Urban Resilience and Spatial Inequality in China: Toward Sustainable Development Under Multi-Dimensional Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
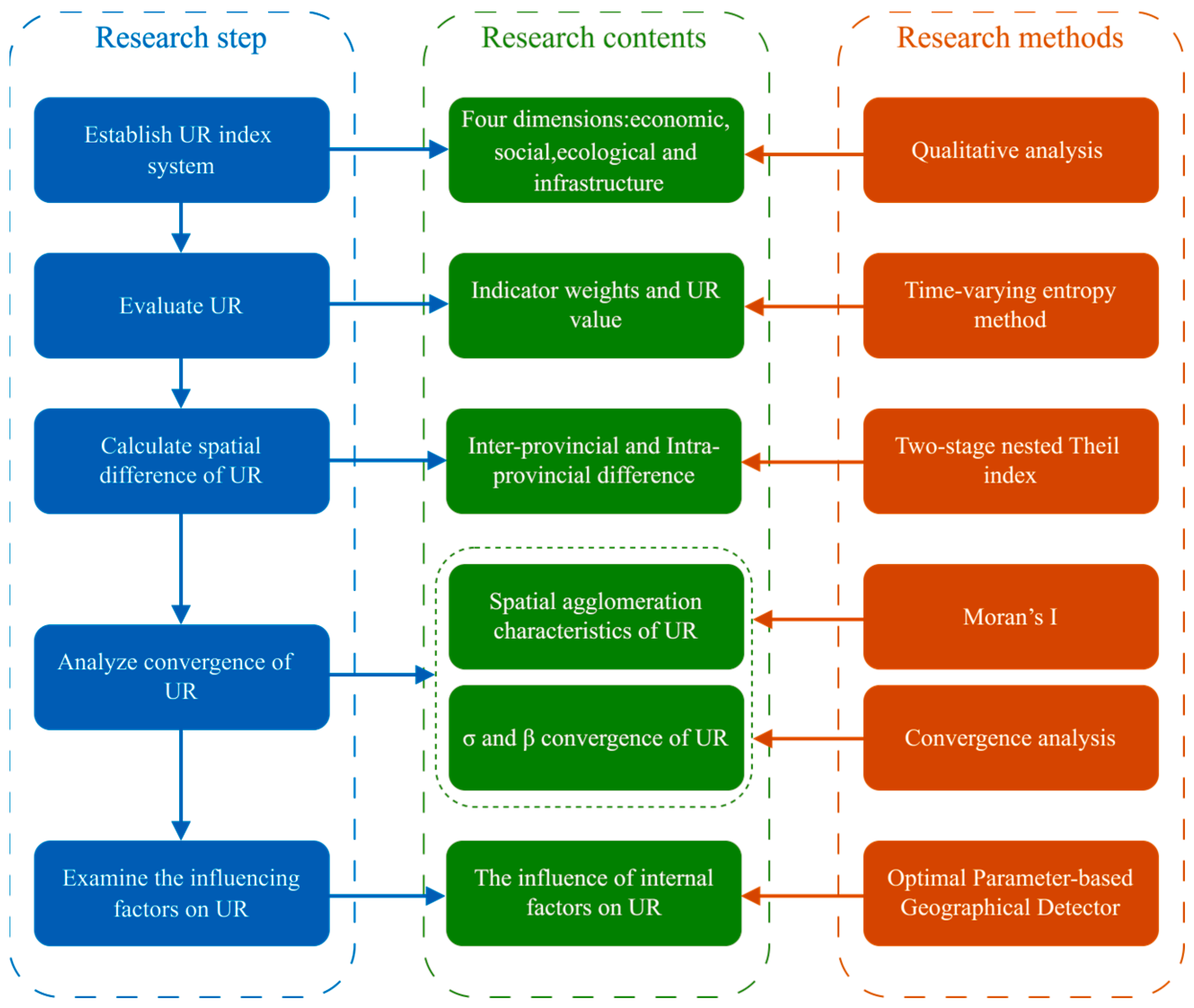
2. Materials and Methods
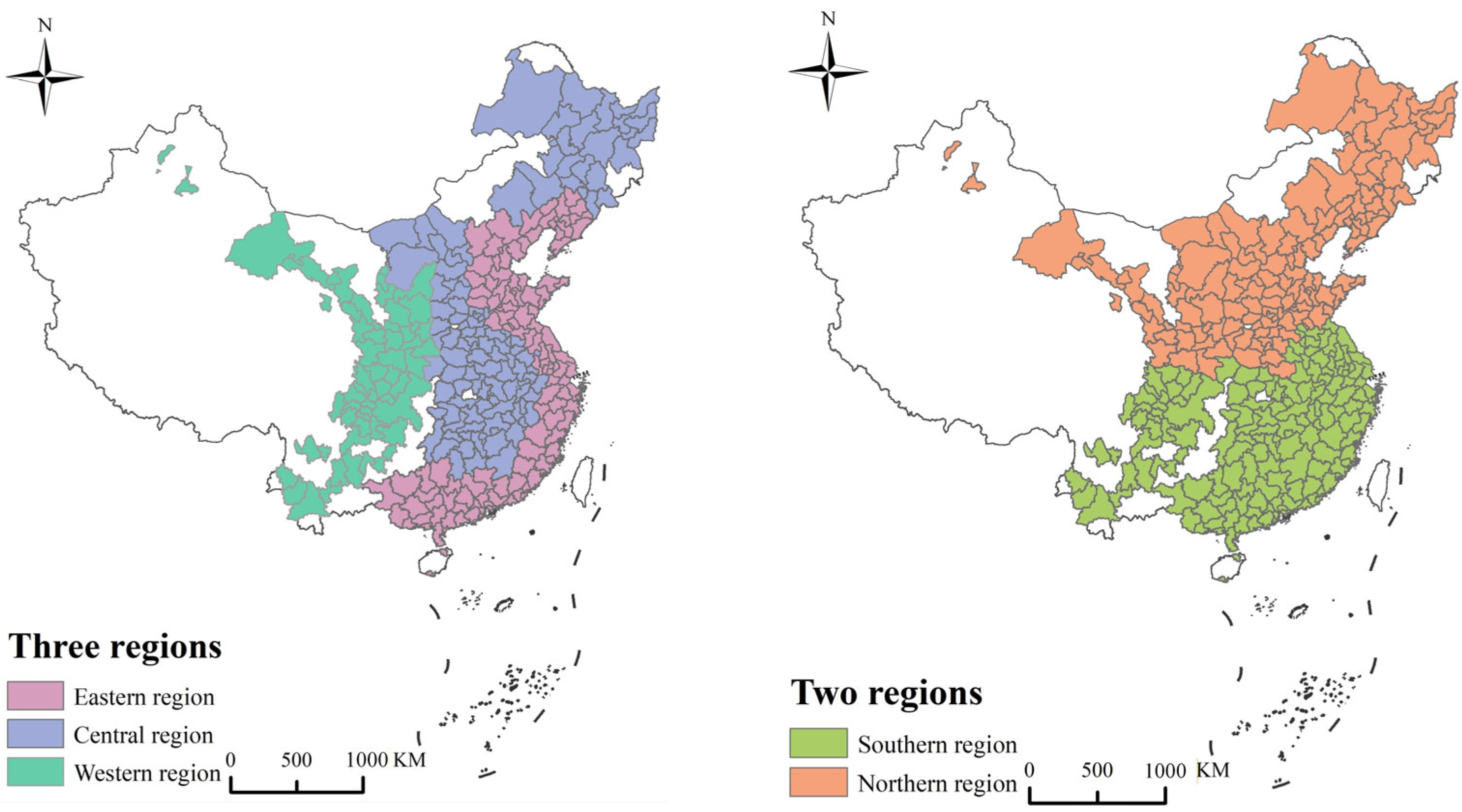
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Indicator System for UR
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Time-Varying Entropy Method
2.3.2. Two-Stage Nested Theil Index
2.3.3. Convergence Analysis Methods
2.3.4. Optimal Parameter-Based Geographical Detector (OPGD)
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution Patterns of UR
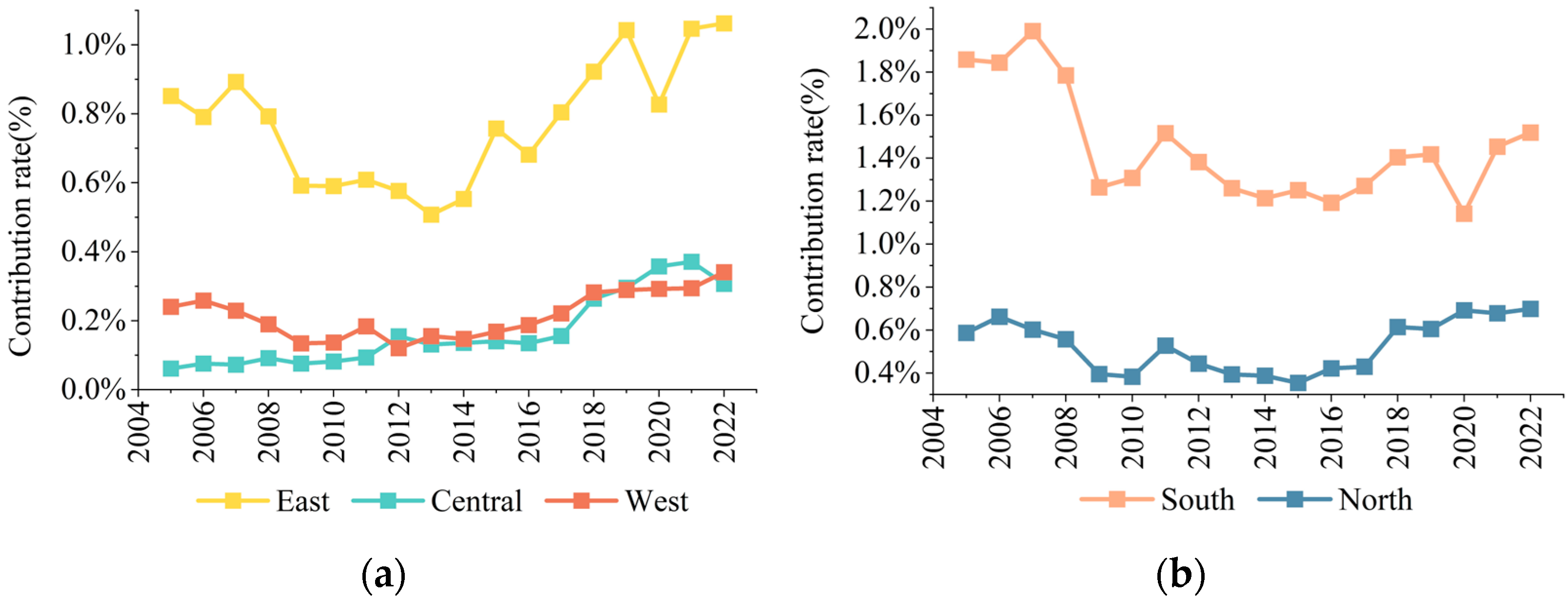
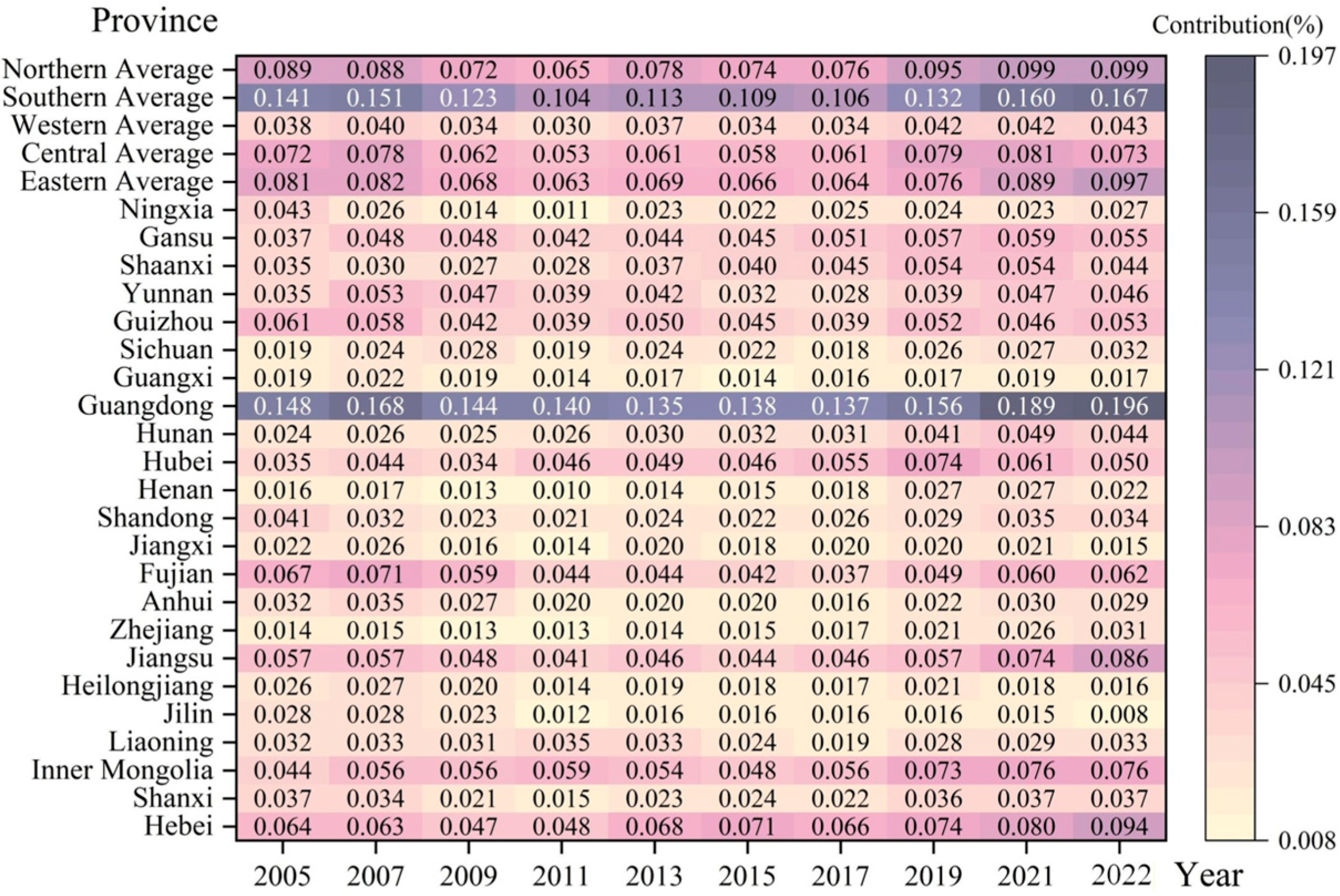
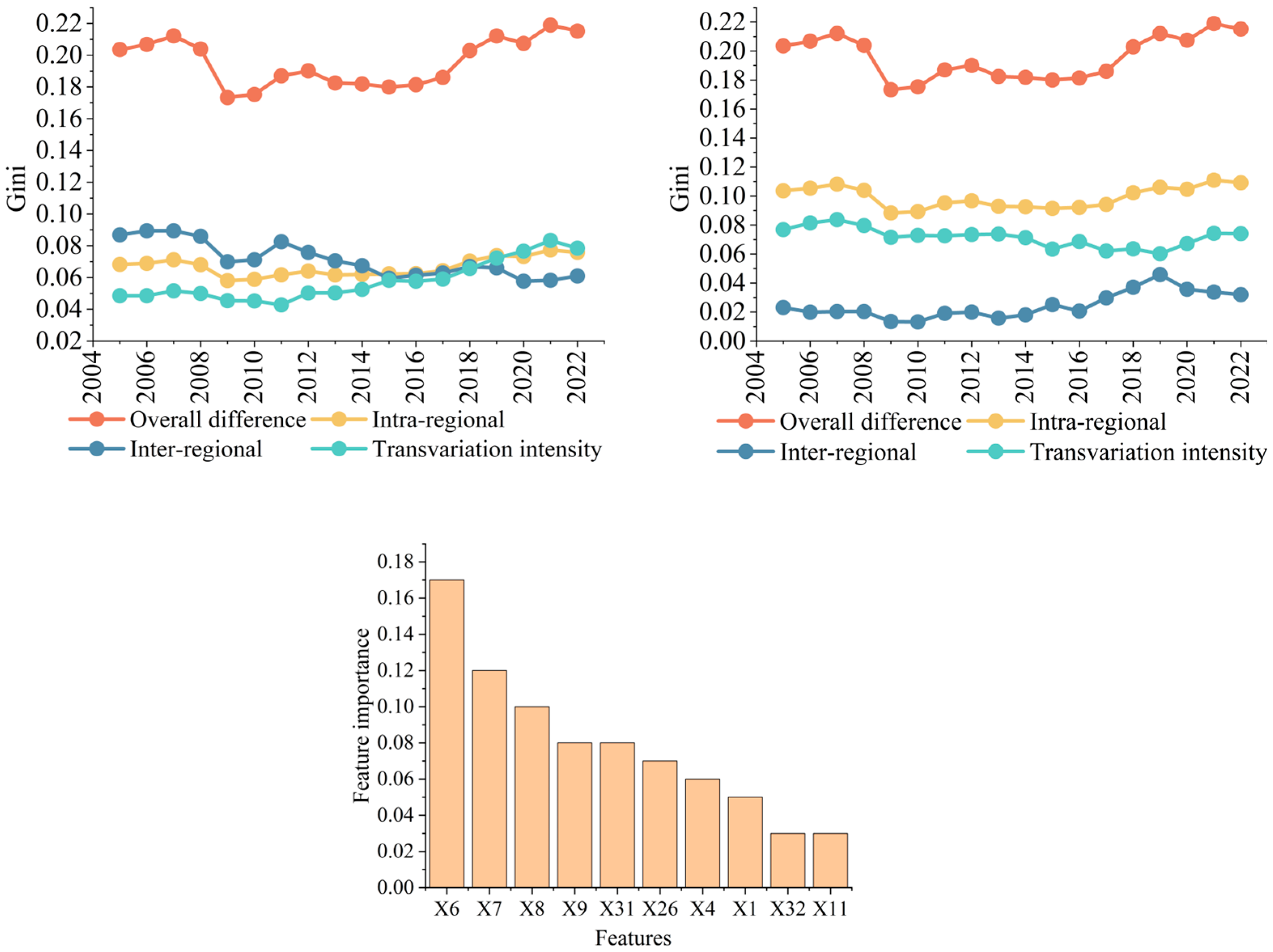
3.2. Spatial Differences and Source Structure Decomposition of UR
3.2.1. Spatial Differences in UR
3.2.2. Inter-Provincial Differences
3.2.3. Intra-Provincial Differences
3.3. Convergence Results of UR
3.3.1. σ Convergence
3.3.2. β Convergence
3.3.3. Conditional Convergence Test
3.3.4. Results of the OPGD
3.4. Robust Check
4. Discussion and Policy Implications
4.1. Discussion
4.2. Policy Implications
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korhonen, J.; Snäkin, J.P. Quantifying the relationship of resilience and eco-efficiency in complex adaptive energy systems. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 120, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habitat, U.N. World Cities Report 2022: Envisaging the Future of Cities; United Nations Human Settlements Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2022; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Lyulyov, O.; Pimonenko, T. Interplay of urbanization and ecological environment: Coordinated development and drivers. Land 2023, 12, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Wang, M.; Yang, D.; Chen, W. Green efficiency of water resources in Northwest China: Spatial-temporal heterogeneity and convergence trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirzadeh, M.; Sobhaninia, S.; Sharifi, A. Urban resilience: A vague or an evolutionary concept? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 81, 103853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lu, X.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluating urban agglomeration resilience to disaster in the Yangtze Delta city group in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Cai, F.; Li, Z. The China Miracle: Development Strategy and Economic Reform, Revised Edition; The Chinese University of Hong Kong Press: Hong Kong, China, 2004; pp. 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y. The Chinese Growth Miracle: Handbook of Economic Growth; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 943–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Meie, P.; Yi, L.; Kexin, C.; Yisong, Z.; Zhou, X. A time-series analysis of urbanization-induced impervious surface area extent in the Dianchi Lake watershed from 1988–2017. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Du, S.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, T.; Zhao, Y.; He, W.; Xue, H.; He, Y.; Gao, X.; et al. Unveiling the impact mechanism of urban resilience on carbon dioxide emissions of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Foundations of Socio-Environmental Research: Legacy Readings with Commentaries; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973; pp. 460–482. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H. Urban resilience and urban sustainability: What we know and what do not know? Cities 2018, 72, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, S.; Falcão, M.J.; Komljenovic, D.; de Almeida, N.M. A systematic literature review on urban resilience enabled with asset and disaster risk management approaches and GIS-based decision support tools. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirzadeh, M.; Sobhaninia, S.; Buckman, S.T.; Sharifi, A. Towards building resilient cities to pandemics: A review of COVID-19 literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resilience Alliance. Assessing Resilience in Social-Ecological Systems: Workbook for Practitioners, Version 2.0. SETS. 2010. Available online: https://www.resalliance.org/files/ResilienceAssessmentV2_2.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2025).
- Kim, Y.; Carvalhaes, T.; Helmrich, A.; Markolf, S.; Hoff, R.; Chester, M.; Li, R.; Ahmad, N. Leveraging SETS resilience capabilities for safe-to-fail infrastructure under climate change. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 54, 101153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A. Resilience of urban social-ecological-technological systems (SETS): A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellmann, T.; Andersson, E.; Knapp, S.; Lausch, A.; Palliwoda, J.; Priess, J.; Scheuer, S.; Haase, D. Reinforcing nature-based solutions through tools providing social-ecological-technological integration. Ambio 2023, 52, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapucu, N.; Ge, Y.; Rott, E.; Isgandar, H. Urban resilience: Multidimensional perspectives, challenges and prospects for future research. Urban Gov. 2024, 4, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Chang, M. Urban resilience assessment and multi-scenario simulation: A case study of three major urban agglomerations in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 111, 107734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Jia, W.; Zhao, H.; Xiang, P. A framework for urban resilience meas-urement and enhancement strategies: A case study in Qingdao, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.; Bower, P.; Webb, R.T.; Munford, L. Measurement of community resilience using the Baseline Resilience Indicator for Communities (BRIC) framework: A systematic review. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 95, 103870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datola, G. Implementing urban resilience in urban planning: A comprehensive framework for urban resilience evaluation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudec, O.; Reggiani, A.; Šiserová, M. Resilience capacity and vulnerability: A joint analysis with reference to Slovak urban districts. Cities 2018, 73, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J. Evolution and analysis of urban resilience and its influencing factors: A case study of Jiangsu Province, China. Nat. Hazards 2022, 113, 1751–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varchandi, S.; Memari, A.; Jokar, M.R.A. An integrated best–worst method and fuzzy TOPSIS for resilient-sustainable supplier selection. Decis. Anal. J. 2024, 11, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Zhao, H.; Yue, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, J.; Zhao, P. Spatial heterogeneity of urban resilience: Quantifying key determinants by spatial ma-chine learning model embedded in density-structure-function frame-work. Cities 2025, 167, 106305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. An interpretable machine learning-assisted urban resilience evaluation and determinants identification: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 134, 106930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, G.; Yao, B.; Wu, J. Urban resilience assessment matrix consid-ering spatiotemporal processes: Model proposal and application. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 135, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sun, Z.; Du, M.D. Drivers of Urban Resilience in Eight Major Urban Agglomerations: Evidence from China. Land 2022, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, S.; Brooks, E.; Mehmood, A. Evolutionary resilience and strategies for climate adaptation. Plan. Theory Pract. 2012, 13, 299–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P. Urban resilience for whom, what, when, where, and why? Urban Geogr. 2019, 40, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, Y.; Fath, B.D.; Hubacek, K.; Yao, H.; Liu, W. The spatio-temporal dynamics of urban resilience in China’s capital cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Shi, J.; Tao, Y. The impact and mechanism of digital finance on ur-ban economic resilience. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2025, 106, 104468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhong, M.; Dong, Y. Digital economy and risk response: How the digital economy affects urban resilience. Cities 2024, 155, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, B.; Yuan, C. The impact of supply chain digitalization on urban resilience: Do industrial chain resilience, green total factor productivity and innovation matter? Energy Econ. 2025, 145, 108443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Sun, H.; Wu, H. How does urban shrinkage influence urban resilience? Empirical evidence from Northeast China. Habitat Int. 2026, 167, 103646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wu, W.; Shang, T.; Wu, P.; Yu, B. Assessing the impact of population urbanization on urban resilience: Empirical evidence from rapidly urbanizing China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2026, 117, 108189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Ma, H. The impact of basic public service provision on urban economic resilience: Evidence from 281 cities in China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 104, 104678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feofilovs, M.; Romagnoli, F. Dynamic assessment of urban resilience to natural hazards. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 62, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Yu, X. Enhancing the resilience of urban energy systems: The role of artificial intelligence. Energy Econ. 2025, 144, 108313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Jiao, Y.; Cheng, N. An Innovative decision-making scheme for the high-quality economy development driven by higher education. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8, 100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorrocks, A.F. The Class of Additively Decomposable Inequality Measures. Econometrica 1980, 48, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, T. Decomposing regional income inequality in China and Indonesia using two-stage nested Theil decomposition method. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2003, 37, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J. The regional differences and random convergence of urban resilience in China. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2022, 28, 979–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K. Econometric Convergence Test and Club Clustering Using Stata. Stata J. 2017, 17, 882–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Hao, X.; Li, J. Effects of public participation on environmental governance in China: A spatial Durbin econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 129042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Jiang, W. How does regional integration policy affect urban resilience? Evidence from urban agglomeration in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xie, W.; Wu, W.-Z.; Zhu, H. Predicting Chinese total retail sales of consumer goods by employing an extended discrete grey polynomial model. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 102, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Bu, Y. The impact of digital inclusive finance on urban economic resilience in China: Spatial spillover and mechanism analysis. Dev. Sustain. Econ. Financ. 2025, 8, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, L. Digital Finance, Talent Aggregation, and Urban Economic Resilience. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 108823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, N.; Mishra, T.; Parthasarathy, D. The impact of floods and cyclones on fiscal arrangements in India: An empirical investigation at the sub-national level. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 110, 104620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.; Demirgüç-Kunt, A.; Levine, R. Financial Institutions and Markets across Countries and over Time: The Updated Financial Development and Structure Database. World Bank Econ. Rev. 2010, 24, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, H.; Gross, L.; Li, X.; Wei, B.; et al. Nighttime light perspective in urban resilience assessment and spatiotemporal impact of COVID-19 from January to June 2022 in mainland China. Urban Clim. 2023, 50, 101591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C. Exploring the spatio-temporal evolution of economic resilience in Chinese cities during the COVID-19 crisis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 84, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, J.; Lu, X.; Wu, C.; Fu, G.; Qin, X. Quantifying security and resilience of Chinese coastal urban ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; LeGates, R.; Zhao, M.; Fang, C. The changing rural-urban divide in China’s megacities. Cities 2018, 81, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cao, X.; Shi, D.; Wang, Y. The “one-city monopoly index”: Measurement and empirical analysis of China. Cities 2020, 96, 102434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Guo, N.; Gao, X.; Wu, F. How carbon emission reduction is going to affect urban resilience. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B. Interregional supply chains of Chinese mineral resource requirements. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuka, H.; Zeng, D.-Z.; Zhao, L. Resource-based cities and the Dutch disease. Resour. Energy Econ. 2015, 40, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Region | Overall | Eastern | Central | Western | South | North |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hausman | 143.37 *** | 92.74 *** | 107.13 *** | 31.29 *** | 127.65 *** | 94.40 *** |
| LM-Error | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.16 | 0.00 | 4.49 ** | 0.58 |
| LM-Lag | 0.45 | 0.01 | 1.50 | 0.10 | 6.22 ** | 0.03 |
| R-LM-Error | 59.29 *** | 45.07 *** | 62.84 *** | 34.98 *** | 73.55 *** | 28.86 *** |
| R-LM-Lag | 184.17 *** | 61.53 *** | 214.56 *** | 43.17 *** | 87.53 *** | 89.03 *** |
| LR-Error | 64.10 *** | 31.87 *** | 46.91 *** | 20.61 *** | 47.61 *** | 50.73 *** |
| LR-Lag | 66.51 *** | 31.79 *** | 62.44 *** | 14.90 ** | 46.62 *** | 54.14 *** |
| Year | Moran’s I | p Value | Year | Moran’s I | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 0.092 | 0.000 | 2014 | 0.086 | 0.000 |
| 2006 | 0.094 | 0.000 | 2015 | 0.090 | 0.000 |
| 2007 | 0.095 | 0.000 | 2016 | 0.086 | 0.000 |
| 2008 | 0.096 | 0.000 | 2017 | 0.095 | 0.000 |
| 2009 | 0.090 | 0.000 | 2018 | 0.093 | 0.000 |
| 2010 | 0.090 | 0.000 | 2019 | 0.091 | 0.000 |
| 2011 | 0.098 | 0.000 | 2020 | 0.081 | 0.000 |
| 2012 | 0.090 | 0.000 | 2021 | 0.079 | 0.000 |
| 2013 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 2022 | 0.077 | 0.000 |
| Variables | Total | Eastern | Central | Western | South | North |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.340 *** (−31.880) | −0.331 *** (−19.102) | −0.362 *** (−21.237) | −0.360 *** (−15.470) | −0.387 *** (−25.049) | −0.316 *** (−21.091) | |
| 0.899 *** (78.189) | 0.810 *** (38.264) | 0.833 *** (47.417) | 0.769 *** (30.225) | 0.857 *** (53.953) | 0.855 *** (51.261) | |
| 0.045 | 0.019 | 0.071 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.064 | |
| V | 0.022 | 0.021 | 0.024 | 0.023 | 0.026 | 0.020 |
| Log-L | 6458.600 | 2588.879 | 2462.477 | 1200.170 | 3516.191 | 2858.708 |
| N | 4794 | 1938 | 1853 | 1003 | 2618 | 2176 |
| Variables | Total | Eastern | Central | Western | South | North |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.349 *** (−32.406) | −0.347 *** (−19.738) | −0.410 *** (−22.969) | −0.392 *** (−16.158) | −0.396 *** (−25.250) | −0.330 *** (−21.863) | |
| 0.872 *** (66.394) | 0.790 *** (35.133) | 0.792 *** (42.154) | 0.732 *** (25.652) | 0.820 *** (44.973) | 0.836 *** (47.095) | |
| EG | 0.001 (0.905) | 0.001 (1.020) | 0.000 (1.888) | −0.002 (−0.684) | 0.001 (1.164) | −0.003 *** (−2.281) |
| MS | 0.004 ** (2.206) | 0.005 ** (2.004) | −0.005 (−1.151) | 0.020 *** (2.585) | 0.005 ** (2.012) | 0.005 (1.440) |
| TC | 0.000 (1.244) | 0.000 * (1.690) | 0.002 *** (3.845) | −0.000 * (−0.066) | −0.000 (−0.401) | 0.001 *** (−3.266) |
| FT | 0.005 (1.048) | 0.005 (0.868) | 0.017 (0.955) | −0.071 * (−1.929) | 0.008 (1.439) | −0.008 (−0.543) |
| FR | −0.027 (−0.623) | −0.073 (−0.914) | 0.035 * (0.436) | 0.065 (0.815) | −0.101 (−1.738) | 0.094 (1.369) |
| FE | −0.003 ** (−2.372) | −0.000 (−0.087) | −0.002 (−1.780) | −0.004 (−0.538) | 0.001 (0.799) | −0.007 *** (−0.390) |
| R2 | 0.094 | 0.028 | 0.072 | 0.035 | 0.045 | 0.056 |
| V | 0.023 | 0.022 | 0.028 | 0.026 | 0.027 | 0.021 |
| Log-L | 6488.948 | 2608.654 | 2513.919 | 1218.888 | 3540.976 | 2898.549 |
| Dimensions | Drivers | Q-Value | p Value | Symbolic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal factors | Per capital GDP | 0.611 | 0.000 | A1 |
| Capital used by foreigners per capita | 0.671 | 0.000 | A2 | |
| Savings deposits per capita | 0.884 | 0.000 | A3 | |
| Ratio of employees | 0.744 | 0.000 | A4 | |
| Per capita fiscal expenditure | 0.723 | 0.000 | A5 | |
| Urban per capita disposable income | 0.658 | 0.000 | B1 | |
| Average wage of working staff | 0.610 | 0.000 | B2 | |
| Public trams per 10,000 people | 0.593 | 0.000 | C1 | |
| External factors | Market size | 0.728 | 0.000 | D1 |
| Technological innovation | 0.523 | 0.000 | D2 |
| Models and Variables | Geographic Distance Matrix | Geo-Economic Spatial Weight Matrix | Mixed Spatial Weight Matrix | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnCRI | −0.355 *** (−32.273) | −0.361 *** (−32.700) | −0.350 *** (−31.583) | −0.360 *** (−32.022) | −0.340 *** (−31.880) | −0.349 *** (−32.406) |
| W. LnCRI | 0.344 *** (23.636) | 0.336 *** (16.166) | 0.270 *** (18.770) | 0.215 *** (12.093) | 0.286 *** (19.649) * | 0.229 *** (12.007) |
| R2 | 0.017 | 0.044 | 0.026 | 0.036 | 0.024 | 0.094 |
| 0.956 *** (116.349) | 0.952 *** (100.919) | 0.775 *** (70.346) | 0.754 *** (64.495) | 0.899 *** (78.189) | 0.872 *** (66.394) | |
| sigma2_e | 0.004 *** (48.853) | 0.003 *** (48.841) | 0.004 *** (48.134) | 0.004 *** (48.146) | 0.004 *** (48.925) | 0.004 *** (48.932) |
| N | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 | 4794 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, G.; Hu, Y.; An, H.; Huang, J.; Shi, T. Urban Resilience and Spatial Inequality in China: Toward Sustainable Development Under Multi-Dimensional Constraints. Land 2025, 14, 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122415
Huang G, Hu Y, An H, Huang J, Shi T. Urban Resilience and Spatial Inequality in China: Toward Sustainable Development Under Multi-Dimensional Constraints. Land. 2025; 14(12):2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122415
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Gaoyan, Yue Hu, Hui An, Jie Huang, and Tao Shi. 2025. "Urban Resilience and Spatial Inequality in China: Toward Sustainable Development Under Multi-Dimensional Constraints" Land 14, no. 12: 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122415
APA StyleHuang, G., Hu, Y., An, H., Huang, J., & Shi, T. (2025). Urban Resilience and Spatial Inequality in China: Toward Sustainable Development Under Multi-Dimensional Constraints. Land, 14(12), 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122415






