Influence of Land-Use Type on Black Soil Features in Indonesia Based on Soil Survey Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
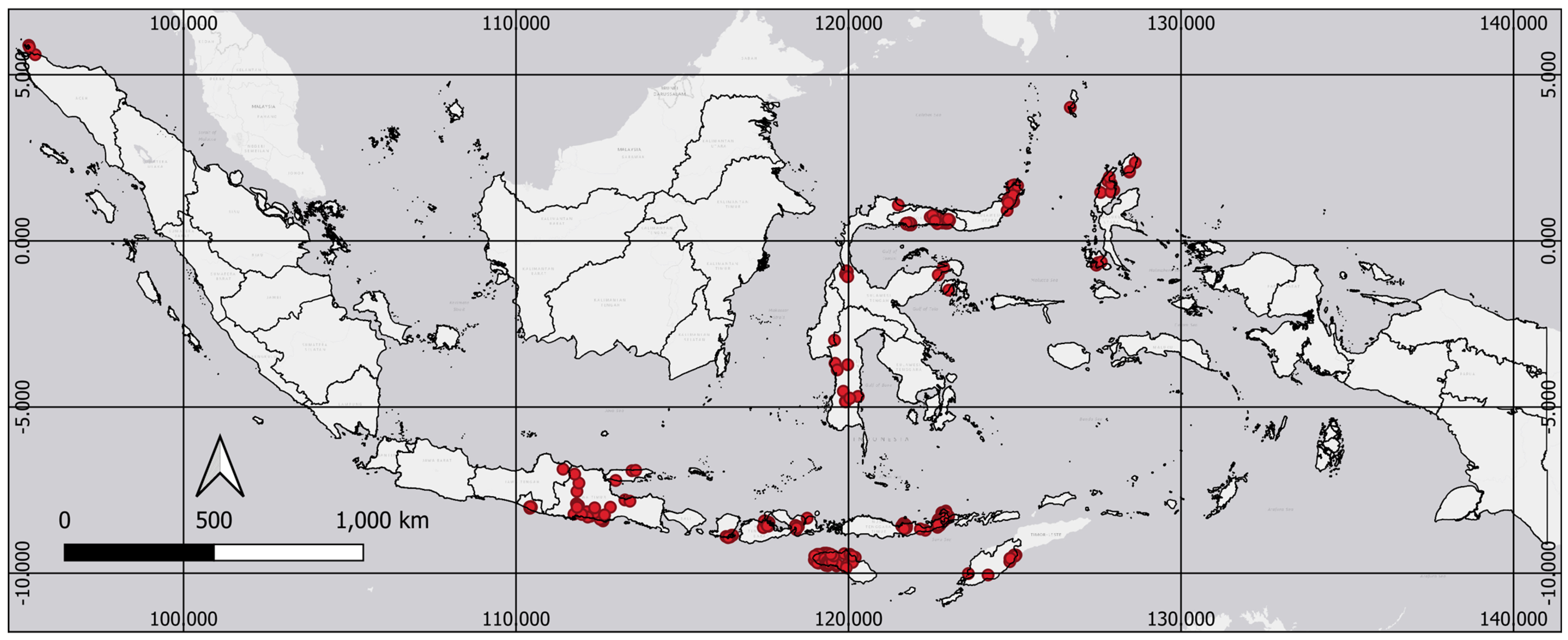
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
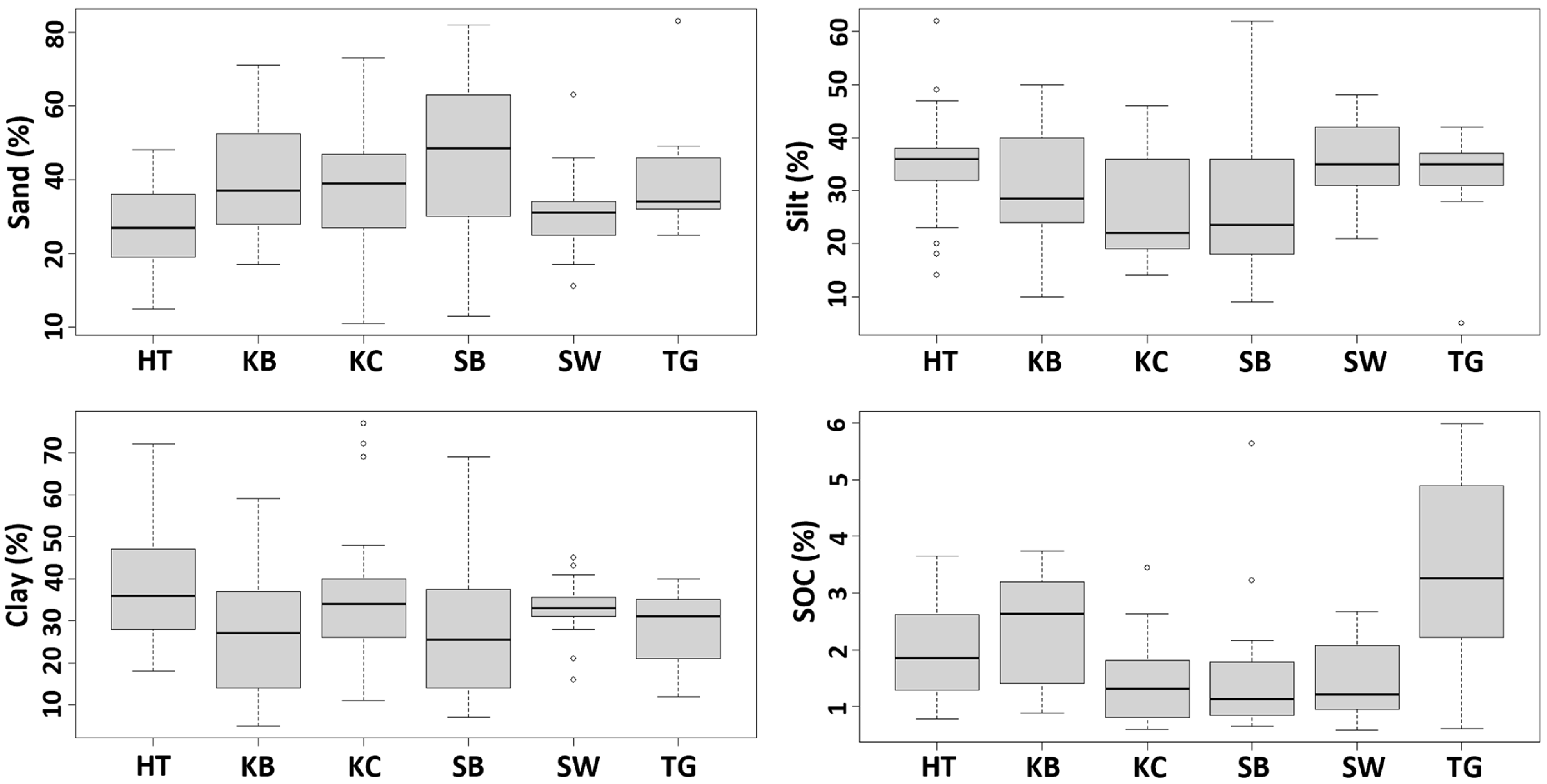
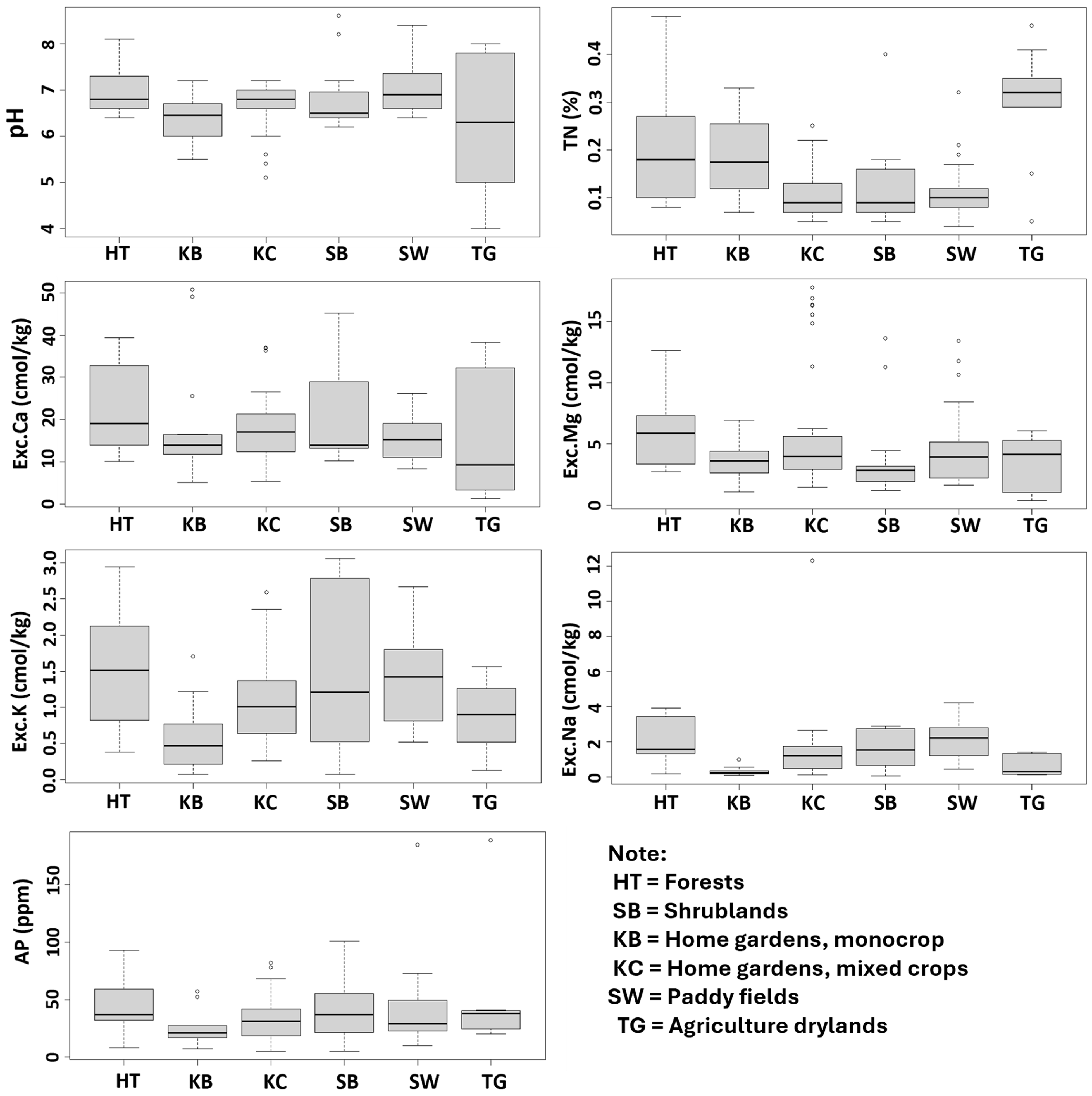
3.1. Soil Property Variation Across Land-Use Types
3.2. Effect Size and Statistical Significance of Mean Differences
3.3. Sensitive Soil Properties Toward Land-Use Change
4. Discussion
4.1. Land-Cover/Use Changes Trigger Changes in Soil Property Level and Direction
4.2. Sensitivity of Hedges’s g-Index and Welch’s t-Test
4.3. Practical Implications and Future Directions
4.4. The Limitation of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Land-Use Type | Parameter | Stable Soil Properties | Regulated Soil Properties | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | SOC | PH | TN | AP | XCa | XMg | XK | XNa | ||
| (………………%……………………) | (%) | (ppm) | (………cmol(+)/kg….……) | |||||||||
| Forest (HT) | n | 37 | 37 | 37 | 34 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 |
| Mean | 27.5 | 34.9 | 37.6 | 2.0 | 7.0 | 0.20 | 43.3 | 22.5 | 6.0 | 1.5 | 2.1 | |
| SD | 11.5 | 8.8 | 13.3 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.11 | 20.6 | 10.0 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 1.2 | |
| CV | 42 | 25 | 35 | 43 | 7 | 54 | 48 | 44 | 44 | 52 | 58 | |
| Shrubland (SB) | n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 15 | 20 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Mean | 44.7 | 28.7 | 26.6 | 1.5 | 6.8 | 0.12 | 42.9 | 20.9 | 3.9 | 1.6 | 1.6 | |
| SD | 24.6 | 16.6 | 15.1 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.08 | 28.0 | 12.7 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 1.1 | |
| CV | 55 | 58 | 57 | 75 | 10 | 66 | 65 | 61 | 94 | 73 | 71 | |
| Monoculture home garden (KB) | n | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 13 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Mean | 40.6 | 31.1 | 28.3 | 2.4 | 6.4 | 0.19 | 23.9 | 18.0 | 3.6 | 0.6 | 0.3 | |
| SD | 17.1 | 10.7 | 17.8 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.08 | 15.2 | 13.1 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| CV | 42 | 34 | 63 | 44 | 7 | 44 | 63 | 73 | 41 | 79 | 77 | |
| Mixed home garden (KC) | n | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 36 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 |
| Mean | 37.9 | 26.6 | 35.5 | 1.4 | 6.7 | 0.11 | 32.2 | 17.6 | 6.0 | 1.1 | 1.4 | |
| SD | 18.7 | 9.6 | 14.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 19.5 | 8.4 | 4.9 | 0.6 | 2.0 | |
| CV | 49 | 36 | 42 | 50 | 7 | 47 | 60 | 48 | 82 | 54 | 137 | |
| Agriculture dryland (TG) | n | 9 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| Mean | 40.6 | 31.9 | 27.6 | 3.4 | 6.2 | 0.30 | 53.9 | 18.4 | 3.4 | 0.9 | 0.7 | |
| SD | 17.7 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 0.13 | 60.2 | 16.0 | 2.3 | 0.5 | 0.6 | |
| CV | 44 | 34 | 36 | 56 | 27 | 43 | 112 | 87 | 66 | 56 | 90 | |
| Paddy field (SW) | n | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| Mean | 30.6 | 36.2 | 33.2 | 1.5 | 7.1 | 0.12 | 41.6 | 15.6 | 4.8 | 1.4 | 2.1 | |
| SD | 11.4 | 7.6 | 7.0 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.07 | 38.8 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 0.6 | 1.1 | |
| CV | 37 | 21 | 21 | 45 | 8 | 56 | 93 | 32 | 75 | 44 | 52 | |
References
- FAO Black Soils Definition. Available online: https://www.fao.org/global-soil-partnership/intergovernmental-technical-panel-soils/gsoc17-implementation/internationalnetworkblacksoils/more-on-black-soils/definition-what-is-a-black-soil/en/ (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Durán, A.; Morrás, H.; Studdert, G.; Liu, X. Distribution, Properties, Land Use and Management of Mollisols in South America. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 511–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Xiong, S.; Huang, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Cui, J.; et al. Rates and Causes of Black Soil Erosion in Northeast China. Catena 2022, 214, 106250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Burras, C.L.; Kravchenko, Y.S.; Duran, A.; Huffman, T.; Morras, H.; Studdert, G.; Zhang, X.; Cruse, R.M.; Yuan, X. Overview of Mollisols in the World: Distribution, Land Use and Management. Can J Soil Sci 2012, 12, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozniak, S.; Havrysh, N.; Yamelynets, T. Chernozems of Ukraine and Its Evolution under the Influence of Anthropogenic Factors. Agronomy 2021, 64, 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Global Status of Black Soils; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Hu, W.; Jia, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shukla, M.K.; et al. Soil Degradation: A Global Threat to Sustainable Use of Black Soils. Pedosphere 2024, 25, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaeman, Y.; Cahyana, D.; Husnain; Nursyamsi, D. Spatial Identification of Black Soils in Indonesia. IOP Conf Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 757, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil Taxonomy. A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; Agricultural Handbook 436; Natural Resources Conservation Service, USDA: Washington DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin, A.; Owens, P.; Láng, V.; Jiang, Z.-D.; Michéli, E.; Krasilnikov, P. “Black Soils” in the Russian Soil Classification System, the US Soil Taxonomy and the WRB: Quantitative Correlation and Implications for Pedodiversity Assessment. CATENA 2021, 196, 104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaeman, Y.; Sukarman; Neswati, R.; Nurdin; Basuki, T. Characteristics and Utilization of Black Soils in Indonesia. Sains Tanah 2023, 20, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, B.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, V.K.; Luthra, N.; Nath, A. Effect of Different Land Uses on Chemical Properties of Soil in a Mollisol. Pharma Innov. J. 2022, 11, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Qiu, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, B.; Shao, M. Response of Soil OC, N and P to Land-Use Change and Erosion in the Black Soil Region of the Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Han, S.; Zhao, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, E. Influence of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties on Mechanical Characteristics under Different Cultivation Durations with Mollisols. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 224, 105520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, B.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, V.K.; Shivran, M.; Serawat, A. Effect of Different Land-Uses Systems on Soil pH, Electrical Conductivity and Micronutrients in Mollisols of Uttarakhand. Biol. Forum–Int. J. 2022, 14, 712–716. [Google Scholar]
- Sulaeman, Y.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Sarwani, M.; Sutandi, A. Harmonizing Legacy Soil Data for Digital Soil Mapping in Indonesia. Geoderma 2013, 192, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrouays, D.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Richer-de-Forges, A.C.; Adhikari, K.; Ballabio, C.; Greve, M.; Grundy, M.; Guerrero, E.; Hempel, J.; Hengl, T.; et al. Soil Legacy Data Rescue via GlobalSoilMap and Other International and National Initiatives. GeoResJ 2017, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempen, B.; Brus, D.J.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Stoorvogel, J.J. Updating the 1:50,000 Dutch Soil Map Using Legacy Soil Data: A Multinomial Logistic Regression Approach. Geoderma 2009, 151, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, B.; Hodúl, M.; Schmidt, M.G. Comparing the Use of Training Data Derived from Legacy Soil Pits and Soil Survey Polygons for Mapping Soil Classes. Geoderma 2017, 290, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.R.; Giasson, E.; Campos, A.R.; Costa, J.J.F.; Silva, E.B.d.; Bonfatti, B.R. Spatial Disaggregation of Multi-Component Soil Map Units Using Legacy Data and a Tree-Based Algorithm in Southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2018, 42, e0170193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellili Bargaoui, Y.; Walter, C.; Michot, D.; Saby, N.P.A.; Vincent, S.; Lemercier, B. Validation of Digital Maps Derived from Spatial Disaggregation of Legacy Soil Maps. Geoderma 2019, 356, 113907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.A.; Palm, C.A.; Buol, S.W. Fertility Capability Soil Classification: A Tool to Help Assess Soil Quality in the Tropics. Geoderma 2003, 114, 157–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balai Penelitian Tanah. Petunjuk Teknis Analisa Kimia Tanah, Tanaman, Air, Dan Pupuk; Balai Penelitian Tanah: Bogor, Indonesia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hedges, L.V. Distribution Theory for Glass’s Estimator of Effect Size and Related Estimators. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A Power Primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T. Two Sample T-Tests for IR Evaluation: Student or Welch? In Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Pisa, Italy, 17–21 July 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1045–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Ruxton, G.D. The Unequal Variance T-Test Is an Underused Alternative to Student’s t-Test and the Mann–Whitney U Test. Behav. Ecol. 2006, 17, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021.
- Lüdecke, D. Esc: Effect Size Computation for Meta Analysis (Version 0.5.1) 2019. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/1249218 (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Haile, G.; Itanna, F.; Teklu, B.; Agegnehu, G. Variation in Soil Properties under Different Land Use Types Managed by Smallholder Farmers in Central Ethiopia. Sustain. Environ. 2022, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Han, J.; Jiao, J.; Han, J.; Zhao, X.; Hu, K.; Kang, Y.; Jaffar, M.T.; Qin, W. Soil Carbon Management Index under Different Land Use Systems and Soil Types of Sanjiang Plain in Northeast China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainepo, B.M.; Gachene, C.K.; Karuma, A. Assessment of Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Carbon Management Index under Different Land Use Types in Olesharo Catchment, Narok County, Kenya. Carbon Balance Manag. 2018, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.G.; Nguyen, H.T.; Kappas, M. Assessment of Soil Quality Indicators under Different Agricultural Land Uses and Topographic Aspects in Central Vietnam. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paustian, K.; Collier, S.; Baldock, J.; Burgess, R.; Creque, J.; DeLonge, M.; Dungait, J.; Ellert, B.; Frank, S.; Goddard, T.; et al. Quantifying Carbon for Agricultural Soil Management: From the Current Status toward a Global Soil Information System. Carbon Manag. 2019, 10, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, K.M.; Sarmah, M.K.; Das, K.N.; Lolesh, P.; Wasifur, R.; Bhoirab, G. Impact of Available N, P2O5 and K2O on Soil Due to Different Management Practices after Growing Sali Rice. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 8, 3306–3309. [Google Scholar]
- Moharana, P.C.; Meena, R.L.; Nogiya, M.; Jena, R.K.; Sharma, G.K.; Sahoo, S.; Jha, P.K.; Aditi, K.; Vara Prasad, P.V. Impacts of Land Use on Pools and Indices of Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen in the Ghaggar Flood Plains of Arid India. Land 2022, 11, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leul, Y.; Assen, M.; Damene, S.; Legass, A. Effects of Land-Use Dynamics on Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen Stock, Western Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2023, 2023, 5080313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, G.; Myo, S.T.Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Lin, Z.; Qian, Z.; Tang, L. Deforestation for Agriculture Temporarily Improved Soil Quality and Soil Organic Carbon Stocks. Forests 2022, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, K.M.; Pordel, N.; Hosseini, V.; Shakeri, Z. Effect of Land-Use Changes on Chemical and Physical Properties of Soil in Western Iran (Zagros Oak Forests). J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaz, B.; Hartemink, A.E.; Zhang, Y.; Stevenson, A.; Kabała, C. Organic Carbon in Mollisols of the World − A Review. Geoderma 2024, 447, 116937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pei, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J. Soil Organic Carbon Depletion in Global Mollisols Regions and Restoration by Management Practices: A Review. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydges, C.R. Effect Size Guidelines, Sample Size Calculations, and Statistical Power in Gerontology. Innov. Aging 2019, 3, igz036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeghy, R.E.; Province, V.M.; Stute, N.L.; Augenreich, M.A.; Koontz, L.K.; Stickford, J.L.; Stickford, A.S.L.; Ratchford, S.M. Carotid Stiffness, Intima–Media Thickness and Aortic Augmentation Index among Adults with SARS-CoV-2. Exp. Physiol. 2022, 107, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Pigoot, T.D. The Power of Statistical Test for Moderators in Meta Analysis. Psychol. Methods 2004, 9, 426–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankinship, J.C.; Niklaus, P.A.; Hungate, B.A. A Meta-Analysis of Responses of Soil Biota to Global Change. Oecologia 2011, 165, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatinec, J.; Buczny, J.; Ondrasek, G. Fly Ash Application Impacts Master Physicochemical Pedovariables: A Multilevel Meta-Analysis. J. Environ. Manage. 2024, 368, 122066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, E.; Getnet, K.; Mekonnen, M. Land Use Change and Its Effect on Selected Soil Properties in the Northwest Highlands of Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, L.P.; Dress, L.R. Spatial Variability and Pedology. In Pedogenesis and Soil Taxonomy I: Concepts and Interaction; Wilding, L.P., Smeck, N.E., Hall, G.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 83–116. [Google Scholar]
| Code | Soil Property | Unit | Laboratory Methods * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stable soil properties | |||
| Sand | Sand fraction content | % | Pipet |
| Silt | Silt fraction content | % | Pipet |
| Clay | Clay fraction content | % | Pipet |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon content | % | Walkley and Black |
| Regulated soil properties | |||
| PH | Soil pH | pH meter, soil: water = 1:5 | |
| TN | Total nitrogen | % | Kjeldahl |
| AP | Available P2O5 | ppm | Olsen |
| XCa | Exchangeable Ca | cmol(+)/kg | NH4OAc 1M, pH 7 |
| XMg | Exchangeable Mg | cmol(+)/kg | NH4OAc 1M, pH 7 |
| XK | Exchangeable K | cmol(+)/kg | NH4OAc 1M, pH 7 |
| XNa | Exchangeable Na | cmol(+)/kg | NH4OAc 1M, pH 7 |
| 1st Land Use | 2nd Land Use | Sand | Silt | Clay | SOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Natural land cover versus natural land cover | |||||
| HT | SB | −0.99 * | 0.51 | 0.78 * | 0.51 |
| B. Natural land cover versus farming use | |||||
| HT | KB | −0.96 * | 0.40 | 0.62 | −0.45 |
| HT | KC | −0.66 * | 0.89 * | 0.15 | 0.79 * |
| HT | TG | −1.00 | 0.32 | 0.77 * | −1.31 |
| HT | SW | −0.27 | −0.15 | 0.37 | 0.64 * |
| SB | KB | 0.18 | −0.16 | −0.10 | −0.79 * |
| SB | KC | 0.32 | 0.16 | −0.59 * | 0.11 |
| SB | TG | 0.17 | −0.21 | −0.07 | −1.31 * |
| SB | SW | 0.71 * | −0.56 | −0.54 | 0.00 |
| C. Farming use versus farming use | |||||
| KB | KC | 0.15 | 0.44 | −0.45 | 1.23 * |
| KB | TG | 0.00 | −0.07 | 0.04 | −0.73 |
| KB | SW | 0.68 | −0.55 | −0.37 | 1.04 * |
| KC | TG | −0.14 | −0.53 | 0.55 | −2.03 * |
| KC | SW | 0.43 | −1.06 * | 0.18 | −0.14 |
| TG | SW | 0.71 | −0.48 | −0.68 | 1.63 * |
| 1st Land Use | 2nd Land Use | PH | TN | AP | XCa | XMg | XK | XNa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Natural land cover versus natural land cover | ||||||||
| HT | SB | 0.35 | 0.78 * | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.69 * | −0.11 | 0.42 |
| B. Natural land cover versus farming use | ||||||||
| HT | KB | 1.18 * | 0.09 | 0.98 * | 0.40 | 0.98 * | 1.26 * | 1.75 * |
| HT | KC | 0.59 * | 1.04 * | 0.55 * | 0.53 * | 0.00 | 0.56 * | 0.42 |
| HT | TG | 0.92 | −0.86 * | −0.35 | 0.36 | 0.97 * | 0.78 * | 1.23 * |
| HT | SW | −0.18 | 0.80 * | 0.06 | 0.79 * | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.00 |
| SB | KB | 0.64 * | −0.86 * | 0.80 * | 0.22 | 0.11 | 1.19 * | 1.63 * |
| SB | KC | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.47 | 0.33 | −0.45 | 0.64 | 0.11 |
| SB | TG | 0.50 | −1.79 * | −0.26 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.73 | 0.92 * |
| SB | SW | −0.45 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.56 | −0.24 | 0.23 | −0.44 |
| C. Farming use versus farming use | ||||||||
| KB | KC | −0.59 * | 1.31 * | −0.44 | 0.04 | −0.56 * | −0.89 * | −0.64 * |
| KB | TG | 0.18 | −1.06 * | −0.78 | −0.03 | 0.11 | −0.66 | −0.99 |
| KB | SW | −1.23 * | 0.92 * | −0.55 | 0.25 | −0.41 | −1.51 * | −2.14 * |
| KC | TG | 0.58 | −2.61 * | −0.73 | −0.08 | 0.56 * | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| KC | SW | −0.74 * | −0.17 | −0.34 | 0.27 | 0.26 | −0.49 | −0.39 |
| TG | SW | −0.82 | 1.89 * | 0.26 | 0.28 | −0.42 | −0.85 * | −1.39 * |
| Pair | Number of Properties | Difference * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Negative (−) | ||
| A. Natural land cover versus natural land cover | |||
| HT vs. SB | 5 | Clay, SOC, TN, XMg | Sand |
| B. Natural land cover versus farming use | |||
| HT vs. KB | 5 | AP, XMg, XK, PH | Sand |
| HT vs. KC | 8 | Silt, SOC, TN, AP, XCa, XK, PH | Sand |
| HT vs. TG | 4 | Clay, XMg, XK, XNa | |
| HT vs. SW | 3 | SOC, TN, XCa | |
| SB vs. KB | 5 | AP, XK, XNa | SOC, TN |
| SB vs. KC | 1 | Clay | |
| SB vs. TG | 1 | TN | |
| SB vs. SW | 0 | ||
| C. Farming use versus farming use | |||
| KB vs. KC | 6 | SOC, TN | XMg, XK, XNa, PH |
| KB vs. TG | 1 | TN | |
| KB vs. SW | 4 | SOC, TN | XK, XNa |
| KC vs. TG | 2 | Silt, TN | |
| KC vs. SW | 2 | Silt, PH | |
| TG vs. SW | 2 | TN | AP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sulaeman, Y.; Maftuáh, E.; Sukarman, S.; Neswati, R.; Nurdin, N.; Basuki, T.; Suriadi, A.; Vasenev, I. Influence of Land-Use Type on Black Soil Features in Indonesia Based on Soil Survey Data. Land 2025, 14, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030599
Sulaeman Y, Maftuáh E, Sukarman S, Neswati R, Nurdin N, Basuki T, Suriadi A, Vasenev I. Influence of Land-Use Type on Black Soil Features in Indonesia Based on Soil Survey Data. Land. 2025; 14(3):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030599
Chicago/Turabian StyleSulaeman, Yiyi, Eni Maftuáh, Sukarman Sukarman, Risma Neswati, Nurdin Nurdin, Tony Basuki, Ahmad Suriadi, and Ivan Vasenev. 2025. "Influence of Land-Use Type on Black Soil Features in Indonesia Based on Soil Survey Data" Land 14, no. 3: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030599
APA StyleSulaeman, Y., Maftuáh, E., Sukarman, S., Neswati, R., Nurdin, N., Basuki, T., Suriadi, A., & Vasenev, I. (2025). Influence of Land-Use Type on Black Soil Features in Indonesia Based on Soil Survey Data. Land, 14(3), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030599







