Vegetation Dynamics and Responses to Climate Variations and Human Activities in the Basin of the Yarlung Tsangpo, Lhasa, and Nianchu Rivers in the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.2.1. NDVI Data
2.2.2. Meteorological Data
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Trend Analysis and Mann–Kendall Test
2.3.2. Partial Correlation Analysis
2.3.3. Hurst Exponent Method
2.3.4. Residual Analysis
3. Results
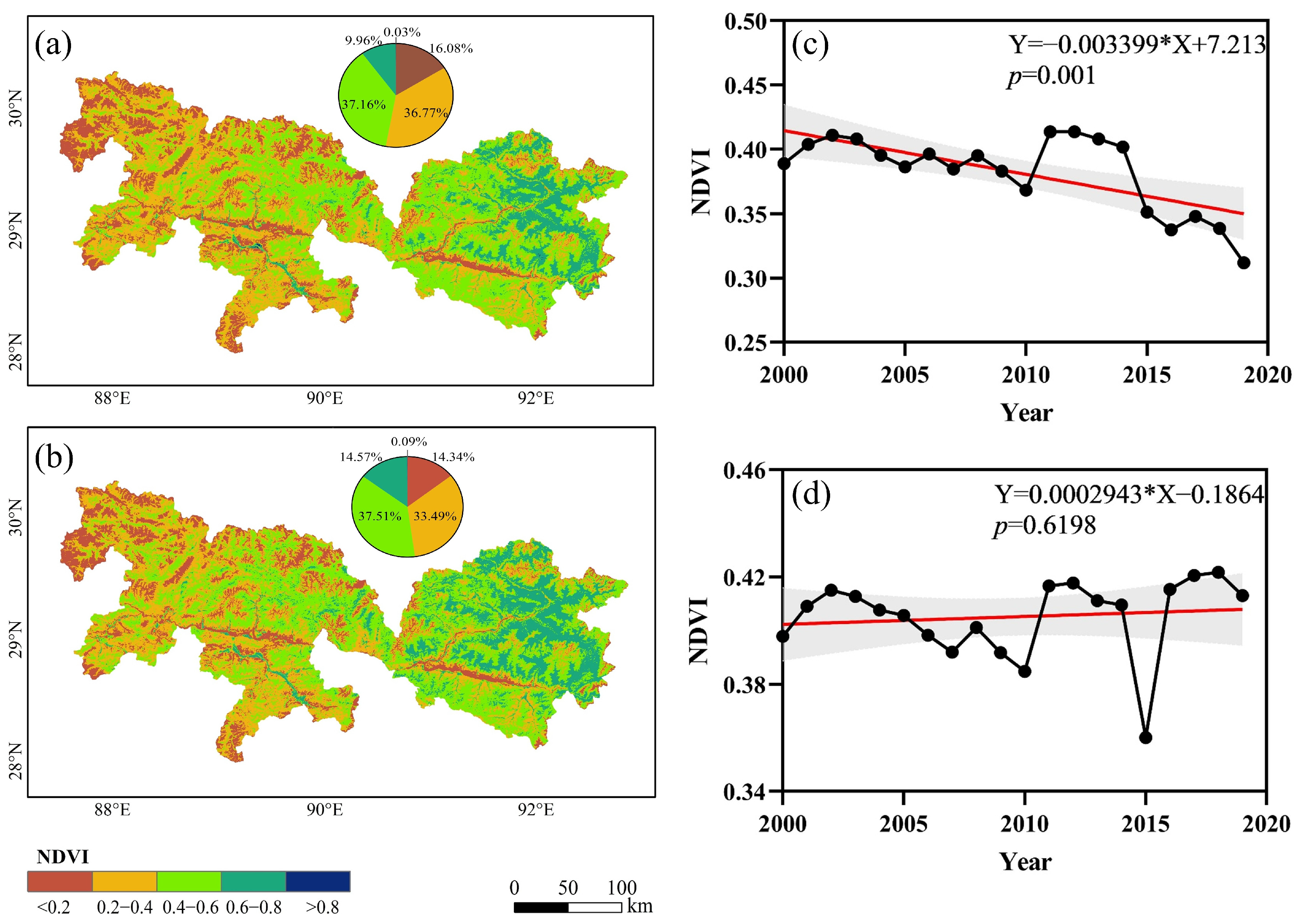
3.1. Spatiotemporal Changes in Vegetation Dynamics
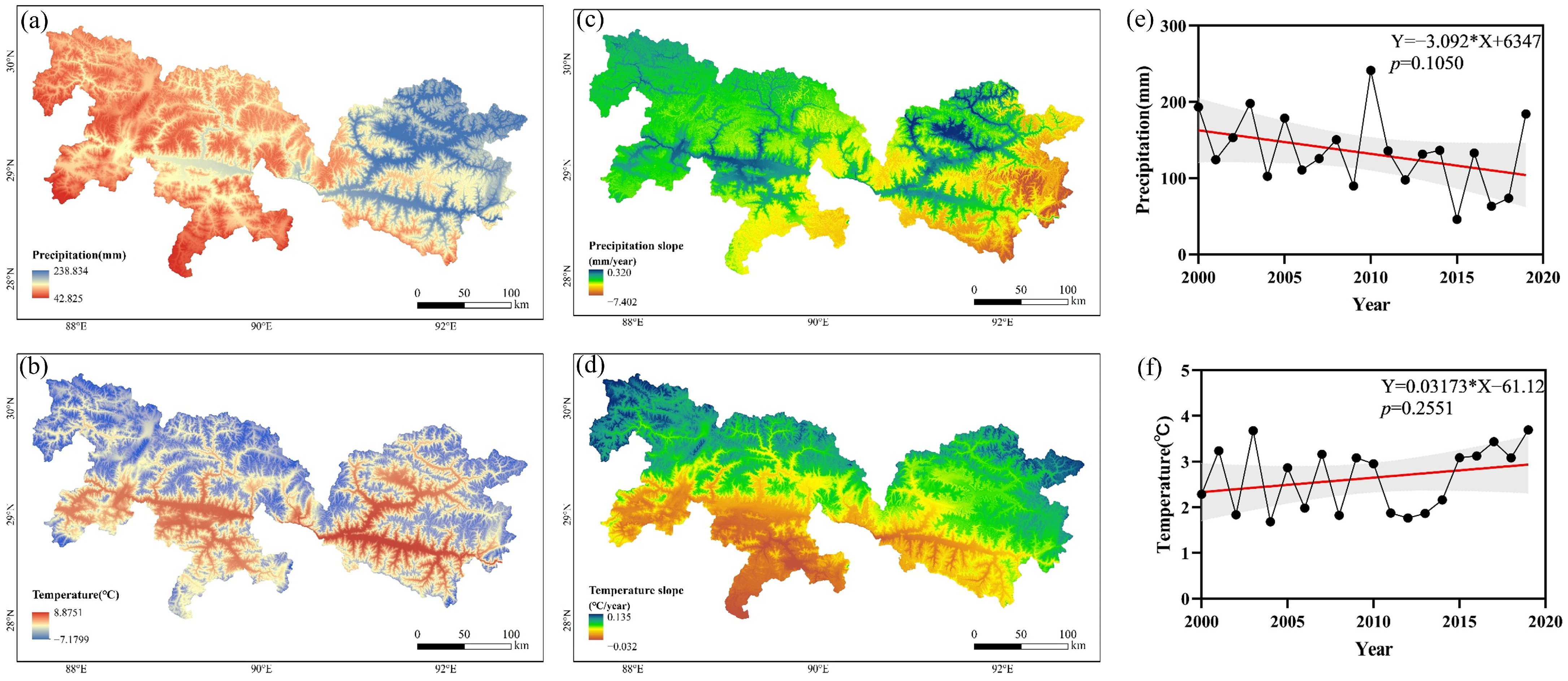
3.2. Changing Trends of Climatic Factors
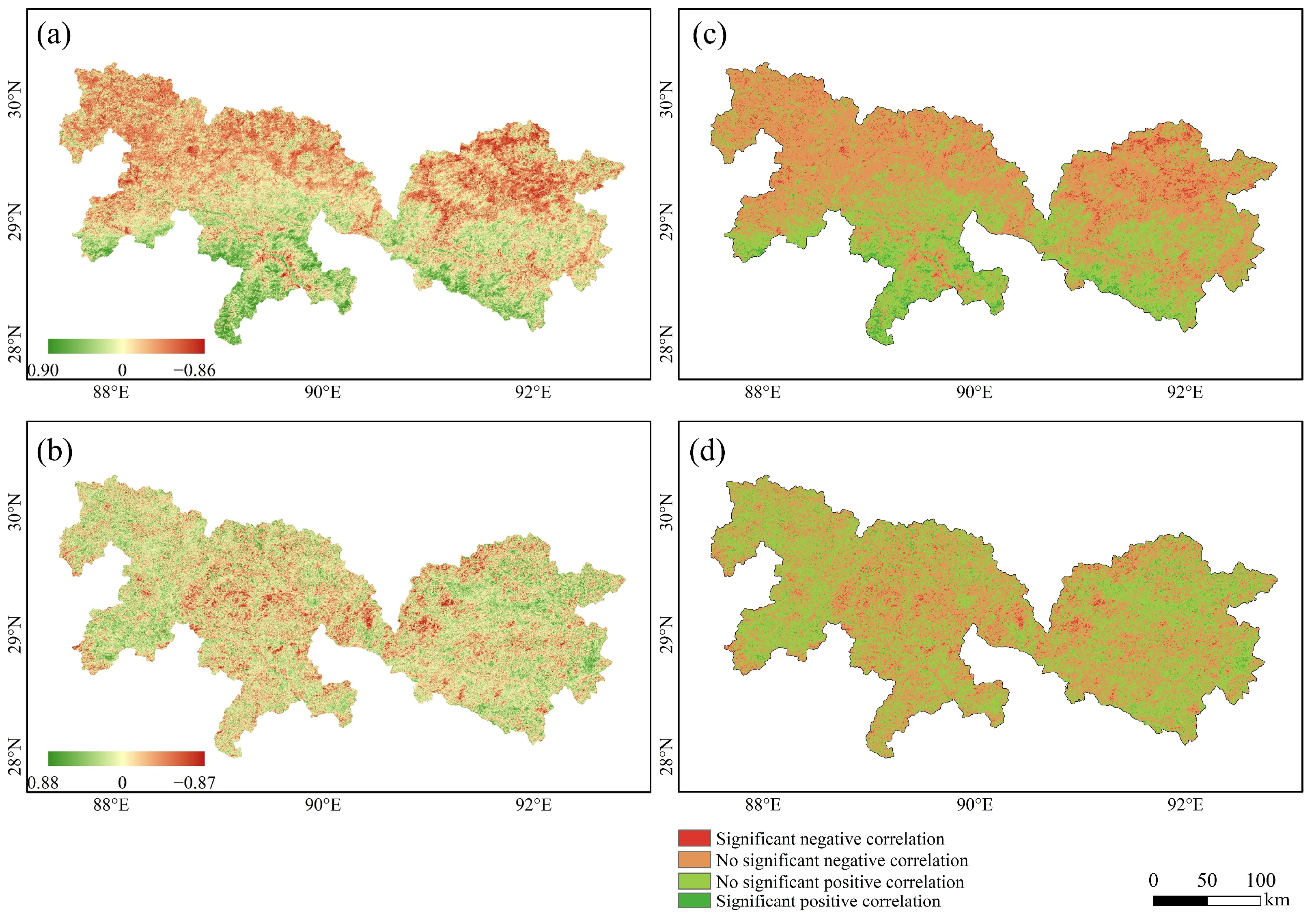
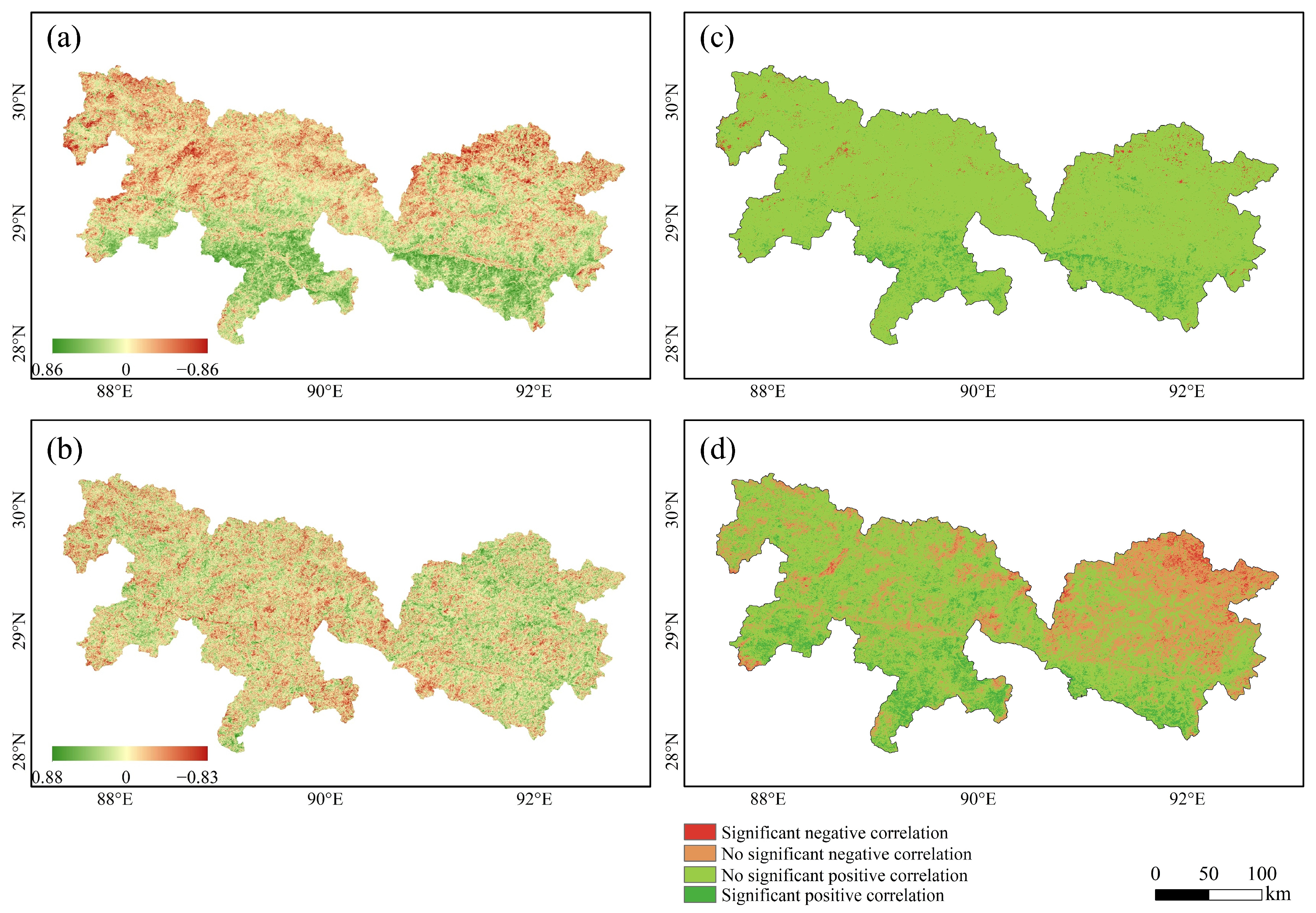
3.3. NDVI Responses to Temperature and Precipitation
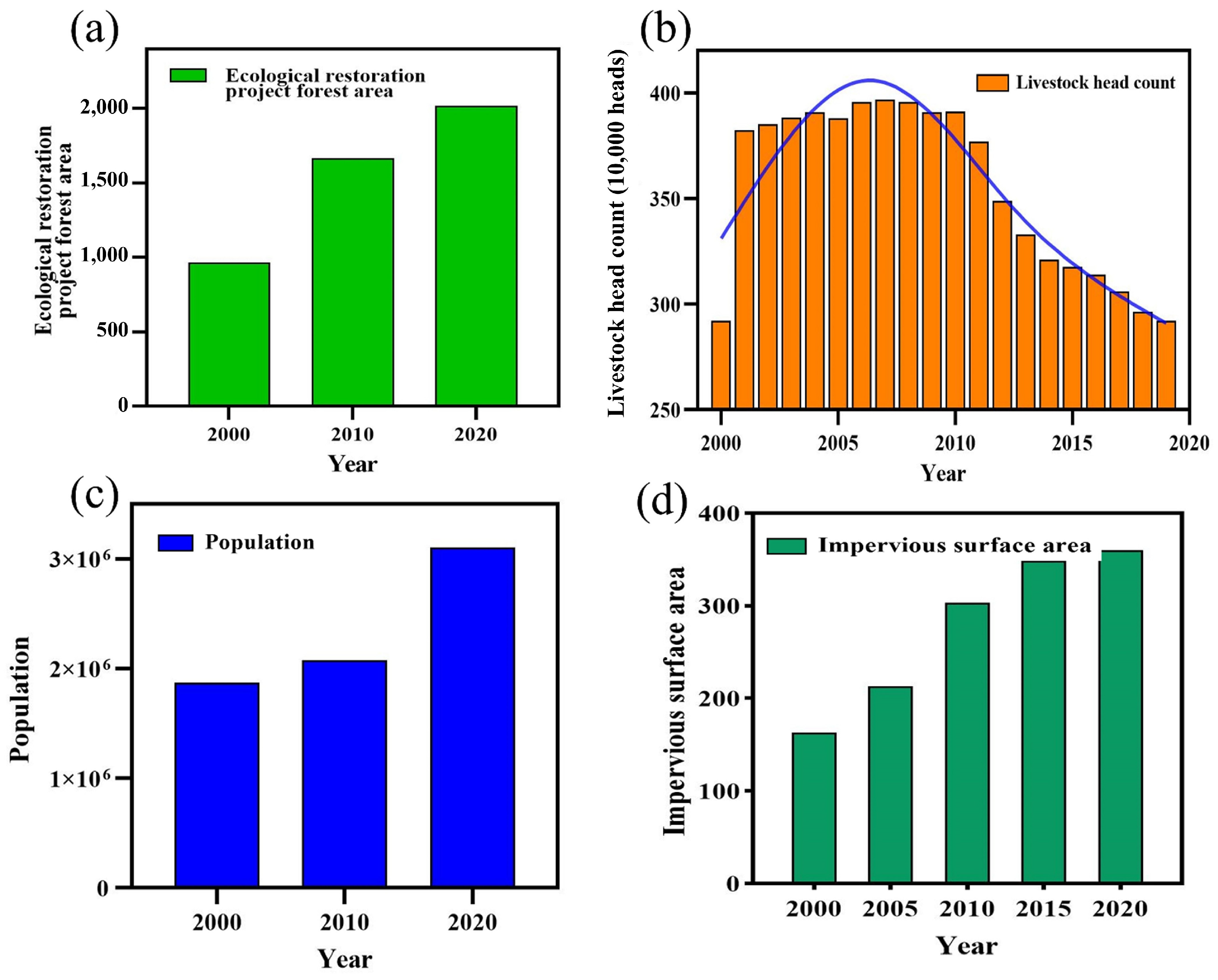
3.4. The Impact of Human Activities on the Vegetation NDVI
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of NDVI
4.2. Effects of Climate on Vegetation NDVI
4.3. The Effects of Human Activities on Vegetation Growth
4.4. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, M.K.; Woodward, F.I. Dynamic responses of terrestrial ecosystem carbon cycling to global climate change. Nature 1998, 393, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xia, J.; Zou, L.; Hong, S. Quantifying the Influences of Natural Factors and Human Activities on NDVI Changes in the Hanjiang River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C. Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2006, 37, 637–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Park, T.; Chen, C.; Lian, X.; He, Y.; Bjerke, J.W.; Chen, A.; Ciais, P.; Tømmervik, H.; et al. Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of global greening. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, J.; John, R.; Joseph, S. Consistent response of vegetation dynamics to recent climate change in tropical mountain regions. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rull, V.; Gonzalez-Samperiz, P.; Pablo Corella, J.; Morellón, M.; Giralt, S. Vegetation changes in the southern Pyrenean flank during the last millennium in relation to climate and human activities: The Montcortes lacustrine record. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 46, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, A.L.; Evans, J.P.; Liu, Y. Detecting dryland degradation using Time Series Segmentation and Residual Trend analysis (TSS-RESTREND). Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 197, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Ren, P. Coupled effect of climate change and human activities on the restoration/degradation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau grassland. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 1299–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, R.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Z.; Tu, X. Spatio-temporal distribution of NDVI and its influencing factors in China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xiong, Q.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Lin, B. Direct and indirect effects of environmental factors, spatial constraints, and functional traits on shaping the plant diversity of montane forests. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zou, B.; Luo, J. Coverage-dependent amplifiers of vegetation change on global water cycle dynamics. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C.; Yohe, G. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature 2003, 421, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Liang, S.L.; Jia, A.L.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, X.T.; Xiao, Z.Q. Validation of the surface daytime net radiation product from version 4.0 GLASS product suite. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tang, L.; Hupy, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Shao, G.F. A commentary review on the use of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in the era of popular remote sensing. For. Res. 2020, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, C. Analyzing ecological environment change and associated driving factors in China based on NDVI time series data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.N.; Li, J.J.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhang, T.B.; Luo, Z.Y.; Pei, X.J. Disentangling the response of vegetation dynamics to natural and anthropogenic drivers over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau using dimensionality reduction and structural equation model. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 554, 121677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.N.; Li, J.J.; Pei, X.J.; Yang, H. Decoupling the response of vegetation dynamics to asymmetric warming over the Qinghai-Tibet plateau from 2001 to 2020. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, J.; Pei, X.; Bian, L.; Zhang, T.; Yi, G.; Bie, X.; Peng, P. Dominance of topography on vegetation dynamics in the Mt. Qomolangma National Nature Reserve: A UMAP and PLS-SEM Analysis. Forests 2023, 14, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, G.; Ren, Z.; Li, P.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Dynamic change of vegetation and its response to climate and topographic factors in the Xijiang River basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11637–11648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ye, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Lu, X.; Liu, G.; Xu, M.; Li, R.; et al. Response of net reduction rate in vegetation carbon uptake to climate change across a unique gradient zone on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. 2021, 203, 111894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Lian, J.; Gong, X. Temporal and Spatial Variations in NDVI and Analysis of the Driving Factors in the Desertified Areas of Northern China From 1998 to 2015. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 633020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Zu, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, M.; Paudel, B. Increasing sensitivity of alpine grasslands to climate variability along an elevational gradient on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamchin, M.; Lee, W.K.; Jeon, S.W.; Jeon, S.W.; Wang, S.W.; Lim, C.H.; Song, C.; Sung, M.J. Long-term trend and correlation between vegetation greenness and climate variables in Asia based on satellite data. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, T. Trend shifts in satellite-derived vegetation growth in Central Eurasia, 1982–2013. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1658–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Lu, Q. Spatiotemporal Variation of Vegetation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Influence of Climatic Factors and Human Activities on Vegetation Trend (2000–2019). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Q.; Mao, F.; Sun, H.; Hou, Y.Y. Study of normalized difference vegetation index variation and its correlation with climate factors in the three-river-source region. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Niu, J.; Berndtsson, R.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. NDVI Dynamics and Its Response to Climate Change and Reforestation in Northern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, B.; Amparo Gilabert, M. Vegetation dynamics from NDVI time series analysis using the wavelet transform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1823–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliot, D.; Latifovic, R.; Olthof, I. Trends in vegetation NDVI from 1km AVHRR data over Canada for the period 1985–2006. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zu, J.; Ding, M.; Paudel, B. Spatiotemporal patterns of vegetation greenness change and associated climatic and anthropogenic drivers on the Tibetan Plateau during 2000–2015. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Fu, Y.H.; Xue, B.L.; Wang, G.Q.; Yu, J.S.; Zuo, D.P.; Xu, Z.X. Spatial heterogeneity of changes in vegetation growth and their driving forces based on satellite observations of the Yarlung Zangbo River basin in the Tibetan plateau. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Fan, B. Shifts of the Mean Centers of Potential Vegetation Ecosystems under Future Climate Change in Eurasia. Forests 2019, 10, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Ciais, P.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Piao, S. Seasonal and interannual changes in vegetation activity of tropical forests in Southeast Asia. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 224, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; He, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, A. Notable shifting in the responses of vegetation activity to climate change in China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 87, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Yin, G.; Tan, J.; Cheng, L.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Mao, J.; Mynei, R.; Peng, S.; et al. Detection and attribution of vegetation greening trend in China over the last 30 years. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostert, P.; Kuemmerle, T.; Prishchepov, A.; Sieber, A.; Lambin, E.; Radeloff, V. Rapid land use change after socio-economic disturbances: The collapse of the Soviet Union versus Chernobyl. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 45201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Luo, H.; Hu, T.; Shao, D.; Cui, Y.; Khan, S.; Luo, Y. Identification of the Roles of Climate Factors, Engineering Construction, and Agricultural Practices in Vegetation Dynamics in the Lhasa River Basin, Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Liang, T.; Hou, F.; Xu, J.; Xue, P. Quantitative spatial analysis of vegetation dynamics and potential driving factors in a typical alpine region on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau using the Google Earth Engine. Catena 2021, 206, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, N.; Liu, Y. Temperature factors are a primary driver of the forest bryophyte diversity and distribution in the southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 527, 120610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, J.; Gong, J.; Li, S. Human footprint in Tibet: Assessing the spatial layout and effectiveness of nature reserves. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, C.; Shen, M.; Yang, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Piao, S. Varying responses of vegetation activity to climate changes on the Tibetan Plateau grassland. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, X. Human-induced grassland degradation/restoration in the central Tibetan Plateau: The effects of ecological protection and restoration projects. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Dong, S.; Su, X.; Wag, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X. Analysis of vegetation change associated with human disturbance using MODIS data on the rangelands of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Rangel 2015, 37, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.; Xue, Y.; Piao, S. Climate Change Trends and Impacts on Vegetation Greening Over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7540–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Marwa, W.A.H.; Mohammed, A.; Liang, P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Bikram, P.; Pan, K.; Sameh, B.; et al. Monitoring the impact of climate change and human activities on grassland vegetation dynamics in the northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau of China during 2000–2015. J. Arid Land 2019, 11, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zheng, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Meng, E.; Guo, Y. Quantitative contribution of climate change and human activities to vegetation cover variations based on GA-SVM model. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Rao, E.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Lu, H.T.; Zhu, J.Y. Ecological risk assessment in Southwest China based on multiple risk sources. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 8992–9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Shen, W.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, Y. China Regional 250 m Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Data Set (2000–2023); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Doraiswamy, P.C.; Hatfield, J.L.; Jackson, T.J.; Akhmedov, b.; Prueger, J.; Stern, A. Crop condition and yield simulations using Landsat and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Li, Y.F.; Li, B.; Hao, Z.B.; Hu, X.Y.; Yu, H.; Xiang, S.Y.; Pascal, M.L.F.; Shen, W.L.; He, A.Q.; et al. A comparative study on the applicability and effectiveness of NSVI and NDVI for estimating fractional vegetation cover based on multi-source remote sensing image. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2184501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gesang, Z.; Fan, J. Soil Erosion Status and Distribution Characteristics in the ‘One River and Two Streams’ Region in Tibet. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 24, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Peng, C.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.P.; Li, M.X.; Zhang, K.R.; Zhang, D.L.; Zhu, Q. Dynamics of vegetation autumn phenology and its response to multiple environmental factors from 1982 to 2012 on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.X.; Xie, Y.L.; Gao, Z.Y.; Zhou, P. Evaluation on Elevation Accuracy of Commonly Used DEM in Five Typical Areas of China. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Yang, H.M.; Wang, D.C. Digital Mapping of Forest Soil Organic Carbon Based on NDVI Time Series Features: A Case Study of Jiyuan Nanshan Forest Farm. Soil Bull. 2024, 4, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Ji, L.; Lei, L.; Wang, C.; Yan, D.; Li, B.; Li, J. Vegetation greenness trend (2000 to 2009) and the climate controls in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 73572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Jiapaer, G.; Bao, A.; Guo, H.; Ndayisaba, F. Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and human activities in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisa, W.; Igbawua, T.; Henchiri, M.; Ali, S.; Zhang, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J. Assessment of climate impact on vegetation dynamics over East Africa from 1982 to 2015. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin & Co., Ltd.: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Tošić, I. Spatial and temporal variability of winter and summer precipitation over Serbia and Montenegro. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2004, 77, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.Q.; Kuang, W.H.; Dou, Y.Y. Dataset of Urban Impervious Surface Area and Green Space Fractions in the Tibetan Plateau (2000–2020); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, F.B. Climates Prevailing in the Yellow-Gray Earth and Yellow-Brown Earth Zones in New Zealand. In Selected Papers in Soil Formation and Classification; Drew, J.V., Ed.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1967; Volume 1, pp. 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Wallis, J.R. Robustness of the rescaled range R/S in the measurement of noncyclic long run statistical dependence. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Evaluation of Earth Observation based global long term vegetation trends—Comparing GIMMS and MODIS global NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Gao, W. Changes in urban vegetation cover and analysis of the influencing factors: A case study of Harbin, Heilongjiang Province, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, J.; Sheng, Y.; Li, Z. The Analysis of Hydrometeorological Characteristics in the Yarlung Tsangpo River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. The impact of climate change on runoff in the Yarlung Tsangpo River basin in the Tibetan Plateau. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Liu, L.; Heng, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. A multi-index evaluation of drought characteristics in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin of Tibetan Plateau, Southwest China. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, W. Changes of land cover in the Yarlung Tsangpo River basin from 1985 to 2005. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Cheng, G.; Li, W.; Sha, Y.; Yang, Y. On the Variation of NDVI with the Principal Climatic Elements in the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1894–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Gao, J.; Liu, Z. Precipitation Drives the NDVI Distribution on the Tibetan Plateau While High Warming Rates May Intensify Its Ecological Droughts. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, B. NDVI-Based Greening of Alpine Steppe and Its Relationships with Climatic Change and Grazing Intensity in the Southwestern Tibetan Plateau. Land 2022, 11, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.Z.; Tang, M.Y. Analysis of spatio-temporal changes and driving vegetation NDVI in coastal areas of China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.E. Long-Term Storage Capacity of Reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ye, B.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Yang, G.J. Variations of NDVI over elevational zones during the past two decades and climatic controls in the Qilian mountains, northwestern China. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2011, 43, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Niu, Q.; Heng, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.X. Transition characteristics of the dry-wet regime and vegetation dynamic responses over the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, Y. Trend analysis of vegetation dynamics in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau using Hurst Exponent. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 14, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoni, D.; Schmid, H.P.; Wayson, C.A.; Potter, H.; Grimmond, C.S.B.; Randolph, J.C. Evidence of increased net ecosystem productivity associated with a longer vegetated season in a deciduous forest in south-central Indiana, USA. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Ding, M. Mapping changing population distribution on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since 2000 with multi-temporal remote sensing and point-of-interest data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, L.W.; Wesche, K.; Trachte, K.; Reudenbach, C.; Bendix, J. Climate variability rather than overstocking causes recent large scale cover changes of Tibetan pastures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guan, Q.; Lin, J.; Tian, J.; Tan, Z.; Li, H. Evolution of NDVI secular trends and responses to climate change: A perspective from nonlinearity and nonstationarity characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 254, 112247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Dai, R.; Jin, T. Spatio-temporal Variation of Vegetation Cover and Its Relationship with Climatic Factors and Human Activities in the Southwest Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, T.; Sun, D. Regional differentiation regularity and influencing factors of population change in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Liu, R.; Ding, L. Influences of Climate Change and Human Activities on NDVI Changes in China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, R.; Steinicke, E. Counterurbanization and Its Socioeconomic Effects in High Mountain Areas of the Sierra Nevada (California/Nevada). Mt. Res. Dev. 2006, 26, 64–71. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/3674394 (accessed on 29 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Diao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhuo, G.; Zhang, Y. Regional-scale vegetation-climate interactions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 65, 101413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Liu, K. Research on the Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities on the NDVI of Arid Areas—A Case Study of the Shiyang River Basin. Land 2024, 13, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



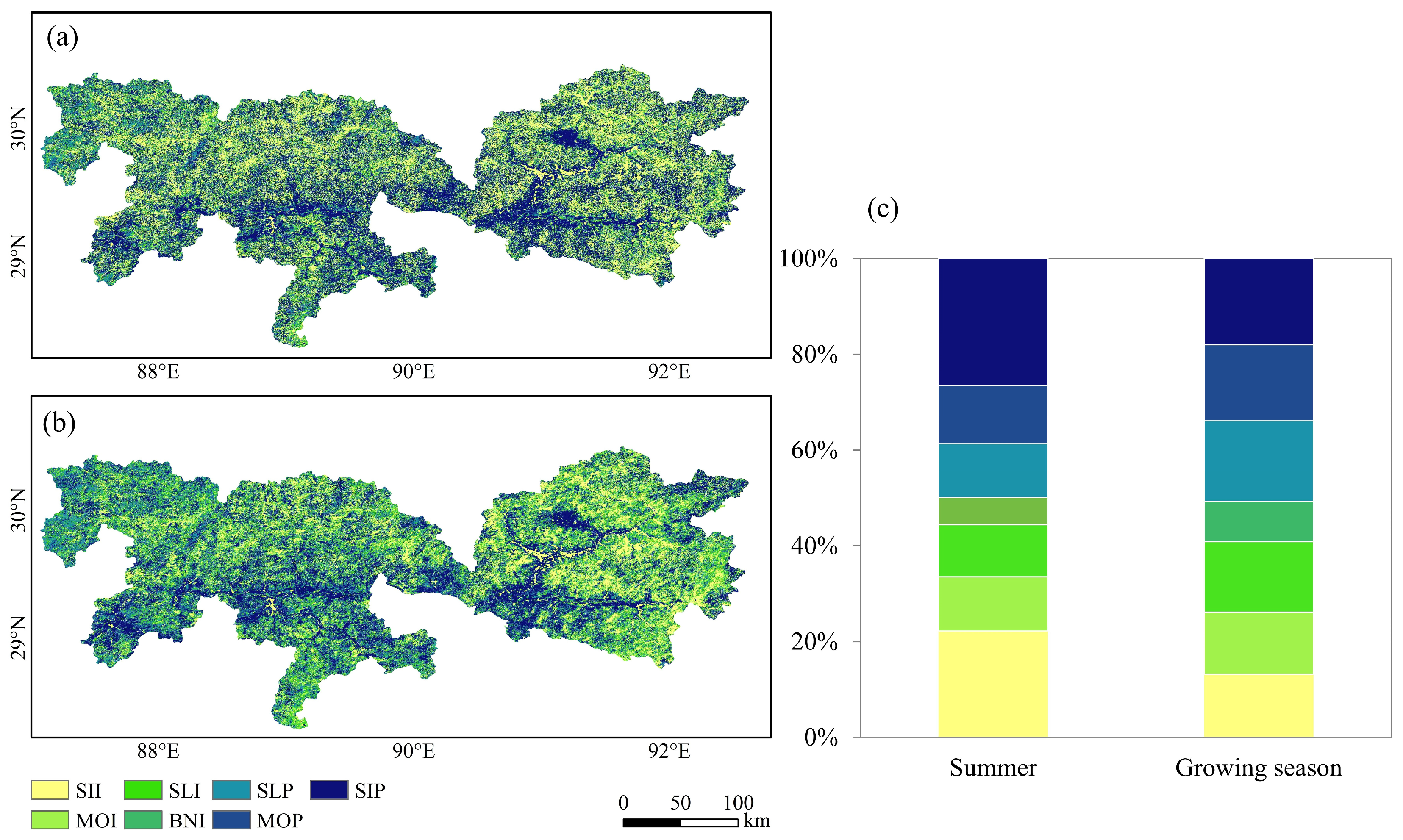
| Slope | Influence Level |
|---|---|
| <−2.0 | Significant inhibition |
| −2.0~−1.0 | Moderate inhibition |
| −1.0~−0.2 | Slight inhibition |
| −0.2~0.2 | Basically no impact |
| 0.2~1.0 | Slight promotion |
| 1.0~2.0 | Moderate promotion |
| ≥2.0 | Significant promotion |
| β | Z | NDVI Trend Types | Area Ratio (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | Growing Season | |||
| β < −0.0005 | |Z| > 1.96 | Significant decrease | 31.65 | 3.18 |
| β < −0.0005 | |Z| < 1.96 | Non-significant decrease | 50.42 | 31.18 |
| β > 0.0005 | |Z| < 1.96 | Non-significant increase | 7.93 | 39.56 |
| β > 0.0005 | |Z| > 1.96 | Significant increase | 1.85 | 7.63 |
| −0.0005 < β < 0.0005 | Z | Stable | 8.15 | 18.45 |
| Change Patterns | Area Ratio (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Summer | Growing Season | |
| Continuous significant decrease | 11.22% | 7.46% |
| Continuous non-significant decrease | 8.12% | 0.99% |
| Uncertain | 76.19% | 76.26% |
| Continuous significant increase | 0.62% | 2.11% |
| Continuous non-significant increase | 1.95% | 8.93% |
| No significant change | 1.90% | 4.26% |
| Correlations | Area Ratio (%) of Temperature | Area Ratio (%) of Precipitation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | Growing Season | Summer | Growing Season | |
| Significant negative correlation | 3.68% | 2.27% | 1.27% | 1.75% |
| Significant positive correlation | 56.96% | 44.51% | 5.38% | 9.77% |
| No significant negative correlation | 36.24% | 50.60% | <0.05% | 26.47% |
| No significant positive correlation | 3.12% | 2.62% | 93.35% | 62.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, C.; Li, J.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Peng, P.; Tang, X. Vegetation Dynamics and Responses to Climate Variations and Human Activities in the Basin of the Yarlung Tsangpo, Lhasa, and Nianchu Rivers in the Tibetan Plateau. Land 2025, 14, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051027
Su C, Li J, Xiang Y, Yang S, Zhang X, Xu D, Wang S, Zhang T, Peng P, Tang X. Vegetation Dynamics and Responses to Climate Variations and Human Activities in the Basin of the Yarlung Tsangpo, Lhasa, and Nianchu Rivers in the Tibetan Plateau. Land. 2025; 14(5):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051027
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Chunbo, Jingji Li, Ying Xiang, Shurong Yang, Xiaochao Zhang, Dinghui Xu, Shijun Wang, Tingbin Zhang, Peihao Peng, and Xiaolu Tang. 2025. "Vegetation Dynamics and Responses to Climate Variations and Human Activities in the Basin of the Yarlung Tsangpo, Lhasa, and Nianchu Rivers in the Tibetan Plateau" Land 14, no. 5: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051027
APA StyleSu, C., Li, J., Xiang, Y., Yang, S., Zhang, X., Xu, D., Wang, S., Zhang, T., Peng, P., & Tang, X. (2025). Vegetation Dynamics and Responses to Climate Variations and Human Activities in the Basin of the Yarlung Tsangpo, Lhasa, and Nianchu Rivers in the Tibetan Plateau. Land, 14(5), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051027







