The Mechanism of Socio-Spatial Evolution in Rural Areas Driven by the Development of the Planting Industry—A Case Study of Yuezhuang Village in Shandong Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Rural Industrialisation and Its Influences on Urban and Rural Areas
2.2. The Flow of Urban–Rural Factors from the Socio-Spatial Dialectic Perspective
3. Case Selection and Methods
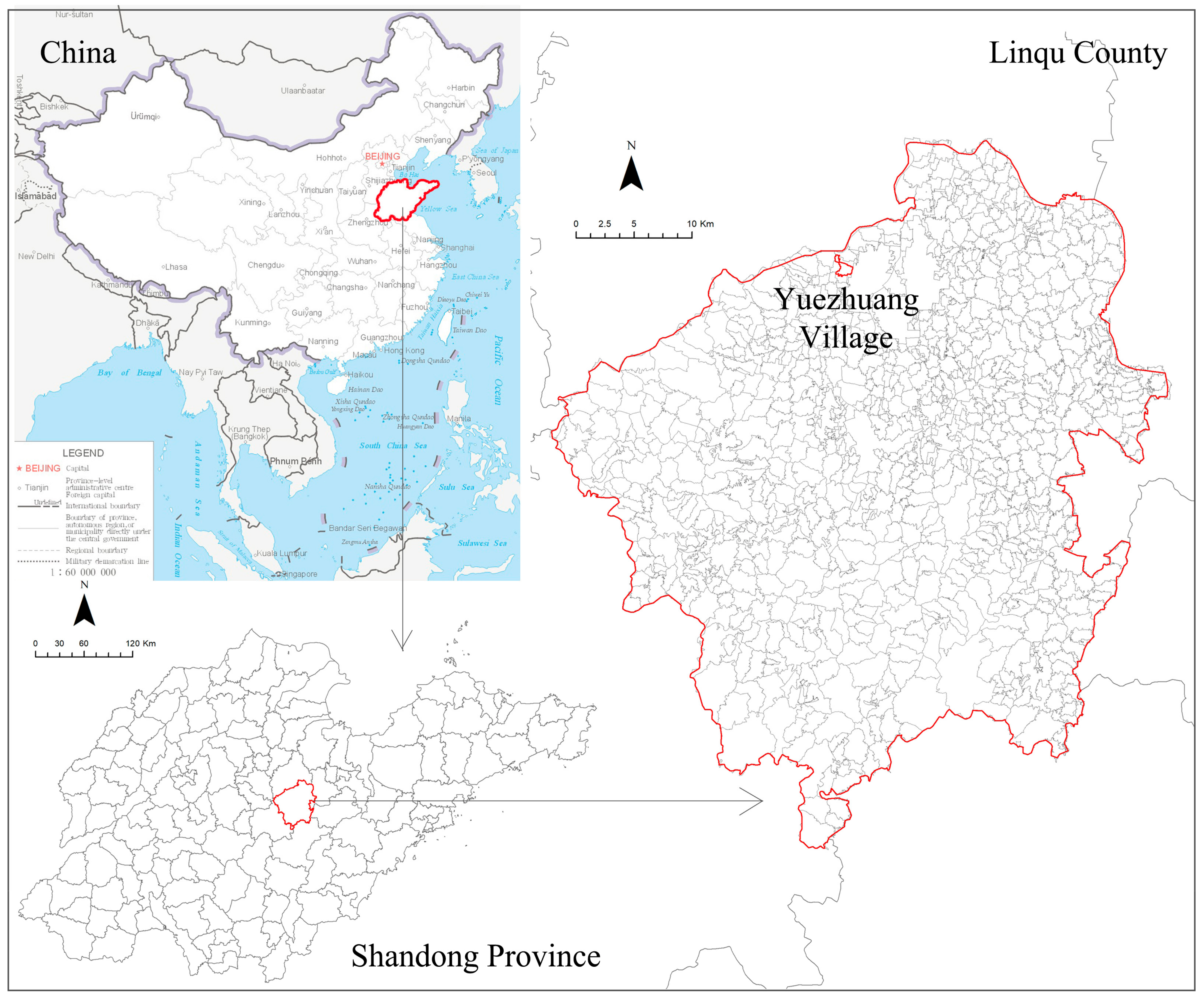
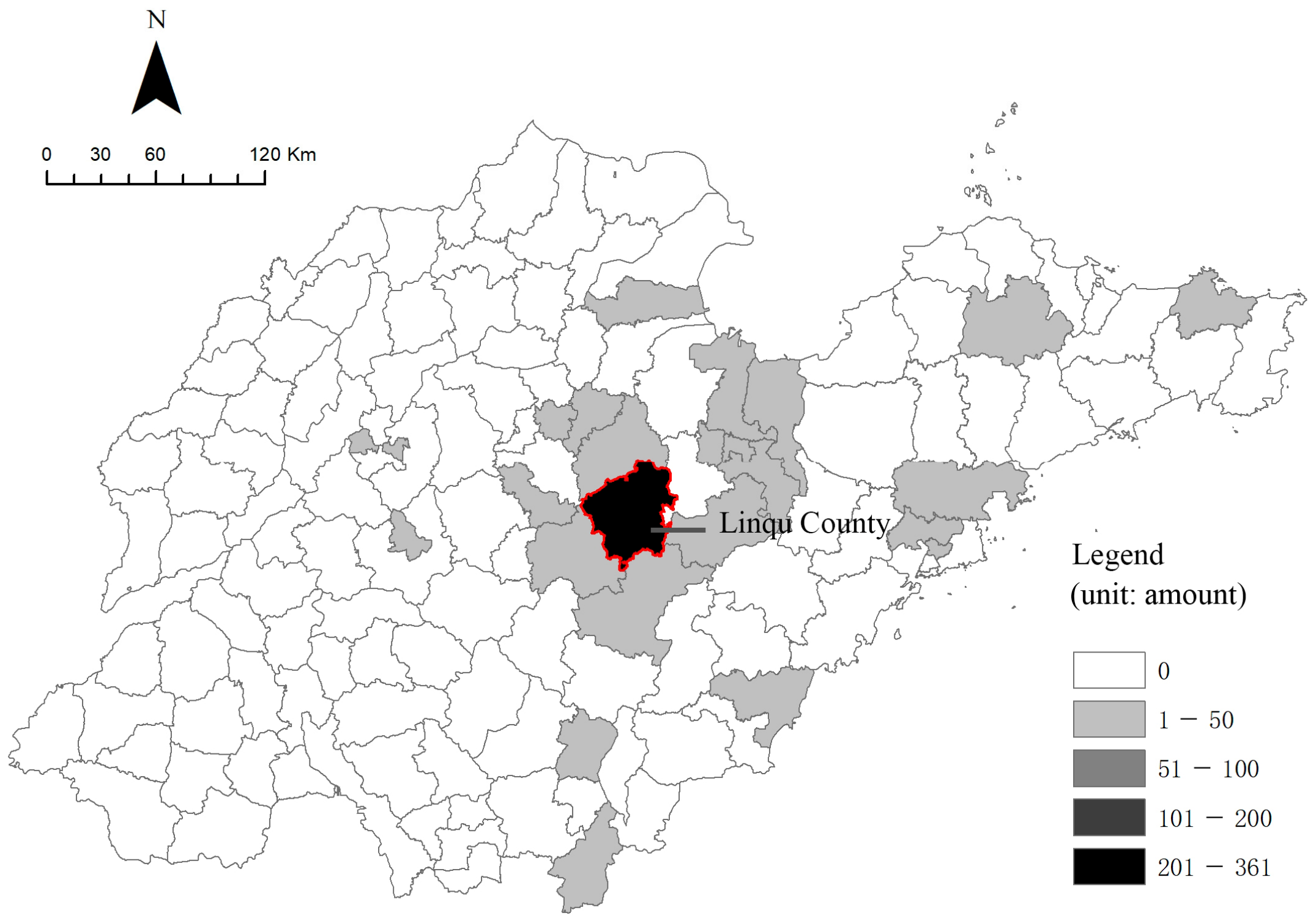
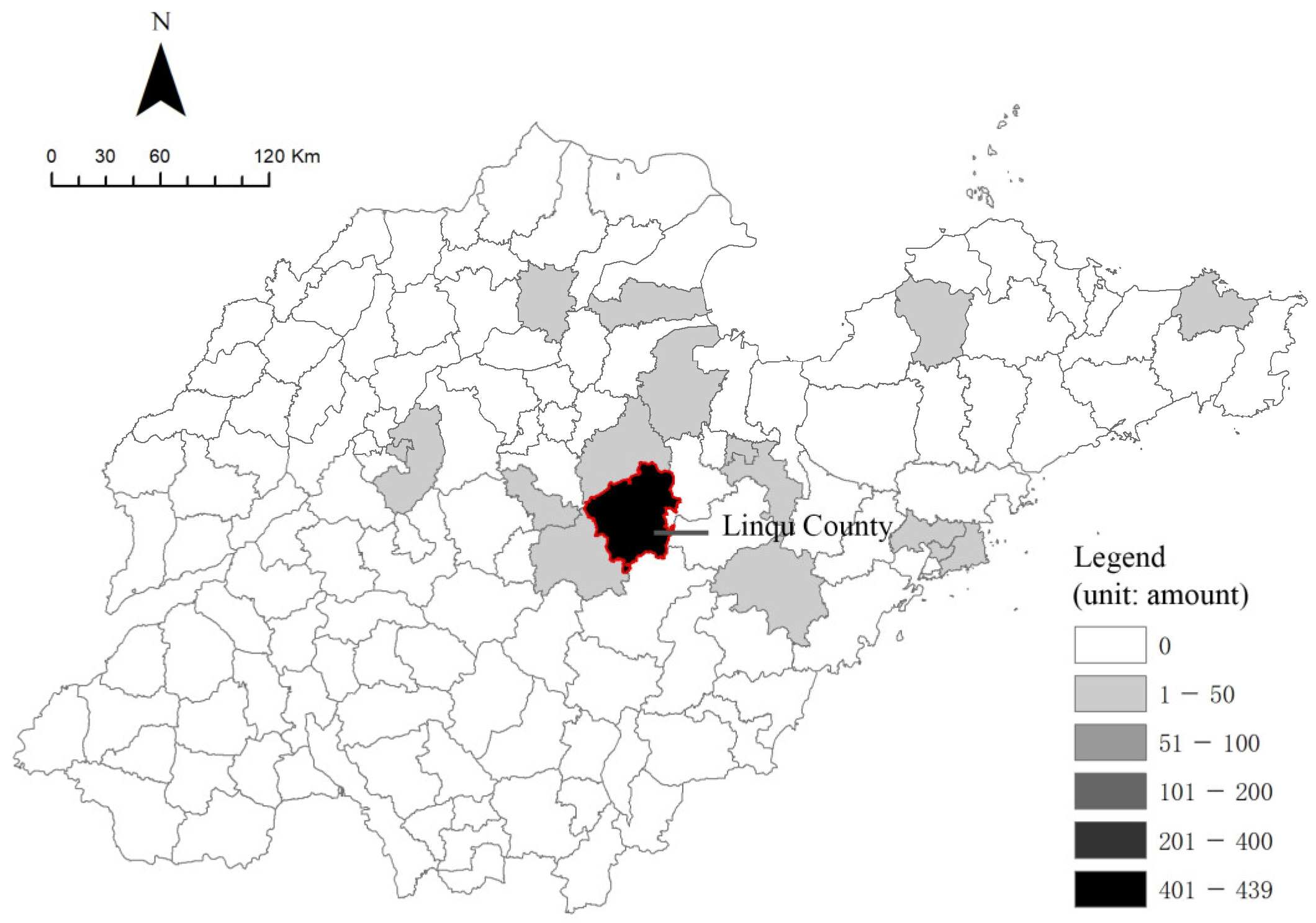
3.1. Case Selection: Yuezhuang Village in Linqu County
3.2. Data and Mixed Method Research
4. Analysis
4.1. Industrial Evolution: The Formation Stages and Annual Activities of the Cherry Industry
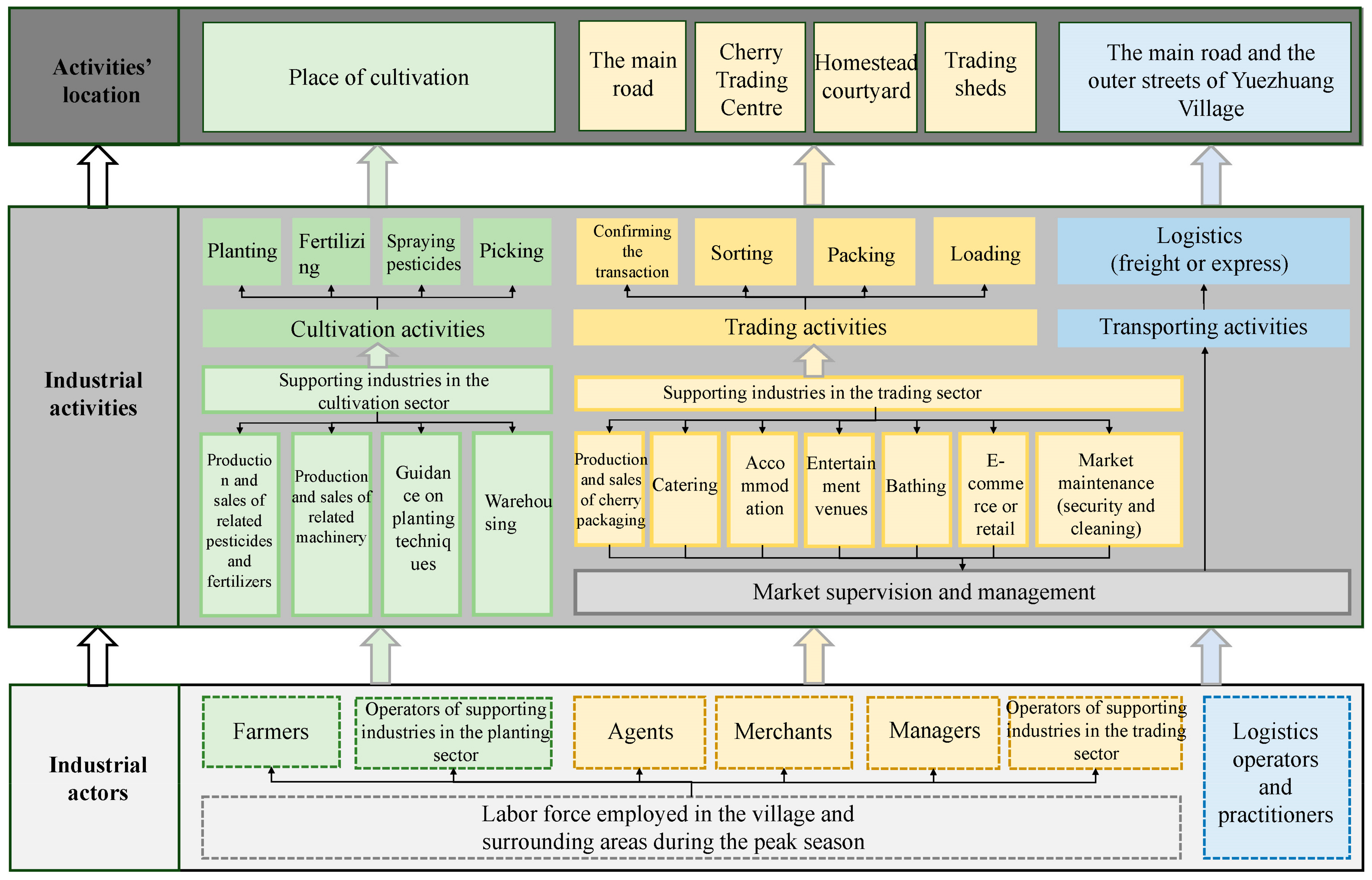
4.2. Social Networks: Actors’ Interactions Driven by Industrial Planting Activity
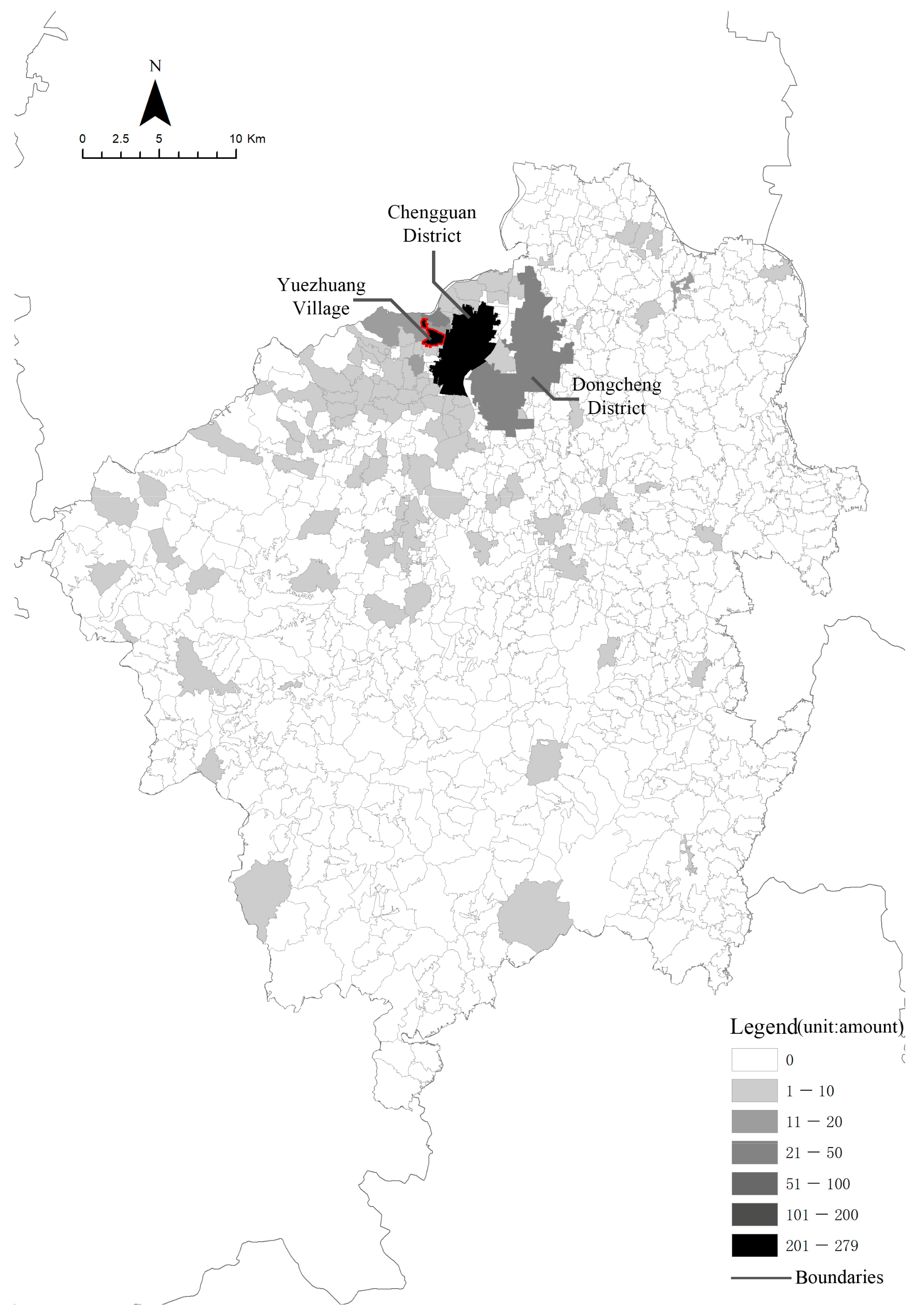
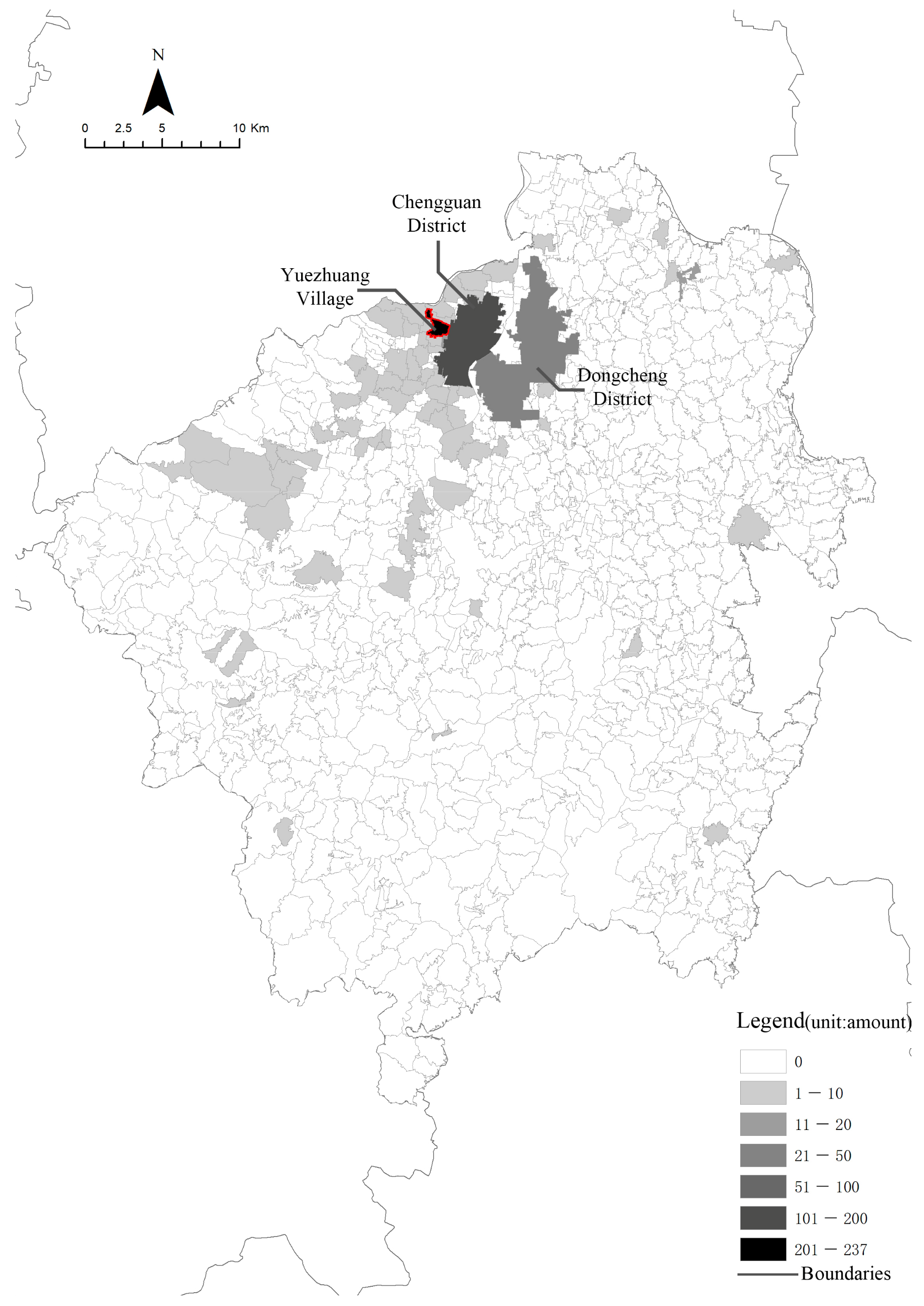
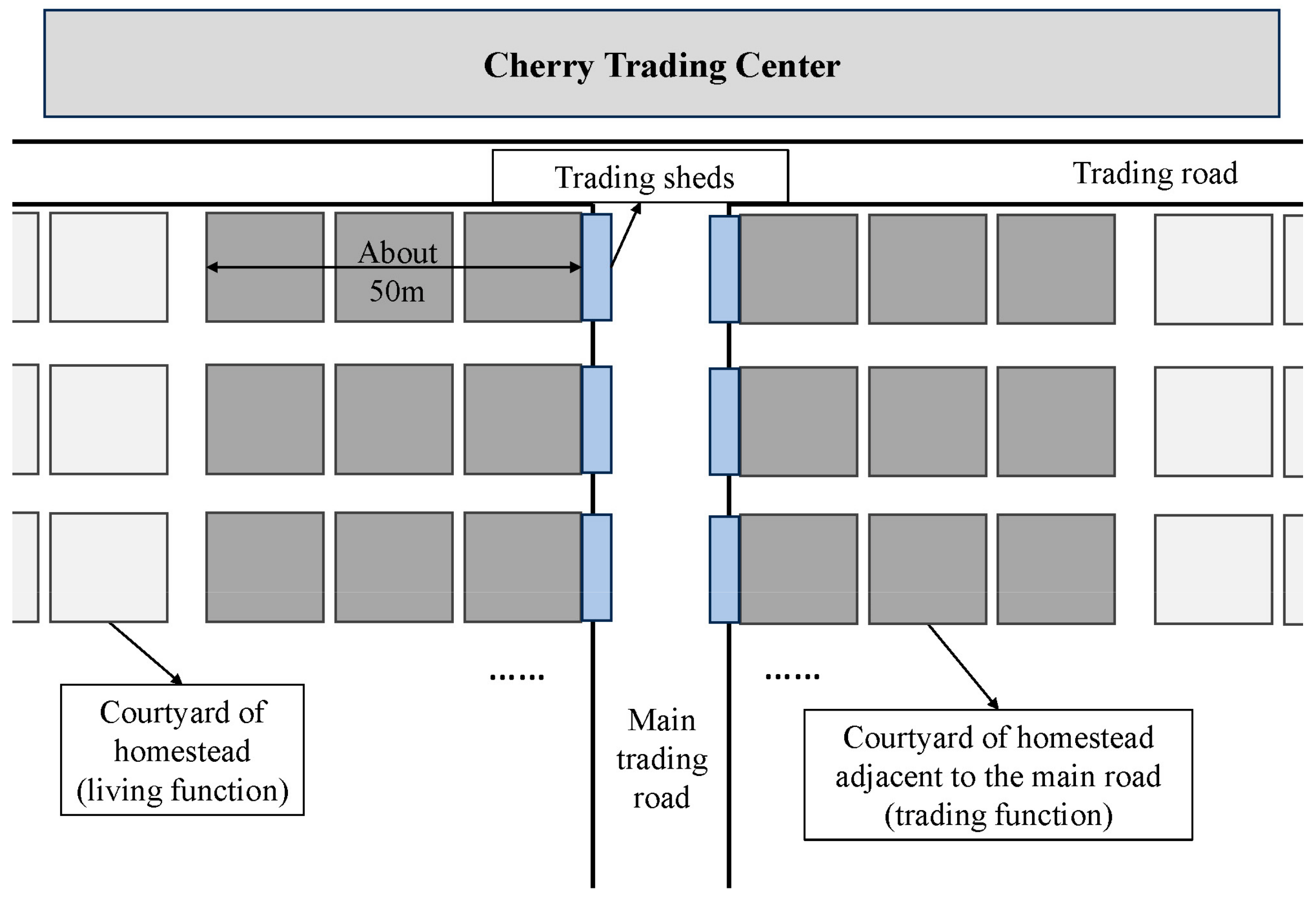
4.3. Spatial Adaptation: The Changes in Land Use and Spatial Functions
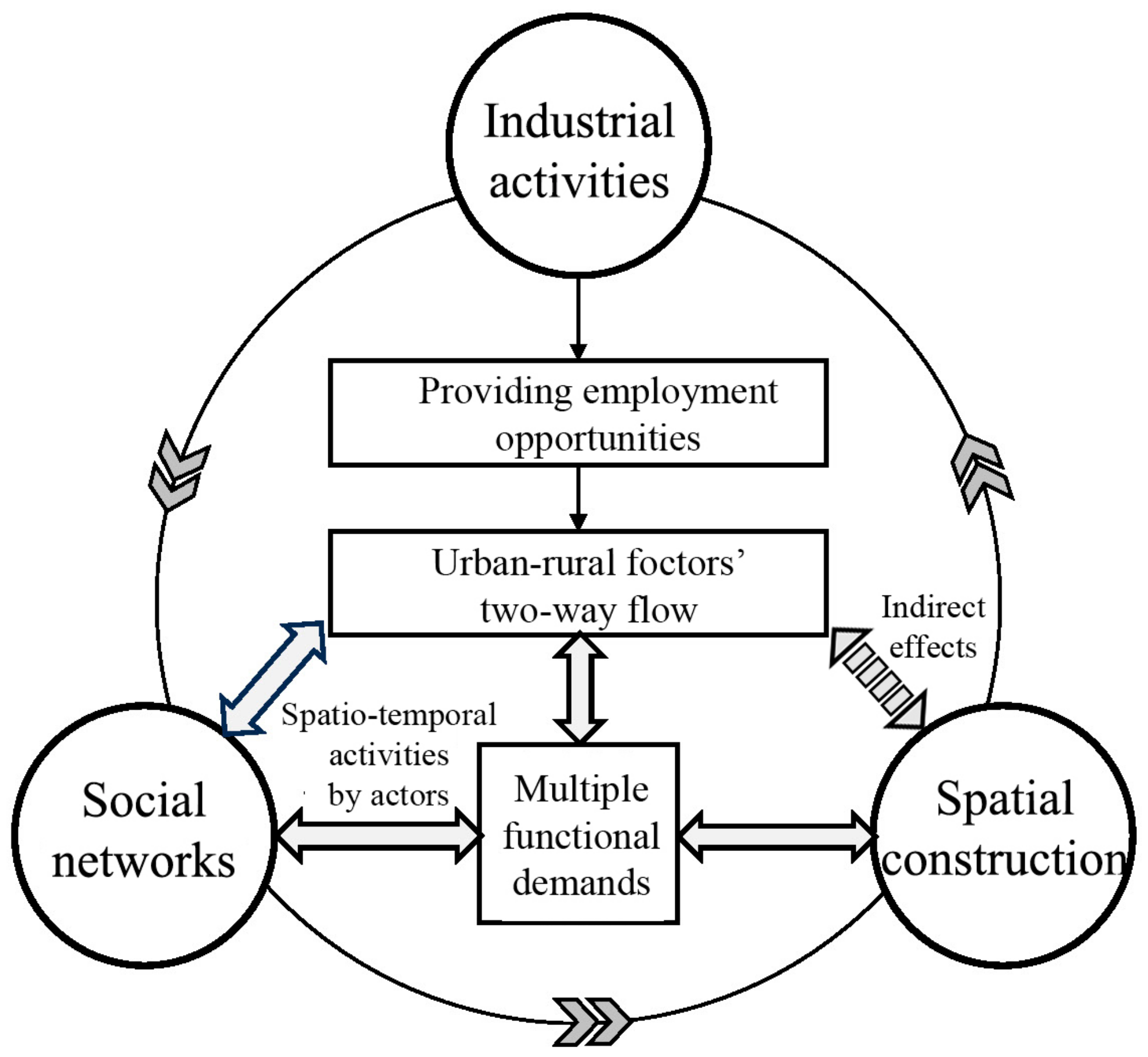
4.4. The Mechanism of Socio-Spatial Evolution Driven by Industrial Development
5. Discussion
5.1. Complexity of the Mechanism
5.2. Current Rural Planning Policies and Planning Inspiration in China
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Statement
References
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Luo, W.; Wang, W.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, W. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of urban-rural integration in China. Prog. Geogr. 2023, 42, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council of China issued Rural Revitalization Strategic Plan (2018–2022)]. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2018-09/26/content_5325534.htm (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Establishing and Improving the Institutional Mechanism and Policy System for Integrated Urban-Rural Development]. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2019-05/05/content_5388880.htm (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Yang, G. Multiple Approaches of Rural Revitalization from the Viewpoint of Urban-rural Co-construction. Planners 2019, 11, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W. The policy changes and future trends of the rural development in the No. 1 document of the Central Committee. Rural Econ. 2017, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Cai, J.M.; Cui, L.; Liu, Y.S. Facilitating rural transformation development by tourism industry: A case study of Panjin, Liaoning Province. Res. Agric. Mod. 2016, 37, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Geng, J.; Chen, X. Rural Restructuring Driven by B&B Industry and Its Implications for Planning: The Case Study of Luoling Village, Moganshan Town. Urban Plan. Forum 2019, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Liu, Q.; Xie, B. The Historical Stages and Characteristics of Urban-rural Relationship Driven by Relevant Elements. Planners 2018, 34, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Huang, F. Effect and Countermeasures for the Drain of Rural Labor Force on Agricultural Modernization. J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. Natl. 2015, 32, 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- The State Council of the PRC. The National Land Use Planning Framework; Xinhua News Agency: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Scientifically promoting the strategy of reclamation and readjustment of rural land in China. China Land Sci. 2011, 25, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, Y. Key issues of land use in China and implications for policy making. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Dilemma of China’s Urbanization and Land Expropriation—Based on the Farmland Property Rights of Thinking. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 14, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X. Urban-Rural Development in China—My Lifetime Reasearch Project. Chinses J. Sociol. 1993, 01, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Yang, Q. Restructuring the State: Policy Transition of Construction Land Supply in Urban and Rural China. Land 2021, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, H.; Lin, M.; Li, C. Rural e-commerce in China: Spatial dynamics of Taobao Villages development in Zhejiang Province. Growth Change 2021, 53, 1082–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. A review of the impact of urban-rural relations on rural areas and farmers. Rural Econ. Sci.-Technol. 2014, 25, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M. Spatial Characteristics and Planning Strategies of Rural Industries Guided by Industrial Revitalization: A Case Study of the Urban Pastoral Complex in the Dongxihu District of Wuhan. City Plan. Rev. 2023, 47, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, M.; Luo, Z.D.; Lan, J. The Development Strategy and Planning Methodology for the Remote Countryside from the Perspective of Country in Flows: Taking Loushang Village of Guizhou Province as a Case. J. Hum. Settl. West China 2021, 36, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhao, M.; Huang, J. The Performance of Spatial Structure and the Choice of Development Model of Mage-City. Urban Plan. Forum 2021, 01, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Lin, S. A Literature Review of the Study on Return Floating Population in China. Hum. Geogr. 2020, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Development Process, Logic, and Prospect of Rural Human Settlements after Reform and Opening-up. City Plan. Rev. 2023, 46, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Yang, G.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y. Understanding Rural Development Driven by Small Local Industries and Its Planning Strategies: The Case of Zhejiang Province. Planners 2021, 37, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Guan, Z. On Rural Spatial Distribution Optimization Based on the Theory of Productivity and Production Relations. J. Hum. Settl. West China 2018, 33, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G. Rural Evolution: Reviewing the Rebirth of Traditional Rural Settlements from the Perspective of “Productivity-Spatial Form” Theory. J. Tongji Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 33, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Amjad, R. Small-scale industries and rural development: Implications for rural industrialisation in Pakistan. In Rural Small Scale Industries and Employment in Africa and Asia: A Review of Programmes and Policies; Chutta, E., Sethuraman, S.V., Eds.; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 93–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kakati, B.K. Gram Swaraj: The Sustainable Model for Rural Industrialisation and Employment. Int. J. Community Soc. Dev. 2021, 3, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agasty, D.M.P. Migration of Labour and Urban-Rural Linkages: A Case Study of Rural India. Indian J. Econ. Dev. 2018, 6. Available online: www.iseeadyar.org (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Krishna, A. Globalised Growth in Largely Agrarian Contexts: The Urban–Rural Divide; Effective States and Inclusive Development Research Centre, The University of Manchester: Manchester, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, T. China’s Rural Industrialization and Agricultural Mechanization. China World Econ. 2023, 31, 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H. Agricultural Specialization Activates the Industry Chain: Implications for Rural Entrepreneurship in China. Agribusiness 2023. early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, J.; Tiwasing, P.; Gorton, M.; Maioli, S.; Newbery, R.; Turner, R. Shining a Spotlight on Small Rural Businesses: How Does Their Performance Compare with Urban? J. Rural Stud. 2019, 68, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, V. Small Scale Industries and Entrepreneurship; Himalaya Publishing House: Mumbai, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Xiang, J. New rural development and rural revitalization path in the era of mobile internet. City Plan. Rev. 2019, 43, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, J. Urban-rural integration approach from the perspectives of pluriactivity and multi-functionalization: The case study of Dinghai District, Zhoushan. Urban Plan. Forum 2019, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N. The urban question as a scale question: Reflections on Henri Lefebvre, urban theory and the politics of scale. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2000, 24, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N. (Ed.) Implosions/Explosions: Towards a Study of Planetary Urbanization. De Gruyter; Jovis: Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, D. The Condition of Postmodernity: An Enquiry into the Origins of Cultural Change; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L. A Theoretical Analysis on the Structural Effects of Space of Flows. Urban Plan. Forum 2021, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N. New Urban Spaces: Urban Theory and the Scale Question; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Heley, J.; Jones, L. Relational Rurals: Some thoughts on relating things and theory in rural studies. J. Rural Stud. 2012, 28, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, C. Henri Lefebvre and the Theory of the Production of Space; Verso: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, H. The Production of Space; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C. The Origins of Socio-Spatial Dialectic. Stud. Dialectics Nat. 2012, 28, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Soja, E.W. Third Space: Journeys to Los Angeles and Other Real-And-Imagined Places; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gottdiener, M.; Hutchison, R. The New Urban Sociology; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q. Sociospatial Dialectics and Its Disciplinary Significance: An Analysis from the Perspective of Geography. Academics 2010, 05, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.; Tan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Guan, M. Space-behavior interaction theory: Basic thinking of general construction. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y. Methodological Problems in Behavioral Geography Study. Areal Res. Dev. 2005, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shortall, S.; Brown, D.L. Guest editorial for special issue on rural inequalities: Thinking about rural inequalities as a cross-national research project. J. Rural Stud. 2019, 68, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Huang, H.; Ma, D.; Chen, L.; Zhao, M. Capturing urban recreational hotspots from GPS data: A new framework in the lens of spatial heterogeneity. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 103, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Yue, Y. The Rural Planning Research Supported by Mobile Positioning Big Data: Progress, Obstacles and Expectation. Urban Rural Plan. 2020, 02, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Spinney, J.E. Mobile positioning and LBS applications. Geography 2003, 88, 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- Sadoun, B.; Al-Bayari, O. LBS and GIS technology combination and applications. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, Amman, Jordan, 13–16 May 2007; IEEE: Toulouse, France, 2007; pp. 578–583. [Google Scholar]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. AAAI Press 1996, 96, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, D.R. DBSCAN spatial clustering algorithm and its application in urban planning. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2005, 3, 51–53+5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Hu, Y. Urban Spatial-Temporal Activity Planning: Concept, Framework and Prospect. Urban Plan. Forum 2022, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, N. Study on the spatial pattern and mechanism of rural population land-industry coordinating development in Huang-Huai-Hai Area. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar]
- UN-Habitat. Compendium of Inspiring Practices on Urban-Rural Linkages: Implementation of Guiding Principles and Framework for Action to Advance Integrated Territorial Development, 3rd ed.; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- UN-Habitat. Compendium of Inspiring Practices on Urban-Rural Linkages: Implementation of Guiding Principles and Framework for Action to Advance Integrated Territorial Development, 2nd ed.; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cattivelli, V. Planning peri-urban areas at regional level: The experience of Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna (Italy). Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros-tonen, M.; Pouw, N.; Bavinck, M. Governing Beyond Cities: The Urban-Rural Interface. In Geographies of Urban Governance; Gupta, J., Pfeffer, K., Verrest, H., Ros-Tonen, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 85–105. [Google Scholar]
- López-goyburu, P.; García-montero, L.G. The urban-rural interface as an area with characteristics of its own in urban planning: A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 43, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
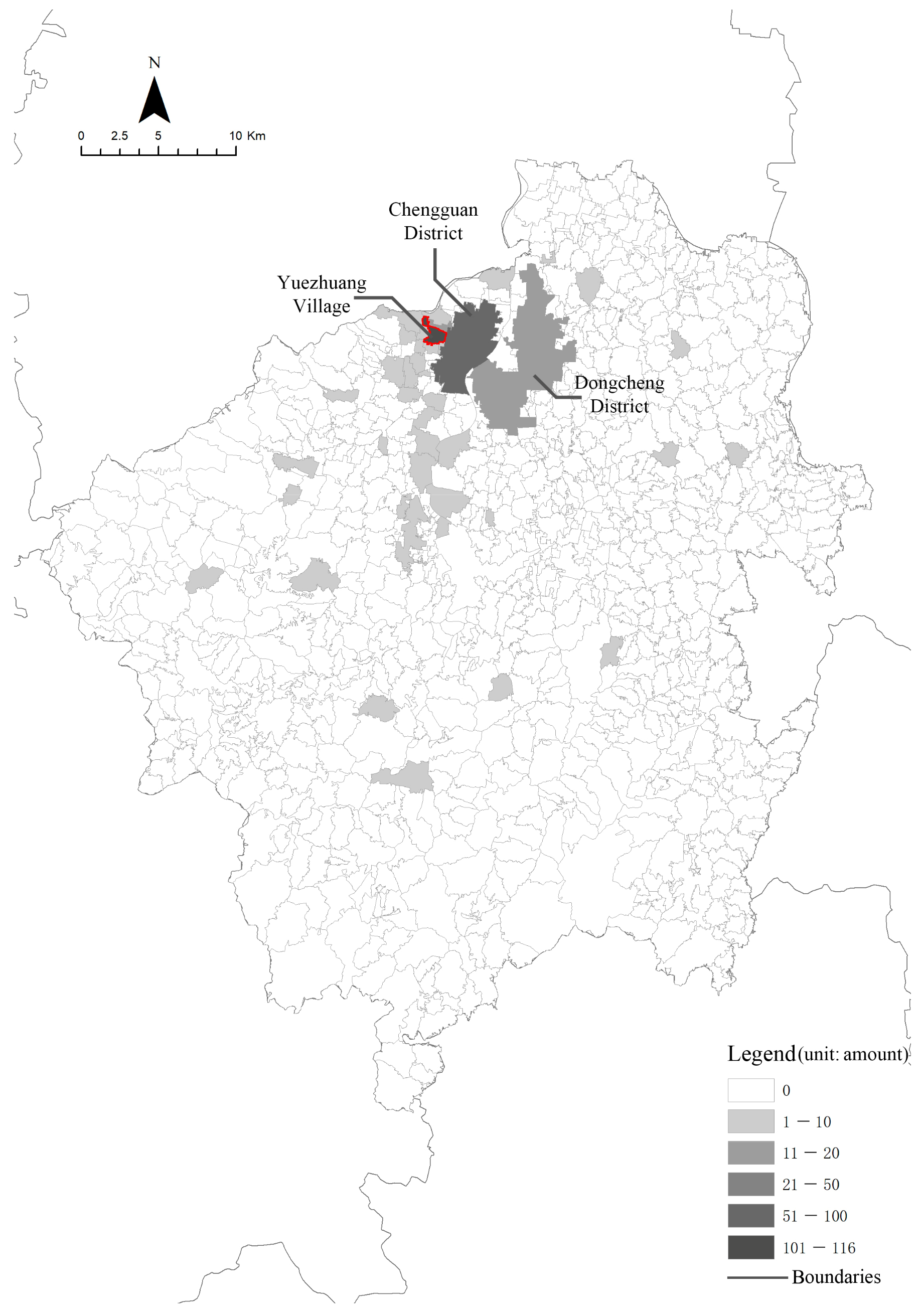
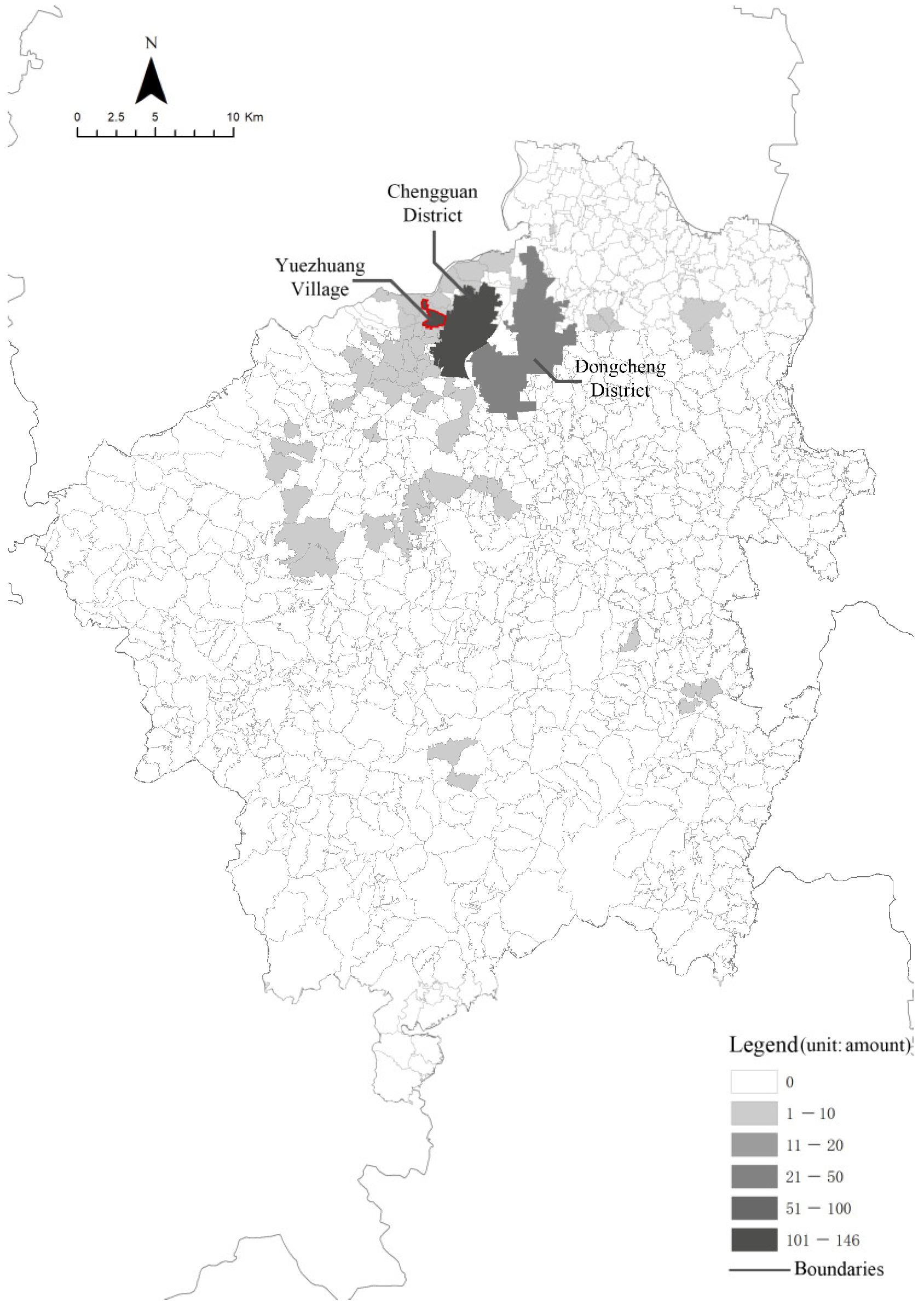
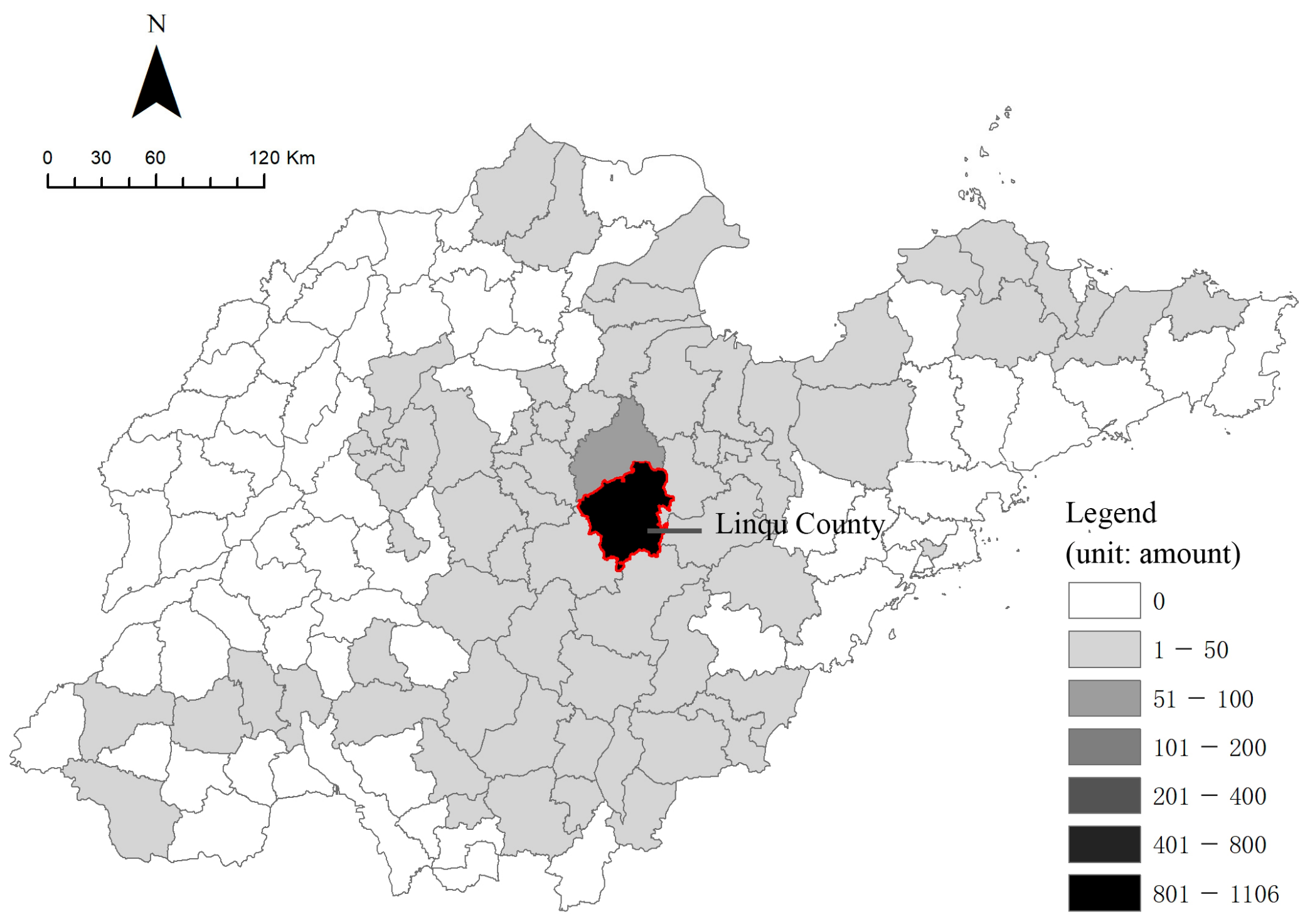
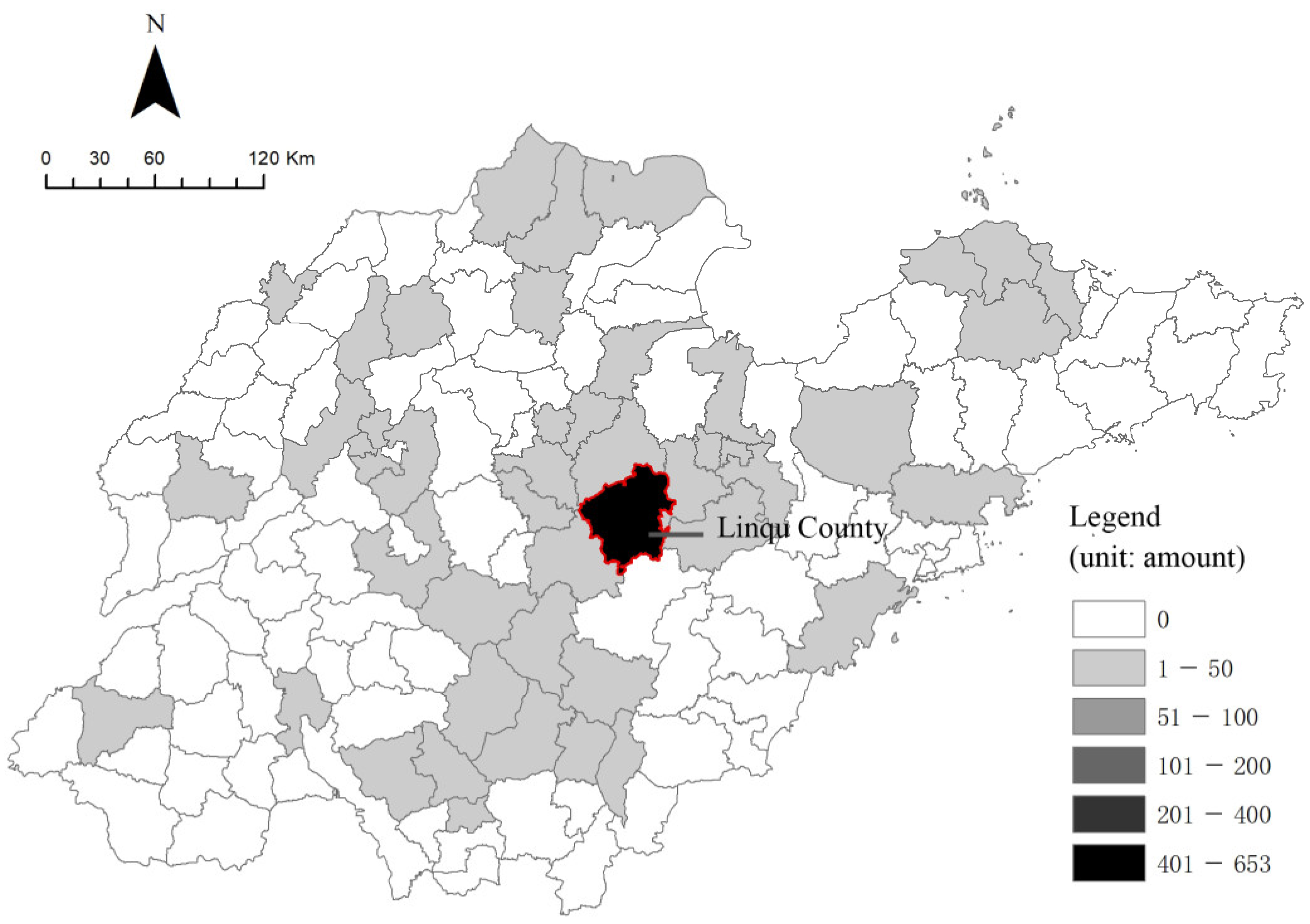
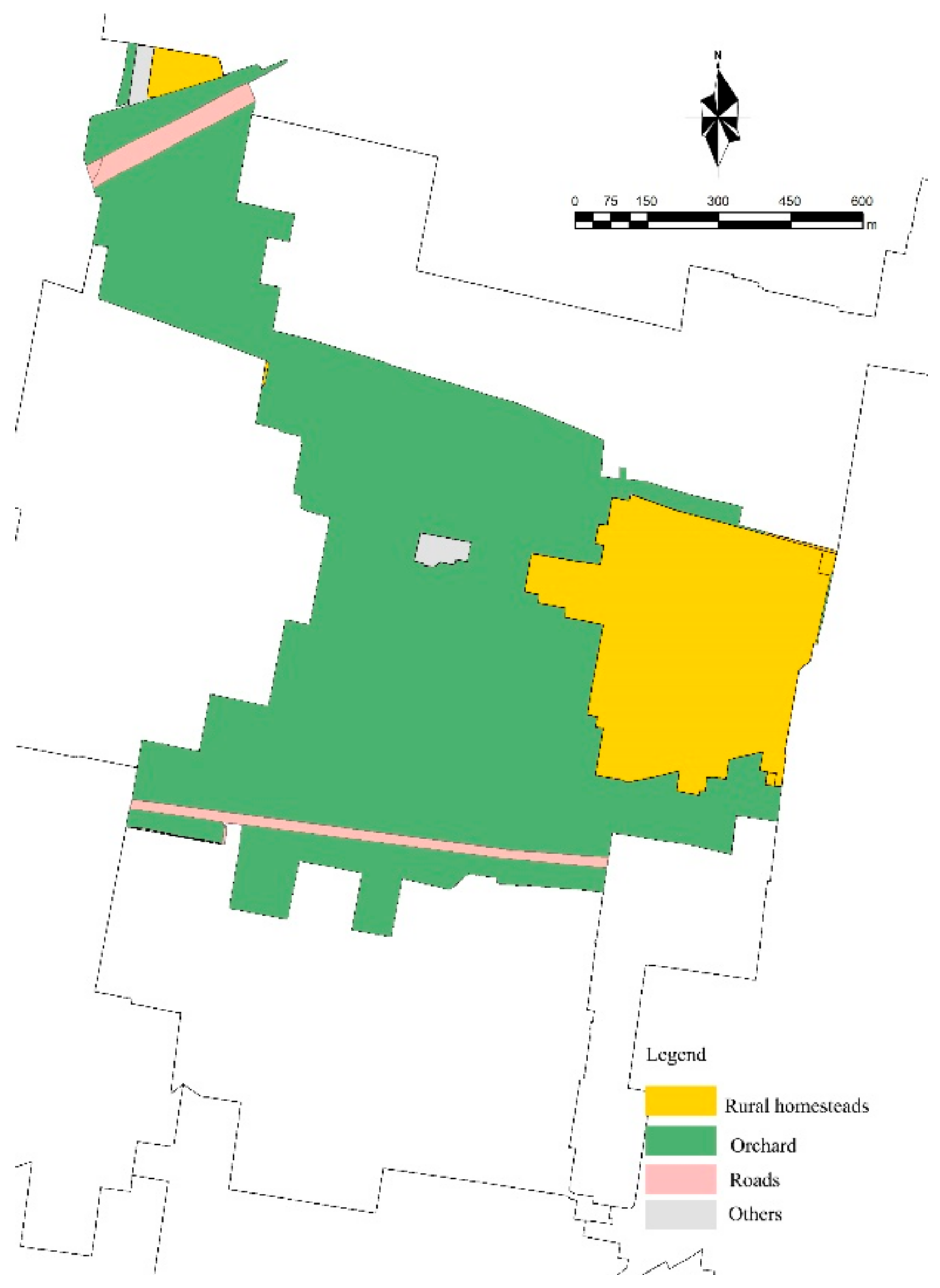
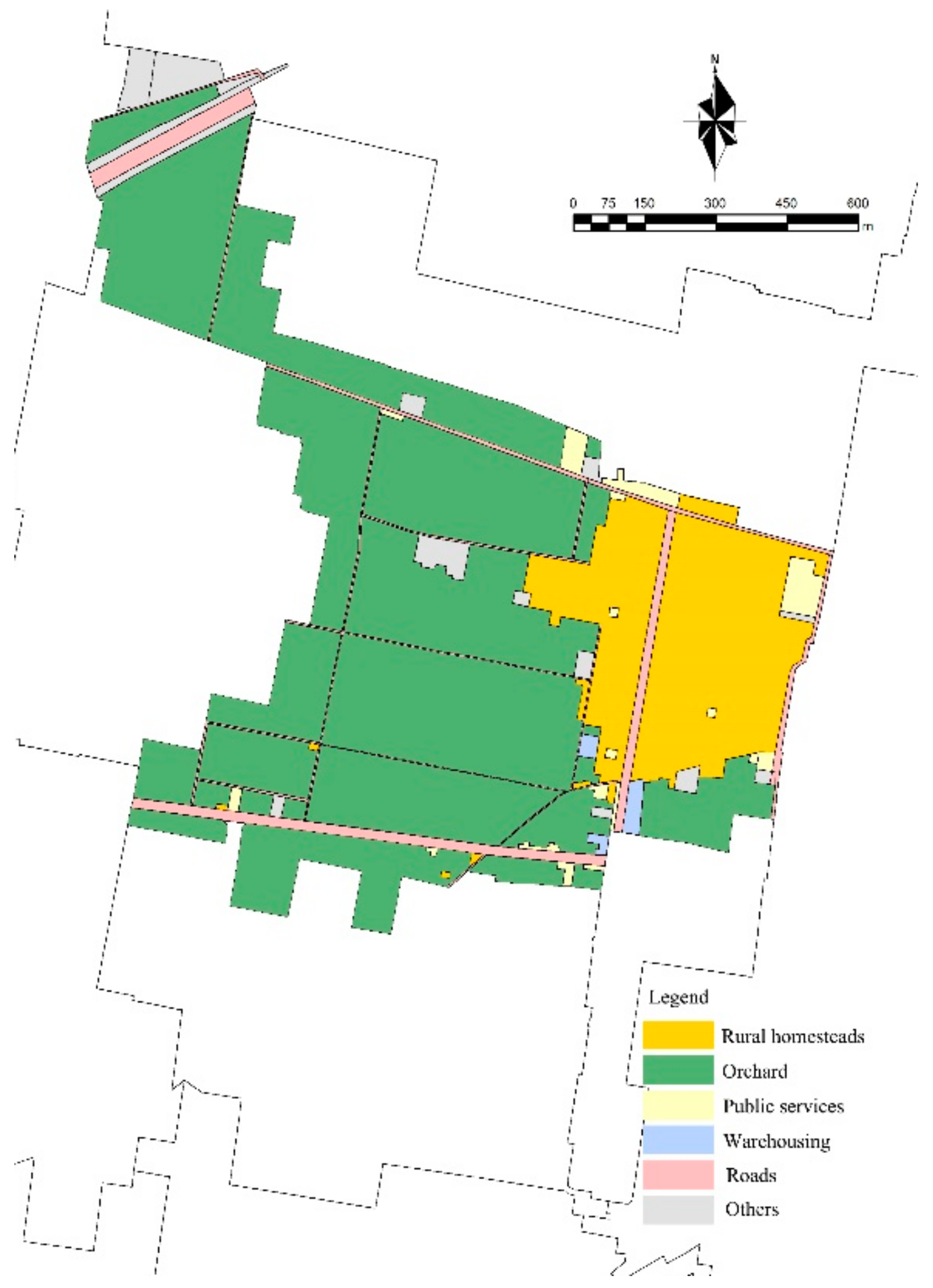
| Types of Land Use | 2009 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|
| Rural homesteads | 0.264 km2 | 0.235 km2 |
| Orchards | 0.913 km2 | 0.855 km2 |
| Roads | 0.039 km2 | 0.080 km2 |
| Public services | 0 km2 | 0.034 km2 |
| Warehousing | 0 km2 | 0.007 km2 |
| Others | 0.044 km2 | 0.049 km2 |
| Total | 1.26 km2 | 1.26 km2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Yang, G. The Mechanism of Socio-Spatial Evolution in Rural Areas Driven by the Development of the Planting Industry—A Case Study of Yuezhuang Village in Shandong Province, China. Land 2024, 13, 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060768
Wang L, Yang G. The Mechanism of Socio-Spatial Evolution in Rural Areas Driven by the Development of the Planting Industry—A Case Study of Yuezhuang Village in Shandong Province, China. Land. 2024; 13(6):768. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060768
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liyao, and Guiqing Yang. 2024. "The Mechanism of Socio-Spatial Evolution in Rural Areas Driven by the Development of the Planting Industry—A Case Study of Yuezhuang Village in Shandong Province, China" Land 13, no. 6: 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060768
APA StyleWang, L., & Yang, G. (2024). The Mechanism of Socio-Spatial Evolution in Rural Areas Driven by the Development of the Planting Industry—A Case Study of Yuezhuang Village in Shandong Province, China. Land, 13(6), 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060768







