Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Different Genera, Host Plants, and Climates: Influence of Soil pH on Plant Growth and Biochemistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Phosphate-Solubilizing Capacity
2.3. Greenhouse Experiment
2.4. Plant Macronutrients
2.5. Physiological and Biochemical Parameters
2.5.1. Photosynthetic Pigments
2.5.2. Anthocyanins
2.5.3. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, Metabolic Activity, Carbohydrates, and Oxidative Damage
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
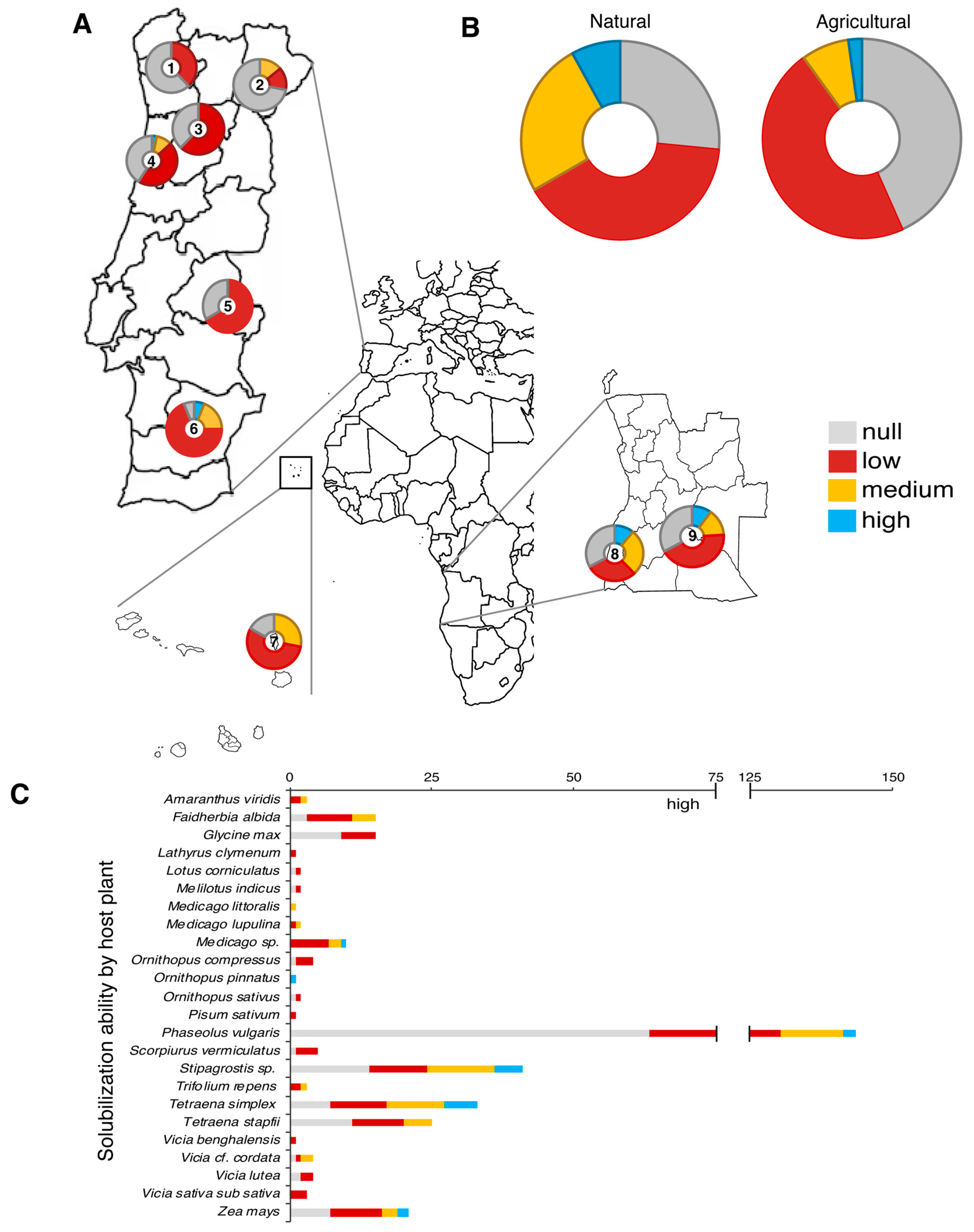
3.1. Ability of Strains to Solubilize Phosphate
3.1.1. Prospecting of PSB Across Distinct Climate Zones
3.1.2. Soil Use and Solubilization Ability
3.1.3. Host Plant and Bacterial Ability to Solubilize P
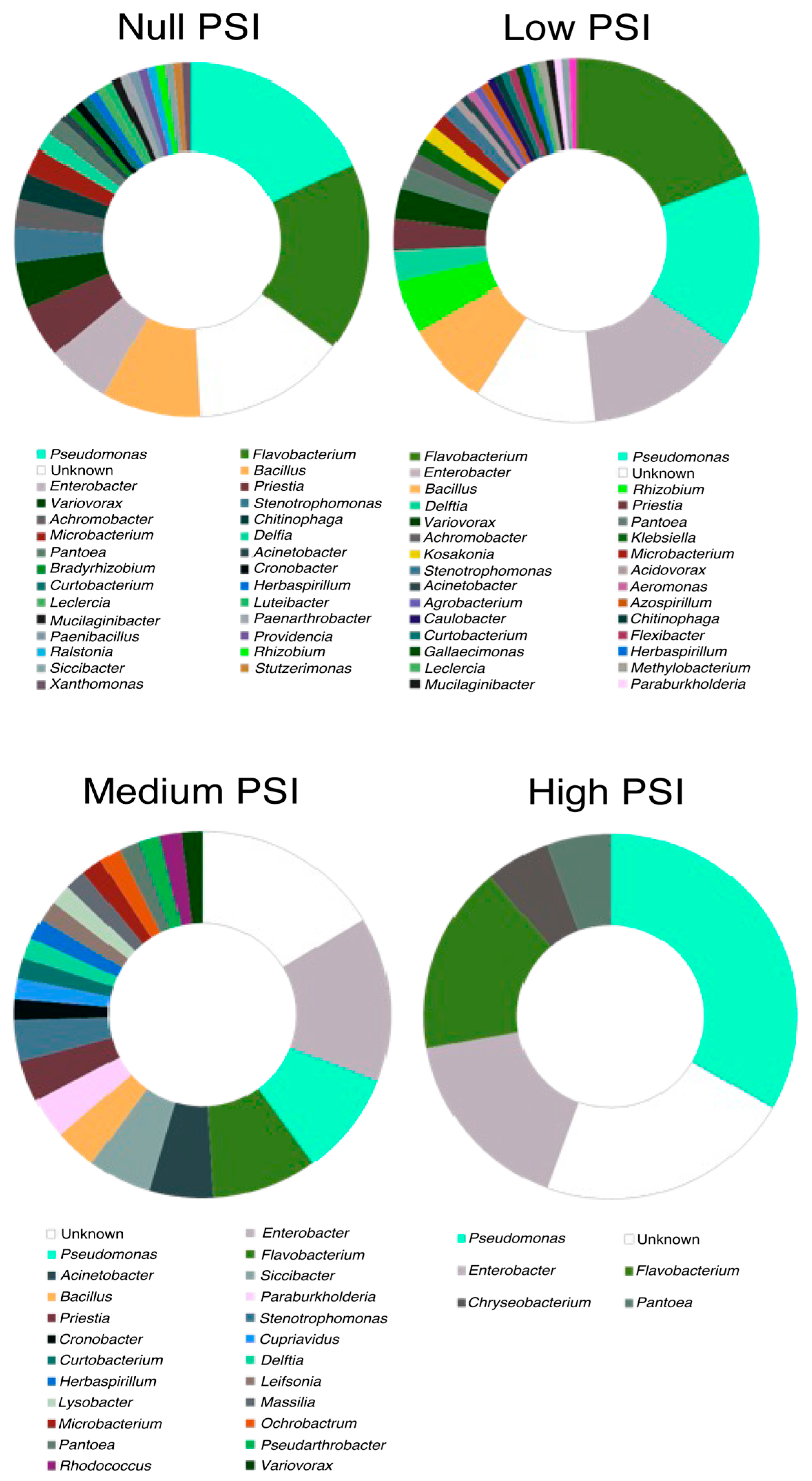
3.1.4. Solubilization per Bacterial Genus
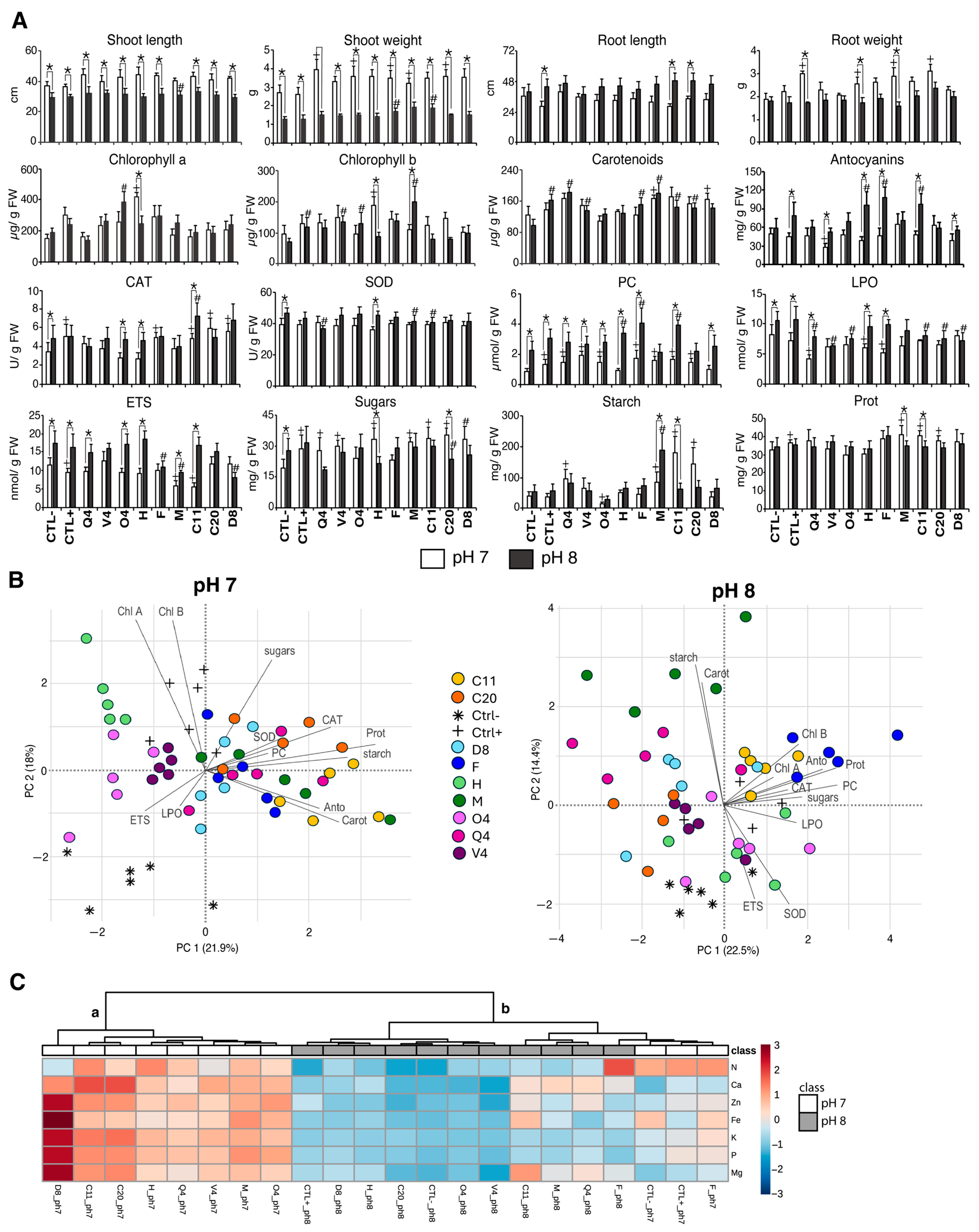
3.2. Influence of PSB on Maize Plants at Two pH Levels
3.2.1. Growth and Biochemistry
3.2.2. Principal Components Analysis
3.2.3. Nutrients
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Soil Type and Land Use on PSB Functional Capacity
4.2. Influence of PSB on Maize Plant Development at Two pH Levels
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Market Research Future. Microbial Inoculant Market Size, Share, Growth | Report, 2034, September 2025. Available online: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com/reports/microbial-inoculant-market-34924 (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- O’Callaghan, M.; Ballard, R.A.; Wright, D. Soil Microbial Inoculants for Sustainable Agriculture: Limitations and Opportunities. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 1340–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargaz, A.; Elhaissoufi, W.; Khourchi, S.; Benmrid, B.; Borden, K.A.; Rchiad, Z. Benefits of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria on Belowground Crop Performance for Improved Crop Acquisition of Phosphorus. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 252, 126842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtaoui, N.; Rabiu, M.K.; Raklami, A.; Oufdou, K.; Hafidi, M.; Jemo, M. Phosphate-Dependent Regulation of Growth and Stresses Management in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 679916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalayu, G. Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganisms: Promising Approach as Biofertilizers. Int. J. Agron. 2019, 2019, 4917256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Oburger, E. Solubilization of Phosphorus by Soil Microorganisms. In Phosphorus in Action: Biological Processes in Soil Phosphorus Cycling; Bünemann, E., Oberson, A., Frossard, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 169–198. ISBN 978-3-642-15271-9. [Google Scholar]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes That Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, C.P.; Uhde-Stone, C.; Allan, D.L. Phosphorus Acquisition and Use: Critical Adaptations by Plants for Securing a Non-renewable Resource. New Phytol. 2003, 157, 423–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojórquez-Quintal, E.; Escalante-Magaña, C.; Echevarría-Machado, I.; Martínez-Estévez, M. Aluminum, a Friend or Foe of Higher Plants in Acid Soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, C.; Selvakumar, G.; Ganeshamurthy, A.N. Acid Tolerant Microbial Inoculants: A Requisite for Successful Crop Production in Acidic Soils. In Phyto and Rhizo Remediation; Arora, N.K., Kumar, N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 235–247. ISBN 978-981-329-664-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Shi, D.; Wang, D. Comparative Effects of Salt and Alkali Stresses on Growth, Osmotic Adjustment and Ionic Balance of an Alkali-Resistant Halophyte Suaeda glauca (Bge.). Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 56, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, W.S.; Fujimori, M.; Tase, K.; Sugiyama, S. Oxidative Stress and Physiological Damage under Prolonged Heat Stress in C3 Grass Lolium perenne. Grassl. Sci. 2011, 57, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, W.S.; Fujimori, M.; Tase, K.; Sugiyama, S. Heat Tolerance and Suppression of Oxidative Stress: Comparative Analysis of 25 Cultivars of the C3 Grass Lolium perenne. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 78, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Das, S.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Phosphate-Solubilizing Microorganisms: Mechanism and Their Role in Phosphate Solubilization and Uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.I.; Pereira, M.C.; de Carvalho, A.M.X.; Buttrós, V.H.; Pasqual, M.; Dória, J. Phosphorus-Solubilizing Microorganisms: A Key to Sustainable Agriculture. Agriculture 2023, 13, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, J.; Xing, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Deng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, P.; Li, Z. Chapter Three—The Effects of Mulch and Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Soil Environment of Crop Plants. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 153, pp. 121–173. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, C.; Cardoso, P.; Santos, J.; Matos, D.; Figueira, E. Bioprospecting Soil Bacteria from Arid Zones to Increase Plant Tolerance to Drought: Growth and Biochemical Status of Maize Inoculated with Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Isolated from Sal Island, Cape Verde. Plants 2022, 11, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, C.; Cardoso, P.; Santos, J.; Matos, D.; Sá, C.; Figueira, E. Application of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria from Cape Verde to Increase Maize Tolerance to Salinity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleńska, E.; Małek, W.; Wójcik, M.; Swiecicka, I.; Thijs, S.; Vangronsveld, J. Beneficial Features of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria for Improving Plant Growth and Health in Challenging Conditions: A Methodical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parray, J.A.; Jan, S.; Kamili, A.N.; Qadri, R.A.; Egamberdieva, D.; Ahmad, P. Current Perspectives on Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 35, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejan, P.; Abdullah, R.; Khadiran, T.; Ismail, S.; Nasrulhaq Boyce, A. Role of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria in Agricultural Sustainability—A Review. Molecules 2016, 21, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuuna, I.A.F.; Prabawardani, S.; Massora, M. Population Distribution of Phosphate-Solubilizing Microorganisms in Agricultural Soil. Microbes Environ. 2022, 37, ME21041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Cai, B. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria: Advances in Their Physiology, Molecular Mechanisms and Microbial Community Effects. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.B.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Trivedi, M.H.; Gobi, T.A. Phosphate Solubilizing Microbes: Sustainable Approach for Managing Phosphorus Deficiency in Agricultural Soils. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, C.; Avice, J.-C.; Laval, K.; Bressan, M. Are Native Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria a Relevant Alternative to Mineral Fertilizations for Crops? Part II: PSB Inoculation Enables a Halving of P Input and Improves the Microbial Community in the Rapeseed Rhizosphere. Rhizosphere 2022, 21, 100480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alori, E.T.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O. Microbial Phosphorus Solubilization and Its Potential for Use in Sustainable Agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janati, W.; Bouabid, R.; Mikou, K.; Ghadraoui, L.E.; Errachidi, F. Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria from Soils with Varying Environmental Conditions: Occurrence and Function. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kour, D.; Rana, K.L.; Kaur, T.; Yadav, N.; Yadav, A.N.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, V.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Saxena, A.K. Biodiversity, Current Developments and Potential Biotechnological Applications of Phosphorus-Solubilizing and -Mobilizing Microbes: A Review. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 43–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; White, J.F. Bioprospecting Desert Plants for Endophytic and Biostimulant Microbes: A Strategy for Enhancing Agricultural Production in a Hotter, Drier Future. Biology 2021, 10, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T.; Santos, J.; Matos, D.; Sá, C.; Pina, D.; Pinto, R.; Cardoso, P.; Figueira, E. Soil Bacteria from the Namib Desert: Insights into Plant Growth Promotion and Osmotolerance in a Hyper-Arid Environment. Land 2024, 13, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, X.-Q.; Ren, J.-H.; Ye, J.-R. Isolation and Identification of Phosphobacteria in Poplar Rhizosphere from Different Regions of China. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janati, W.; Mikou, K.; El Ghadraoui, L.; Errachidi, F. Isolation and Characterization of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria Naturally Colonizing Legumes Rhizosphere in Morocco. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 958300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.; Muralidharan, G.; Sudhakar, E. Isolation and Identification of Elite Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria from Soil under Paddy Cultivation. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2014, 11, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, M.; Rjeibi, M.R.; Gatrouni, M.; Mateus, D.M.R.; Asses, N.; Pinho, H.J.O.; Abbes, C. Isolation, Identification, and Characterization of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Tunisian Soils. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, W.; Aman, H.; Irshad, U.; Azeem, M.; Iqbal, A.; Nazir, R. Analysis of Ecological Attributes of Bacterial Phosphorus Solubilizers, Native to Pine Forests of Lower Himalaya. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 112, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzum, N.; Khan, F.I.; Hossain, M.Z.; Islam, M.N.; Saha, M.L. Isolation and Identification of Pigment Producing Bacteria from the Ratargul Swamp Forest Soil. Dhaka Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, S.; Guerrero, L.D.; Makhalanyane, T.P.; Le, P.T.; Seely, M.; Cowan, D.A. Metagenomic Analysis Provides Insights into Functional Capacity in a Hyperarid Desert Soil Niche Community. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1875–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, P.; Alves, A.; Silveira, P.; Sá, C.; Fidalgo, C.; Freitas, R.; Figueira, E. Bacteria from Nodules of Wild Legume Species: Phylogenetic Diversity, Plant Growth Promotion Abilities and Osmotolerance. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, E.M.D.A.P. Aspectos da Tolerância Salina em Pisum sativum L.: Influência da Nutrição Azotada. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, R.; Lopes, T.; Fidalgo, C.; Alves, A.; Cardoso, P.; Figueira, E. Bacteria Associated with the Roots of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Different Development Stages: Diversity and Plant Growth Promotion. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikovskaya, R. Mobilization of Phosphorus in Soil in Connection with Vital Activity of Some Microbial Species. Mikrobiologiya 17: 362–370. Plant Soil 1948, 287, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An Efficient Microbiological Growth Medium for Screening Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrah, K.S.; Antao, S.M. Apatite, Ca10(PO4)6(OH,F,Cl)2: Structural Variations, Natural Solid Solutions, Intergrowths, and Zoning. Minerals 2022, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrik, B.; Elabed, A.; El Modafar, C.; Douira, A.; Amir, S.; Filali-Maltouf, A.; El Abed, S.; El Gachtouli, N.; Mohammed, I.; Koraichi, S.I. Reusing Phosphate Sludge Enriched by Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria as Biofertilizer: Growth Promotion of Zea mays. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, K.S.; Arshad, M.; Zahir, Z.; Cheema, M.A. Comparative Efficacy of Qualitative and Quantitative Methods for Rock Phosphate Solubilization with Phosphate Solubilizing Rhizobacteria. Soil Environ. 2010, 29, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Somasegaran, P.; Hoben, H.J. Handbook for Rhizobia: Methods in Legume-Rhizobium Technology; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4613-8375-8. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.; Reis, A.P.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Rocha, F.; Patinha, C.; Dias, A.C.; Sequeira, C.; Terroso, D. Assessing the Control Exerted by Soil Mineralogy in the Fixation of Potentially Harmful Elements in the Urban Soils of Lisbon, Portugal. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.F.; Bailey, J.S. Organic Carbon, Total Carbon, and Total Nitrogen Determinations in Soils of Variable Calcium Carbonate Contents Using a Leco CN-2000 Dry Combustion Analyzer. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 3243–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R.; Lichtenthaler, H. Formulae and Program to Determine Total Carotenoids and Chlorophylls A and B of Leaf Extracts in Different Solvents. In Advances in Photosynthesis Research: Proceedings of the VIth International Congress on Photosynthesis, Brussels, Belgium, 1–6 August 1983, Volume 2; Sybesma, C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 9–12. ISBN 978-94-017-6368-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Xie, X.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y. Effect of Sunlight-Exposure on Antioxidants and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in ‘d’Anjou’ Pear in Relation to Superficial Scald Development. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, F.D.; Packard, T.T. Respiration and the Activity of the Respiratory Electron Transport System in Marine Zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1975, 20, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, T.G.; King, F.D. The Measurement of Respiratory Electron-Transport-System Activity in Marine Zooplankton. Mar. Biol. 1975, 30, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide Dismutase: Improved Assays and an Assay Applicable to Acrylamide Gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.H.; Borg, L.A. A Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Catalase Activity in Small Tissue Samples. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 174, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.W.; Hogden, C.G. The biuret reaction in the determination of serum proteins: 1. A study of the conditions necessary for the production of a stable color which bears a quantitative relationship to the protein concentration. J. Biol. Chem. 1940, 135, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, C.S.; Oliveira, R.; Bento, F.; Geraldo, D.; Rodrigues, J.V.; Marcos, J.C. Simplified 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine Spectrophotometric Assay for Quantification of Carbonyls in Oxidized Proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 458, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal Lipid Peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hui, F.; Xu, L.; Viau, C.; Spigelman, A.F.; MacDonald, P.E.; Wishart, D.S.; Li, S.; et al. MetaboAnalyst 6.0: Towards a Unified Platform for Metabolomics Data Processing, Analysis and Interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W398–W406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-P.; Liu, H.-Q.; Zhou, H.-L.; Dong, Z.-G.; Bai, X.-H.; Bai, P.; Qiao, J.-J. Isolation and Characterization of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Betel Nut (Areca catechu) and Their Effects on Plant Growth and Phosphorus Mobilization in Tropical Soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yan, Z.; Wang, G.; Xue, W.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, D. A Bacterium Isolated from Soil in a Karst Rocky Desertification Region Has Efficient Phosphate-Solubilizing and Plant Growth-Promoting Ability. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kour, D.; Rana, K.L.; Yadav, A.N.; Yadav, N.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Hesham, A.E.-L.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Saxena, A.K. Drought-Tolerant Phosphorus-Solubilizing Microbes: Biodiversity and Biotechnological Applications for Alleviation of Drought Stress in Plants. In Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria for Sustainable Stress Management: Volume 1: Rhizobacteria in Abiotic Stress Management; Sayyed, R.Z., Arora, N.K., Reddy, M.S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 255–308. ISBN 9789811365362. [Google Scholar]
- Aliyat, F.Z.; Maldani, M.; El Guilli, M.; Nassiri, L.; Ibijbijen, J. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Isolated from Phosphate Solid Sludge and Their Ability to Solubilize Three Inorganic Phosphate Forms: Calcium, Iron, and Aluminum Phosphates. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Fan, X.; Patel, J.S.; Zhang, M. Characterization of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Isolated from Calcareous Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, E.A.P.; Xavier, J.F.; Arcênio, F.S.; Amaya, R.L.; Gonçalves, J.V.S.; Rouws, L.F.M.; Zonta, E.; Coelho, I.S. Characterization and Evaluation of Potential Halotolerant Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria from Salicornia fruticosa Rhizosphere. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1324056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Qian, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, P.; Hu, J.; Lu, B.; He, Y.; Tang, S.; Shen, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganisms Increase Soil Phosphorus Availability: A Review. Geomicrobiol. J. 2024, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, J.D.; Monteiro, P.H.R.; Rivadavea, W.R.; Barbosa, M.; Cordeiro, R.D.; Garboggini, F.F.; Auer, C.G.; da Silva, G.J. Potential of Endophytic Bacteria from Acacia mearnsii: Phosphate Solubilization, Indole Acetic Acid Production, and Application in Wheat. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Ouakrim, E.H.; Chakhchar, A.; El Modafar, C.; Douira, A.; Amir, S.; Ibnsouda-Koraichi, S.; Belkadi, B.; Filali-Maltouf, A. Valorization of Moroccan Phosphate Sludge Through Isolation and Characterization of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria and Assessment of Their Growth Promotion Effect on Phaseolus vulgaris. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 2673–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreshizadeh, S.; Calvo-Peña, C.; Ruiz-Muñoz, M.; Otero-Suárez, R.; Coque, J.J.R.; Cobos, R. Pseudomonas taetrolens ULE-PH5 and Pseudomonas Sp. ULE-PH6 Isolated from the Hop Rhizosphere Increase Phosphate Assimilation by the Plant. Plants 2024, 13, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, D.; Rana, K.L.; Sheikh, I.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, A.N.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Saxena, A.K. Alleviation of Drought Stress and Plant Growth Promotion by Pseudomonas libanensis EU-LWNA-33, a Drought-Adaptive Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 90, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouremani, N.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Silini, A.; Rabhi, N.E.H.; Bouket, A.C.; Belbahri, L.; Bouremani, N.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Silini, A.; Rabhi, N.E.H.; et al. Osmotolerant Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria Mitigate Adverse Effects of Drought Stress on Wheat Growth. AIMS Microbiol. 2024, 10, 507–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, F.; AlYahya, S.A.; AlNadhari, S.; Alasmari, H.; Alhoshani, F.; Wainwright, M. Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria and Fungi in Desert Soils: Species, Limitations and Mechanisms. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, G.; Banerjee, P.; Sharma, R.K.; Maity, J.P.; Etesami, H.; Shaw, A.K.; Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, H.-B.; Chen, C.-Y. Management of Phosphorus in Salinity-Stressed Agriculture for Sustainable Crop Production by Salt-Tolerant Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria—A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndung’u-Magiroi, K.W.; Herrmann, L.; Okalebo, J.R.; Othieno, C.O.; Pypers, P.; Lesueur, D. Occurrence and Genetic Diversity of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria in Soils of Differing Chemical Characteristics in Kenya. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rfaki, A.; Zennouhi, O.; Aliyat, F.Z.; Nassiri, L.; Ibijbijen, J. Isolation, Selection and Characterization of Root-Associated Rock Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria in Moroccan Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabati, J.; Nezami, A.; Yousefi, A.; Oskoueian, E.; Oskoueian, A.; Ahmadi-Lahijani, M.J. Biofertilizers Containing Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Enhance Nutrient Uptake and Improve the Growth and Yield of Chickpea Plants in an Arid Environment. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, A.; Wilkinson, E.; Britt, D.W.; Kaundal, A. A Review of Plant–Microbe Interactions in the Rhizosphere and the Role of Root Exudates in Microbiome Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantigoso, H.A.; Newberger, D.; Vivanco, J.M. The rhizosphere microbiome: Plant–microbial interactions for resource acquisition. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 2864–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Narayanan, M.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria: Their Agroecological Function and Optimistic Application for Enhancing Agro-Productivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantigoso, H.A.; Manter, D.K.; Fonte, S.J.; Vivanco, J.M. Root Exudate-Derived Compounds Stimulate the Phosphorus Solubilizing Ability of Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya, M.; Islam, E.U.; Rasul, M.; Farooq, I.; Mahreen, N.; Tawab, A.; Irfan, M.; Rajput, L.; Amin, I.; Yasmin, S. Differential Root Exudation and Architecture for Improved Growth of Wheat Mediated by Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 744094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vives-Peris, V.; de Ollas, C.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Pérez-Clemente, R.M. Root Exudates: From Plant to Rhizosphere and Beyond. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastogeer, K.M.G.; Tumpa, F.H.; Sultana, A.; Akter, M.A.; Chakraborty, A. Plant Microbiome–an Account of the Factors That Shape Community Composition and Diversity. Curr. Plant Biol. 2020, 23, 100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collavino, M.M.; Sansberro, P.A.; Mroginski, L.A.; Aguilar, O.M. Comparison of in Vitro Solubilization Activity of Diverse Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Native to Acid Soil and Their Ability to Promote Phaseolus vulgaris Growth. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Xie, J.; Xue, X.; Jiang, Y. Screening of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria and Their Abilities of Phosphorus Solubilization and Wheat Growth Promotion. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, D.; Yadav, A.N. First Report on Novel Psychrotrophic Phosphorus-Solubilizing Ochrobactrum thiophenivorans EU-KL94 from Keylong Region in Great Himalayas and Their Role in Plant Growth Promotion of Oats (Avena sativa L.). Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zutter, N.; Ameye, M.; Bekaert, B.; Verwaeren, J.; De Gelder, L.; Audenaert, K. Uncovering New Insights and Misconceptions on the Effectiveness of Phosphate Solubilizing Rhizobacteria in Plants: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 858804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducousso-Détrez, A.; Lahrach, Z.; Fontaine, J.; Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui, A.; Hijri, M. Cultural Techniques Capture Diverse Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria in Rock Phosphate-Enriched Habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1280848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirui, C.K.; Njeru, E.M.; Runo, S. Diversity and Phosphate Solubilization Efficiency of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria Isolated from Semi-Arid Agroecosystems of Eastern Kenya. Microbiol. Insights 2022, 15, 11786361221088991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, A.V.; de Oliveira, A.J.; Tanabe, I.S.B.; Silva, J.V.; da Silva Barros, T.W.; da Silva, M.K.; França, P.H.B.; Leite, J.; Putzke, J.; Montone, R.; et al. Antarctic Lichens as a Source of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria. Extremophiles 2021, 25, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, I.; Kang, M.; Seo, T. Chryseobacterium caseinilyticum Sp. Nov., a Casein Hydrolyzing Bacterium Isolated from Rice Plant and Emended Description of Chryseobacterium piscicola. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.-L.; Li, C.-J.; Jiang, X.-W.; Zhi, X.-Y. Chryseobacterium paridis Sp. Nov., an Endophytic Bacterial Species Isolated from the Root of Paris polyphylla Smith Var. Yunnanensis. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 4777–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, T.; Chi, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, N.; Chen, M.; Pan, L.; Qi, P. Isolation and Characterization of Halotolerant Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria Naturally Colonizing the Peanut Rhizosphere in Salt-Affected Soil. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdoğan, D.K.; Akçelik, N.; Akçelik, M. Genetic Diversity and Characterization of Plant Growth-Promoting Effects of Bacteria Isolated from Rhizospheric Soils. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mažylytė, R.; Kaziūnienė, J.; Orola, L.; Valkovska, V.; Lastauskienė, E.; Gegeckas, A. Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganism Bacillus Sp. MVY-004 and Its Significance for Biomineral Fertilizers’ Development in Agrobiotechnology. Biology 2022, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.; Klepa, M.S.; Olchanheski, L.R.; de Alencar Almeida, M.; Chicora, K.; Prestes, L.; Rodrigues, E.P.; Hungria, M.; da Silva Batista, J.S. Phenotypic and Genomic Characterization of Phosphate-Solubilizing Rhizobia Isolated from Native Mimosa and Desmodium in Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 3321–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, A.C.; Gurjar, N.S.; Sharma, S. Co-Inoculation of Non-Symbiotic Bacteria Bacillus and Paraburkholderia Can Improve the Soybean Yield, Nutrient Uptake, and Soil Parameters. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 67, 3041–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Zineb, A.; Trabelsi, D.; Ayachi, I.; Barhoumi, F.; Aroca, R.; Mhamdi, R. Inoculation with Elite Strains of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Enhances the Effectiveness of Fertilization with Rock Phosphates. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.; Wagh, J.; Archana, G.; Naresh Kumar, G. Sucrose Dependent Mineral Phosphate Solubilization in Enterobacter asburiae PSI3 by Heterologous Overexpression of Periplasmic Invertases. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami-Karvani, Z.; Chitsaz-Esfahani, Z. Phosphorus Solubilization: Mechanisms, Recent Advancement and Future Challenge. In Soil Microbiomes for Sustainable Agriculture: Functional Annotation; Yadav, A.N., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 85–131. ISBN 978-3-030-73507-4. [Google Scholar]
- Timofeeva, A.M.; Galyamova, M.R.; Sedykh, S.E. Plant Growth-Promoting Soil Bacteria: Nitrogen Fixation, Phosphate Solubilization, Siderophore Production, and Other Biological Activities. Plants 2023, 12, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandić, V.; Krnjaja, V.; Simić, A.; Petričević, M.; Gogić, M.; Brankov, M.; Stanojković, A. Effect of pH on Germination and Seedling Growth of Maize. Biotechnol. Anim. Husb. 2023, 39, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ma, Y.; Rui, M.; Lv, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Is High pH the Key Factor of Alkali Stress on Plant Growth and Physiology? A Case Study with Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedlings. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Jin, S.; Yang, S. The Impact of Alkaline Stress on Plant Growth and Its Alkaline Resistance Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y. How Do Plants Maintain pH and Ion Homeostasis under Saline-Alkali Stress? Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1217193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E.; Møller, I.M.; Murphy, A.S. Plant Physiology and Development; Sinauer Associates, Incorporated, Publishers: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-60535-353-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Ying, Y.; Shi, W. The Role of Phosphate-Solubilizing Microbial Interactions in Phosphorus Activation and Utilization in Plant–Soil Systems: A Review. Plants 2024, 13, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Bagnazari, M.; Mohammadi, M. Seaweed and Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Biofertilizers Ameliorate Physiochemical Traits and Essential Oil Content of Calendula officinalis L. under Drought Stress. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 328, 112653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Pan, F.; Kong, X.; Lang, J.; Ye, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, G.; Han, L.; Zhou, N. Effects of Inoculation with Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria on the Physiology, Biochemistry, and Expression of Genes Related to the Protective Enzyme System of Fritillaria taipaiensis P. Y. Li. Phyton Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 93, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangue-Yapseu, G.Y.; Tola, A.J.; Missihoun, T.D. Proteome-Wide Analysis of Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Protein Carbonylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1049681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastochkina, O.V.; Garipova, S.R.; Pusenkova, L.I.; Garshina, D.Y.; Baymiev, A.K.; Koryakov, I.S. Effect of Endophytic Bacteria Bacillus subtilis on Seedling Growth and Root Lignification of Pisum sativum L. under Normal and Sodium Chloride Salt Conditions. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 70, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labudda, M. Lipid Peroxidation as a Biochemical Marker for Oxidative Stress during Drought. In An Effective Tool for Plant Breeding; E-Wydaw: Poznan, Poland, 2013; pp. 1–12. Available online: http://www.e-wydawnictwo.eu/document/document preview/3342 (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Lopes, T.; Costa, P.; Cardoso, P.; e Silva, J.A.; Figueira, E. Inducing Drought Resilience in Maize Through Encapsulated Bacteria: Physiological and Biochemical Adaptations. Plants 2025, 14, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, T.; Cruz, C.; Cardoso, P.; Pinto, R.; Marques, P.A.A.P.; Figueira, E. A Multifactorial Approach to Untangle Graphene Oxide (GO) Nanosheets Effects on Plants: Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Inoculation, Bacterial Survival, and Drought. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilakarathne, A.S.; Liu, F.; Zou, Z. Plant Signaling Hormones and Transcription Factors: Key Regulators of Plant Responses to Growth, Development, and Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Signaling in Plants. In Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Shil, S.; Rime, J.; Alice, A.K.; Yumkhaibam, T.; Mounika, V.; Singh, A.P.; Kundu, M.; Lalhmangaihzuali, H.; Hazarika, T.K.; et al. Phytohormonal Signaling in Plant Resilience: Advances and Strategies for Enhancing Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Plant Growth Regul. 2025, 105, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.; Cardoso, P.; Carneiro, B.; Pinto, G.; Bedia, C.; Figueira, E. Maize Crops Under Rising Temperatures: Bacterial Influence on Biochemical and Lipidomic Changes Induced by Heat. Plants 2025, 14, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Fan, Y.; Han, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Enhancing Stimulation of Cyaniding, GhLDOX3 Activates Reactive Oxygen Species to Regulate Tolerance of Alkalinity Negatively in Cotton. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Effects of Different Metal Ions on the Stability of Anthocyanins as Indicators. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 300, 52015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.; Tattini, M.; Gould, K.S. Multiple Functional Roles of Anthocyanins in Plant-Environment Interactions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 119, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, J.; Cardoso, P.; Rocha, R.; Pinto, R.; Lopes, T.; Patinha, C.; Guilherme, R.; Ferreira, A.; Figueira, E. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Different Genera, Host Plants, and Climates: Influence of Soil pH on Plant Growth and Biochemistry. Land 2025, 14, 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102065
Santos J, Cardoso P, Rocha R, Pinto R, Lopes T, Patinha C, Guilherme R, Ferreira A, Figueira E. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Different Genera, Host Plants, and Climates: Influence of Soil pH on Plant Growth and Biochemistry. Land. 2025; 14(10):2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102065
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Jacinta, Paulo Cardoso, Ricardo Rocha, Ricardo Pinto, Tiago Lopes, Carla Patinha, Rosa Guilherme, António Ferreira, and Etelvina Figueira. 2025. "Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Different Genera, Host Plants, and Climates: Influence of Soil pH on Plant Growth and Biochemistry" Land 14, no. 10: 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102065
APA StyleSantos, J., Cardoso, P., Rocha, R., Pinto, R., Lopes, T., Patinha, C., Guilherme, R., Ferreira, A., & Figueira, E. (2025). Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria from Different Genera, Host Plants, and Climates: Influence of Soil pH on Plant Growth and Biochemistry. Land, 14(10), 2065. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102065










