Evolution of Ecological Environment Quality in Metropolitan Suburbs and Its Interaction with Tourism Development: The Case of Huangpi District, Wuhan City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
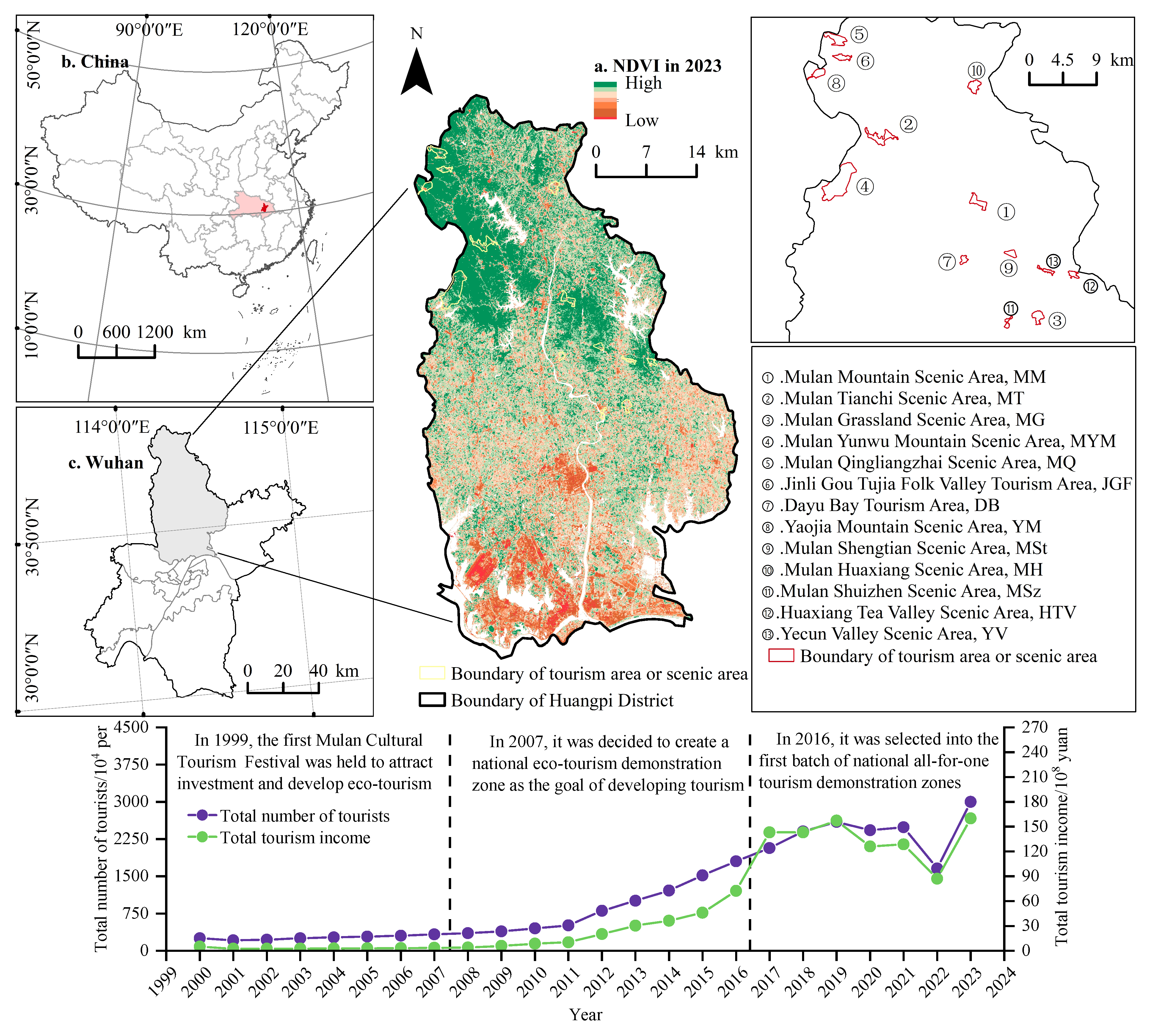
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Method for Evaluating Ecological Environment Quality
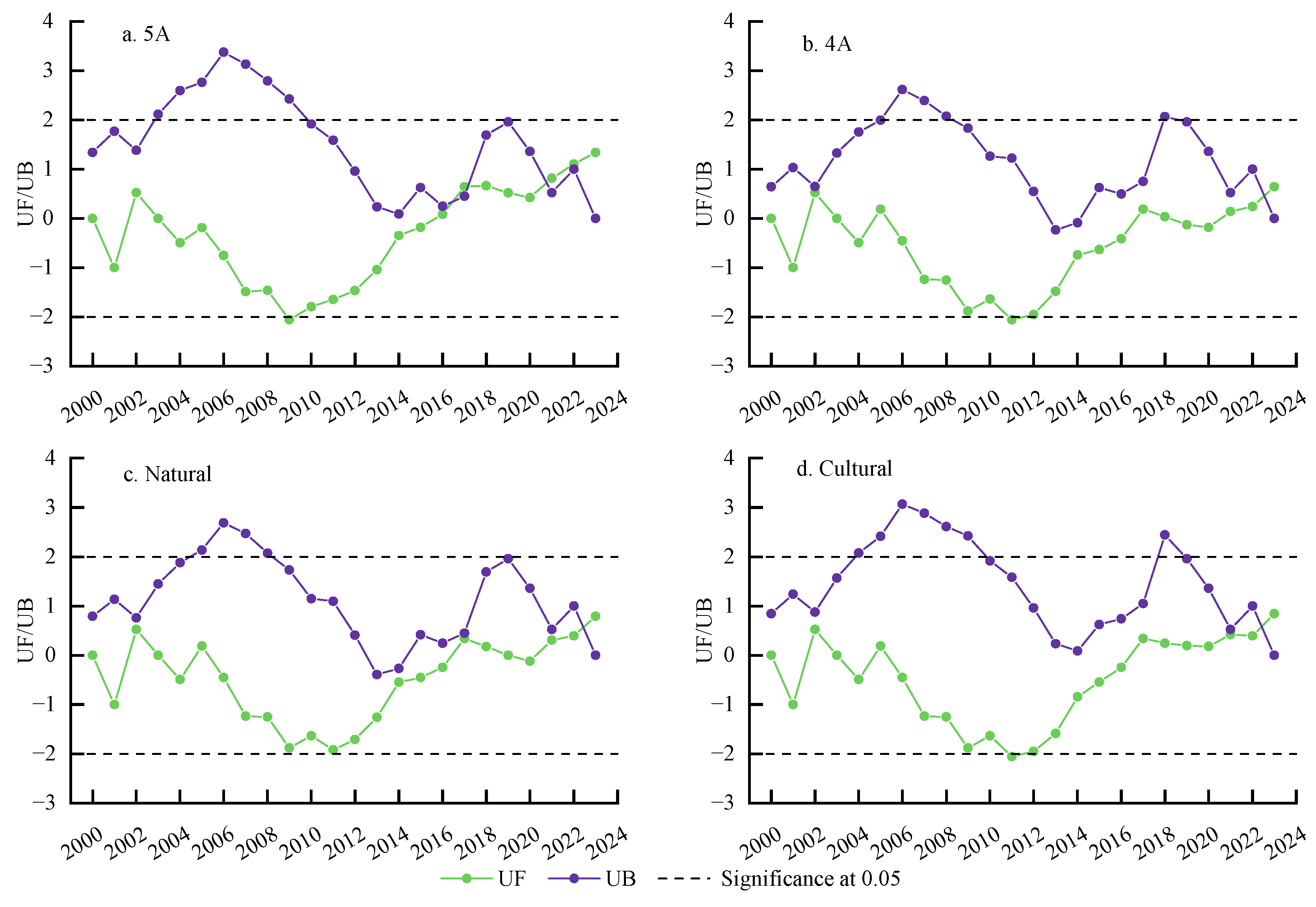
2.3.2. Analysis of the Trends in Ecological Environment Quality
2.3.3. Method for Analyzing the Degree of Change in Ecological Environment Quality
2.3.4. Method for Analyzing the Impact of TD on EEQ
3. Results
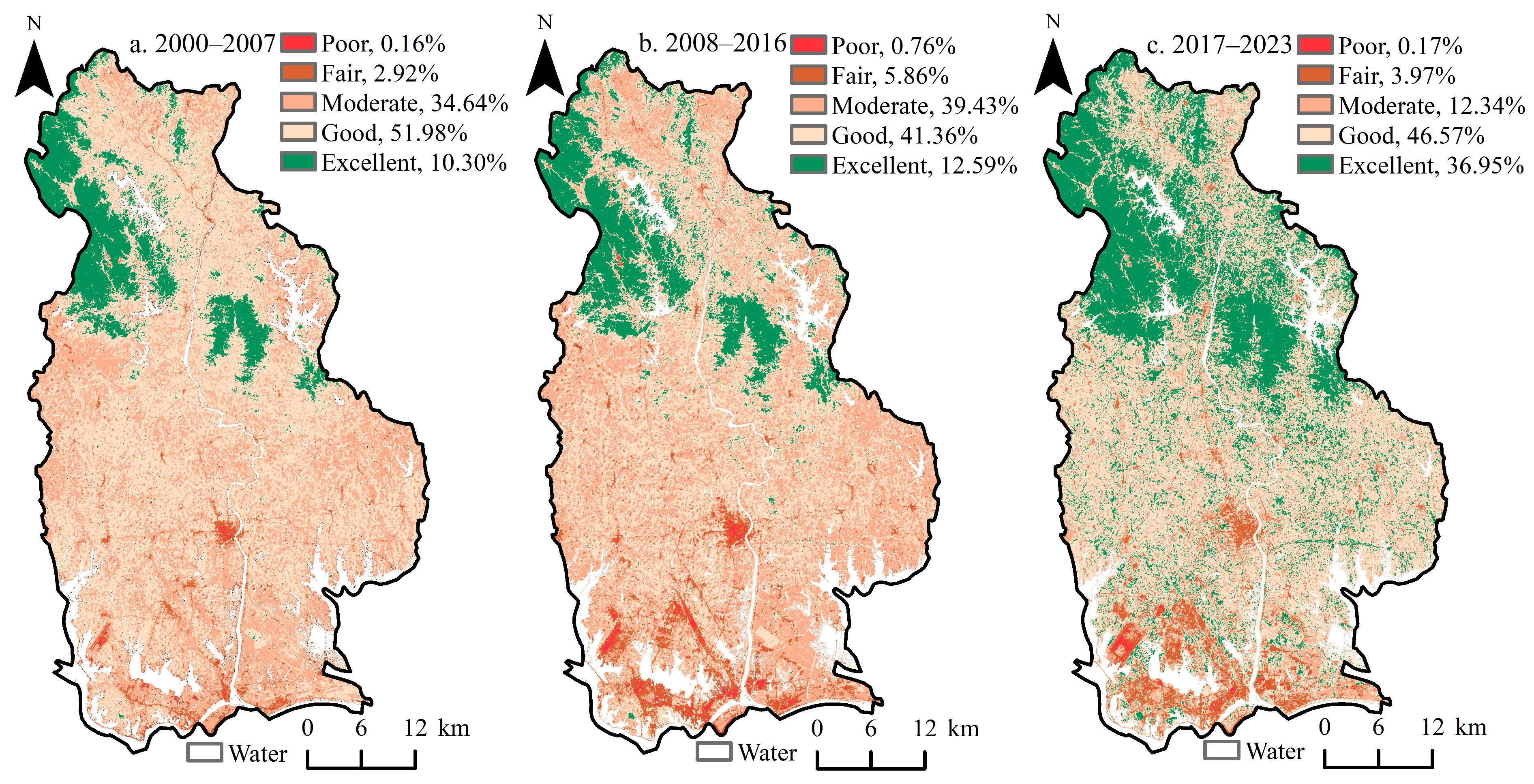
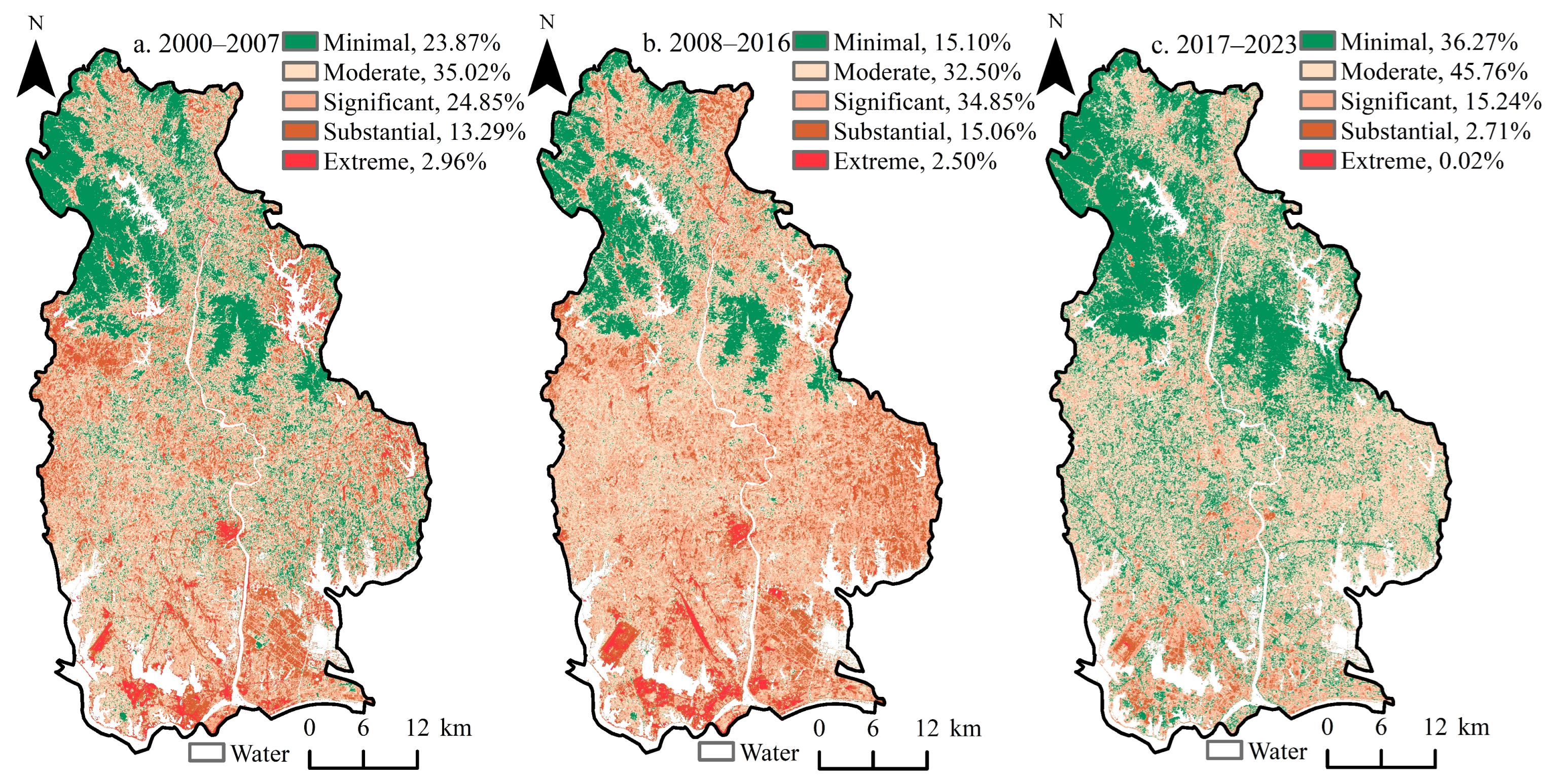
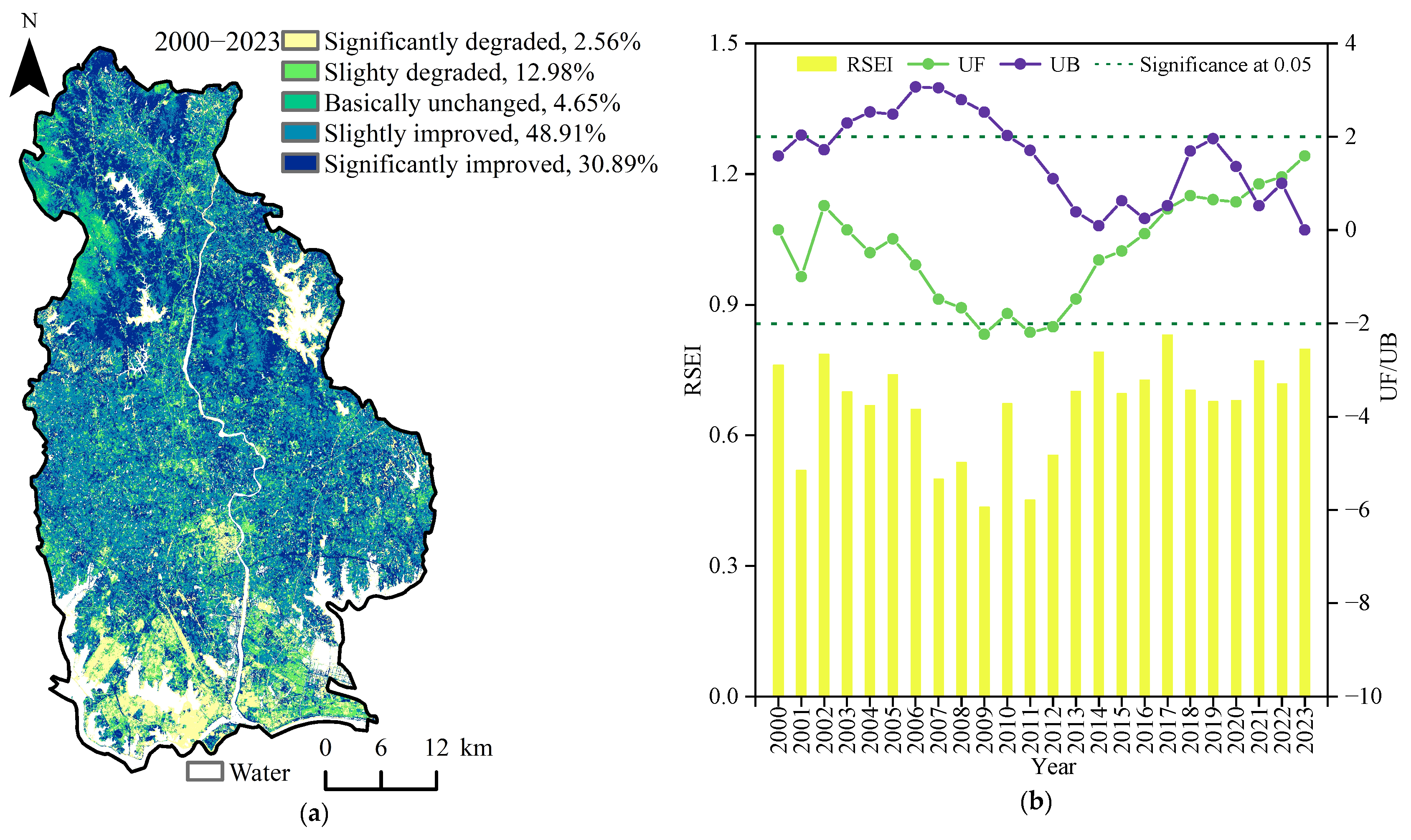
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of EEQ
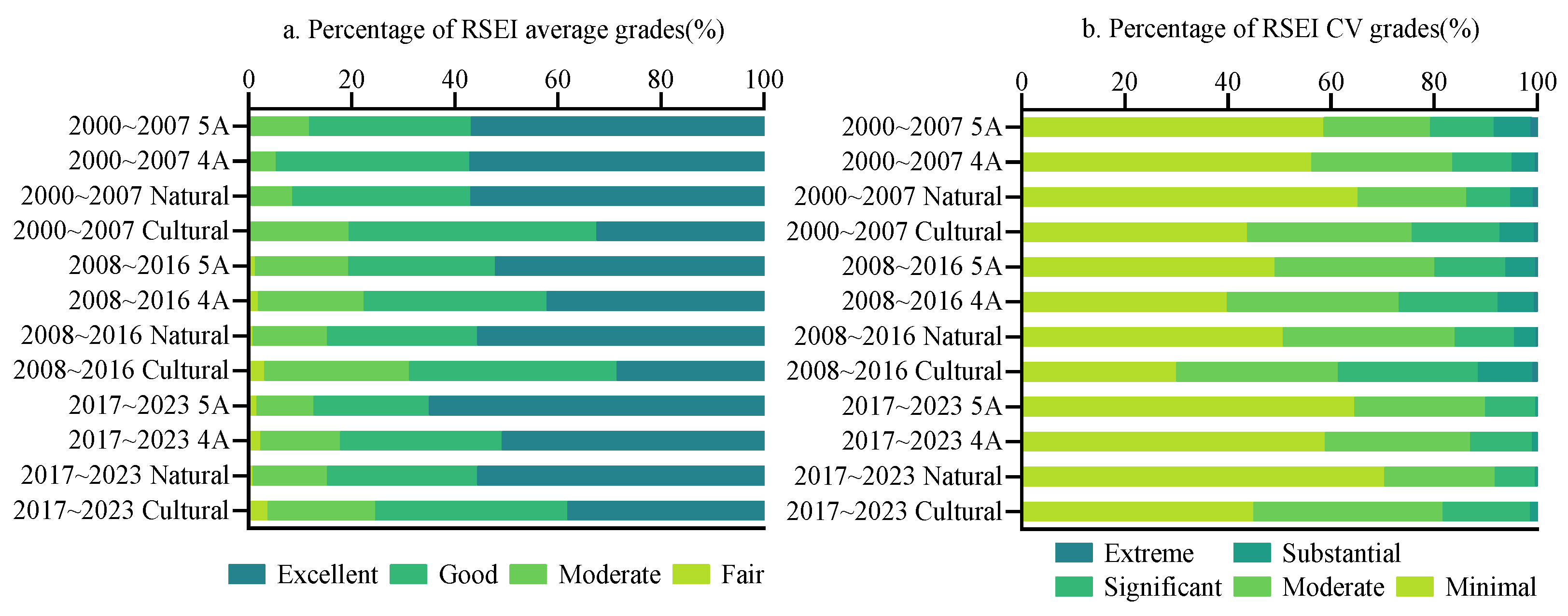
3.2. Evolution of the EEQ in Scenic Spots of Different Grades and Types
3.3. Impact of TD on EEQ
3.3.1. Differences in the Average RSEI Values Under Different Scenarios
3.3.2. Differences in the RI Under Different Scenarios
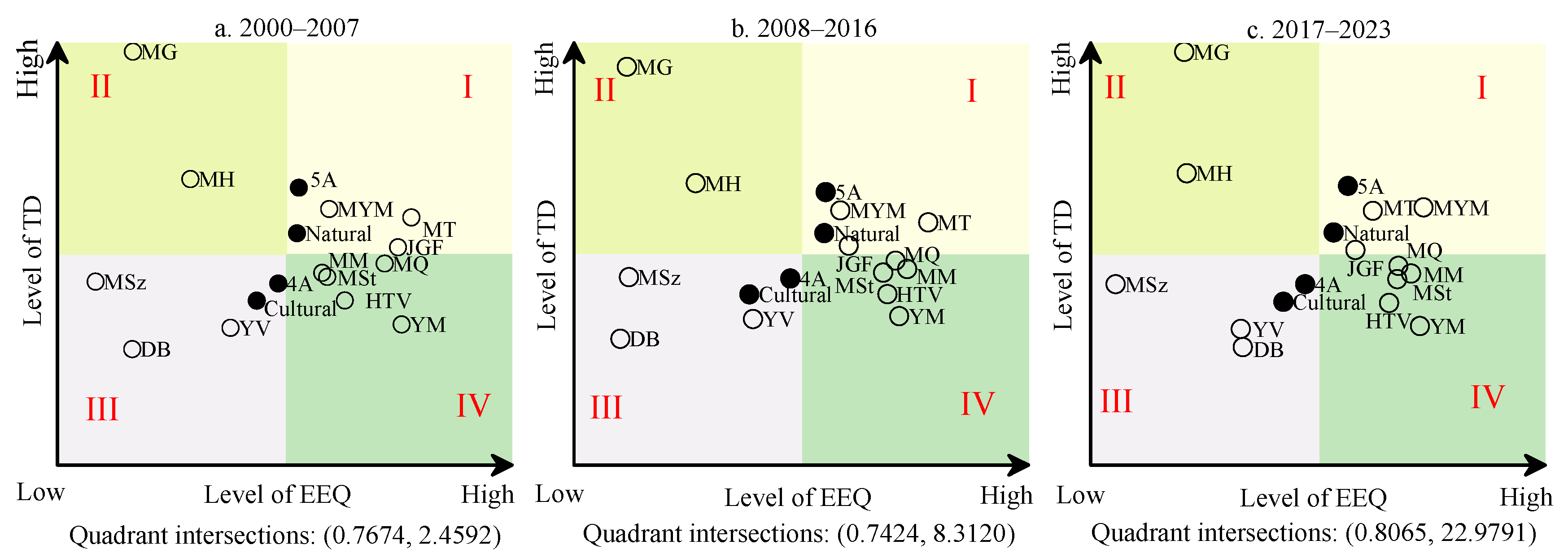
3.3.3. State of Coordination Between TD and RSEI
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Differences in the EEQ in Huangpi District
4.2. Impact of TD on EEQ in Huangpi District at Different Stages
4.3. Limitations and Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Shi, K.; Wu, Y. Identifying and evaluating suburbs in China from 2012 to 2020 based on SNPP–VIIRS nighttime light remotely sensed data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Qian, J.; Wang, L. Village classification in metropolitan suburbs from the perspective of urban-rural integration and improvement strategies: A case study of Wuhan, central China. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 105748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. The study on recreation-scape planning and landscape ecological protection of urban-rural fringe: A typical case study of Beijing. Geogr. Res. 2003, 22, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, R.; Qiu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, T.; Zou, J.; Wang, H. The next step in suburban rural revitalization: Integrated whole-process landscape management linking ecosystem services and landscape characteristics. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 111999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Chen, L.; Long, C.; Duan, P. Tourism gentrification of traditional villages and towns in the suburbs of big cities in China: A case study of Zhujiajiao Ancient Town in Shanghai. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2023, 78, 2535–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, A. Mix leading to success? Exploring the innovative development model in peri-urban China. Habitat. Int. 2018, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.I.; Mansur, A.V.; Ascensão, F.; Colbert, M.; Crossman, K.; Elmqvist, T.; Gonzalez, A.; Güneralp, B.; Haase, D.; Hamann, M.; et al. Research gaps in knowledge of the impact of urban growth on biodiversity. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, H.; Zhong, L. Evolution of the landscape pattern in the Xin’an River Basin and its response to tourism activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, M.; Zeren, I.; Sevik, H.; Cakir, C.; Akpinar, H. A study on the determination of the natural park’s sustainable tourism potential. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, J.; Lou, K.; Yang, L. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between urbanization and ecological environment in Shaanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Assessing sustainability of urbanization by a coordinated development index for an Urbanization-Resources-Environment complex system: A case study of Jing-Jin-Ji region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, M.; Lin, S. Impact of land urbanization on the quality of the ecological environment: Analysis based on the local-neighboring area perspective. Prog. Geogr. 2023, 42, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Shi, J.; Qu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, T.; Niu, Z.; Yang, R.; Gong, P. Assessing the ecological vulnerability of protected areas by using Big Earth Data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Wen, Y.; Fan, W.; Liu, Q.; Tarolli, P. Monitoring the coastal wetlands dynamics in Northeast Italy from 1984 to 2016. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; Wu, S.; Yan, Y.; Niu, Y.; Yang, F.; Xie, C. Monitoring land surface thermal environments under the background of landscape patterns in arid regions: A case study in Aksu river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Lin, W.; Chen, G.; Guo, P.; Zeng, Y. Wetland ecosystem health assessment through integrating remote sensing and inventory data with an assessment model for the Hangzhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Fu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y. Spatiotemporal change detection of ecological quality and the associated affecting factors in Dongting Lake Basin, based on RSEI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Xing, X.; Wei, L. Coupling eco-environmental quality and ecosystem services to delineate priority ecological reserves—A case study in the Yellow River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, Q.; Duan, Y.; Ma, S. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of eco-environmental quality in Yanhe Watershed (China) using the Remote-Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI). Land 2024, 13, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Bai, Z.; Zheng, B. Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving forces of ecological environment quality in coastal cities: A remote sensing and land use perspective in Changle District, Fuzhou. Land 2024, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Chen, S. Analysis of quality evolution of important ecological function areas and implementation effects of the ecological redline in Jiangsu Province, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 8933–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, S.; Peng, P.; Chen, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, M. Unraveling the Ecological Tapestry: A Comprehensive Assessment of Changtang Nature Reserve’s Ecological and Environmental Using RSEI and GEE. Land 2023, 12, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Behzad, H.M.; Tahir, M.; Li, C. The impact of ecotourism on ecosystem functioning along main rivers and tributaries: Implications for management and policy changes. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, Z. Coordination or contradiction? The spatiotemporal relationship between ecological environment and tourism development within the tourism ecological security framework in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhong, L. Identifying conflicts tendency between nature-based tourism development and ecological protection in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, F.; Dong, Y. Analysis of the tourism-economy-ecology coupling coordination and high-quality development path in karst Guizhou Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, N. Environmental Education Catalyzed by Tourism: Ecoliteracy Initiatives on the Coast of Kenya. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.G.; Dietz, T.; Liu, J. Global relationships between biodiversity and nature-based tourism in protected areas. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 34, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Ampong, E.A. Historical trajectories of tourism development policies and planning in Ghana, 1957–2017. Tour. Plan. Dev. 2019, 16, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Ye, W. Tourism circular economy: Identification and measurement of tourism industry ecologization. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z. An integrated approach to evaluating the coupling coordination between tourism and the environment. Tour. Manag. 2015, 46, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Kim, C.; Kim, G.; Jeong, J.; Lee, W. Social big data informs spatially explicit management options for national parks with high tourism pressures. Tour. Manag. 2020, 81, 104136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, C.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.; Andrada, R.I.T. Quantifying nature-based tourism in protected areas in developing countries by using social big data. Tour. Manag. 2019, 72, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, L.; Li, D. Evolution characteristics and driving factors of basin multi-scale landscape pattern under the tourism disturbances: A case study of the Xin’an River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 3415–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, G.; Qin, Q.; Huang, Z.; Hu, M. Change of rural recreational agriculture landscape pattern and driving factors under the development of tourism: A case study of Wuyuan, Jiangxi. Prog. Geogr. 2023, 42, 1556–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhong, L. Measuring and reducing the ecological risk of community tourism for ecosystem conservation. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Lin, M.; Wen, L.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, F.; Ge, Y.; Li, B. Exploring the spatial and temporal evolution of landscape ecological risks under tourism disturbance: A case study of the Min River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Feng, R.; Xi, J.; Huijbens, E.H.; Gao, Y. Distinguishing the impact of tourism development on ecosystem service trade-offs in ecological functional zone. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Kumar, J.; Qin, Q.; Kannan, S. Assessing the coupling coordination degree between all-for-one tourism and ecological civilization; case of Guizhou, China. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 19, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, L. Assessment of land use/cover changes and its ecological effect in karst mountainous cities in central Guizhou Province: Taking Huaxi District of Guiyang City as a case. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 3429–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Wang, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal variations in eco-environmental quality and responses to drought and human activities in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China from 1990 to 2022. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Shi, L.; Yan, J. Effects of large-scale land consolidation projects on ecological environment quality: A case study of a land creation project in Yan’an, China. Environ. Int. 2024, 183, 108392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, X.; Qin, Y.; Xu, F. Spatiotemporal differentiation and mechanisms of ecological quality in Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Zan, C.; Ren, J.; Yang, L.; Wen, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, L. Using the Google Earth Engine to rapidly monitor impacts of geohazards on ecological quality in highly susceptible areas. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Lyv, F.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal change and drivers of ecosystem quality in the Loess Plateau based on RSEI: A case study of Shanxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yang, H.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Q. Exploring trade-offs between residential and industrial functions in rural areas and their ecological impacts across transitioning agricultural systems: Evidence from the metropolitan suburbs of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Tsai, H. Enhancing tourism carbon emission efficiency through industry agglomeration: Evidence from China. Tour. Manag. 2025, 110, 105170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Hou, H.; Xu, C.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Ren, J. Spatiotemporal evolution and multi-scale coupling effects of land-use carbon emissions and ecological environmental quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huangpi District People’s Government. Government Work Report 2017. Available online: https://www.huangpi.gov.cn/ywdt/gzbb/202004/t20200424_1110553.html (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Zhang, B.; Xia, Q.; Dong, J.; Li, L. Research on the Impact of Land Use Change on the Spatio-temporal Pattern of Carbon Storage in Metropolitan Suburbs: Taking Huangpi District of Wuhan City as an Example. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2023, 39, 699–712. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Du, Y. Analysis of ecological quality in Lhasa Metropolitan Area during 1990–2017 based on remote sensing and Google Earth Engine platform. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, H.; Ren, J.; Yu, W.; Cong, N.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C.; Li, X.; Qiao, Z. Towards ecological civilization: Spatiotemporal heterogeneity and drivers of ecological quality transitions in China (2001–2020). Appl. Geogr. 2024, 173, 103439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Tian, H.; Wu, X.; Gao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Piao, S.; Lv, N.; Pan, N.; Fu, B. Accelerated increase in vegetation carbon sequestration in China after 2010: A turning point resulting from climate and human interaction. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 5848–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation and analysis of the impact of coastal urban impervious surfaces on ecological environments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remot. Sens. 2023, 16, 8721–8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y. Tourism Revenue Increases 87-Fold in 20 Years: How Huangpi District of Wuhan Became a Leading Tourism Hub in China. Available online: https://www.sohu.com/a/504070064_121123902 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Geng, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Plausible response of urban encroachment on ecological land to tourism growth and implications for sustainable management, a case study of Zhangjiajie, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C. Evaluation and drive mechanism of tourism ecological security based on the DPSIR-DEA model. Tour. Manag. 2019, 75, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, E. Spatial-temporal changes in ecosystem services and the trade-off relationship in mountain regions: A case study of Hengduan Mountain region in Southwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangpi District People’s Government. The List of the First Batch of National All-for-One Tourism Demonstration Zones Has Been Announced, with Huangpi District Being Included. Available online: https://www.huangpi.gov.cn/ywdt/bmzc/202001/t20200113_777130.html (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Chen, H. Land use trade-offs associated with protected areas in China: Current state, existing evaluation methods, and future application of ecosystem service valuation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, F. Destination island effects: A theoretical framework for the environmental impact assessment of human tourism activities. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2014, 10, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | WET | NDVI | NDBSI | LST | PC1 (%) | Year | WET | NDVI | NDBSI | LST | PC1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.01384 | 0.9342 | −0.1836 | −0.2093 | 71.49 | 2013 | 0.0244 | 0.9346 | −0.3375 | −0.1095 | 71.97 |
| 2001 | 0.0003 | 0.8144 | −0.3433 | −0.4679 | 54.94 | 2014 | 0.0009 | 0.9997 | −0.0002 | −0.0240 | 89.92 |
| 2002 | 0.0433 | 0.9489 | −0.2481 | −0.2091 | 66.12 | 2015 | 0.0193 | 0.9493 | −0.2867 | −0.1276 | 65.75 |
| 2003 | 0.0237 | 0.9098 | −0.0831 | −0.1902 | 70. 31 | 2016 | 0.0004 | 0.9883 | −0.1415 | −0.0570 | 70.99 |
| 2004 | 0.0051 | 0.9912 | −0.3186 | −0.0659 | 59.63 | 2017 | 0.0108 | 0.9981 | −0.0032 | −0.0610 | 88.96 |
| 2005 | 0.0268 | 0.8980 | −0.4191 | −0.1315 | 72.63 | 2018 | 0.0359 | 0.9433 | −0.3255 | −0.0542 | 64.86 |
| 2006 | 0.0501 | 0.9506 | −0.2941 | −0.0852 | 85.95 | 2019 | 0.0500 | 0.9323 | −0.3385 | −0.1170 | 72.04 |
| 2008 | 0.0019 | 0.9768 | −0.2006 | −0.0745 | 73.57 | 2020 | 0.0101 | 0.9998 | −0.0047 | −0.0189 | 94.72 |
| 2009 | 0.0690 | 0.6202 | −0.7516 | −0.2137 | 53.59 | 2021 | 0.0110 | 0.9996 | −0.0010 | −0.0270 | 91.51 |
| 2010 | 0.0712 | 0.8691 | −0.4107 | −0.1269 | 74.78 | 2022 | 0.0385 | 0.9321 | −0.3472 | −0.0956 | 91.51 |
| 2011 | 0.0323 | 0.9250 | −0.3641 | −0.1039 | 55.35 | 2023 | 0.1604 | 0.7567 | −0.6115 | −0.1668 | 71.08 |
| 2012 | 0.0517 | 0.9563 | −0.2502 | −0.1423 | 75.51 |
| Year | Average | t | p | Average | t | p | Average | t | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inside | Outside | 5A | 4A | Natural | Cultural | |||||||
| 2000–2007 | 0.7674 | 0.6420 | 2.263 | 0.040 | 0.7805 | 0.7616 | 0.735 | 0.042 | 0.7787 | 0.7420 | 1.143 | 0.035 |
| 2008–2016 | 0.7424 | 0.6165 | 2.453 | 0.030 | 0.7631 | 0.7331 | 0.392 | 0.045 | 0.7619 | 0.6985 | 0.766 | 0.041 |
| 2017–2023 | 0.8066 | 0.7383 | 2.444 | 0.026 | 0.8334 | 0.7947 | 1.698 | 0.021 | 0.8206 | 0.7750 | 1.943 | 0.011 |
| Region Types | All Areas | Outside | Inside | 5A | 4A | Natural | Cultural |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2007 | −0.0067 | −0.0100 | −0.0148 | −0.1141 | −0.3594 | −0.1572 | −0.5294 |
| 2008–2016 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | 0.0068 | 0.0075 | 0.0063 | 0.0111 |
| 2017–2023 | −0.0001 | −0.0001 | −0.0001 | −0.0014 | −0.0013 | −0.0014 | −0.0006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Xie, S.; Sun, J.; Qiao, H.; Feng, J.; Xie, X. Evolution of Ecological Environment Quality in Metropolitan Suburbs and Its Interaction with Tourism Development: The Case of Huangpi District, Wuhan City. Land 2025, 14, 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051032
Yang D, Xie S, Sun J, Qiao H, Feng J, Xie X. Evolution of Ecological Environment Quality in Metropolitan Suburbs and Its Interaction with Tourism Development: The Case of Huangpi District, Wuhan City. Land. 2025; 14(5):1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051032
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Danli, Shuangyu Xie, Jianwei Sun, Huafang Qiao, Jiaxiao Feng, and Xiaoyi Xie. 2025. "Evolution of Ecological Environment Quality in Metropolitan Suburbs and Its Interaction with Tourism Development: The Case of Huangpi District, Wuhan City" Land 14, no. 5: 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051032
APA StyleYang, D., Xie, S., Sun, J., Qiao, H., Feng, J., & Xie, X. (2025). Evolution of Ecological Environment Quality in Metropolitan Suburbs and Its Interaction with Tourism Development: The Case of Huangpi District, Wuhan City. Land, 14(5), 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051032






