Abstract
Drawing on the longitudinal dataset from 262 cities at the provincial tier and higher across China between 2011 and 2022, this research employs the production model to formulate the China Urban Industrial Land Mismatch Index, quantifying the extent of industrial land misalignment across China. It also analyzes its spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and regional differentiation characteristics, and explores the influence of China’s urban industrial land discordance on the advancement of urban ecological modernization. The key insights are outlined below. Firstly, across the entire spectrum of Chinese urban centers, cities from the eastern, central, and western zones, as well as those situated along the Yangtze River and the Yellow River basins, exhibit comparable patterns in industrial land misalignment. The extent of industrial land discordance has diminished, regional disparities have lessened to some degree, and there is an absence of polarization or the Matthew effect. Secondly, the variation in industrial land discordance within cities in the eastern region is the most pronounced, followed by the central region, with the western region showing the least disparity. The greatest contrast in the urban industrial land mismatch is found between the eastern and central regions. The primary driver of the discrepancy in industrial land misalignment across the eastern, central, and western regions is predominantly the ultra-variable density, followed by intra-regional disparities, with inter-regional differences contributing the least. Furthermore, the variation in the industrial land mismatch within cities in the Yangtze River Basin surpasses that within cities in the Yellow River Basin. The disparity in industrial land misalignment between the two follows a pattern of initially increasing, then decreasing, and subsequently rising again. The primary origin of this discrepancy lies within regional variations, followed by ultra-variable density, with inter-regional differences contributing the least. Thirdly, the regression analysis reveals that the discordance in industrial land use across Chinese cities exerts a substantial negative influence on urban ecological evolution. This effect operates through technological innovation and the employment levels in the secondary sector. Fourthly, industrial land discordance significantly hampers urban ecological advancement in the eastern region, shows a negative but statistically insignificant impact in the central region, and has a positive yet inconsequential effect in the western region. Moreover, the misalignment of industrial land exerts a notable suppressive influence on the ecological modernization of cities within the Yangtze River Basin, while it plays a significant role in fostering the ecological modernization of cities in the Yellow River Basin. Fifth, the mismatch of urban industrial land has produced significant negative spatial spillover effects on urban ecological modernization.
1. Introduction
As urbanization continues to accelerate, municipalities across the globe are increasingly confronted with a constellation of challenges, including surging demographic expansion, constrained resource distribution, ecological degradation, and lagging infrastructural development. Within this context, the misallocation of industrial land has crystallized into a pervasive structural dilemma in the domain of urban land governance. This issue not only precipitates direct declines in land-use efficiency but profoundly mirrors the institutional divergences and systemic frictions among nations and regions, particularly with respect to regulatory frameworks, the intensity of governmental intervention, the degrees of market liberalization, and the stages of industrial evolution [1]. In developing nations and transitional economies (such as China, Vietnam, and others), the land tenure system remains insufficiently marketized, granting governments substantial authority over land supply. Industrial land is frequently allocated to enterprises at artificially low costs through non-market instruments, such as administrative allotments and negotiated transfers, aimed at attracting foreign direct investment, fostering industrial agglomeration, and expediting urban industrialization. While this policy trajectory has catalyzed manufacturing expansion and economic growth in the short term, it has concurrently precipitated pronounced resource misallocations. On one front, land distribution is disproportionately skewed toward heavy industry and export-oriented manufacturing, whereas emerging sectors, service industries, and small and medium-sized enterprises often face significant barriers to land access. On another front, the absence of a competitive market-entry mechanism enables “inferior” firms to inefficiently occupy land resources, thereby undermining aggregate land-use efficiency [2].
As resource constraints and environmental problems become more prominent, the extensive growth model driven by factor input is no longer sustainable [3]. The basic national conditions of rapid industrialization and the tendency to overemphasize the gross domestic product (GDP) in performance appraisals have encouraged local governments to support “Industrial cities” by expanding the scale of industrial land at very low environmental pollution costs [4]. This development model ignores the limited nature and ecological constraints of the city’s own development environment, causing industrial land development to approach the “ceiling” of urban development capacity, resulting in a spatial imbalance between the city’s industrial land supply capacity and the actual development intensity [5]. As environmental problems behind rapid economic development become more prominent, the green economy has become a rational development model that coordinates economic development and environmental protection in a harmonious unity, and a spatially balanced industrial land development model is the key to achieving green development [6]. However, scant research has examined the spatiotemporal dynamics of industrial land misallocation and its regional heterogeneities, nor has it systematically investigated the pathways toward achieving urban ecological modernization.
This study enriches the extant corpus by precisely delineating the spatiotemporal patterns of urban industrial land disequilibrium and regional disparities. It further interrogates the ramifications of industrial land misallocation on the trajectory of urban ecological modernization, thereby endeavoring to elucidate concrete pathways toward ecological advancement through the lens of urban land governance. More specifically, this inquiry furnishes several distinctive contributions to the existing body of knowledge. Firstly, from the perspective of the industrial land mismatch (ILM), the specific path for cities to achieve ecological modernization is explored, which not only supplements the research on the ecological effects of industrial land spatial imbalance, but improves the research on the path to achieve urban ecological modernization. Second, from the perspective of input–output, the difference between the potential output and the actual output of the effective input of industrial land resources is used to measure the degree of the ILM. The research scale is also lowered to the prefecture-level city level to examine the spatiotemporal evolution and regional differentiation characteristics of industrial land imbalance in Chinese cities, enriching the research on the evaluation of the ILM at the meso level. Third, not only is the heterogeneity analysis based on the geographical spatial differences between the east, central, and west, but the regional differences are discussed based on the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the Yellow River Basin cities, revealing the differences in the impact of the ILM on urban ecological modernization in different economic belts. The spatial effect of the ILM on urban ecological modernization is further analyzed, enriching the relevant empirical research in the field of ecological effects of the ILM.
To attain the aforementioned objectives, this paper addresses several critical inquiries: How can the mismatch of industrial land be quantified? What are the spatiotemporal distribution patterns and regional variations in the imbalance of industrial land? In what ways does this misallocation influence the realization of urban ecological modernization? Does the impact exhibit heterogeneity across regions with varying resource endowments? What potential pathways exist through which industrial land misalignment affects urban ecological modernization, and is there a spatial dimension to this effect? Resolving these questions enhances theoretical discourse on fostering sustainable development within the framework of market-oriented land factor allocation reforms. The insights derived from this analysis bear significant implications for the policymaking process of government authorities.
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. Literature Review
2.1.1. Research on the Mismatch of Industrial Land Resources
Resource allocation is one of the core issues in economic research. Resource misallocation refers to the inefficiency in the distribution of production factors within an economy, resulting in suboptimal performance and a deviation of output from the idealized equilibrium state [7]. The allocation of land resources can be analyzed and discussed from the aspects of the allocation of agricultural land and construction land, the allocation of construction land indicators between different cities, and the allocation of construction land in cities among different industries and uses [8]. The allocation of urban land for diverse industrial applications is intricately linked to processes such as urban renewal and structural shifts in industrial composition [9]. Considering the availability of data and the fact that many local governments have adopted the “double second-hand” land supply strategy of “low-price transfer” of industrial land and “high-price transfer” of commercial and service land, which has led to the spread and expansion of industrial land, the abandonment and inefficient use of industrial parks [10], the current imbalance in the structure of industrial land and commercial and residential land will inevitably have a significant impact on the urban economic development model and resource and environmental quality [11]. Moreover, in numerous nations, land resources function not only as a production input but serve as a financial instrument for economic activities in advanced economies, including the United States [12], Germany [13], and Norway [14].
Land allocation, as a critical resource, has garnered significant global attention. In China, the issue of land resource misallocation is primarily driven by the government’s pursuit of fiscal revenue. Conversely, the causes of land misallocation in other countries exhibit considerable heterogeneity. In Sweden, public land development is marred by corruption, as decision-making power over land allocation rests with the authorities, hindering efficient resource distribution [15]. In Guatemala, the concentration of land ownership, coupled with complex and costly land transfer procedures, exacerbates the mismatch in land resources [16]. Comparable challenges are observed in countries like Russia, where outdated and inefficient systems contribute to the misallocation of land [17]. For a long time, the differences in factors in space have been recognized as spatial imbalance [18]. However, some scholars believe that the unbalanced regional development caused by differences in economic structure is an objective fact and cannot be regarded as spatial imbalance. Spatial imbalance should be considered from the geographical dimension to determine whether the spatial development intensity and supply capacity are coordinated [19,20]. As such, many scholars have continued this idea and evaluated the spatial balance of land use by examining the matching relationship between spatial supply capacity and development intensity. Some scholars have analyzed the spatiotemporal characteristics and evolution laws of China’s land use spatial balance based on 31 provinces in China [21]. In addition, there are also studies specifically focusing on the characteristics of land spatial balance in specific provinces [22].
In summary, the existing literature on the definition, evaluation methods, and spatiotemporal characteristics of land use spatial imbalance is relatively mature, but it is mostly limited to the spatiotemporal characteristics of the balance of provincial construction land, and lacks an investigation of the mismatch of industrial land at the prefecture-level city level. This study focuses on the mismatch of industrial land between different cities, and mainly explores the supply distortion of urban industrial land. Combined with the resource mismatch theory, the degree of the land resource mismatch is manifested as the difference in the marginal output of land with different uses. The greater the difference in the marginal output, the more serious the land resource mismatch [23].
2.1.2. Research on Urban Ecological Modernization
The theory of ecological modernization emerged as a critical introspection on the trajectory of modernization itself. It crystallized amidst efforts to contend with the ecological degradation engendered by industrialization and to initiate systemic ecological renewal. Throughout the modernization continuum, humanity’s capacity to manipulate the natural world has been relentlessly amplified, gradually transmuting the pristine environment into an increasingly synthetic domain. Although this transformation has bestowed immense conveniences upon society, it has concurrently precipitated grave dilemmas, such as resource exhaustion, environmental contamination, and ecological disintegration. As modernization has advanced, these afflictions have intensified in scale and complexity. In 1962, American scholar Rachel Carson catalyzed widespread environmental consciousness with the publication of Silent Spring; a decade later, the Club of Rome’s seminal report, The Limits to Growth (1972), further galvanized expansive inquiry into the intricate interplay between humanity, the environment, and the broader biosphere.
Giddens clearly pointed out that “ecological threats are the result of socially organized knowledge, which is constructed through the impact of industrialism on the material world.” Ecological modernization aspires to harmonize the inherent tension between environmental stewardship and economic advancement [24,25]. Some scholars contend that ecological innovation, particularly breakthroughs in green technologies, can serve as a catalyst for sustainable economic expansion [26]. Proponents of ecological modernization theory maintain that modernization possesses an intrinsic capacity for self-correction and refinement, thereby rendering sustainable development attainable. Within a hyper-modernized societal framework, industrialization, technological innovation, economic proliferation, and capitalism are perceived not merely as reconcilable with ecological sustainability, but as pivotal engines propelling environmental transformation [27].
The Chinese modern ecological view creatively proposed “modernization of harmonious coexistence between man and nature” on the basis of adhering to the Marxist view of nature, advocating the harmonious unity of man, nature, and modernization. Ecological construction has created green and low-carbon development conditions and foundations for urban modernization with beautiful mountains, rivers, and environment, and has become an important part of modernization construction. This constitutes a superior platform, and is a distinctive feature of urban modernization construction in the new era of China. Ecologicalization has become the basic level and symbol of progress in Chinese urban modernization construction [28]. Ecological construction has completely changed the extensive, pollution-prone, and low-grade construction model, and has enabled modernization construction to move to a high-quality, high-efficiency, and high-level stage.
When Mol and Zhang et al. employed the theoretical prism of ecological modernization to interrogate China’s environmental governance, their primary concerns revolved around several pivotal questions: whether China’s contemporary environmental reforms could be apprehended as instances of ecological modernization; what idiosyncratic features these reforms exhibit, and how China’s developmental pathways align with or depart from the ecological modernization archetypes established in Europe [24,29]. At present, urban ecology is often considered to be a green development model with low consumption and low pollution, which optimizes the original ecological pattern and improves the level of environmental quality in the process of urban development. Some scholars have constructed an urban ecological index system based on the composition of the ecosystem [30] and the characteristics of the ecosystem, from the aspects of the structure, function, and coordination of the urban ecosystem [31]. In addition, some studies have constructed a corresponding evaluation system based on the evaluation index system of ecosystem health, mainly from the aspects of the vitality, elasticity, and resilience of the urban ecosystem [32]. At present, the relevant research on the coupled and coordinated development of urban modernization construction and ecological construction has also made certain progress, such as urban low-carbon and new urbanization [33], economic development and resources and environment [34], urbanization and the ecological environment [35], and urban competitiveness and the ecological environment [36].
2.1.3. Research on the Impact of the Industrial Land Resource Mismatch on Urban Ecological Modernization
The academic community has confirmed that industrial land is an important factor affecting green growth. For example, the rapid expansion of industrial land has led to a great leap forward in spatial urbanization based on land development, which contains the risks of reduced land use efficiency and increased carbon emission intensity, which is not conducive to urban green economic growth [37,38,39,40], and significantly decelerates the trajectory of urban ecological modernization [41].
However, the predominant focus of the existing scholarship has been on the direct repercussions of industrial land expansion, with scant attention paid to the internal structural imbalances within land allocation. In fact, the misalignment of industrial land—such as the occupation of substantial land resources by high energy-consuming, low-output industries, the constraint of high-end manufacturing and green sectors by inadequate land supply, or the disjunction between industrial land use and the overarching spatial organization of the city—remains prevalent across various urban typologies. This imbalance not only exacerbates land use inefficiencies and wastage but impedes energy utilization efficiency and fosters heightened pollution emissions, thereby obstructing the deeper endogenous drivers of ecological modernization [42,43,44].
More crucially, the pathways through which industrial land imbalance influences urban ecological modernization are likely to entail intricate, multi-layered mechanisms. For instance, from the standpoint of resource allocation, such imbalances undermine the city’s overall green production efficiency; from the perspective of innovation incentives, the misalignment of land resources diminishes the spatial foundations necessary for the emergence of green industries, thereby stifling technological advancements and impeding the broader green transformation; and from the lens of environmental governance, the concentrated clustering of inefficient industrial land exacerbates local environmental burdens and amplifies governance costs [45,46,47]. These mechanisms have yet to be thoroughly elucidated and empirically substantiated in the existing studies, leaving significant gaps in the scholarly understanding of the pivotal role that land factor allocation plays in the trajectory of urban ecological modernization.
Consequently, this study investigates the spatiotemporal dynamics and regional variations of the industrial land mismatches across Chinese cities. By examining the intricate interplay between industrial land allocation structures and the ecological modernization process, it aims to deepen the identification of underlying mechanisms, to enrich the theoretical framework, and to incorporate the heterogeneous characteristics of multi-scaled and diverse urban contexts. This approach further explores the spatial spillover effects of urban industrial land on ecological modernization, complemented by a comprehensive empirical analysis. Such an endeavor will not only broaden the applicability of ecological modernization theory within the context of cities in developing economies but provide empirical insights that can inform the development of more nuanced land resource management strategies and policies for green transformation.
2.2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
The spatial imbalance of industrial land is a state in which the intensity of industrial land development does not match the supply capacity. This causes the industrial economic development to exceed or underutilize the supply capacity. That is, spatial economic activities are not divided and allocated according to the comparative advantages of supply capacity. This will lead to incoordination between economic layout and resource and environmental carrying capacity, resulting in the coexistence of resource waste due to insufficient effective development in space and environmental pollution caused by overdevelopment [19,48]. This continuous imbalance will inevitably lead to ecological efficiency loss. The spatial mismatch of industrial land violates the principle of efficient resource allocation, resulting in the coexistence of relative shortage and relative surplus of industrial land between cities [49].
The spatial imbalance of industrial land is manifested in the coexistence of overdevelopment and underdevelopment. The impact of the two on urban ecological modernization is explained with the help of spatial equilibrium theory. From the perspective of spatial equilibrium theory (Figure 1), the industrial land supply capacity curve (S) and the development intensity curve (D) move with the changes in development cost (P) and development quantity (Q). In theory, there is a threshold for the development capacity of industrial land, so the supply curve is concavely inclined upward and infinitely approaches the limit development capacity [22]. In the figure, represents the equilibrium point of spatial development and supply, and the corresponding is the development cost when the equilibrium state is reached.
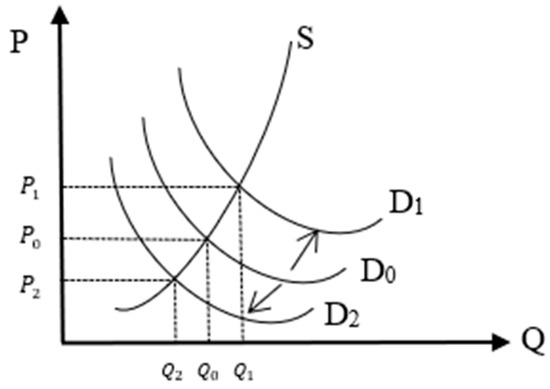
Figure 1.
Equilibrium Theory Analysis.
For overdeveloped areas (Figure 1), the main manifestation is that the intensity of industrial land development exceeds its supply capacity. According to spatial equilibrium theory, when the demand for regional industrial land development is strong, the development intensity curve moves upward from to . At this time, the new equilibrium point is (,). The supply curve becomes steeper from to , which means that the cost of land development per unit area increases, which is often manifested as an increase in social environmental costs and the negative environmental effects of economic growth [19]. At this time, represents the spatial imbalance point of overdevelopment of industrial land. For underdeveloped areas (Figure 1), the main manifestation is that the intensity of industrial land development is lower than the supply capacity. According to spatial equilibrium theory, when the spatial development intensity of industrial land decreases, the demand curve moves to the lower left by , and the development cost and development quantity drop to and , respectively. At this time, represents the spatial imbalance point of underdeveloped industrial land. Similarly, taking the land development breadth index, which has the largest contribution rate to the intensity of industrial land development, as an example, when the land development breadth index continues to decrease, it means that the supply of industrial land in the region continues to decrease. This may lead to insufficient supply of industrial land and the inability to support industrial agglomeration, expand the negative externalities of economic agglomeration, cause urban crowding effects, and aggravate environmental pollution, thereby damaging the green economy [50] and inhibiting the realization of urban ecological modernization. Based on this, this study proposes Hypothesis 1.
Hypothesis 1:
Industrial land misallocation hinders the realization of urban ecological modernization.
At present, local governments are one of the important subjects of the innovation-driven development strategy and play a leading role in promoting innovation. However, under the “land-based development” model, local governments often focus more on short-term profits when supplying industrial land. A large number of industrial enterprises with low technology content and backward processes have survived and made profits because of the relaxed industrial land transfer method and preferential entry conditions. After obtaining a certain profit, these enterprises are prone to lack the motivation and pressure for technological innovation and tend to continue to use the original technology, which inhibits their innovation vitality. At the same time, the subsidized infrastructure construction provided by local governments when “using land to attract investment” has a capitalization effect, which also provides biased conditions for them to maintain and promote the existing land supply strategy. The two-way feedback between the two has caused the local government’s biased behavior of “focusing on infrastructure and neglecting technology” to continue to deepen, affecting the improvement of innovation capabilities [51]. Relevant studies have shown that emerging technologies are the root cause of improving energy efficiency, and have a direct impact on carbon emission efficiency and the ecological environment [52]. Specifically, when a region has a high technological innovation capability, it can gradually eliminate old technologies with backward technology, low output value, and resource consumption. Instead, it can vigorously develop emerging technologies with advanced technology, high output value, and environmental friendliness to reduce unnecessary resource consumption and carbon emissions in the production and construction process [53], thereby achieving urban ecological modernization. Based on this, this study proposes Hypothesis 2.
Hypothesis 2:
Industrial land mismatch affects urban ecological modernization through technological innovation.
The ILM can expand the scale of industrial land, reduce industrial land prices, and increase urban employment opportunities for agricultural population. In order to win development opportunities, local governments use the competitive advantage of industrial land transfer prices to attract further investment. Industrial parks are built to gather industrial enterprises and recruit a large number of employees to provide employment opportunities for migrant workers, attracting labor to gather in industrial industries. Labor concentration may lead to negative externalities such as rising congestion costs and excessive production scale, excessive consumption of energy and reduced utilization rate [54], and failure to utilize the development of the ecological environment, thereby hindering the realization of urban ecological modernization. Based on this, this study proposes Hypothesis 3.
Hypothesis 3:
Industrial land mismatch affects urban ecological modernization by attracting secondary industry employees.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Resource
Based on data availability and completeness, this paper selects panel data of 262 cities at or above the prefecture level in China from 2011 to 2022 as the research basis. The industrial land area data comes from the “China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook”, and other input–output data, and control variable data are all from the “China City Statistical Yearbook” and the statistical yearbooks, statistical bulletins, and WIND databases of various prefecture-level cities.
3.2. Definition of Variables
3.2.1. Explained Variables: Urban Ecological Modernization (EM)
Urban development is inherently constrained by the natural ecological environment. Cities cannot function in isolation from the broader web of nature. The finite resources, spatial limitations, and environmental capacity of the planet stipulate that the development trajectory of modern industrial cities is fundamentally unsustainable, inevitably leading to what is known as the “limits to growth”. It is this intrinsic unsustainability of modern industrial urbanism that has precipitated the current global ecological and environmental crises, emerging as a “bottleneck” in the evolution of human urban civilization. If the ongoing urbanization process persists along the conventional path of industrial modernization, the natural ecosystem will be unable to sustain the growth of human urban systems, risking the collapse of the Earth’s ecological balance. This predicament compels modern industrial cities to undergo ecological transformation as a prerequisite for securing the sustainable future of human urban civilization.
The harmonious coexistence of man and nature is a distinctive feature [55]. On the one hand, in the early stages of modernization, the relatively extensive development model caused serious environmental problems and aggravated the resource and environmental pressures in cities [56]. Urban ecological modernization refers to the process of transforming contemporary industrial cities into ecologically integrated urban entities. Central to this process is the infusion of “ecological” principles into the concept of “modernization”, alongside the establishment of urban technological infrastructures, economic production models, and socio-ecological systems that align with the imperatives of natural ecological balance. By enhancing the ecological efficiency of urban systems, this transformation seeks to mitigate and ultimately avert the adverse impacts urban systems exert on the natural environment, fostering a harmonious and coordinated evolution between cities and nature. Grounded in the Marxist perspective on nature, China’s modern ecological philosophy introduces the innovative concept of the “modernization of harmonious coexistence between humanity and nature”, advocating for the seamless integration of human society, nature, and modernization. Ecological construction, in this context, has laid the groundwork for green and low-carbon urban development, fostering the creation of cities that are visually and environmentally appealing, while simultaneously contributing to the modernization process. This approach has become a defining feature and foundational platform for urban modernization in China’s new era, with ecological integration now symbolizing the fundamental progress of urban modernization in the country [30].
Ecological modernization evaluation pertains to the assessment of the dynamic interplay between modernization and the natural environment, constituting a critical component of the broader modernization evaluation framework. This evaluation focuses on the process of ecological modernization, aiming to uncover the underlying principles governing this transformation and to inform the development of pertinent strategies. The generalized theory of ecological modernization serves as the foundational theoretical framework for such evaluations. The ecological modernization index primarily captures the alterations in measurable environmental variables, such as ecological transformations, and the interrelationships between ecological economics and ecological society. In practice, the environmental domain encompasses numerous quantifiable indicators, alongside certain qualitative measures; therefore, the ecological modernization index reflects only a segment of the broader ecological modernization phenomenon, rather than providing a comprehensive depiction of it. In recent years, scholars have proposed three methods for measuring the land resource mismatch. First, from an economic perspective, the difference in marginal output of land resources among different entities, sectors, and regions is used as the theoretical starting point, and the “distortion coefficient” of factor prices is used as the measurement standard [57]. Second, from the institutional background of China’s “development through land”, the mismatch of land resources is measured by the distortion of the supply structure of industrial land and commercial and residential land [58]. Third, from the perspective of input–output, the mismatch is measured by the difference between the potential output of effective land resource input and the actual output [59]. The third method combines the resource mismatch theory from an economic perspective with the basic national conditions of China’s government intervention in land transfer, providing good experience for this study.
Based on the existing research [60,61], this study constructs an urban ecological modernization index system from six dimensions. Considering data acquisition and operability, the index system finally constructed includes six dimensions and ten specific measurement indicators (Table 1). Building on the research of [60,62], the annual mean concentration of PM2.5 and the frequency of inversion days are employed as indicators of air pollution. Existing methodologies for assessing pollution reduction [61,63] are utilized to evaluate the diminution of pollutants via industrial sulfur dioxide emissions, while energy consumption is quantified through energy use per unit of GDP. Drawing from the prior studies [60], the dimension of pollution treatment is gauged by the centralized processing rate of sewage treatment plants and the rate of non-hazardous disposal of municipal waste. The urban greening dimension is assessed by indicators such as the green coverage rate of developed areas, the per capita park green space, and the ratio of environmental protection investment to GDP. Lastly, the dimension of green technology is represented by the volume of green patent applications.

Table 1.
Urban ecological modernization indicator system.
3.2.2. Core Explanatory Variables: Industrial Land Mismatch (ILM)
Based on the existing research [54], this study measures the spatial mismatch of industrial land from the perspective of input–output and constructs a production function that includes land factors. The specific formula is shown in Formula (1):
where,
represents industrial output value,
represents technological level,
represents capital,
represents labor,
represents land, and
, , and represent the elasticity coefficients of capital, labor, and land, respectively.
In order to avoid heteroskedasticity and multicollinearity, the model is logarithmically processed, as shown in Formula (2):
where,
, , , , , , , and are consistent with Formula (1).
The contribution rate of industrial land to economic growth is shown in Formula (3):
where,
and represent the growth rates of industrial land and industrial output value, respectively, and
is the contribution rate of industrial land to economic growth.
By analyzing the deviation between the actual allocation of industrial land and the optimal allocation, the mismatch degree of industrial land is calculated. The specific ideas are as follows.
First, based on the contribution rate of industrial land to economic output, the output value contributed by the expansion of industrial land in each city is calculated, as shown in Formula (4):
where,
represents the industrial output value of the expansion of industrial land in city ,
represents the contribution rate of industrial land to economic growth, and
represents the industrial output value of city .
Second, based on the proportion of the output value contributed by the expansion of industrial land in different cities to the output value contributed by the expansion of industrial land in all sample cities, the ideal proportion of industrial land used by each city is calculated, as shown in Formula (5):
where,
represents the ideal proportion of industrial land used by each city, and
represents the industrial output value of the expansion of industrial land in city .
Third, based on the ideal proportion of industrial land used by each city and the total amount of industrial land allocated, the theoretical optimal allocation of industrial land for each city is calculated, as shown in Formula (6):
where,
represents the optimal allocation of industrial land in city , and
represents the total allocation of industrial land in all sample cities.
Finally, the difference between the actual allocation and the optimal allocation is compared to calculate the mismatch degree of industrial land, as shown in Formula (7):
where,
represents the mismatch degree of industrial land in city , and
represents the actual allocation of industrial land in city .
When > 0, it means that the actual allocation of industrial land is greater than the optimal allocation, which is an excess mismatch.
When < 0, it means that the actual allocation of industrial land is less than the optimal allocation, which is a shortage mismatch.
3.2.3. Control Variables
Referring to the existing relevant studies [64,65], the following control variables are selected. First, the population development level is represented by the natural population growth rate. The natural population growth rate is closely related to social and historical development, and is also an important factor affecting urban ecological modernization. Second, the level of economic development is measured by GDP per capita. Third, the level of opening up to the outside world is represented by the proportion of actual utilization of foreign capital in GDP. The level of economic development can significantly affect the city’s environment and further affect the city’s ecological modernization. Fourth, the urbanization level, measured by the urbanization rate, is measured by the ratio of the urban population to the total regional population. On the one hand, the advancement of urbanization has led to the transfer of labor from rural to urban areas, and the high technological content of urban enterprises can improve the efficiency of labor allocation, thereby accelerating the realization of urban ecology. On the other hand, the continuous improvement of the urbanization level can increase energy consumption and pollutant emissions, thereby inhibiting the realization of urban ecological modernization. Therefore, the relationship between the urbanization level and urban ecological modernization is uncertain. Fifth, industrial structure, measured by the proportion of the secondary industry output value to GDP. The industrial structure can explain that, when the proportion of secondary industry in the local economic structure is too high, labor-intensive enterprises and capital-intensive enterprises occupy the market, and emit a large amount of waste gas in production, which is not conducive to regional environmental health and hinders the realization of urban ecological modernization.
3.2.4. Mechanism Variables
First, technological innovation refers to the way in which the innovator develops intellectual property into commodities through new processes and technologies, and trades them in the market [66,67]. Some scholars use the number of patent authorizations to represent technological innovation capabilities, but the number of patent authorizations is easily affected by various factors and has time lags. Therefore, based on the relevant research [68], this study uses R&D expenditure to represent the level of technological innovation. Second, drawing on the relevant research [69], employment in the secondary industry was selected as the discussion mechanism, and it was measured by the number of employees in the secondary industry..
3.3. Model
3.3.1. Baseline Model
In order to study the impact of the industrial land mismatch on urban ecological modernization, this paper uses a panel regression model for empirical analysis. The model design is shown in Formula (8):
where,
and represent cities and years, respectively,
represents the level of urban ecological modernization of city in year ,
represents the industrial land mismatch index,
represents a series of control variables,
and represent city fixed effects and year fixed effects, respectively, and
represents the random error term.
3.3.2. Spatial Model
Due to geographical proximity and technological relevance, urban development has spatial dependence characteristics. At the same time, the mismatch of industrial land in a city not only directly affects the ecological modernization level of the city, but has a spatial spillover effect on the ecological modernization level of neighboring cities.
Therefore, this study introduces a spatial econometric model to explore the impact of the spatial mismatch of industrial land on urban ecological modernization. Common spatial econometric models include the spatial Durbin model, the spatial error model, and the spatial lag model. In view of this, referring to the relevant literature [70], a generalized spatial econometric model is set, as shown in Formula (9):
where,
and represent cities and years, respectively,
represents the spatial autocorrelation coefficient of urban ecological modernization level,
represents the level of urban ecological modernization of city i in year t,
represents the industrial land mismatch index,
represents a series of control variables,
and represent city fixed effects and year fixed effects, respectively,
represents the random error term, and
represents the inverse of the spatial geographic distance matrix.
4. Results
4.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of the Industrial Land Mismatch in Chinese Cities
Considering the spatial correlation characteristics of the industrial land mismatch, in order to accurately estimate the overall distribution of the industrial land mismatch, an extended distribution dynamics model is adopted, and Kernel estimation and Markov chain analysis are used in combination. The distribution pattern and change trend of the industrial land mismatch in China are described, and the dynamic changes of the relative positions of the industrial land mismatch in various regions and the probability of development transfer are clarified.
4.1.1. Kernel Density Estimation of the Industrial Land Mismatch
Figure 2 illustrates the kernel density estimation trajectory of the evolution of the urban ILM across China from 2011 to 2022. Broadly speaking, the degree of the mismatch has undergone pronounced cyclical oscillations, exhibiting an evolutionary pattern characterized by “overall decline—periodic rebound—further attenuation”. Several critical inflection points punctuate the curve, vividly capturing the entangled influences of multiple forces, including economic structural realignments, reforms in the land tenure system, and the metamorphosis of local governmental behaviors. First, during the period from 2011 to 2015, the kernel density curve exhibited a pronounced leftward shift, with the principal peak progressively concentrating within the zone of the lower mismatch, signifying a sustained decline in the degree of urban industrial land misallocation. This trajectory can be largely attributed to two forces: on one hand, following the 2008 financial crisis, the central government intensified macroeconomic regulation and vigorously advanced the “economical and intensive land use” initiative, prompting local authorities to expedite the rectification and reclamation of inefficient and idle industrial parcels; on the other hand, the structural deceleration of economic growth and mounting pressures for industrial transformation compelled local governments to enhance resource allocation efficiency, gradually constraining the once-prevalent model of extensive land expansion. Second, between 2016 and 2018, the kernel density curve underwent a conspicuous rightward displacement, accompanied by a flattening of the main peak and an expansion in distributional breadth, indicating a phase of partial recovery in the mismatch levels and a widening of regional disparities—marking the second critical inflection point. This reversal is deeply rooted in regional divergences in the execution of early supply-side structural reforms, particularly regarding capacity reduction and inventory de-stocking policies. To mitigate intensifying economic headwinds, several localities reverted to strategies of low-cost land supply and aggressive investment solicitation, thereby triggering a reemergence of land resource misallocation. Simultaneously, the enduring reliance of local governments on land transfer revenues fostered short-termist behaviors, exacerbating inefficiencies and further entrenching imbalances in spatial resource distribution. Thirdly, from 2019 to 2022, the kernel density curve shifted leftward once more, with a marked elevation of the principal peak and a discernible contraction in the curve’s spread, reflecting a continued alleviation of the mismatch and a narrowing of regional heterogeneity. During this interval, the state robustly promoted market-oriented reforms in factor allocation and promulgated a series of policies targeting the transfer, repurposing, and redevelopment of underutilized industrial land, thereby optimizing the mechanisms of land supply and demand. Concurrently, the reinforcement of green development assessment frameworks, alongside the articulation of the “dual carbon” objectives, substantially curtailed the spatial proliferation of high-pollution, high energy-consuming industries, elevated the proportion of efficient and high-quality land supplies, and, in turn, facilitated the systemic optimization of urban land use structures. In terms of distributional morphology, the kernel density curve consistently exhibited a unimodal structure throughout the study period, with no emergence of bifurcated or multimodal patterns. This suggests that, despite cyclical fluctuations in the mismatch levels, pronounced polarization did not materialize, and the degree of divergence in the industrial land mismatch across cities remained relatively moderate. Such a trend underscores the initial efficacy of initiatives aimed at constructing a unified national land market and advancing regional coordinated development. Nevertheless, the volatility observed in certain years signals the necessity for heightened vigilance regarding latent risks stemming from uneven regional development and disparities in policy execution.
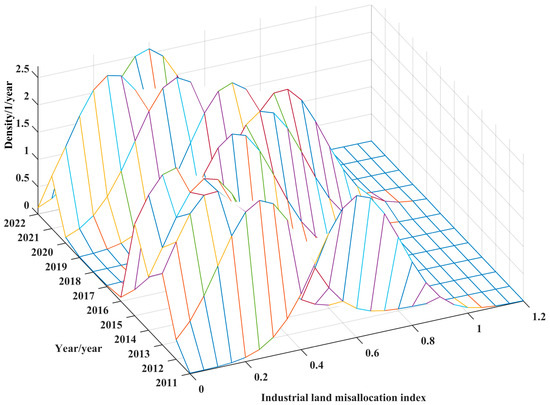
Figure 2.
Kernel density estimation of Chinese urban samples.
Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 present the kernel density estimation outcomes for the urban ILM across eastern, central, and western China from 2011 to 2022. Across all three macro-regions, several shared tendencies emerge: a general attenuation of the mismatch intensity, a convergence in distributional disparities, and an absence of pronounced polarization. Specifically, the kernel density curves underwent a pronounced leftward shift between 2011 and 2015, a transient rightward drift from 2016 to 2018, followed by a renewed leftward migration during 2019–2022. Cumulatively, this trajectory reflects a progressive alleviation of the mismatch severity. The apex of the primary peak exhibited a “first-decline-then-recovery” pattern, accompanied by a gradual broadening of the distributional span, suggesting that, as the mismatch diminished, inter-regional disparities likewise contracted. Throughout, the unimodal nature of the distribution persisted, evidencing no emergent bifurcation or structural schism in industrial land allocation across cities.
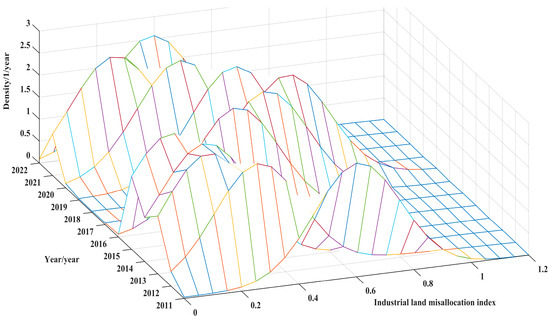
Figure 3.
Kernel density estimation of cities in the eastern region.
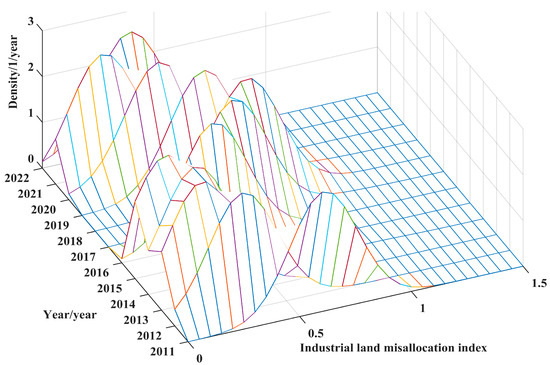
Figure 4.
Kernel density estimation of cities in the central region.
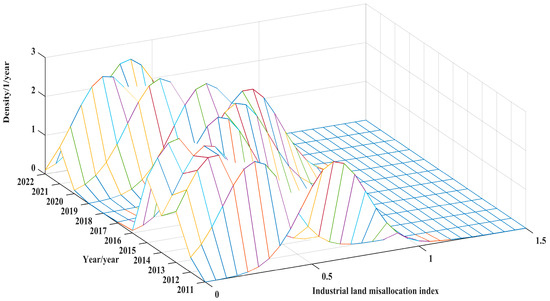
Figure 5.
Kernel density estimation of cities in the western region.
The underlying mechanisms propelling this evolutionary trend derive from the synergistic interplay of multiple forces under the ongoing refinement of resource allocation efficiency. On one front, the deepening marketization of land governance and the recalibration of land supply systems have amplified factor price signals, facilitating the rechanneling of land resources toward higher marginal productivity sectors across urban systems. Concurrently, the regional coordinated development agenda has enhanced factor mobility and spatial connectivity, unleashing spatial spillover effects that have bolstered the allocative efficiency of less advantaged areas, particularly in the central and western hinterlands. Furthermore, industrial restructuring, the ascendance of emerging industries, and the expansion of infrastructure networks have intensified land utilization rates while mitigating geographical friction. Augmented urban governance capacities and advances in scientific spatial planning have likewise curtailed instances of allocation inefficiency. Although the overarching trendlines are broadly consistent among the three regions, the internal drivers exhibit notable heterogeneity: the eastern region predominantly harnesses spontaneous market mechanisms for optimization, the central region pivots around policy-guided industrial relocation, and the western region chiefly leverages strategic state investments and institutional inducements to elevate efficiency. These regional distinctions reveal that, under the broader framework of unified market system construction, different territories have realized dynamic rectifications of the ILM through differentiated yet convergent trajectories, encapsulating a pattern of “coordinated convergence amid path dependence”.
Figure 6 and Figure 7 illustrate the evolutionary trajectories of the kernel density estimations of the urban ILM within the Yangtze River Basin and the Yellow River Basin from 2011 to 2022. Both regions exhibit a broadly analogous pattern characterized by an overarching decline in the mismatch severity, a convergence of regional disparities, and the absence of pronounced polarization. In terms of distributional shifts, the kernel density curves in both basins underwent a phased fluctuation: a leftward displacement from 2011 to 2015, a rightward adjustment during 2016–2017, another leftward realignment in 2018, a minor rightward oscillation between 2019 and 2020, followed by a definitive leftward shift from 2021 to 2022. The overarching movement towards the left underscores the persistent alleviation of the ILM. Regarding distributional morphology, the rising prominence of the main peak coupled with the gradual broadening of the curve suggests that, as the mismatch diminished, inter-city allocation efficiency differentials progressively converged. Simultaneously, the enduring unimodal structure without emergent multi-peaked patterns indicates the absence of extreme spatial bifurcation or polarization. Although the overall tendencies between the two basins align, divergences persist in the tempo and volatility of the adjustment. The Yangtze River Basin demonstrates a relatively stable, incremental mitigation of the mismatch with limited amplitude of oscillations; whereas, the Yellow River Basin manifests more pronounced periodic perturbations, indicative of a non-linear and fragmented adjustment trajectory. The deeper causality behind these divergences lies in stark contrasts in industrial composition, economic underpinnings, and spatial governance capacity. As the principal axis of China’s economic dynamism, the Yangtze River Basin benefits from a more mature market architecture, denser industrial agglomerations, and superior land-use efficiencies, underpinned by a robust endogenous resource allocation mechanism. Conversely, the Yellow River Basin contends with structural handicaps, such as a weaker industrial base, more rigid land endowments, and underdeveloped cross-regional coordination frameworks, thereby relying heavily on exogenous policy interventions and infrastructural augmentation to recalibrate the mismatch. Moreover, the Yangtze River Economic Belt initiated integrative policies earlier and more systematically, forging a relatively cohesive framework for factor mobility and spatial governance. By contrast, the Yellow River Basin lagged in institutional consolidation, resulting in suboptimal resource circulation and slower land-use responsiveness. This divergence in the evolutionary cadence of the mismatch accentuates the pivotal role of institutional quality, economic density, and factor mobility elasticity in sculpting regional land allocation efficiencies.
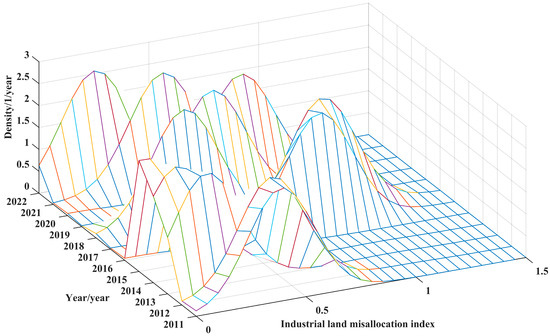
Figure 6.
Kernel density estimation of cities in the Yangtze River Basin.
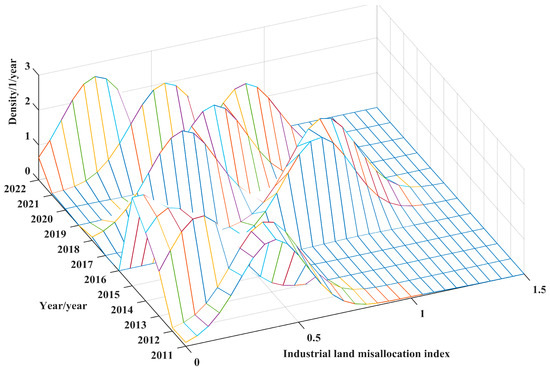
Figure 7.
Kernel density estimation of cities in the Yellow River Basin.
4.1.2. Markov Chain Analysis of the Industrial Land Mismatch in Chinese Cities
- (1)
- Prediction of Long-term Evolution Trend Based on the Traditional Markov Chain Model
While the kernel density curve captures the distributional contours and dynamic oscillations of the ILM, it fails to depict its long-term evolutionary trajectory. To address this, this study adopts a traditional Markov chain model to forecast the mismatch transitions across Chinese cities. The mismatch degrees are segmented into four categories (I-low, II-medium–low, III-medium–high, IV-high) via the quartile method, and a one-period lag transition probability matrix is constructed (Table 2). The findings suggest strong path dependence: most cities retain their initial state after one year. Notably, 56.32% of the low-mismatch cities remain stable, though 33.21% leap to a medium–high level, exposing latent volatility. Over half (55.05%) of the medium–low cities regress to a low mismatch, underscoring poor stability. Medium–high cities exhibit the greatest mobility, with nearly symmetrical upward and downward shifts, while the high-mismatch cities show a significant corrective trend—over 67% transition downward, with 32.78% directly falling to medium–low levels. These dynamics stem from phased regulatory adjustments in land supply by local governments, industrial upgrading pressures necessitating efficiency gains, and occasional leapfrogging by the medium- and low-mismatch cities driven by aggressive investment strategies.

Table 2.
Traditional Markov probability transfer matrix (k = 4).
- (2)
- Long-term Evolution Trend Prediction Based on the Spatial Markov Chain Model
To compensate for the traditional Markov chain’s neglect of spatial spillover dynamics, this study incorporates a spatial Markov chain model to examine how neighboring cities’ mismatch levels influence the mobility of the local industrial land mismatches. By introducing spatial lag terms, a spatial transition probability matrix is constructed, comparing shifts across different neighborhood mismatch backgrounds (k = 1–4), as detailed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Spatial Markov transition probability matrix.
The results reveal that the adjacent cities’ mismatch degrees markedly shape the stability and transition pathways of local states. When neighboring cities exhibit a low mismatch (k = 1), the probability of local cities escalating to a medium–high mismatch surges to 48.45%. Conversely, under medium–low neighboring conditions (k = 2), the probability of local cities maintaining a low mismatch rises sharply to 85.16%. By contrast, proximity to medium–high or high-mismatch cities (k = 3, k = 4) amplifies the likelihood of upward jumps for low-level cities and intensifies “path locking” among high-level cities. Overall, the ILM demonstrates strong spatial interdependence and pronounced path sensitivity, with neighborhood contexts acting as pivotal external constraints on transition dynamics. Underlying these patterns are several mechanisms. First, land-use strategies across cities often exhibit competitive imitation, making neighboring behavior a critical “reference system” for local adjustments. Second, industrial linkages, infrastructure, and labor markets create spatial “mismatch agglomeration” or “low-mismatch diffusion” effects. Third, the deficiencies in regional coordination and cross-jurisdictional governance magnify the externalities of neighboring policies, exacerbating spatial contagion. In essence, spatial adjacency not only reinforces the inertia of the ILM but fosters inter-regional evolutionary coupling, underscoring the imperative of transcending a localized focus and advancing coordinated regional governance in mismatch rectification.
4.2. Regional Differentiation Characteristics of the Mismatch Degree of Urban Industrial Land in China
In order to further explore the regional differentiation of the mismatch degree of urban industrial land in China, the Dagum Gini coefficient decomposition method is used to decompose it spatially.
4.2.1. Overall Gap
Based on the Dagum Gini coefficient calculation formula, the overall difference in the mismatch degree of urban industrial land in China from 2011 to 2022 is measured, and the results are shown in Figure 8. The overall gap in the mismatch degree of industrial land in China increased from 0.0170 in 2011 to 0.1269 in 2015, dropped sharply in 2016, and began to rise slowly in 2017, rising to 0.0570 in 2021, and fell in 2022. This shows that the overall difference in the mismatch degree of industrial land in China from 2011 to 2022 fluctuated greatly.
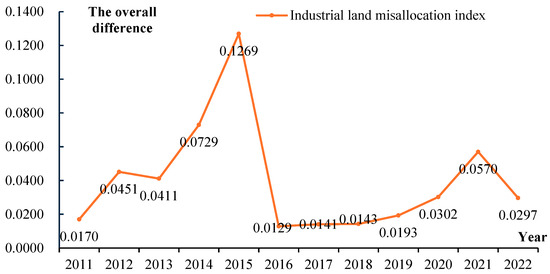
Figure 8.
Overall differences in the degree of ILM in China.
4.2.2. Decomposition Based on Samples from the East, Central, and West
- (1)
- Intra-regional and Inter-regional Differences
Table 4 reports the intra-regional and inter-regional differences in the degree of the urban ILM in the eastern, central, and western regions from 2011 to 2022. The results show that there are differences in the Gini coefficients within the region. The difference in the degree of the urban ILM in the eastern region is the largest, with an average Gini coefficient of 0.0523. The second is the central region, with a Gini coefficient of 0.0373. Finally, the western region has an average Gini coefficient of 0.0252. However, the average Gini coefficients of all the regions are between 0.01 and 0.04, and the Gini coefficients are relatively small. The main reason for this phenomenon is that the degree of the ILM between different cities within the region is relatively small and relatively balanced. The degree of the urban ILM in the eastern, the central, and the western regions showed a fluctuating trend of first rising, then falling, and then rising again. During the observation period, the regional gap in the degree of the urban ILM between the eastern and central regions was the largest, with an average Gini coefficient of 0.0454. The regional differences in the degree of the urban ILM between the eastern and western regions were large, with an average Gini coefficient of 0.0388. The regional differences in the degree of the urban ILM between the central and western regions were relatively small, with an average Gini coefficient of 0.0316. From the perspective of evolution, the gap between the urban areas in the eastern and central, eastern and western, and central and western regions fluctuated between 0.01 and 0.07, and the average annual growth rates of their Gini coefficients were 0.39%, 0.36%, and 0.33%, respectively, all of which were on an upward trend.

Table 4.
Intra-regional and inter-regional differences in the degree of ILM in eastern, central, and western cities.
Table 4 reports the intra-regional and inter-regional differences in the degree of the ILM in cities in the Yangtze River Basin and the Yellow River Basin from 2011 to 2022. The results show that there are differences in the Gini coefficients within the region, and the difference in the degree of the ILM in cities in the Yangtze River Basin is greater, with an average Gini coefficient of 0.0772. The difference in the degree of the ILM in cities in the Yellow River Basin is smaller, with an average Gini coefficient of 0.0650. However, the average Gini coefficients of all regions are between 0.01 and 0.08, and the Gini coefficients are relatively small. The main reason for this phenomenon is that the difference in the degree of the ILM between different cities within the region is relatively small. During the observation period, the regional differences in the degree of the ILM between cities in the Yangtze River Basin and cities in the Yellow River Basin showed a trend of first rising, then falling, and then rising again. The average Gini coefficient was 0.0718, ranging from 0.005 to 0.450, and the average annual growth rate of the Gini coefficient was 68.98%.
- (2)
- Sources of Regional Disparity and its Contribution
Based on the eastern, central, and western samples, the mismatch of industrial land in China was decomposed to obtain the sources of regional disparity and its contribution rate, as shown in Figure 9. During the sample period, the average annual difference in the mismatch of urban industrial land in the eastern, central, and western regions was 0.0139, and the average annual contribution rate was 34.64%. The average annual difference between the regional differences was 0.0087, and the average annual contribution rate was 26.15%. The average annual difference in the super-variable density was 0.0174, and the average annual contribution rate was 39.21%. It is found that the source of the difference in the urban ILM in the eastern, central, and western regions is mainly the super-variable density, followed by regional differences, and the difference between regions accounts for the smallest proportion. The evolution trend of net differences within the region shows a trend of slow increase in fluctuations, the super-variable density shows a trend of increasing in fluctuations, and the contribution of inter-regional differences shows a trend of decreasing in fluctuations. Through comparison, it is found that reducing the mismatch of urban industrial land requires paying attention to reducing the relative gap between cities in the eastern, central, and western regions, rationally allocating resources for land use, and promoting regional coordinated development.
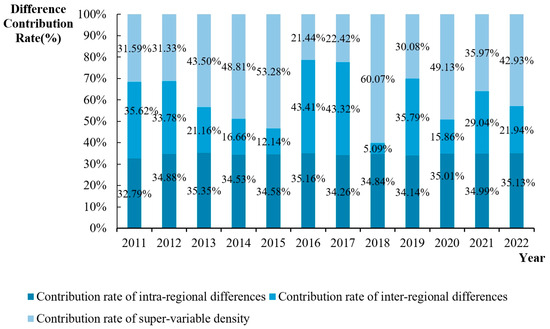
Figure 9.
Time series evolution of the contribution rate of regional differences in the degree of the urban ILM in the eastern, central, and western regions.
Based on the samples of cities in the Yangtze River Basin and the Yellow River Basin, the mismatch degree of industrial land in China was decomposed, and the sources of regional disparity and its contribution rate were obtained. The results are shown in Figure 10. During the sample period, the average annual difference value within the region was 0.0445, and the average annual contribution rate was 55.13%. The average annual difference value between the regional differences was 0.0059, and the average annual contribution rate was 14.22%. The average annual difference value of the super-variable density was 0.0284, and the average annual contribution rate was 30.65%. It is found that the main source of the difference in the degree of the ILM between the cities in the Yangtze River Basin and the cities in the Yellow River Basin is the difference within the region, followed by the super-variable density, and the difference between the regions accounts for the smallest proportion. The evolution trend of the intra-regional differences increases in fluctuations, the inter-regional differences increase in fluctuations, and the super-variable density shows a trend of first decreasing and then increasing. The average annual increase rates of the net difference value within the region, the super-variable density, and the net difference value between the regions are 72.64%, 196%, and 85.96%, respectively. A comparison shows that the source of the imbalance in the degree of the ILM between the cities in the Yangtze River Basin and the cities in the Yellow River Basin is mainly due to the difference in the super-variable density.
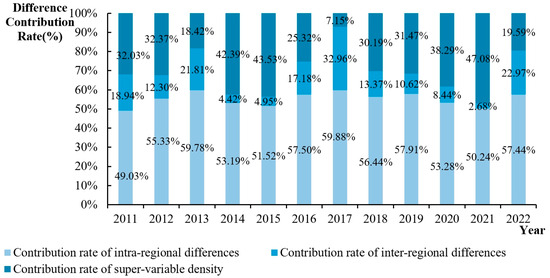
Figure 10.
Time series evolution of the contribution rate of regional differences in the mismatch degree of urban industrial land in the Yangtze River Basin and the Yellow River Basin.
4.3. Empirical Analysis of the Impact of the Industrial Land Mismatch on Urban Ecological Modernization
4.3.1. Baseline Regression Results
Table 5 presents the baseline regression outcomes assessing the influence of the industrial land mismatch (ILM) on urban ecological modernization across Chinese cities. Regression (1) reveals that, after accounting for the city and for temporal fixed effects, the coefficient of the principal explanatory variable ILM remains significantly negative, passing the 1% confidence threshold. This affirms that industrial land misallocation exerts a pronounced inhibitory effect on the trajectory of urban ecological modernization. Specifically, distorted land distribution induces dual structural maladies: underutilized and inefficient resource deployment in lagging areas, and ecological overburden and degradation in overdeveloped regions. The entanglement of these dynamics progressively undermines green economic efficiency and stifles ecological modernization. Delving deeper, three principal mechanisms underpin this phenomenon. First, the land mismatch fosters excessive resource concentration within traditional, energy-intensive, low-value-added industries; while emerging green and tech-driven sectors are throttled by constrained land availability. This impedes innovation capacity and debilitates the city’s technological and green transformation momentum. Second, spatial imbalance intensifies localized industrial clustering, leading to pollutant densities that surpass environmental thresholds and amplify inter-regional pollution spillovers. Third, persistent land misallocation distorts market price signals, erodes resource-use efficiency, and hampers the urban industrial structure’s evolution towards high-value, low-carbon configurations. In sum, the ILM systematically derails urban ecological modernization by corroding factor market efficiencies, heightening environmental stressors, and obstructing the path to industrial upgrading and sustainable growth.

Table 5.
Baseline regression empirical results.
The estimation results for the control variables reveal a relatively coherent mechanism shaping urban ecological modernization. First, the coefficient for economic development level stands at 0.003 and passes the 1% significance test, suggesting that economic expansion robustly advances ecological modernization. This aligns with the early stage of the “Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC)” hypothesis, wherein rising fiscal capacity, technological investment, and environmental infrastructure provision form a solid material and institutional bedrock for ecological advancement.
Second, the urbanization level exhibits a significantly negative coefficient, indicating that current urbanization dynamics impede ecological modernization. This underscores that China’s urbanization remains predominantly quantity-driven, with quality enhancements lagging. Rapid spatial sprawl, aggressive industrial land conversion, and short-term infrastructure investments have exacerbated ecological burdens and urban maladies, thereby constraining green transformation. Conversely, the coefficient for industrial structure is significantly positive at the 1% level, confirming the pivotal role of economic restructuring in catalyzing ecological progress. Transitioning from pollution-intensive, energy-heavy industries to high-tech, eco-friendly sectors has curtailed environmental degradation per unit output and bolstered green total factor productivity, furnishing endogenous momentum for ecological evolution. The coefficient for opening to the global economy is 8.075, significant at the 10% level, indicating that external integration modestly facilitates ecological modernization. Openness has transmitted capital, technology, and managerial spillovers, enhancing the local firms’ green innovations and environmental governance through mechanisms like environmental standards convergence and global competitive pressures. Finally, the population development level registers a coefficient of 7.386, highly significant at the 1% level, underscoring the fundamental role of human capital enhancement. Improved population quality not only elevates demand for superior ecological environments, pressuring governments toward better environmental stewardship, but invigorates innovation capacity and fosters green industry incubation, fundamentally accelerating urban ecological modernization.
In sum, economic growth, industrial upgrading, globalization, and high-caliber human capital emerge as critical engines of ecological modernization, while deficient urbanization quality persists as a principal constraint. This insight suggests that future urban policies should emphasize the synchronized advancement of urbanization quality, industrial greening, and human capital accumulation to realize a virtuous cycle between economic vitality and ecological civilization construction.
4.3.2. Robustness Check
- (1)
- One Period Lag
In order to overcome the endogeneity problem caused by the mutual causation of urban industrial land misallocation and urban ecological modernization, the robustness test was conducted using urban industrial land misallocation lagged by one period. The results in column (1) of Table 6 show that the ILM index in one lagged period is significantly negative. It can be seen that, after robustness testing, the research conclusion of this study still holds. This shows that by rationally allocating land and appropriately reducing the proportion of industrial land, the city can accelerate the goal of ecological modernization.

Table 6.
Robustness test results.
- (2)
- Bilateral Shrinking Processing
In order to explore whether the outliers in the sample have a significant impact on the regression results, all continuous variables were bilaterally winsorized by 1%, and the regression was rerun. The regression results are shown in column (2) of Table 6. The results show that the estimated coefficient of the ILM has changed but is still significantly positive at the 1% level; that is, the outliers in the sample have little impact on the regression results. The above benchmark regression results passed the robustness test.
- (3)
- Replacing Explanatory Variables
In addition to the degree of allocation, there are many other ways to measure land element allocation. For example, the ratio of secondary industry land to tertiary industry land can also well indicate the status of land element allocation. Therefore, this study draws on the existing research [65] and chooses the ratio of industrial land to commercial land (XIS) to replace the ILM index for robustness testing. From the results in column (3) of Table 6, we can see that the XIS has a significant negative impact on urban ecological modernization. This result means that the negative impact of the industrial land mismatch on urban ecological modernization is robust and reliable.
4.3.3. Mechanism Inspection
The previous section has confirmed that the industrial land misallocation can significantly inhibit the realization of urban ecological modernization, so what is its mechanism? Based on the previous theoretical analysis, this section examines technological innovation and secondary industry employees mechanisms, respectively, and further examines the impact of the industrial land mismatch on the realization of urban ecological modernization through mechanism design. This section refers to the existing research [71] to theoretically clarify the impact of the mechanism variables on the explained variables.
- (1)
- Technological Innovation
Column (1) of Table 7 scrutinizes the influence of the industrial land mismatch on technological innovation. The results reveal that the ILM coefficient is −0.003, and significantly negative at the 1% confidence level, implying that the land mismatch markedly impedes innovation dynamics. This inhibitory effect can be elucidated through the institutional logic underpinning local government land allocation practices. Within the prevailing “land-driven development” paradigm, local authorities prioritize transferring industrial land at discounted prices and with lax conditions to expedite manufacturing investment and stimulate short-term economic output [72]. Although this strategy attracts enterprises, it simultaneously dilutes technological and environmental entry thresholds, allowing a proliferation of low-tech, innovation-deficient firms to anchor themselves [73,74].

Table 7.
Mechanism test results.
Benefiting from low-cost land and government-sponsored infrastructure, these enterprises frequently lack incentives for technological advancement, further stifling the regional innovation milieu [75]. Moreover, the capitalization of public infrastructure investments under the “land-based financing” model entrenches the current land supply and fiscal dependency framework, rendering transitions toward an innovation-led land allocation system exceedingly difficult [76]. This institutional misalignment not only erodes the role of technological innovation in economic upgrading but indirectly impairs ecological enhancement and carbon efficiency improvements [77]. The extant literature underscores that technological innovation constitutes the linchpin for augmenting energy efficiency and curbing carbon emissions [52]. Regions endowed with robust innovation capabilities are more adept at phasing out obsolete, energy-intensive industries and fostering emergent, environmentally benign sectors, thereby optimizing resource use, mitigating pollution burdens, and advancing ecological modernization. Consequently, the industrial land mismatch indirectly undermines urban ecological modernization by constraining technological innovation capacity, thus corroborating Hypothesis 2.
- (2)
- Secondary Industry Employees
Column (2) of Table 7 interrogates the influence of the industrial land mismatch on secondary industry employment. The findings indicate that the ILM coefficient stands at 3.053, and is significantly positive at the 1% level, suggesting that the land mismatch substantially expands the employment scale within the secondary sector, exerting profound implications for urban ecological modernization. This outcome illustrates that the distorted allocation of industrial land not only undermines resource efficiency but reshapes environmental outcomes through alterations in labor structures [78]. Mechanistically, the industrial land mismatch typically entails the oversupply of land for industrial purposes at concessionary prices. Incentivized by this, local governments adopt “land cost depression” tactics to attract manufacturing capital, fueling the proliferation of industrial parks, and generating abundant employment opportunities for rural migrant laborers [79]. Labor thereby transitions en masse from agricultural sectors to manufacturing, culminating in an industry–population agglomeration structure predominantly characterized by traditional manufacturing. While this model spurs employment and short-term economic growth, it simultaneously engenders significant negative externalities. On one hand, the rapid expansion of the secondary sector predominantly occurs within low- and mid-end manufacturing industries, characterized by minimal technological sophistication and high resource intensity, leading to considerably greater environmental degradation than services or high-tech sectors [80,81]. On the other hand, the clustering of labor-intensive industries triggers spatial “crowding effects”, intensifying infrastructure strain, escalating energy consumption, and diminishing resource-use efficiency [54].
These dynamics collectively erode the ecological carrying capacity of urban systems and obstruct improvements in green productivity and ecological modernization. Thus, the industrial land mismatch amplifies environmental and resource pressures by swelling secondary industry employment, thereby retarding the urban green transition. This mechanism validates Hypothesis 3, and highlights the latent ecological costs and institutional rigidities embedded within the current land-centric development paradigm.
4.3.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
Considering the large differences in economic development and production factors among different cities, the impact of the industrial land mismatch on the realization of urban ecological modernization may vary among cities. Based on this, analyzing the impact of the industrial land mismatch in different regions on the realization of urban ecological modernization is conducive to accurately grasping the impact of the industrial land mismatch on urban ecological modernization and providing theoretical reference for promoting Chinese-style modernization.
This study divides the research sample into eastern, central, and western cities based on geographical location heterogeneity for specific analysis. The empirical results are shown in columns (1)–(3) of Table 8. The estimated coefficient of the ILM in the eastern region is −0.012, and is significant at the 5% level. The estimated coefficient of the industrial land misallocation in the central region is −0.002, but it is not significant. The estimated coefficient of the ILM in the western region is 0.003, which is not significant. From this point of view, the industrial land mismatch has a significant negative impact on urban ecological modernization in the eastern region, a negative but not significant impact on the central region, and a positive and insignificant impact on the western region. This may be because the eastern region has a higher level of economic development, higher population density, faster industrial development, relatively scarce resources, and may face more serious resource misallocation problems. However, the economic development level of the central and western regions is relatively low, and the mismatch of their industrial land resources has a relatively limited impact on the realization of urban ecological modernization.

Table 8.
Heterogeneity analysis results.
As a national strategy targeting the river basin economy, the ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the Yellow River Basin are key areas for collaboratively promoting the construction of a modern and powerful socialist country. In view of this, further regression analysis was conducted on the impact of the mismatch of industrial land resources between the cities in the Yangtze River Basin and the cities in the Yellow River Basin on urban ecological modernization. The results are shown in columns (4)–(5) of Table 8. The estimated coefficient of the degree of the ILM in the Yangtze River Economic Belt is −0.012, and is significant at the 1% level. The estimated coefficient of urban industrial land misallocation in the Yellow River Basin is 0.116, and is significant at the 1% level.
From this point of view, the mismatch of industrial land has a significant inhibitory effect on the ecological modernization of cities in the Yangtze River Basin, and has a significant promoting effect on the ecological modernization of cities in the Yellow River Basin. The reason may be that the Yangtze River Economic Belt has a high level of economic development, and the misallocation of industrial land resources can bring about a multiplier effect, making it have a greater negative impact on cities in the Yangtze River Basin. The cities in the Yellow River Basin have a lower level of economic development and cover a larger area. Investing more industrial land is conducive to local industrial development and accelerates the local modernization process to a certain extent. The ecological and economic effects it brings are greater than the environmental damage effects it brings.
4.3.5. Further Analysis: Spatial Effects
- (1)
- Moran Index Results
Before conducting spatial panel regression, first use the global Moran’s I index to test whether there is spatial dependence in urban ecological modernization. The results in Table 9 show that the global Moran’s I results of urban ecological modernization from 2011 to 2022 are all positive and significant. It shows that urban ecological modernization has significant spatial positive autocorrelation; that is, urban ecological modernization in various regions has strong spatial dependence. In order to specifically analyze the spatial correlation of each city, this study measured the local Moran index of urban ecological modernization in 2011 and 2022 and drew a Moran scatter plot. The results are shown in Figure 11 and Figure 12. The ecological modernization levels of most cities are concentrated in the first and third quadrants, indicating that there is a positive spatial correlation in urban ecological modernization. In view of this, this study believes that it is necessary to further select an appropriate spatial econometric model to analyze the spatial effect of the industrial land mismatch on urban ecological modernization.

Table 9.
Global Moran’s I results.
Figure 11.
Local Moran Index in 2011.
Figure 12.
Local Moran Index in 2022.
- (2)
- Spatial Durbin Results
Given the pronounced spatial spillover effects of urban ecological modernization revealed by prior empirical findings, this study further incorporates a spatial econometric framework to rectify the shortcomings of conventional panel regressions in addressing spatial interdependencies. Controlling for temporal and individual fixed effects, parameter estimation is systematically undertaken. After rigorous comparison across various model diagnostics—including the LM test, the Hausman test, and the Wald test—the Spatial Durbin Model (SDM) emerges as the optimal specification for regression analysis. Detailed estimation outcomes are presented in Table 10. Within the SDM structure, the coefficient of the spatially lagged explanatory variable captures the magnitude and directionality of the variable’s cross-border influence. The results disclose that the spatial lag coefficient for the industrial land mismatch is significantly negative at the 1% level, illustrating that distorted urban industrial land allocation not only undermines local ecological modernization but impairs the green transition trajectories of adjacent cities through spatial spillovers. This adverse spatial externality underscores the expansive ecological ramifications precipitated by regional disparities in resource distribution.

Table 10.
Regression results of the Spatial Durbin Model.
Specifically, the urban industrial land misallocation often manifests as excessive land exploitation and ecological overburdening in some locales, juxtaposed against widespread underutilization and resource idleness elsewhere. Through spatial interlinkages, overdeveloped areas impose environmental externalities on neighboring systems, while underdeveloped territories fail to catalyze green economic growth. This “excess–deficiency” bifurcated disequilibrium diminishes regional green productivity and systematically impedes the ecological modernization of urban clusters. Thus, advancing cross-regional land optimization and fostering cooperative ecological governance emerges as an indispensable pathway to surmount the current spatial predicaments hindering ecological modernization.
5. Discussion
This study found that the industrial land mismatch in all samples of Chinese cities, including cities in the eastern, central, and western regions, cities in the Yangtze River Basin, and cities in the Yellow River Basin, showed similar trends. The degree of the industrial land mismatch has decreased, the regional differences have narrowed to a certain extent, and there is no polarization phenomenon. This is similar to the conclusion of the existing studies on the industrial land resource mismatch [48,49]. Compared with other studies, this study further analyzed the dynamic evolution characteristics of the industrial land mismatch in urban samples from different regions of China as well as the differences between the regions. This study found that there is no Matthew effect in the industrial land mismatch in the different regions of China, and there is no polarization phenomenon between the cities. The difference in the degree of the industrial land mismatch within cities in the eastern region is the largest, followed by the central region, and finally the western region. The difference in the industrial land resource mismatch between the eastern and central regions is the largest. The main source of the difference in the industrial land mismatch among cities in the eastern, central, and western regions is the super-variable density, followed by intra-regional differences, and the smallest proportion is inter-regional differences. This is due to the imbalance of regional development in China [82], resource mismatch [83], and other differences.
As a national strategy targeting the river basin economy, the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the Yellow River Basin Ecological Protection are key areas for the coordinated promotion of the construction of a socialist modern power [84]. This study found that the difference in the industrial land mismatch within the cities in the Yangtze River Basin is greater than that within the cities in the Yellow River Basin. The difference in the industrial land mismatch between the two shows a trend of first rising, then falling, and then rising again. The main source of the difference is the difference within the region, followed by the super-variable density, and the difference between the regions accounts for the smallest proportion. This is because there are differences in the economic development and the ecological governance between the Yangtze River Basin and the Yellow River Basin.
This study further delves into the multidimensional impact mechanisms and regional heterogeneities underlying the influence of the urban industrial land mismatch on ecological modernization. Broadly, industrial land misallocation markedly impedes the trajectory of urban ecological modernization—a conclusion consonant with the prior scholarship highlighting the deleterious effects of resource misallocation on green development and economic efficiency [48,58,65]. Mechanistic dissection reveals two principal conduits through which this inhibition materializes. First, the mismatch compresses the spatial and resource endowments essential for technological innovation, attenuating regional capacities for green R&D, and complicating the mitigation of ecological risks such as carbon emissions and energy overconsumption, particularly in territories with modest technological bases. Second, the industrial land mismatch reshapes the labor structure by fueling the absorption of employment into the secondary sector, thereby indirectly amplifying ecological strain [54].
At the regional echelon, pronounced heterogeneities emerge. In the eastern region, the negative ecological externalities of the industrial land mismatch are exacerbated by intensified development pressure and acute resource scarcity. By contrast, in the central and western regions—where industrialization remains nascent—the marginal utility of industrial land remains unsaturated, rendering the negative impacts comparatively muted and statistically insignificant. These divergences reflect the underlying disparities in resource allocation logic, industrial upgrading trajectories, and ecological governance capacities across the regions. A more granular comparison between the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the Yellow River Basin further elucidates the spatial asymmetries. In the Yangtze River Basin, the cities exhibit heightened susceptibility to mismatch-induced ecological degradation, attributable to dense industrial clustering and acute resource supply–demand imbalances, which amplify the ecological “multiplier” effects of the mismatch. Conversely, the cities within the Yellow River Basin, constrained by lower economic maturity, derive greater marginal gains from industrial land allocation; thus, the resultant ecological costs are partially offset, yielding a relatively benign or positive net effect. Moreover, the spatial econometric evidence substantiates the existence of potent spillover dynamics: the industrial land mismatches in one locality propagate ecological burdens to neighboring jurisdictions, culminating in a dual contagion of resource inefficiency and environmental deterioration. This “spatial mismatch–ecological fragility” externality mechanism engenders systemic vulnerabilities across urban networks, underscoring the pressing necessity of fostering inter-regional coordination to advance green land governance [85].
Building on the foregoing findings, this study advances several policy propositions aimed at optimizing industrial land allocation and elevating urban ecological modernization. First, the supply structure of construction land should be recalibrated in alignment with population dynamics and the stage of economic maturation. In cities facing land shortages, a judicious expansion of industrial land supply is warranted to ease factor bottlenecks; conversely, in locales plagued by surplus mismatch, land provision should be curtailed, fiscal dependence on land revenues diminished, and incentives for industrial upgrading and innovation enhanced. Second, it is imperative to fortify a market-driven allocation system for land and production factors, dismantling the inefficient “self-supply and self-demand” paradigm entrenched within local governments. This can be achieved by reinforcing the market regulation of land supply and demand, intensifying the utilization of the existing land stock, pivoting industrial land development from quantitative expansion toward qualitative enhancement, and mitigating the environmental externalities associated with land use. Simultaneously, the establishment of cross-regional factor mobility frameworks is essential to foster a dynamic equilibrium and sustainable configuration of industrial land spatial patterns. Lastly, a differentiated regional governance framework must be instituted to remedy spatial disequilibria. In areas burdened by excessive development intensity, efforts should concentrate on bolstering infrastructure resilience, strengthening ecological governance, and delineating strict development boundaries. By contrast, underdeveloped regions should focus on the scientific reservation of industrial land, rational guidance of industrial expansion, augmentation of land use efficiency, and enhancement of economic development quality, thereby averting resource wastage and the transference of ecological burdens.
6. Conclusions
Drawing upon panel data from 262 prefecture-level and above cities in China spanning 2011 to 2022, this study constructs an industrial land mismatch index, systematically investigates its spatiotemporal evolution, and assesses its repercussions on urban ecological modernization. The principal findings are as follows. Overall, the industrial land mismatch in Chinese cities exhibits a declining trajectory, regional disparities have narrowed, and no marked polarization is observed. Cities across the eastern, central, and western regions, as well as within the Yangtze and the Yellow River basins, demonstrate a broadly consistent evolution pattern. A Markov chain analysis reveals pronounced spatial dependence, with the mismatch levels in neighboring cities influencing the dynamic transition of the local mismatch, characterized by notable instability and path dependence. Decomposition of the Dagum Gini coefficient indicates that disparities in the industrial land mismatch are predominantly driven by hypervariable density and intra-regional differences, while inter-regional discrepancies remain modest. The east displays the widest internal variation, with greater disparity within the Yangtze River Basin compared to the Yellow River Basin, alongside considerable fluctuations across the basins.
Moreover, the industrial land mismatch exerts a significant inhibitory effect on urban ecological modernization, primarily by constraining technological innovation and amplifying the environmental burden of the secondary sector. The eastern cities and those within the Yangtze River Basin bear the brunt of these negative impacts, whereas the cities in the central and western regions and the Yellow River Basin exhibit distinct patterns. Additionally, the industrial land mismatch produces a pronounced negative spatial spillover, implying that regional allocation imbalances not only impede local ecological transitions but stifle the green development of adjacent cities.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by J.H. and R.D. The first draft of the manuscript was written by K.L., and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Excellent Graduate Training Program of Shaanxi Normal University under Grant [number LHRCTS23012].
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
References
- Duranton, G.; Puga, D. Chapter 48—Micro-Foundations of Urban Agglomeration Economies. In Handbook of Regional and Urban Economics; Henderson, J.V., Thisse, J.-F., Eds.; Cities and Geography; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 4, pp. 2063–2117. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Yeh, A.; Wu, F. Land Commodification: New Land Development and Politics in China since the Late 1990s. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2009, 33, 890–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Z.; Liu, X. Find Report on City and Industrial Innovation in China; Fudan Institute of Industrial Development: Shanghai, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, X. The Exhaustion of China’s “Land-Driven Development” Mode: An Analysis Based on Threshold Regression. J. Manag. World 2020, 36, 80–92, 119, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, J. Study on the Meaning of Space Balance and Condition Assessment from the Perspective of Supply and Demand Driven—A Case of Shandong Province. Soft Sci. 2016, 30, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Guo, J.; Lin, J.; Ou, M. Territorial spatial equilibrium under the concept of ecological civilization: An analytical framework based on two kinds of wealth. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 945–959. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.; Song, K.; Bai, J. Market Segmentation, Resource Misallocation and Environmental Pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, P.; Ma, G. Land resource mismatch and China productivity differences of industrial firms. J. Manag. World 2016, 8, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, K.Y.; Palacios, M.R.; Morales Gomez, C.A. Governance and Policy Limitations for Sustainable Urban Land Planning. The Case of Mexico. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 259, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Du, X. Government Intervention and Land Misallocation: Evidence from China. Cities 2017, 60, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tan, S.; Pan, Z.; Hao, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. The Spatial Spillover Effect and Nonlinear Relationship Analysis between Land Resource Misallocation and Environmental Pollution: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artioli, F. Sale of Public Land as a Financing Instrument. The Unspoken Political Choices and Distributional Effects of Land-Based Solutions. Land Use Policy 2021, 104, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, T.; Spit, T. Dilemmas of Involvement in Land Management—Comparing an Active (Dutch) and a Passive (German) Approach. Land Use Policy 2015, 42, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.; Fearnley, N. Policy Transfer of Public Transport Funding Schemes—The Case of Norway. Res. Transp. Econ. 2014, 48, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, E.; Falkenbach, H.; Viitanen, K. Securing Public Objectives in Large-Scale Urban Development: Comparison of Public and Private Land Development. Land Use Policy 2018, 78, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britos, B.; Hernandez, M.A.; Robles, M.; Trupkin, D.R. Land Market Distortions and Aggregate Agricultural Productivity: Evidence from Guatemala. J. Dev. Econ. 2022, 155, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda Dower, P.; Pyle, W. Land Rights, Rental Markets and the Post-Socialist Cityscape. J. Comp. Econ. 2019, 47, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hou, Y. Multi-perspective Observation and Policy Response to Regional Unbalanced Development in China. J. Manag. World 2019, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Sun, W.; Zhao, H. The Spatial Imbalanced Pattern and State Assessment of Regional Development. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2010, 65, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X. Assessment of the Equilibrium Degree and Limitation Degree of Yangtze River Economic Blet’s Land Development. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2017, 26, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Spatial Balance Degrees on Land Use in China. China Land Sci. 2017, 31, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Qin, X. Land use spatial equilibrium from the perspective of supply and demand matching: A case study of Jiangsu Province. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Du, X. Review on the Land Resource Misallocation Studies. China Land Sci. 2014, 28, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, A.P.J. Environment and Modernity in Transitional China: Frontiers of Ecological Modernization. Dev. Change 2006, 37, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Gouldson, A. Environmental Policy and Industrial Innovation: Integrating Environment and Economy through Ecological Modernisation. Geoforum 2000, 31, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.C. Introduction: The Origins and Evolving Nature of Ecological Modernisation. In The Emergence of Ecological Modernisation; Routledge: London, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-1-315-81254-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H. A Literature Review and Prospect of China’s Ecological Modernization Transformation at Home and Abroad. Marx. Real. 2015, 05, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z. The Relationship between Urban Modernization and Ecological, Characteristic and Humanization. Urban Dev. Stud. 2021, 28, 1–2+9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Mol, A.P.J.; Sonnenfeld, D.A. The Interpretation of Ecological Modernisation in China. Environ. Politics 2007, 16, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Xie, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. Study and Design of Eco-city Sustainable Development Index System and Assessment Methodology. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2006, 6, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Gao, J. The study on the indicator system for the evaluation of eco-city. J. Shanghai Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2007, 2, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Xu, X. The indices and the evaluation method of eco-city. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 8, 2090–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Lv, B. Coupling Coordinating between Carbon Emissions and Urbanization—A Case of Chinese Low Carbon Pilot Cities. J. Beijing Inst. Technol. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2017, 19, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; He, J. The Dynamic Coupling Model of Coordinated Development between Regional Economic and Ecological Environment Systems Based on Jiangsu Province. Soft Sci. 2010, 24, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, M. Evaluation on coordinative and harmonious development between regional urbanization and urban ecological environment—Comparison between thirty provinces and municipalities of China. West Forum 2007, 17, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Wang, N. An Empirical Study on the Coupling Model of Ecological Environment and Urban Competitiveness. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 10, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Arvin, M.B.; Pradhan, R.P.; Norman, N.R. Transportation Intensity, Urbanization, Economic Growth, and CO2 Emissions in the G-20 Countries. Util. Policy 2015, 35, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Xue, P.; Gong, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effects of Land Use Patterns on the Interannual Variations of Carbon Sinks of Terrestrial Ecosystems in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zheng, F. Effects of Land Use Patterns on Carbon Emission in Jiangsu Province. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2008, 24, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Cai, D. How does the Industrial Land Misallocation Affect Regional Green Development. China Land Sci. 2021, 35, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, C.; Xiao, H.; Zhong, Q.; Weng, Q. Unequal Impacts of Urban Industrial Land Expansion on Economic Growth and Carbon Dioxide Emissions. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Zhang, A. Can China’s Market-Oriented Reform Improve the Efficiency of Industrial Land Use? A Panel Data Empirical Analysis at Prefecture Level From 2007–2019. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 884958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liang, Y.F.; Dou, W. How Does Urban Industrial Structure Upgrading Affect Green Productivity? The Moderating Role of Smart City Development. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2025, 72, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cai, L.; Zhang, X. New Industrial Land Use Policy and Firms’ Green Technology Innovation in China—An Empirical Study Based on Double Machine Learning Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1356291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Industrial Upgrading and Its Influence on Green Land Use Efficiency. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, Q.; Wei, X. Effect of China’s Land Resource Allocation Method on Enterprise Technological Innovation: Promoting or Inhibiting. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 766246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Yi, Z. How Does Urban Green Development Affect Land Use Efficiency? Empirical Analysis Based on 285 Cities in China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2025, 34, 3425–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q. The Influence of Spatial Imbalance of Urban Industrial Land on Green Economy in China. J. Hebei Univ. Econ. Bus. 2024, 45, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haung, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, A. The relationship between industrial land price and industrial structure change. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shao, S.; Fan, M. The Desire to Benefit but to Lose: Land Supply Bias and Urban Green Total Factor Productivity Growth. J. Guizhou Univ. Financ. Econ. 2022, 40, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Zhao, L. Land Resource Misallocation, Spatial Strategy Interaction and Urban Innovation Capability. China Land Sci. 2021, 35, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, L.; Han, L. Impact of biased technological advances in different types of capital technologies on carbon emission efficiency. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2022, 42, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J. The impact of green technological innovation on the spatiotemporal evolution of carbon emission efficiency of resource-based cities in China. Geogr. Res. 2023, 42, 878–894. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Xia, Q.; Dong, J. Spatial effect of land resource misallocation on carbon emission efficiency and its influence path: Empirical evidence from 108 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Sci. 2023, 45, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. The Modernization of Harmonious Coexistence between Humanity and Nature: Historical Achievements, Contradictory Challenges and Realization Paths. J. Manag. World 2023, 39, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhou, C.; Gu, C.; Chen, L.; Li, S. Theoretical analysis of interactive coupled effects between urbanization and eco-environment in mega-urban agglomerations. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 531–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-T.; Klenow, P.J. Misallocation and Manufacturing TFP in China and India. Q. J. Econ. 2009, 124, 1403–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Li, Y. Empirical Analysis of Spatial Spillover Effect Stems from Land Resource Misallocation and Economic Fluctuation. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Shao, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, Q. The impact of spatial misallocation of urban industrial land on industrial TFP in China. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 2511–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H. Multi-dimensional measurement of levels of Chinese mega-city modernization: Theoretical logic, spatial-temporal characteristics and improving path. Urban Probl. 2023, 05, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Zhang, Q. Construct a scientific and rational evaluation index system for Chinese-style modernization. Academics 2022, 06, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, W.; Hong, M.; Neophytou, A.M. Urbanization Exacerbates Disparities in Exposure to Air Pollution in China. Environ. Res. 2025, 267, 120661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Qiao, X.; Seyler, B.C.; Tang, Y. Air Pollution Reduction in China: Recent Success but Great Challenge for the Future. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D. Land Resource Misallocation and City Innovation Capacity: Based on Chinese City-level Panel Data Analysis. China J. Econ. 2020, 7, 86–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X. Industrial Land Misallocation, Industrial Structure and High-quality Economic Development. World Surv. Res. 2024, 09, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Yao, Y.; Wu, X. Digital Finance, Technological Innovation, and Carbon Dioxide Emissions. Econ. Anal. Policy 2023, 80, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Li, R.; Gao, X. Bank Competition with Technological Innovation Based on Evolutionary Games. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 89, 742–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Li, Q.; Ding, L. Intellectual Property Protection, Innovation Drive and High-Quality Development of Manufacturing Industry: A Moderated Mediating Effect Analysis. Econ. Probl. 2023, 02, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Ma, Q.; Peng, J. The Theoretical Mechanism and Empirical Test of Digital Economy Driving Chinese Modernization. Soc. Sci. Front. 2023, 07, 250–256. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Blanco-González-Tejero, C.; Sendra, F.J. The Spatial Difference-in-Difference Measurement of Policy Effect of Environmental Protection Interview on Green Innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 191, 122511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T. Mediating Effects and Moderating Effects in Causal Inference. China Ind. Econ. 2022, 05, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Henderson, J.V.; Zhang, Q. China’s Land Market Auctions: Evidence of Corruption? RAND J. Econ. 2013, 44, 488–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, W.; Tan, X.; Li, Q. Identification and Driving Mechanism of the Industrial Land Use Transition in China. Habitat Int. 2023, 138, 102848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Y.; Balland, P.-A.; Zheng, S. Industrial Land Policy and Economic Complexity of Chinese Cities. Ind. Innov. 2022, 29, 367–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Land Marketization and Urban Innovation Capability: Evidence from China. Habitat Int. 2022, 122, 102540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S.; Yi, F. Urbanization of Capital or Capitalization on Urban Land? Land Development and Local Public Finance in Urbanizing China. Urban Geogr. 2011, 32, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Huang, M. Land Misallocation and Carbon Emissions: Evidence from China. Land 2022, 11, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S. Land Use Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Urban Agglomerations in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mount, T.D.; Boisvert, R.N. Industrialization, Urbanization and Land Use in China. J. Chin. Econ. Bus. Stud. 2004, 02, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zenou, Y. Urban Villages and Housing Values in China. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2012, 42, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lyu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Industrial Agglomeration Externalities, Local Governments’ Competition and Environmental Pollution: Evidence from Chinese Prefecture-Level Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; He, C. Regional inequality: Theoretical review, research progress, and prospects. Prog. Geogr. 2024, 43, 1839–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Lu, S. A Study on Loan Interest Rate Liberalization, Banking Competition and Resource Misallocation in Cities. Economist 2024, 07, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Ming, M. Driving Mechanisms, Evolutionary Trends and Policy Options for the Basic Modernization of Western Chinese Cities. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. Soc. Sci. 2021, 03, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q. Influence of Industrial Land Spatial Mismatching on Urban Innovation in Yangtze River Delta Region. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).