Research on Enhancing Urban Land Use Efficiency Through Digital Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
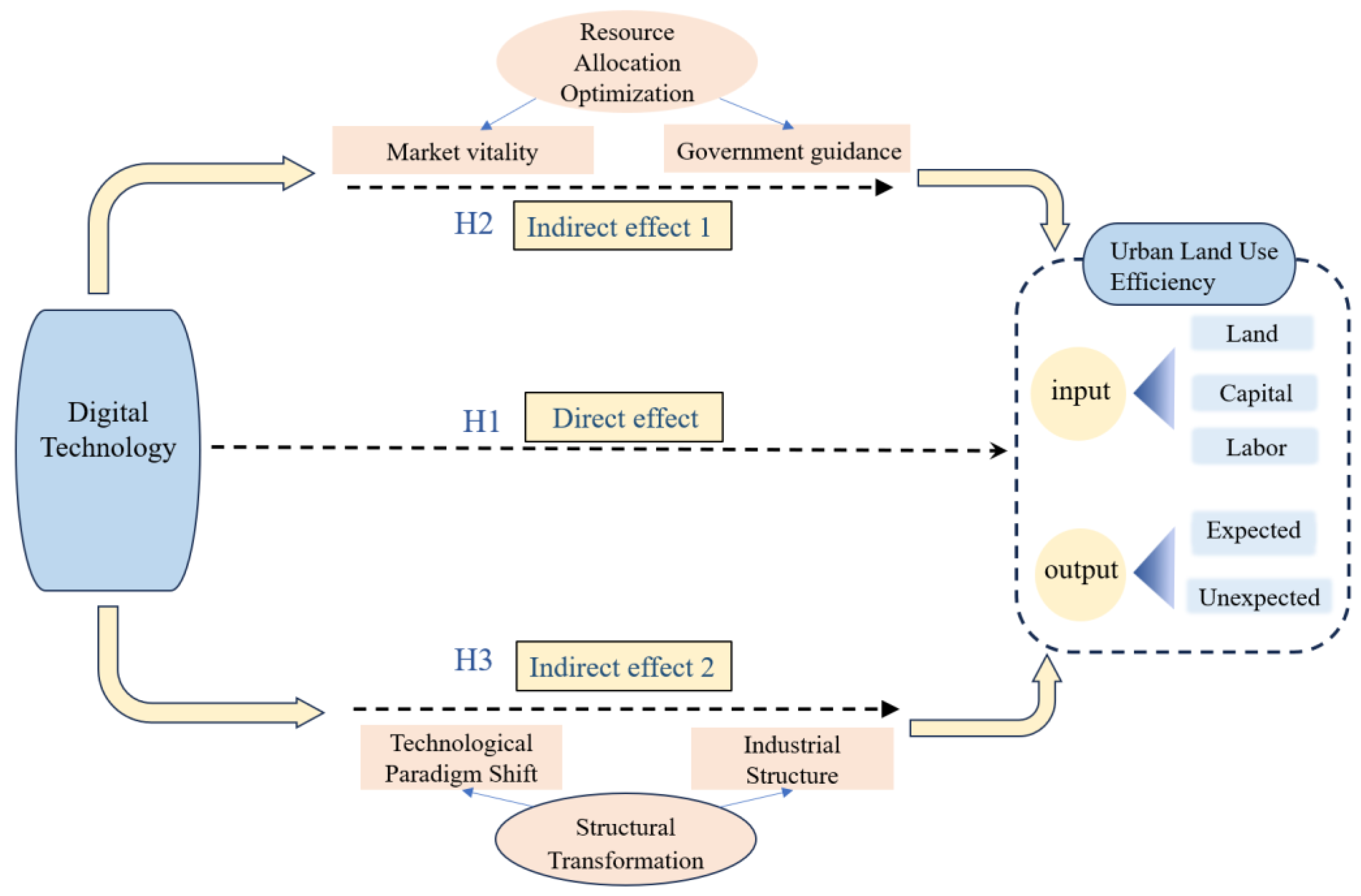
2. Theoretical Foundations and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Impact of Digital Technologies on Urban Land Use Efficiency
2.2. Mechanisms of Digital Technology’s Impact on Urban Land Use Efficiency
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Empirical Model Construction
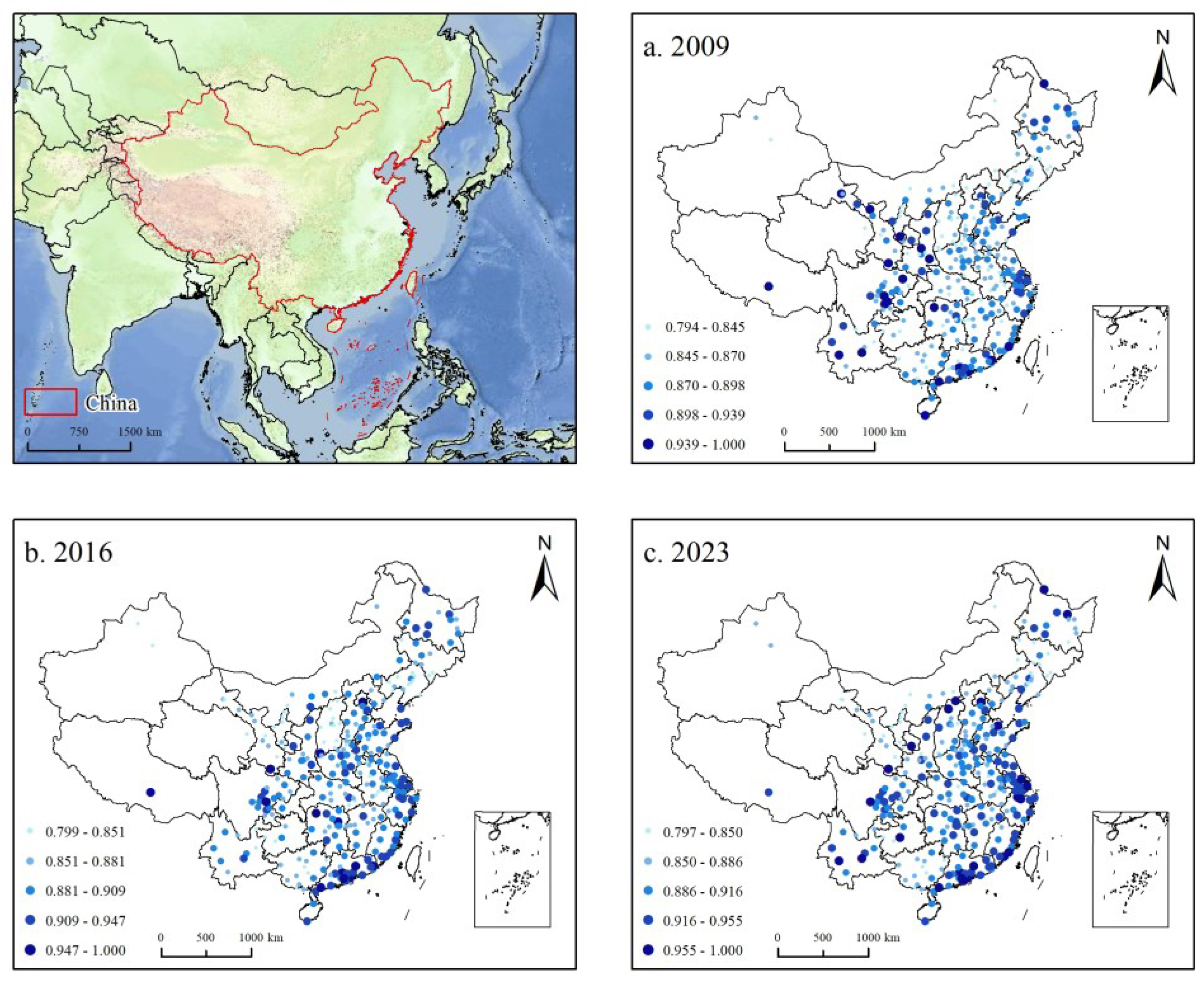
3.2. Data Sources
3.3. Variable Descriptions
3.3.1. Dependent Variable
3.3.2. Core Explanatory Variables
3.3.3. Mediating Variables
3.3.4. Control Variables
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Benchmark Regression
4.2. Robustness Tests
4.3. Endogeneity Tests
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.4.1. Location and Structural Heterogeneity
4.4.2. Heterogeneity in Factor Inputs and Allocation
4.5. Mechanism Verification
4.5.1. Micro Resource Allocation Mechanism
4.5.2. Macro-Structural Transformation Mechanism
5. Further Analysis
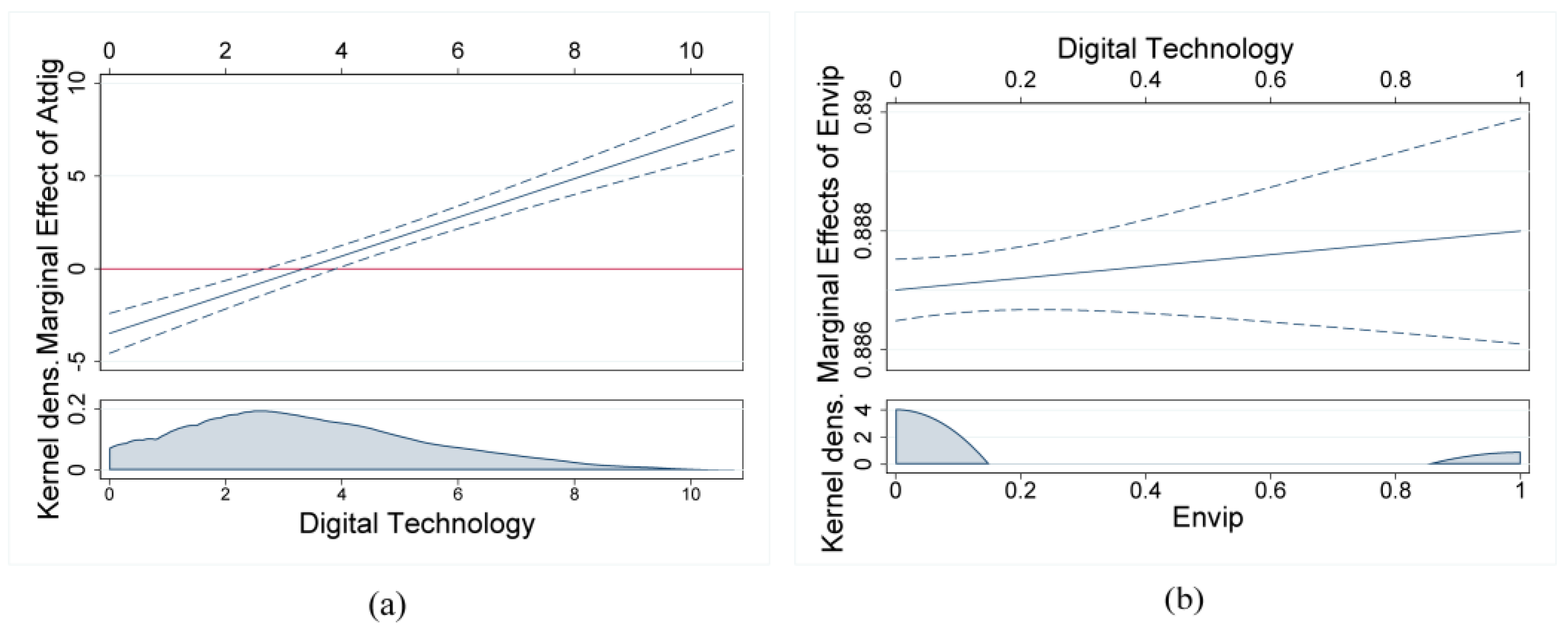
5.1. Further Analysis: Synergistic Mechanisms of Digital Technology’s Empowering Effects
5.1.1. The Modulating Effect of Government Digital Attention: Signal Transmission and Resource Allocation
5.1.2. Regulatory Effects of Environmental Policy: Green Constraints and Technological Induction
5.1.3. Analysis of Heterogeneity in Moderating Effects
6. Discussion, Conclusions and Policy Implications
6.1. Discussion
6.2. Conclusions
6.3. Policy Recommendations
6.3.1. Deepen the Application of Digital Technologies to Expand the Technical Boundaries for Enhancing Land Use Efficiency
6.3.2. Develop Differentiated Strategies to Optimize Regional Synergies in Digital Technologies
6.3.3. Strengthen the Multidimensional Role of Digital Technologies and Ensure the Smooth Transmission of Technological Dividends to Enhance Land Efficiency
6.3.4. Establish a Synergistic Policy Framework to Enhance the Adaptability of Digital Technologies in Empowering Land Use Efficiency
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, D.; Zhang, J.; An, B.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yan, Y.; Peng, G. Research on urban land green use efficiency and influencing factors based on DEA and ESTDA models: Taking 284 cities in China as an example. Ecol. Ind. 2024, 160, 111824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhou, S.; Ao, X.; Yang, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z. Unveiling the nonlinear drivers of urban land resources on carbon emissions: The mediating role of industrial upgrading and technological innovation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 108000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.; Buerkert, A.; Hoffmann, E.; Schlecht, E.; von Cramon-Taubade, S.; Tscharntke, T. Implications of agricultural transitions and urbanization for ecosystem services. Nature 2014, 515, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumoulidis, D.; Varvaris, I.; Hadjimitsis, D.; Gabriele, M.; Brumana, R.; Gitas, I.; Georgopoulos, N.; Abdollahnejad, A.; Gkounti, E.; Stavrakoudis, D.; et al. Profiling Land Use Planning: Legislative Structures in Five European Nations. Land 2025, 14, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillan, J.; Heipke, C. Assessing Patterns and Trends in Urbanization and Land Use Efficiency Across the Philippines: A Comprehensive Analysis Using Global Earth Observation Data and SDG 11.3.1 Indicators. PFG–J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2024, 92, 569–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Khan, J.; Mobeen, A.; Jaafar, W.; Kemarau, R. Estimating the plausible projections of land use/land cover dynamics in Jhelum and Chenab River basins using satellite imageries and machine learning models in Google Earth Engine. Geocarto Int. 2025, 40, 2491640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Feng, H.; Meng, Y.; Yue, L. Analysis of the spatio-temporal evolution of sustainable land use in China under the carbon emission trading scheme: A Measurement Idea Based on the DID MODEL. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavina, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Freire, S.; Florio, P.; Ehrlich, D.; Tommasi, P.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T. Land use efficiency of functional urban areas: Global pattern and evolution of development trajectories. Habitat. Int. 2022, 123, 102543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Introduction to land use and rural sustainability in China. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhou, M.; Huang, L.; Shan, L.; Wang, K. Assessing the dynamic land utilization efficiency and relevant driving mechanism in in-situ urbanized rural areas: A case study of 1979 administrative villages in Hangzhou. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 101, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Duan, K.; Yang, L.; Wei, X. Land Regulation and Local Service Provision: Can Economic Growth and Environmental Protection Be Achieved Simultaneously? Land 2024, 13, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.; Zevenbergen, J. Urban land management under rapid urbanization: Exploring the link between urban land policies and urban land use efficiency in Ethiopia. Cities 2024, 153, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, C.; Wen, F. Cointegration test and granger causality test for the relationship between urbanization and urban land use structure—A case study of Chongqing. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2010, 30, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Camagni, R.; Gibelli, M.; Rigamonti, P. Urban mobility and urban form: The social and environmental costs of different patterns of urban expansion. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 40, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Su, A.; Su, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Weng, W. Does the establishment of development zones really improve industrial land use efficiency? Implications for China’s high-quality development policy. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cai, Z.; Jin, L. Urban green land use efficiency of resource-based cities in China: Multidimensional measurements, spatial-temporal changes, and driving factors. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 104, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhang, T.; Shen, T. Spatial-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban land use structure efficiency: Evidence from 282 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 500, 145275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lian, G.H.; Jin, X.; Fu, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y. The impact of labor force shrinkage on urban land use efficiency. Resour. Sci. 2024, 46, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Tang, Y. The Spatial Changes of Transportation Infrastructure and Its Threshold Effects on Urban Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from China. Land 2021, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Shan, T.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, W. Does the Digital Economy Promote Green Land Use Efficiency? Sustainability 2025, 17, 7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Fang, C.; Wang, Z.; Bao, C. Spatial relationship of high-speed transportation construction and land-use efficiency and its mechanism: Case study of Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Newman, G.; Kim, J. Neighborhood decline and mixed land uses: Mitigating housing abandonment in shrinking cities. Land Use Policy 2019, 83, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Luo, Q.; Yu, H.; Liu, J.; Xia, W. Spatial–Temporal Evolution of the Coupling Coordination Degree between Water and Land Resources Matching and Cultivated Land Use Eco-Efficiency: A Case Study of the Major Grain-Producing Areas in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Land 2023, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Fan, Y.; Wen, C. Systematic coupling and multistage interactive response of the urban land use efficiency and ecological environment quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Xu, W.; Gu, Z.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. A new framework of land use efficiency for the coordination among food, economy and ecology in regional development. Sci. Total Env. 2020, 710, 135670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Jia, S.; Cui, X. From efficiency to resilience: Unraveling the dynamic coupling of land use economic efficiency and urban ecological resilience in Yellow River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.; Anderson, S.; Costanza, R.; Kubiszewski, I. The ecological economics of land degradation: Impacts on ecosystem service values. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 129, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, R.; Chen, J. Does industrial land marketization reform faciliate urban land use efficiency? Int. Rev. Econ. 2024, 96, 103609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, X. Different pathways, same goal: Configuring different types of policy tools to improve the urban land green use efficiency. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y. Study the effect of industrial structure optimization on urban land-use efficiency in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lin, N.; Dong, Y.; Tang, Y. How Does New Energy Demonstration City Policy Promote Urban Land Use Efficiency in China? The Mediating Effect of Industrial Structure. Land 2023, 12, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; He, Z. The impact of green finance policy on land ecological security: City-level evidence from China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 105, 105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wen, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, A.; Gil, J.M. Synergistic impacts of carbon emission trading policy and innovative city pilot policy on urban land green use efficiency in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 118, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.; Choy, L.; Webster, C. Institutional innovations in land development and planning in the 20th and 21st centuries. Habitat. Int. 2018, 75, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Guo, J.; Zhou, J. Impact of digital governance on the green utilization efficiency of urban land. Land Use Policy 2025, 153, 107539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Q. How Do National Key Development Zones Affect Land-Use Eco-Efficiency? Evidence from Counties in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.; Kim, T.; Hewings, G. Information technology impacts on urban spatial structure in the Chicago region. Geogr. Anal. 2002, 34, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, P.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H. Measuring the efficiency and driving factors of urban land use based on the DEA method and the PLS-SEM model—A case study of 35 large and medium-sized cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D. Profiting from innovation in the digital economy: Enabling technologies, standards, and licensing models in the wireless world. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 1367–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z.; Dhunny, Z. On big data, artificial intelligence and smart cities. Cities 2019, 89, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.; Salazar, I.; Vargas, P. Does information technology improve open innovation performance? An examination of manufacturers in Spain. Inf. Syst. Res. 2017, 28, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik-Zada, E.; Gatto, A.; Niftiyev, I. E-government and petty corruption in public sector service delivery. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2022, 36, 3987–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lin, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Xu, H. Does Smart City Construction Improve the Green Utilization Efficiency of Urban Land? Land 2021, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Weber, D.; De Bie, K. Assessing the value of public lands using public participation GIS (PPGIS) and social landscape metrics. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, B.; Geurs, K.; Chorus, C. Information, communication, travel behavior and accessibility. J. Transp. Land Use 2013, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Thill, J.C.; Peiser, R.B. Land pricing and its impact on land use efficiency in post-land-reform China: A case study of Beijing. Cities 2016, 50, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, X. The Impact of Government Digital Transformation on Land Use Efficiency: Evidence from China. Land 2024, 13, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Ye, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liang, B. Smart Cities, Smarter land Use? Unveiling the efficiency gains from China’s digital urban transformation. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Efficiency of construction land allocation in China: An econometric analysis of panel data. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.F.; Zeng, M. Assessing the impact of digital economy on green development efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Energy Econ. 2022, 112, 106127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Anitesh, B.; Andrew, B.W. Virtual field experiments for a digital economy: A new research methodology for exploring an information economy. Decis. Support. Syst. 2002, 32, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhu, P.; Qiu, C.; Wang, X. The Impact of Digital Technology Innovation on Enterprise Market Value. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2023, 40, 68–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Xiao, D.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Can the digital economy address the loss of green development efficiency due to resource mismatch? Evidence from China’s land transaction markets. J. Environ. Plann. Manag. 2023, 68, 406–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y. Utilizing ESG frameworks to improve environmental performance in digital economy entrepreneurial firms: Using digital technologies for green development. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2025, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhou, G.; Gan, X. Key Digital Technology, Local Fiscal Resources and Unified National Market. Public Financ. Res. 2025, 46, 116–128. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Wang, X. Innovation Networks, Key Core Technologies and R&D Resource Allocation: Based on a Cross-regional, Cross-technology Knowledge Spillover Network Model. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2025, 42, 157–179. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, R.; Aziz, G.; Khan, M.S. The Nexus Between Intensive Land Utilization, Energy Efficiency, and Economic Growth: Application of Advanced Econometric Approaches. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 2217–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Xue, S.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Q.; Ali, M.; Xu, R.; Xu, J.; Ding, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; et al. Framework of land use planning for an energy producing city of Northwest China based on water-energy-food nexus. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 142126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.W.; Li, X.S.; Chen, J.Q. Integration of land use resilience and efficiency in China: Analysis of spatial patterns, differential impacts on SDGs, and adaptive management strategies. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 175, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, B.; Guo, G.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. Unlocking the Power of Economic Agglomeration: How Digital Finance Enhances Urban Land Use Efficiency Through Innovation Ability and Rationalization of Industrial Structure in China. Land 2024, 13, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandra, U.; Mikhail, Z.; Olesya, G.; Lyudmila, P. Information space of the land reclamation industry in the digital economy of the agroindustrial complex of the Russian Federation. SHS Web Conf. 2021, 106, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T. Digital economy, CO2 emissions and China’s environmental sustainable development-an analysis based on TVP-VAR model. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 84, 1945–1957. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ming, Z. Synergy degree measurement of traditional manufacturing and green industry driven by digital economy in Yangtze River Delta region. Data Sci. Informetr. 2024, 4, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, W.; Yan, D. Breaking the resource curse: The impact of digital economy on the sustainable transformation of resource-based cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 113, 105707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Nian, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, R. Inhibit or Promote: Assessing the Impact of Digital Economy on Poverty Reduction in the Belt and Road Initiative Countries. Appl. Spat. Anal. 2025, 18, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, H.; Kong, Q. Poison or antidote? Exploring the effect of polycentric urban spatial structure on ecological resilience. Cities 2025, 165, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. The divergent effects of spatial structure of urban agglomerations on carbon emission reduction capacity. Urban Clim. 2025, 63, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xu, L. Digitalization and innovation: How does the digital economy drive technology transfer in China? Econ. Model. 2024, 136, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Bai, J. Evaluating the synergistic effects of digital economy and government governance on urban low-carbon transition. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 105, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indicator Type | Primary Indicator | Indicator Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Land Input | Construction Land Area | km2 |
| Capital Input | Fixed Capital Stock | - | |
| Labor Input | Employment in the secondary and tertiary industries | 10,000 person | |
| Energy Input | The product of the total energy consumption at the provincial level and the ratio of each city’s GDP to the GDP of its respective province | - | |
| Expected Output | Economic Benefits | The sum of the value added of the secondary and tertiary industries | CNY 100 million |
| Unexpected Output | Pollution Output | Total Carbon Emissions | 1,000,000 |
| Variable Properties | Variable Name | Variable Symbol | Mean | Sd | Min | Max | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dependent variable | Land Use Efficiency | Gue | 0.887 | 0.0390 | 0.794 | 1 | 4065 |
| Explanatory variable | Digital Technology | Dig | 3.440 | 2.197 | 0 | 11.25 | 4065 |
| Mediating variable | Market vitality | Entre | 10.53 | 0.938 | 7.919 | 14.24 | 4065 |
| Government guidance | Ins | 0.0170 | 0.0180 | 0 | 0.207 | 4065 | |
| Green Technology Innovation | Gtech | 2.644 | 1.810 | 0 | 9.373 | 4065 | |
| Industrial Structure | Ind | 2.302 | 0.144 | 1.831 | 2.846 | 4065 | |
| Control variables | Government intervention | Gov | 0.198 | 0.102 | 0.0440 | 1.027 | 4065 |
| Urbanization Level | Urb | 0.393 | 0.209 | 0.0750 | 1 | 4065 | |
| Economic Density | Eco | 7.260 | 1.308 | 2.806 | 12.06 | 4065 | |
| Human capital | Caph | 0.0200 | 0.0250 | 0 | 0.185 | 4065 | |
| Level of informatization | Inf | 1.057 | 0.760 | 0.134 | 10.17 | 4065 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Gue | Gue | |
| Dig | 0.006 *** | 0.004 *** |
| (9.490) | (5.668) | |
| Gov | −0.018 * | |
| (−1.649) | ||
| Urb | 0.018 *** | |
| (3.343) | ||
| Eco | 0.036 *** | |
| (15.424) | ||
| Caph | −0.106 ** | |
| (−1.996) | ||
| Inf | −0.002 | |
| (−1.485) | ||
| _cons | 0.866 *** | 0.611 *** |
| (394.377) | (34.125) | |
| City | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4065 | 4065 |
| R2 | 0.816 | 0.840 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replace the Dependent Variable | Shorter Sample Interval | Replace Explanatory Variables | Tail Trimming | |
| Dig | 0.030 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.003 *** | |
| (2.946) | (3.310) | (4.676) | ||
| L.Dig | 0.003 *** | |||
| (5.172) | ||||
| Gov | −0.250 | −0.013 | −0.001 | −0.030 *** |
| (−1.629) | (−0.890) | (−0.130) | (−2.632) | |
| Urb | −0.296 ** | 0.026 *** | 0.019 *** | 0.019 *** |
| (−2.495) | (3.034) | (3.393) | (3.590) | |
| Eco | 1.080 *** | 0.041 *** | 0.041 *** | 0.033 *** |
| (25.836) | (12.299) | (17.444) | (13.565) | |
| Caph | −4.383 *** | −0.043 | −0.120 ** | −0.163 *** |
| (−4.674) | (−0.687) | (−2.256) | (−2.888) | |
| Inf | −0.105 *** | −0.002 | −0.001 | −0.003 |
| (−3.370) | (−1.581) | (−1.055) | (−1.242) | |
| _cons | −5.889 *** | 0.580 *** | 0.571 *** | 0.643 *** |
| (−18.142) | (22.781) | (30.925) | (35.034) | |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4065 | 2710 | 3794 | 4065 |
| R2 | 0.989 | 0.878 | 0.859 | 0.837 |
| Variable | IV1 | |
|---|---|---|
| First-Stage | Second-Stage | |
| Dig | 0.036 *** | |
| (6.817) | ||
| IV1 | −0.004 *** | |
| (−8.74) | ||
| Gov | 0.404 | −0.039 *** |
| (1.15) | (−3.130) | |
| Urb | −0.005 | 0.018 *** |
| (−0.03) | (2.818) | |
| Eco | 0.673 *** | 0.015 *** |
| (11.59) | (3.364) | |
| Caph | 3.412 ** | −0.225 *** |
| (2.32) | (−3.170) | |
| Inf | −0.052 | 0.001 |
| (−1.32) | (0.386) | |
| Anderson LM | 80.69 | |
| (statistic p-value) | [0.000] | |
| C-D Wald F | 76.44 | |
| (10% threshold) | (16.38) | |
| City | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4065 | |
| Variable | Regional Heterogeneity | Urban Structural Heterogeneity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | Central | Western | Highly Centralized | Low Centralization | |
| Dig | −0.001 | 0.001 | 0.005 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.003 ** |
| (−1.345) | (0.949) | (3.879) | (5.417) | (2.092) | |
| Gov | −0.006 | −0.025 | −0.055 *** | −0.030 ** | 0.004 |
| (−0.377) | (−1.403) | (−3.167) | (−2.252) | (0.214) | |
| Urb | 0.011 ** | 0.022 ** | −0.011 | 0.026 *** | −0.014 |
| (2.320) | (2.403) | (−0.586) | (5.504) | (−0.935) | |
| Eco | 0.050 *** | 0.032 *** | 0.049 *** | 0.034 *** | 0.037 *** |
| (18.585) | (8.176) | (8.112) | (11.791) | (9.080) | |
| Caph | −0.291 *** | −0.071 | 0.340 *** | −0.071 * | −0.042 |
| (−3.539) | (−0.882) | (3.524) | (−1.754) | (−0.343) | |
| Inf | 0.001 | −0.003 | −0.008 * | 0.001 * | −0.013 *** |
| (0.903) | (−0.593) | (−1.674) | (1.901) | (−2.953) | |
| _cons | 0.504 *** | 0.651 *** | 0.569 *** | 0.623 *** | 0.626 *** |
| (21.564) | (21.579) | (13.961) | (28.056) | (21.784) | |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 1485 | 1365 | 1200 | 2406 | 1634 |
| R2 | 0.919 | 0.828 | 0.811 | 0.869 | 0.823 |
| Variable | Land Industrialization | Digital Workforce Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Dig | 0.000 | 0.004 *** | 0.001 | 0.005 *** |
| (0.202) | (5.508) | (0.960) | (5.943) | |
| Gov | −0.033 ** | −0.012 | −0.019 | −0.022 |
| (−2.133) | (−0.972) | (−0.908) | (−1.531) | |
| Urb | 0.004 | 0.022 *** | 0.021 ** | 0.013 ** |
| (0.700) | (3.363) | (2.162) | (2.013) | |
| Eco | 0.053 *** | 0.033 *** | 0.046 *** | 0.033 *** |
| (23.180) | (11.168) | (12.082) | (10.578) | |
| Caph | −0.130 ** | −0.281 *** | −0.038 | −0.281 *** |
| (−2.113) | (−3.650) | (−0.495) | (−3.152) | |
| Inf | 0.003 *** | −0.005 | 0.001 | −0.006 *** |
| (4.619) | (−1.541) | (0.729) | (−2.613) | |
| _cons | 0.459 *** | 0.646 *** | 0.549 *** | 0.641 *** |
| (21.366) | (29.924) | (18.075) | (27.979) | |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 966 | 3084 | 1231 | 2805 |
| R2 | 0.944 | 0.820 | 0.867 | 0.845 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entre | Insu | Gtech | Ind | |
| Dig | 0.048 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.526 *** | 0.004 *** |
| (5.681) | (5.735) | (29.082) | (2.826) | |
| Gov | −0.004 | −0.000 | −0.325 | −0.081 *** |
| (−0.034) | (−0.058) | (−1.203) | (−3.673) | |
| Urb | −0.055 | −0.004 | 0.194 | 0.024 * |
| (−0.684) | (−1.418) | (1.205) | (1.931) | |
| Eco | 0.439 *** | 0.012 *** | 0.196 *** | 0.006 |
| (14.480) | (11.643) | (3.336) | (1.213) | |
| Caph | 1.959 ** | 0.099 ** | 0.301 | −0.341 *** |
| (2.305) | (2.112) | (0.288) | (−2.933) | |
| Inf | −0.051 * | −0.003 ** | −0.076 *** | 0.032 *** |
| (−1.779) | (−2.278) | (−2.598) | (7.814) | |
| _cons | 7.216 *** | −0.075 *** | −0.532 | −0.081 *** |
| (30.838) | (−9.019) | (−1.165) | (−3.673) | |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4065 | 4065 | 4065 | 4065 |
| R2 | 0.933 | 0.762 | 0.938 | 0.925 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Atdig | Envip | |
| Dig | 0.002 *** | 0.002 *** |
| (2.899) | (3.449) | |
| Atdig | −3.479 *** | |
| (−6.340) | ||
| Envip | −0.008 *** | |
| (−3.687) | ||
| c.Dig##c.Atdig | 1.043 *** | |
| (10.403) | ||
| c.Dig##c.Encip | 0.002 *** | |
| (7.046) | ||
| Gov | −0.011 | −0.001 |
| (−0.968) | (−0.085) | |
| Urb | 0.017 *** | 0.019 *** |
| (2.943) | (3.296) | |
| Eco | 0.036 *** | 0.041 *** |
| (15.346) | (17.327) | |
| Caph | −0.162 *** | −0.116 ** |
| (−3.025) | (−2.195) | |
| Inf | −0.001 | −0.003 *** |
| (−1.391) | (−3.026) | |
| _cons | 0.617 *** | 0.576 *** |
| (34.410) | (31.238) | |
| City | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes |
| N | 3955 | 3780 |
| R2 | 0.843 | 0.860 |
| Variable | Atdig | Encip | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | Central | Western | Eastern | Central | Western | |
| Dig | −0.001 | 0.000 | 0.002 | −0.001 | −0.000 | 0.003 *** |
| (−0.864) | (0.132) | (1.158) | (−1.313) | (−0.483) | (2.708) | |
| Atdig | −0.363 | −1.495 ** | −5.184 *** | |||
| (−0.429) | (−2.111) | (−4.718) | ||||
| Encip | −0.005 ** | −0.015 *** | −0.008 | |||
| (−2.214) | (−4.200) | (−0.951) | ||||
| c.Dig##c. Atdig | 0.132 | 0.540 *** | 1.649 *** | |||
| (1.028) | (3.817) | (6.462) | ||||
| c.Dig##c.Encip | 0.001 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.003 ** | |||
| (3.610) | (3.655) | (2.384) | ||||
| Gov | 0.004 | −0.020 | −0.055 *** | −0.016 | −0.007 | −0.034 * |
| (0.219) | (−1.098) | (−3.134) | (−0.963) | (−0.379) | (−1.796) | |
| Urb | 0.012 ** | 0.024 *** | −0.011 | 0.013 *** | 0.024 ** | −0.009 |
| (2.476) | (2.605) | (−0.534) | (2.649) | (2.530) | (−0.441) | |
| Eco | 0.048 *** | 0.032 *** | 0.047 *** | 0.050 *** | 0.038 *** | 0.055 *** |
| (16.934) | (8.280) | (7.618) | (19.246) | (9.749) | (8.525) | |
| Caph | −0.279 *** | −0.120 | 0.171 * | −0.235 *** | −0.105 | 0.249 *** |
| (−3.322) | (−1.393) | (1.826) | (−2.785) | (−1.297) | (2.672) | |
| Inf | 0.000 | −0.004 | −0.007 | 0.000 | −0.007 | −0.008 * |
| (0.100) | (−0.833) | (−1.509) | (0.293) | (−1.486) | (−1.697) | |
| _cons | 0.519 *** | 0.651 *** | 0.593 *** | 0.503 *** | 0.615 *** | 0.526 *** |
| (21.164) | (21.655) | (14.289) | (22.175) | (20.308) | (11.885) | |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 1428 | 1350 | 1164 | 1386 | 1260 | 1120 |
| R2 | 0.918 | 0.830 | 0.818 | 0.924 | 0.840 | 0.834 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Wang, N. Research on Enhancing Urban Land Use Efficiency Through Digital Technology. Land 2025, 14, 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112294
Fu Y, Wang N. Research on Enhancing Urban Land Use Efficiency Through Digital Technology. Land. 2025; 14(11):2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112294
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yunpeng, and Ning Wang. 2025. "Research on Enhancing Urban Land Use Efficiency Through Digital Technology" Land 14, no. 11: 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112294
APA StyleFu, Y., & Wang, N. (2025). Research on Enhancing Urban Land Use Efficiency Through Digital Technology. Land, 14(11), 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112294











