Abstract
Riverine and lacustrine shorelines are crucial for human survival and development, but their natural and ecological environments are highly fragile and sensitive. Intensified human activities have placed unprecedented pressure on the shoreline ecosystem of the Yangtze River Basin. This study investigates the degradation of river and lake shorelines and its cascading effects on ecological service functions. Using Sentinel-2 as the primary data source, we analyzed land use/cover changes and ecosystem service values (ESV) in the Huanggang and Taihu sections of the Yangtze River from 2018 to 2022. The supervised classification results using the support vector machine (SVM) algorithm exceeded 95% accuracy. In the Huanggang section, vegetation was significantly converted into cultivated land and built-up areas (−6.17 km2), while in the Taihu section, water bodies were largely transformed into agricultural land (−3.77 km2). In this study, we quantified changes in ESV using the unit area equivalent factor method, adjusted based on net primary productivity, precipitation, and the soil conservation coefficient. The results indicate that the ESV ranking in both sections follows the order: water conservation > environmental purification > biodiversity > soil conservation. From 2018 to 2022, the ESV in the Huanggang section declined due to forest and grassland loss and an increase in bare land. In contrast, ecological restoration and habitat protection policies contributed to an improvement in ecosystem service functions in the Taihu section, with various ESV components increasing as follows: soil conservation (8.79%) > biodiversity (6.67%) > environmental purification (5.98%) > water conservation (5.52%). These findings provide valuable insights for decision-making in the protection and management of the Yangtze River Basin ecosystem.
1. Introduction
River ecosystems are a crucial component in maintaining the functions of the Earth’s biosphere. As the primary zone of water–land interaction, their shorelines provide more than 65% of the ecosystem services of global inland waters, including water conservation and biodiversity maintenance [1,2]. Between 2000 and 2020, the global natural shoreline retreat rate reached 1.2% per year, directly contributing to a 37% decline in the carbon sink function of wetlands [3]. This crisis is particularly pronounced in urbanizing river basins. As one of the largest river ecosystems in the world, the Yangtze River Basin spans approximately 19% of China’s land area. The ecological health of its shorelines is critical for sustaining regional development. However, in recent years, shoreline hardening and wetland encroachment have caused the natural shoreline retention rate in the middle reaches to decline sharply from 72% in 2000 to 58% in 2020 [4,5]. Consequently, this has led to a series of ecological crises, including increased soil erosion and habitat fragmentation. Accurately quantifying the multidimensional impacts of human activities on shoreline ecosystems has thus become a pressing issue in global watershed management.
Riverine and lacustrine shorelines encompass all areas adjacent to lakes, rivers, wetlands, and other water bodies with significant resource value [6,7]. These ecosystems exhibit strong edge effects and rank among the most complex within the Earth’s biosphere [8]. Scholars have evaluated shoreline resources from various perspectives, providing a theoretical foundation for shoreline space research [9,10]. Hou et al. defined the Yangtze River shoreline protection scope from the perspective of ecological conservation as “river bank-river bank-buffer zone” [6]. The protection and utilization of riverine and lacustrine shorelines are crucial for maintaining ecosystem stability, sustaining river and lake health, and promoting sustainable economic and social development. However, inadequate management of shoreline protection, development, and utilization, along with a limited understanding of the relationship between shoreline usage patterns and river and lake functions, poses severe threats to these ecosystems.
To enhance the efficiency of shoreline resource utilization while safeguarding the ecological integrity of lakes, it is imperative to study the evolution of riverine and lacustrine shorelines and conduct comprehensive ecological monitoring and evaluation. Traditional shoreline supervision relies on manual inspections and medium- to low-resolution remote sensing data, which suffer from limitations such as low spatial resolution, time lag, and an inability to detect subtle land use/cover changes (LUCC) [11]. Currently, shoreline research primarily focuses on extracting shoreline ecological types using remote sensing images and analyzing the spatiotemporal evolution of coasts, lakeshores, and river shorelines [12,13,14]. However, most studies on shoreline evolution emphasize coastlines, while research on the evolution and functional loss of inland river and lake shorelines remains scarce. Additionally, shoreline extraction methods predominantly rely on single remote sensing image-based water body indices, which lack accuracy in dynamic ecological assessments.
Ecosystem services are fundamental to human survival and development. They refer to the life-supporting goods and services derived—either directly or indirectly—from the structure, processes, and functions of ecosystems. Valuing ecosystem services provides a critical foundation for environmental protection, ecological function zoning, environmental-economic accounting, and the formulation of ecological compensation policies [15,16]. The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment Report indicated that 15 of the 24 globally assessed ecosystem services (approximately 60%) are degrading [17]. Ecosystem service value (ESV) quantifies the ecological benefits provided by an ecosystem to human society, serving as an indicator of ecosystem health and influencing human well-being [18,19]. The equivalent factor method per unit area, known for its simplicity and comprehensive nature, is widely employed in ESV assessments [20,21]. Xie et al. refined this method by incorporating literature research, expert knowledge, statistical data, and remote sensing monitoring to enhance its applicability [16]. Scholars have conducted extensive basin-scale ESV assessments, such as Karabulut et al.’s evaluation of the Danube River Basin in Europe [22] and studies by Qi et al., Morri et al., and Dang et al. on the service functions of forests, wetlands, and grasslands [23,24,25]. Talukdar et al. investigated the impact of LUCC and human activities on basin service functions [26]. However, existing basin-scale studies fail to emphasize the distinct characteristics of riverine and lacustrine shorelines, leading to a misalignment between assessment scales and shoreline ecological processes. Additionally, conventional ESV assessments often employ static equivalent factor methods, which lack integration with remote sensing-derived ecological parameters and local ecological processes, limiting their effectiveness in supporting management decisions, particularly in regions experiencing high-intensity disturbances.
Valuable shoreline resources are extensively distributed along the mainstream of the Yangtze River and its major tributaries in China, encompassing not only ports, industrial enterprises, and logistics hubs but also biodiversity conservation areas, water ecological protection zones, and wetlands [5,27]. “The Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt Based on the Golden Waterway” and “The Overall Plan for the Reform of the Ecological Civilization System” outline clear requirements for the rational development and conservation of the Yangtze River shoreline [28,29]. However, challenges persist in balancing ecological protection and economic development along the river’s mainstream and tributaries. This conflict primarily manifests in tensions between agricultural expansion, urban construction, aquaculture, sand and gravel mining, and the need for ecological conservation [30,31]. The expansion of shoreline-related infrastructure has led to wetland degradation and adverse ecological consequences for coastal water and land environments.
In light of these considerations, this study examines the Huanggang section, a frontier of urbanization in the middle reaches, and the Taihu section, a demonstration area for ecological restoration in the lower reaches, as case studies. The objective is to construct a comprehensive assessment framework linking shoreline destruction, ecological processes, and service loss. By utilizing Sentinel-2 multispectral data and Esri’s Wayback sub-meter historical imagery, a high-precision shoreline land use/land cover (LULC) database covering 2018 to 2022 was developed. The support vector machine (SVM) classification algorithm was employed to resolve spectral confusion among complex shoreline features. Additionally, the equivalent factor was refined by integrating net primary productivity (NPP), precipitation, and soil conservation parameters, thereby establishing a localized dynamic equivalent factor. In this study, we aim to analyze shoreline degradation and its impacts on ecological service functions, providing empirical insights into shoreline degradation mechanisms and functional loss under diverse environmental pressures.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Yangtze River originates from the southwestern side of Geladandong Peak in the Tanggula Mountains on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, often referred to as the “Roof of the World”. Flowing through central China from west to east (90°33′–122°25′ E and 24°30′–35°45′ N). The Yangtze River basin spans approximately 1.8 million square kilometers, representing about one-fifth of China’s total land area, and is abundant in natural resources.
This study examines the Huanggang and Taihu sections of the Yangtze River as case study areas (Figure 1). These two regions, located in the middle and lower reaches of the river, exhibit distinct ecological gradients and varying degrees of human interference. The Huanggang section features diverse shoreline types, including natural, artificial, and semi-natural shorelines influenced by human activities. In recent years, rapid economic development and accelerated urbanization have exerted increasing pressure on river and lake shorelines, with shoreline degradation emerging as a critical issue. The Taihu section, situated on the southern periphery of the Yangtze River Delta, represents a key lake ecosystem within the Yangtze River Basin. However, prolonged high-intensity human activities have resulted in significant water quality issues in the Taihu Lake Basin, severe ecological degradation of the lakeside zone, and persistent shoreline damage that demands urgent attention.
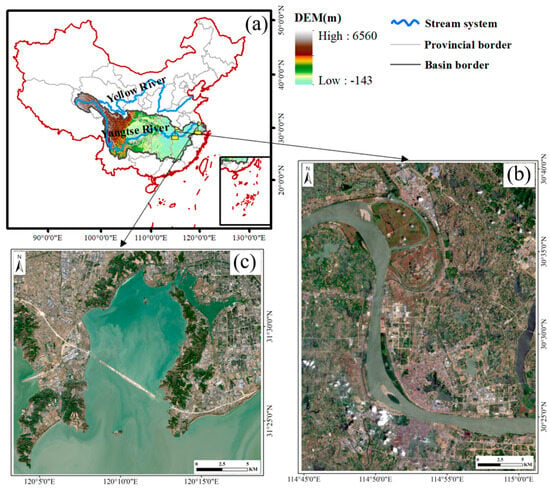
Figure 1.
(a) Location of the study area in China. (b) Remote sensing image of the Huanggang segment in 2022 (Sentinel-2B true color composite image). (c) Remote sensing image of the Taihu segment in 2022 (Sentinel-2B true color composite image).
2.2. Data Source
This study integrates multi-source remote sensing data with ground statistical data to construct a comprehensive framework for the ecological monitoring of riverine and lacustrine shorelines. A multi-temporal and multi-spatial observation system is primarily built upon Sentinel-2 MSI (MultiSpectral Instrument) satellite images and Google Earth high-resolution imagery (Table 1). Sentinel-2, a high-resolution multispectral satellite operated by the European Space Agency, is primarily used for land monitoring [32,33]. The Sentinel-2 satellite carries a multispectral instrument (MSI) that captures data across 13 spectral bands at spatial resolutions of 10 m, 20 m, and 60 m. The Sentinel-2 data used in this study are sourced from the ESA Copernicus Data Center (https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 15 September 2024)).

Table 1.
Remote sensing dataset information used in this study.
For ground verification, Google Earth images were utilized to construct a high-precision reference dataset. These images comprise multi-resolution satellite imagery and aerial photographs. They are integrated into a virtual Earth, where image resolution at a given spatial scale is determined by zoom levels [34]. To capture fine-scale LUCC, Google Earth images with a spatial resolution of 0.6 m at Zoom Level 19 were selected as the validation dataset.
Socioeconomic data were primarily derived from the Statistical Communiqué of National Economic and Social Development of Huanggang City and Wuxi City (2018 and 2022), focusing on three key indicators: grain output, cultivated land area, and grain prices. Additionally, annual raster data on NPP, precipitation (PRE), and soil conservation were obtained from the Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform (RESDP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 16 September 2024)) and are mainly used for ESV calculations.
2.3. Methods
This study focuses on the Huanggang and Taihu sections of the Yangtze River, using remote sensing data as the primary source to monitor shoreline changes, assess LUCC in the surrounding areas, and evaluate ecosystem service value (ESV). Riverine and lacustrine shorelines are transitional zones where water and land meet, extending along both riverbanks and around lakes. The shoreline boundary is defined as the demarcation line drawn along the river’s course or the lake’s perimeter to establish the vertical extent of various shoreline functional zones [35,36]. In this study, we carefully considered shoreline extraction rules and characteristics, selecting the water–land boundary as the baseline based on different shoreline utilization types. A 2000 m buffer zone perpendicular to the baseline was delineated to define the shoreline study area.
Field research indicates that this spatial range effectively encompasses key ecological processes, species distributions, and the integrity of ecological functions within the shoreline ecosystem. Across the land–water gradient, factors such as soil moisture content, vegetation types, and microclimatic conditions vary significantly. For instance, hydrophytic species dominate near the water’s edge, gradually transitioning to mesophytes and xerophytes with increasing distance inland. A 2000 m buffer zone effectively encompasses this gradient and preserves the natural continuity of the ecological transition zone. This range effectively captures the transport of materials—such as nutrients and sediments—from rivers to adjacent terrestrial ecosystems.
2.3.1. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Land Use Classification
Riverine and lacustrine shorelines’ delineation and classification form the foundation for ecological and environmental assessments. Based on shoreline land characteristics obtained from monitoring surveys, Sentinel-2 imagery was classified and visually interpreted for land use.
In this study, we employed the Support Vector Machine (SVM) as the core algorithm for supervised classification. SVM is a machine learning method grounded in statistical learning theory. It utilizes kernel functions to transform nonlinear problems into linear ones, significantly reducing computational complexity [37]. SVM effectively identifies support vectors that optimize class separability, thereby constructing a classifier that maximizes the margin between categories and mitigates inter-spectral confusion in remote sensing images [38,39].
Following the “Land Use Status Classification” (GB/T 21010-2017) [40] and the specific conditions of the study area, land use was categorized into five types: water bodies, cultivated land, forest and grass vegetation, bare land, and built-up areas. A total of 250 training samples (30–50 per category) were collected and evenly distributed across the Huanggang and Taihu sections. SVM classification was applied, followed by refinement using field survey data to ensure accuracy.
2.3.2. Ecosystem Service Value Assessment
Since precipitation and runoff variations in the study area are minimal, and acquiring fundamental ecological and environmental data is challenging, we employed the unit-area equivalent factor method to estimate the ESV. The results were adjusted based on the specific ecological conditions of the study area.
Given the characteristics of riverine and lacustrine shorelines, this study focuses on four key ecological service functions closely linked to shoreline ecosystems: water conservation, soil conservation, biodiversity, and environmental purification. Water conservation: Vegetation and soil on riverine and lacustrine shorelines play a crucial role in regulating the hydrological cycle and maintaining water resource stability [41]. Shoreline degradation directly reduces the capacity for water conservation, increasing the risks of water shortages and flooding. Soil conservation: Shoreline vegetation stabilizes soil and prevents erosion, thus mitigating soil and water loss. When shorelines are damaged, soil erosion intensifies, leading to land degradation and river siltation [42]. Biodiversity: Riverine and lacustrine shorelines serve as habitats for diverse organisms. Their destruction results in habitat loss, species decline, and ecosystem imbalance [43]. Environmental purification: Shoreline vegetation and soil filter pollutants, improving water quality. However, shoreline degradation diminishes this purification capacity, worsening water pollution [44].
- (1)
- Equivalent factor adjustment
Building on previous studies, Xie et al. developed a dynamic evaluation method for China’s terrestrial ESV using the unit-area value equivalent factor method, integrating model calculations and geographic information spatial analysis [16,45]. However, the ecosystem equivalent factor table proposed by Xie et al. is based on China’s average ecosystem conditions. Therefore, ESV estimations must be modified to reflect the specific ecological environment of the study area. We adjusted the ESV for the Huanggang and Taihu sections by incorporating regional variations in NPP, rainfall, and soil conservation. The ESV for water conservation was adjusted using the rainfall correction factor, while the ESV for environmental purification and biodiversity services was modified based on the NPP correction factor [46]. The ESV for soil conservation was adjusted according to the soil conservation correction factor. The corresponding formulas are provided below.
where Ki represents the adjustment coefficient of NPP/PRE/soil conservation in the study area in the i-th year, and Xi and Xi represent the average values of NPP/PRE/soil conservation in the study area and the country in the i-th year, respectively.
- (2)
- Standard Equivalence Factor Value
The value of a standard equivalent factor (standard equivalent) refers to the economic value of the annual grain output generated by farmland with an average yield of one hectare (1 ha). To determine different ESV values across ecosystems, the first step is to establish the value of a standard equivalent, followed by the calculation of ESV per unit area for each ecosystem based on the relative equivalence of each service. Drawing on the findings of previous studies and expert consultation, the grain yield per unit area was multiplied by the total grain cultivation area, and the cost–benefit ratio of grain production was incorporated to comprehensively estimate the value of the standard equivalent factor [20,21,46]. The corresponding calculation formula is provided below.
where D represents the equivalent factor value, which corresponds to the ESV per unit area. The factor 1/7 represents the benefit–cost ratio of grain production. P denotes the grain yield per unit area, calculated as the total grain yield divided by the cultivated land area, while Q represents the grain price.
To enhance computational accuracy and ensure data comparability, the grain yield per unit area was averaged over the years 2018 and 2022, while the grain price was based on the national average in 2022. The equivalent factor table in this study is derived from the latest research findings [16] and the computed standard equivalent factor value to generate the ESV per unit area table for the study area (Table 2). The classification of ecosystem types follows the land use categorization.

Table 2.
Ecological service value per unit area by land use type in the study area (Yuan/km2).
3. Results
3.1. LULC Monitoring
3.1.1. LULC Extraction Based on SVM
In this study, we defined a 2000 m buffer zone along the banks of the Huanggang and Taihu sections of the Yangtze River and employed the SVM classification method to generate shoreline land use classification maps. Google Earth images were used to collect validation samples for accuracy assessment of the classification results. The classification accuracy assessment indicated that the overall accuracy for the Huanggang section reached 96.91% in 2018 and 95.72% in 2022, with corresponding Kappa coefficients of 0.9376 and 0.9446. For the Taihu section, the overall accuracy reached 99.31% in 2018 and 96.09% in 2022, with Kappa coefficients of 0.9473 and 0.9475. The overall classification accuracy exceeded 95%, and the Kappa coefficients remained above 0.93, indicating high classification reliability.
LULC classification results revealed that the predominant land use types in the Huanggang and Taihu sections were water, cultivated land, forested and grassland areas, bare land, and built-up areas (Figure 2). A quantitative assessment of land use distribution in the study areas indicated that the Huanggang section was primarily composed of cultivated land, water, and built-up areas, whereas forested and grassland areas, along with bare land, covered relatively smaller proportions. In contrast, the Taihu study area was dominated by water, forested and grassland areas, and built-up areas, whereas cultivated and bare land occupied smaller proportions.
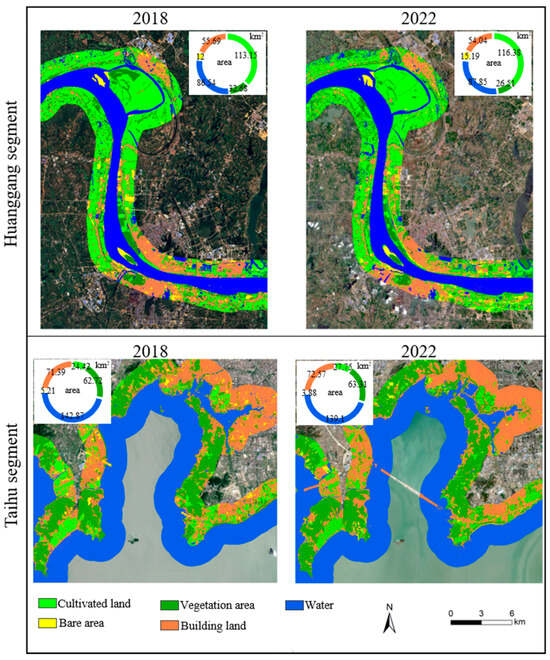
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of the land use/land cover and area in the Huanggang and Taihu segments of the Yangtze River in 2018 and 2022.
3.1.2. LULC Change Detection
The statistical analysis of LUCC in the Huanggang and Taihu sections (Section 3.1.1) indicates that forested and grassland areas, as well as cultivated land, underwent significant changes in the Huanggang section, decreasing by 6.17 km2 and 3.23 km2, respectively. In contrast, bare land, water, and built-up areas experienced minor changes of 3.18 km2, 1.30 km2, and 1.65 km2, respectively. For the Taihu section, water and cultivated land underwent significant changes of 3.77 km2 and 3.34 km2, respectively, whereas bare land, built-up areas, and forested and grassland areas exhibited minor changes of 1.34 km2, 1.18 km2, and 0.59 km2, respectively.
The classification results from 2018 to 2022 were analyzed alongside high-resolution images from Google Earth to assess shoreline changes in the study area (Figure 3). The analysis revealed that a substantial portion of the forested area in the Huanggang section has been converted into cultivated land, with significant portions of forested and cultivated land further transformed into built-up areas. The expansion of agricultural land and the acceleration of urbanization have led to the occupation of extensive forest and grassland areas, resulting in a net decline in total vegetation cover. In the Taihu section, the most notable LUCC is the reciprocal conversion among cultivated land, vegetation area (forest and grass), and built-up areas. Among the sources contributing to the increase in cultivated land, forest and grassland were the primary contributors. Similarly, numerous forested and agricultural areas in the Taihu section have been converted into built-up areas. Previous studies have also indicated a decline in forested areas and an expansion of built-up land in the study region [47].
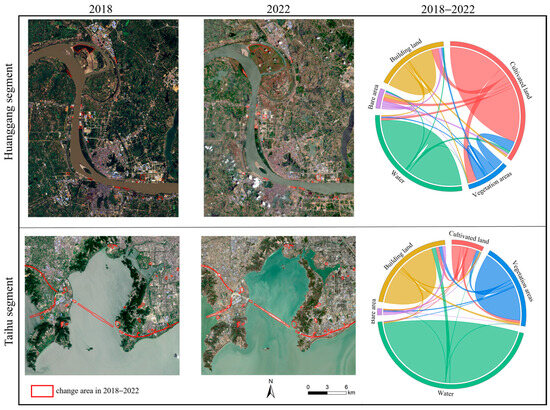
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of LUCC and LULC transfer information in the Huanggang and Taihu segments of the Yangtze River from 2018 to 2022.
3.2. The Results of Ecosystem Service Value Assessment
3.2.1. ESV Analysis of Different Ecosystems
The ESV of different ecosystem types in the Huanggang section varied significantly between 2018 and 2022 (Figure 4). For the cultivated land ecosystem, the ESV of soil conservation and water conservation were relatively high, amounting to 25,171,621.8 yuan and 6,598,386.3 yuan in 2018 and 25,926,973.57 yuan and 6,796,391.13 yuan in 2022, respectively. Biodiversity had the second highest ESV, while environmental purification had the lowest. Conversely, in the bare land ecosystem, environmental purification had the highest ESV, reaching 259,218.5 yuan in 2018 and 328,450.61 yuan in 2022. Soil conservation and biodiversity ranked second, with nearly identical values. In the water ecosystem, water conservation was the predominant service, accounting for more than 90% of the total ESV of the water body.
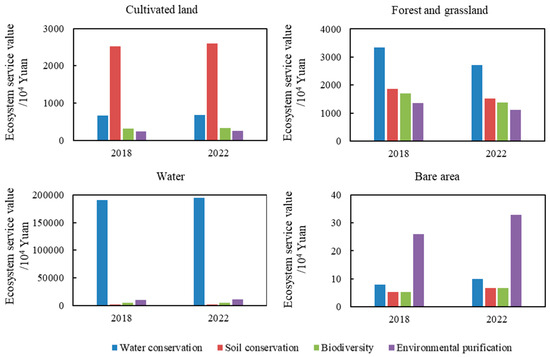
Figure 4.
Ecosystem service value of different land use types in the Huanggang section of the Yangtze River.
The ESV of cultivated land and water bodies remained relatively stable between 2018 and 2022, while the ESV of forests, grasslands, and bare land fluctuated notably. The ESV of forests and grasslands in the Huanggang section declined in 2022 compared to 2018, whereas the ESV of bare land exhibited an upward trend. Yang et al. found that the ESV of soil conservation and biodiversity in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River (including the Huanggang section) declined between 1995 and 2014 [48], a trend consistent with the findings of this study from 2018 to 2022. This suggests that soil conservation and biodiversity in the Huanggang section require enhancement in the coming years.
Figure 5 shows that the ESV of different ecosystem types in the Taihu section has fluctuated over time, exhibiting both increases and decreases between 2018 and 2022. Among the cultivated land ecosystem services, the ESV ranking is as follows: soil conservation (5,322,781.8 yuan and 6,551,926.1 yuan) > water conservation (1,395,292.3 yuan and 1,717,495.2 yuan) > biodiversity (671,807.4 yuan and 826,942.1 yuan) > environmental purification (516,774.9 yuan and 636,109.3 yuan). For forest and grassland ecosystems, water conservation had the highest ESV, reaching 62,923,775.1 yuan in 2018 and 68,786,733.2 yuan in 2022. This was followed by soil conservation, biodiversity, and environmental purification.
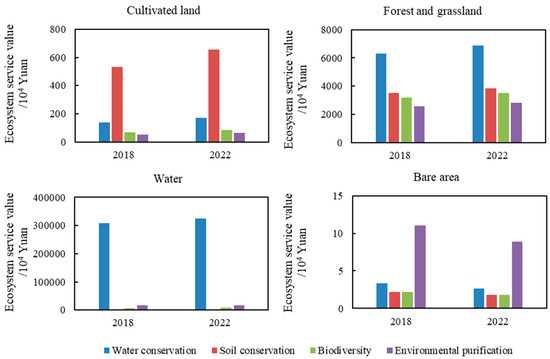
Figure 5.
Ecosystem service value of different land use types in the Taihu section of the Yangtze River.
In the water ecosystem, water conservation was the dominant ecosystem service, accounting for more than 90% of the total water body ESV. Similar findings have been reported in previous studies [49]. Unlike the Huanggang section, the ESV of cultivated land and forest and grass vegetation areas in the Taihu section increased between 2018 and 2022, with cultivated land experiencing significant changes. Meanwhile, the ESV of bare land in the Taihu section declined in 2022 compared to 2018.
3.2.2. ESV Analysis of Single Service Function
The total ESV of four key ecosystem services—water conservation, soil conservation, biodiversity, and environmental purification—was calculated for the study area, and the total value of individual services in 2018 and 2022 was determined (Figure 6). The analysis indicates that the ESV of different service functions in the Huanggang section of the riverine and lacustrine shorelines follows the ranking order of water conservation > environmental purification > biodiversity > soil conservation. Water conservation exhibited the highest ESV, reaching 1,951,125,453 yuan in 2018 and 1,976,673,089 yuan in 2022. Environmental purification ranked second, with values of 1,200,630,742 yuan in 2018 and 1,193,655,27 yuan in 2022.
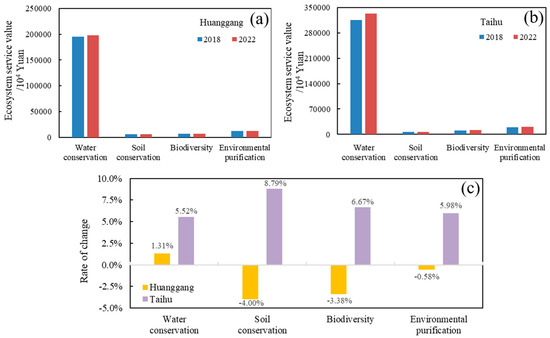
Figure 6.
(a) Ecosystem service value of single ecosystem service function in the Huanggang section in 2018 and 2022, (b) ecosystem service value of single ecosystem service function in the Taihu section in 2018 and 2022, and (c) ecosystem service value change rate of single ecosystem service function from 2018 to 2022.
The ranking of ESV for different ecosystem service functions in the Taihu section aligns with that of the Huanggang section. In order, it is water conservation > environmental purification > biodiversity > soil conservation. Among them, water conservation had the highest ESV, reaching 3156 billion yuan in 2018 and 3330 billion yuan in 2022. Environmental purification ranked second, with values of 1940 billion yuan in 2018 and 2056 billion yuan in 2022. Furthermore, the value of various ecosystem services increased in 2022 compared to 2018.
Figure 6c indicates that the ESV of water conservation in the Huanggang section increased by 1.31% from 2018 to 2022. Conversely, the ESV of soil conservation, biodiversity, and environmental purification declined by 4.00%, 3.38%, and 0.58%, respectively. The decreases in soil conservation and biodiversity services are primarily attributed to the reduction in forest and grass vegetation areas and the expansion of cultivated and bare land in the Huanggang section.
Compared to the Huanggang section, the magnitude of change in the ESV of the Taihu section was more significant. The ESV of all four ecosystem services in the Taihu section increased, following the order: soil conservation (8.79%) > biodiversity (6.67%) > environmental purification (5.98%) > water conservation (5.52%). Previous studies indicate that from 2000 to 2009, declining environmental capacity and rising pollution emissions led to a reduction in the environmental purification function of Taihu Lake [50]. However, the results of this study suggest an improvement in Taihu’s environmental purification function in recent years. Overall, the ecosystem service functions and ESV of the Taihu section exhibit stability and are progressing toward a more sustainable trajectory.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Driving Mechanism of LULC and Its Ecological Effects
The LUCC of the Huanggang and Taihu sections exhibited substantial differences between 2018 and 2022. The forest and grass vegetation area in the Huanggang section declined by 6.17 km2, while cultivated land and built-up areas expanded by 3.23 km2 and 1.65 km2, respectively. In contrast, the Taihu section experienced significant fluctuations in water and cultivated land areas, with changes of 3.77 km2 and 3.34 km2, respectively. An analysis of socioeconomic data revealed that urbanization in the Huanggang section (with an annual GDP growth rate of 8.2%, according to the Huanggang Statistical Bulletin) directly contributed to the expansion of built-up land, leading to the conversion of forest and grass vegetation into cultivated land and artificial surfaces. Conversely, changes in water bodies in the Taihu section may be linked to water environment governance policies in the Yangtze River Delta region, such as the Taihu Basin Water Environment Comprehensive Governance Plan, and the region’s intensive agricultural production model.
Notably, both regions exhibit a trend of conversion from cultivated land to built-up land, aligning with the “natural-to-artificial surface binary transition” observed in the urbanization process of river basins worldwide [51]. This LUCC has cascading effects on ecosystem service functions. For instance, the reduction in forest and grass vegetation in the Huanggang section weakened soil retention capacity, leading to a 4.00% decline in soil conservation ESV. In contrast, the Taihu section mitigated human activity pressures through policies such as returning farmland to lakes, resulting in a 5.52% increase in its water conservation ESV.
Water conservation ESV dominates in the Huanggang section (>90%); however, its growth rate (1.31%) is considerably lower than that of the Taihu section (5.52%). Further analysis suggests that the expansion of bare land in the Huanggang section contributed to a 0.58% decrease in environmental purification ESV, corroborating the positive correlation between vegetation coverage and pollutant interception capacity [52,53]. Despite high-intensity human disturbances, the soil conservation ESV of the Taihu section increased by 8.79%, likely due to lakeside ecological restoration projects aimed at enhancing vegetation-based soil stabilization.
Additionally, changes in biodiversity ESV exhibited opposite trends in the two regions, with a 3.38% decline in the Huanggang section and a 6.67% increase in the Taihu section. This disparity underscores differences in ecological management effectiveness. For example, the Taihu section maintained habitat connectivity through the establishment of wetland protection areas, whereas the Huanggang section lacked systematic biological corridor planning. Thus, for the Huanggang section, it is advisable to establish ecological red lines and implement vegetation restoration projects (e.g., constructing riverbank buffer zones with a minimum width of 100 m), prioritizing native species such as maple, poplar, and reed to enhance soil stability. Furthermore, the successful ecological strategies applied in the Taihu section could be extended to similar regions in the lower Yangtze River, though they must be integrated with cultivated land occupation and compensation balance systems to mitigate potential food security risks.
4.2. Limitations and Future Work
In this study, we extracted LULC types in the Huanggang and Taihu sections of the Yangtze River using remote sensing and evaluated the ESV. We employed high-resolution Sentinel-2 images in combination with supervised classification using an SVM to detect subtle changes in land cover types, thereby addressing the limitations of traditional methods in detecting small-scale land cover changes. Utilizing time-series data from 2018 and 2022, the relationship between LUCC and ESV was quantitatively assessed, thereby overcoming the limitation of static assessments in capturing ecological dynamics.
However, this study has certain limitations that require further investigation. We employed a supervised classification method. The authors of future studies should apply multiple classification methods, including deep learning techniques, which have gained significant attention in recent years, to enable a comprehensive comparative analysis of classification results. The sensitivity of the equivalent factor method to local climate heterogeneity (e.g., extreme precipitation events) and the accuracy of the adjusted ESV remain insufficiently quantified. While the delineation of the 2000 m buffer zone complies with water conservancy project specifications, it may underestimate the true extent of the ecologically sensitive lakeside belt [54]. Moreover, we only assessed four ecosystem service functions. The authors of future studies should broaden the scope of evaluation based on specific needs and integrate ecosystem process models (e.g., InVEST) to enhance the dynamic response capabilities of ESV assessment, thereby facilitating a more comprehensive evaluation of the ESV in the Yangtze River Basin.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we systematically addressed the limitations of traditional methods with respect to data accuracy, regional adaptability, and dynamic monitoring by employing high-precision remote sensing classification in conjunction with a localized ESV model, thereby providing a robust scientific tool for ecological management in the Yangtze River Basin. The main conclusions are as follows.
- (1)
- Using remote sensing imagery, we employed the SVM supervised classification method to extract the current LULC types of the study area. The classification achieved high accuracy, with an overall accuracy exceeding 95% and a Kappa coefficient above 0.93. In the Huanggang study area, the dominant land use types are cultivated land, water bodies, and buildings, whereas forest and grass vegetation areas, as well as bare land, occupy relatively smaller proportions. Similarly, in the Taihu study area, the primary land use types are water bodies, forest and grass vegetation areas, and buildings, with cultivated land and bare land covering smaller areas.
- (2)
- Statistical analysis of land use types indicates significant changes in forest and grass vegetation areas (6.17 km2) and cultivated land (3.23 km2) in the Huanggang section. Conversely, bare land, water bodies, and buildings exhibited minor changes. In the Taihu section, significant changes were observed in water bodies (3.77 km2) and cultivated land (3.34 km2), whereas bare land, buildings, and forest and grass vegetation areas experienced relatively minor changes. In the Huanggang study area, forest land was primarily converted into cultivated land. In contrast, in the Taihu study area, forest land and cultivated land were predominantly converted into built-up areas.
- (3)
- The ESV varies across different land use types, with forests, grasslands, and water bodies contributing the most. Between 2018 and 2022, the reduction in forest and grass vegetation areas, coupled with an increase in bare land, resulted in a declining ESV trend in the Huanggang section. The decline in soil conservation and biodiversity service values is directly linked to the reduction in forest and grassland areas, as well as the expansion of cultivated land. In contrast, the ecosystem services in the Taihu section are improving, with increases observed across all ESV functions: soil conservation (8.79%) > biodiversity (6.67%) > environmental purification (5.98%) > water conservation (5.52%).
- (4)
- For the Huanggang section, it is recommended to strictly restrict the conversion of forested and grassland areas to cultivated land and built-up zones. Priority should be given to the designation of ecological red lines within 100 m on either side of the riverbank, accompanied by the implementation of buffer zone construction projects. Locally adapted species should be selected for vegetation restoration to enhance soil conservation and biodiversity functions. Farmer participation in the “Grain-for-Green” should be encouraged through ecological compensation policies, aiming to reconcile ecological conservation objectives with economic development requirements. Additionally, a transboundary habitat connectivity network should be established along the riverbank to prevent habitat fragmentation.
- (5)
- For the Taihu section, vegetation and soil stabilization initiatives—such as reed planting belts and ecological slope protection—should be promoted. The implementation of the policy for returning farmland to lakes must be strengthened, and it is suggested that downstream regions develop a coordinated “water area–vegetation” protection plan modeled after the Taihu approach. When advancing ecological restoration, it is essential to integrate the cultivated land requisition–compensation balance system (e.g., compensation through cultivated land quality improvement) to mitigate adverse impacts on food security associated with land conversion. A long-term ecological monitoring network should be established, integrating this study’s analytical framework to evaluate policy effectiveness in real time.
Furthermore, the methodological approaches and analytical framework utilized in this study can be directly applied to similar regional studies. Future research could enhance multi-source data integration, dynamic modeling, and policy tool innovation to improve the predictive power of the model and the efficiency of policy implementation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z. and S.W.; methodology, X.Z. and K.L.; formal analysis, X.Z.; visualization, X.Z.; data curation, X.Z.; writing—original draft, X.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.Z., K.L., S.W. and X.L.; investigation, X.Z. and K.L.; supervision, S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42401357, and the International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals (CBAS), grant number CBASYX0906.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the providers of all of the data used in this study, and we would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers and editors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kok, S.; Le Clec’h, S.; Penning, W.E.; Buijse, A.D.; Hein, L. Trade-offs in ecosystem services under various river management strategies of the Rhine Branches. Ecosyst. Serv. 2025, 72, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S.; Ghermandi, A.; Portela, R.; Wang, X. Global values of coastal ecosystem services: A spatial economic analysis of shoreline protection values. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 11, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava Gajre, R.; Rahman, M.S.; Ghosh, T.; Friess, D.A. Variations in biophysical characteristics of mangroves along retreating and advancing shorelines. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Hou, L.-J.; Liao, Y.-D. Strengthening efficient usage, protection, and restoration of Yangtze River shoreline. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, D.; Duan, B.Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Chen, S. Evaluation of vegetation restoration effectiveness along the Yangtze River shoreline and its response to land use changes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Yang, S.; Chen, D.; Da, B.; Wu, T.; Liao, Y. Study on definition of shoreline protection scope for the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Hohai Univ. 2022, 50, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondie, A. Improving management of shoreline and riparian wetland ecosystems: The case of Lake Tana catchment. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2010, 10, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.K.; Crawford, T.W.; Islam, S. Shoreline Change Analysis along Rivers and Deltas: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis of the Shoreline Study Literature from 2000 to 2021. Geosciences 2022, 12, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.N.; Gao, J.W.; Xu, S.D.; Tang, S.; Guo, M.T. Establishing an evaluation index system of Coastal Port shoreline resources utilization by objective indicators. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 217, 106003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Medina, Y.G.; Plata-Rocha, W.; Monjardin-Armenta, S.A.; Franco-Ochoa, C. Assessment and Forecast of Shoreline Change Using Geo-Spatial Techniques in the Gulf of California. Land 2023, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.A.B.; Aquino da Silva, A.G.; Reyes Perez, Y.A.; Stattegger, K.; Vital, H. Evaluation of decadal shoreline changes along the Parnaíba Delta (NE Brazil) using satellite images and statistical methods. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 202, 105513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, D.N.; Nikolakopoulos, K.G. Assessment and Quantification of the Accuracy of Low- and High-Resolution Remote Sensing Data for Shoreline Monitoring. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, F.J.; Fernandez-Luque, I.; Aguilar, M.A.; Lorca, A.M.G.; Viciana, A.R. The integration of multi-source remote sensing data for the modelling of shoreline change rates in a mediterranean coastal sector. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 1148–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lloyd, H.; Zhang, Z.W.; Li, D.L. Rapid Reclamation and Degradation of Suaeda salsa Saltmarsh along Coastal China’s Northern Yellow Sea. Land 2021, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbach, S.; Kugel, C.; Lausch, A.; Seppelt, R. Analysis of historic changes in regional ecosystem service provisioning using land use data. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L.M. Dynamic changes in the value of China’s ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, R.P. Securing the future in the anthropocene: A critical analysis of the millennium ecosystem assessment scenarios. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, S.S.K.; van Teeffelen, A.J.A.; Verburg, P.H. Integrating socio-cultural perspectives into ecosystem service valuation: A review of concepts and methods. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 114, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, M.; Ghosh, D.; Mandal, B.; Das, S. Estimating and mapping the value of cultural ecosystem services in an urban landscape context. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 177, 103556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhou, L.F.; Wang, T.L. Assessment of ecosystem services value in Linghekou wetland based on landscape change. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2022, 15, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; Jiang, M.; Xue, Z.; Lu, X.; Zou, Y. A consistent ecosystem services valuation method based on Total Economic Value and Equivalent Value Factors: A case study in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecol. Complex. 2017, 29, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, A.; Egoh, B.N.; Lanzanova, D.; Grizzetti, B.; Bidoglio, G.; Pagliero, L.; Bouraoui, F.; Aloe, A.; Reynaud, A.; Maes, J.; et al. Mapping water provisioning services to support the ecosystem-water-food-energy nexus in the Danube river basin. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 17, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K. Forest restoration efforts drive changes in land-use/land-cover and water-related ecosystem services in China’s Han River basin. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 126, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, E.; Pruscini, F.; Scolozzi, R.; Santolini, R. A forest ecosystem services evaluation at the river basin scale: Supply and demand between coastal areas and upstream lands (Italy). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 37, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.; Zhao, F.; Teng, Y.; Teng, J.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Scale dependency of trade-offs/synergies analysis of ecosystem services based on Bayesian Belief Networks: A case of the Yellow River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Singha, P.; Shahfahad; Mahato, S.; Praveen, B.; Rahman, A. Dynamics of ecosystem services (ESs) in response to land use land cover (LU/LC) changes in the lower Gangetic plain of India. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.X.; Zhang, L.P.; Kuang, R.Y. Shoreline change of Chongming Dongtan and response to river sediment load: A remote sensing assessment. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Council, the People’s Republic of China. Guiding Opinions on Promoting the Development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt Based on the Golden Waterway. 2014. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2014/content_2758494.htm (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- The CPC Central Committee, the state council. Overall Plan of Ecological Civilization System Reform. 2015. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2015/content_2941157.htm (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Elahi, E.; Zhu, M.; Khalid, Z.; Wei, K. An empirical analysis of carbon emission efficiency in food production across the Yangtze River basin: Towards sustainable agricultural development and carbon neutrality. Agric. Syst. 2024, 218, 103994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Ding, J.; An, X.; Wang, Z. An optimization model of sand and gravel mining quantity considering healthy ecosystem in Yangtze River, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhammou, Y.; Alcaraz-Segura, D.; Guirado, E.; Khaldi, R.; Achchab, B.; Herrera, F.; Tabik, S. Sentinel2GlobalLULC: A Sentinel-2 RGB image tile dataset for global land use/cover mapping with deep learning. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Roy, D.P.; De Lemos, H.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.K. A global Swin-Unet Sentinel-2 surface reflectance-based cloud and cloud shadow detection algorithm for the NASA Harmonized Landsat Sentinel-2 (HLS) dataset. Sci. Remote Sens. 2025, 11, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Jia, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, R.; Ren, C.; Wang, Z. Advancing mangrove species mapping: An innovative approach using Google Earth images and a U-shaped network for individual-level Sonneratia apetala detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 218, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, B.; Lu, S.; Gu, G.; Liu, Y. Evaluating the migration of boundary river shorelines and coastal land cover changes for the Beilun River between China and Vietnam. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, V.C. Analytical solutions of one-line model of shoreline change on the evolution of river delta on a coast bounded by solid boundaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 264, 107649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdy, S.I.; Mohamed, M.M. Regional mapping and monitoring land use/land cover changes: A modified approach using an ensemble machine learning and multitemporal Landsat data. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2184500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.C.; Duarte, L.; Teodoro, A.C. Comparative Study of Random Forest and Support Vector Machine for Land Cover Classification and Post-Wildfire Change Detection. Land 2024, 13, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhmousa, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Ghanbari, H.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Ghamisi, P.; Homayouni, S. Support Vector Machine Versus Random Forest for Remote Sensing Image Classification: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6308–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 21010-2017; Current Land Use Classification. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Li, J.; Xie, B.; Gao, C.; Zhou, K.; Liu, C.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, J.; Xie, J. Impacts of natural and human factors on water-related ecosystem services in the Dongting Lake Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.Q.; Feng, H.; Gao, T.Z. The Effect of Empowerment on the Adoption of Soil and Water Conservation Technology in the Loess Plateau of China. Land 2023, 12, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musetsho, K.D.; Chitakira, M.; Ramoelo, A. Ecosystem Service Valuation for a Critical Biodiversity Area: Case of the Mphaphuli Community, South Africa. Land 2022, 11, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Notte, A.; Dalmazzone, S. Sustainability assessment and causality nexus through ecosystem service accounting: The case of water purification in Europe. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Ecol. Econ. 1998, 25, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Wu, J. The Driving Factors of the Tradeoff-Synergistic Relationship Among Forest Ecosystem Service Values in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Forests 2024, 15, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yin, J.; Lv, L. Study on change of ecosystem service value in Nanjing section of the Yangtze River shoreline. Jiangsu Water Resour. 2021, 11, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, S.; Qu, S. Terrain gradient effect of ecosystem service value in middle reach of Yangtze River, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Cheng, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y. Changes of land use and ecosystem service functions in Yangtze river basin from 2000 to 2010. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2017, 26, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Luo, W.; Du, T.; Li, Z.; Lu, Y. Valuation of changes of ecosystem services of Tai Lake in recent 10 years. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, X.; Lü, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, T. Combining spatiotemporal interactions of ecosystem services with land patterns and processes can benefit sensible landscape management in dryland regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Lin, C.; Huang, L.; Qiu, G.; Cheng, N. Did green infrastructure improve water purification ecosystem services in Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration? Evidence from total phosphorus. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Zheng, J.; Cui, X.; He, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, C.; Tan, B. Suitable coverage and slope guided by soil and water conservation can prevent non-point source pollution diffusion: A case study of grassland. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Yang, F. Ecological resilience in water-land transition zones: A case study of the Dongting Lake region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).