Assessing Land Footprint of Urban Agglomeration and Underlying Socioeconomic Drivers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Data
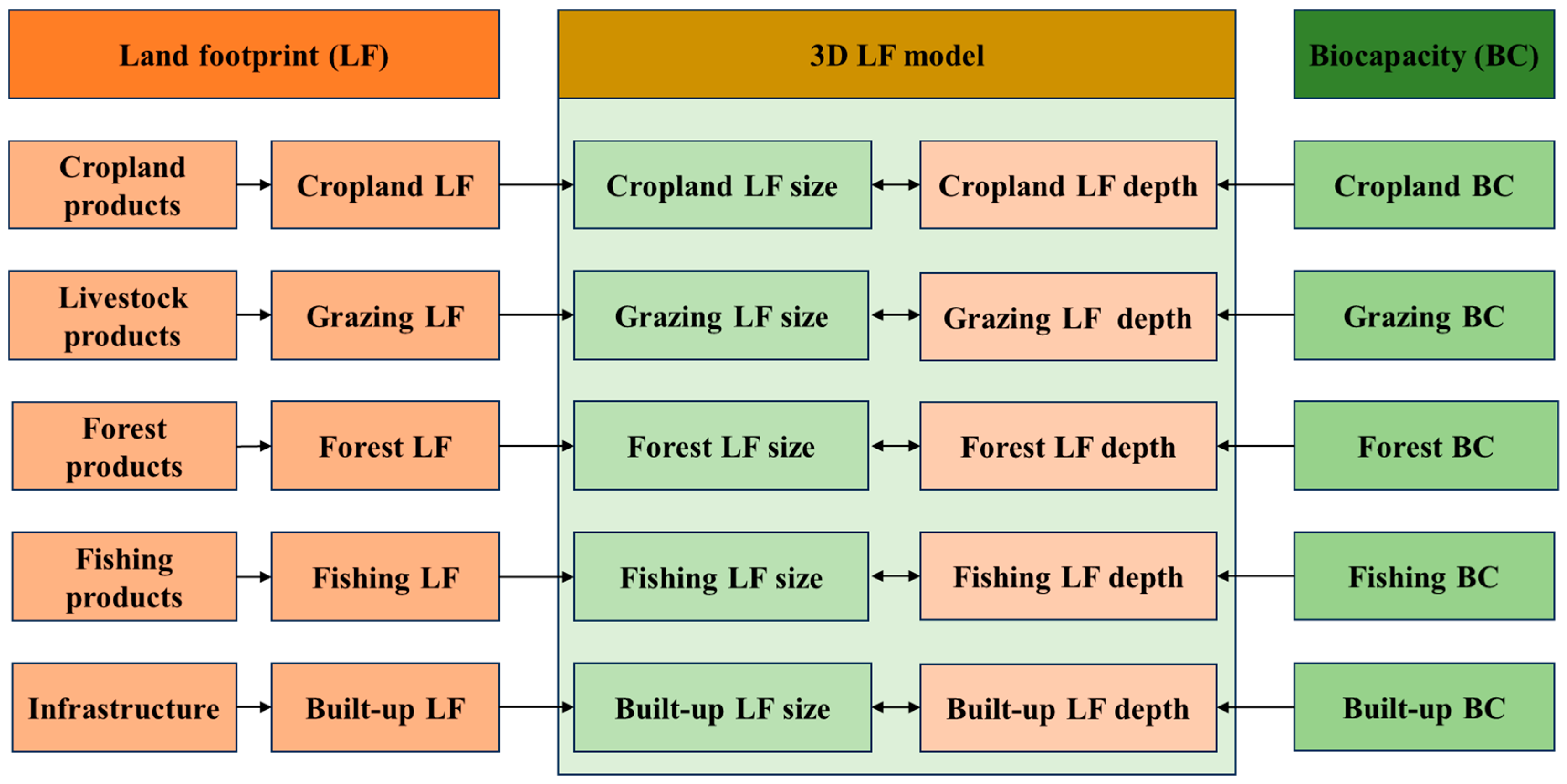
2.1. Land Footprint Analysis
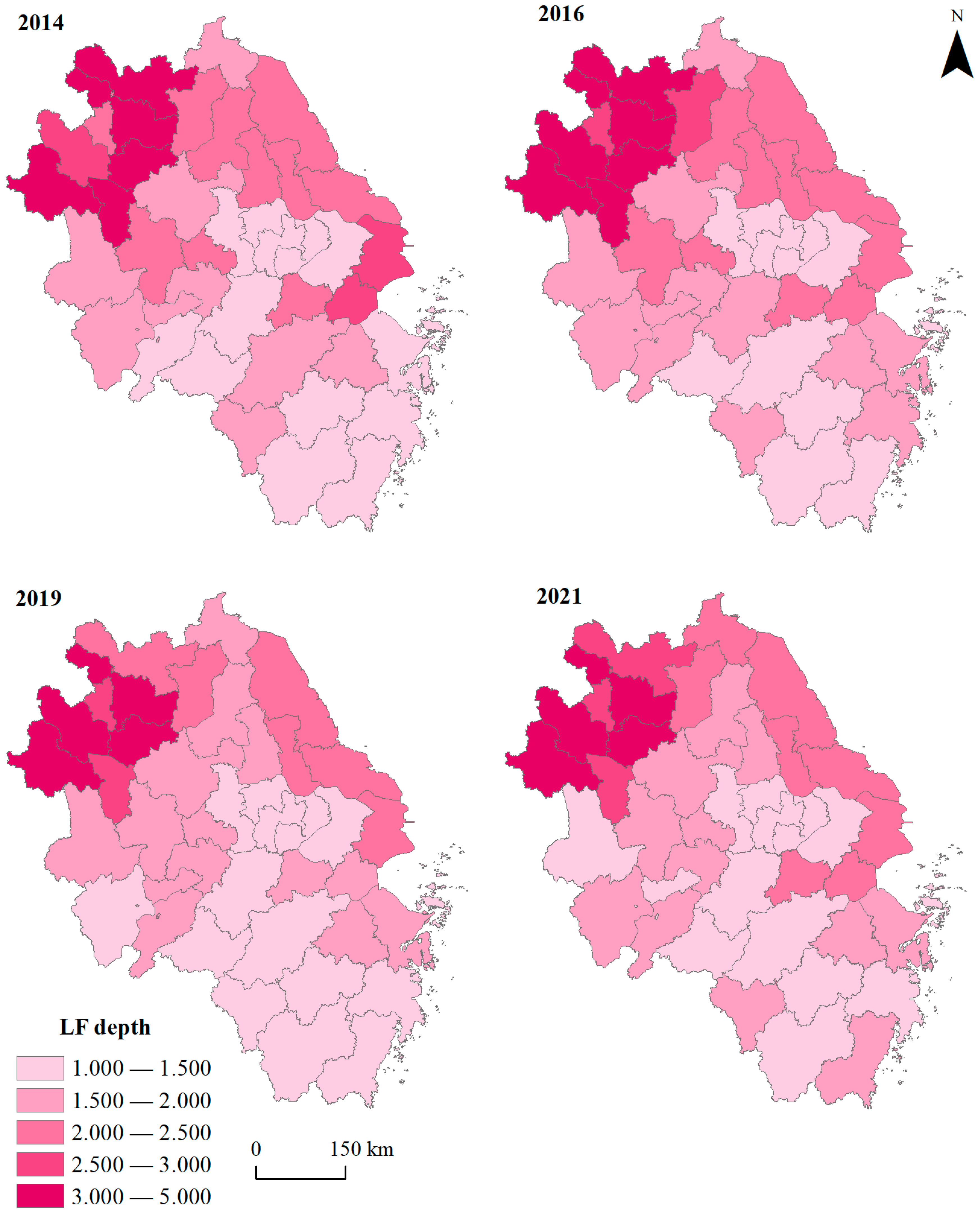
2.2. Land Footprint Size and Depth Analysis
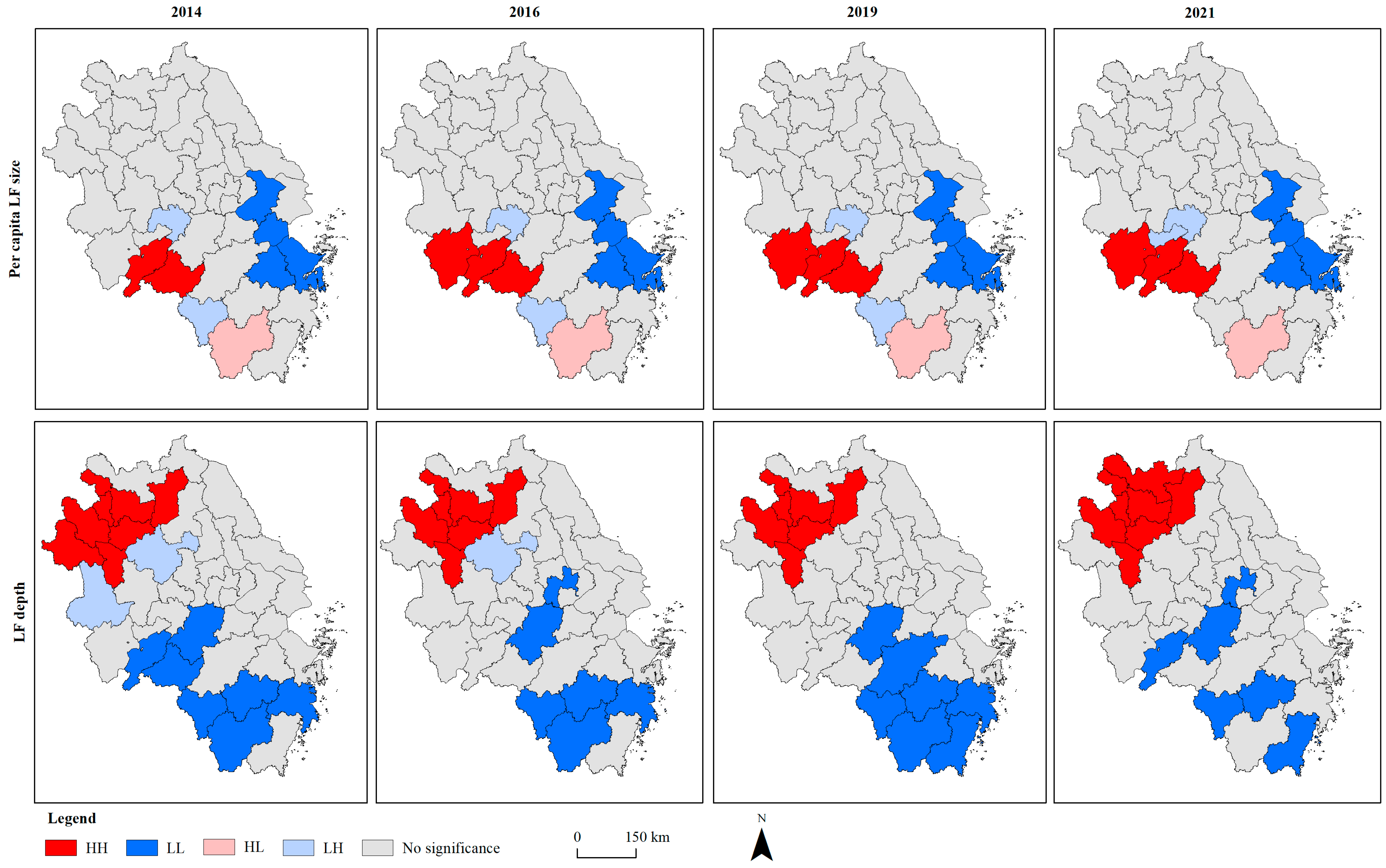
2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.4. Spatial Econometric Analysis
2.5. Data Sources
3. Results
3.1. Sustainability of Land Use in YRD Cities
3.1.1. Cropland
3.1.2. Grazing Land
3.1.3. Forest Land
3.1.4. Fishing Grounds
3.1.5. Built-Up Land
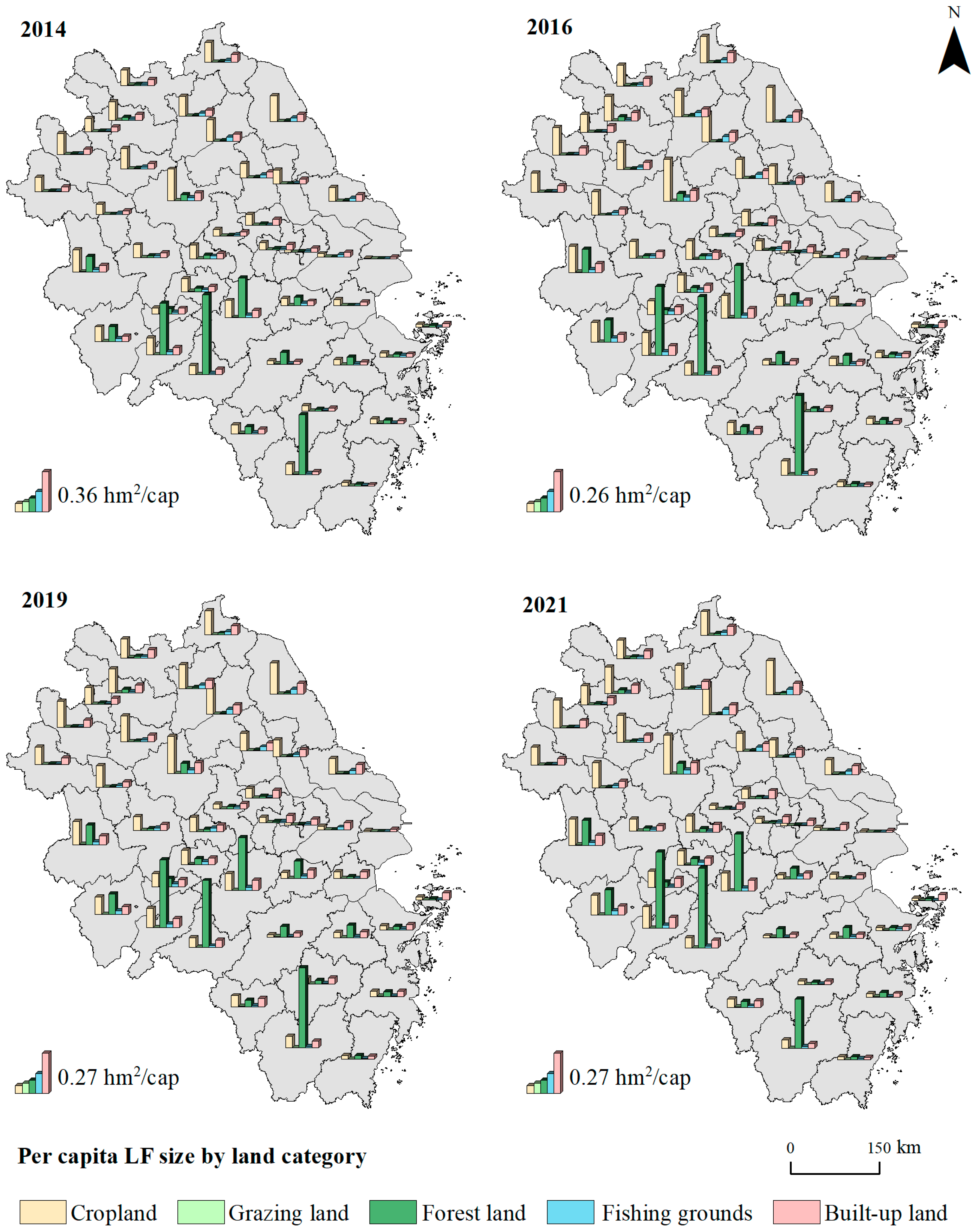
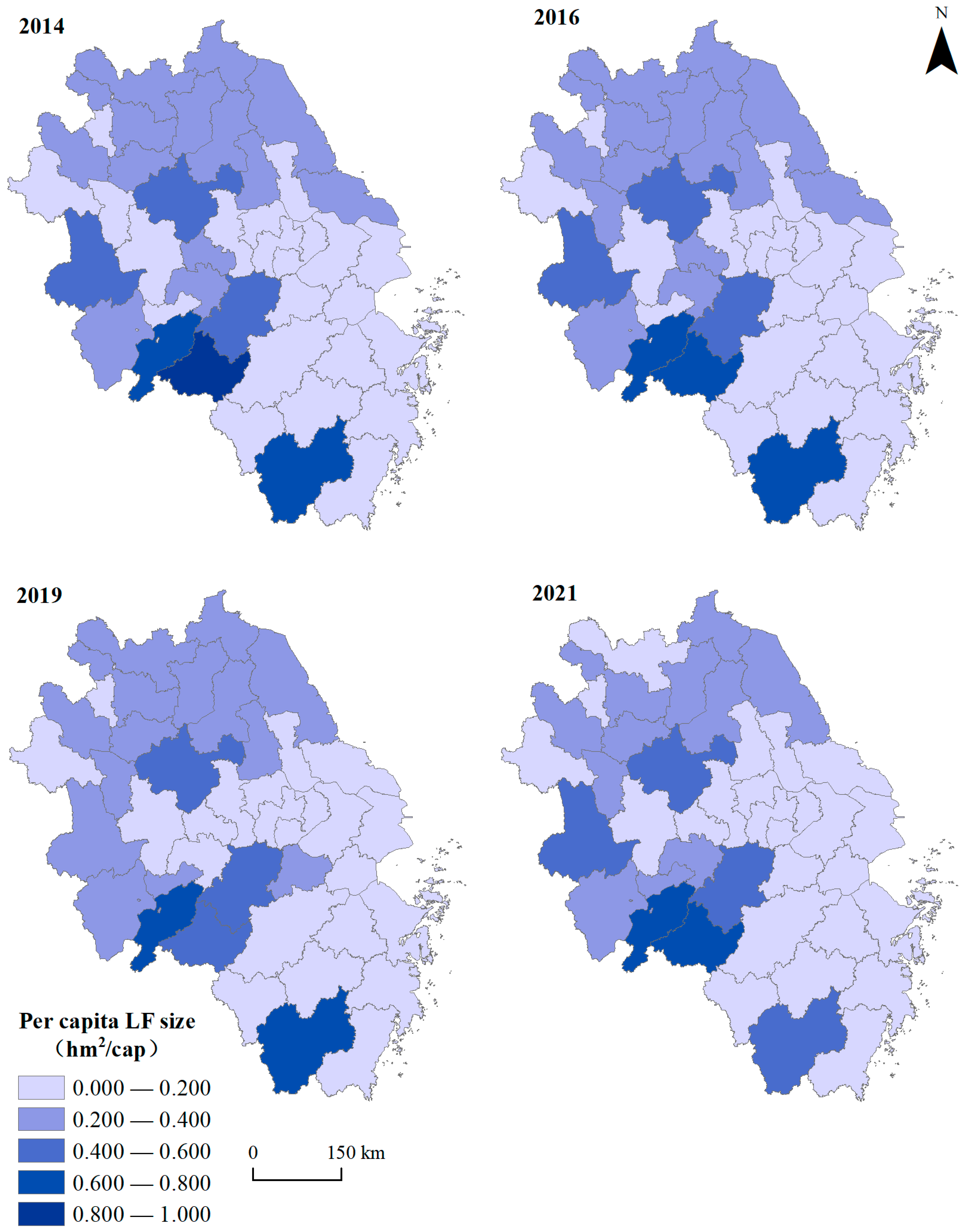
3.1.6. Aggregation of Land
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation of Sustainability of Land Use in YRD Cities
3.3. Socioeconomic Drivers Underlying Sustainability of Land Use in the YRD
4. Discussion
4.1. Scientific Contribution Analysis
4.2. Limitations and Uncertainties
4.3. Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crutzen, P.J. Geology of mankind. Nature 2002, 415, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Fang, K.; Xu, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, Q.; et al. CO2 sequestration technologies may undermine China’s Sustainable Development Goals through the climate-energy-air-health cascade. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Wu, X.; Fang, K.; Lin, D. Identifying drivers of county-level industrial carbon intensity by a generic machine learning framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 454, 142276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, F.; Bai, X.; Bondre, N.; Broadgate, W.; Chen, C.A.; Dube, O.P.; Erisman, J.W.; Glaser, M.; van der Hel, S.; Lemos, M.C.; et al. Down to earth: Contextualizing the Anthropocene. Glob. Environ. Change 2016, 39, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, A.; Đurović, G.; Hanscom, L.; Knežević, J. Think globally, act locally: Implementing the sustainable development goals in Montenegro. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 84, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raworth, K. A doughnut for the Anthropocene: Humanity’s compass in the 21st century. Lancet Planet. Health 2017, 1, e48–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Teksoz, K.; Durand-Delacre, D.; Sachs, J.D. National baselines for the Sustainable Development Goals assessed in the SDG Index and Dashboards. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chau, S.N.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Dietz, T.; Wang, J.; Winkler, J.A.; Fan, F.; Huang, B.; et al. Assessing progress towards sustainable development over space and time. Nature 2020, 577, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Xiao, R.; Fei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wan, Y.; Tan, W.; Jiang, X.; Gao, W.; Guo, Y. Analyzing “economy-society-environment” sustainability from the perspective of urban spatial structure: A case study of the Yangtze River delta urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 96, 104691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; Daly, L.; Fioramonti, L.; Giovannini, E.; Kubiszewski, I.; Mortensen, L.F.; Pickett, K.E.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V.; De Vogli, R.; Wilkinson, R. Modelling and measuring sustainable wellbeing in connection with the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 130, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; Daly, H.E. Natural capital and sustainable development. Conserv. Biol. 1992, 6, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.; Van der Perk, J.; Chiesura, A.; van Vliet, A. Importance and threat as determining factors for criticality of natural capital. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 44, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelenc, J.; Ballet, J. Strong sustainability, critical natural capital and the capability approach. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 112, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodland, R.; Daly, H. Environmental sustainability: Universal and non-negotiable. Ecol. Appl. 1996, 6, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randers, J.; Rockström, J.; Stoknes, P.E.; Goluke, U.; Collste, D.; Cornell, S.; Donges, J. Achieving the 17 sustainable development goals within 9 planetary boundaries. Glob. Sustain. 2019, 2, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, M.; Rees, W.E. Perceptual and structural barriers to investing in natural capital: Economics from an ecological footprint perspective. Ecol. Econ. 1997, 20, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borucke, M.; Moore, D.; Cranston, G.; Gracey, K.; Iha, K.; Larson, J.; Lazarus, E.; Morales, J.C.; Wackernagel, M.; Galli, A. Accounting for demand and supply of the biosphere’s regenerative capacity: The National Footprint Accounts’ underlying methodology and framework. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 24, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfreda, C.; Wackernagel, M.; Deumling, D. Establishing national natural capital accounts based on detailed ecological footprint and biological capacity assessments. Land Use Policy 2004, 21, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrahmoune, A.; Lahboub, Y.; Ghmari, A.E. Ecological footprint accounting: A multi-scale approach based on net primary productivity. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2019, 77, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekins, P.; Simon, S. Estimating sustainability gaps: Methods and preliminary applications for the UK and the Netherlands. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 37, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Dong, C.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic evolution of the ecological footprint of arable land in the Yellow and Huaihai Main grain producing area based on structural equation modeling and analysis of driving factors. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.S.; Galli, A.; Niccolucci, V.; Lin, D.; Hanscom, L.; Wackernagel, M.; Bastianoni, S.; Marchettini, N. Stocks and flows of natural capital: Implications for ecological footprint. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccolucci, V.; Bastianoni, S.; Tiezzi, E.B.P.; Wackernagel, M.; Marchettini, N. How deep is the footprint? A 3D representation. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2819–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccolucci, V.; Galli, A.; Reed, A.; Neri, E.; Wackernagel, M.; Bastianoni, S. Towards a 3D national ecological footprint geography. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Q.; Fang, K.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Fang, C.; Shen, Y. Tracking national sustainability of critical natural capital and the socioeconomic drivers in the context of the Belt and Road Initiative. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, D. Natural capital utilization based on a three-dimensional ecological footprint model: A case study in northern Shaanxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Du, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, H. Sustainability evaluation of natural capital utilization based on 3D EF model: A case study in Beijing City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Yu, H.; Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Klemeš, J.J.; Xie, W.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Sustainability evaluation based on the three-dimensional ecological footprint and human development index: A case study on the four island regions in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Fang, S. Sustainability assessment of natural capital based on the 3D ecological footprint model: A case study of the Shennongjia national park pilot. Sustainability 2019, 11, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Shi, L. Sustainability of the use of natural capital in a city: Measuring the size and depth of urban ecological and water footprints. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wei, Z.; Xie, X.; Ren, J.; Zhou, H. Dynamic change and driving force of natural capital in Qinghai Province based on the three-dimensional ecological footprint, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Fei, L.; Kang, S. Analysis and prediction of urban agglomeration ecological footprint based on improved three-dimensional ecological footprint and shared socioeconomic pathways. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Wang, Q.; Tian, L. Green development of Yangtze River Delta in China under population-resources-environment-development-satisfaction perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, W. Spatial and temporal differentiation and influencing factors of environmental governance performance in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Qu, L.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Yao, R.; Zhou, X.; Li, J. Land use/cover predictions incorporating ecological security for the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F. Exploration of coupling effects in the Economy–Society–Environment system in urban areas: Case study of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107858. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, R.; Wang, F.; Yu, J. Spatiotemporal changes in sustainable development and its driving force in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuček, L.; Klemeš, J.J.; Kravanja, Z. A review of footprint analysis tools for monitoring impacts on sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 34, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.S.; Galli, A.; Niccolucci, V.; Lin, D.; Bastianoni, S.; Wackernagel, M.; Marchettini, N. Ecological footprint: Refining the carbon footprint calculation. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Wu, C.; Dong, L. The use of land natural capital in the context of urbanization. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yan, S.; An, N.; Yao, Q. Using ecological footprint analysis to evaluate sustainable development in Lushan County, China. Land 2024, 13, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, M. Exploring the spatial spillover effects of industrialization and urbanization factors on pollutants emissions in China’s Huang-Huai-Hai region. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Applied spatial econometrics: Raising the bar. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2010, 5, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, W. The calculation of China’s equivalence factor under ecological footprint model based on net primary production. J. Nat. Resour. 2009, 24, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Li, W.; Xie, G. Estimation of China ecological footprint production coefficient based on net primary production. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 592–597. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Tao, F.; Leng, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T. Multi-scale analysis on sustainability and driving factors based on three-dimensional ecological footprint: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.A.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K.; Dyke, J.G.; Haberl, H.; Hossain, M.S.; Langdon, P.G.; Lenton, T.M.; Raworth, K.; Brown, S.; et al. Safe and just operating spaces for regional social-ecological systems. Glob. Environ. Change 2014, 28, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.W.; Fanning, A.L.; Lamb, W.F.; Steinberger, J.K. A good life for all within planetary boundaries. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Fang, K.; Liu, G.; Guo, S. Has the carbon emission trading scheme induced investment leakage in China? Firm-level evidence from China’s stock market. Energy Econ. 2025, 141, 108091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, K. Does international trade reduce global carbon inequality? Evidence from a producer-consumer shared responsibility. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Indicator | Abbreviation | Indicator | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Per capita disposable income | PCDI | Proportion of secondary industry added value to GDP | PSIV |
| Per capita GDP | PCGDP | Proportion of total export value to GDP | PEV |
| Population density | PD | Proportion of total import value to GDP | PIV |
| Proportion of built-up area | PBA | Urbanization rate | UR |
| Proportion of primary industry added value to GDP | PPIV |
| 2014 | 2016 | 2019 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 0.167 | 0.159 | 0.134 | 0.265 |
| p-value | 0.033 | 0.039 | 0.073 | 0.004 |
| Z-score | 2.075 | 1.941 | 1.682 | 3.093 |
| 2014 | 2016 | 2019 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 0.493 | 0.569 | 0.609 | 0.539 |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Z-score | 5.406 | 6.225 | 6.596 | 5.828 |
| Variable | OLS | SLM |
|---|---|---|
| CONSTANT | −2.088 | −2.025 |
| lnPD | 0.008 | 0.001 |
| lnPBA | 0.376 | 0.372 |
| lnUR | 0.029 * | 0.018 |
| lnPCGDP | −6.396 × 10−6 | −5.016 × 10−6 |
| lnPCDI | 2.178 × 10−5 | 2.599 × 10−5 * |
| lnPPIV | 12.309 ** | 8.723 ** |
| lnPSIV | 1.514 | 1.196 |
| lnPIV | −0.344 | −0.488 |
| lnPEV | −0.439 | −0.459 |
| R2 | 0.531 | 0.618 |
| Log-likelihood | −29.509 | −26.371 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Meng, X.; Fang, K. Assessing Land Footprint of Urban Agglomeration and Underlying Socioeconomic Drivers. Land 2025, 14, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030580
Chen X, Meng X, Fang K. Assessing Land Footprint of Urban Agglomeration and Underlying Socioeconomic Drivers. Land. 2025; 14(3):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030580
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xianpeng, Xianda Meng, and Kai Fang. 2025. "Assessing Land Footprint of Urban Agglomeration and Underlying Socioeconomic Drivers" Land 14, no. 3: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030580
APA StyleChen, X., Meng, X., & Fang, K. (2025). Assessing Land Footprint of Urban Agglomeration and Underlying Socioeconomic Drivers. Land, 14(3), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14030580






