Projected Soil Erosion Risk Under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: A Case Study with RUSLE Modelling in Sakarya, Türkiye
Abstract
1. Introduction
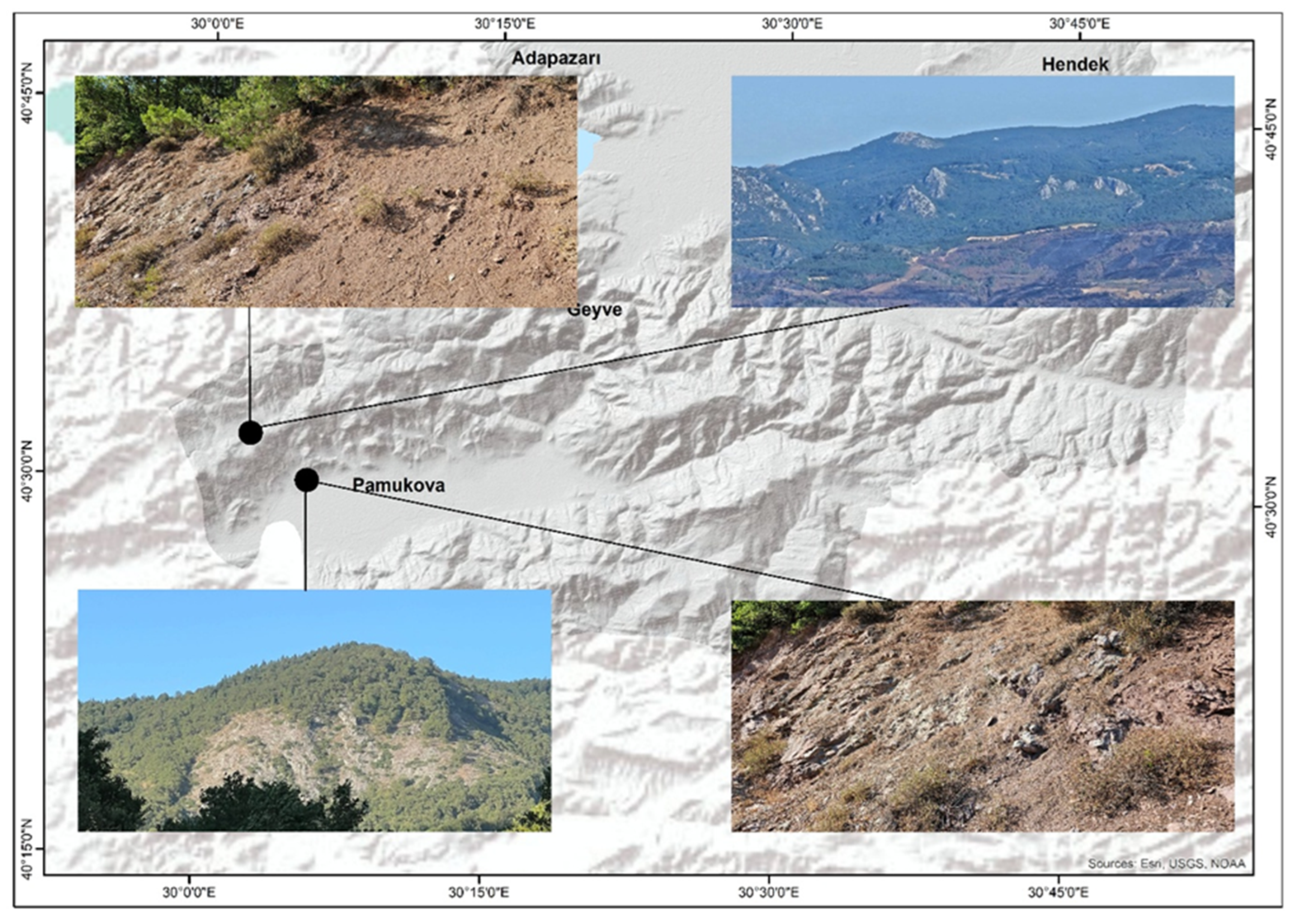
Characteristics of the Study Area
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Model
- A: average annual soil loss (t/ha·year);
- R: rainfall erosivity factor (MJ·mm/ha·h·year);
- K: soil erodibility factor (t·h/MJ·mm);
- LS: slope length and steepness factor (dimensionless);
- C: cover management factor (dimensionless);
- P: conservation of support-practice factor (dimensionless),
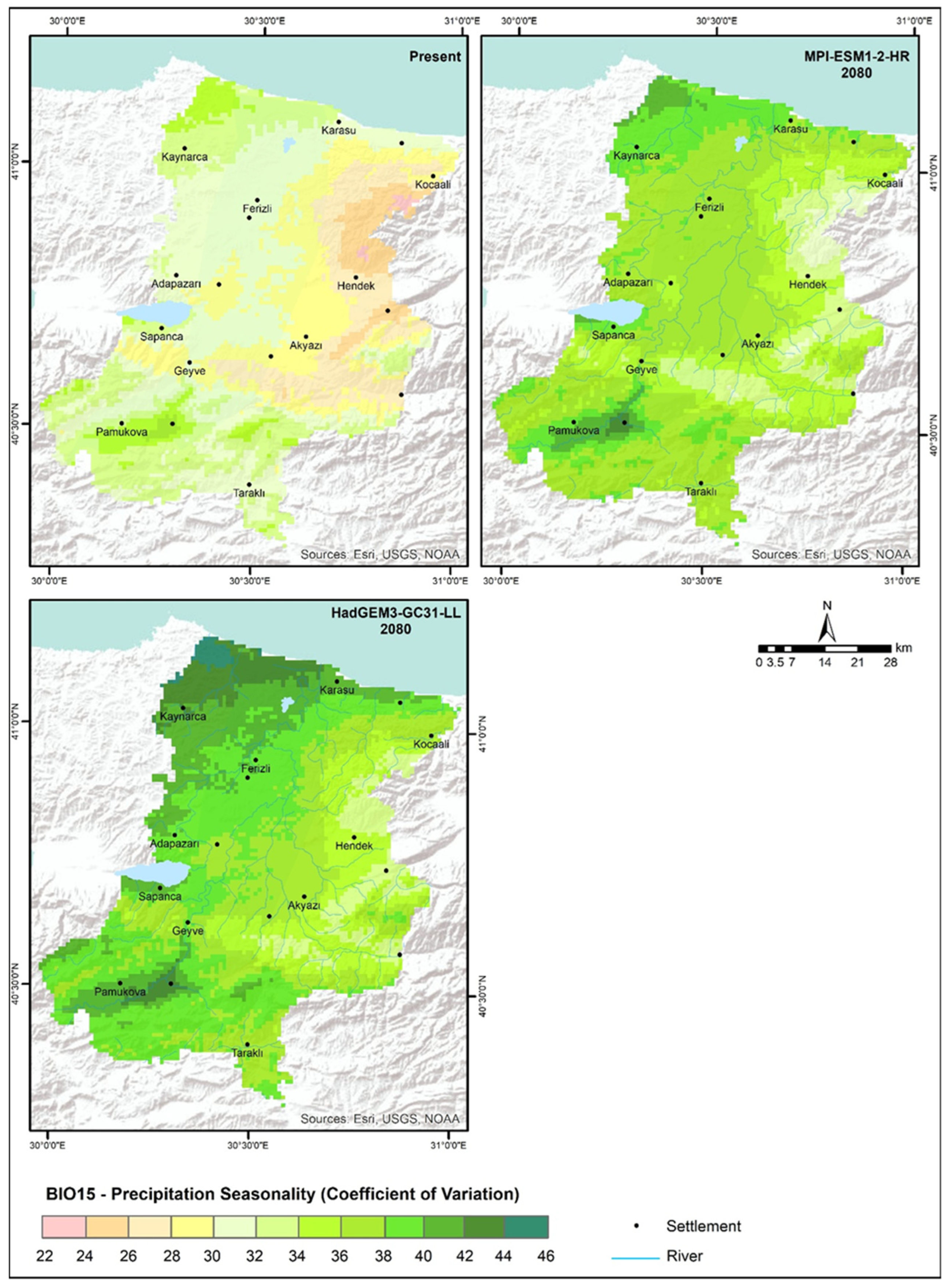
2.1.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
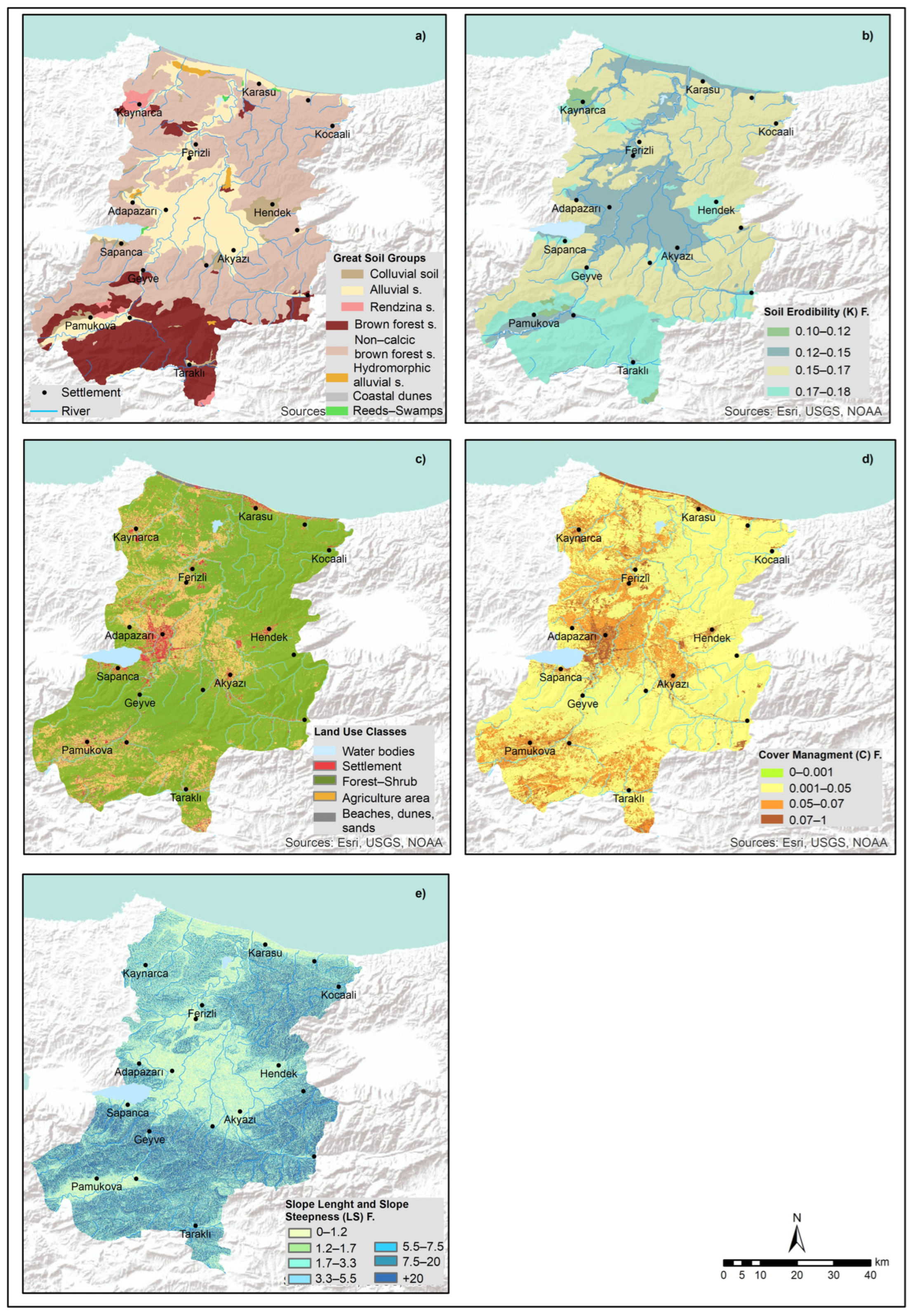
2.1.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
2.1.3. Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS)
2.1.4. Cover Management Factor (C)
2.1.5. Conservation of Support-Practice Factor (P)
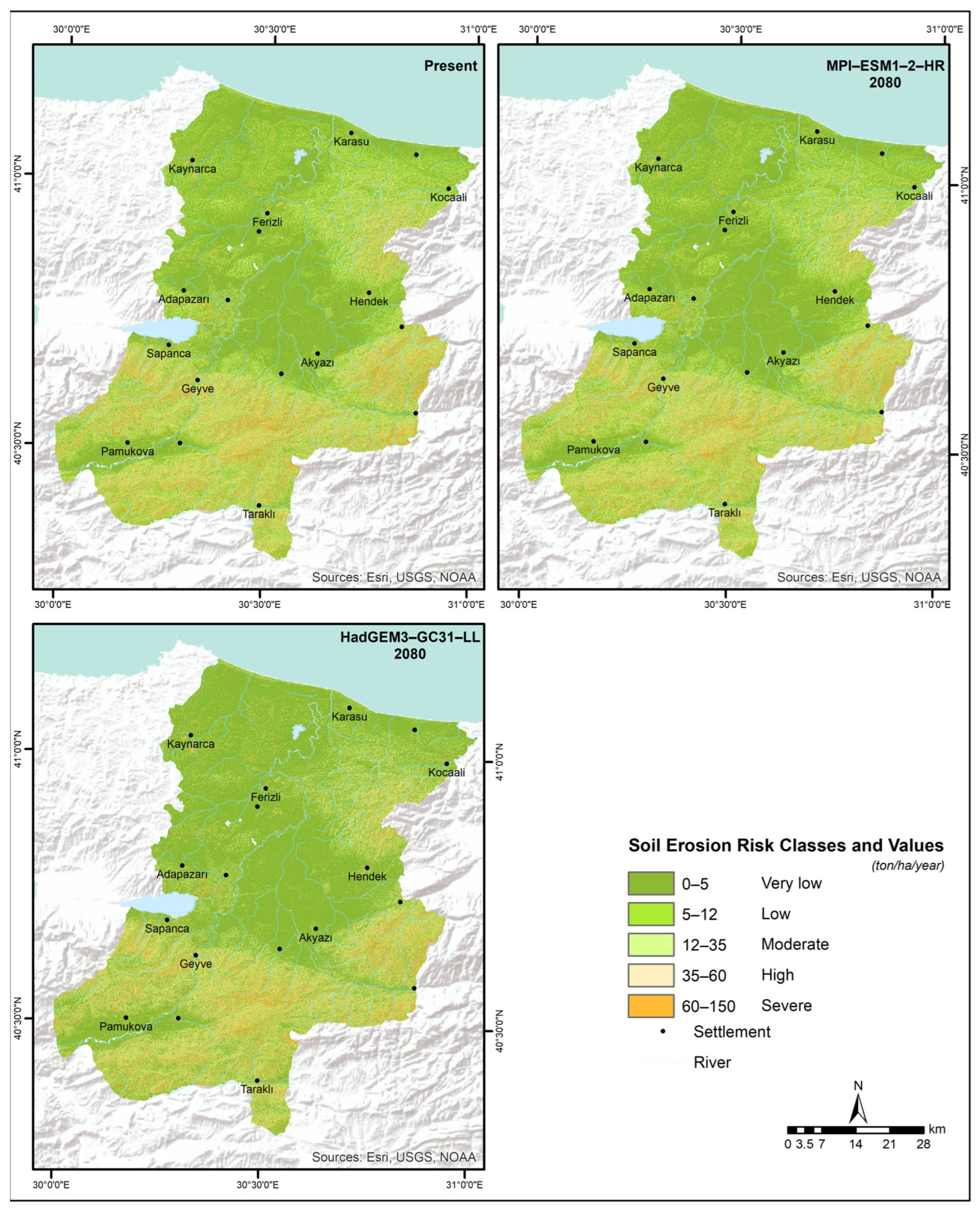
3. Results
Evaluation of RUSLE Model Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Preparing regional-scale risk maps to prioritize the protection of the most vulnerable areas;
- Promoting soil and water conservation practices (terracing, afforestation, cover crops, minimum tillage);
- Developing collaborative plans among local authorities, farmers, and scientists;
- Designing strategies that consider the socio-economic dimension (farmers’ livelihoods, rural development);
- Monitoring and reporting targets in alignment with SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) and SDG 15 (Life on Land), which is of critical importance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalay, İ. Vegetation. In The Soils of Turkey; Kapur, S., Akça, E., Günal, H., Eds.; World Soils Book Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Soil Erosion: The Greatest Challenge for Sustainable Soil Management; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2019; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Global soil status, processes and trends. In Status of The World’s Soil Resources (SWSR); Main Report of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; FAO: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake, D.; Morimoto, T.; Ranagalage, M. Accessing the Soil Erosion Rate Based on RUSLE Model for Sustainable Land Use Management: A Case Study of the Kotmale Watershed, Sri Lanka. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, B.; Ikiel, C.; Atalay Dutucu, A.; Koç, D.E. Erosion Susceptibility Analysis in Datça and Bozburun Peninsulas, Turkey. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2021, 45, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpul, G.; Şahin, S.; İnce, K.; Küçümen, A.; Akdağ, M.A.; Demirtaş, İ.; Çetin, E. Türkiye Su Erozyonu Atlası; Çölleşme Ve Erozyonla Mücadele Genel Müdürlüğü Yayınları: Ankara, Turkey, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cürebal, İ.; Efe, R.; Soykan, A.; Sönmez, S. Üç boyutlu modelleme kullanılarak siltasyon miktarının ölçülmesi: Çaygören Barajı örneği. In Proceedings of the III Jeomorfoloji Sempozyumu Bildiriler Kitabı Içinde, Hatay, Turkey, 4–6 October 2012; pp. 729–738. [Google Scholar]
- Pınar, M.Ö.; Şahin, S.; Madenoğlu, S.; Erpul, G. Derinöz Baraj Havzasında Şiddetli Erozyon Alanlarının Belirlenmesi ve Rezervuar Sediment Yükünün Hesaplanması. Su Kaynakları 2020, 5, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Fıçıcı, M.; Soykan, A. MPSİAC & RUSLE Yöntemleriyle Karşılaştırmalı Erozyon Analizi: Madra Barajı Havzası. Jeomorfol. Araştırmalar Derg. 2022, 8, 28–47. [Google Scholar]
- Atalay Dutucu, A.; Mutlu, Y.E. Yuvacık Barajı Havzası’nda Erozyon Risk Analizi. Ege Coğrafya Derg. 2022, 31, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echogdali, F.Z.; Boutaleb, S.; Taia, S.; Ouchchen, M.; Id-Belqas, M.; Kpan, R.B.; Abioui, M.; Aswathi, J.; Sajinkumar, K.S. Assessment of soil erosion risk in a semi-arid climate watershed using SWAT model: Case of Tata basin, South-East of Morocco. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korup, O.; Görüm, T.; Hayakawa, Y. Without power? Landslide inventories in the face of climate change. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, K.; Fawcett, D.; Cugulliere, A.; Benford, S.; Jones, D.; Leng, R. Vegetation expansion in the subnival Hindu Kush Himalaya. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 1608–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Atesoglu, A.; Ayyildiz, E.; Karakaya, I.; Bulut, F.S.; Serengil, Y. Land cover and drought risk assessment in Türkiye’s mountain regions using neutrosophic decision support system. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, F.; Erlat, E.; Türkeş, M. Impact of climate variability on the surface of Lake Tuz (Turkey), 1985–2016. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2020, 20, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.T.; Rounsevell, M.; Sehgal, J.; Varally, G. Land degradation and desertification. In Climate Change 1995, Impacts, Adaptations and Mitigation of Climate Change: Scientific-Technical Analyses; Watson, R.T., Zinyowera, M.C., Moss, R.H., Eds.; Contributing of WG II to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 171–189. [Google Scholar]
- Türkeş, M. Kuraklık, çölleşme ve birleşmiş milletler çölleşme ile savaşım sözleşmesi’nin ayrıntılı bir çözümlemesi. Marmara Üniversitesi Avrupa Araştırmaları Enstitüsü Avrupa Araştırmaları Derg. 2012, 20, 7–55. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, H.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Chappell, A.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z. Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on RUSLE and CMIP5 climate models. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Biavetti, I.; Montanarella, L.; Borrelli, P. Soil Erosion in Europe: From Policy Developments to Models, Indicators and New Research Challenges. In Global Degradation of Soil and Water Resources: Regional Assessment and Strategies; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 319–333. [Google Scholar]
- Patriche, C.V. Applying RUSLE for soil erosion estimation in Romania under current and future climate scenarios. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 34, e00687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bammou, Y.; Benzougagh, B.; Bensaid, A.; Igmoullan, B.; Al-Quraishi, A.M.F. Mapping of current and future soil erosion risk in a semi-arid context (haouz plain-Marrakech) based on CMIP6 climate models, the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and RUSLE. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 1501–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Himics, M.; Scarpa, S.; Matthews, F.; Bogonos, M.; Borrelli, P. Projections of soil loss by water erosion in Europe by 2050. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 124, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Matthews, F.; Liakos, L.; Bezak, N.; Diodato, N.; Ballabio, C. Global rainfall erosivity projections for 2050 and 2070. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinson, A.O.; AuBuchon, J.S. A new method for calculating C factor when projecting future soil loss using the Revised Universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) in semi-arid environments. Catena 2023, 26, 107067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, R.; Kendon, E.J.; Constantine, J.A.; Schindewolf, M.; Hall, I.R. Soil erosion in a British watershed under climate change as predicted using convection-permitting regional climate projections. Geosciences 2023, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarinas, N.; Tsakiridis, N.L.; Kalopesa, E.; Zalidis, G.C. Soil loss estimation by water erosion in agricultural areas introducing artificial intelligence geospatial layers into the RUSLE model. Land 2024, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifi, S.; Aydi, A.; Bouamrane, A.; Zaghdoudi, S.; Gasmi, M. Appraisal of soil erosion risk in northeastern Tunisia using geospatial data and integrated approach of RUSLE model and GIS. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 133, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terranova, O.; Antronico, L.; Coscarelli, R.; Iaquinta, P. Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: An application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 2009, 112, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezici, K.; Şengül, S.; Kesgin, E. Assessment of soil erosion risk in the mountainous region of northeastern Türkiye based on the RUSLE model and CMIP6 climate projections. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 84, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.; Dursun, İ. Assessment of pre-and post-fire erosion using the RUSLE equation in a watershed affected by the forest fire on Google Earth Engine: The study of Manavgat River Basin. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 2499–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezer, D.; İkiel, C.; Atalay Dutucu, A.; Öğütlü, A.; Aydın, A.; Tunalı Çokluk, S.; Ustaoğlu, B. İklim Değişikliğine Uyum Sürecinde Sıcak Hava Dalgalarının Zamansal ve Mekansal Analizi Sakarya İli Örneği. Presented at the TMMOB 8. Coğrafi Bilgi Sistemleri Kongresi (Uzamsal Zekâ ile Kolektif Bilinç), Ankara, Türkiye, 20–22 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ustaoğlu, B. Sakarya’nın iklim özellikleri. In Sakarya’nın Fiziki, Beseri ve Iktisadi Cografya Özellikleri; Sakarya Universitesi Yayını: Sakarya, Turkey, 2018; pp. 163–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ikiel, C.; Dutucu, A.A.; Ustaoglu, B.; Kilic, D.E. Land use and land cover (LULC) classification using Spot-5 image in the Adapazari Plain and its surroundings, Turkey. Tojsat 2012, 2, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Döker, M.F.; Kaçmaz, M.; İkiel, C. Sakarya’da Nüfusun Gelişimi ve Dağılışı; Yeni Anadolu Yayıncılık: Çankaya, Turkey, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ayva, C.; Dutucu, A.A.; Ustaoğlu, B. İklim Değişikliğinin Su Kaynaklarina Etkisi Ve Uyum Önerileri: Kirazdere Havzasi Örneği. Firat Univ. J. Soc. Sci. 2022, 33, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, O.Y.; Akkemik, Ü.; Dogan, Ö.H.; Yilmaz, H.; Sevgi, O.; Sevgi, E. The missing part of the past, current, and future distribution model of Quercus ilex L.: The eastern edge. Iforest-Biogeosciences For. 2024, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, E.S.; Örücü, Ö.K.; Gülcü, S.; Dirlik, S.; Hoşgör, E. Prediction of the shift of the distribution of Pinus brutia Ten. Under future climate model. New For. 2025, 56, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinelhub by Planet Labs. Available online: https://www.sentinel-hub.com (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Tağil, Ş. Tuzla Çayı Havzasında (Biga Yarımadası) CBS-Tabanlı RUSLE Modeli Kullanarak Arazi Degradasyonu Risk Değerlendirmesi. Ekoloji Derg. 2007, 16, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Hagras, A. Estimating water erosion in the EL-Mador Valley Basin, South-West Matrouh City, Egypt, using revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model through GIS. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). In USDA Agriculture Handbook; National Agricultural Statistics Services: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; p. 703. [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma, E.; Charman, P.; Gibbons, F.; Hurni, H.; Moldenhauer, W.C.; Panichapong, S. Terminology for Soil Erosion and Conservation; International Society of Soil Science: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Woldegebrael, S.M.; Romano, N.; Pumo, D.; Deidda, R.; Ippolito, M.; Cannarozzo, M.; Langousis, A.; Serafeim, A.V.; Manfreda, S.; Nasta, P. Empirical approaches to estimate rainfall erosivity from coarse temporal resolution precipitation data in the Mediterranean region. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 996, 180122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldırım, C.; Schildgen, T.F.; Echtler, H.; Melnick, D.; Strecker, M.R. Late Neogene and active orogenic uplift in the Central Pontides associated with the North Anatolian Fault: Implications for the northern margin of the Central Anatolian Plateau, Turkey. Tectonics 2011, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldous, H.M.J. An Approximation of the Rainfall Factor in the USLE. In Assessment of Erosion; De Boodt, M., Gabriels, D., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1980; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- WorldClim. Available online: https://www.worldclim.org/data/index.html (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, M.; Cürebal, İ. Rusle (3d) modeli kullanılarak toprak erozyonu tahmini; Atikhisar Barajı Havzası örneği (Çanakkale). Memba Su Bilim. Derg. 2025, 11, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.; Sena, D.R.; Mandal, U.; Kashyap, P.S.; Dash, S.S. Integrated GIS-based RUSLE approach for quantification of potential soil erosion under future change scenarios. Envion. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelagay, H.S.; Minale, A.S. Soil loss estimation using GIS and Remote sensing techniques: A case of Koga watershed, Northwestern Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özden, Ş.; Özden, M. Türkiye Toprak Erozyon Tahmin Modeli. In TURTEM, Başbakanlık Türkiye Köy Hizmetleri Genel Müdürlüğü; Toprak ve Gübre Araştırma Enstitüsü Müdürlüğü Yayınları: Ankara, Turkey, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal, K.; Das Bhattacharya, S. A review of RUSLE model. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 689–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS-A case study of Nethravathi basin. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, Y.; Nawaiseh, S. Spatial assessment of soil erosion risk using RUSLE and GIS techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 4649–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitasova, H.; Hofieka, J.; Zlocha, M.; Iverson, L.R. Modeling Topographic Potential for Erosion and Deposition Using GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1996, 10, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. Topographically Complex Landscape Units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthes, J.M.; Tomazoni, J.C.; Guimarães, E.; Gomes, T.C. Use of geographic information system in determining the topographic factor of the Catorze river basin Southwest, P.R. Braz. J. Phys. Geogr. 2012, 5, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, C.; Alewell, C.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L. Estimating the soil erosion cover management factor at European scale. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Soil Erosion and Conservation, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Erkal, T. Çobanlar Havzası′nda (Afyonkarahisar) Toprak Erozyonunun Değerlendirilmesi. J. Acad. Soc. Sci. Stud. 2012, 5, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, B.; Holden, S.T.; Quimo, S. Conservation practices and their impact on land productivity in Sub-Saharn Africa. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.S.; Pani, P. Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS techniques: A case study of Barakar River basin, Jharkhand, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2015, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, H.; Herweg, K.; Portner, B.; Liniger, H. Soil and water conservation in a changing world: Lessons learned from the WOCAT SLM database. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, H.R.; Hensel, S. Soil erosion and conservation in Europe: Past and present research trends. Catena 2020, 194, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, B. Matlab’da İklim Veri Analiz ve Uygulamaları; Anka Matbaa: İstanbul, Turkey, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- MGM. Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/iklim/iklimdegisikligi.aspx?s=projeksiyonlar (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Bağçaci, S.Ç.; Yucel, I.; Duzenli, E.; Yilmaz, M.T. Intercomparison of the expected change in the temperature and the precipitation retrieved from CMIP6 and CMIP5 climate projections: A Mediterranean hot spot case, Turkey. Atmos. Res. 2021, 256, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, B.; Koç, D.E. Sakarya′nın toprak özellikleri. In Sakarya’nın Fiziki, Beseri ve İktisadi Cografya Özellikleri; Sakarya Universitesi: Yayını, Sakarya, Turkey, 2018; pp. 263–286. [Google Scholar]
- T.C. Başbakanlık Köy Hizmetleri Genel Müdürlüğü. Sakarya İli Arazi Varlığı; Bakanlık Yayınları: Ankara, Turkey, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- T.C. Köy İşleri Bakanlığı Topraksu Genel Müdürlüğü. Sakarya İli Toprak Envanter Raporu; Bakanlık Yayınları: Ankara, Turkey, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- T.C. Gıda Tarım ve Hayvancılık Bakanlığı. Sakarya’nın Sayısal Toprak Verileri; Bakanlık Yayınları: Ankara, Turkey, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cebel, H.; Akgül, S.; Doğan, O.; Elbaşı, F. Türkiye büyük toprak gruplarının erozyona duyarlılık “K” faktörleri. Toprak Su Derg. 2013, 2, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Doğan, O.; Cebel, H.; Akgül, S.; Küçükçakar, N. Türkiye Büyük Toprak Grupları (K) Faktörleri, Köy Hizmetleri APK Dairesi Başkanlığı Toprak ve Su Kaynakları Araştırma Şube Müdürlüğü Yayın No:111, Rehber No: 17, Ankara. Toprak Su Derg. 2000, 2, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Turoglu, H.; Aykut, T. Ergene Nehri Havzası için hidromorfometrik analizlerle taşkın duyarlılık değerlendirmesi. Jeomorfol. Araştırmalar Dergis 2019, 2, 1–15. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/article-file/685038 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Stefanidis, S.; Alexandridis, V.; Chatzichristaki, C.; Stefanidis, P. Assessing soil loss by water erosion in a typical Mediterranean ecosystem of northern Greece under current and future rainfall erosivity. Water 2021, 13, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A new European slope length and steepness factor (LS-Factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, G.; Merchán, L.; Sánchez, J.Á. Spatial Representation of Soil Erosion and Vegetation Affected by a Forest Fire in the Sierra de Francia (Spain) Using RUSLE and NDVI. Land 2025, 14, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Ordóñez, A.; Duane, A.; Gil-Tena, A.; De Cáceres, M.; Aquilué, N.; Guerra, C.A.; Geijzendorffer, I.R.; Fortin, M.J.; Brotons, L. Future impact of climate extremes in the Mediterranean: Soil erosion projections when fire and extreme rainfall meet. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 3040–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Leng, G. Global soil water erosion responses to climate and land use changes. Catena 2024, 241, 108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, B.; Tunçat, K.A.; Koç, D.E. Impacts of climate change on precipitation and temperature climatology in türkiye from present to future perspective. In Urban Commons, Future Smart Cities and Sustainability; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 403–426. [Google Scholar]
- Koç, D.E.; Dutucu, A.A.; Ustaoğlu, B. İklim Değişikliğine Uyum Kapsamında Sürdürülebilir Su Kaynakları Yönetimi İçin Sapanca Gölü Havzası′nda Kuraklık Risk Analizi. In Kuramdan Uygulamaya Ekonomi ve Sosyal Bilimlerde Akademik Araştırmalar-I; Hiper Yayın: Singapore, 2022; pp. 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ustaoğlu, B.; Mutar, Ş. İklim Değişikliği Kapsamında Sürdürülebilir Su Yönetimi Açısından Türkiye’deki Ekstrem Yağışların Analizi. Yeni Türkiye Derg. 2025, 31, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Günlü, A.; Sivrikaya, F.; Ünal, H.E. Prediction of Land Use and Land Cover Changes from 2018 to 2042 Using CA-Markov: A Case Study from Türkiye. Kastamonu Univ. J. For. Fac. 2025, 25, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci Kadak, M.; Ozturk, S.; Mert, A. Predicting climate-based changes of landscape structure for Turkiye via global climate change scenarios: A case study in Bartin river basin with time series analysis for 2050. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 13289–13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

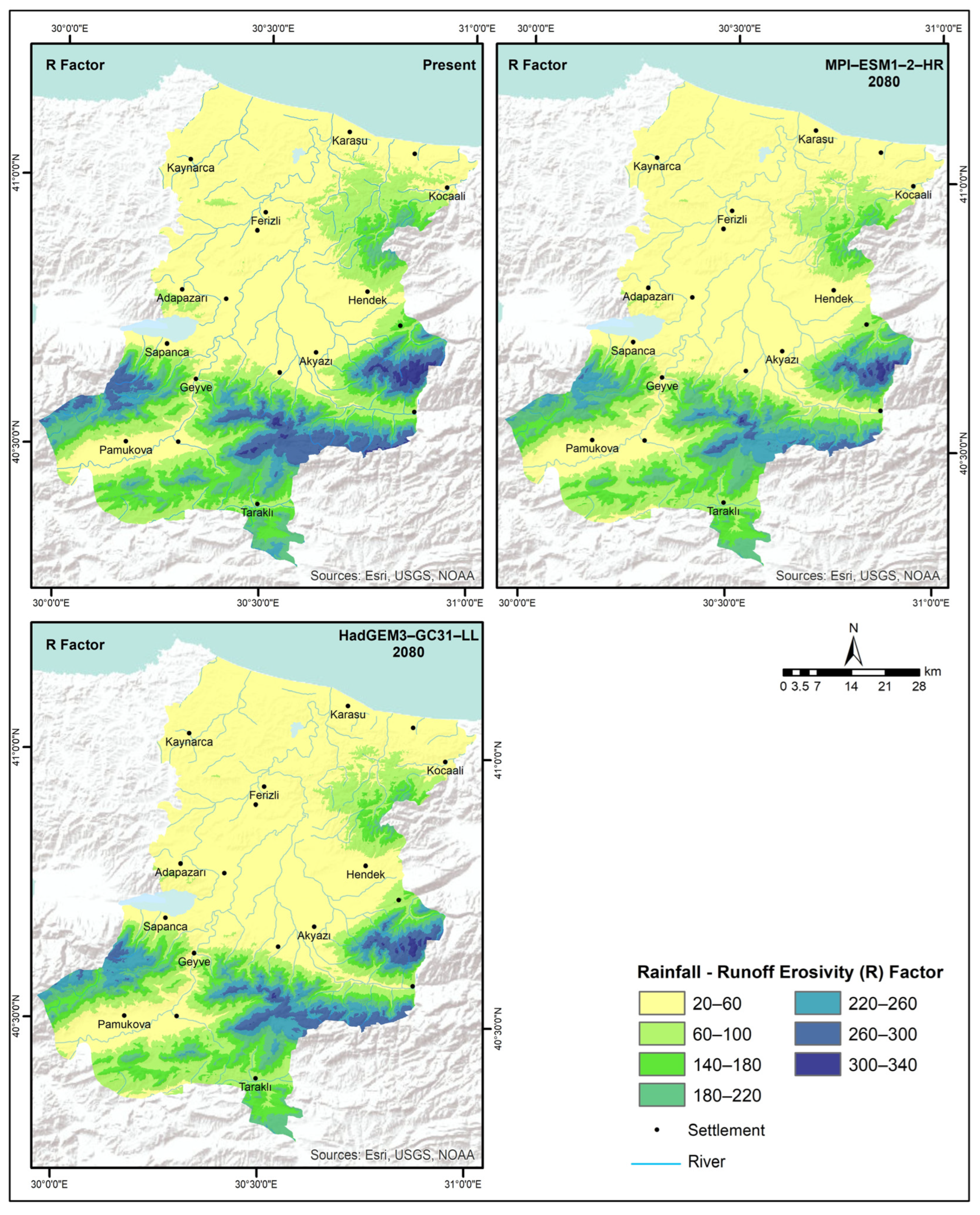

| Elevation (m) | Present | MPI-ESM1-2-HR 2061–2080 | HadGEM3-GC31-LL 2061–2080 | Present | MPI-ESM1-2-HR 2061–2080 | HadGEM3-GC31-LL 2061–2080 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFI | R Factor Values | |||||
| 0–100 | 56.9 | 52.8 | 54.6 | 85.5 | 68.1 | 75.9 |
| 100–200 | 61.0 | 56.5 | 58.2 | 102.5 | 83.4 | 90.9 |
| 200–300 | 69.3 | 64.2 | 65.9 | 137.1 | 115.7 | 122.7 |
| 300–400 | 73.6 | 68.2 | 69.8 | 154.8 | 132.4 | 139.2 |
| 400–500 | 77.8 | 72.3 | 73.9 | 172.5 | 149.4 | 156.0 |
| 500–600 | 82.1 | 76.4 | 77.9 | 190.4 | 166.6 | 173.0 |
| 600–700 | 86.4 | 80.6 | 82.1 | 208.4 | 184.0 | 190.3 |
| 700–800 | 90.8 | 84.8 | 86.3 | 226.4 | 201.5 | 207.7 |
| 800–900 | 95.1 | 89.0 | 90.5 | 244.6 | 219.2 | 225.3 |
| 900–1000 | 99.5 | 93.3 | 94.7 | 262.7 | 237.0 | 243.0 |
| 1000–1100 | 103.8 | 97.6 | 99.0 | 281.0 | 254.9 | 260.7 |
| 1200–1300 | 108.2 | 101.9 | 103.3 | 299.3 | 272.8 | 278.6 |
| 1300–1400 | 112.6 | 106.2 | 107.6 | 317.6 | 290.9 | 296.6 |
| 1400–1500 | 117.0 | 110.5 | 111.9 | 335.9 | 309.0 | 314.6 |
| 1500–1600 | 121.4 | 111.8 | 113.2 | 354.3 | 314.4 | 319.9 |
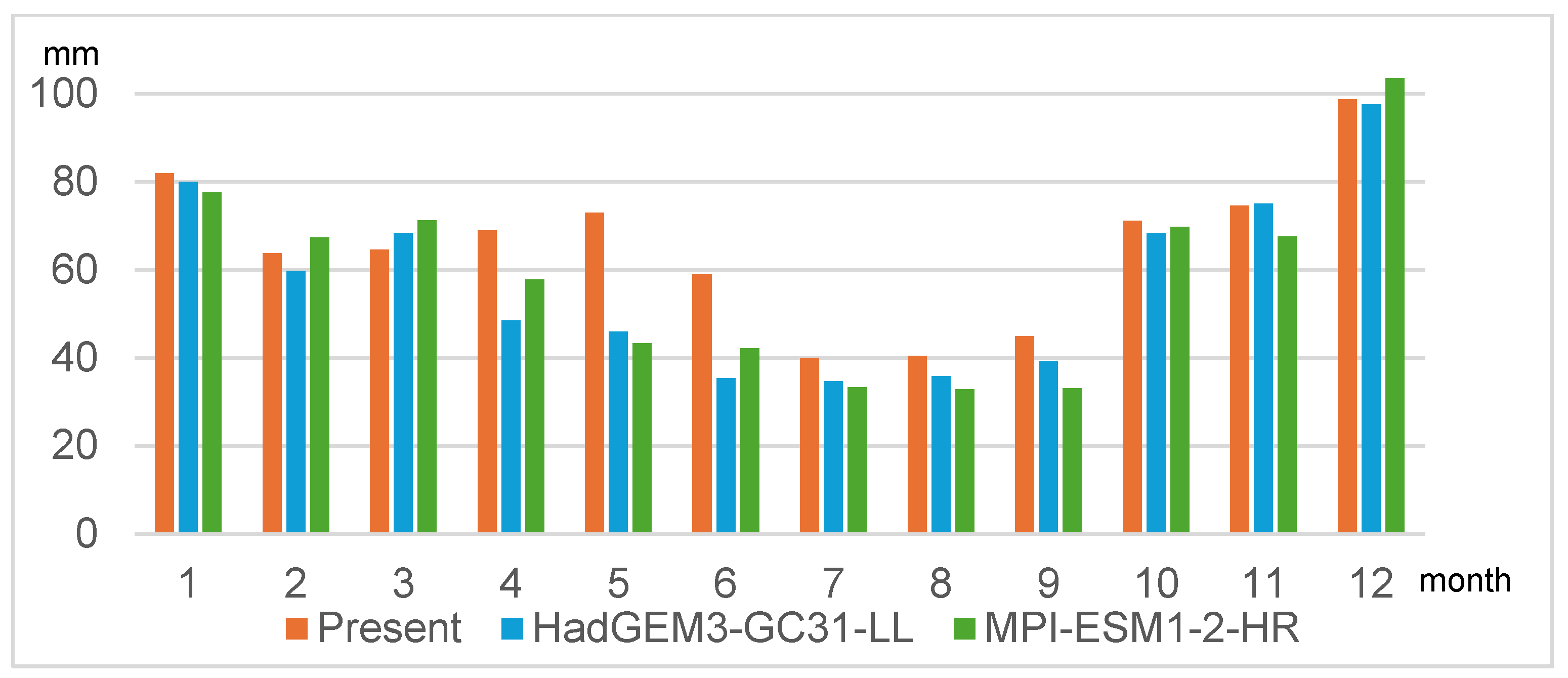
| Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | 82.0 | 63.8 | 64.6 | 69.0 | 73.0 | 59.0 | 40.0 | 40.4 | 44.9 | 71.1 | 74.6 | 98.8 | 781.2 |
| HadGEM3 GC31-LL | 80.0 | 59.8 | 68.3 | 48.5 | 45.9 | 35.4 | 34.7 | 35.8 | 39.2 | 68.4 | 75.0 | 97.6 | 688.6 |
| MPI-ESM1-2-HR | 77.7 | 67.3 | 71.2 | 57.8 | 43.3 | 42.2 | 33.3 | 32.8 | 33.0 | 69.8 | 67.6 | 103.6 | 699.6 |
| Great Soil Groups | Area | K Factor Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | % | ||
| Colluvial soil | 130 | 2.8 | 0.18 |
| Brown forest s. | 878 | 18.8 | 0.18 |
| Rendzina s. | 1 | 0.02 | 0.12 |
| Alluvial s. | 964 | 20.6 | 0.15 |
| Non-calcic brown forest s. | 2654 | 56.7 | 0.17 |
| Hydromorphic alluvial s. | 32 | 0.7 | 0.15 |
| Coastal dunes | 19 | 0.4 | 0.18 |
| Reeds-Swamps | 4 | 0.1 | 0.15 |
| LS Factor Value | LS Factor Classes | Area (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–1.2 | Very low | 45.7 |
| 1.2–1.7 | Slightly low | 1.6 |
| 1.7–3.3 | Low | 4.9 |
| 3.3–5.5 | Moderate | 5.7 |
| 5.5–7.7 | Moderate high | 4.3 |
| 7.7–20 | High | 17.0 |
| +20 | Very high | 20.8 |
| Class | Soil Loss (t/ha/yr) | Present (%) | MPI-ESM1-2-HR SSP85 2061–2080 (%) | HadGEM3-GC31-LL SSP85 2061–2080 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very low | 0–5 | 58.9 | 60.8 | 59.8 |
| Low | 5–12 | 9.9 | 10.3 | 10.3 |
| Moderate | 12–35 | 15.2 | 14.8 | 15.1 |
| High | 35–60 | 6.3 | 5.7 | 5.9 |
| Severe | 60–150 | 9.8 | 8.4 | 8.9 |
| Total | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dutucu, A.A.; Koç, D.E.; Ustaoğlu, B. Projected Soil Erosion Risk Under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: A Case Study with RUSLE Modelling in Sakarya, Türkiye. Land 2025, 14, 2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112153
Dutucu AA, Koç DE, Ustaoğlu B. Projected Soil Erosion Risk Under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: A Case Study with RUSLE Modelling in Sakarya, Türkiye. Land. 2025; 14(11):2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112153
Chicago/Turabian StyleDutucu, Ayşe Atalay, Derya Evrim Koç, and Beyza Ustaoğlu. 2025. "Projected Soil Erosion Risk Under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: A Case Study with RUSLE Modelling in Sakarya, Türkiye" Land 14, no. 11: 2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112153
APA StyleDutucu, A. A., Koç, D. E., & Ustaoğlu, B. (2025). Projected Soil Erosion Risk Under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways: A Case Study with RUSLE Modelling in Sakarya, Türkiye. Land, 14(11), 2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112153






