Ecological Security Pattern Construction Based on Multi-Scenario Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Shiyang River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
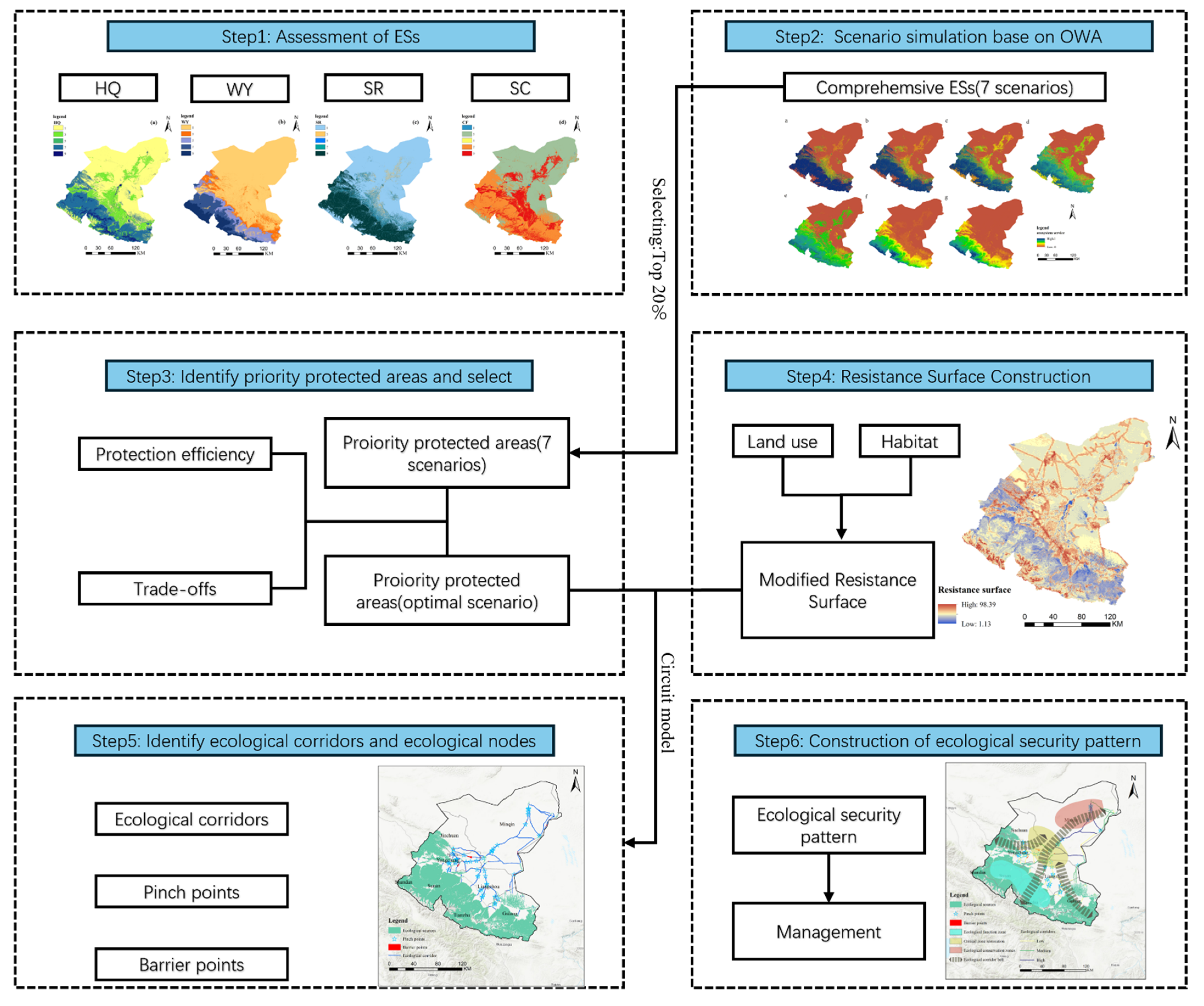
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
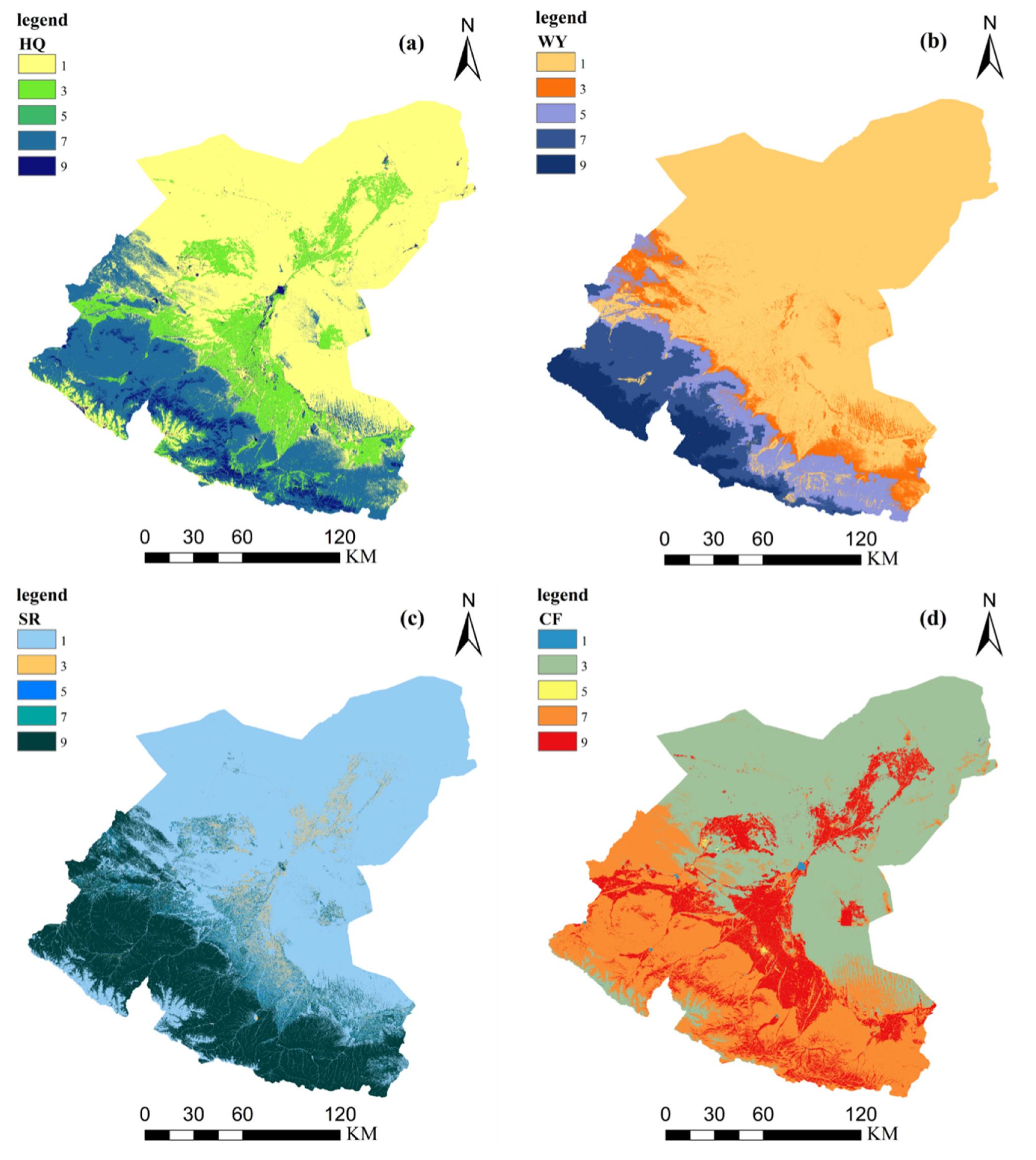
2.3.1. Evaluation of Ecosystem Service Importance
- (1)
- Habitat Quality
- (2)
- Water Yield
- (3)
- Soil Retention
- (4)
- Carbon Sequestration
2.3.2. OWA-Based Priority Area Scenario Simulation
- (1)
- Principle of the OWA Method
- (2)
- Identification Steps for Priority Areas
2.4. Ecological Network Construction
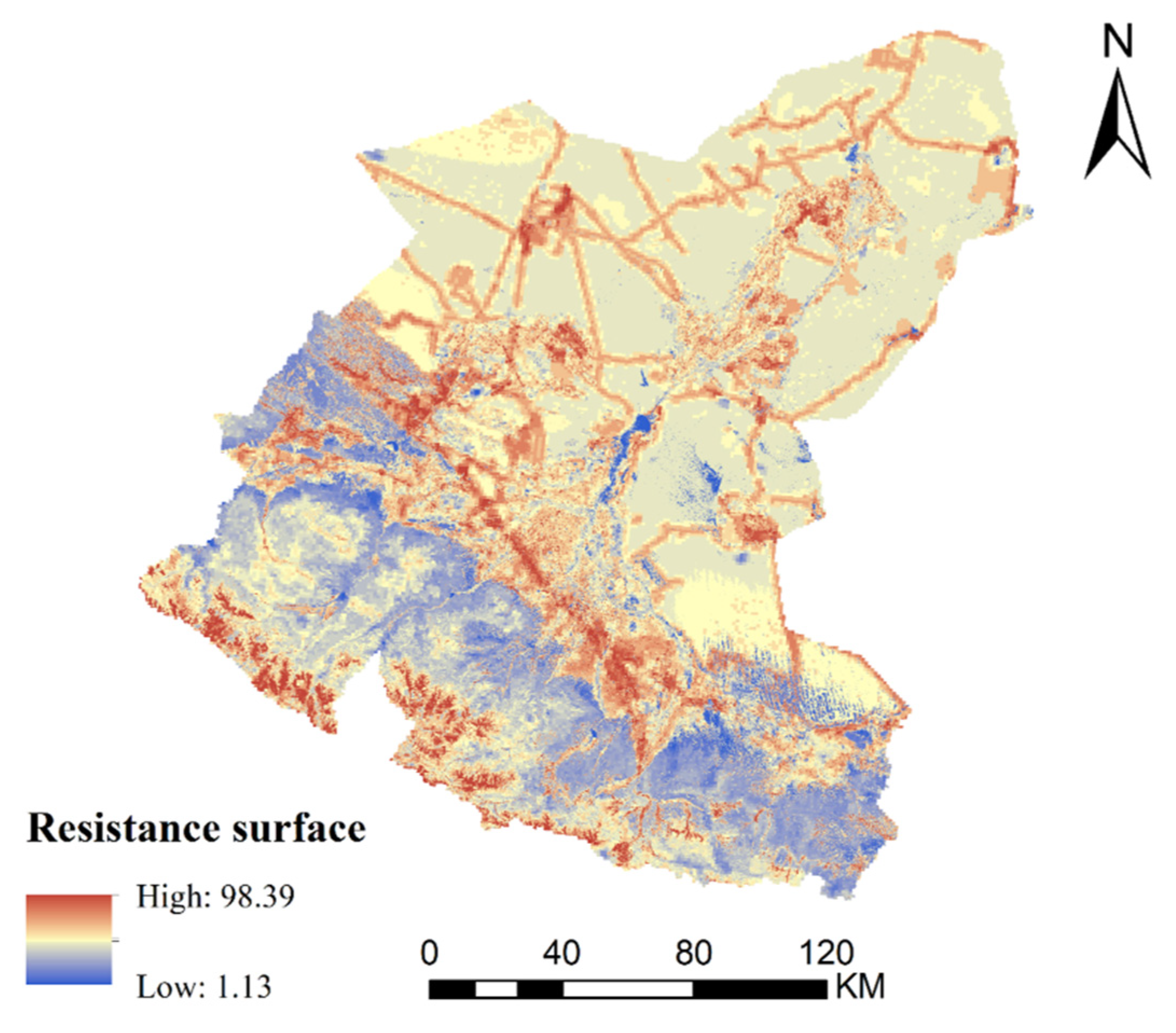
2.4.1. Basic Resistance Surface
2.4.2. Resistance Surface Modification
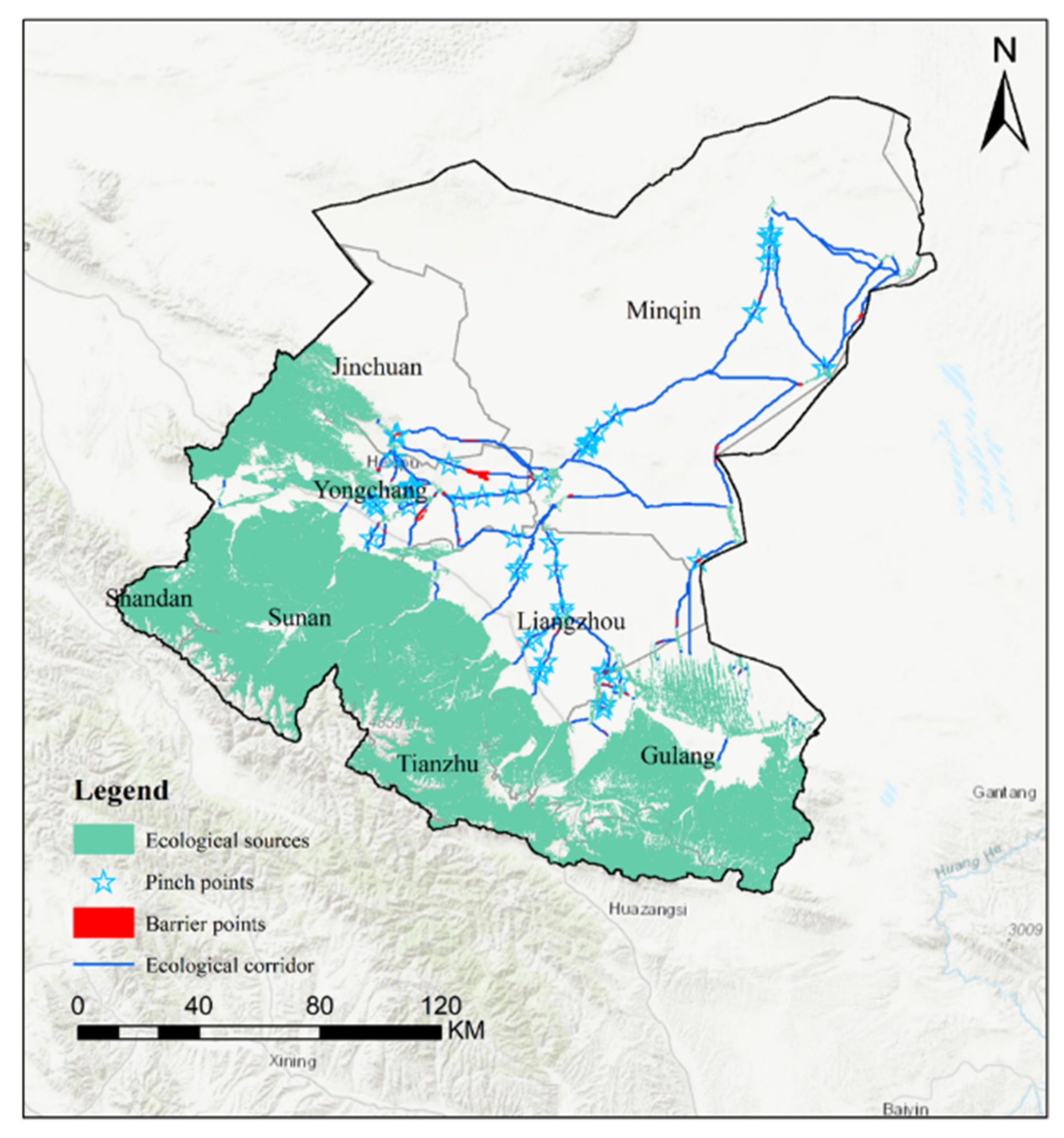
2.4.3. Ecological Corridor Delineation and Key Areas Detection
- (1)
- Ecological Corridor Extraction
- (2)
- Identification of Key Areas Based on the Circuit Model
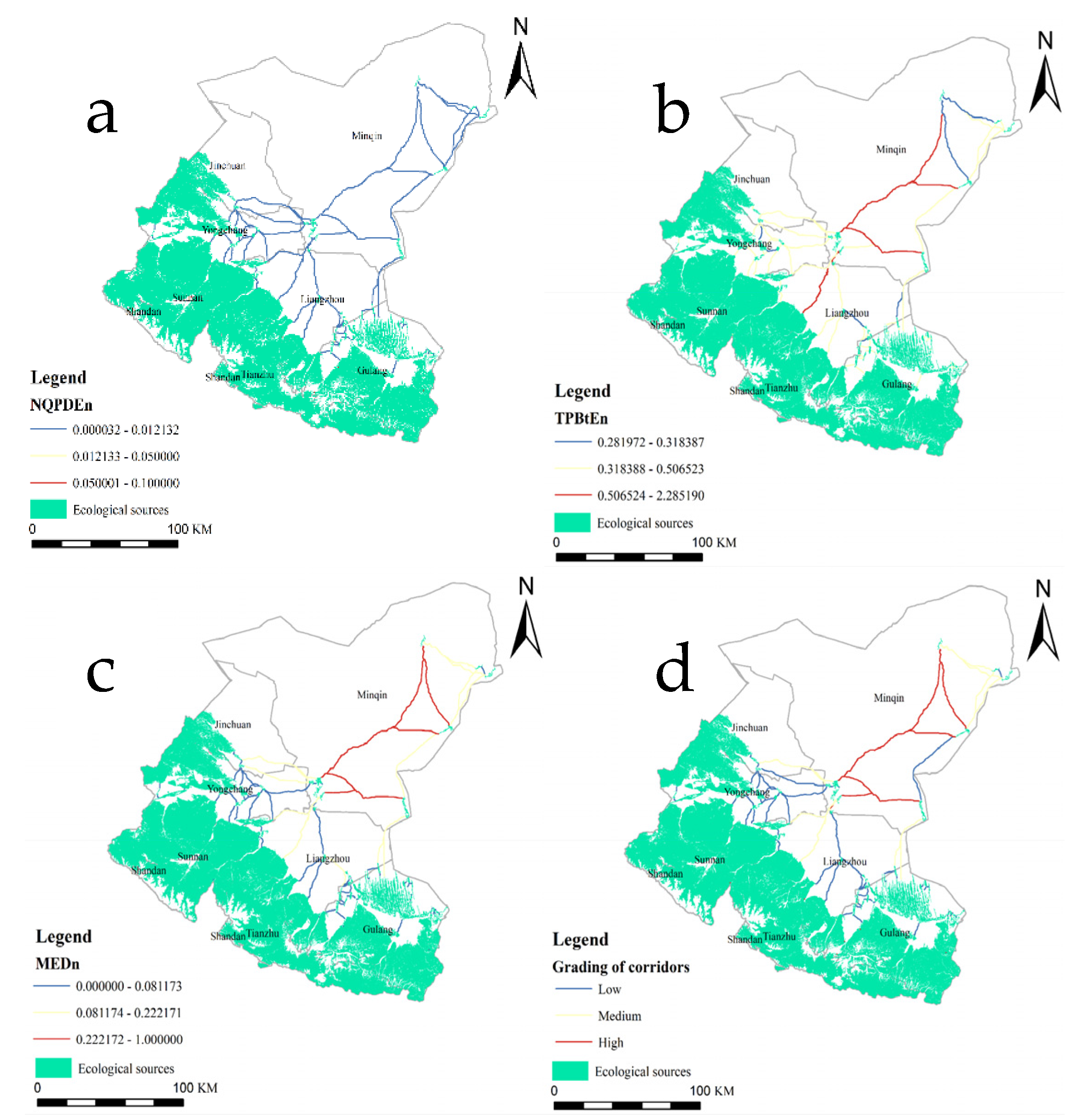
2.4.4. Ecological Network Evaluation Based on Space Syntax
2.4.5. NQPDE
2.4.6. TPBt
2.4.7. MED
3. Results
3.1. Ecosystem Service Assessment and Multi-Scenario Simulation
3.1.1. Spatial Pattern of Ecosystem Services
3.1.2. Priority Area Scenario Simulation Based on OWA
3.1.3. Priority Conservation Areas and Protection Efficiency Under Different Scenarios
3.2. ESP Construction
3.2.1. Ecological Source
3.2.2. Resistance Surface Construction
3.2.3. Identification of Ecological Corridors
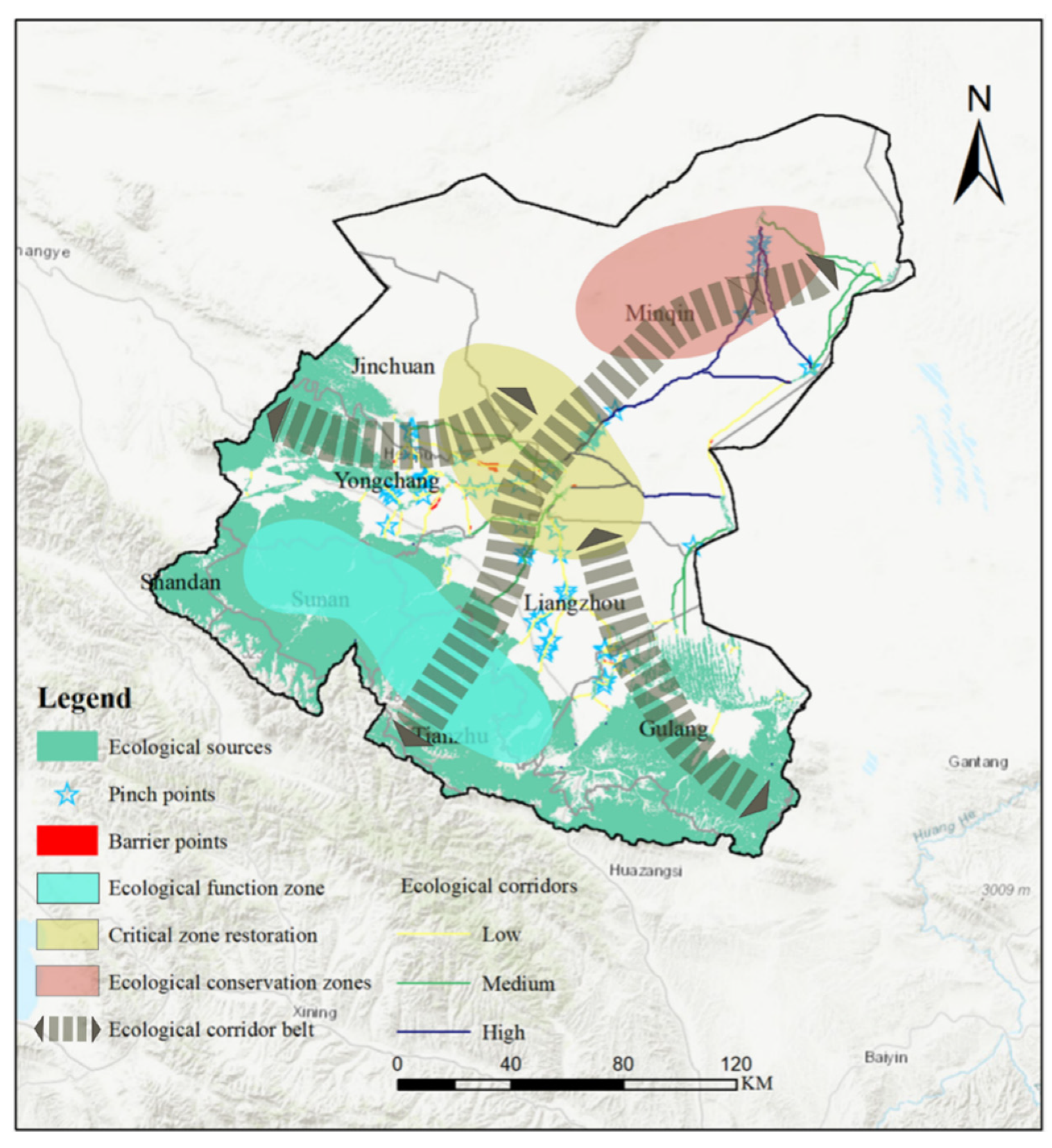
3.2.4. Identification of Critical Areas
3.2.5. Spatial Syntax Evaluation of Ecological Network Structure
3.2.6. Ecological Conservation and Restoration Strategy
4. Discussion
4.1. Identification of Ecological Source Areas Based on OWA Multi-Attribute Decision-Making
4.2. Evaluation of Ecological Network Using Spatial Syntax
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, K.R.; Venter, O.; Fuller, R.A.; Allan, J.R.; Maxwell, S.L.; Negret, P.J.; Watson, J.E.M. One-third of global protected land is under intense human pressure. Science 2018, 360, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; He, C.; Huang, Q.; Shi, P.; Zhang, D.; Güneralp, B. Impacts of urban expansion on natural habitats in global drylands. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.N.; Ulrike, G.; Frank, N.; Do, M.H.; Paudel, G.P. Security risks from climate change and environmental degradation: Implications for sustainable land use transformation in the Global South. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 63, 101322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C.; Pan, J.H. Identification and optimization of ecological security pattern in the Gansu section of the Yellow River Basin from a supply-demand perspective. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 6973–6984. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Jiang, H.; Gu, T.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J. Sustainable landscape pattern: A landscape approach to serving spatial planning. Landsc. Ecol. 2022, 37, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Han, Y. Integrating spatial continuous wavelet transform and kernel density estimation to identify ecological corridors in megacities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 199, 103815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.J. Strategic points identification in landscape ecology and the surface model of theoretical geography. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1998, 53, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.J. Landscape ecological security patterns for biodiversity conservation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1999, 19, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Li, H.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.N.; Yang, Y. Identification and optimization strategies of ecological security pattern in Xiong’an New Area. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.M.; Lu, H.J. Research progress on urban ecological network analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 4258–4267. [Google Scholar]
- Vergnes, A.; Kerbiriou, C.; Clergeau, P. Ecological corridors also operate in an urban matrix: A test case with garden shrews. Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 16, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, Y. Construction of an ecological security pattern in Jiangnan water network area based on an integrated approach: A case study of Gaochun, Nanjing. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 109719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.S.; Ma, H.K.; Peng, J. Construction of urban ecological security pattern based on “functional nodes–key corridors”: A case study of Shenzhen City. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.R.; Kuang, W.H.; Liu, W.D.; Liu, A.L.; Pan, T. Optimization of ecological spatial structure of Guanzhong urban agglomeration based on ecological security pattern. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 441–452. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Li, B.; Yang, L.L.; Zhang, X.S. Importance assessment of ecosystem services in arid regions of Northwest China: A case study of Altay Prefecture. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2016, 30, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, X. Incorporating ecological risk index in the multi-process MCRE model to optimize the ecological security pattern in a semi-arid area with intensive coal mining: A case study in northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Koch, E.W.; Silliman, B.R.; Hacker, S.D.; Wolanski, E.; Primavera, J.; Granek, E.F.; Polasky, S.; Aswani, S.; Cramer, L.A.; et al. Coastal ecosystem-based management with nonlinear ecological functions and values. Science 2008, 319, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauman, K.A.; Daily, G.C.; Duarte, T.K.; Mooney, H.A. The nature and value of ecosystem services: An overview highlighting hydrologic services. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2007, 32, 67–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; Beard, T.D., Jr.; Bennett, E.M.; Cumming, G.S.; Cork, S.J.; Agard, J.; Dobson, A.P.; Peterson, G.D. Trade-offs across space, time, and ecosystem services. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Tellez, R.; Zhong, E.; Zuhu, Y.; Peña De La Cruz, A. A local spatial decision support system for developing countries based on MCA, fuzzy sets and OWA—Case study of a municipality in Cuba. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, 16, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J.; Rinner, C. Exploring multicriteria decision strategies in GIS with linguistic quantifiers: A case study of residential quality evaluation. J. Geogr. Syst. 2005, 7, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y. Balancing multiple ecosystem services in conservation priority setting. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 30, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaensen, F.; Chardon, J.P.; De Blust, G.; Swinnen, E.; Villalba, S.; Gulinck, H.; Matthysen, E. The application of ‘least-cost’ modelling as a functional landscape model. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, S.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Li, H.; Wu, J. Applying ant colony algorithm to identify ecological security patterns in megacities. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 117, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Li, Z.G.; Fang, S.M. Construction and optimization of ecological security pattern based on genetic algorithm and graph theory: A case study of Wuhan City. Prog. Geogr. 2022, 42, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, B.G.; Albano, C.M.; Anantharaman, R.; Beier, P.; Fargione, J.; Graves, T.A.; Gray, M.E.; Hall, K.R.; Lawler, J.J.; Leonard, P.B.; et al. Circuit-theory applications to connectivity science and conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2018, 33, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, J.; Ji, P.; Deng, X.; Yang, Y. Constructing the ecological security pattern of Nujiang Prefecture based on the framework of “importance–sensitivity–connectivity”. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Zhu, M.N.; Zhang, X.R.; Ma, J.H.; Zhou, J.T.; Cheng, T.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Tu, Y.; Yao, W.J.; Ma, J. Construction of ecological security pattern in the Sanjiangyuan region based on the “source-resistance-corridor” model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 4609–4623. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.Y.Y.; Liu, J.W.; Chen, C.X. Construction of ecological network of nature reserves in the Lancang River Basin, Yunnan Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Luo, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Dong, W. Construction and optimization of ecological security pattern in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in northwestern Sichuan. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.H.; Yang, L.S.; Feng, Q.; Su, Y.Q.; Zou, X.Y.; He, W.H. Spatiotemporal variation and driving factors of water yield service supply and demand in the Shiyang River Basin. Chin. J. Desert Res. 2024, 44, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zou, Y. Construction of an ecological security pattern based on ecosystem sensitivity and the importance of ecological services: A case study of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J.H. Optimization of ecological security pattern in arid inland river basin based on ecosystem service value reconstruction: A case study of Ganzhou District, Zhangye City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 3455–3467. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.C.; Deng, X.Y.; Qi, Y.F.; Wang, P.K. Construction of ecological security pattern in Henan Province based on MSPA, circuit theory and space syntax. Environ. Sci. 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.F.; Zhao, K.F.; Shao, Z.; Li, L. Spatio-temporal analysis of carbon sequestration of wetlands in Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area based on the InVEST model. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bagstad, J.K.; Semmens, J.D.; Winthrop, R. Comparing approaches to spatially explicit ecosystem service modeling: A case study from the San Pedro River Arizona. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.Y.; Zhai, T.L. Diagnosis and identification of key areas for ecological protection and restoration in territorial spatial ecological security pattern: A case study of Yantai City. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 190–203. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Li, Z.S.; Chen, X.J.; Zhou, H.L.; Gui, J. Spatio-temporal Changes and Influencing Factors of Ecosystem Service Functions in Hexi Region from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Ecol. 2023, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.R.; Zhou, J.J.; Lei, L.; Xiang, J.; Huang, M.; Feng, W.; Zhu, G.; Wei, W.; Wang, J. Identification of driving factors of water yield in the upper reaches of the Shiyang River based on the InVEST model. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 38, 3789–3799. [Google Scholar]
- Donohue, R.J.; Roderick, M.L.; McVicar, T.R. Incorporating key ecohydrological processes into Budyko’s hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436–437, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, R.R. Quantifier guided aggregation using OWA operators. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 1998, 11, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.; Mendoza, G.; Regetz, J.; Polasky, S.; Tallis, H.; Cameron, D.R.; Chan, K.M.A.; Daily, G.C.; Goldstein, J.; Kareiva, P.M.; et al. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, R.; Su, W.C.; Quan, X.Y.; Huang, X.F. Identification of ecological security pattern in the quiet zone of China’s FAST telescope based on OWA and circuit theory. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 9636–9651. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y. Study on the construction of the ecological security pattern of the Lancang River Basin (Yunnan section) based on InVEST-MSPA-Circuit Theory. Sustainability 2022, 15, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.W.; Yu, K.Y.; Xie, Z.; Yang, W.F.; Liu, J.A. Optimization of green infrastructure network in Fuzhou City based on habitat quality model. J. Southwest For. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 43, 118–125. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, R.; Xue, C.; Xia, Z. Ecological sensitivity evaluation and explanatory power analysis of the Giant Panda National Park in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.N.; Du, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Beier, P. Circuit theory predicts gene flow in plant and animal populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19885–19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.L.; Cao, G.C.; Yan, X.; Su, W.F.; Xian, Q.L. Identification of ecological security pattern based on InVEST model and circuit theory: A case study of Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 45, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.Y.; Wang, S.G.; Chen, B. Construction of ecological security pattern and assessment of ecological resilience based on ecosystem services: A case study of Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 4650–4661. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.M.; Shen, M.; Zhong, L. Construction of ecological security pattern in Pudacuo National Park. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, Z.; Wei, M.; Wang, M.; Shi, H.; Ruckstuhl, K.; Yang, W.; Alves, J. Small patches play a critical role in the connectivity of the Western Tianshan landscape, Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, M.H.; Zhou, Q.G.; Meng, H.B.; Peng, C.H.; Liu, X.W. Construction of ecological security pattern in a mega mountain city based on circuit theory: A case study of the metropolitan area of Chongqing. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 319–325+334. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhu, G.; Guo, C. Shiyang River ecosystem problems and countermeasures. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Feng, Q.; Lu, T.; Adamowski, J.F.; Yin, Z.; Hatami, S.; Wen, X. The response of agroecosystem water use efficiency to cropland change in northwest China’s Hexi Corridor. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 276, 108062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.W.; Wei, X.M.; Zhang, L.; Bi, W.T. Evaluation of ecological and environmental quality in the Shiyang River Basin. Chin. Rural. Water Hydropower 2007, 119, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Xu, Q.; Yi, J.; Zhong, X. Integrating CVOR-GWLR-Circuit model into construction of ecological security pattern in Yunnan Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 81520–81545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Peng, J. Ecosystem services-based decision-making: A bridge from science to practice. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 135, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.H.; Li, L. Optimization of ecological security pattern in the Gansu section of the Yellow River Basin using OWA and circuit models. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Coupling ecosystem services supply and human ecological demand to identify landscape ecological security pattern: A case study in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. Urban Ecosyst. 2017, 20, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Guo, X.N.; Hu, Y.N.; Liu, Y.X. Construction of mountain ecological security pattern based on geological hazard sensitivity: A case study of Yuxi City, Yunnan Province. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.G.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Guo, C.X.; Yang, X.J.; Xu, X.J.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.M.; Zhou, H.Y. Construction of ecological network in Guangzhou City based on morphological spatial pattern analysis and minimum cumulative resistance model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar]


| Date Type | Data Sources | Spatial Resolution | Time Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | ESA WorldCover | 10 m | Annual |
| Elevation (DEM) | China Geospatial Data Cloud | 30 m | — |
| Precipitation | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center | 1 km | Monthly |
| Evapotranspiration | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center | 1 km | Monthly |
| Soil Data | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center | 1 km | Annual |
| NDVI | Resource and Environment Science Data Center | 250 m | Monthly |
| Road Network | OpenStreetMap | - | Annual |
| Land Use | Habitat Suitability | Cropland | Bulit-Up | Bare |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Tree cover | 1 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| Grassland | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| Water body | 1 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.6 |
| Ice | 1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| wetland | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Bare | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bulit-up | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Threat Factor | Maximum Impact Distance (km) | Weight | Decline Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.5 | 0.7 | linear |
| Bare | 3 | 1 | exponential |
| Bulit-up | 0.8 | 0.2 | linear |
| Land Use | Evapotranspiration Coefficient | Maximum Root Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.65 | 2000 |
| Tree cover | 1 | 3500 |
| Grassland | 0.65 | 2400 |
| Water body | 1.1 | 1000 |
| Ice | 0.2 | 10 |
| wetland | 0.6 | 1000 |
| Bare | 0.5 | 500 |
| Bulit-up | 0.3 | 10 |
| Land Use | Crop Management Coefficient | Engineering Measures Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.22 | 1 |
| Tree cover | 0.06 | 1 |
| Grassland | 0.07 | 1 |
| Water body | 0 | 1 |
| Ice | 1 | 1 |
| wetland | 1 | 1 |
| Bare | 1 | 1 |
| Bulit-up | 0.3 | 0 |
| Land Use | C Above | C Below | C Soil | C Dead |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | 0.1 | 1.5 | 9.1 | 0 |
| Tree cover | 0.6 | 1.6 | 8.4 | 0.6 |
| Grassland | 0.8 | 2.2 | 15.8 | 0.06 |
| Water body | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ice | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| wetland | 0.2 | 1.0 | 7.0 | 0.95 |
| Bare | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bulit-up | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Resistance Types | Factors | Resistance Value | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land-use | ESA WorldCover | ||
| Forest | 1 | ||
| Grassland | 5 | ||
| Cropland | 10 | ||
| Bare Land | 15 | ||
| Water Body | 1 | ||
| Built-up | 20 | ||
| Habitat Quality | Generated by the Habitat Quality Module of the InVEST Model | ||
| 0–0.13 | 1 | ||
| 0.13–0.35 | 5 | ||
| 0.35–0.56 | 10 | ||
| 0.56–0.74 | 15 | ||
| 0.74–1 | 20 |
| Evaluation | Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Sensitive | Mildly Sensitive | Moderately Sensitive | Highly Sensitive | Extremely Sensitive | |
| 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | |
| Land-use | Forest, Water Body | Grassland | Cropland | Bare Land | Built-up |
| NDVI | ≤0.18 | (0.18, 0.33] | (0.33, 0.44] | (0.44, 0.60] | >0.60 |
| Railway buffer (m) | >2000 | (1500, 2000] | (1000, 1500] | (500, 1000] | ≤500 |
| Highway buffer (m) | >1500 | (1000, 1500] | (500, 1000] | (100, 500] | ≤100 |
| Water Body buffer (m) | >1000 | (700, 1000] | (500, 700] | (100, 500] | ≤100 |
| Soil erosion | Using the natural break method to classify into five grades. | ||||
| Districts | Habitat Quality | Water Yield | Soil Retention | Carbon Sequestration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minqin | 0.12 | 0.82 | 7.6 | 13.0 |
| Jinchuan | 0.16 | 22.3 | 59.8 | 17.1 |
| Yongchang | 0.30 | 102.3 | 223.0 | 32.6 |
| Shandan | 0.35 | 335.1 | 234.5 | 10.4 |
| Sunan | 0.51 | 449.4 | 390.1 | 14.1 |
| Liangzhou | 0.25 | 46.9 | 155.8 | 43.2 |
| Tianzhu | 0.50 | 316.4 | 347.8 | 15.9 |
| Gulang | 0.33 | 86.56 | 225.4 | 25.6 |
| Scenario | Risk Coefficient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0001 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 0.871 | 0.062 | 0.039 | 0.028 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 0.500 | 0.207 | 0.159 | 0.134 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.250 |
| 5 | 2 | 0.063 | 0.187 | 0.313 | 0.437 |
| 6 | 10 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.055 | 0.944 |
| 7 | 100,000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Scenario | Protection Efficiency | Mean Efficiency | Trade-Off | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Retention | Habitat Quality | Water Yield | Carbon Sequestration | |||
| 1 | 2.67 | 2.51 | 2.67 | 1.26 | 2.28 | 0 |
| 2 | 2.94 | 2.53 | 2.66 | 1.26 | 2.35 | 0.25 |
| 3 | 2.76 | 2.67 | 2.8 | 1.16 | 2.35 | 0.68 |
| 4 | 2.97 | 2.68 | 2.73 | 1.26 | 2.41 | 1 |
| 5 | 2.76 | 2.61 | 3.27 | 1.42 | 2.53 | 0.68 |
| 6 | 2.42 | 2.54 | 4.3 | 0.50 | 2.44 | 0.21 |
| 7 | 2.72 | 2.54 | 3.40 | 0.53 | 2.30 | 0 |
| Cropland | Grassland | Bare | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pinch points | 43 | 20 | 27 |
| Barriers | 22 | 5 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Li, G.; Song, Z. Ecological Security Pattern Construction Based on Multi-Scenario Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Shiyang River Basin. Land 2025, 14, 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112159
Guan Y, Zhang F, Feng Q, Wei Y, Li G, Song Z. Ecological Security Pattern Construction Based on Multi-Scenario Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Shiyang River Basin. Land. 2025; 14(11):2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112159
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Yingbin, Fuping Zhang, Qi Feng, Yongfeng Wei, Guangwen Li, and Zhiyuan Song. 2025. "Ecological Security Pattern Construction Based on Multi-Scenario Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Shiyang River Basin" Land 14, no. 11: 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112159
APA StyleGuan, Y., Zhang, F., Feng, Q., Wei, Y., Li, G., & Song, Z. (2025). Ecological Security Pattern Construction Based on Multi-Scenario Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Shiyang River Basin. Land, 14(11), 2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112159







