Dynamics of Meteorological and Agricultural Drought in the Karnali River Basin, Nepal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Drought Indices
3.2.1. NDVI (Ecological Drought Index)
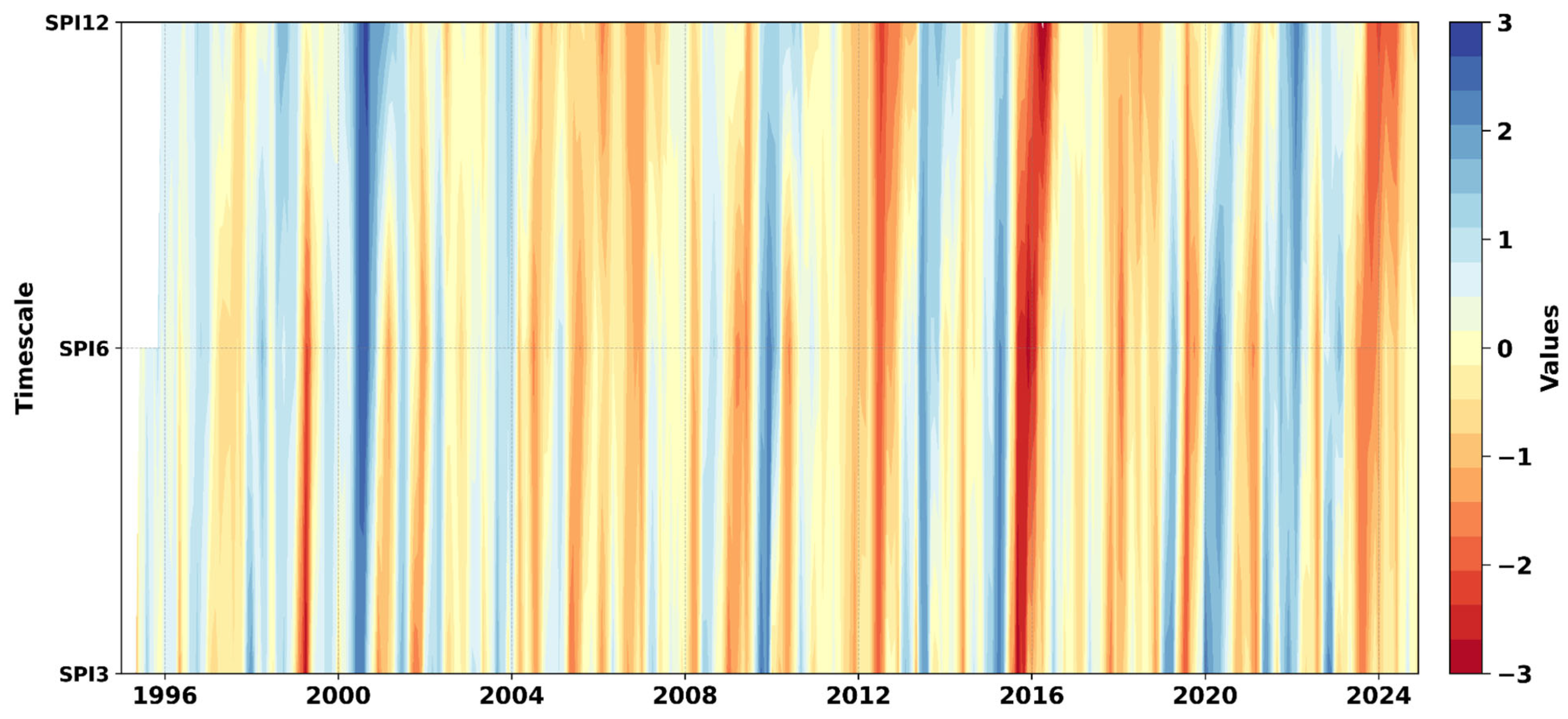
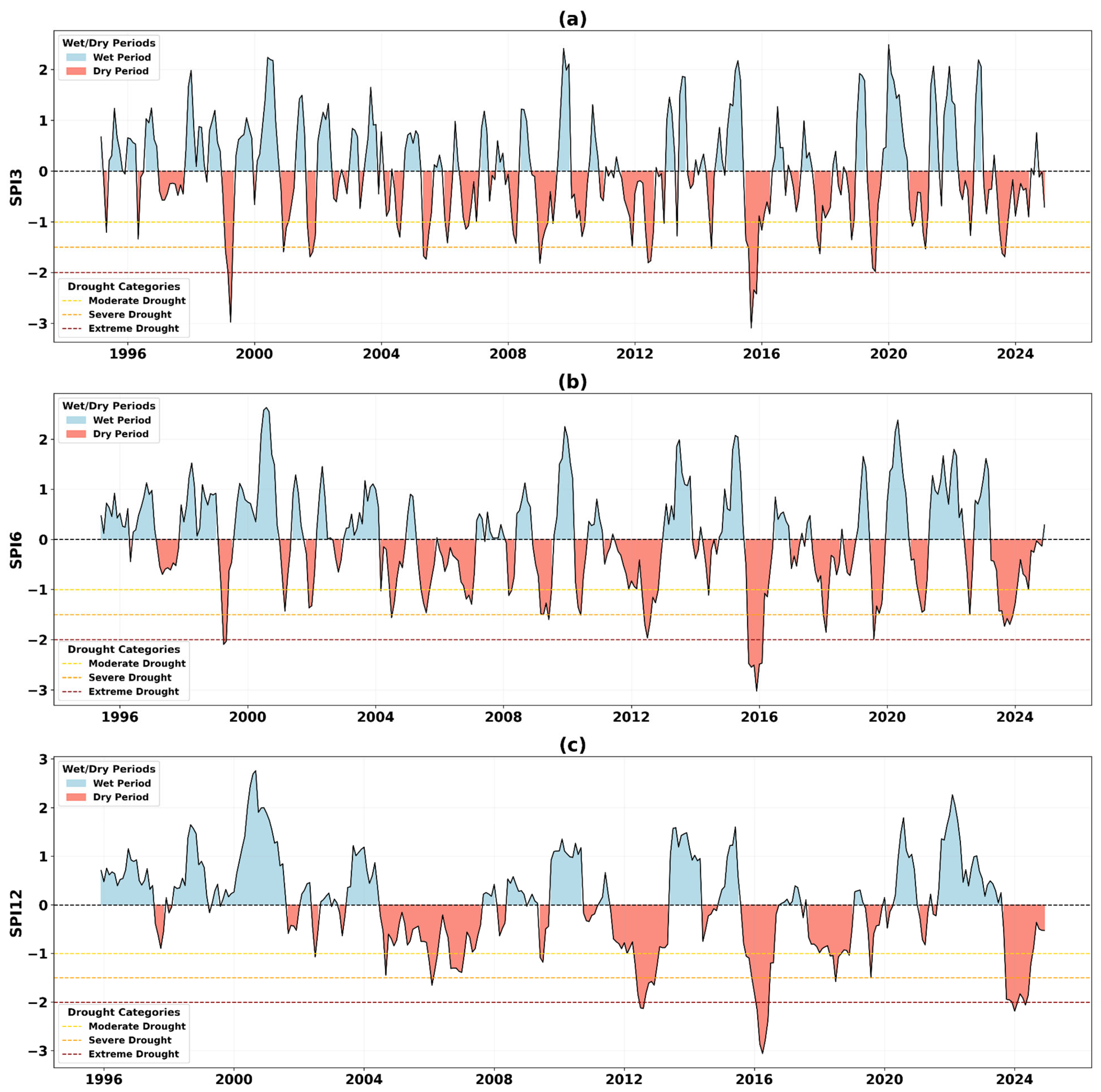
3.2.2. SPI Calculation (Meteorological Drought Index)
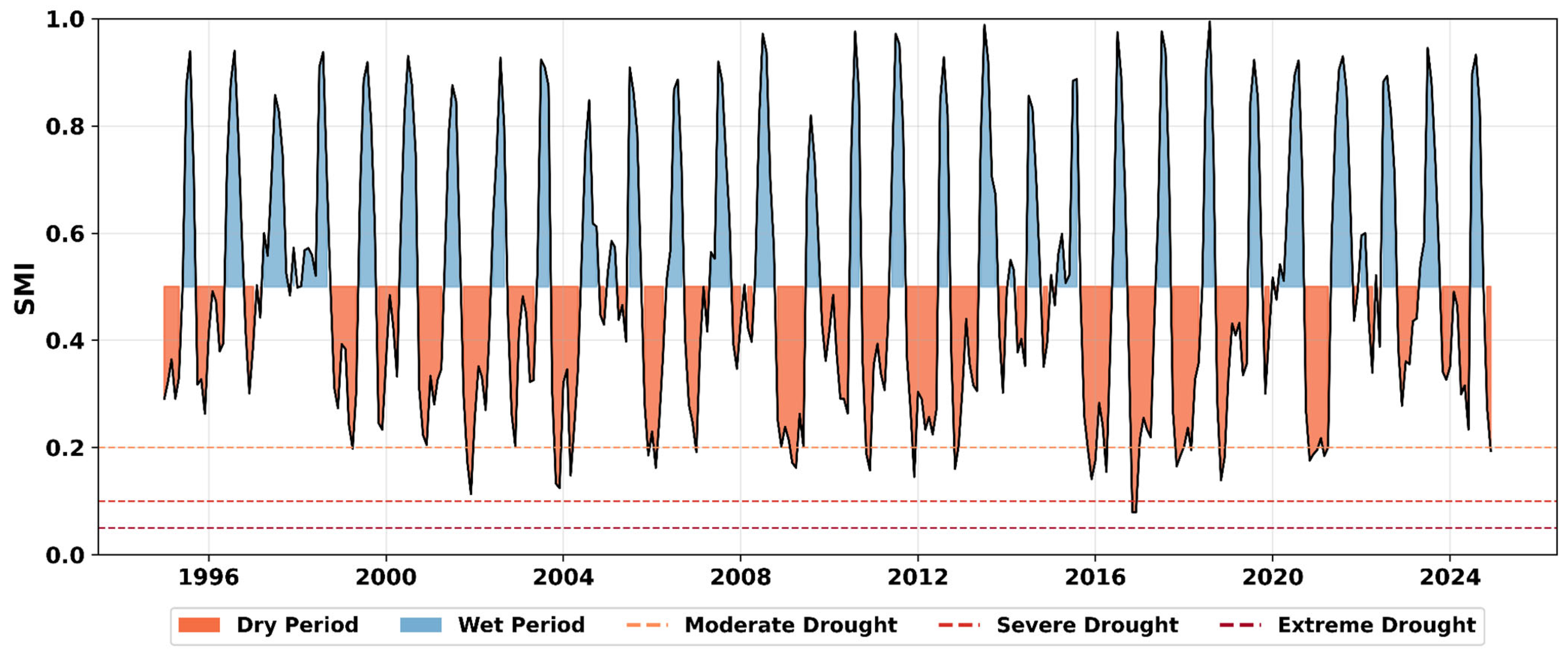
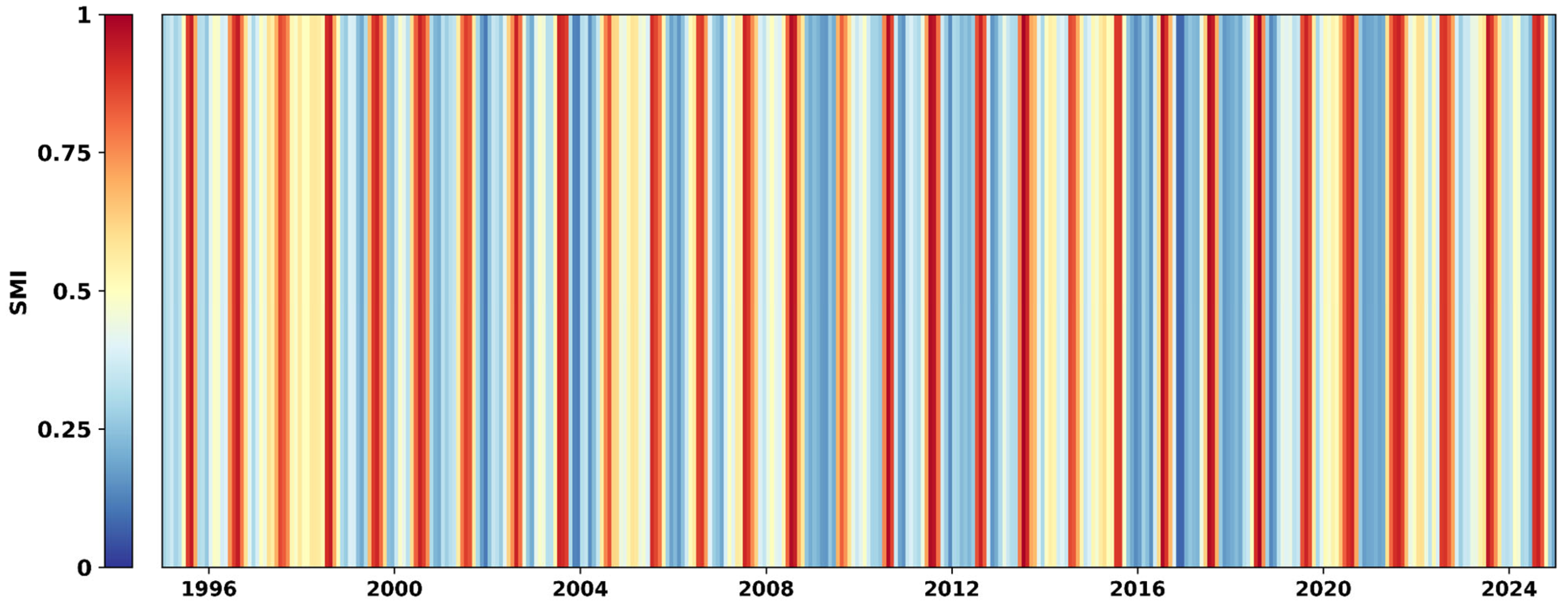
3.2.3. SMI Calculation (Hydrological Drought Index)
3.2.4. Composite Agricultural and Meteorological Indices
3.3. Trend Analysis and Visualization
3.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Results
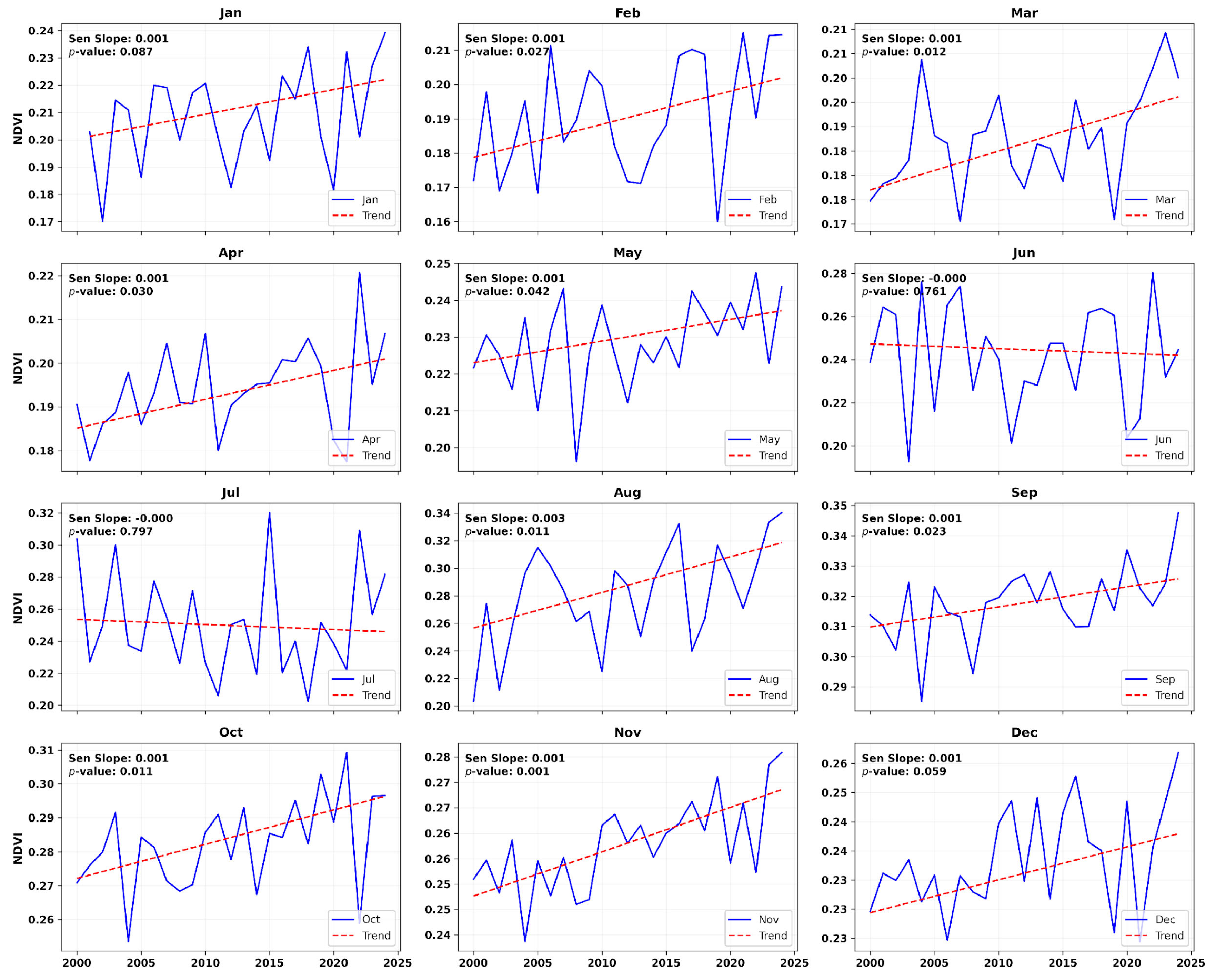
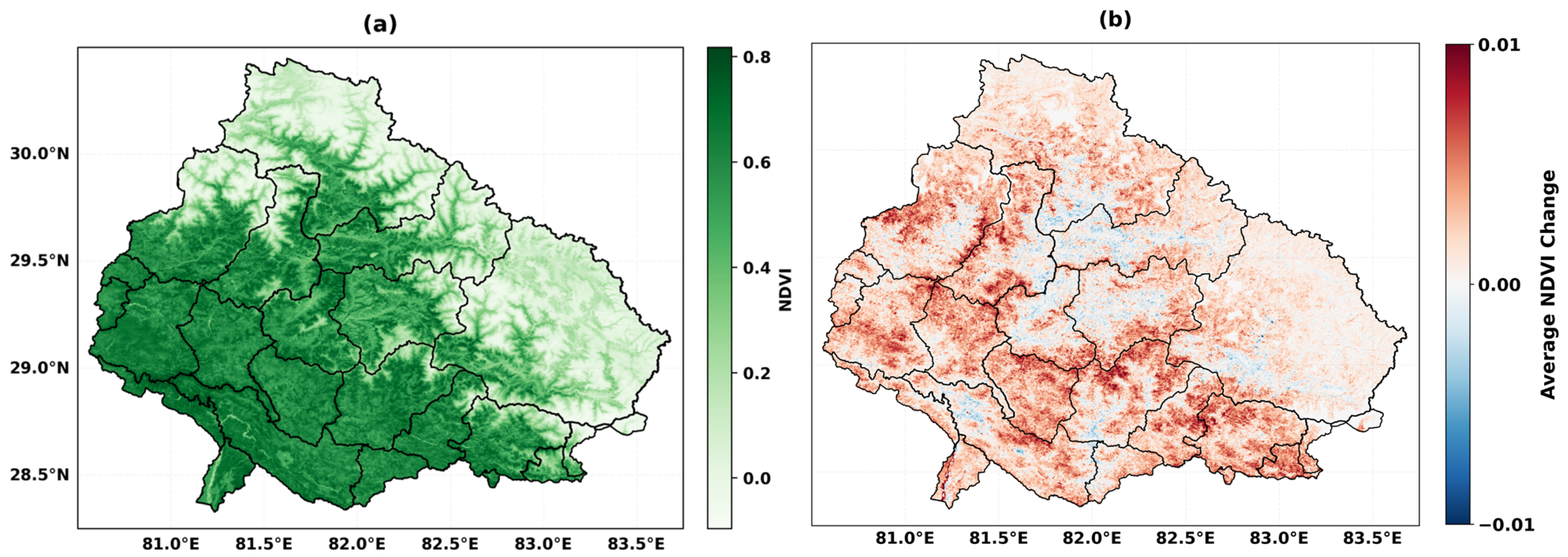
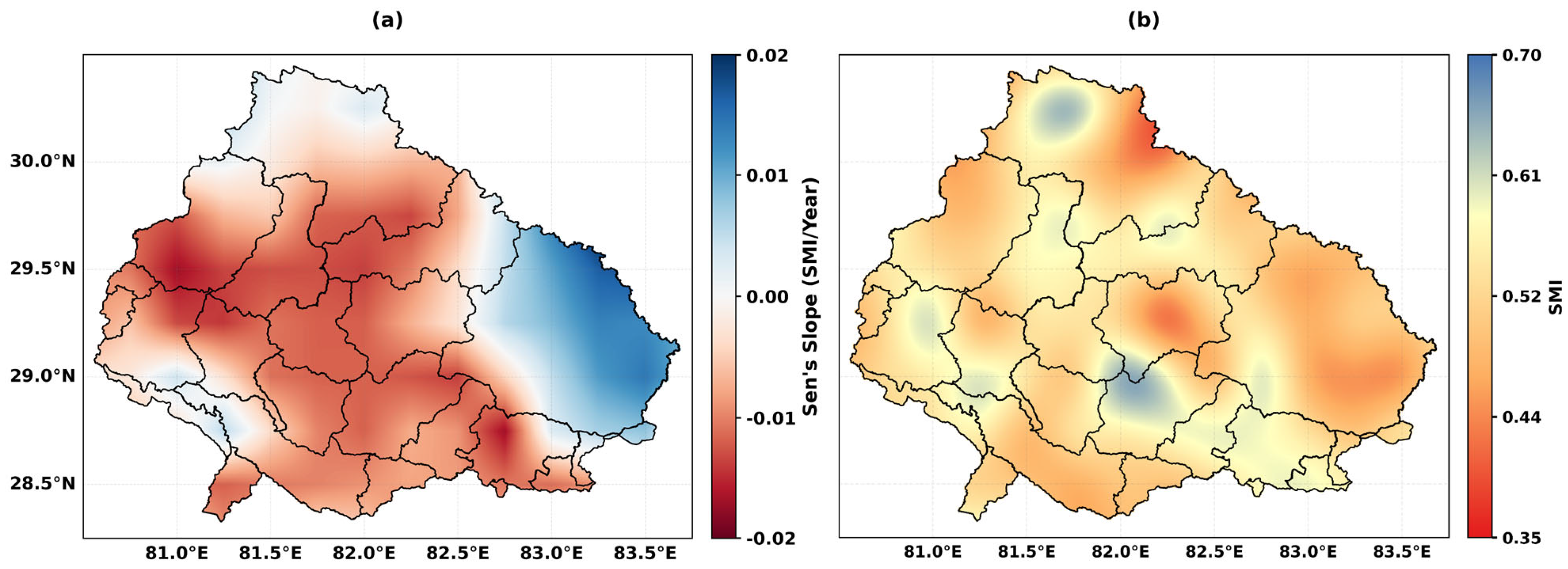
4.1. Long-Term Trends in Drought Indicators
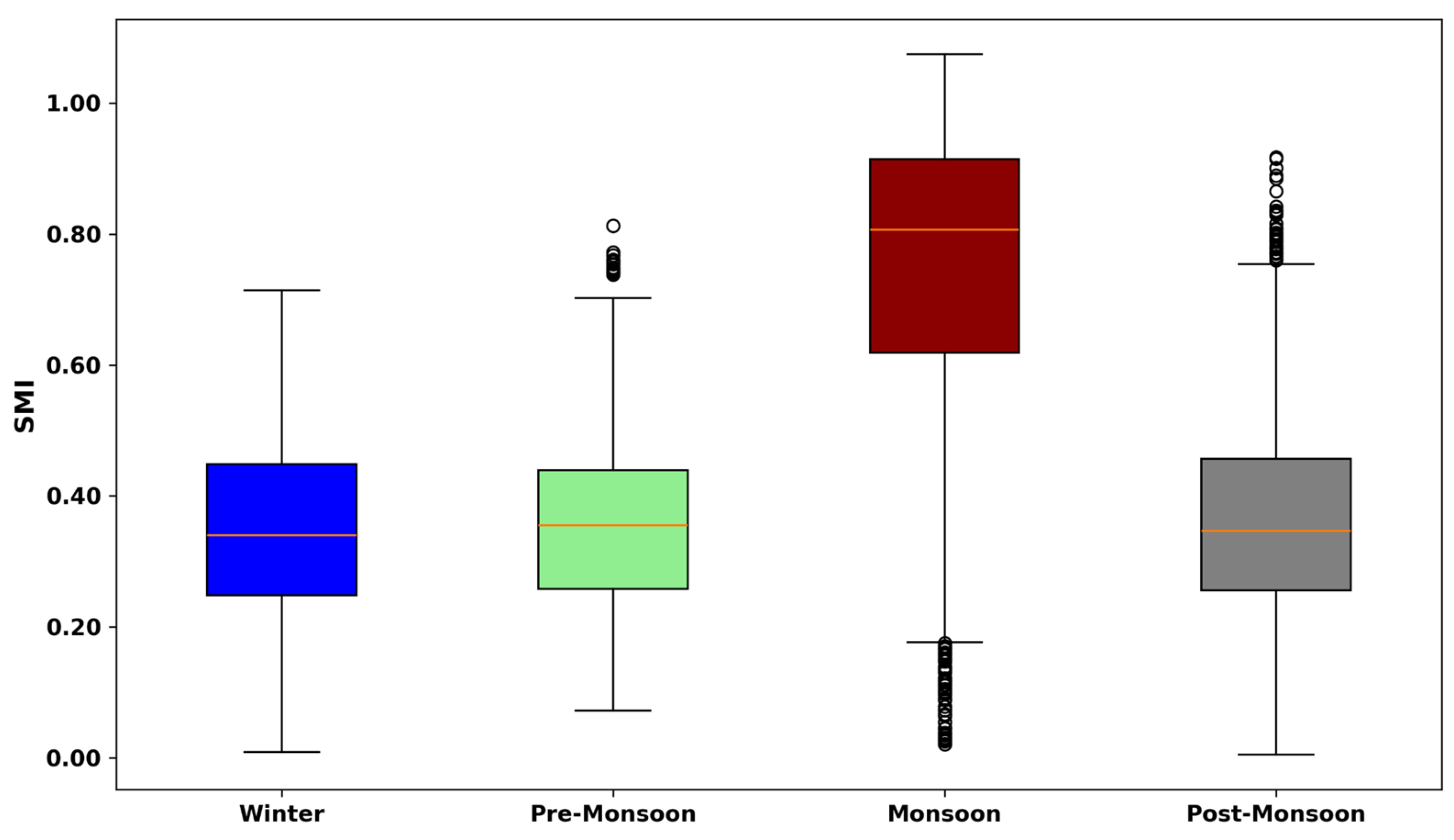
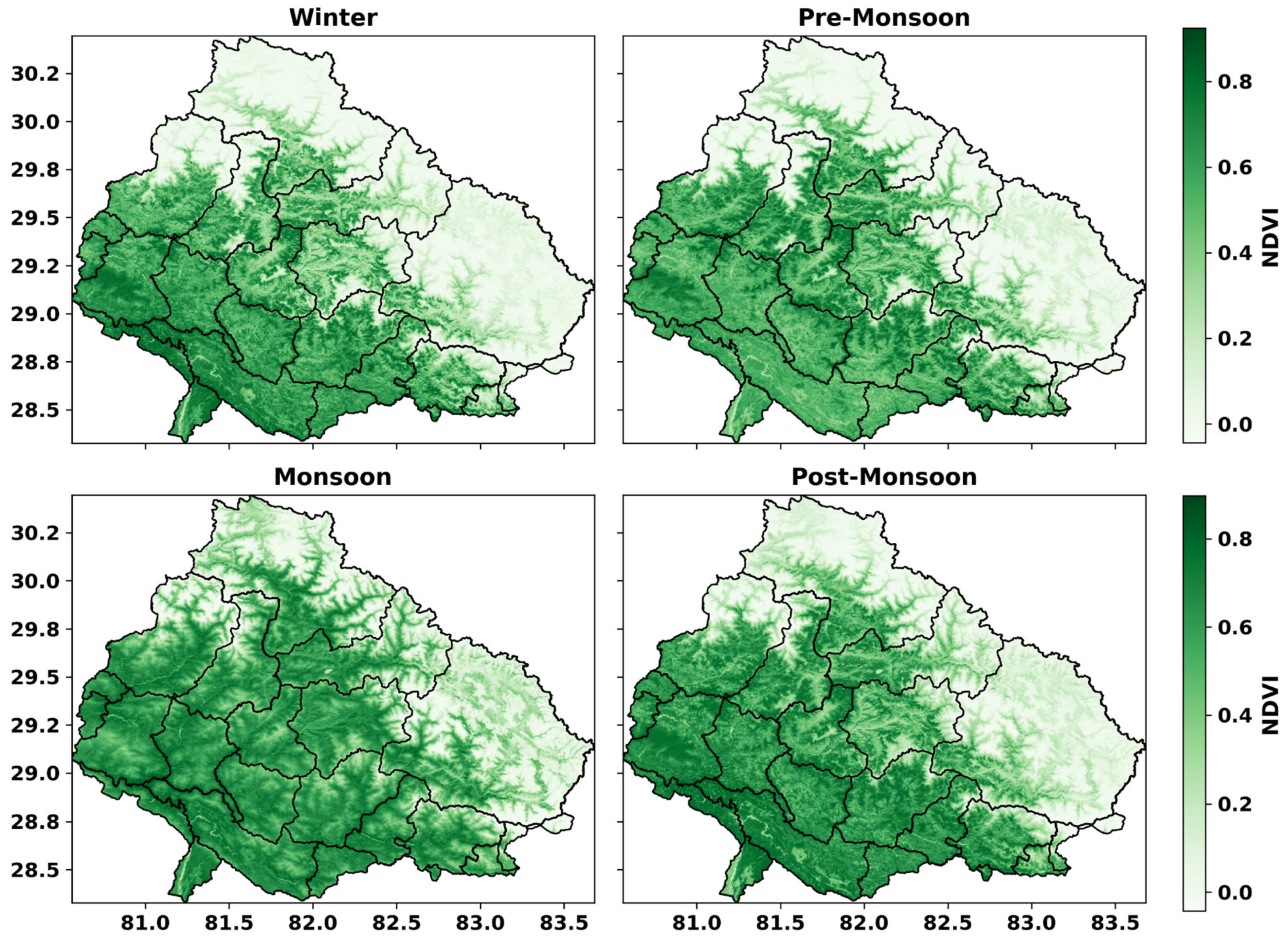
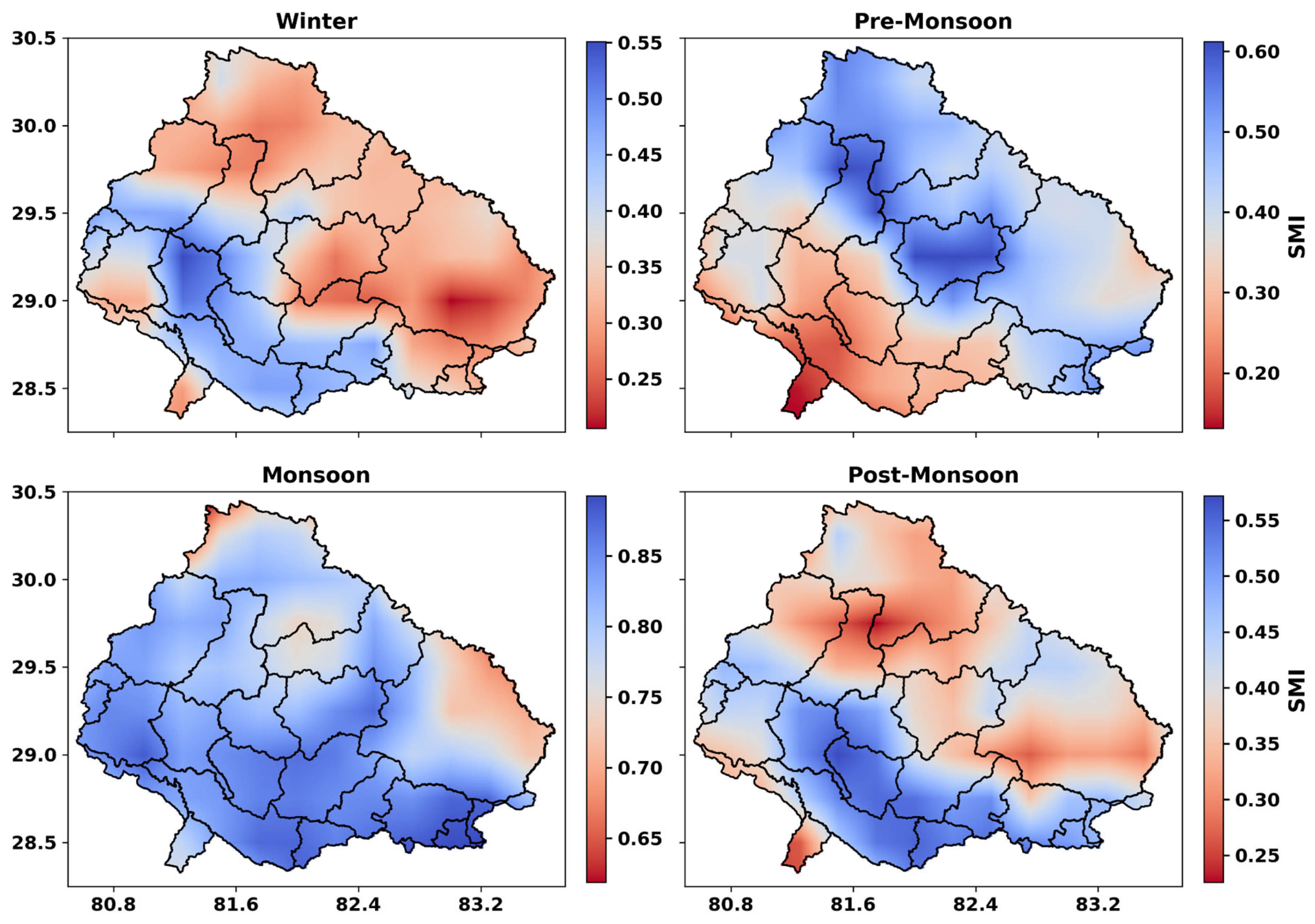
4.2. Seasonal Drought Dynamics
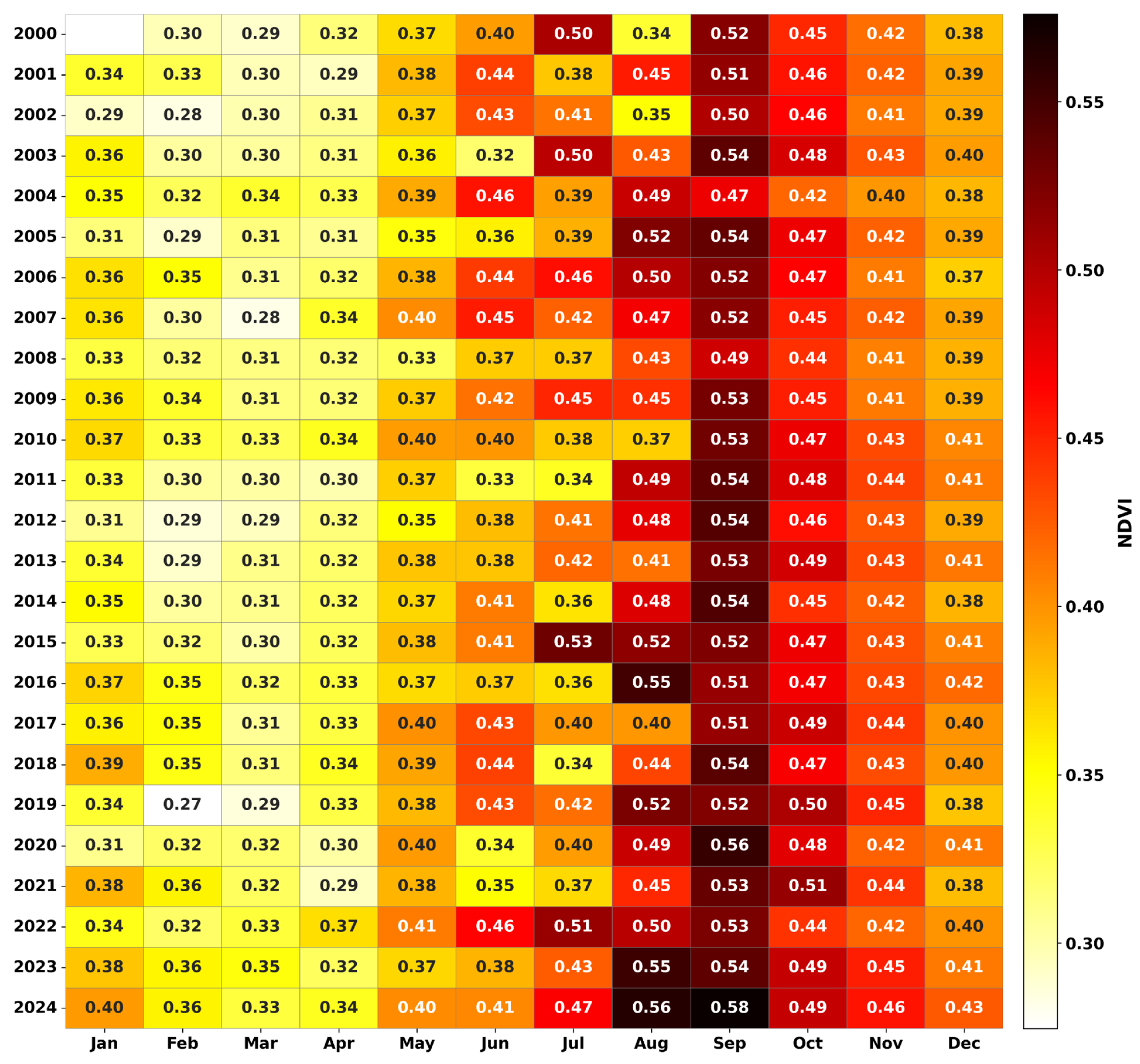
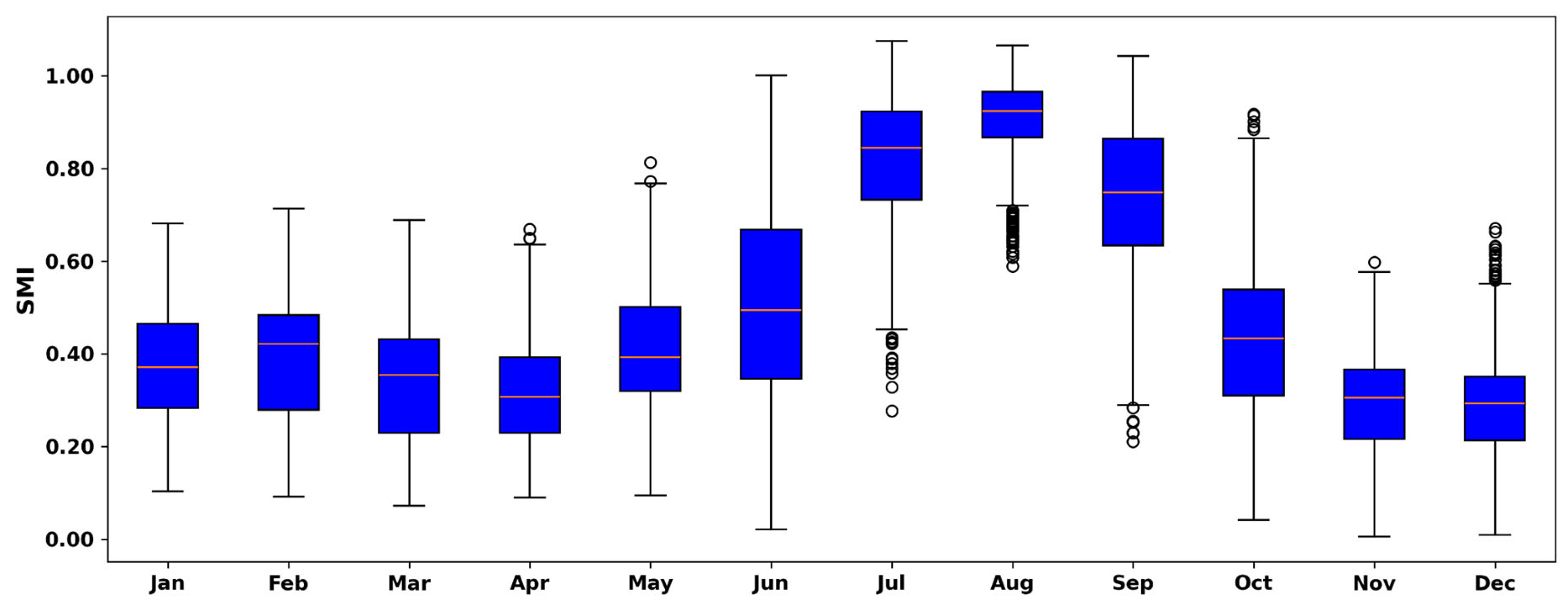
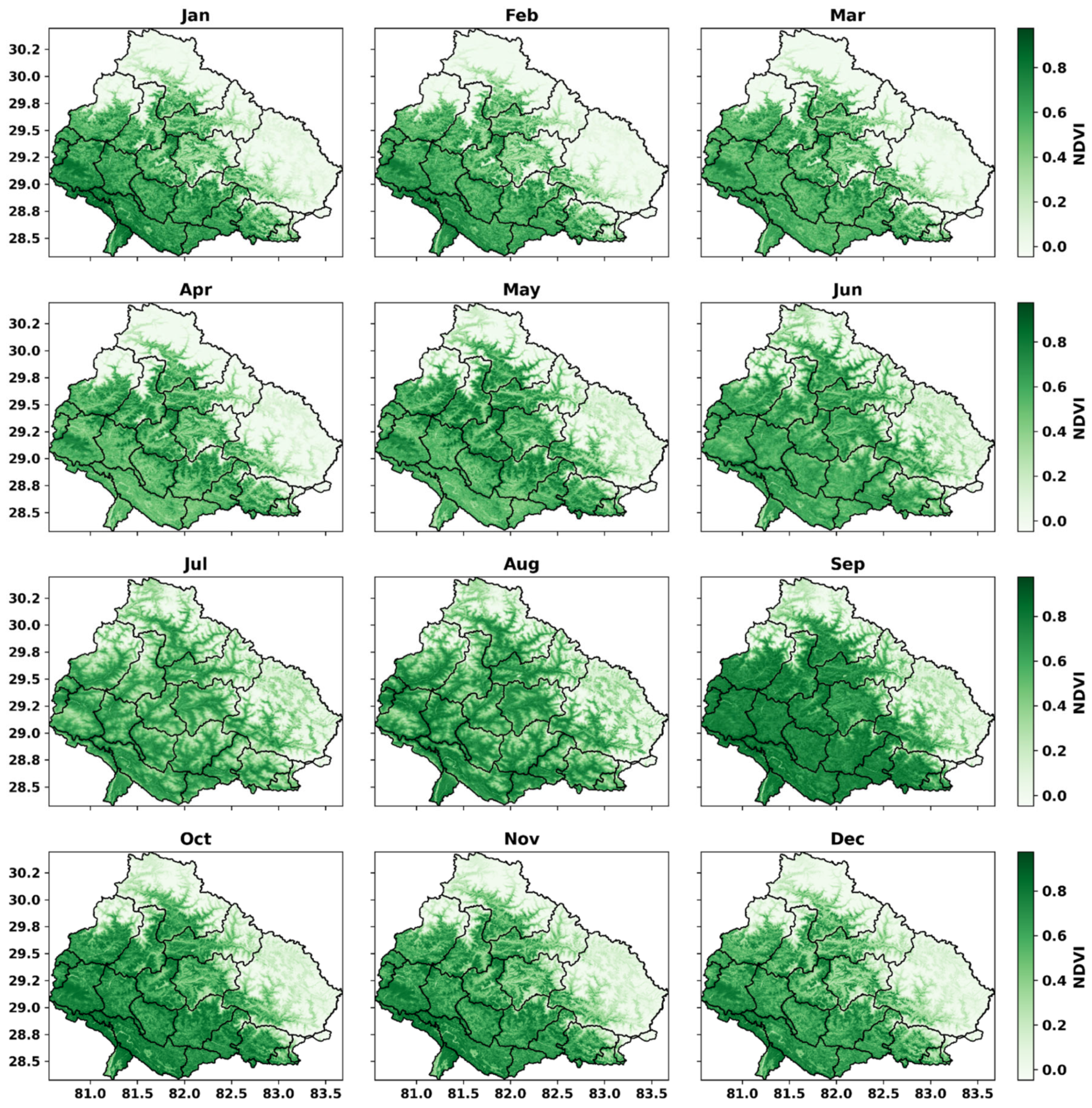
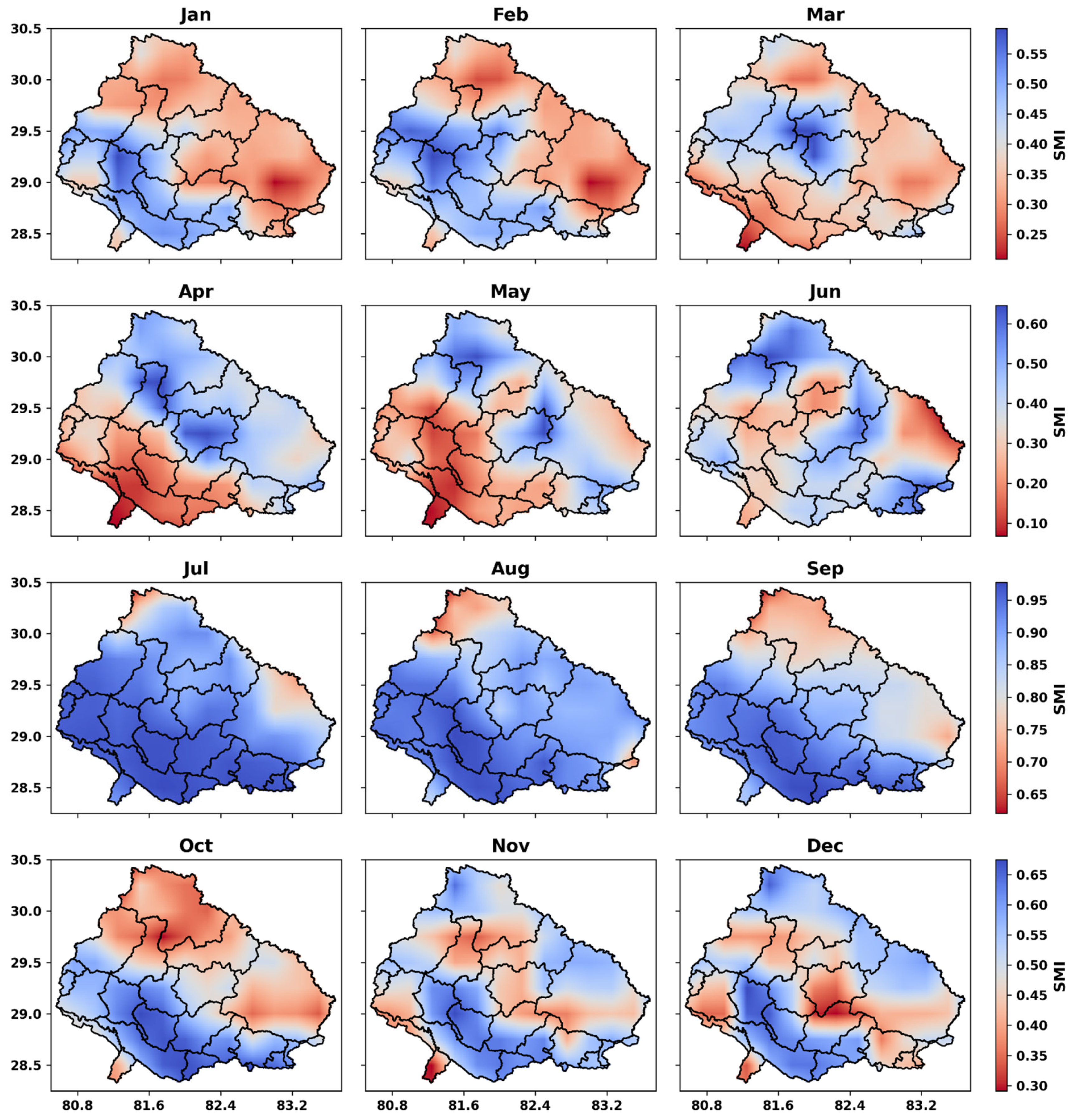
4.3. Monthly Drought Variability
4.4. Spatial Patterns of Drought
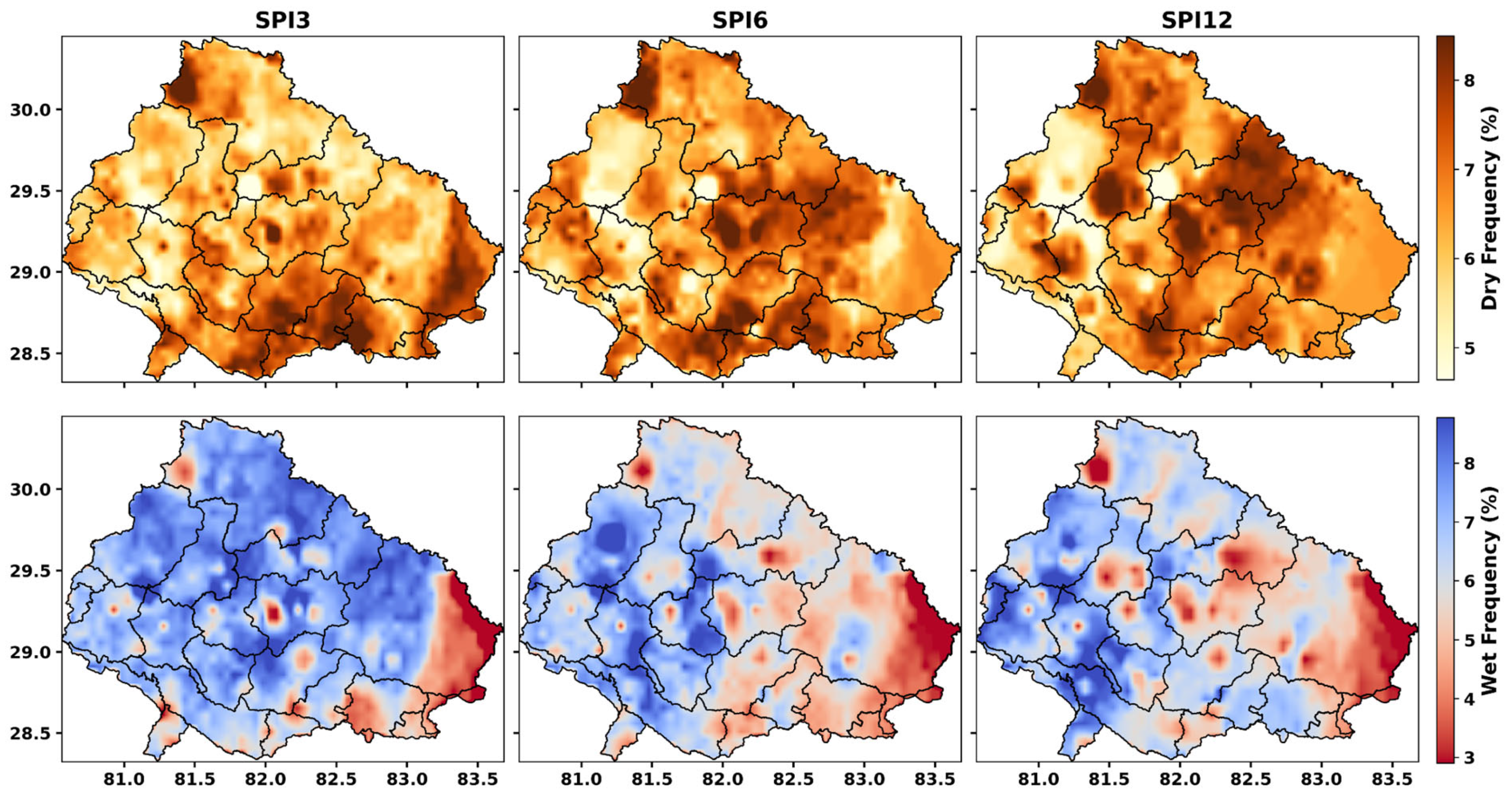
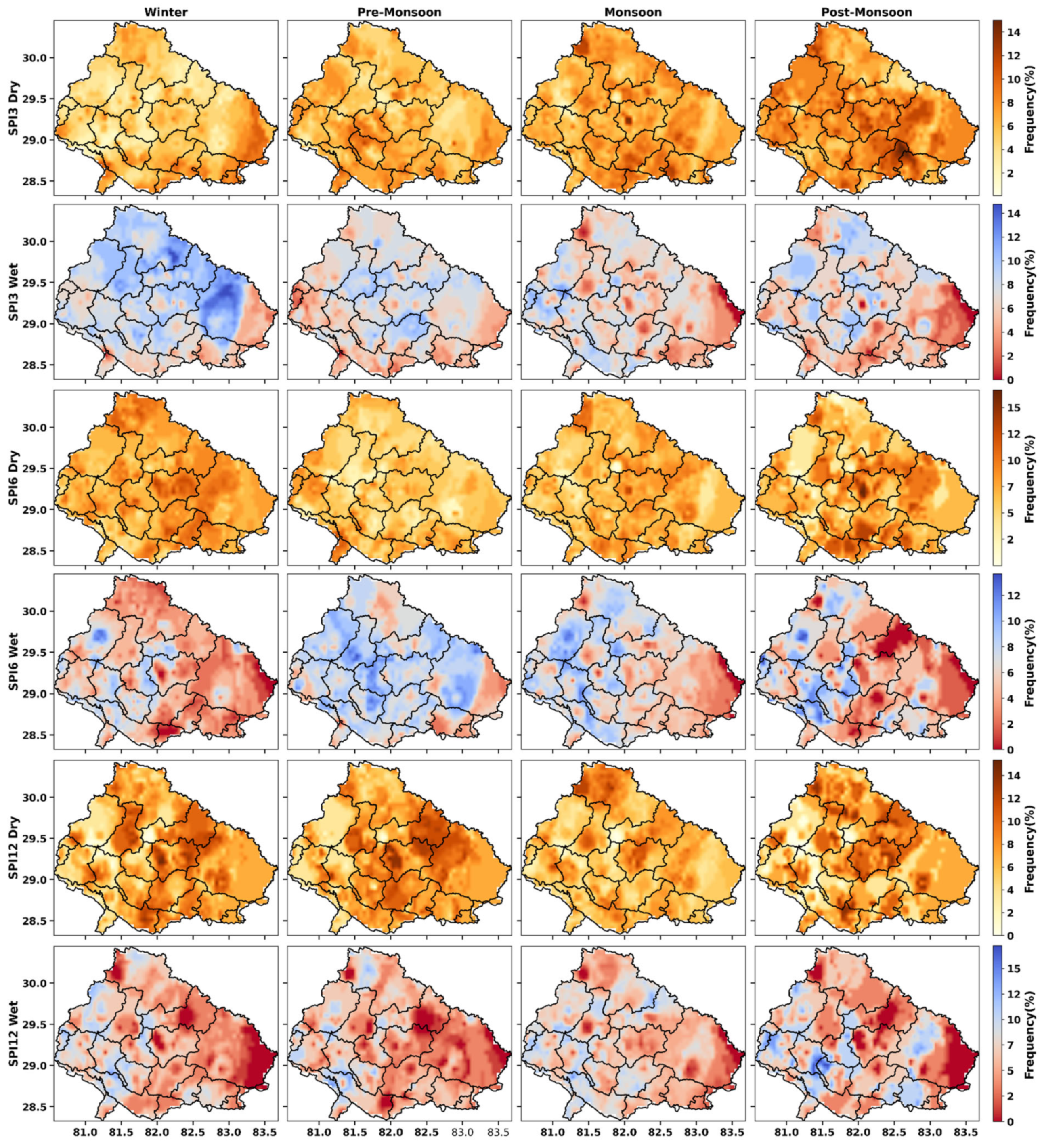
4.5. Categorical Classification of Drought
4.6. Meteorological and Agricultural Composites
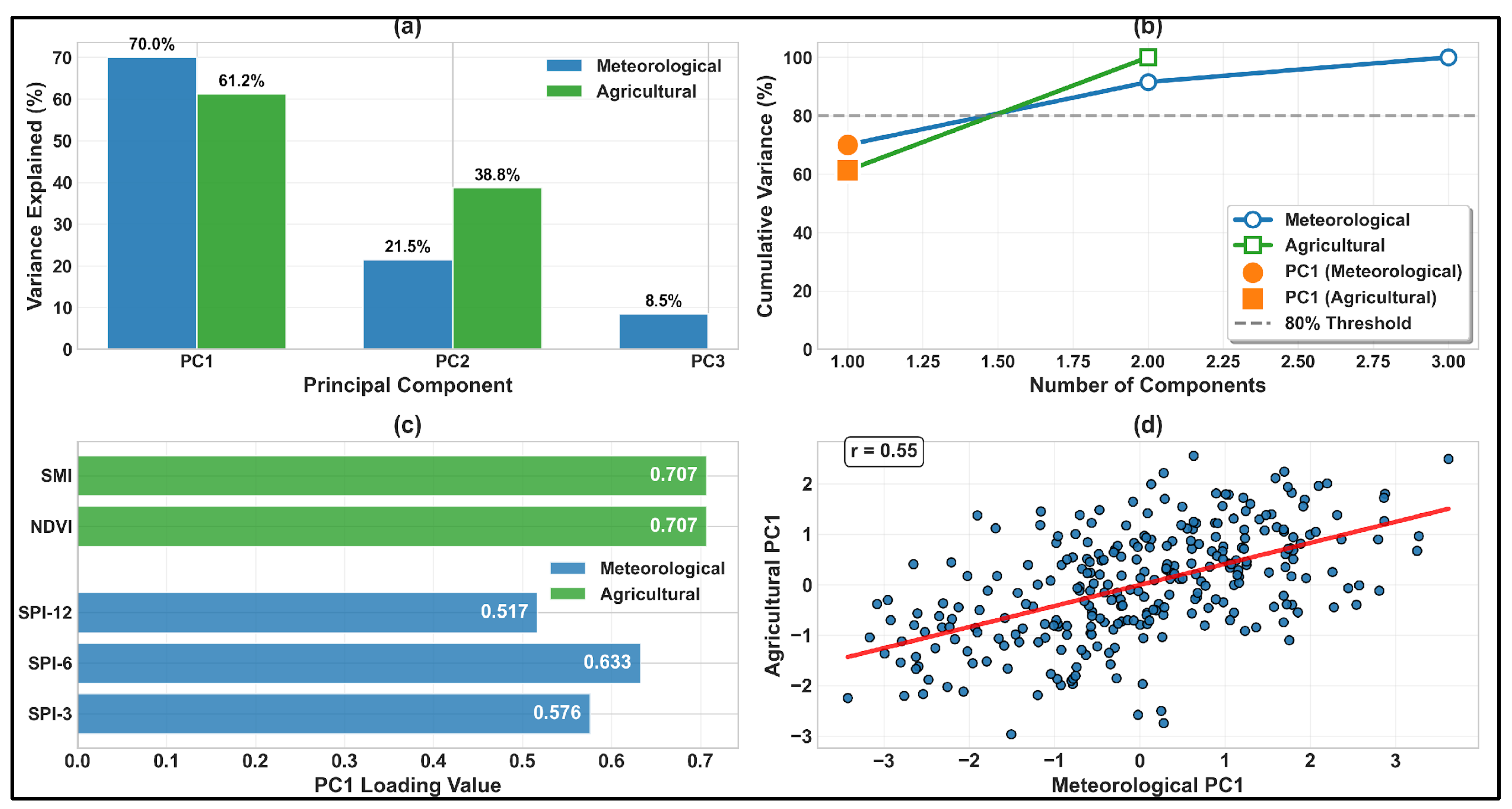
4.6.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
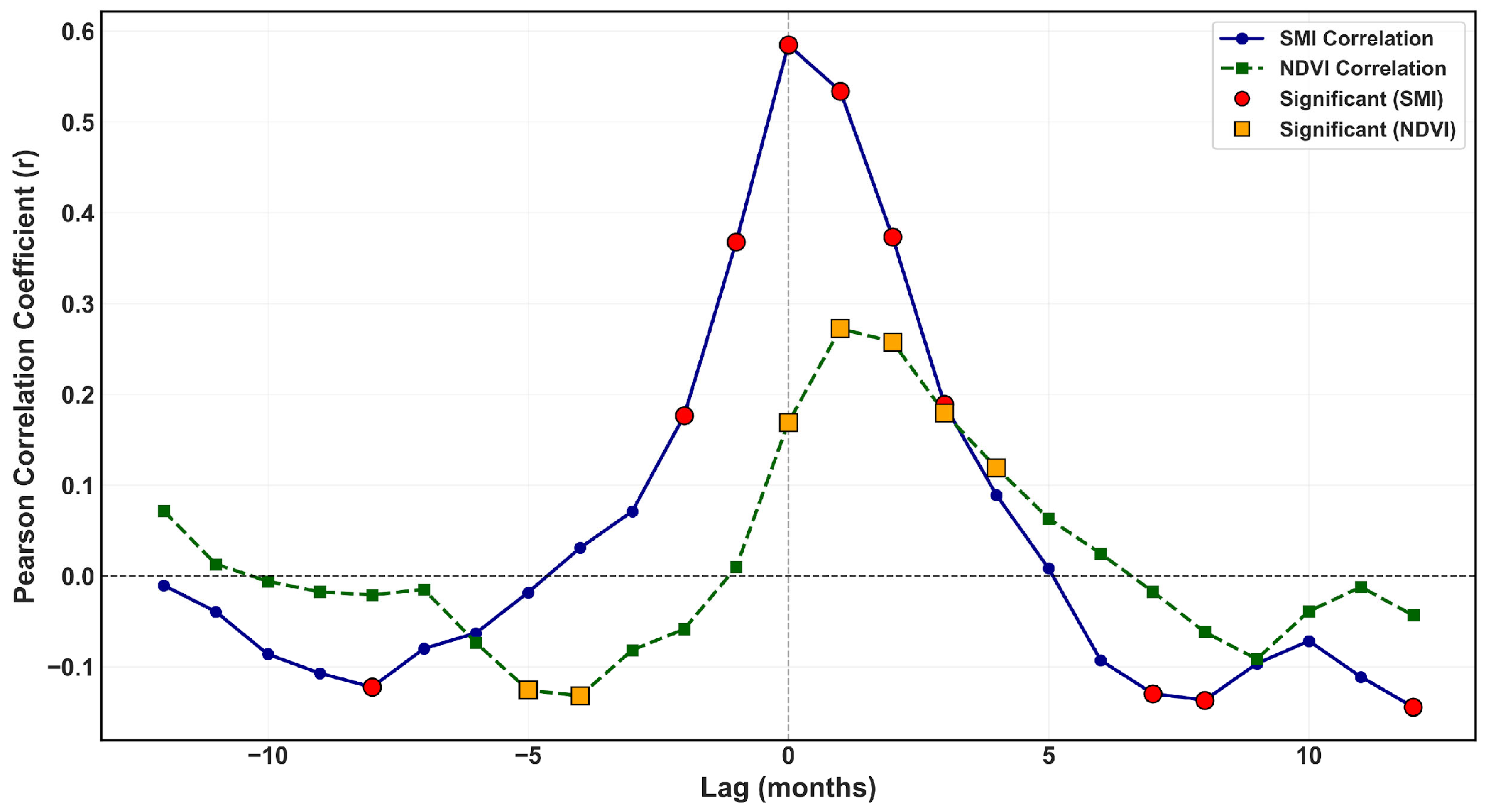
4.6.2. Lag Analysis
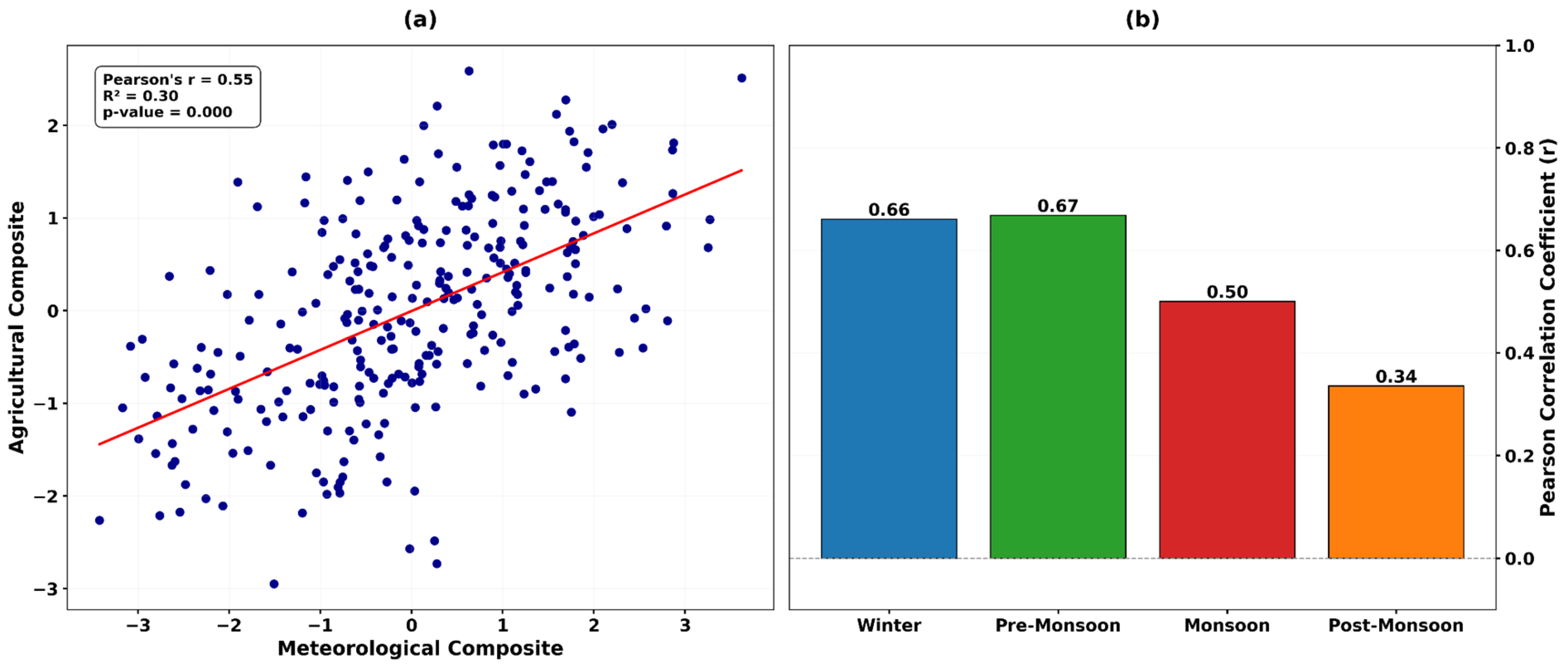
4.6.3. The Composite Correlation
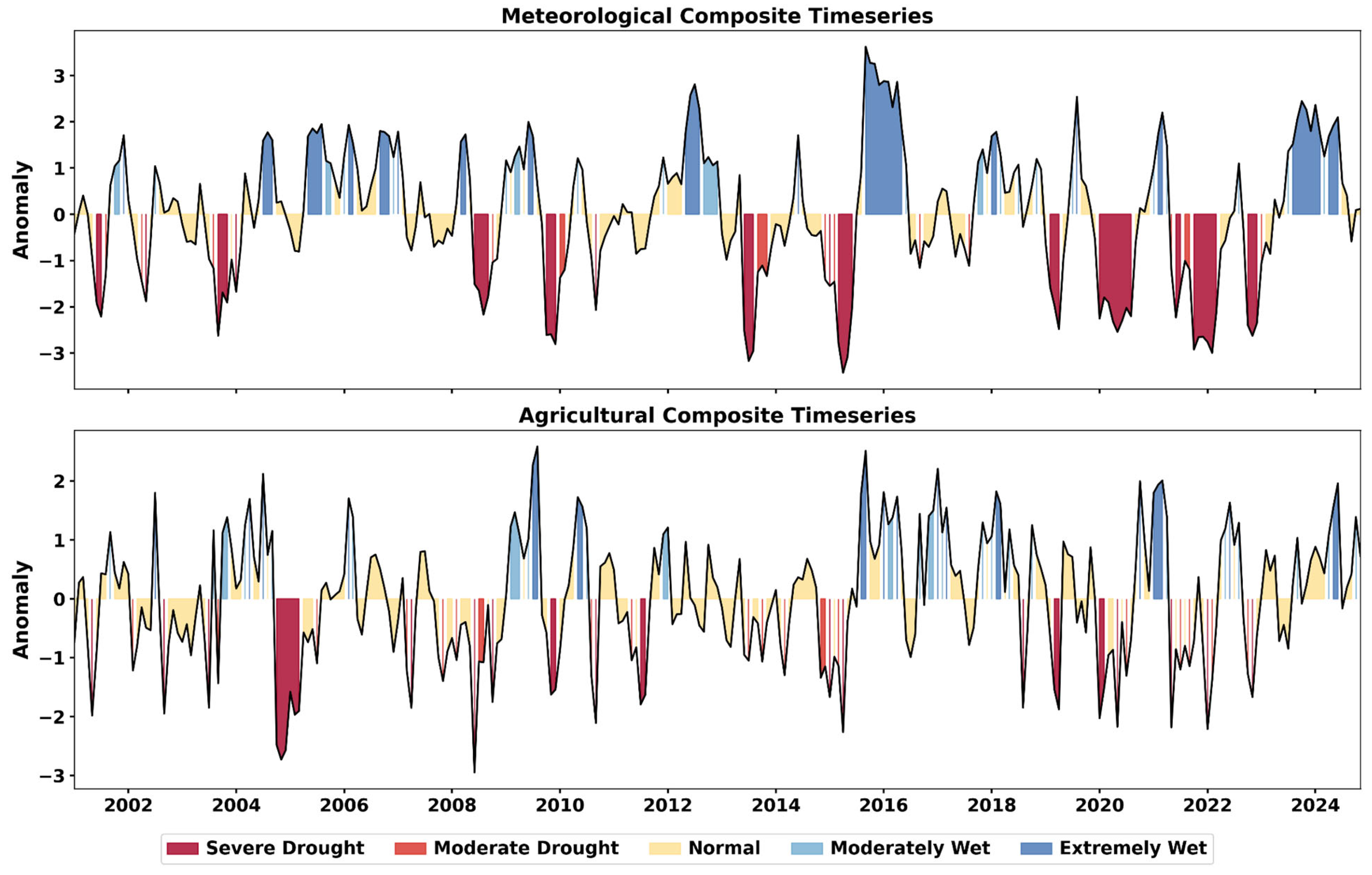
4.6.4. Time Series and Categorical Comparison
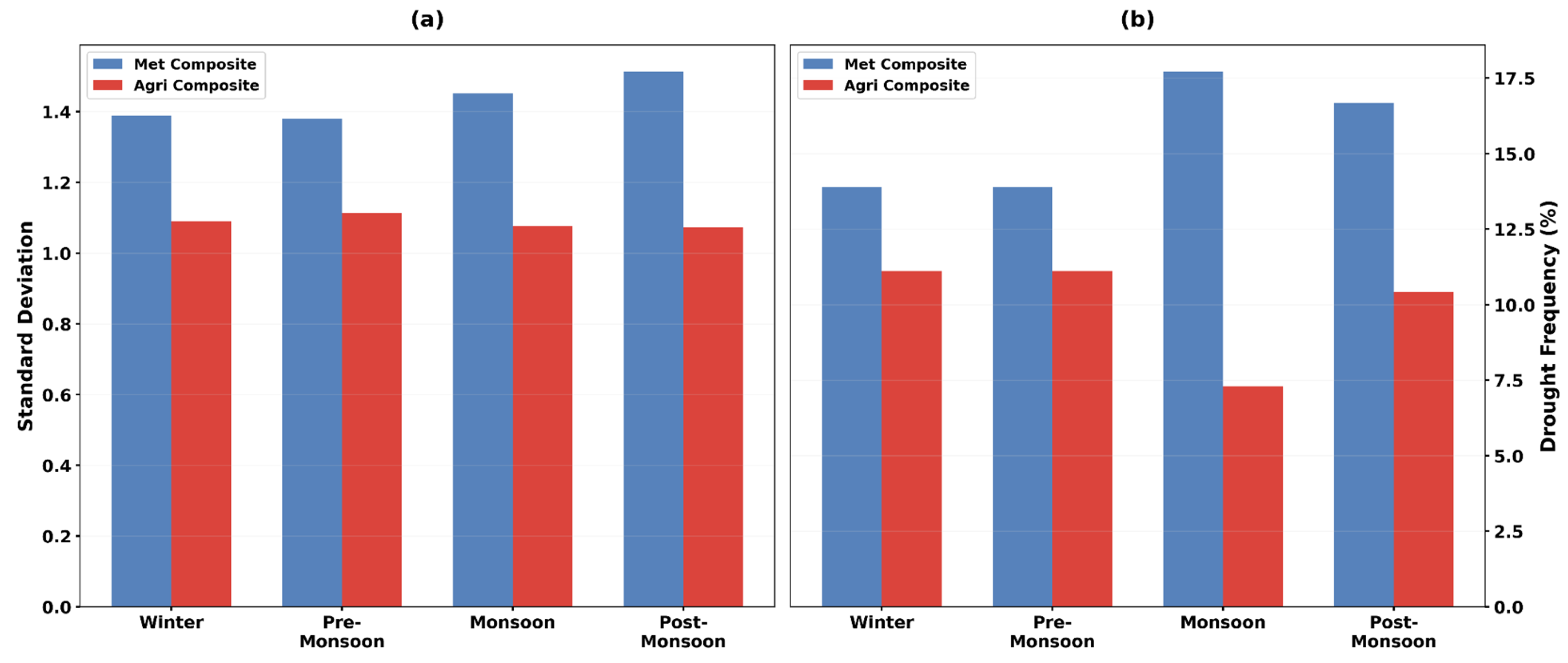
4.6.5. Seasonal Variability & Drought Frequency
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.; Pulwarty, R.S. Drought and Water Crises: Lessons Drawn, Some Lessons Learned, and the Road Ahead. In Drought and Water Crises; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC AR6 Synthesis Report: Climate Change 2023—IPCC. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/sixth-assessment-report-cycle/ (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Wilhite, D.A.; Glantz, M.H. Understanding: The Drought Phenomenon: The Role of Definitions. Water Int. 1985, 10, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Hasson, S.U.; Schickhoff, U.; Scholten, T.; Böhner, J. Rising Precipitation Extremes across Nepal. Climate 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ma, X.; Yin, J.; Omer, A.; Habtemicheal, B.A.; Saleem, F.; Iyakaremye, V.; Syed, S.; Arshad, M.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal characteristics of meteorological drought variability and trends (1981–2020) over South Asia and the associated large-scale circulation patterns. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 2261–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potopová, V.; Boroneanţ, C.; Boincean, B.; Soukup, J. Impact of agricultural drought on main crop yields in the Republic of Moldova. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2063–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, N.M.; Xiong, D.; Neupane, N.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, Y.; Deng, W. Spatiotemporal assessment of drought and its impacts on crop yield in the Koshi River Basin, Nepal. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2024, 155, 1679–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Below, R.; Grover-Kopec, E.; Dilley, M. Documenting Drought-Related Disasters: A Global Reassessment. J. Environ. Dev. 2007, 16, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.; Svoboda, M.; Hayes, M. Understanding the Complex Impacts of Drought: A Key to Enhancing Drought Mitigation and Preparedness. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, M.; Ikeda, M. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Drought in Nepal using Standardized Precipitation Index and its Relationship with Climate Indices. J. Hydrol. Meteorol. 2010, 7, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthi, J.; Dahal, P.; Shrestha, M.L.; Aryal, S.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Lakhankar, T.; Jha, A.K.; Sharma, M.; Karki, R. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Rainfall in the Gandaki River Basin of Nepal Himalaya. Climate 2015, 3, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniya, B.; Tang, Q.; Xu, X.; Haile, G.G. Chhipi-Shrestha Spatial and Temporal Variation of Drought Based on Satellite Derived Vegetation Condition Index in Nepal from 1982–2015. Sensors 2019, 19, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, V.P.; Sharma, A.; Dhaubanjar, S.; Bharati, L.; Joshi, I.R. Climate Shocks and Responses in Karnali-Mahakali Basins, Western Nepal. Climate 2019, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatiwada, K.R.; Panthi, J.; Shrestha, M.L.; Nepal, S. Hydro-Climatic Variability in the Karnali River Basin of Nepal Himalaya. Climate 2016, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthi, B.B. Analysis of Agricultural Drought and its Effects on Productivity at Different District of Nepal. J. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2014, 19, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastakoti, R.C.; Bharati, L.; Bhattarai, U.; Wahid, S.M. Agriculture under changing climate conditions and adaptation options in the Koshi Basin. Clim. Dev. 2017, 9, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, B.; Zhang, L.; Rijal, S. Crop Cycles and Crop Land Classification in Nepal Using MODIS NDVI. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 1, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchiola, D.; Brunetti, L.; Soncini, A.; Polinelli, F.; Gianinetto, M. Impact of climate change on agricultural productivity and food security in the Himalayas: A case study in Nepal. Agric. Syst. 2019, 171, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, B.; Maharjan, N.; Dotel, J. Drought assessment on barley and millet production in Karnali Province, Nepal. Nepal J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, N.; Mahat, D.; Manandhar, S.; Regmi, B.; Panday, U.S.; Karki, S. Analyzing Trend and Pattern of Agricultural Drought: A Case Study of Karnali and Sudurpashchim Provinces. J. Geoinform. Nepal 2021, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagale, D.; Sigdel, M.; Aryal, D. Drought Monitoring over Nepal for the Last Four Decades and Its Connection with Southern Oscillation Index. Water 2021, 13, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, P.; Shrestha, N.S.; Shrestha, M.L.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Panthi, J.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Jha, A.; Lakhankar, T. Drought risk assessment in central Nepal: Temporal and spatial analysis. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1913–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatiwada, K.R.; Pandey, V.P. Characterization of hydro-meteorological drought in Nepal Himalaya: A case of Karnali River Basin. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2019, 26, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamal, K.; Sharma, S.; Khadka, N.; Haile, G.G.; Joshi, B.B.; Xu, T.; Dawadi, B. Assessment of drought impacts on crop yields across Nepal during 1987–2017. Meteorol. Appl. 2020, 27, e1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, A.; Maharjan, M.; Talchabhadel, R.; Thapa, B.R. Characterizing Meteorological Droughts in Nepal: A Comparative Analysis of Standardized Precipitation Index and Rainfall Anomaly Index. Earth 2022, 3, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Solanki, H.; Sharma, P.J. Dynamic evolution of meteorological and hydrological droughts under climatic and anthropogenic pressures in water-scarce regions. Hydrol. Process. 2024, 38, e15290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahady, A.B.; Klopries, E.-M.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Wolf, S. Drought Analysis Methods: A Multidisciplinary Review with Insights on Key Decision-Making Factors in Method Selection. Water 2025, 17, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.M.; Lupo, A.R.; Hunt, S.; Aloysius, N. Refining Drought Assessment: A Multi-Dimensional Analysis of Condition Monitoring Observer Reports in Missouri (2018–2024). Atmosphere 2025, 16, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A. A multivariate approach for persistence-based drought prediction: Application to the 2010–2011 East Africa drought. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.; Im, J.; Carbone, G.J. Monitoring agricultural drought for arid and humid regions using multi-sensor remote sensing data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2875–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookhagen, B.; Burbank, D.W. Toward a complete Himalayan hydrological budget: Spatiotemporal distribution of snowmelt and rainfall and their impact on river discharge. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.B.; Wake, C.P.; Dibb, J.E.; Mayewski, P.A. Precipitation fluctuations in the Nepal Himalaya and its vicinity and relationship with some large scale climatological parameters. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 20, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayava, J.L.; Adhikary, S.; Bajracharya, O.R. Spatial and temporal variation of surface air temperature at different altitude zone in recent 30 years over Nepal. MAUSAM 2017, 68, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, E.; von Hardenberg, J.; Provenzale, A. Precipitation in the Hindu-Kush Karakoram Himalaya: Observations and future scenarios. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, S.A.; Dyer, J.S. Cubic-Spline Interpolation: Part 1. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2001, 4, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junninen, H.; Niska, H.; Tuppurainen, K.; Ruuskanen, J.; Kolehmainen, M. Methods for imputation of missing values in air quality data sets. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2895–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulhus, J.L.H.; Kohler, M.A. Interpolation of missing precipitation records. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1952, 80, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, R.P.; Dayawansa, N.D.K.; Ratnasiri, M.D. A comparison of methods used in estimating missing rainfall data. J. Agric. Sci.–Sri Lanka 2007, 3, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G. Missing data filling method based on linear interpolation and lightgbm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1754, 012187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, R.; Nielson, G. Smooth interpolation of large sets of scattered data. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1980, 15, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, Y.-K. Point Rainfall Estimation for a Mountainous Region. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1983, 109, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.G.; Younes, K.; Esmaeil, A.; Fatemeh, T. Assessment of Geostatistical Methods for Spatial Analysis of SPI and EDI Drought Indices. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 15, 474–482. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.K.; Desai, V.R. Spatial and temporal drought analysis in the Kansabati river basin, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2005, 3, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didan, K. MODIS/Terra Vegetation Indices 16-Day L3 Global 250m SIN Grid V061. NASA Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center. Earth Science Data Systems, NASA. 2021. Available online: https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/data/catalog/lpcloud-mod13q1-061 (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Zhang, H.; Chang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. NDVI dynamic changes and their relationship with meteorological factors and soil moisture. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, E.C.; Ramesh, K.V.; Hari, S. Quantification and understanding the observed changes in land cover patterns in Bangalore. International. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2017, 8, 597–603. [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Lakhankar, T.; Anadón, J.D. Mapping and Attributing Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Trends for Nepal. Remote. Sens. 2017, 9, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniya, B.; Tang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Sun, S.; Techato, K. Spatial and Temporal Variation of NDVI in Response to Climate Change and the Implication for Carbon Dynamics in Nepal. Forests 2018, 9, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhan, G.; Hill, S.; Tadesse, T.; Atnafu, S. Using Satellite Images for Drought Monitoring: A Knowledge Discovery Approach. J. Strateg. Innov. Sustain. 2011, 7, 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, A.; Umar, M.; Mansha, M.; Khan, M.S.; Javed, M.N.; Gao, H.; Bin Farhan, S.; Iqbal, I.; Abdullah, S. Assessment of drought conditions using HJ-1A/1B data: A case study of Potohar region, Pakistan. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 1019–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference, Applied Climatology, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, W.; Lemoine, G.; Rott, H. A Method for Estimating Soil Moisture from ERS Scatterometer and Soil Data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, S.; Korres, W.; Reichenau, T.G.; Schneider, K. Soil moisture index from ERS-SAR and its application to the analysis of spatial patterns in agricultural areas. J. Appl. Remote. Sens. 2018, 12, 022206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenacre, M.; Groenen, P.J.F.; Hastie, T.; D’Enza, A.I.; Markos, A.; Tuzhilina, E. Principal component analysis. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2022, 2, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demšar, U.; Harris, P.; Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; McLoone, S. Principal Component Analysis on Spatial Data: An Overview. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2013, 103, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Yoon, J.-H.; Gillies, R.R.; Cho, C. What Caused the Winter Drought in Western Nepal during Recent Years? J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8241–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, P.; Shrestha, M.L.; Panthi, J.; Pradhananga, D. Modeling the future impacts of climate change on water availability in the Karnali River Basin of Nepal Himalaya. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamal, K.; Sharma, S.; Pokharel, B.; Shrestha, D.; Talchabhadel, R.; Shrestha, A.; Khadka, N. Changing pattern of drought in Nepal and associated atmospheric circulation. Atmos. Res. 2021, 262, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Hamal, K.; Khadka, N. Drought characteristics over Nepal Himalaya and their relationship with climatic indices. Meteorol. Appl. 2021, 28, e1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods. 1948. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Rank%20correlation%20methods&publication_year=1975&author=Kendall%2CM (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Yue, S.; Wang, C. The Mann-Kendall Test Modified by Effective Sample Size to Detect Trend in Serially Correlated Hydrological Series. Water Resour. Manag. 2004, 18, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, N.M.; Xiong, D.; Neupane, N.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, Y.; Deng, W. Estimating and analyzing the spatiotemporal characteristics of crop yield loss in response to drought in the koshi river basin, Nepal. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2023, 152, 1053–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H.; et al. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Mirchi, A.; Madani, K.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Nazemi, A.; Alborzi, A.; Anjileli, H.; Azarderakhsh, M.; Chiang, F.; Hassanzadeh, E.; et al. Anthropogenic Drought: Definition, Challenges, and Opportunities. Rev. Geophys. 2021, 59, e2019RG000683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Piao, S.; Knapp, A.K.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Yuan, W.; Running, S.; Mao, J.; Shi, X.; Ciais, P.; et al. Decoupling of greenness and gross primary productivity as aridity decreases. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2022, 279, 113120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, Y.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J. Drought risks are projected to increase in the future in central and southern regions of the Middle East. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, J.; Pei, X.; Yang, H. Decoupling the response of vegetation dynamics to asymmetric warming over the Qinghai-Tibet plateau from 2001 to 2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Tramblay, Y.; Reig, F.; González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Beguería, S.; Brunetti, M.; Kalin, K.C.; Patalen, L.; Kržič, A.; Lionello, P.; et al. High temporal variability not trend dominates Mediterranean precipitation. Nature 2025, 639, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andujar, E.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Yi, C.; Kogan, F. Ecosystem Drought Response Timescales from Thermal Emission versus Shortwave Remote Sensing. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 8434020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheater, H.S.; Pomeroy, J.W.; Pietroniro, A.; Davison, B.; Elshamy, M.; Yassin, F.; Rokaya, P.; Fayad, A.; Tesemma, Z.; Princz, D.; et al. Advances in modelling large river basins in cold regions with Modélisation Environmentale Communautaire—Surface and Hydrology (MESH), the Canadian hydrological land surface scheme. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Ding, H.; Wu, M.; Shi, M.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. A comprehensive drought monitoring method integrating multi-source data. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

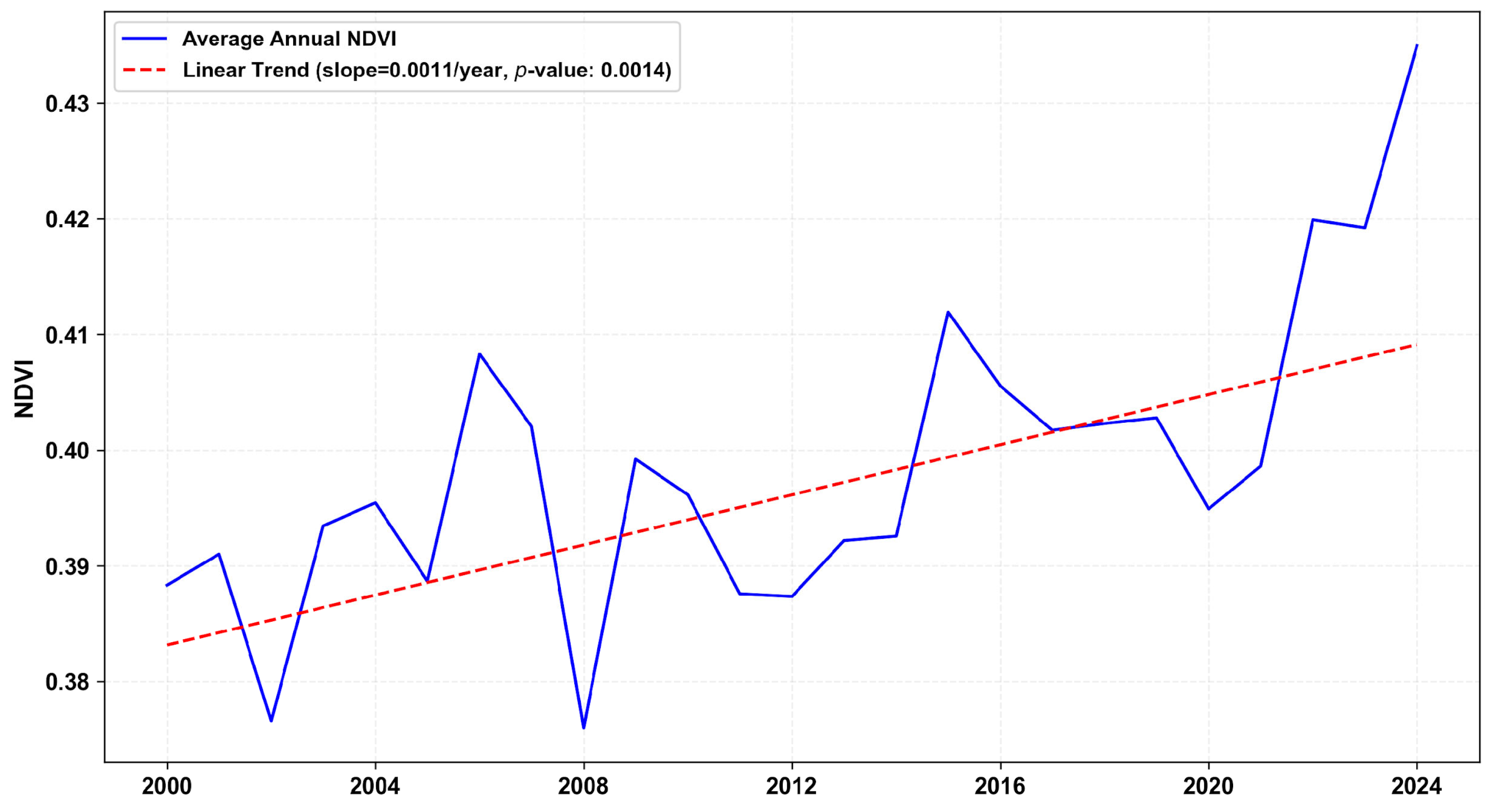
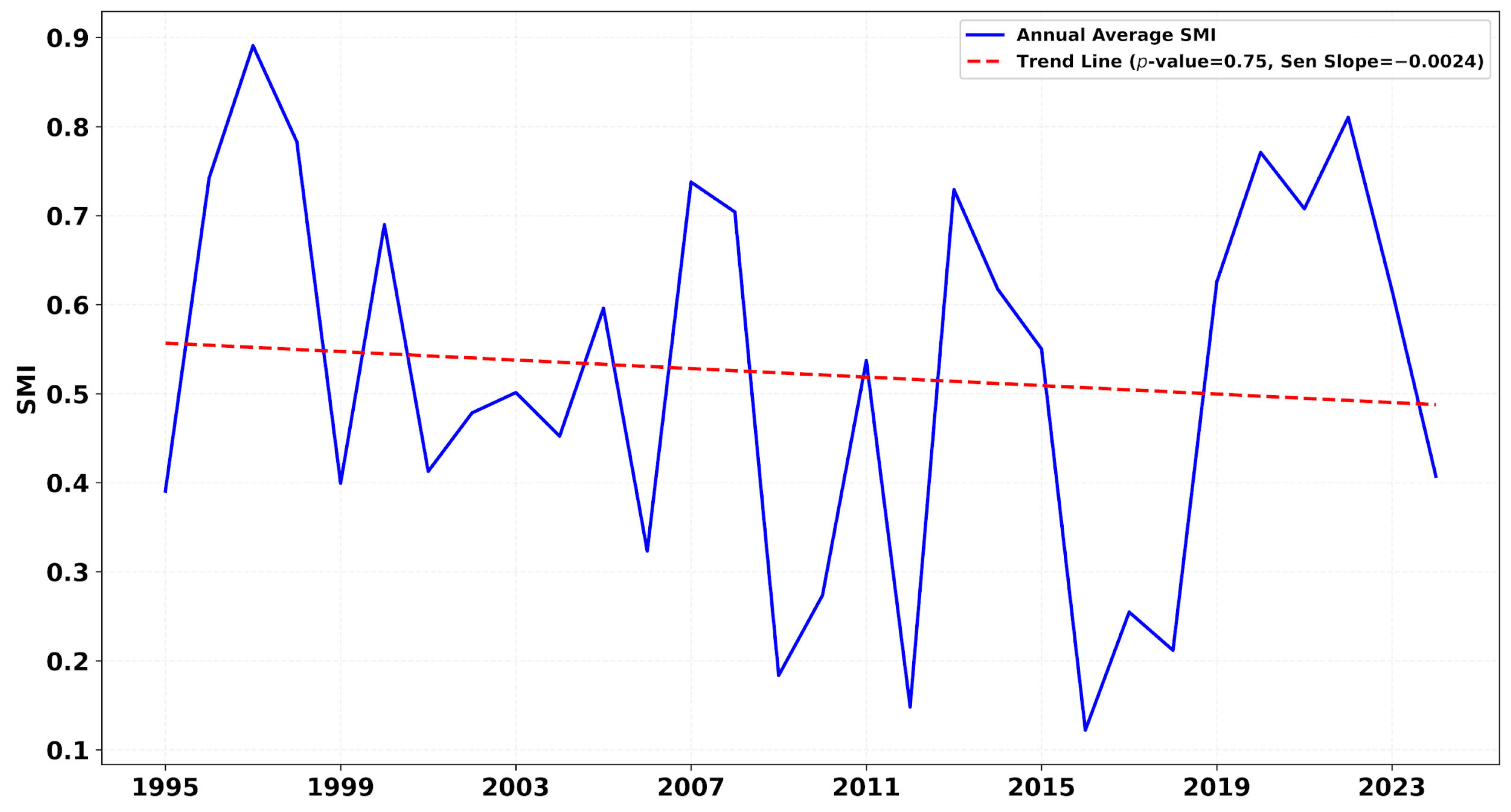
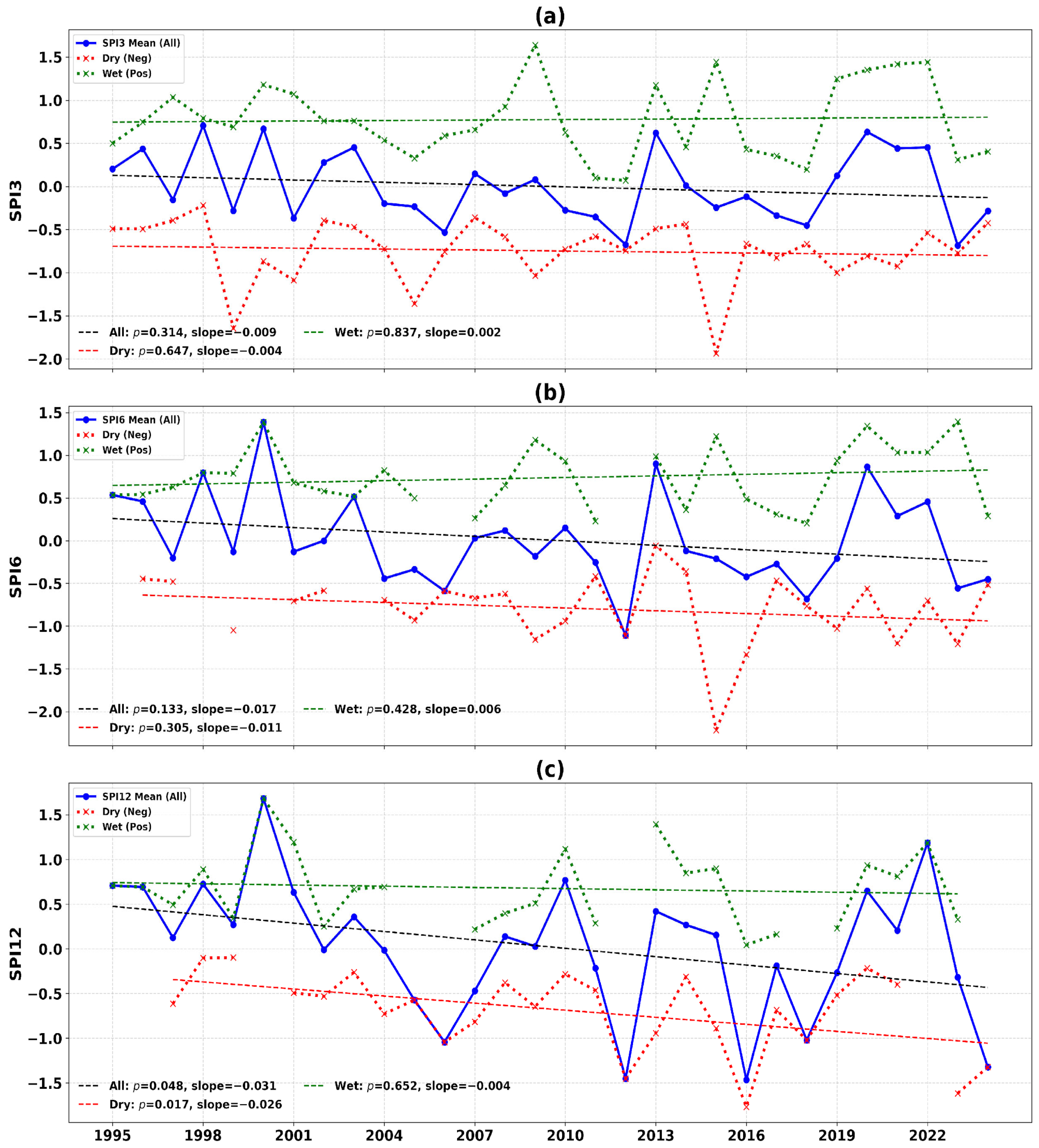
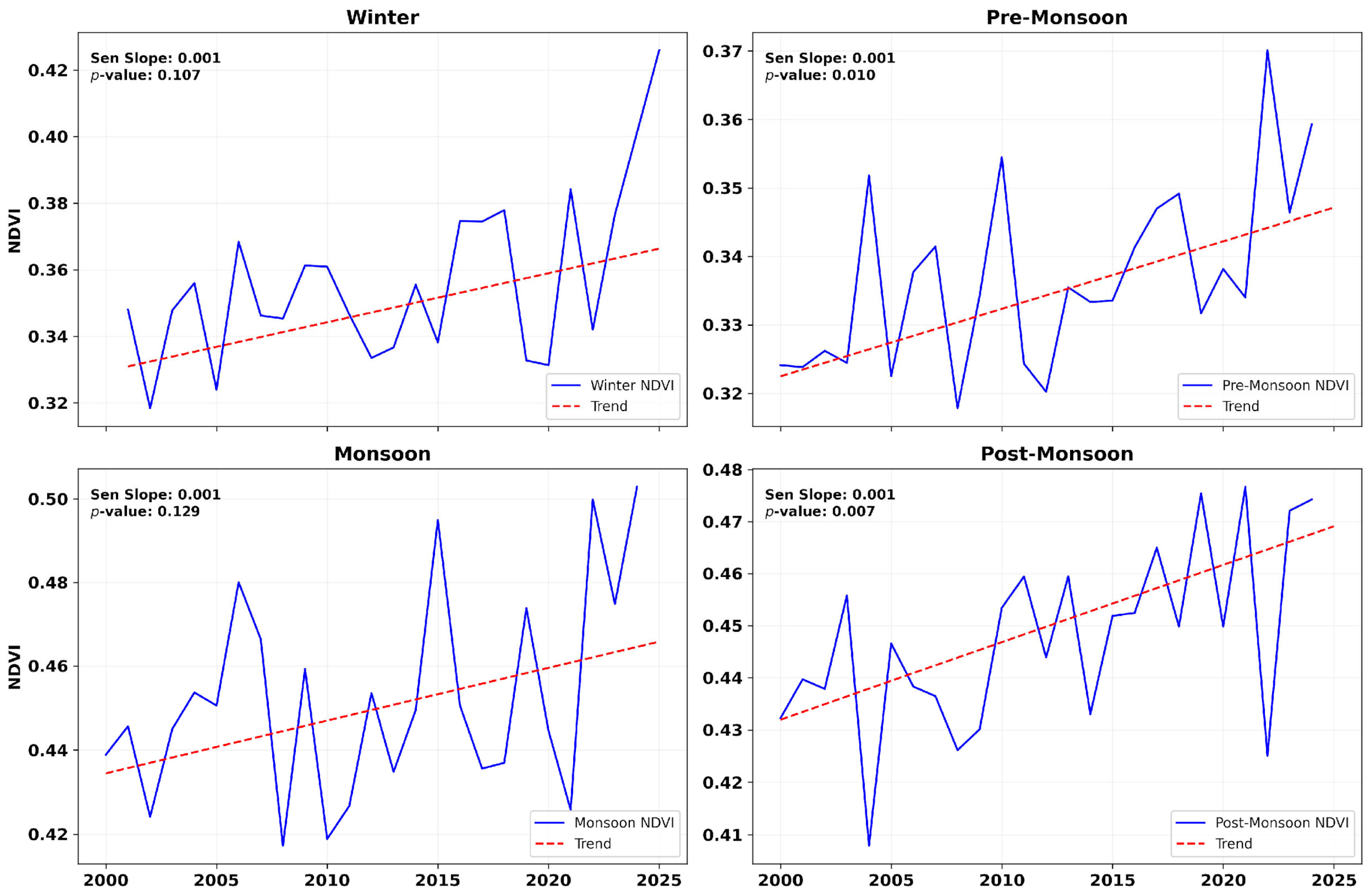
| Z Score Range | Drought Category |
|---|---|
| >0 | No drought |
| 0 to −0.99 | Mild drought |
| −1.00 to −1.49 | Moderate drought |
| −1.50 to −1.99 | Severe drought |
| ≤−2.00 | Extreme drought |
| Percentile Range | Drought Category |
|---|---|
| >0.40 | No drought |
| 0.20 to 0.40 | Mild drought |
| 0.10 to 0.20 | Moderate drought |
| 0.05 to 0.10 | Severe drought |
| <0.05 | Extreme drought |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aryal, K.; Pradhananga, D.; Aryal, D.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Sigdel, R. Dynamics of Meteorological and Agricultural Drought in the Karnali River Basin, Nepal. Land 2025, 14, 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112271
Aryal K, Pradhananga D, Aryal D, Krakauer NY, Sigdel R. Dynamics of Meteorological and Agricultural Drought in the Karnali River Basin, Nepal. Land. 2025; 14(11):2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112271
Chicago/Turabian StyleAryal, Kumar, Dhiraj Pradhananga, Deepak Aryal, Nir Y. Krakauer, and Rajesh Sigdel. 2025. "Dynamics of Meteorological and Agricultural Drought in the Karnali River Basin, Nepal" Land 14, no. 11: 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112271
APA StyleAryal, K., Pradhananga, D., Aryal, D., Krakauer, N. Y., & Sigdel, R. (2025). Dynamics of Meteorological and Agricultural Drought in the Karnali River Basin, Nepal. Land, 14(11), 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112271








