Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and Detection of Their Driving Mechanisms in Southeast Coastal China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
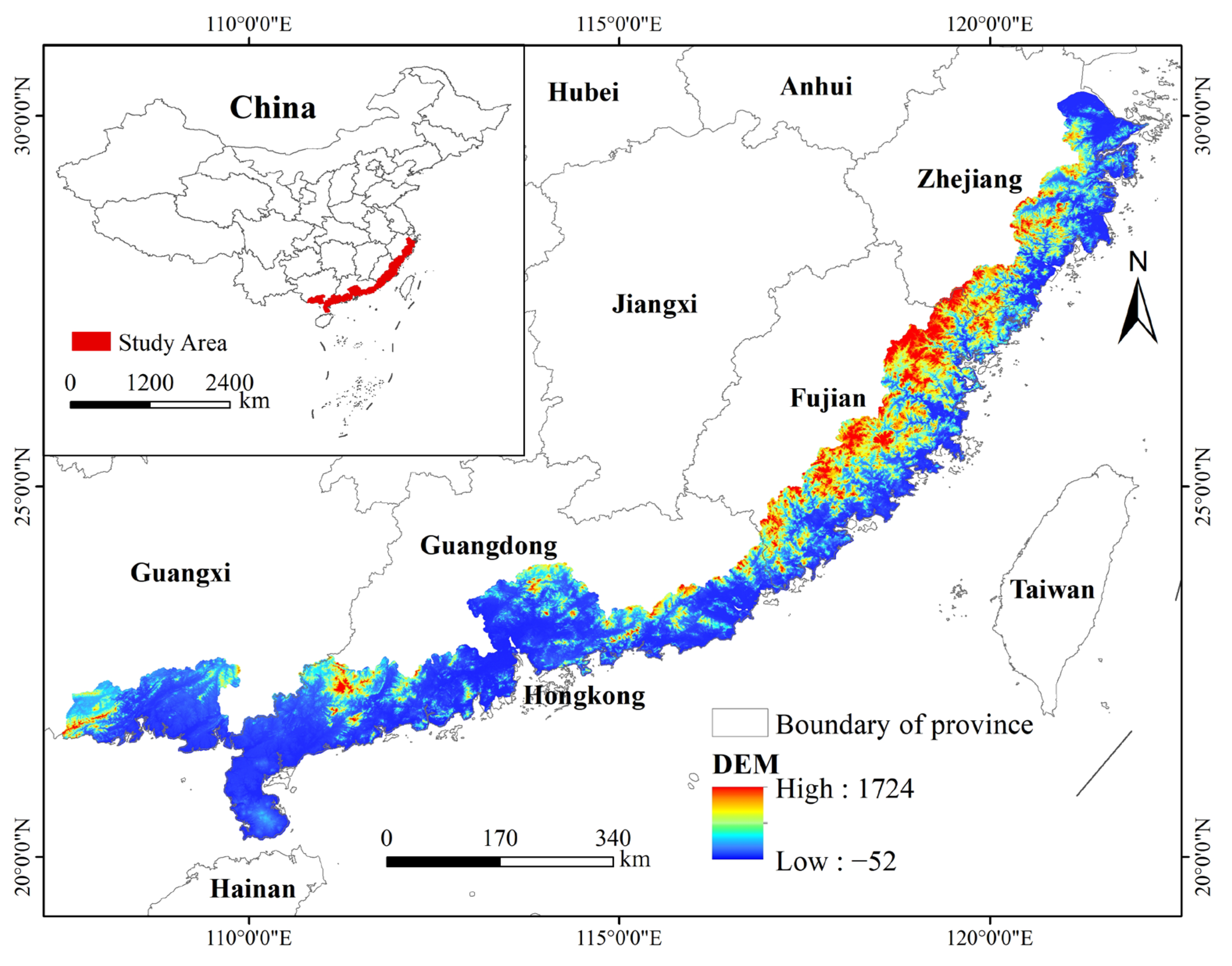
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. The Delineation of Multi-Scale Frameworks
2.4. Estimation of Ecosystem Services (ESs)
2.5. Driving Factors Indicator System
2.6. Quantification of Trade-Offs and Synergies in Ecosystem Services
2.7. Geodetector-Based Analysis of Ecosystem Service Drivers
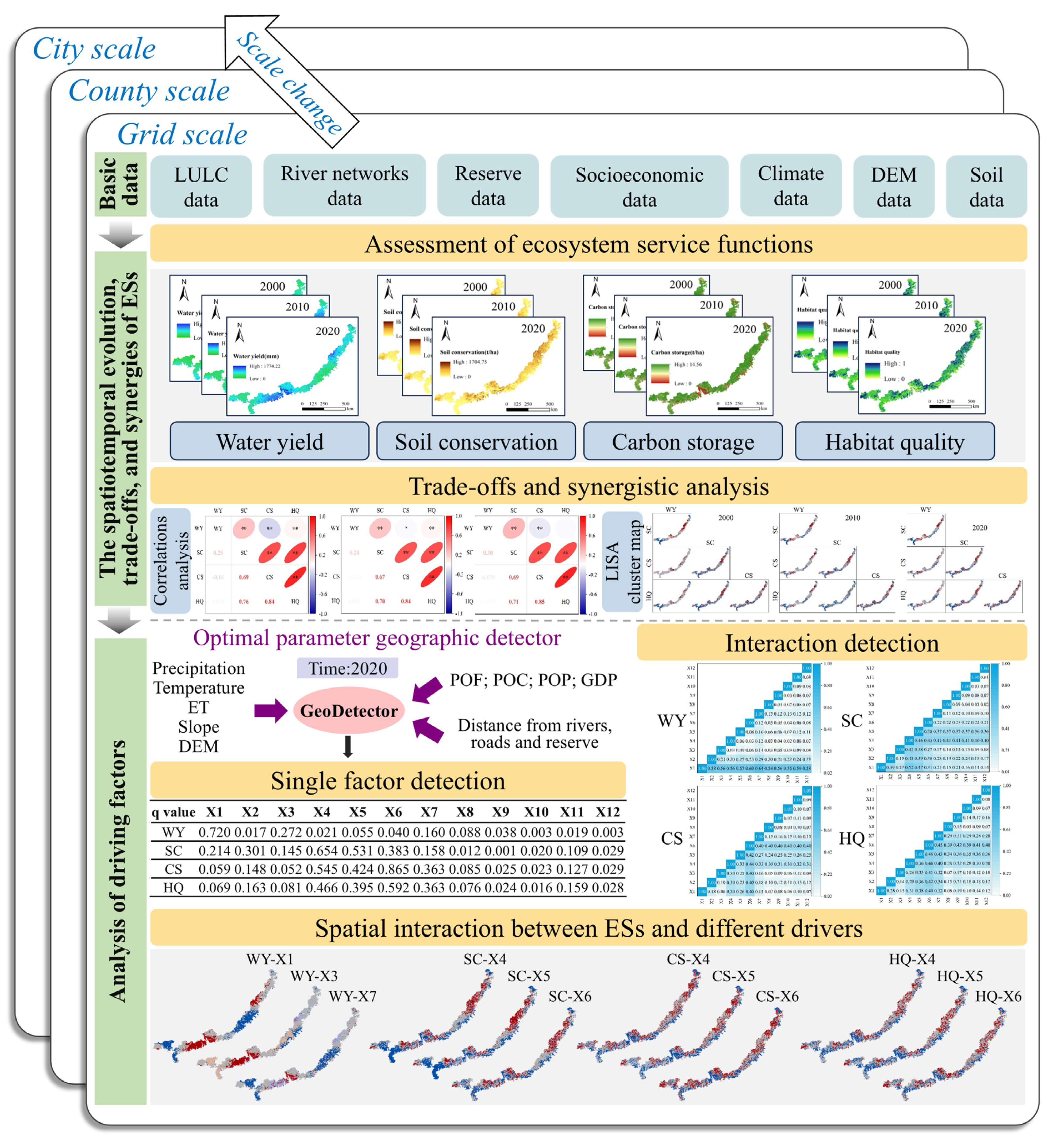
2.8. Technical Approach
3. Results
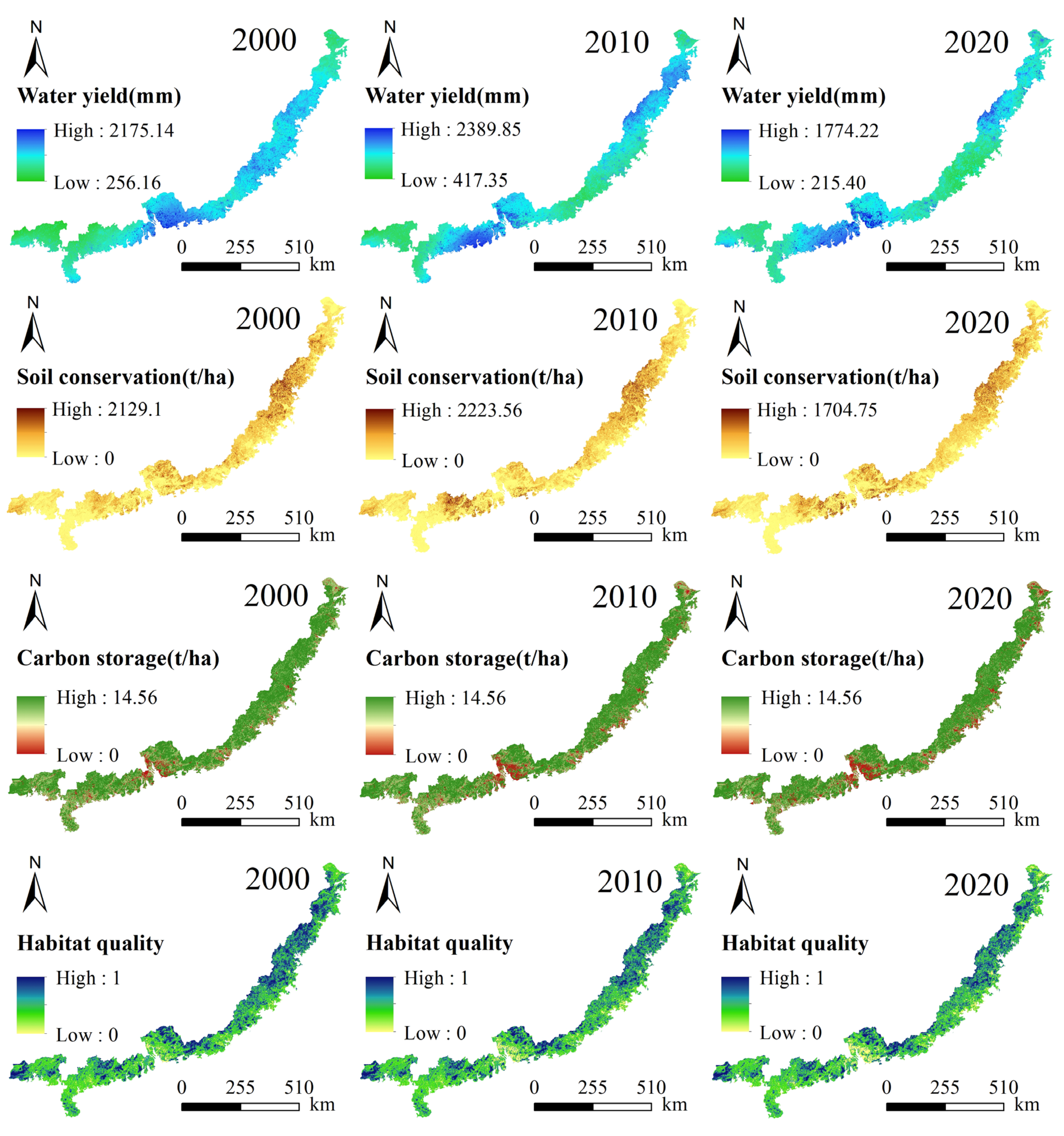
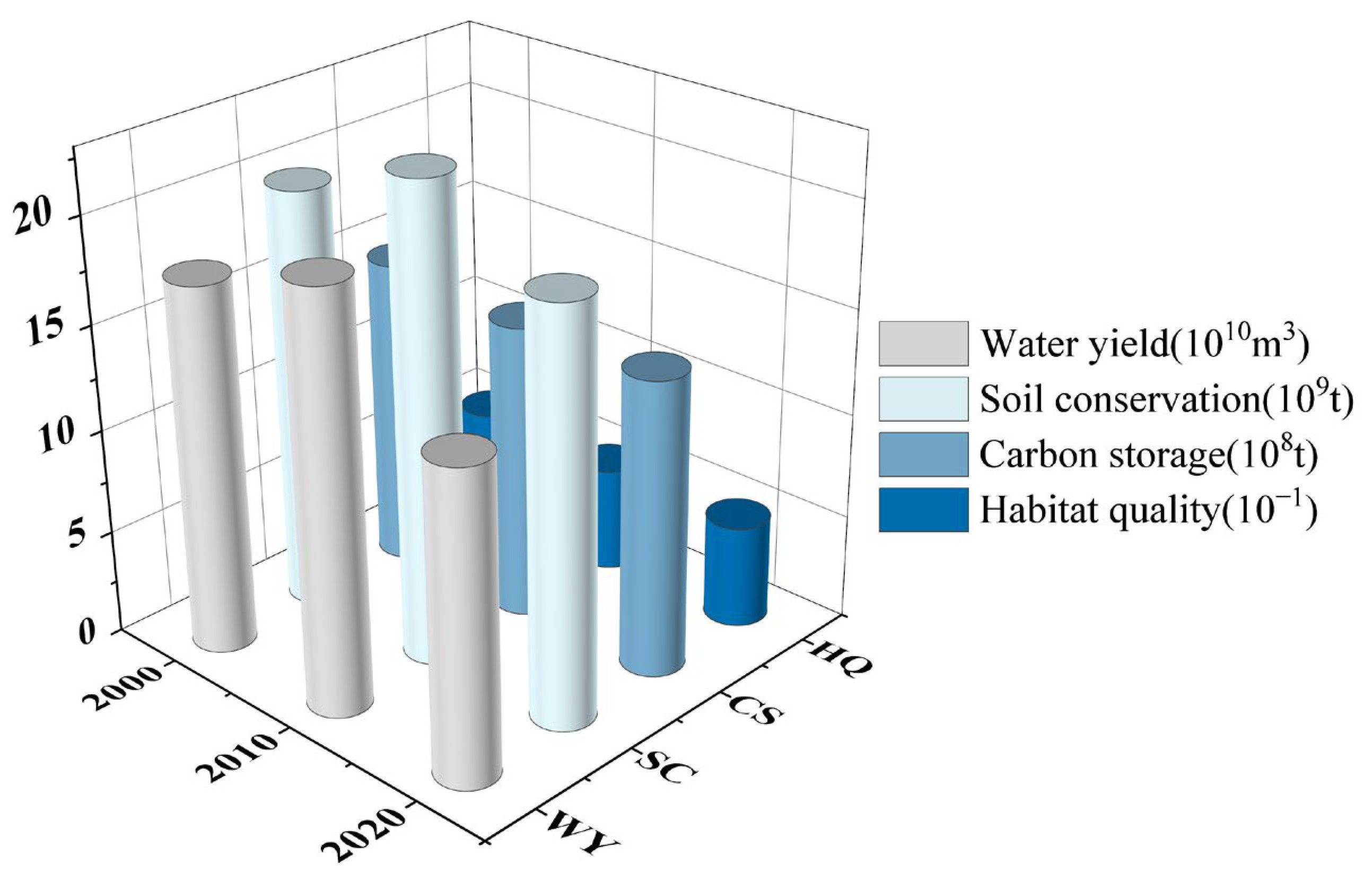
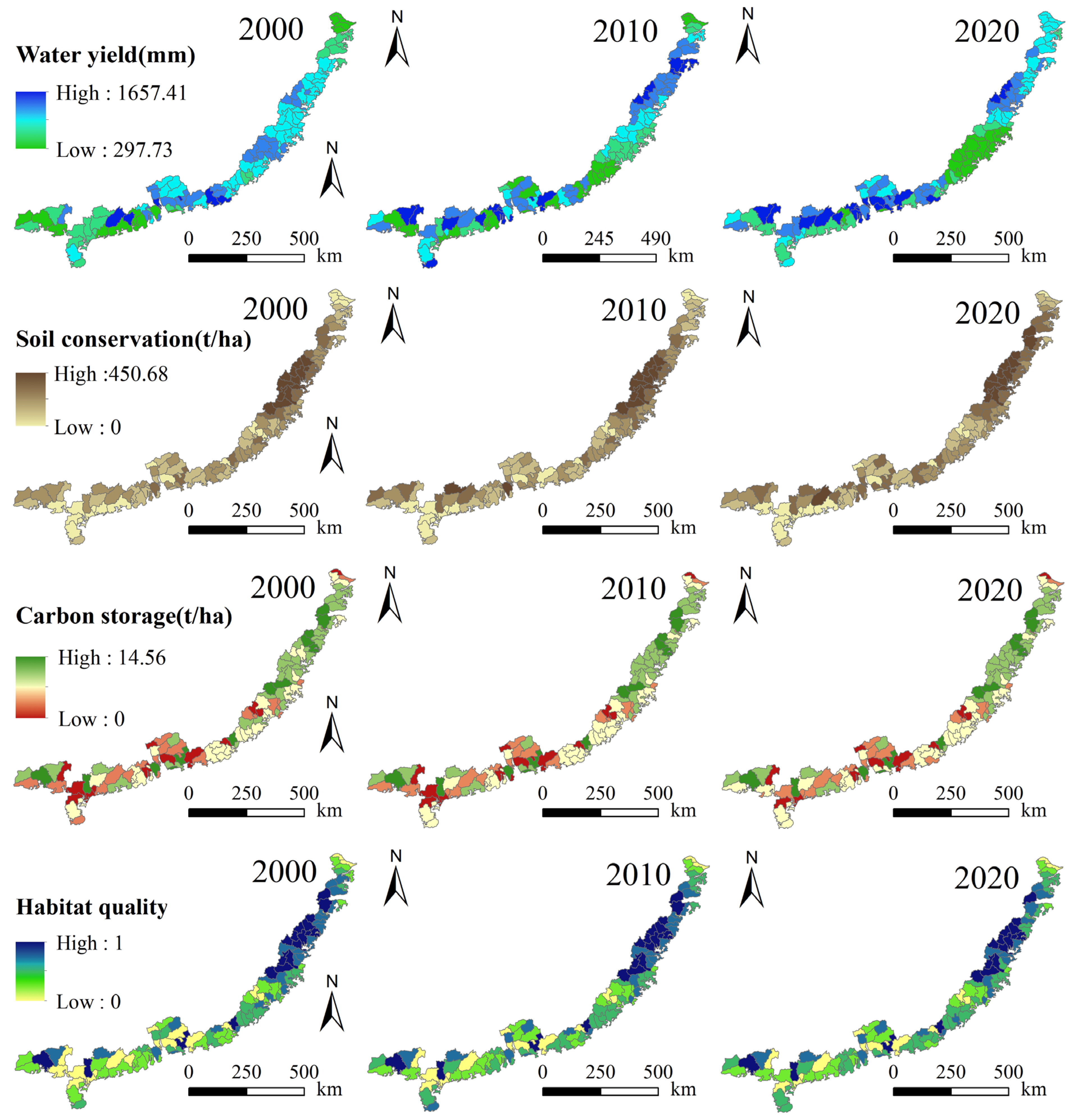
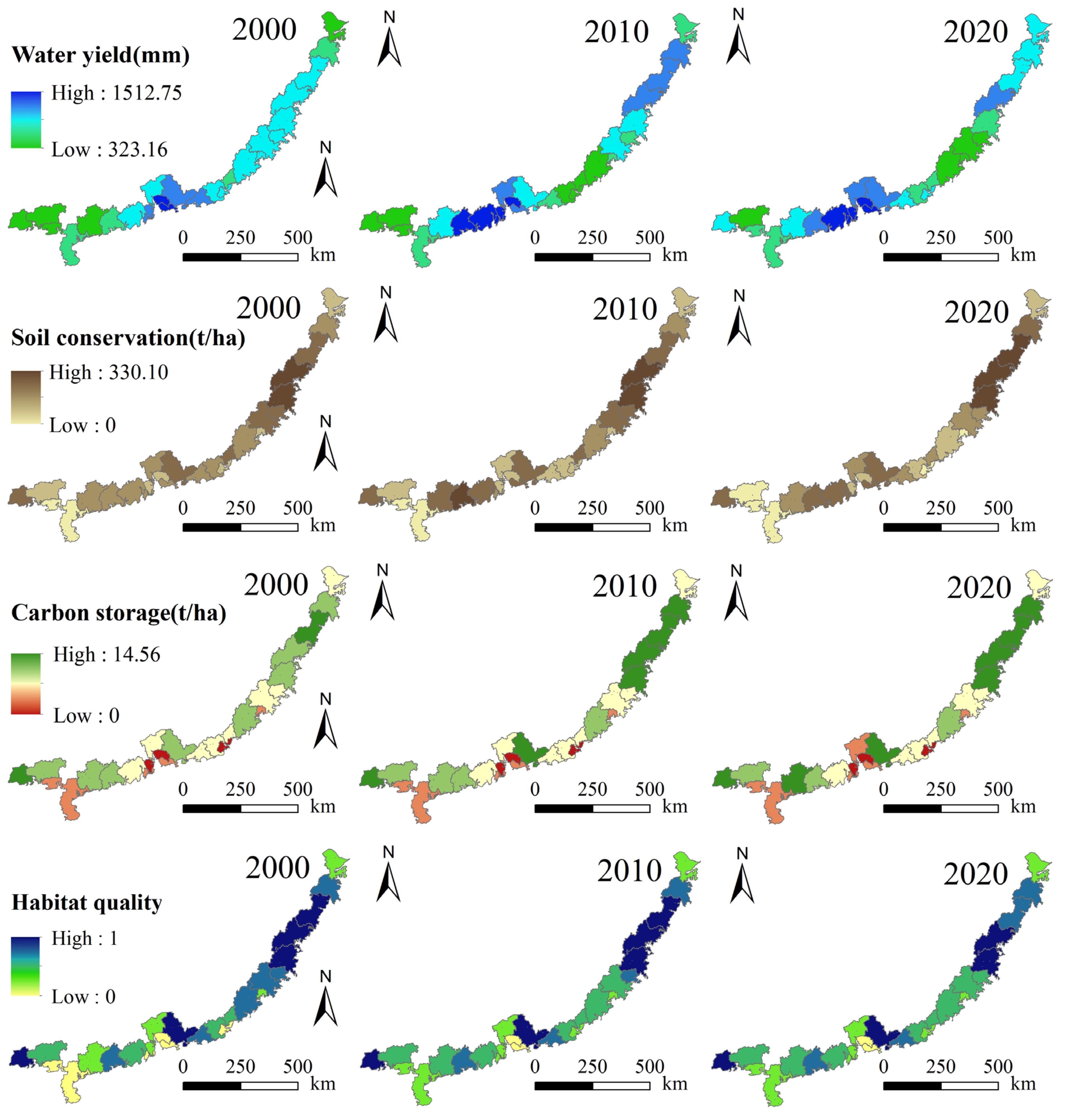
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution Patterns of ESs
3.2. Trade-Offs and Synergistic Relationships in ESs
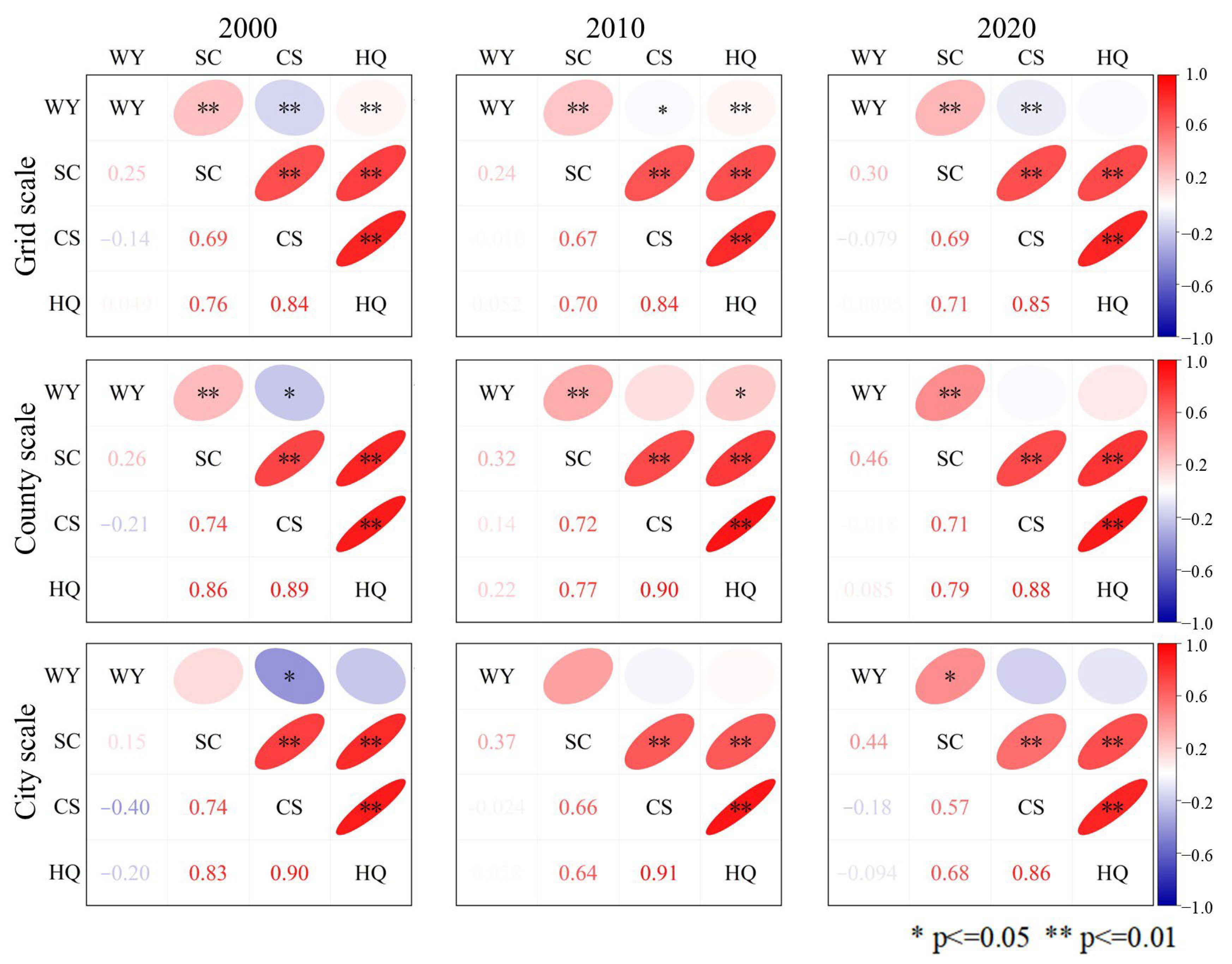
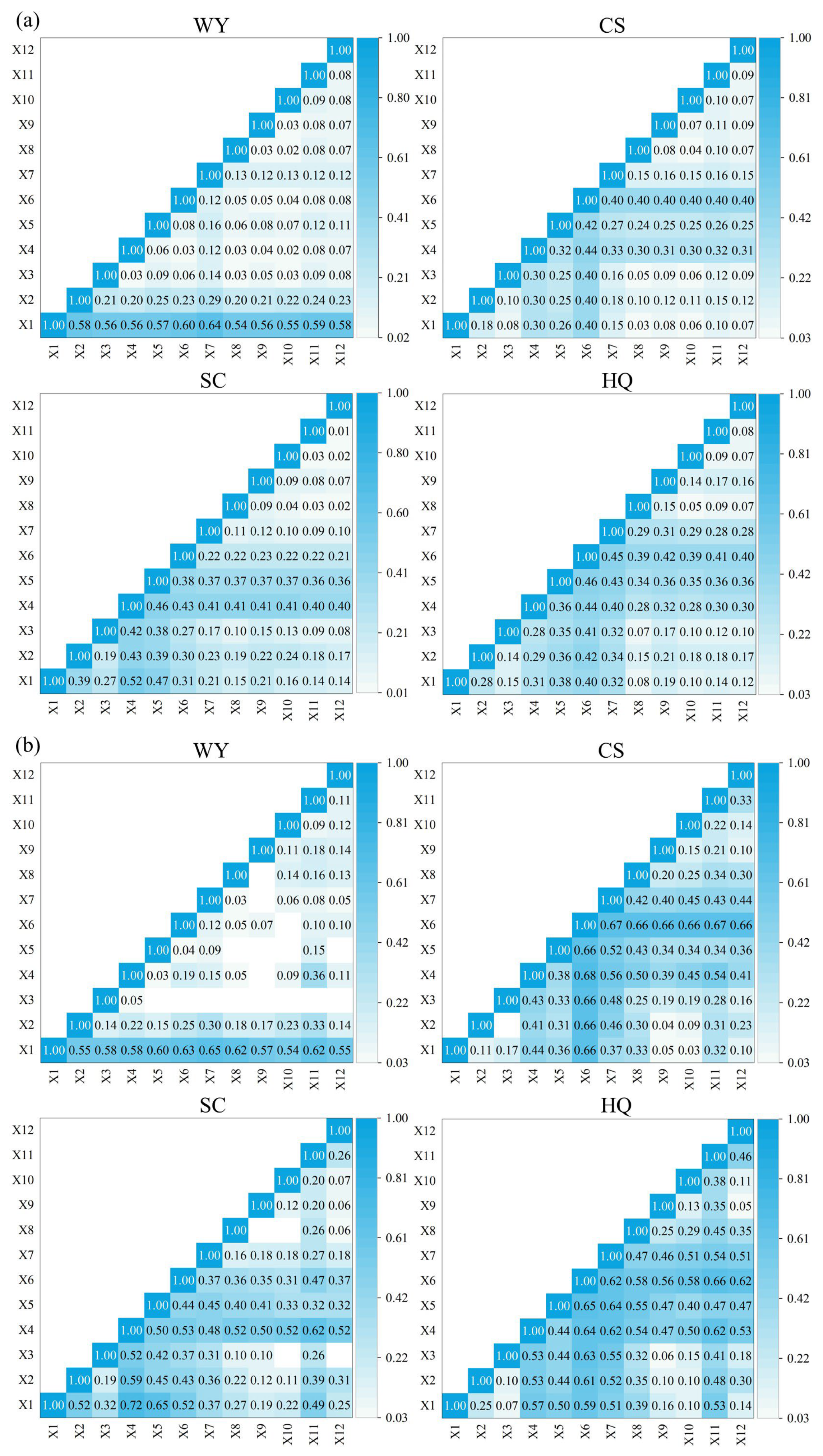
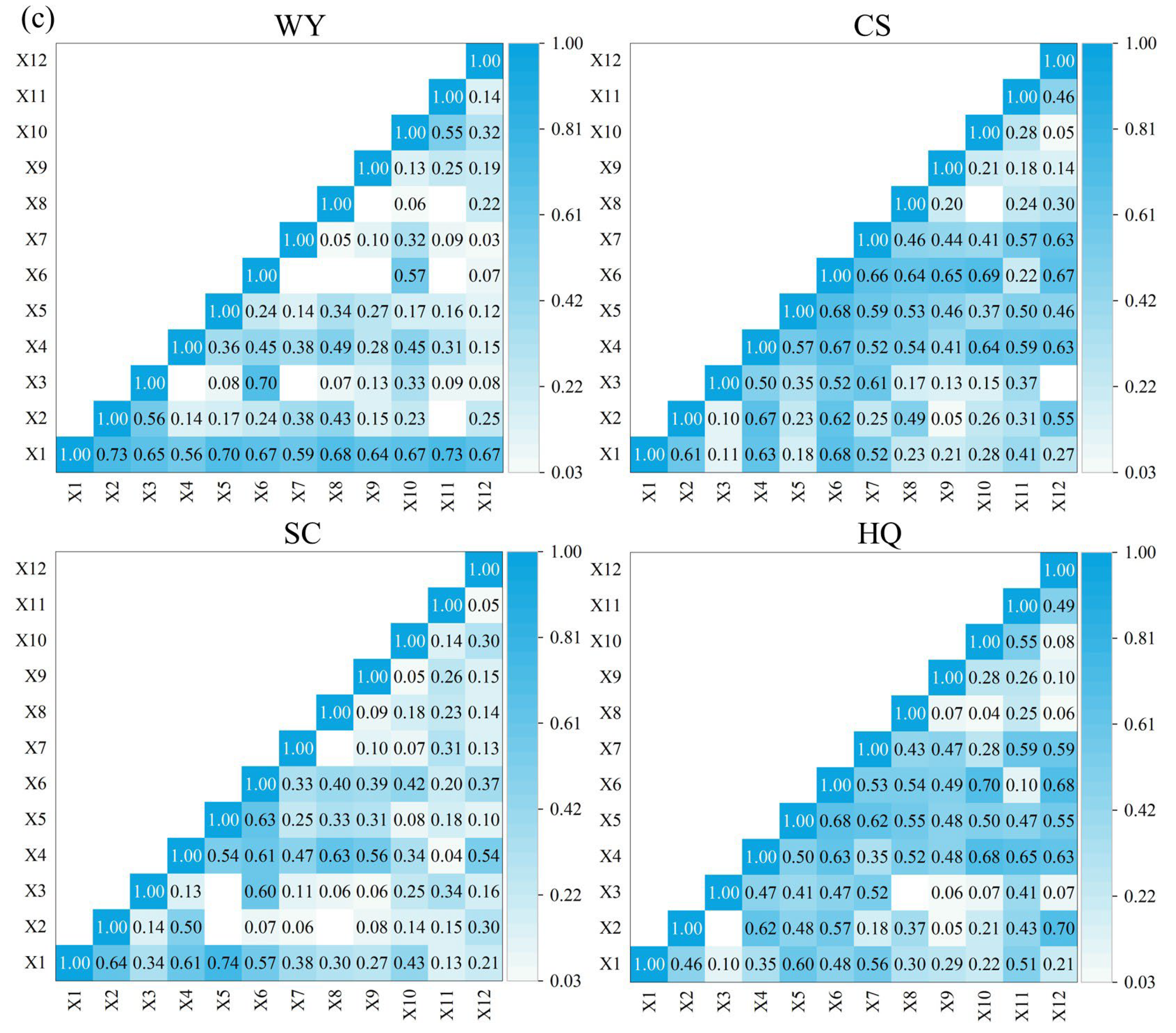
3.2.1. Spearman’s Correlation Coefficients Among ESs
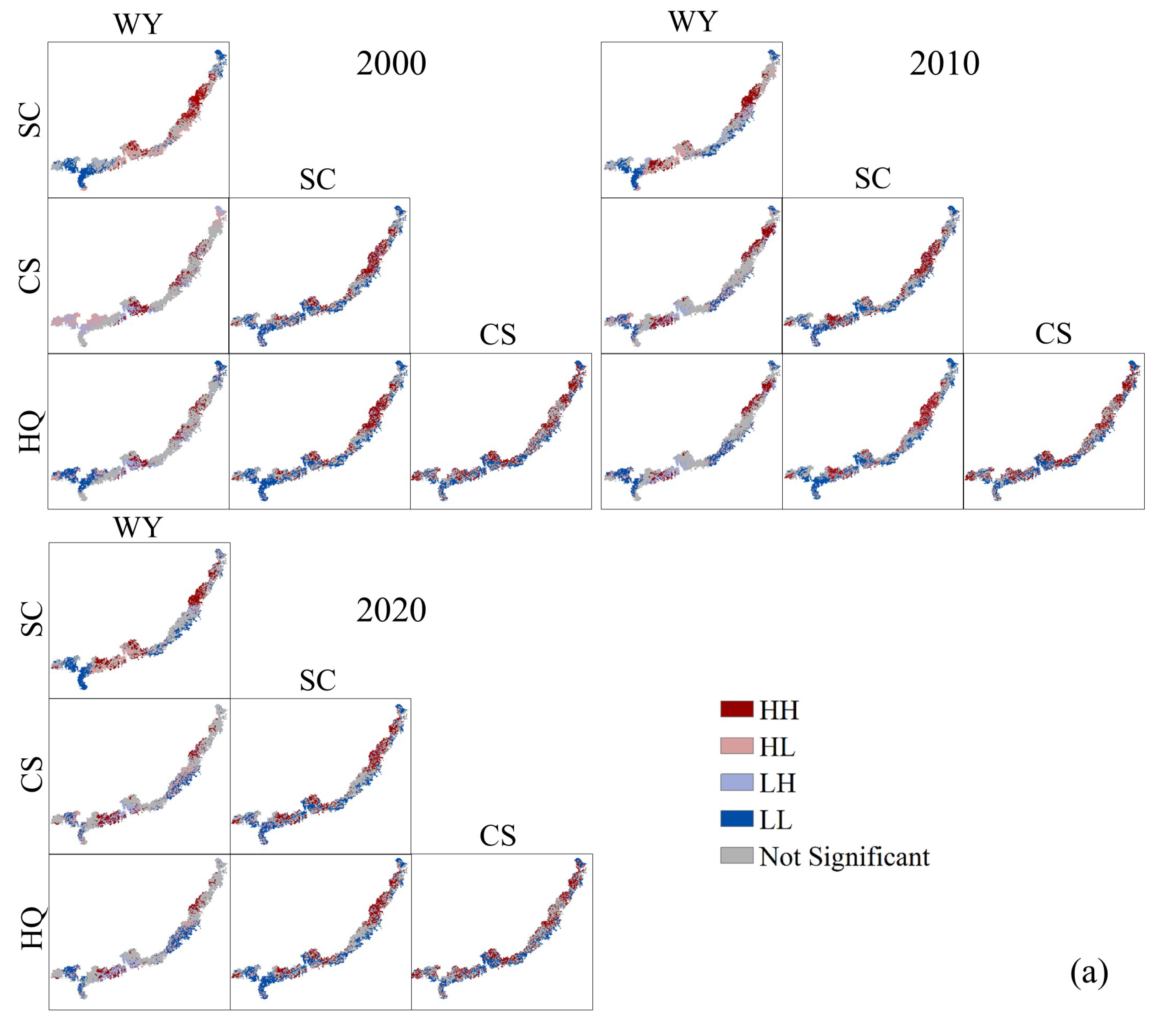
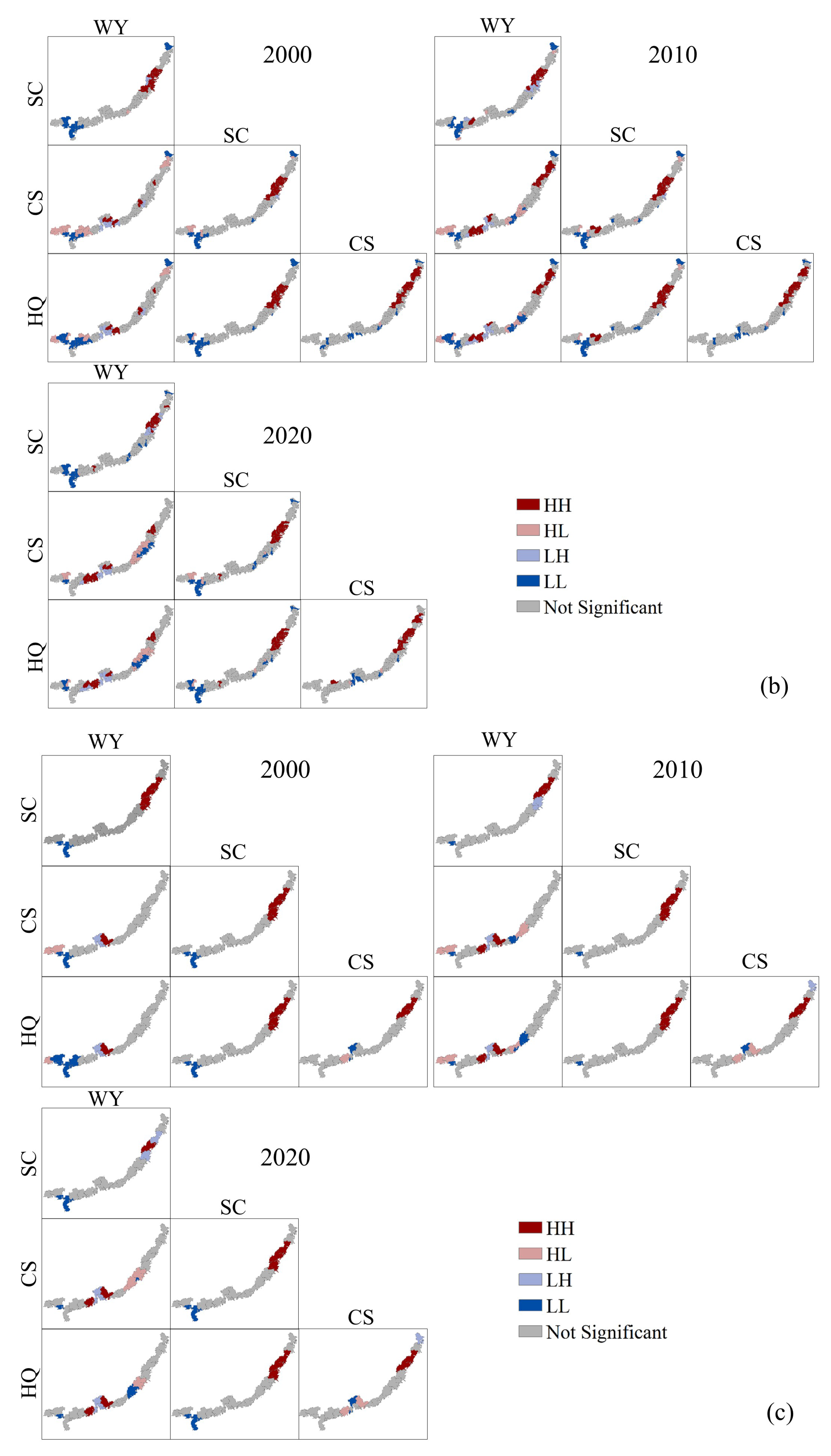
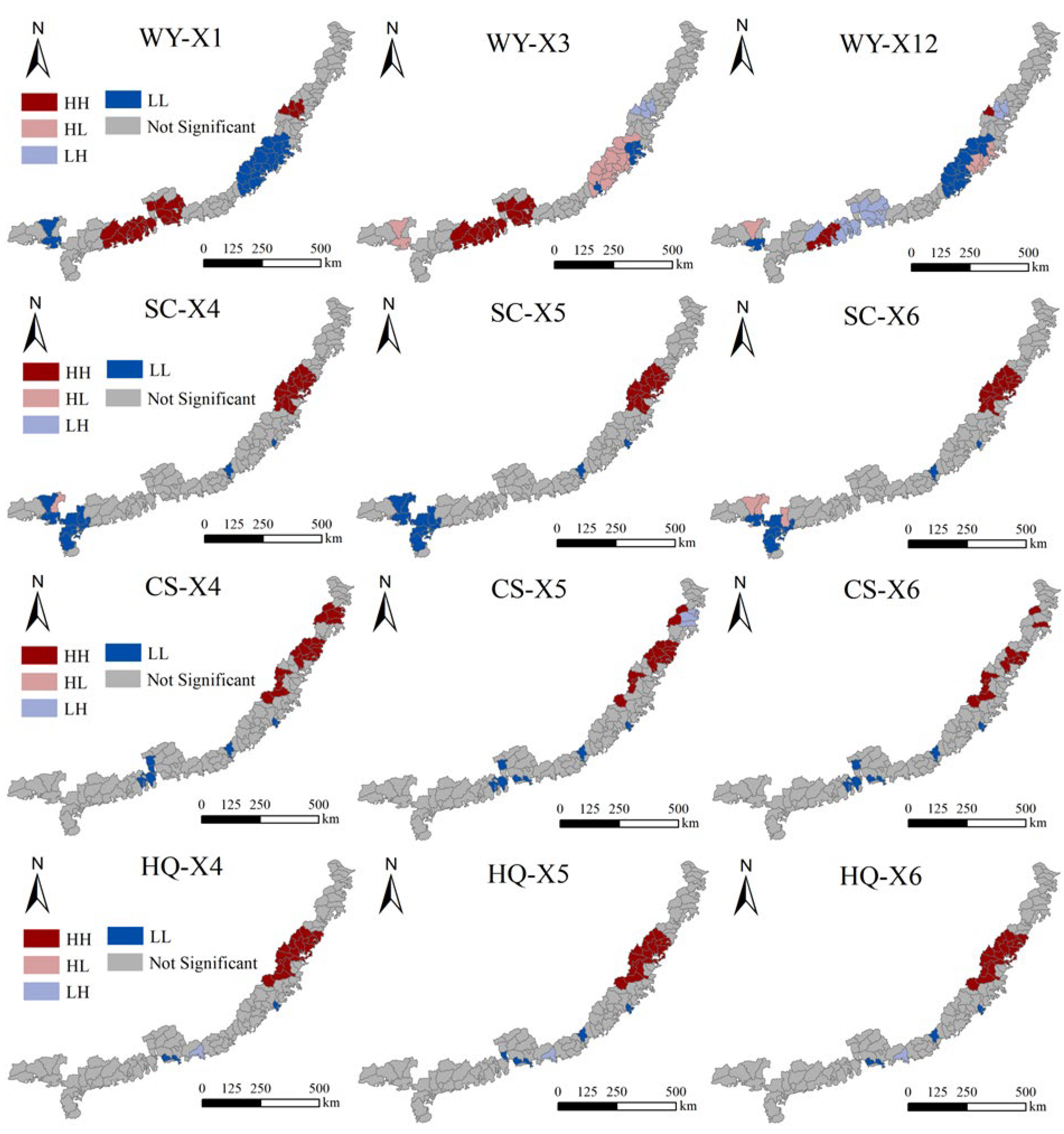
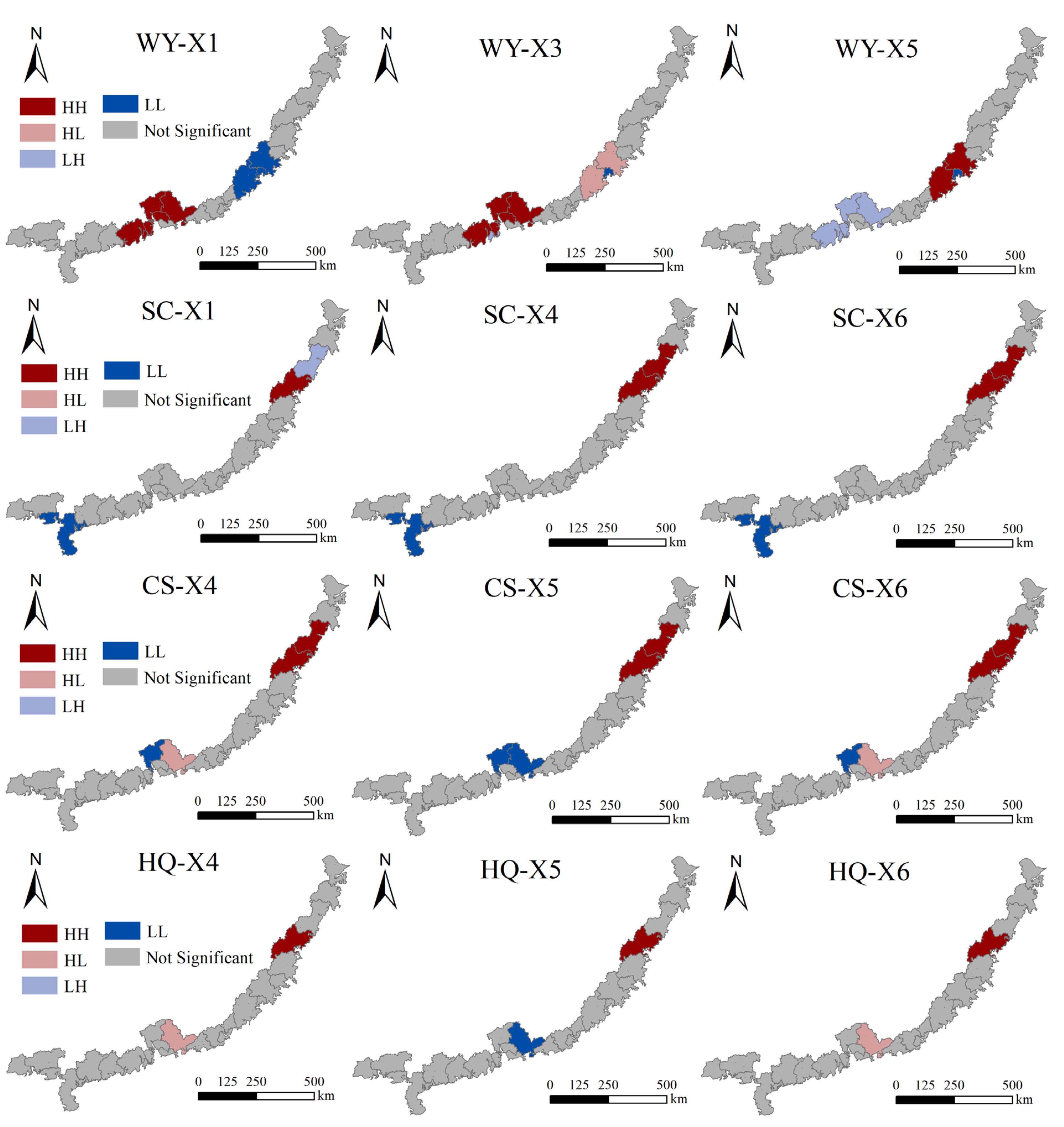
3.2.2. Multiscale Spatial Agglomeration Characteristics of ESs
3.3. Driving Factors Analysis of ESs
3.3.1. Impact of Individual Factors on ESs
3.3.2. Effects of Multifactor Interactions on ESs
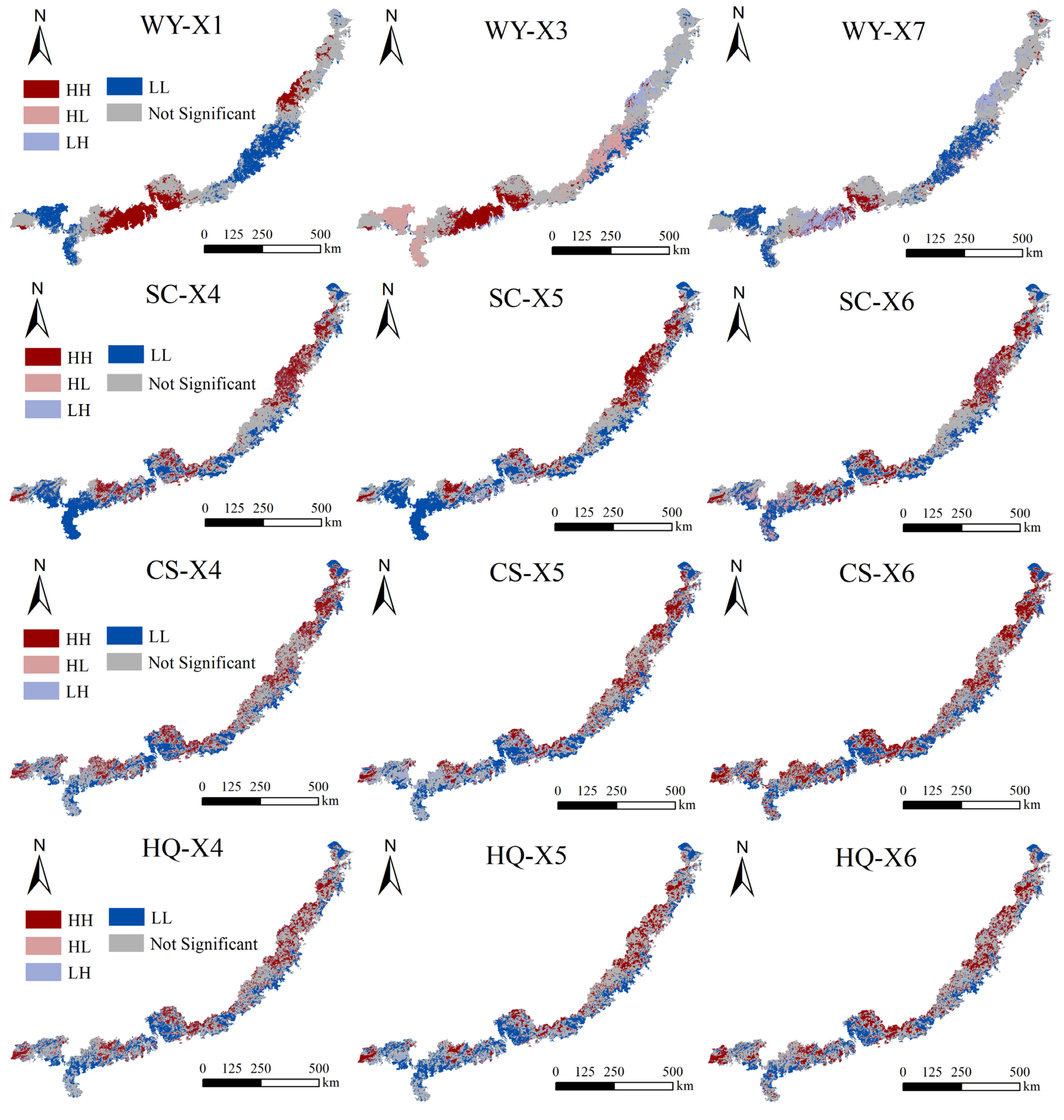
3.4. Spatial Interaction Between ESs and Different Drivers
4. Discussion
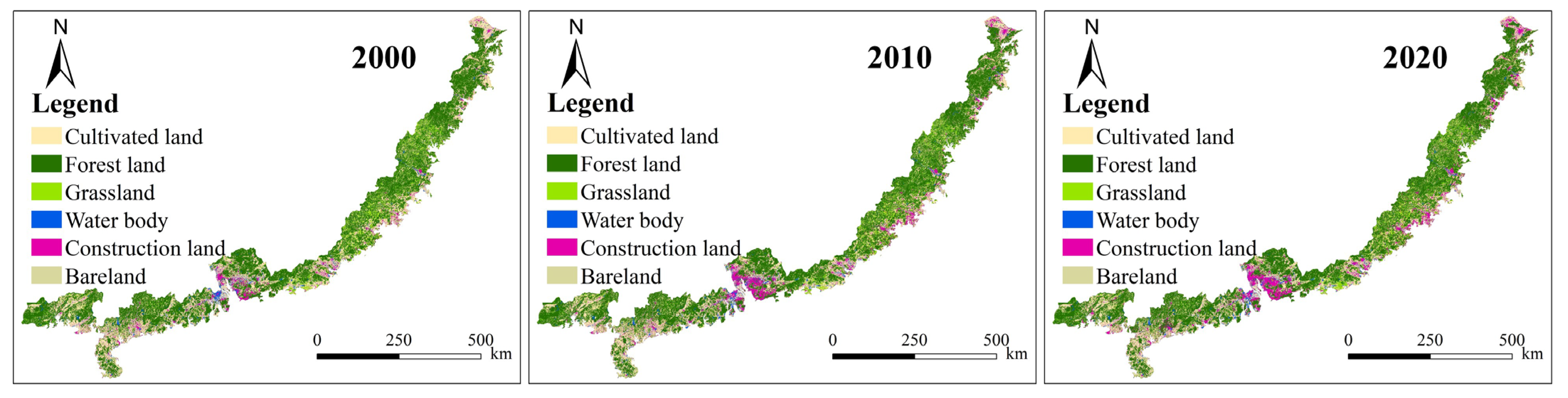
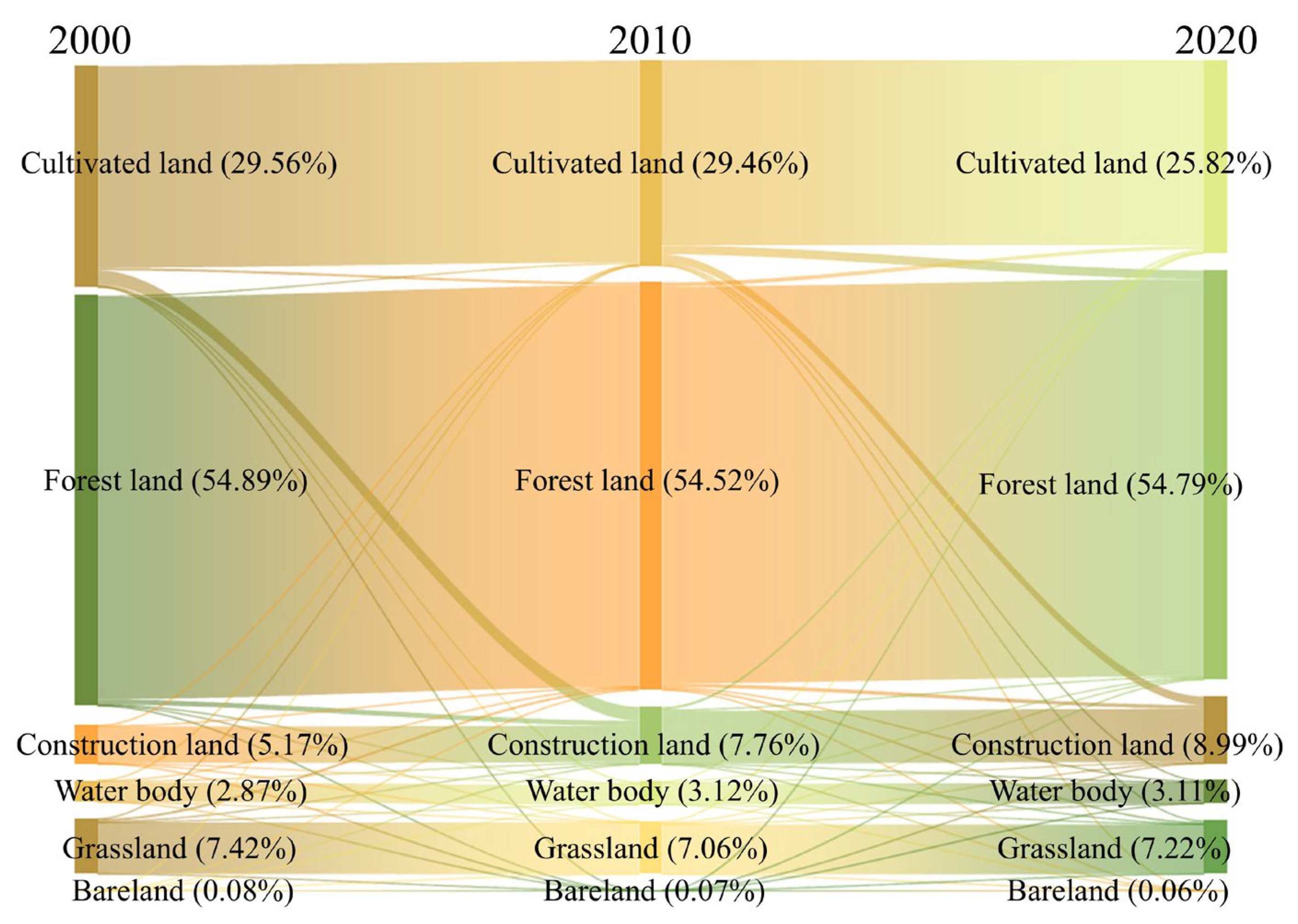
4.1. Spatiotemporal Interactions of LULC Changes with Changes in ESs
4.2. Scale Effects of Ecosystem Services and Ecosystem Services Trade-Offs and Synergies
4.3. Spatial Heterogeneity Attribution of Driving Factors for ESs
4.4. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Among the four ESs assessed in this study, three (excluding water yield) exhibited a spatial pattern of increasing provision from coastal to inland areas. All four ESs demonstrated significant scale dependency in their spatial distributions, with clustering intensity notably strengthening as the analytical scale expanded from grid to city level.
- (2)
- Synergistic relationships dominated the interactions among ESs, with correlation strength generally intensifying at larger spatial scales. The strongest functional connections were consistently observed at the county scale.
- (3)
- Natural factors were identified as the dominant drivers of ES patterns, exhibiting greater influence than anthropogenic factors. The explanatory power of both driver categories increased with spatial scale. From an interaction perspective, interactions between factors of the same type generally yielded stronger explanatory power than any single factor. Furthermore, interactions between anthropogenic and natural factors significantly enhanced the explanatory power of individual anthropogenic factors.
- (4)
- The spatial aggregation patterns between ESs and their driving factors varied considerably across different drivers. However, for any given driver, its spatial association with a specific ES remained highly consistent across different spatial scales, demonstrating remarkable pattern stability.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cochran, F.; Daniel, J.; Jackson, L.; Neale, A. Earth observation-based ecosystem services indicators for national and subnational reporting of the sustainable development goals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 244, 111796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Li, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Weng, A.; Jin, Y.; Cai, G.; Lin, Y.; Chen, B. Exploring the evolution of coupled natural-cultural ecosystem services and their geographically scaled driven modeling in a coastal city of Southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 361, 121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Ordóñez, A.; Ramsauer, J.; Coll, L.; Brotons, L.; Ameztegui, A. Ecosystem services provision by Mediterranean forests will be compromised above 2 °C warming. Glob. Chang. Biol 2021, 27, 4210–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahad, S.; Sonmez, O.; Saud, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, C.; Adnan, M.; Turan, V. Sustainable Soil and Land Management and Climate Change; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Brauman, K.A.; Daily, G.C.; Duarte, T.K.e.; Mooney, H.A. The Nature and Value of Ecosystem Services: An Overview Highlighting Hydrologic Services. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2007, 32, 67–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Gu, Y.; Zou, C.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X. Temporal variation and spatial scale dependency of the trade-offs and synergies among multiple ecosystem services in the Taihu Lake Basin of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, F.; Lu, N.; Kou, L. Land use optimization for future ecosystem service demands: A case study in the Yanhe watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 520, 146121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Lei, G. Mapping the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service relationships and bundles in Ningxia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Lü, Y.; Chen, W.; Fu, B. Temporal variation and spatial scale dependency of ecosystem service interactions: A case study on the central Loess Plateau of China. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1201–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, M.; Lin, H.; Qureshi, S.; Cao, A.; Ma, Y. Understanding the dynamics and factors affecting cultural ecosystem services during urbanization through spatial pattern analysis and a mixed-methods approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, B. Scale effects on the relationships between land characteristics and ecosystem services- a case study in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusi, K.K.; Khattabi, A.; Mhammdi, N.; Lahssini, S. Prospective evaluation of the impact of land use change on ecosystem services in the Ourika watershed, Morocco. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Che, X.; Wang, Z. Exploring new methods for assessing landscape ecological risk in key basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 461, 142633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Jiang, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, E.; Guo, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J. Understanding scale effects and differentiation mechanisms of ecosystem services tradeoffs and synergies relationship: A case study of the Lishui River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, H. Trade-off/synergistic changes in ecosystem services and geographical detection of its driving factors in typical karst areas in southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Zhang, Q.; Joshi, P.K.; Sutton, P.C.; Keesstra, S.; Roy, P.S.; Pilla, F.; Basu, B.; Wang, Y.; Jha, S.; et al. Examining effects of climate change and land use dynamic on biophysical and economic values of ecosystem services of a natural reserve region. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.; Clarke, K.C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J.; Jia, X.; Li, J. Spatial correlations among ecosystem services and their socio-ecological driving factors: A case study in the city belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia, China. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 108, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhao, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, C. Ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies relationships and their driving factor analysis based on the Bayesian belief Network: A case study of the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y. Spatio-temporal variation of ecosystem services and the response to urbanization: Evidence based on Shandong province of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landuyt, D.; Broekx, S.; Goethals, P.L.M. Bayesian belief networks to analyse trade-offs among ecosystem services at the regional scale. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, Y.; Hao, S.; Xu, W.; Lv, L.; Yu, S. Spatial-temporal variation and tradeoffs/synergies analysis on multiple ecosystem services: A case study in the Three-River Headwaters region of China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cord, A.F.; Bartkowski, B.; Beckmann, M.; Dittrich, A.; Hermans-Neumann, K.; Kaim, A.; Lienhoop, N.; Locher-Krause, K.; Priess, J.; Schröter-Schlaack, C.; et al. Towards systematic analyses of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: Main concepts, methods and the road ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Zang, F. The trade-offs and synergies of the ecological-production-living functions of grassland in the Qilian mountains by ecological priority. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 327, 116883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Z.; Asiedu Kumi, M. Multi-Scale Analysis of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs/Synergies in the Yangtze River Delta. Land 2024, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, D.; Jing, W.; Rong, T. Analyzing spatio-temporal changes and trade-offs/synergies among ecosystem services in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P. Scale effect and spatially explicit drivers of interactions between ecosystem services—A case study from the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 785, 147389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi Mashizi, A.; Sharafatmandrad, M. Management of soil-related ecosystem services in semi-arid regions of Iran using key environmental drivers. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 381, 125181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Marinello, F. Exploration of eco-environment and urbanization changes in coastal zones: A case study in China over the past 20 years. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, W.; Gong, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, W.; Ren, H. Exploring ecosystem responses to coastal exploitation and identifying their spatial determinants: Re-orienting ecosystem conservation strategies for landscape management. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Identification of land use conflicts in China’s coastal zones: From the perspective of ecological security. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 213, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kumar, S.; Ye, Z. Exploring the interaction and driving factors of urban compactness and carbon emission intensity in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wu, S.; Xu, X. An Overview of China’s Regional Development and Overall Pattern. In The Great Change in the Regional Economy of China under the New Normal; Song, X., Wu, S., Xu, X., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Hou, Y.; Xue, X. Ecosystem service multifunctionality assessment and coupling coordination analysis with land use and land cover change in China’s coastal zones. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 797, 149033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Teng, Y.; Chu, X.; Kumi, M.A. Spatio-temporal variations of ecosystem services and their drivers in the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wei, S.; Li, Z. Spatiotemporal pattern of trade-offs and synergistic relationships among multiple ecosystem services in an arid inland river basin in NW China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R. The erosion-productivity impact calculator (EPIC) model: A case history. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1990, 329, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Chen, J.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J. Assessment of coordinative relationship between comprehensive ecosystem service and urbanization: A case study of Yangtze River Delta urban Agglomerations, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Soriano, C.; García-Llorente, M.; Norström, A.; Meacham, M.; Peterson, G.; Castro, A.J. Integrating supply and demand in ecosystem service bundles characterization across Mediterranean transformed landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Tian, P.; Wang, Z.; Shen, X. Spatio-temporal evolution of habitat quality in the East China Sea continental coastal zone based on land use changes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Li, M. Constructing Ecological Networks Based on Habitat Quality Assessment: A Case Study of Changzhou, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Jin, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, J. Understanding trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services to support the decision-making in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Wood, S.; Guerry, A.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; et al. InVEST User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project, Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA; The Nature Conservancy: Arlington, VA, USA; World Wildlife Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G.; Donato, D.C.; Romme, W.H. Consequences of spatial heterogeneity for ecosystem services in changing forest landscapes: Priorities for future research. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Lyu, K.; Feng, C.; Yao, L.; Zheng, R. Human Activity-Driven Spatiotemporal Interactions of Ecosystem Services in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region: Insights from Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data and Multi-Scale Analysis. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2025, 28, 100912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Kang, F.; Han, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, Z. Exploring drivers of ecosystem services variation from a geospatial perspective: Insights from China’s Shanxi Province. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Yao, W.; Tu, Y. Exploring the spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem services and influencing factors on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Identifying the impacts of natural and human factors on ecosystem service in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Yuan, S.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: Implications for spatial planning and management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. The spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem services bundles and the social-economic-ecological drivers in the Yellow River Delta region. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorilla, R.S.; Poirazidis, K.; Detsis, V.; Kalogirou, S.; Chalkias, C. Socio-ecological determinants of multiple ecosystem services on the Mediterranean landscapes of the Ionian Islands (Greece). Ecol. Modell. 2020, 422, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, B. Spatial differences of ecosystem services and their driving factors: A comparation analysis among three urban agglomerations in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 725, 138452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, M.; Li, M.; Xia, B. Spatio-temporal changes in ecosystem service value in response to land-use/cover changes in the Pearl River Delta. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Cui, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y. Climate and human activities shaping carbon-water-food interactions: Implications for governance in the Yangtze River Basin and its sub-basins, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ma, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, W. Identifying the trade-offs and synergies of land use functions and their influencing factors of Lanzhou-Xining urban agglomeration in the upper reaches of Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, C.; Xu, G.; Chen, L.; Yang, C. Exploring the relationship and influencing factors of cultivated land multifunction in China from the perspective of trade-off/synergy. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 149, 110171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y. Environmental health risk detection with GeogDetector. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 33, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaojia, H.; Jijun, W.; Xin, W. The scale effect and differentiation mechanism of the relationship between ecosystem services in the grain for green area: A case study of Ansai District. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1791–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Xin, C.; Yang, Y.; Xin, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, K.; Ma, X.; Chen, H. Remote Sensing Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality in Gansu Province and Quantitative Identification of Its Driving Factors. Huanjing Kexue 2025, 46, 3730–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hu, Y.N.; Wu, J. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607-608, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, X.; Ou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Evaluation of Biodiversity Maintenance Capacity in Forest Landscapes: A Case Study in Beijing, China. Land 2023, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Evolution of the Spatiotemporal Pattern of Urban Industrial Land Use Efficiency in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Su, D.; Cao, Y. A multi-scale framework for understanding spatial scale effects on ecosystem service heterogeneity, interactions, drivers and their socio-ecological impact pathways for adaptive management. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 516, 145757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, S. Uncovering the relationships between ecosystem services and social-ecological drivers at different spatial scales in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Su, D.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Fang, X.; Wu, Q.; Cao, Y. Uncovering scale effects on spatial patterns and interactions of multiple cropland ecosystem services. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 6781–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G. Scale effect on spatial patterns of ecosystem services and associations among them in semi-arid area: A case study in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 598, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidi, N.; Spray, C. Ecosystem services bundles: Challenges and opportunities for implementation and further research. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 113001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingxuan, L.; Hong, Z.; Guizhen, H.; Xiaoyu, Z.; Yong, L. Dynamic evolution and driving factors of water conservation service function in the Yellow River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 2761–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, S.; Wen, Y.; Chen, H. Study on the driving factors of ecosystem service value under the dual influence of natural environment and human activities. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, Z.; Yihe, L.; Bojie, F.; Lichang, Y.; Dandan, Y. The effects of vegetation coverage changes on ecosystem service and their threshold in the Loess Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Fang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, G. A systematic coupling analysis framework and multi-stage interaction mechanism between urban land use efficiency and ecological carrying capacity. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 853, 158444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.H.; Zevenbergen, J.A.; Lengoiboni, M. Urban land use efficiency in Ethiopia: An assessment of urban land use sustainability in Addis Ababa. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Chen, G.; Su, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, C. Ecological management zoning based on static and dynamic matching characteristics of ecosystem services supply and demand in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 448, 141599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Type | Resolution | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| LULC data | Raster | 30 m | Resources and Environmental Sciences and Data Centre, Chinese Academy of Sciences (RESDC) (https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 12 June 2024) |
| River networks data | |||
| Reserve data | |||
| GDP | |||
| Population | |||
| Precipitation data | Raster | 1 km | National Tibetan Plateau Science Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/, accessed on 5 July 2024) |
| Temperature data | Raster | 1 km | |
| Evapotranspiration data | Raster | 1 km | |
| DEM | Raster | 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 21 June 2024) |
| Soil data | Raster | 1 km | Harmonized World Soil Database (https://www.fao.org/, accessed on 30 June 2024) |
| ESs | Calculation Methods | Calculation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Water yield | InVEST Model Water Yield Module | where is the actual evapotranspiration of grid cell ; is the rainfall of grid cell [34]. |
| Soil conservation | InVEST Model Soil Conservation Module | where and representing the potential erosion amount and the actual erosion. is the rainfall erosion factor. is the soil erodibility factor. is the slope length factor. is the vegetation cover and management factor. is the soil and water conservation factor [35,36,37]. |
| Carbon storage | InVEST Model Carbon Module | is aboveground biogenic carbon stock. is belowground biogenic carbon stock. is soil carbon stock. is dead organic carbon stock [38,39]. |
| Habitat quality | InVEST Model Habitat Quality Module | where is the habitat suitability, which takes a value between 0 and 1; is the habitat degradation of grid in ; is the normalization constant, which takes a value of 2.5 [40]; and is the half-saturation constant, which is usually half the maximum value of habitat degradation [41,42]. |
| Types | Driving Factors | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Natural factors | Mean annual precipitation (X1) | [45] |
| Mean annual temperature (X2) | ||
| Mean annual evapotranspiration (X3) | [46] | |
| Slope (X4) | [47] | |
| DEM (X5) | [48] | |
| Human factors | Proportion of forest (X6) | [49] |
| Proportion of construction (X7) | ||
| POP (X8) | [50] | |
| GDP (X9) | [51] | |
| Accessibility factors | Distance from rivers (X10) | [52] |
| Distance from roads (X11) | ||
| Distance from reserve (X12) |
| Judgments Based | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Weaken, nonlinear | |
| Weaken, uni- | |
| Enhance, bi- | |
| Independent | |
| Enhance, nonlinear |
| q Value | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WY | grid | 0.720 | 0.017 | 0.272 | 0.021 | 0.055 | 0.040 | 0.160 | 0.088 | 0.038 | 0.003 | 0.019 | 0.003 |
| county | 0.775 | 0.001 | 0.331 | 0.180 | 0.158 | 0.153 | 0.042 | 0.089 | 0.111 | 0.103 | 0.169 | 0.213 | |
| city | 0.909 | 0.150 | 0.491 | 0.212 | 0.590 | 0.408 | 0.154 | 0.143 | 0.283 | 0.250 | 0.433 | 0.070 | |
| SC | grid | 0.214 | 0.301 | 0.145 | 0.654 | 0.531 | 0.383 | 0.158 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.020 | 0.109 | 0.029 |
| county | 0.334 | 0.078 | 0.059 | 0.680 | 0.909 | 0.586 | 0.368 | 0.187 | 0.047 | 0.032 | 0.349 | 0.082 | |
| city | 0.407 | 0.158 | 0.148 | 0.759 | 0.352 | 0.654 | 0.306 | 0.067 | 0.056 | 0.131 | 0.363 | 0.023 | |
| CS | grid | 0.059 | 0.148 | 0.052 | 0.545 | 0.424 | 0.865 | 0.363 | 0.085 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 0.127 | 0.029 |
| county | 0.194 | 0.211 | 0.034 | 0.664 | 0.745 | 0.956 | 0.555 | 0.514 | 0.195 | 0.140 | 0.470 | 0.087 | |
| city | 0.459 | 0.431 | 0.299 | 0.823 | 0.791 | 0.970 | 0.625 | 0.568 | 0.462 | 0.127 | 0.710 | 0.180 | |
| HQ | grid | 0.069 | 0.163 | 0.081 | 0.466 | 0.395 | 0.592 | 0.363 | 0.076 | 0.024 | 0.016 | 0.159 | 0.028 |
| county | 0.203 | 0.190 | 0.011 | 0.639 | 0.728 | 0.778 | 0.596 | 0.477 | 0.173 | 0.082 | 0.544 | 0.053 | |
| city | 0.410 | 0.342 | 0.143 | 0.695 | 0.721 | 0.841 | 0.595 | 0.322 | 0.373 | 0.096 | 0.688 | 0.096 | |
| Land Use and Land Cover Type (km2) | Cultivated Land | Forest | Grassland | Water Body | Construction Land | Bareland | Sum (2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 43,117 | 2517.1 | 434.8 | 766.9 | 5129 | 2.9 | 51,967.7 |
| Forest | 1178.6 | 92,443.9 | 699.7 | 294.3 | 1872.1 | 6.1 | 96,494.7 |
| Grassland | 207.7 | 951.1 | 11,471.5 | 61.2 | 362.4 | 2.5 | 13,056.4 |
| Water body | 248 | 142.9 | 36.6 | 4149.7 | 463.5 | 1.5 | 5042.2 |
| Construction land | 632.5 | 254.2 | 45.9 | 202.2 | 7960.7 | 0.3 | 9095.8 |
| Bareland | 4.4 | 6.2 | 9.7 | 6.8 | 14.4 | 99.9 | 141.4 |
| Sum (2000) | 45,388.2 | 96,315.4 | 12,698.2 | 5481.1 | 15,802.1 | 113.2 | 17,5798.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Fu, X.; Huang, J.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y. Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and Detection of Their Driving Mechanisms in Southeast Coastal China. Land 2025, 14, 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112101
Zhang H, Fu X, Huang J, Xu Z, Wu Y. Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and Detection of Their Driving Mechanisms in Southeast Coastal China. Land. 2025; 14(11):2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112101
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoran, Xin Fu, Jin Huang, Zhenghe Xu, and Yu Wu. 2025. "Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and Detection of Their Driving Mechanisms in Southeast Coastal China" Land 14, no. 11: 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112101
APA StyleZhang, H., Fu, X., Huang, J., Xu, Z., & Wu, Y. (2025). Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and Detection of Their Driving Mechanisms in Southeast Coastal China. Land, 14(11), 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112101








