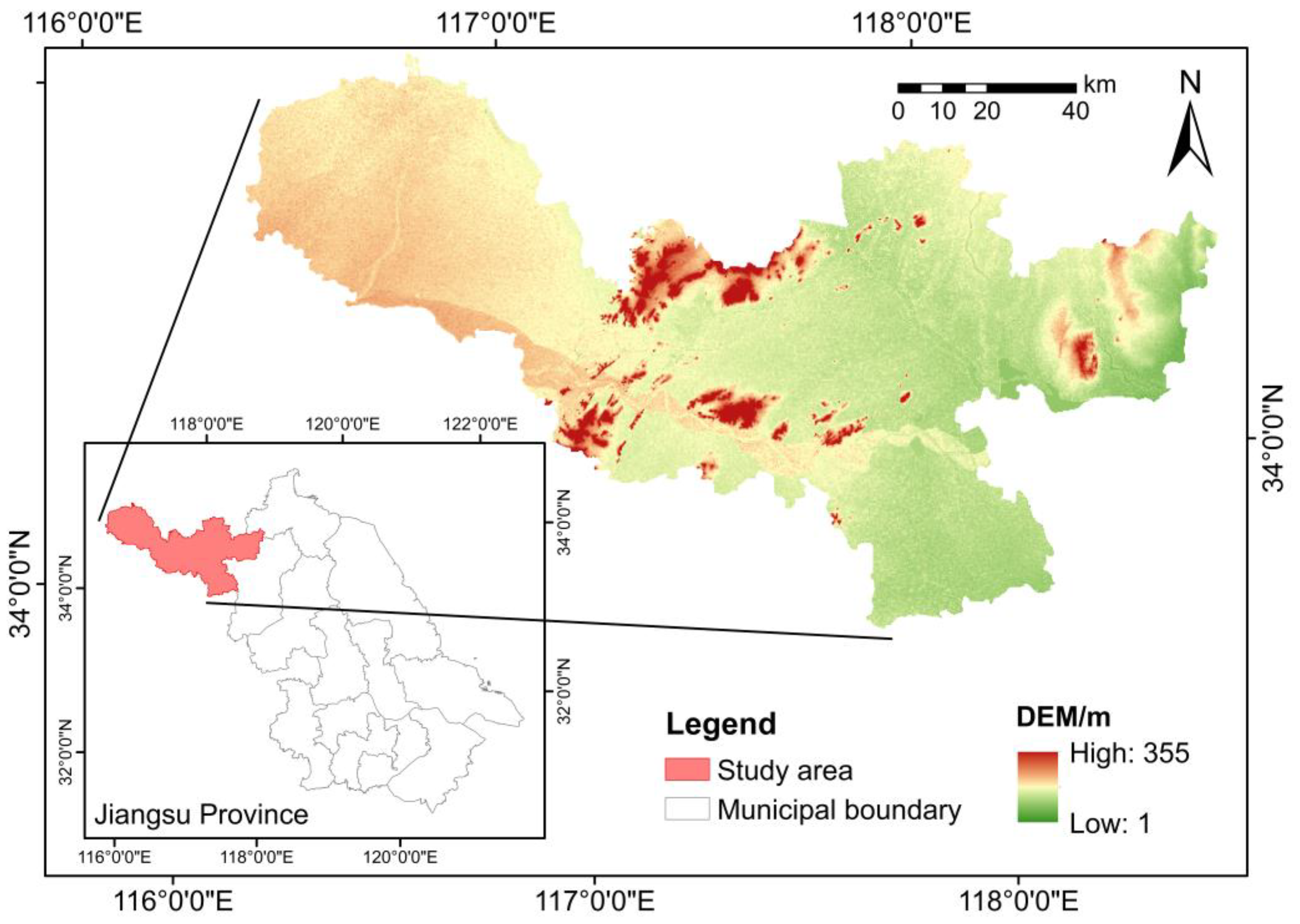
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Assessment Modeling of UER
2.2.2. Spatial Autocorrelation
2.2.3. Multi-Scale Geographically Weighted Regression Models
2.3. Data Sources
3. Results
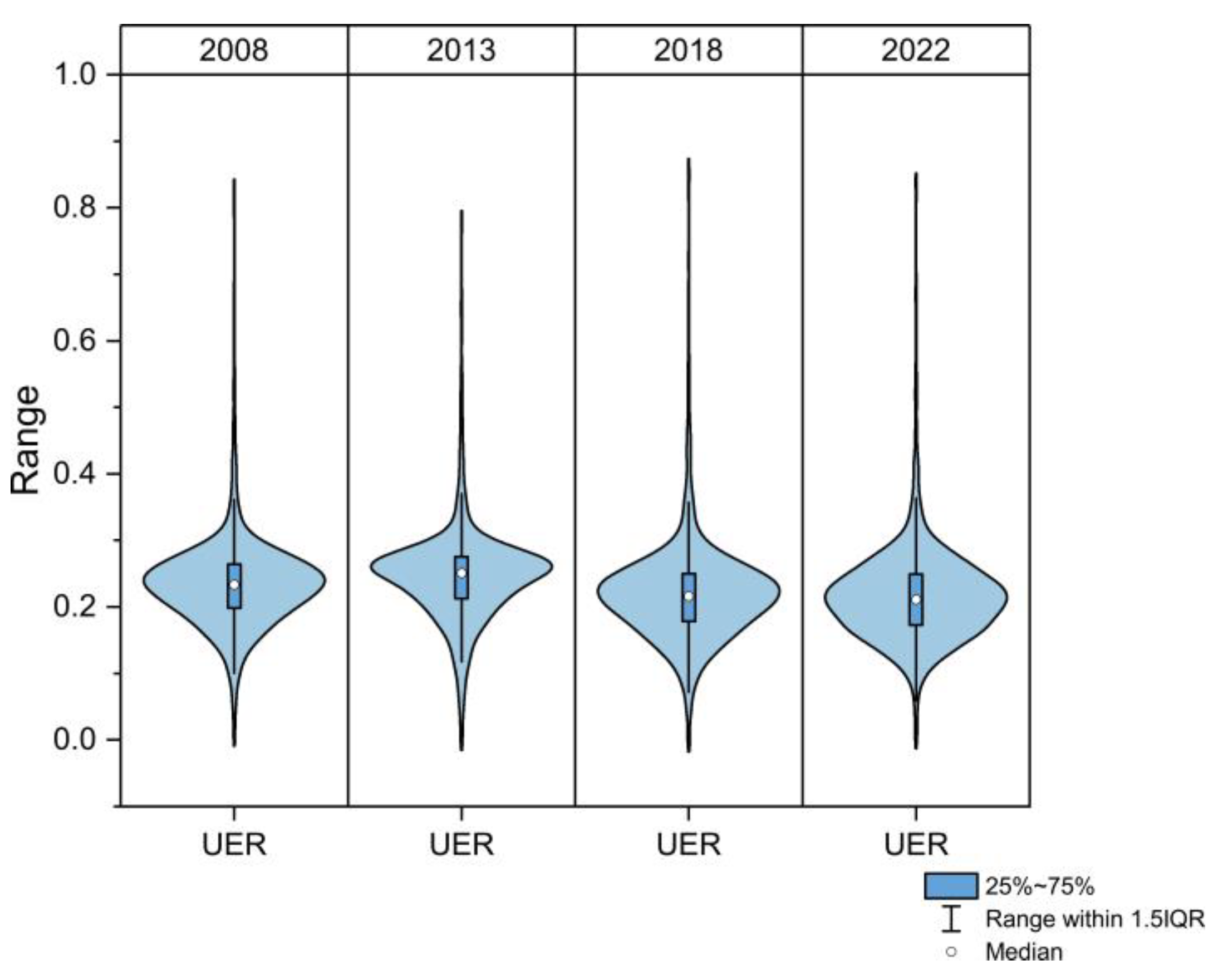
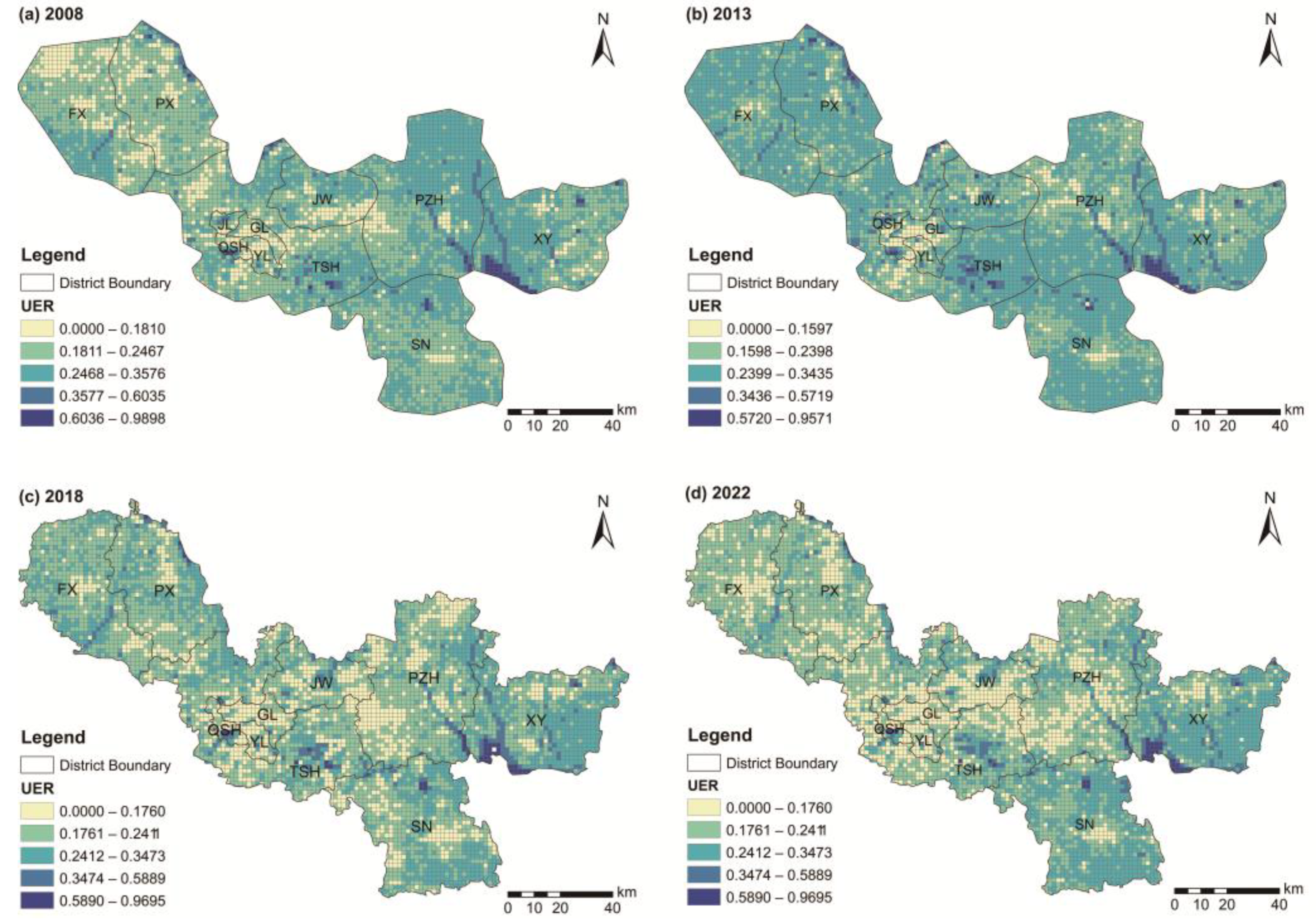
3.1. Temporal-Spatial Variation Characteristics of UER
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Characteristics of UER
3.2.1. Global Autocorrelation Feature
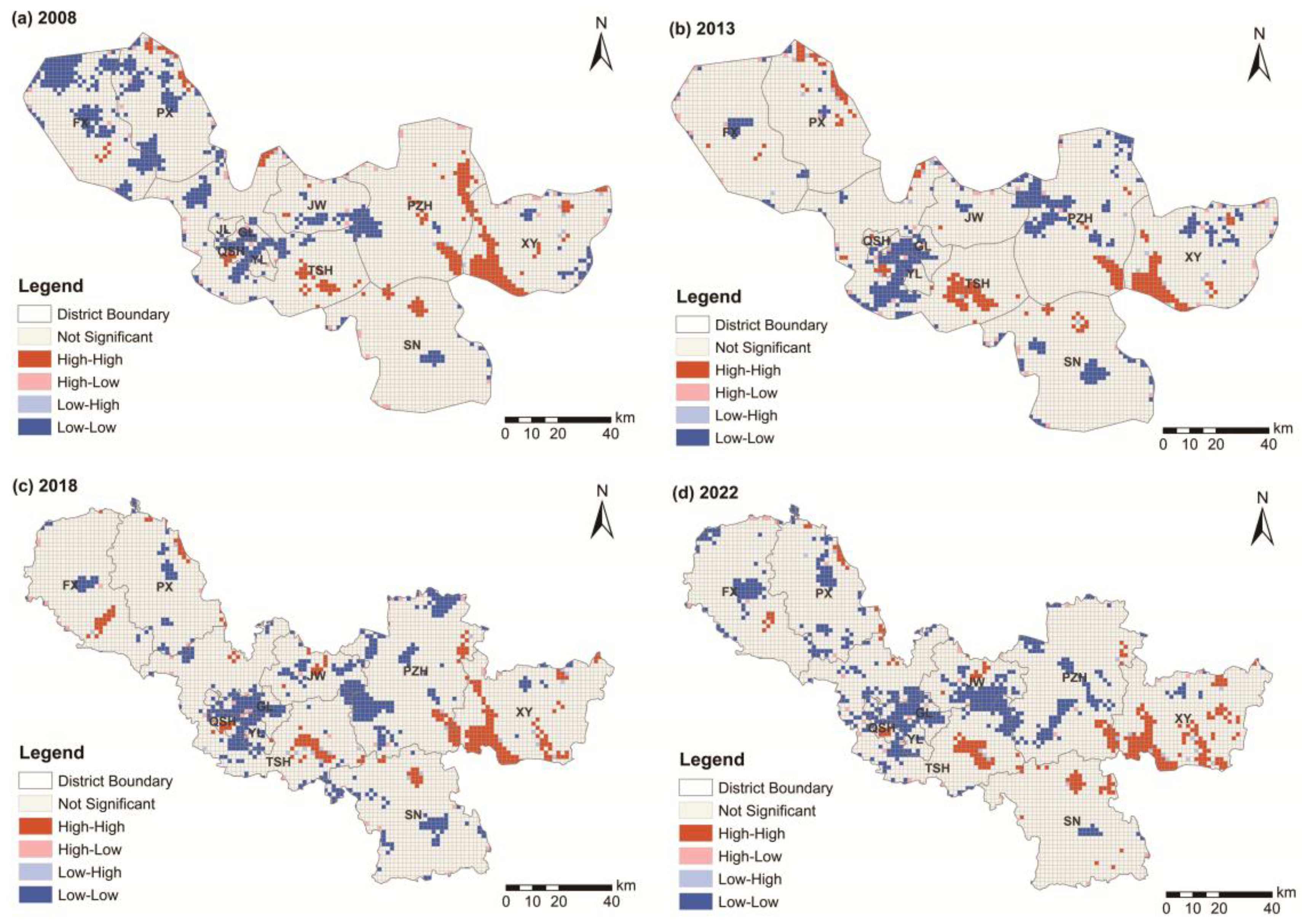
3.2.2. Local Autocorrelation Feature
3.3. Analysis of Influencing Factors on UER in Xuzhou City
3.3.1. Impact Factor Identification and Model Comparison
3.3.2. Scale Differences of Influencing Factors
3.3.3. Spatial Pattern of Regression Coefficients for Influencing Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal Characteristics of UER
4.2. Spatial Characteristics of UER
4.3. Influencing Factors of UER
4.4. Policy Implications and Recommendations
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- From a temporal point of view, the UER of Xuzhou City generally showed a decreasing trend between 2008 and 2022; from a spatial point of view, low-resilience areas have expanded outward from the city center, while high-resilience areas are primarily concentrated around large water bodies such as rivers and lakes.
- (2)
- Xuzhou City’ UER has strong spatial autocorrelation. The global Moran’s I index showed an overall increasing trend from 2008 to 2022, and the spatial convergence and agglomeration trend of UER is most obvious in 2022. The local spatial autocorrelation analysis reveals that UER in Xuzhou City is primarily characterized by H-H and L-L clustering. In contrast, H-L and L-H clustering zones are more sporadically distributed and cover a smaller area. From 2008 to 2022, the H-H clusters basically remain stable mainly distributed in Luoma Lake and surrounding areas in the southeast of Xuzhou City, Lüliang Mountain Scenic Area and Yunlong Lake Scenic Area and other areas with good ecological environments; the L-L clusters are mainly located in Xuzhou city center, Pizhou city center, Suining county seat, and Fengxian county seat and other areas with frequent anthropogenic activities.
- (3)
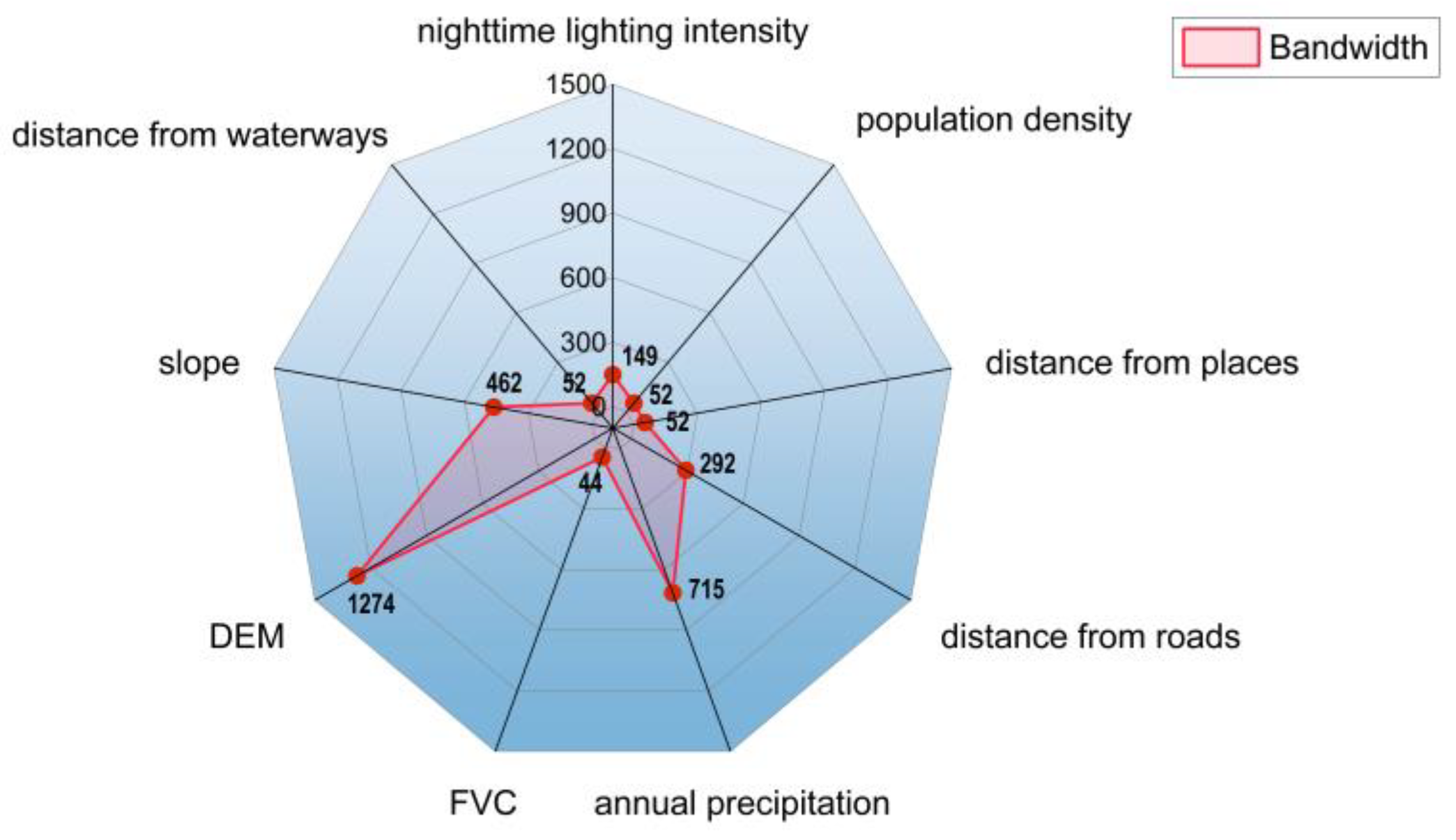
- Comparing the data fitting ability of OLS, GWR, and MGWR models, the MGWR model, which has a better fitting effect, was used to study the influencing factors of UER in Xuzhou City, and the grading of the influencing strengths from the mean absolute values of the coefficients were: population density > nighttime lighting intensity > annual precipitation > distance from water system > distance from highway > FVC > DEM > slope > distance from town. Population density and nighttime lighting intensity are the key influences on the spatial pattern of UER, and each region’s UER is impacted differently by several factors, so local governments should formulate policies according to local conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Q.; Meng, F.; Li, F.; Liu, G.; Yang, Z. A Conceptual Framework for Enhancing Urban Resilience with Green and Blue Infrastructure from the Perspective of Food-Energy-Water Nexus. Urban Dev. Stud. 2022, 29, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Dong, P.; Lu, Y. Spatial-Temporal Analysis and Influencing Factors of Ecological Resilience in Yangtze River Delta. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2022, 31, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Folke, C.; Carpenter, S.; Elmqvist, T.; Gunderson, L.; Holling, C.S.; Walker, B. Resilience and Sustainable Development: Building Adaptive Capacity in a World of Transformations. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2002, 31, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L. A Quantitative Framework to Evaluate Urban Ecological Resilience: Broadening Understanding through Multi-Attribute Perspectives. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1144244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.; Benayas, J.; Justel, A.; Sisto, R.; Montes, C.; Sanz-Casado, E. A Holistic Index-Based Framework to Assess Urban Resilience: Application to the Madrid Region, Spain. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; He, M.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Wei, Y. Spatio-temporal Analysis and Driving Forces of Urban Ecosystem Resilience Based on Land Use: A Case Study in the Great Bay Area. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wei, G. Assessment of Ecological Resilience and Its Response Mechanism to Land Spatial Structure Conflicts in China’s Southeast Coastal Areas. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, L.; Chao, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiu, M.; Luo, P.; Zhu, Y. Construction of the Ecological Security Pattern of Mu Us Sandy Land on the Basis of the “Source- Resistance- Corridor” Theory. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Long, Y.; Yang, L.; Ding, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, T. Impacts of Urbanization on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecological Resilience in the Plateau Lake Area in Central Yunnan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Xue, D.; Ma, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Ecological Resilience in the Shanxi–Shaanxi–Inner Mongolia Energy Zone with Multi-Scenario Simulation. Land 2024, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.D.; Fang, C.L.; Liu, H.M. Progress and Prospect of Urban Resilience Research. Prog. Geogr. 2020, 39, 1717–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. From Fail-Safe to Safe-to-Fail: Sustainability and Resilience in the New Urban World. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Barker, K.; Ramirez-Marquez, J.E. A Review of Definitions and Measures of System Resilience. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 145, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, J. Dynamic Evolution and Obstacle Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Niu, J. Co-Evolution of Tourism Economy and Urban Ecological Resilience in Shandong Province. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 2591–2608. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Evaluating Urban Ecosystem Resilience Using the DPSIR Framework and the ENA Model: A Case Study of 35 Cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Xu, S. Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience Based on PSR Framework in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Land 2023, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Gan, X.; Li, Z.S. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Ecological Resilience and Ecological Risk and Construction of Ecological Zones in Sichuan Province. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, X.; Cui, J. Temporal and Spatial Relationship Between Ecological Eesilience and Land Use Intensity in Xi’an City. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 2463–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Ru, S.; Xue, F. Spatio-temporal pattern and dynamic evolution of ecological resilience in the Yellow River Basin: Based on the analysis of emergy ecological footprint model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2024, 34, 136–147. [Google Scholar]
- Xiu, C.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q. Evaluation of Urban Resilience of Dalian City Based on the Perspective of “Size-Density-Morphology. ” Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 2315–2328. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Sheng, Y. Spatiotemporal differences and influencing factors of economic and ecological resilience of water resources in Xinjiang based on the PSR model. Arid Land Geogr. 2023, 46, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Study on the coupling coordination between urban ecological resilience and economic development level—Taking Jiangsu Province as an example. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2023, 39, 299–308, 318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Miao, C.; Chen, Z. Urban ecological resilience, social networks and its influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin. Arid Land Geogr. 2025, 48, 130–142. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, R.; Huang, T. Analyzing Spatial-Temporal Patterns and Driving Mechanisms of Ecological Resilience Using the Driving Force-Pressure-State-Influence-Response and Environment-Economy-Society Model: A Case Study of 280 Cities in China. Systems 2024, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Fan, X.; Xie, Q. Spatio-Temporal Evolution And Multi-Scale Barrier Factor Analysis Of Ecological Resilience of Agricultural Water Resources: A Case Study of Nine Provinces in the Yellow River Basin. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2025, 46, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.Y.; Dong, Z.; Chen, B. Spatio-Temporal Analysis and Simulation of Urban Ecological Resilience: A Case Study of Hangzhou. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, T.; Hu, H.; Fu, S.; Kong, A. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in the Yangtze River Delta. Areal Res. Dev. 2023, 42, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Cao, X. Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Ecological Resilience under Urban Renewal and Its Influencing Mechanisms around the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Xie, H. Spatio-Temporal Patterns and driving Factors of Ecological Resilience in Urban Agglomerations in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 40, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.M.; Niu, J.L. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Acta Eologica Sin. 2023, 43, 8309–8320. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, H.; Ou, M.; Feng, X.; Wu, S. Spatio-temporal variations and influencing factors of ecological resilience in the Aquatic-Terrestrial Ecotone of Poyang Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 9514–9526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Z.; Lin, J.; Xie, J.; Su, K. The Coupling Relationship between Urbanization and Ecological Resilience in the Pearl River Delta. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhong, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Spatial-Temporal Differentiation and Driving Factors of Ecological Resilience in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gong, H.; Liu, Y. The research of spatio-temporal characteristics and influence factors of Wenzhou ecological resilience based on the potential-elastic-stability model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 3253–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, L. Spatio-Temporal Pattern Evolution and Dynamic Simulation of Urban Ecological Resilience in Guangdong Province, China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, L. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in the Yellow River Basin. Arid Land Geogr. 2024, 47, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, M.; Jin, X.; Yao, J.; Guo, F. A Multi-Scenario Simulation and Driving Factor Analysis of Production–Living–Ecological Land in China’s Main Grain Producing Areas: A Case Study of the Huaihe River Eco-Economic Belt. Agriculture 2025, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Sun, K. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling Coordination of Urban Ecological Resilience and New Quality Productivity at the Provincial Scale in China. Land 2024, 13, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Shi, C.; Peng, K. Spatial-Temporal Adaptation and Interactive Response of New-Type Urbanization and Ecological Resilience in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 699–714. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Lu, R.; Ye, Z. Economic Development Quality and Ecological Resilience of China’s Land Border Cities Coupling Measure and Interactive Response. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 44, 256–268. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Ren, H. Coupled Coordination and the Spatial Connection Network Analysis of New Urbanization and Ecological Resilience in the Urban Agglomeration of Central Guizhou, China. Land 2024, 13, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Sha, Y.; Chen, Y. The Coupling Coordination and Influencing Factors of Urbanization and Ecological Resilience in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Land 2024, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huo, X.; Hong, Y.; Yu, C.; de Jong, M.; Cheng, B. How Urban Greening Policy Affects Urban Ecological Resilience: Quasi-Natural Experimental Evidence from Three Megacity Clusters in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Zhang, X. Coupled Climate-Environment-Society-Ecosystem Resilience Coordination Analytical Study-A Case Study of Zhejiang Province. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lim, U. Urban Resilience in Climate Change Adaptation: A Conceptual Framework. Sustainability 2016, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, C.; Meijerink, S.; Moccia, F.D.; Ache, P. Urban Flood Resilience, a Discursive-Institutional Analysis of Planning Practices in the Metropolitan City of Milan. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cai, X.; Yu, Q.; Proverbs, D.; Xia, T. Modelling Trends in Urban Flood Resilience towards Improving the Adaptability of Cities. Water 2024, 16, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccloy, M.W.D.; Andringa, R.K.; Maness, T.J.; Smith, J.A.; Grace, J.K. Promoting Urban Ecological Resilience through the Lens of Avian Biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 12, 1302002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yao, F.; Wu, P.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, T. Research on the Contribution of Urban Land Surface Moisture to the Alleviation Effect of Urban Land Surface Heat Based on Landsat 8 Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10737–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, C.; Cao, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, T.; Huang, Z. Assessment of Ecological Environment Quality and Their Drivers in Urban Agglomeration Based on a Novel Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, G.; Chen, L.; Ting, Z.; Long, L.; Jue, X.; Linyu, M. The Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land Use Ecological Efficiency in the Huaihai Economic Zone: Insights from a Multi-Dimensional Framework and Geospatial Modeling. Land 2025, 14, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ge, Q. Ecological Resilience of Three Major Urban Agglomerations in China from the “Environment–Society” Coupling Perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Qureshi, S.; Bruns, A.; Zhu, X. Applying the Concept of Spatial Resilience to Socio-Ecological Systems in the Urban Wetland Interface. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 42, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, F.; Cao, W. Dynamic Analysis of an Ecological Security Pattern Relying on the Relationship between Ecosystem Service Supply and Demand: A Case Study on the Xiamen-Zhangzhou-Quanzhou City Cluster. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 4327–4340. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.M.; Kong, H.M.; Guan, W.B.; Fu, B.J. Ecosystem Health Assessment: Methods and Directions. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2001, 21, 2106–2116. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Wu, J.; Peng, S. Concept of Ecosystem Management and Its Essential Elements. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2000, 11, 455–458. [Google Scholar]
- XIE, G.; Zhen, L.; LU, C.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C. Expert Knowledge Based Valuation Method of Ecosystem Services in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 911–919. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C.-X. Study on Ecosystem Services Value of Food Production in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2005, 13, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Pei, F.; Hu, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Ecosystem Service Value in Jiangsu Province Based on LUCC. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 6801–6811. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, R.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Chang, Y.; He, H.-S. Scaling Effects on Landscape Pattern Indices. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 14, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, B.; Nie, W. The Impact of Connectivity in Natural Protected Areas on the Resilience of Urban Ecological Networks: A Research Framework Based on Hierarchical Disturbance Scenario Simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 164, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Pan, J. The Stability of Landscape Pattern in Lanzhou, Gansu, China. J. Desert Res. 2016, 36, 556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Dilixiati, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lei, Y. Stability of Forest Landscape Pattern in Altai Mountains. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 38, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.F.; Chen, D.L.; Li, W.J.; Wang, Y.L. Stability of Landscape Pattern of Land Use: A Case Study of Changde. Sci. Geogr. Sin 2013, 33, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; She, J.; Chen, D.; She, Y.; Deng, J. Landscape pattern analysis of Dongfang city based on the stability evaluation model. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2016, 36, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yu, Q.; Hu, L.; Zhang, S.; Fu, T.; Zhou, X.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, H. Ecosystem Health Assessment Based on Analysis of a Land Use Database. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 44, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, H.; Hu, X. Linking Ecosystem Services and Landscape Patterns to Assess Urban Ecosystem Health: A Case Study in Shenzhen City, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 143, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Lou, H.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Evolution Assessment of Landscape Ecological Resilience Based on Adaptive Cycling in Changsha–Zhuzhou–Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration, China. Land 2025, 14, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, G. Spatial Disparity and Driving Factors of Green Development Efficiency in Chinese Cities. Res. Econ. Manag. 2020, 41, 11–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ru, S.; Ma, R. Evaluation, Spatial Analysis and Prediction of Ecological Environment Vulnerability of Yellow River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M.; Harris, P. Geographically Weighted Regression with Parameter-Specific Distance Metrics. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; He, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, L.; Ni, J. Policy Implications for Synergistic Management of PM2.5 and O3 Pollution from a Pattern-Process-Sustainability Perspective in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An Extended Time Series (2000–2018) of Global NPP-VIIRS-like Nighttime Light Data from a Cross-Sensor Calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shi, X. Analysis of Spatial Autocorrelation Patterns of Land Use and Influence Factors in Loess Hilly Region—A Case Study of Changhe Basin of Jincheng City. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.M.; Gao, B.; Li, C.; Wu, Y. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Landscape Ecological Risk and Influential Factors in Yunnan Border Mountainous Area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 7458–7469. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of the resilience of the coastal complex ecosystem in the East China Sea from 2001 to 2020. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2024, 43, 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Y.; You, L.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Huang, J.X. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Multi-Pond Landscape Change and Their Driving Factors in the Chaohu Basin, China. Acta Ecol. Sin 2018, 38, 6280–6291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Feng, R.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K. Exploring the Driving Factors of Remote Sensing Ecological Index Changes from the Perspective of Geospatial Differentiation: A Case Study of the Weihe River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data | Sources |
|---|---|
| Landsat Series of Remote Sensing Images | United States Geological Survey website (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/) |
| Administrative Boundaries by Year | The UC Berkeley Library (https://www.lib.berkeley.edu/), MAPWORLD GIS (https://www.tianditu.gov.cn/) |
| Socio-economic Data | Xuzhou Statistical Yearbook and National Compendium of Cost and Benefit of Agricultural Products |
| Population Density Data | LandScan Global Population Data (https://landscan.ornl.gov) |
| Nighttime Lighting Data | An extended time-series (2000–2023) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data [75] |
| Annual Precipitation Data | National Earth System Science Data Center (https://www.geodata.cn) |
| Fractional Vegetation Cover (FVC) Data | Geographic Data Sharing Infrastructure, global resources data cloud (www.gis5g.com) |
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Data | |
| Slope Data | Calculations based on DEM data |
| Places Data | Geospatial Data Cloud site, Computer Network Information Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.gscloud.cn) |
| Waterways Data | |
| Roads Data |
| Years | Global Moran’s I | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 0.586684 | 0.000 |
| 2013 | 0.450728 | 0.000 |
| 2018 | 0.580713 | 0.000 |
| 2022 | 0.588907 | 0.000 |
| Index | OLS | GWR | MGWR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residual sum of squares | / | 3275.6 | 858.5 |
| R2 | 0.343 | 0.343 | 0.828 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.341 | 0.341 | 0.791 |
| AICc | −12,458 | 12,071 | 7509 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Chen, L. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in Xuzhou City. Land 2025, 14, 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051048
Zhang T, Wang X, Li X, Zhu X, Li L, Chen L. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in Xuzhou City. Land. 2025; 14(5):1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051048
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ting, Xiulian Wang, Xinai Li, Xuan Zhu, Long Li, and Longqian Chen. 2025. "Spatio-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in Xuzhou City" Land 14, no. 5: 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051048
APA StyleZhang, T., Wang, X., Li, X., Zhu, X., Li, L., & Chen, L. (2025). Spatio-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Urban Ecological Resilience in Xuzhou City. Land, 14(5), 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051048







