Risk Assessment on Organochlorine Pesticides in Agricultural Soils of Eastern City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
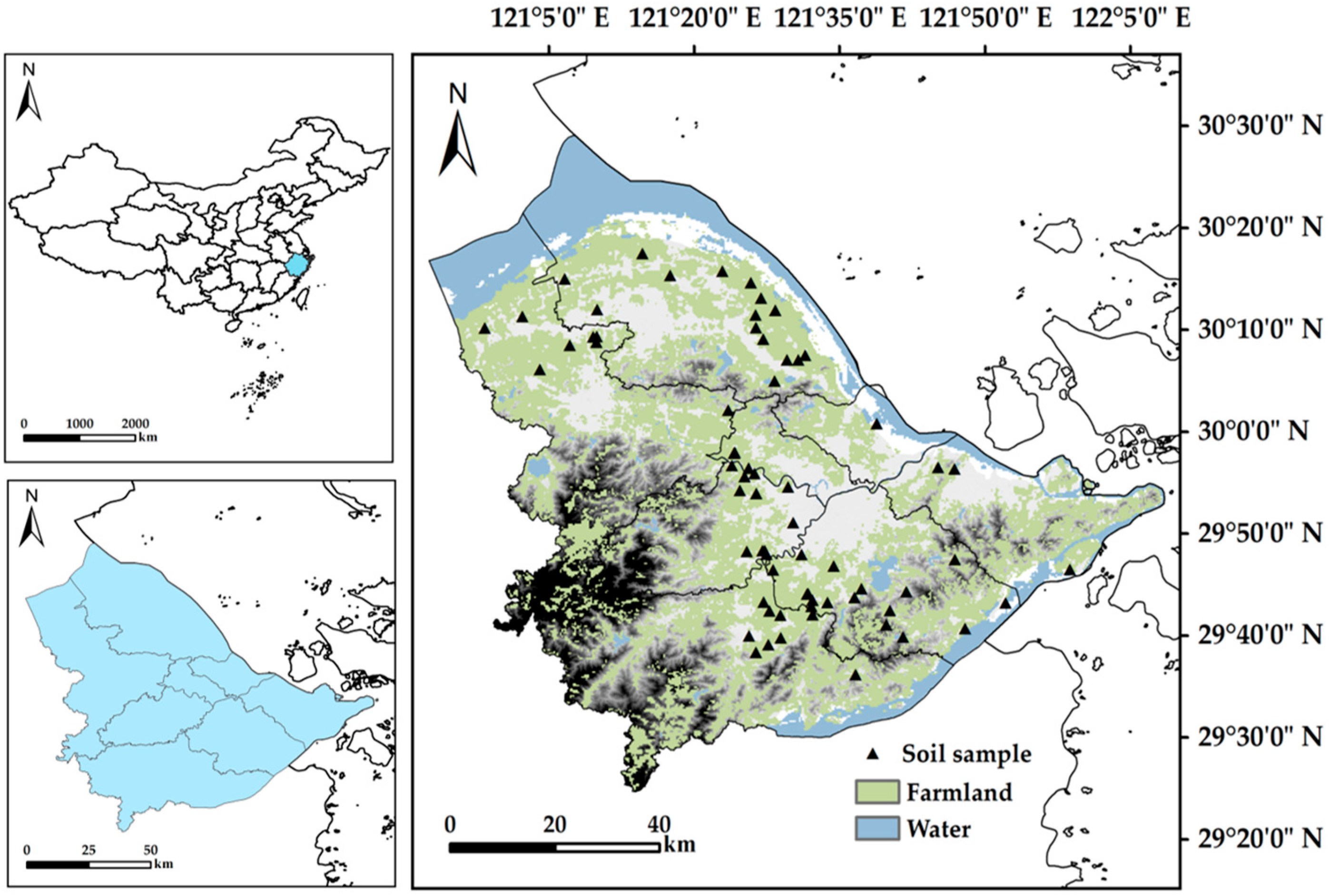
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Testing
2.2.1. Sample Preparation and Instrumental Analysis
2.2.2. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.3. Health Risk Assessment
2.4. Monte Carlo Simulation
2.5. Ecological Risk (Eco-Risk) Assessment
2.5.1. Effects Range Low/Median
2.5.2. The Mean ERM Quotients
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
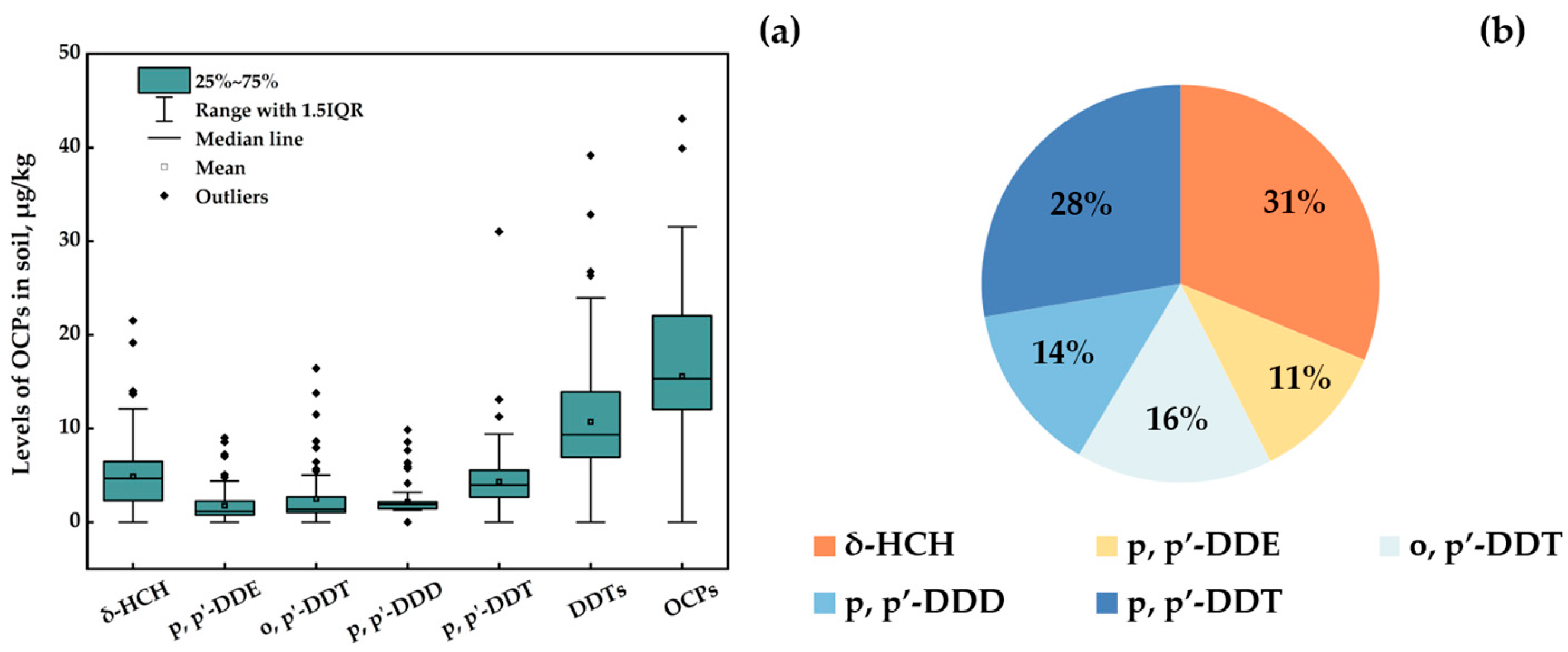
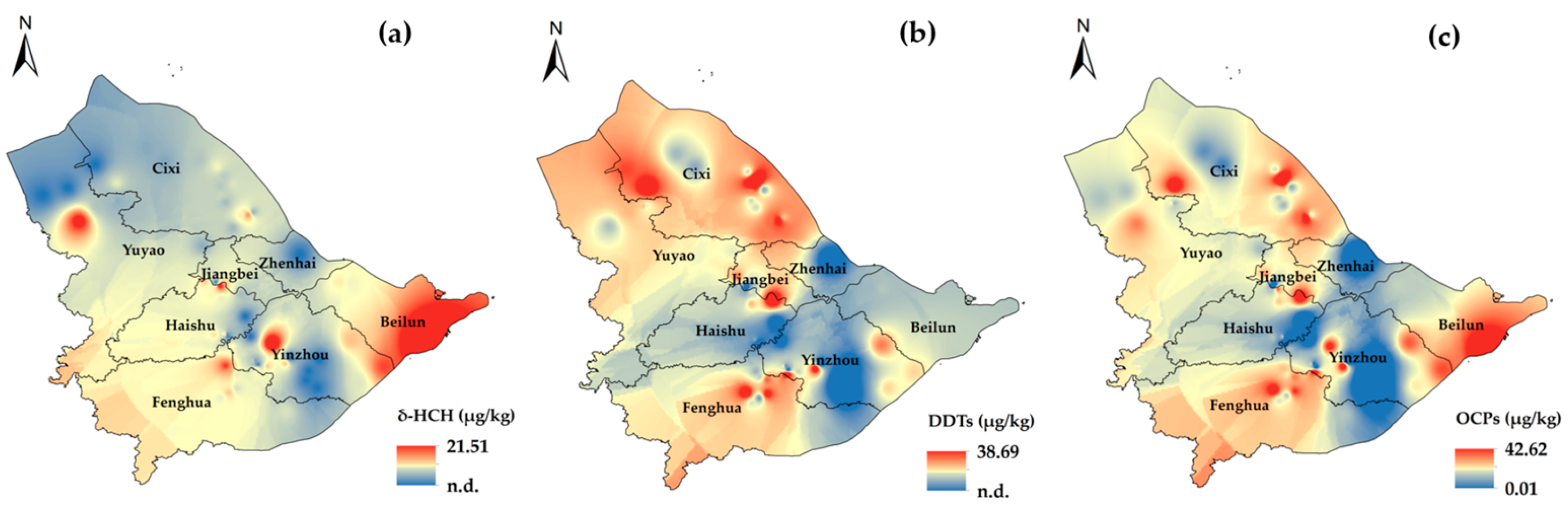
3.1. Residual Characteristics of OCPs
3.2. Health Risk Assessment (HRA)
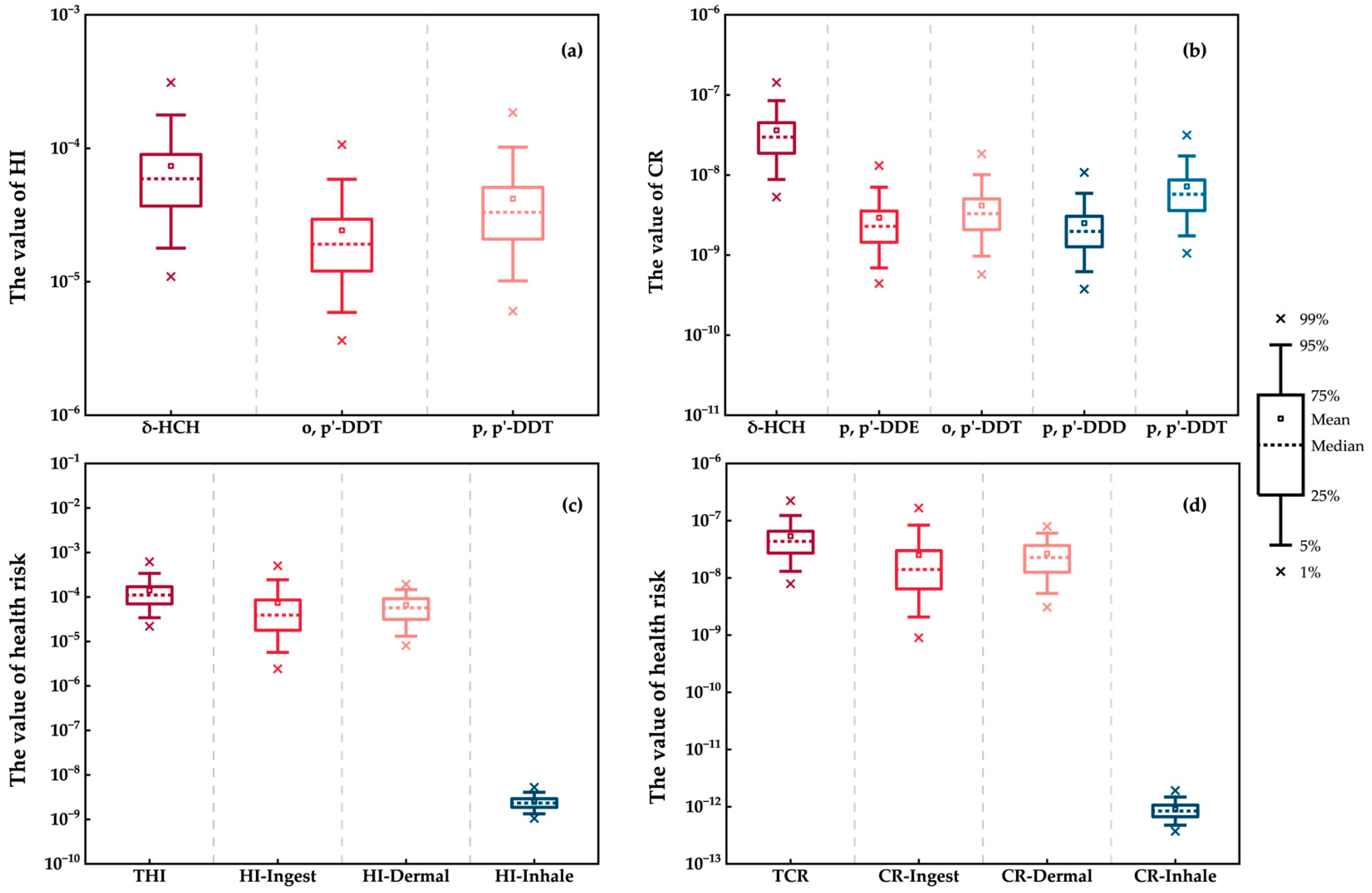
3.2.1. Non-Carcinogenic Health Risk Evaluation
3.2.2. Carcinogenic Health Risk Evaluation
3.2.3. Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo
3.3. Eco-Risk Assessment
3.3.1. Environmental Quality Assessment
3.3.2. Eco-Risk Assessment of DDTs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Qi, S.H.; Li, X.D.; Peng, X.Z. Concentrations, enantiomeric compositions, and sources of HCH, DDT and chlordane in soils from the Pearl River Delta, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 372, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Z.J.; Wu, X.G. Organochlorine pesticides in riparian soils and sediments of the middle reach of the Huaihe River: A traditional agricultural area in China. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, S.L.; Ni, Z.L.; Qu, M.H.; Zhong, D.L.; Ye, C.F.; Tang, F.B. Pesticides in persimmons, jujubes and soil from China: Residue levels, risk assessment and relationship between fruits and soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafi, K.; Fattahi, N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Pirsaheb, M.; Azizzadeh, N.; Noori, M. Trace analysis of some organophosphorus pesticides in rice samples using ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.F.; Feng, J.Y.; Li, G. Occurrence and possible sources of organochlorine pesticides in soils of Ningbo, East China. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh 2019, 109, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.M.; Shan, Z.J. Production and application of pesticides and factor analysis for their pollution in environment in China. Adv. Environ. Sci. 1996, 4, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kafaei, R.; Arfaeinia, H.; Savari, A.; Mahmoodi, M.; Rezaei, M.; Rayani, M.; Sorial, G.A.; Fattahi, N.; Ramavandi, B. Organochlorine pesticides contamination in agricultural soils of southern Iran. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.L.; Xu, C.; Yao, Y.J.; Liu, K.; Yang, F.X.; Tang, M.L.; Liu, W.P. Status, influences and risk assessment of hexachlorocyclohexanes in agricultural soils across China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12140–12147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyani, R.; Dehdashti, B.; Heidari, Z.; Sharafi, S.M.; Mahmoodzadeh, M.; Amin, M.M. Biomonitoring of organochlorine pesticides and cancer survival: A population-based study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 300, 37357–37369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the Reople’s Republic of China. Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the Reople’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.H.; Huo, L.; Zhang, R.; Gu, X.F.; Chen, G.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, W.B.; Hui, K.L.; Jiang, Y. Effect of soil-groundwater system on migration and transformation of organochlorine pesticides: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Liu, J.Y.; Huang, Y.; Yi, Y.L. Ecological hazards of residual pesticides in farmland soils and the pollution remediation technology progress. Adv. Environ. Prot. 2018, 8, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, M.M.; Achal, V. A comprehensive review on environmental and human health impacts of chemical pesticide usage. Emerging Contam. 2025, 11, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Liu, M.H.; Zhang, T.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Lu, K.J. Characterization, sources and risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), organophosphorus pesticides (OPPs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in agricultural soils from Jilin Province in Northeast China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, G.; Atreya, K.; Scheepers, P.T.J.; Geissen, V. Concentration and distribution of pesticide residues in soil: Non-dietary human health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Zhou, H.J.; Cao, C.T.; Ai, T.; Xing, H.H.; Sun, J.T. Levels, Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Organochlorine Pesticides in Agricultural Soils from the Pearl River Delta of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.Y.; Liang, J.H.; Shi, H.D.; Yan, T.Z.; He, Z.X.; Li, L.; Hu, H.L. Health risk assessment of heavy metals based on source analysis and Monte Carlo in the downstream basin of the Zishui. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 117975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lu, Q.; Cai, L.M.; Chen, L.G.; Wang, H.Z. Characteristics of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment in Urban Parks at a Megacity of Central China. Toxics 2023, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci.Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzelai, A.; Vega, M.; Angulo, E. Deriving ecological risk-based soil quality values in the Basque Country. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violintzis, C.; Arditsoglou, A.; Voutsa, D. Elemental composition of suspended particulate matter and sediments in the coastal environment of Thermaikos Bay, Greece: Delineating the impact of inland waters and wastewaters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.P.; Fang, L.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, W.P.; Yuan, H.J.; Jantunen, L.; Li, Y.F. Residues of currently and never used organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soils from Zhejiang province, China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2982–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.X.; Li, S.J.; Yang, B.J.; Qian, F.Z.; Gao, Z.G.; Zhu, L.B.; Ying, H.M.; Xu, N.B.; Weng, Y.B. Study on residues of persistent organochloride pesticides in agricultural soils of Ningbo. In Proceedings of the Persistent Organic Pollutants Forum 2010 and the 5th National Symposium on Persistent Organic Pollutants, Nanjing, China, 17–18 May 2010; pp. 122–123. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.Y.; Fu, X.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, Y.G. Health risk assessment of persistent toxic substances in agricultural soils of Ningbo. Mod. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 4, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.H.; You, Z.J.; Shentu, J.K.; Zhong, H.Y.; Chai, L.Y. Residual level and ecological risk assessment of OCPs and PCBs in sediments of mudflat shellfish culturing areas in Ningbo, Zhejiang Province of East China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Administration for Market Regulation. Criteria for Qualification Accreditation and Review of Inspection and Testing Institutions; State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/IEC 17043:2023; Conformity Assessment—General Requirements for the Competence of Proficiency Testing Providers. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- HJ 835-2017; Soil and Sediment—Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides–Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the Reople’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Napo, G.; Akpataku, K.V.; Seyf-Laye, A.-S.M.; Gnazou, M.D.T.; Bawa, L.M.; Djaneye-Boundjou, G. Assessment of shallow groundwater quality using water quality index and human risk assessment in the Vogan-Attitogon Plateau, Southeastern (Togo). J. Environ. Pollut. Hum. Health 2021, 9, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.R.; Barik, M.; Jha, V.; Sahoo, S.K.; Sahoo, N.K. Hydrogeochemical analysis and geospatial modeling for delineation of groundwater pollution and human health risks assessment of Cuttack district, India. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2021, 31, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Ma, J.H.; Ruan, X.L.; Chen, X. Compound health risk assessment of cumulative heavy metal exposure: A case study of a village near a battery factory in Henan Province, China. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2020, 22, 1408–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.L.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Q.; Mcbean, E.; Lin, X.J. A multi-objective optimal model for groundwater remediation under health risk assessment in a petroleum contaminated site. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Xiamen, China, 3–5 September 2018; pp. 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Hadei, M.; Sharafi, K. Human health risk assessment by Monte Carlo simulation method for heavy metals of commonly consumed cereals in Iran- Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.P.; Yang, X.Y. Environmental health risk assessment of contaminated soil based on Monte Carlo method: A case of PAHs. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 2522–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yun, X.Y.; Zhang, M.M.; Wang, J. Occurrence and assessment of organochlorine pesticides in the agricultural topsoil of Three Gorges Dam region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5001–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.J.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, P.; Guo, W.; An, S.S. Residual characteristics, health risks, and influencing factors of organochlorine pesticides in soil of cultivated land in Hehuang Valley. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2024, 44, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, J.; Lei, Y.C.; Deng, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhang, C.L. Residue characteristics, sources and risk assessment of organochlorinepesticides in typical farmland soil. Environ. Chem. 2023, 42, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, K.; Vallero, D.A.; Lewis, R.G. Factors Influencing the Distribution of Lindane and Other Hexachlorocyclohexanes in the Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 4373–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Lu, H.; Luo, H.X.; Li, R.A.; Zhu, Y.G. Study on residual organochlorined pesticides of cultivated soils in Cixi City, Zhejing, China. J. Ningbo Univ. (Nat. Sci. Eng. Ed.) 2006, 19, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, H.J.; Dai, J.R.; Pang, X.G.; Zhao, X.Q.; Liu, H.F. Residues and spatial distribution characteristics of organochlorine pesticides DDTs in soil of Linyi City, Shandong Province. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Yang, G.Y. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in surface soil of pearl river delta economic zone. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 2954–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.T.; Xue, H.H.; Zhang, S.C.; Pei, J.; Xiang, X.X.; Wang, X.W.; Sun, S.B.; Yao, H. Residue characteristics, sources and risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in riparian soils of the Yangtze River Basin. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 3897–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z. Study on the pollution characteristics of organochlorine pesticide residues in farmland soil in the Yellow River Basin. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.W.; Qi, Y.L.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.X.; Wang, J. Concentrations, distribution, sources and risk assessment of organohalogenated contaminants in soils from Kenya, Eastern Africa. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, J.; Syed, J.H.; Mahmood, A.; Ali, U.; Rehman, M.Y.A.; Malik, R.N.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Investigation of organochlorine pesticides from the Indus Basin, Pakistan: Sources, air–soil exchange fluxes and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.K.; Albanese, S.; Chen, W.; Lima, A.; Doherty, A.L.; Piccolo, A.; Arienzo, M.; Qi, S.; De Vivo, B. The status of organochlorine pesticide contamination in the soils of the Campanian Plain, southern Italy, and correlations with soil properties and cancer risk. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W. Research on residual characteristics, risk assessment and environmental behavior of POPs in urban soil—A case study of Changchun City. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook. Volume I General Factors. 1996. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-factors-handbook-2011-edition (accessed on 12 March 2025).

| The Value of m-ERM-q | Risk Level |
|---|---|
| ≤0.1 | Low |
| 0.1 < m-ERM-q ≤ 0.5 | Medium-Low |
| 0.5 < m-ERM-q ≤ 1.5 | Medium-High |
| >1.5 | High |
| Sampling Locations | HCHs (µg·kg−1) | DDTs (µg·kg−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kaifeng City, China | 45.35 | 119.76 | [38] |
| The Three Gorges Dam region, China | 1.27 | 1.80 | [36] |
| Qinghai Province, China | 4.78 | 7.76 | [37] |
| The Pearl River Delta, China | 4.52 | 34.2 | [16] |
| The Yangtze River Basin, China | 13.04 | 8.90 | [43] |
| Yellow River basin, China | 6.23 | 16.78 | [44] |
| Mai Mahiu, Kenya | 1.50 | 3.51 | [45] |
| Narok, Kenya | 1.62 | 4.71 | [45] |
| The Indus Basin, Pakistan | 15.41 | 142.26 | [46] |
| The Campanian Plain, Italy | 1.38 | 107 | [47] |
| The Mean of the HI | The Maximum of the HI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingest | Dermal | Inhale | Total | Ingest | Dermal | Inhale | Total | |
| δ-HCH | 1.13 × 10−5 | 4.93 × 10−6 | 1.82 × 10−9 | 1.63 × 10−5 | 5.02 × 10−5 | 2.18 × 10−5 | 8.03 × 10−9 | 7.19 × 10−5 |
| o, p’-DDT | 3.48 × 10−6 | 1.74 × 10−6 | 6.40 × 10−10 | 5.22 × 10−6 | 2.29 × 10−5 | 1.14 × 10−5 | 4.22 × 10−9 | 3.44 × 10−5 |
| p, p’-DDT | 6.02 × 10−6 | 3.00 × 10−6 | 1.11 × 10−9 | 9.02 × 10−6 | 4.34 × 10−5 | 2.16 × 10−5 | 7.97 × 10−9 | 6.50 × 10−5 |
| DDTs | 9.50 × 10−6 | 4.74 × 10−6 | 1.75 × 10−9 | 1.42 × 10−5 | 6.63 × 10−5 | 3.31 × 10−5 | 1.22 × 10−8 | 9.94 × 10−5 |
| OCPs | 2.08 × 10−5 | 9.66 × 10−6 | 3.56 × 10−9 | 3.05 × 10−5 | 1.16 × 10−4 | 5.48 × 10−5 | 2.02 × 10−8 | 1.71 × 10−4 |
| The Mean of the CR | The Maximum of the CR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingest | Dermal | Inhale | Total | Ingest | Dermal | Inhale | Total | |
| δ-HCH | 6.13 × 10−9 | 2.24 × 10−9 | 9.01 × 10−13 | 8.37 × 10−9 | 2.71 × 10−8 | 9.91 × 10−9 | 3.98 × 10−12 | 3.70 × 10−8 |
| p, p’-DDE | 4.19 × 10−10 | 2.11 × 10−10 | 7.79 × 10−14 | 6.30 × 10−10 | 2.14 × 10−9 | 1.08 × 10−9 | 3.98 × 10−13 | 3.22 × 10−9 |
| o, p’-DDT | 5.92 × 10−10 | 2.99 × 10−10 | 8.70 × 10−14 | 8.90 × 10−10 | 3.90 × 10−9 | 1.97 × 10−9 | 5.74 × 10−13 | 5.87 × 10−9 |
| p, p’-DDD | 3.61 × 10−10 | 1.80 × 10−10 | 6.64 × 10−14 | 5.42 × 10−10 | 1.65 × 10−9 | 8.24 × 10−10 | 3.04 × 10−13 | 2.48 × 10−9 |
| p, p’-DDT | 1.02 × 10−9 | 5.16 × 10−10 | 1.50 × 10−13 | 1.54 × 10−9 | 7.37 × 10−9 | 3.72 × 10−9 | 1.08 × 10−12 | 1.11 × 10−8 |
| DDTs | 2.39 × 10−9 | 1.21 × 10−9 | 3.82 × 10−13 | 3.60 × 10−9 | 1.51 × 10−8 | 7.59 × 10−9 | 2.36 × 10−12 | 2.27 × 10−8 |
| OCPs | 8.52 × 10−9 | 3.45 × 10−9 | 1.28 × 10−12 | 1.20 × 10−8 | 4.21 × 10−8 | 1.75 × 10−8 | 6.34 × 10−12 | 5.97 × 10−8 |
| The Range of Residual Content (µg·kg−1) | Risk Screening Value (µg·kg−1) | Pass Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCHs | n.d.–21.52 | 100 | 100 |
| DDTs | n.d.–39.16 | 100 | 100 |
| ERL (µg·kg−1) | ERM (µg·kg−1) | Range (µg·kg−1) | <ERL (%) | ERL~ERM (%) | >ERM (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p, p’-DDE | 2.2 | 27 | n.d.–9.00 | 73.91 | 26.09 | 0 |
| p, p’-DDD | 2 | 20 | n.d.–9.85 | 56.52 | 43.48 | 0 |
| p, p’-DDT | 1 | 7 | n.d.–31.01 | 21.74 | 65.22 | 13.04 |
| DDTs | 1.58 | 46.1 | n.d.–39.16 | 17.39 | 82.61 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Han, R. Risk Assessment on Organochlorine Pesticides in Agricultural Soils of Eastern City, China. Land 2025, 14, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030612
Chen S, Wang H, Han R. Risk Assessment on Organochlorine Pesticides in Agricultural Soils of Eastern City, China. Land. 2025; 14(3):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030612
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shaoting, Hongmei Wang, and Ruiming Han. 2025. "Risk Assessment on Organochlorine Pesticides in Agricultural Soils of Eastern City, China" Land 14, no. 3: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030612
APA StyleChen, S., Wang, H., & Han, R. (2025). Risk Assessment on Organochlorine Pesticides in Agricultural Soils of Eastern City, China. Land, 14(3), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030612








