Impact of Land Use and Climate Change on Streamflow: An Assessment Using a Semi-Empirical Model in the Guishui Watershed of North China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
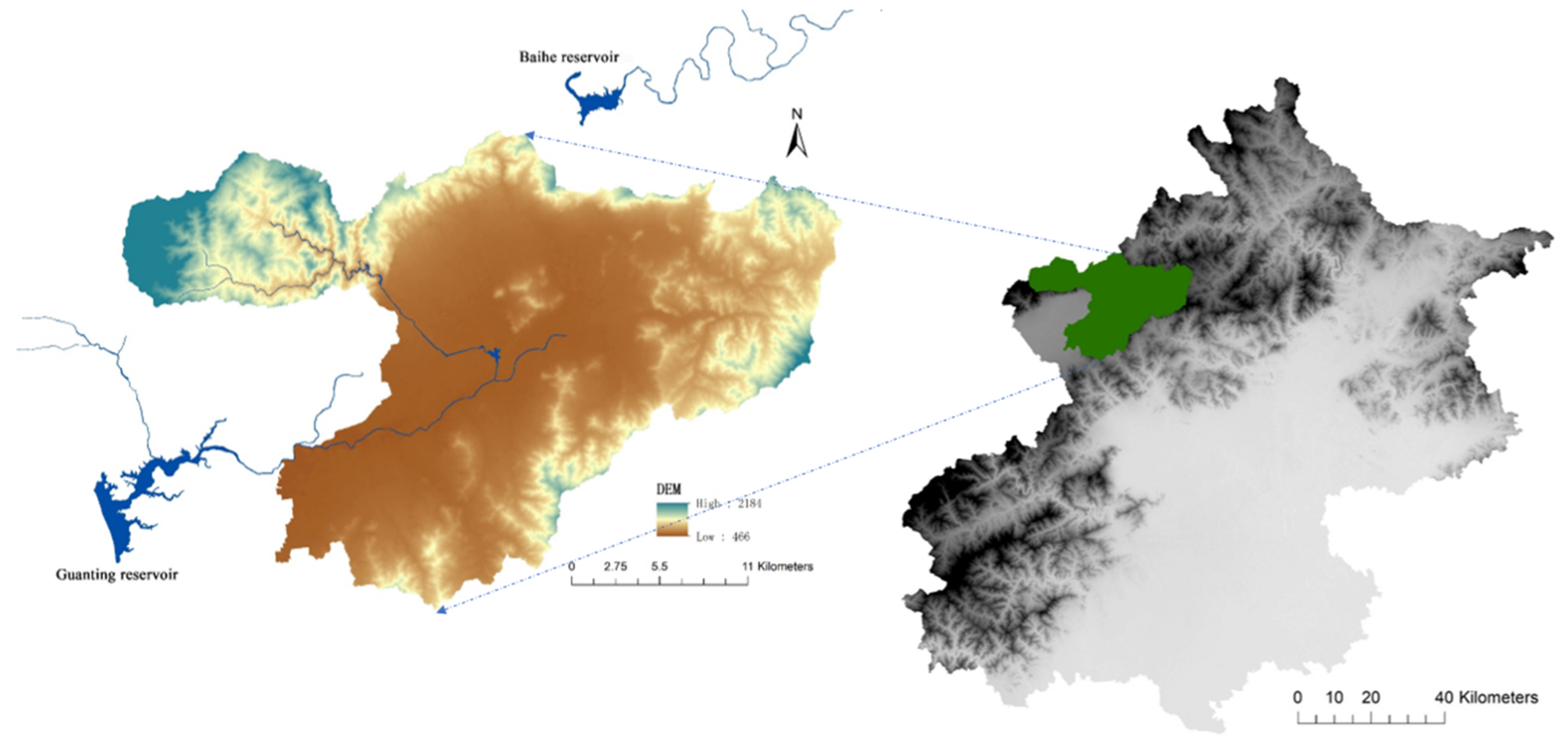
2.1. Study Scope
2.2. Hydrological Model
2.3. Pilot Catchment
2.4. Model Adjustment
2.5. Data for North China
3. Results
3.1. Discharge Data Selection
3.2. Model Calibration
3.3. Impact of Afforestation on Guishui Watershed
3.4. Impact of Climatic Changes on the Guishui Watershed
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Afforestation in North China
4.2. The Impact of Afforestation on Total Flow
4.3. Model Application
5. Conclusions
- (1)
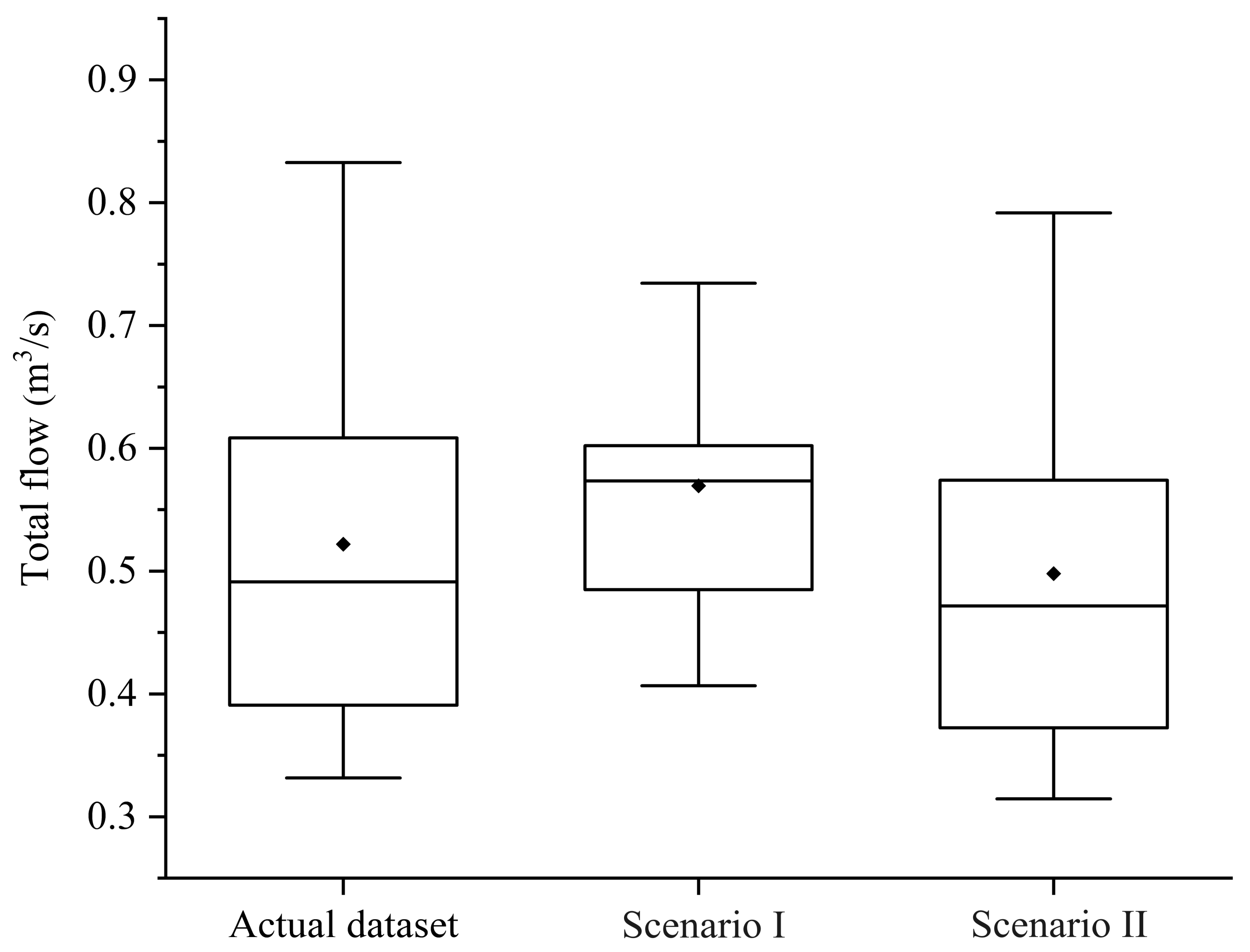
- Afforestation is a major factor in decreased total flow in the Guishui watershed. The total flow increased by around 24% compared with the actual dataset in the constant scenario and decreased by 5% compared with the actual dataset in the forest scenario. Meanwhile, temperature and precipitation had no significant change trend;
- (2)
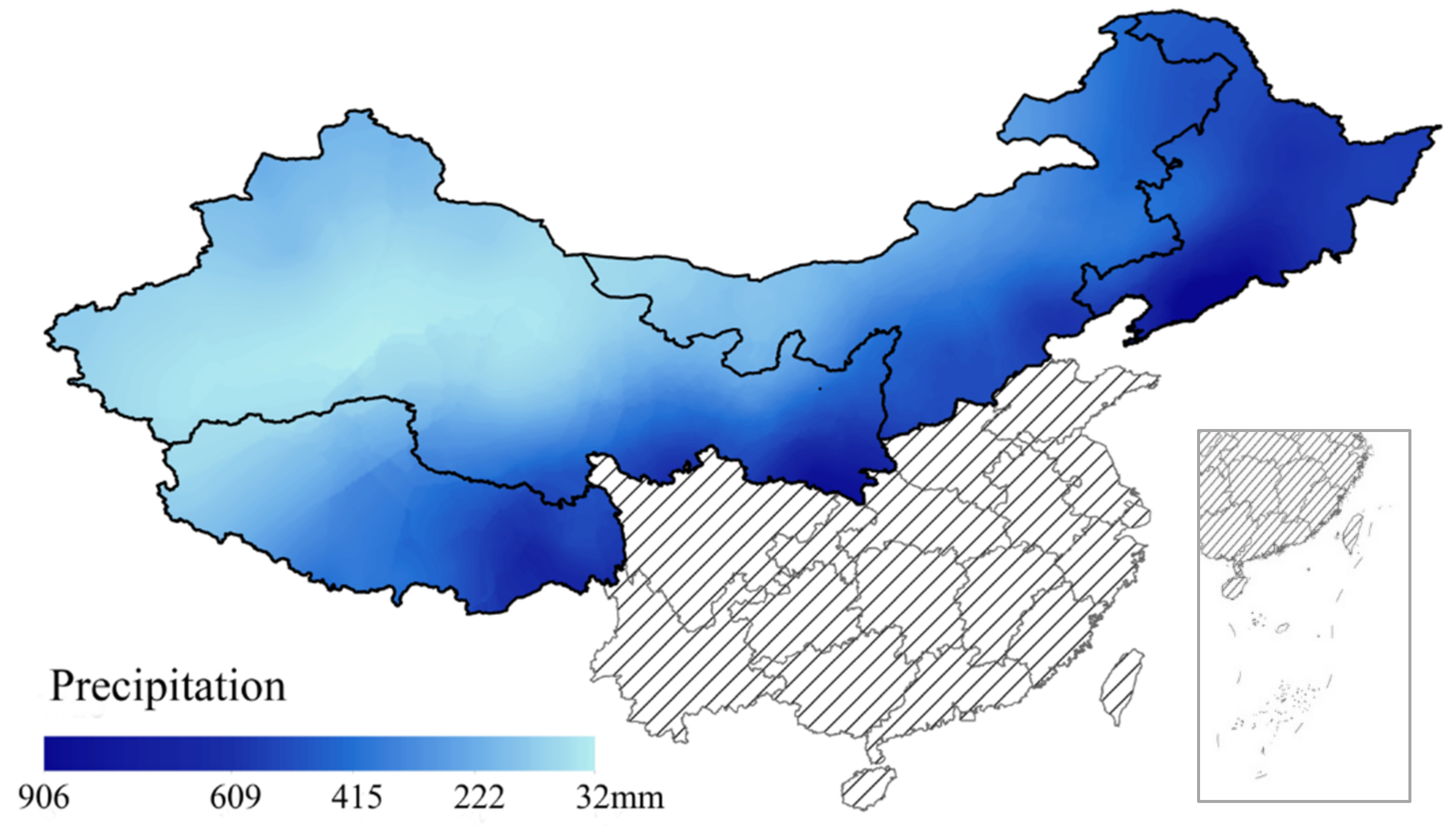
- When forest coverage increases, the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau are the most sensitive areas regarding total flow in North China. Meanwhile, in the northeast district, afforestation will not influence the total flow too much as this area benefits from a suitable climate and soil conditions. In the central–north and northwest districts, where the annual precipitation is under 520 mm and 790 mm, afforestation should be performed carefully due to detrimental effects on streamflow;
- (3)
- This research also proved that the PhosFate model is a suitable management planning tool for North China due to its low data demand.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newell, R.G.; Stavins, R.N. Climate Change and Forest Sinks: Factors Affecting the Costs of Carbon Sequestration. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2000, 40, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Xu, X. Carbon sequestration by forestation across China: Past, present, and future. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domke, G.M.; Oswalt, S.N.; Walters, B.F.; Morin, R.S. Tree planting has the potential to increase carbon sequestration capacity of forests in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24649–24651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldman, J.W.; Overbeck, G.E.; Negreiros, D.; Mahy, G.; Le Stradic, S.; Fernandes, G.W.; Durigan, G.; Buisson, E.; Putz, F.E.; Bond, W.J. Where Tree Planting and Forest Expansion are Bad for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. BioScience 2015, 65, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Walsh, M.G.; Sanderman, J.; Wheeler, I.; Harrison, S.P.; Prentice, I.C. Global mapping of potential natural vegetation: An assessment of machine learning algorithms for estimating land potential. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Li, Z. Incorporation of potential natural vegetation into revegetation programmes for sustainable land management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3503–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, F.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Fisher, B.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Tang, Y.; Yu, D.W.; Wilcove, D.S. Opportunities for Biodiversity Gains under the World’s Largest Reforestation Programme. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z.-p.; Li, R. Effects of the grain-for-green program on soil erosion in China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2012, 27, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, C. Impacts of afforestation, deforestation, and reforestation on forest cover in China from 1949 to 2003. J. For. 2006, 104, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Piao, S.; Li, L.Z.X.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Huang, L.; Lian, X.; Peng, S.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Divergent hydrological response to large-scale afforestation and vegetation greening in China. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, S.; Qiao, D.; Yuan, W.; He, Y. Broadening the scope of forest transition inquiry: What does China’s experience suggest? For. Policy Econ. 2020, 118, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, R.; Greb, S.; Block, P. Temporal Changes in Streamflow and Attribution of Changes to Climate and Landuse in Wisconsin Watersheds. Jawra J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, J.Y.G.; Da Silva, R.M.; Carvalho Neto, J.; Montenegro, S.M.G.; Santos, C.; Silva, A. Assessment of land-use change on streamflow using GIS, remote sensing and a physically-based model, SWAT. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2014, 364, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawtree, D.; Nunes, J.P.; Keizer, J.J.; Jacinto, R.; Santos, J.; Rial-Rivas, M.E.; Boulet, A.K.; Tavares-Wahren, F.; Feger, K.H. Time series analysis of the long-term hydrologic impacts of afforestation in the Águeda watershed of north-central Portugal. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3033–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, B.; Lakshman, N.; Purandara, B.K. Hydrological impacts of afforestation—A review of research in India. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, F.M.; Müller, A.; Küchler, W. Possible impacts of climate change on natural vegetation in Saxony (Germany). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2005, 50, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, J.-P.M.; Bartholomeus, R.P.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Cirkel, D.G.; van Ek, R.; Fujita, Y.; Janssen, G.M.C.M.; Spek, T.J.; Runhaar, H. A probabilistic eco-hydrological model to predict the effects of climate change on natural vegetation at a regional scale. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 835–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futang, W.; Zong-ci, Z. Impact of Climate Change on Natural Vegetation in China and its Implication for Agriculture. J. Biogeogr. 1995, 22, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Folberth, C.; Yang, H.; Röckström, J.; Abbaspour, K.; Zehnder, A.J. A global and spatially explicit assessment of climate change impacts on crop production and consumptive water use. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, G.; Tubiello, F.; Velthuizen, H.; Wiberg, D. Climate change impacts on irrigation water requirements: Effects of mitigation, 1990–2080. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2007, 74, 1083–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapalan, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Franks, S.W.; Gupta, V.K.; Karambiri, H.; Lakshmi, V.; Liang, X.; Mcdonnell, J.J.; Mendiondo, E.M.; O’Connell, P.E. IAHS Decade on Predictions in Ungauged Basins (PUB), 2003–2012: Shaping an exciting future for the hydrological sciences. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Bull. 2003, 48, 857–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Bao, A.M.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.W. Daily flow modeling in arid ungauged basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2009, 20, 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Gui, D.; Lei, J.; Feng, X.; Zeng, F.; Zhou, J.; Mao, D. Reconstructing meteorological time series to quantify the uncertainties of runoff simulation in the ungauged Qira River Basin using data from multiple stations. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X. The change analysis of soil erosion in the upper basin of Guanting reservoir. In Proceedings of the The 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics: GIScience in Change, Geoinformatics 2010, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, A.S.; Honti, M.; Clement, A. Design of best management practice applications for diffuse phosphorus pollution using interactive GIS. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2008, 57, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, A.; Honti, M.; Zessner, M.; Eder, A.; Clement, A.; Bl?schl, G. Identification of phosphorus emission hotspots in agricultural catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honti, M. Controlling River Eutrophication under Conflicts of Interests—A GIS Modeling Approach. Water 2015, 7, 5078–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batelaan, O.; De Smedt, F. WetSpass: A flexible, GIS based, distributed recharge methodology for regional groundwater modelling. IAHS Publ. 2001, 269, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, J.; Gong, H.; Cheng, X. Future climate change impacts on the ecohydrology of Guishui River Basin, China. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2014, 14, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Jiang, Q.o. Scenario analysis on the management practices and optimization of rural non-point source pollution with the coupling of source-process-end: A case study of the Guishui river basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank correlation methods. Br. J. Psychol. 1990, 25, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Qiang, Z.; Deliang, C. Stochastic modeling of daily precipitation in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2004, 14, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, G. Climate warming over the past half century has led to thermal degradation of permafrost on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Guo, L.; Yu, Y.; Luo, D.; Chu, G. Storm runoff generation in headwater catchments on the Chinese Loess Plateau after long-term vegetation rehabilitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, G. Environmental dispersion in a tidal wetland with sorption by vegetation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 22, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.E.; Zhang, L.; McMahon, T.A.; Western, A.W.; Vertessy, R.A. A review of paired catchment studies for determining changes in water yield resulting from alterations in vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 310, 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, T. Effects of large-scale afforestation project on the ecosystem water balance in humid areas: An example for southern China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 89, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yihdego, Y.; Webb, J. Modelling of seasonal and long-term trends in lake salinity in southwestern Victoria, Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahe, G.; Paturel, J.-E.; Servat, E.; Conway, D.; Dezetter, A. The impact of land use change on soil water holding capacity and river flow modelling in the Nakambe River, Burkina-Faso. J. Hydrol. 2005, 300, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; Beniston, M.; García-Ruiz, J.M. Environmental change and water management in the Pyrenees: Facts and future perspectives for Mediterranean mountains. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 61, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Tejeda, E.; Ceballos-Barbancho, A.; Llorente-Pinto, J.M. Hydrological response of Mediterranean headwaters to climate oscillations and land-cover changes: The mountains of Duero River basin (Central Spain). Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 72, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

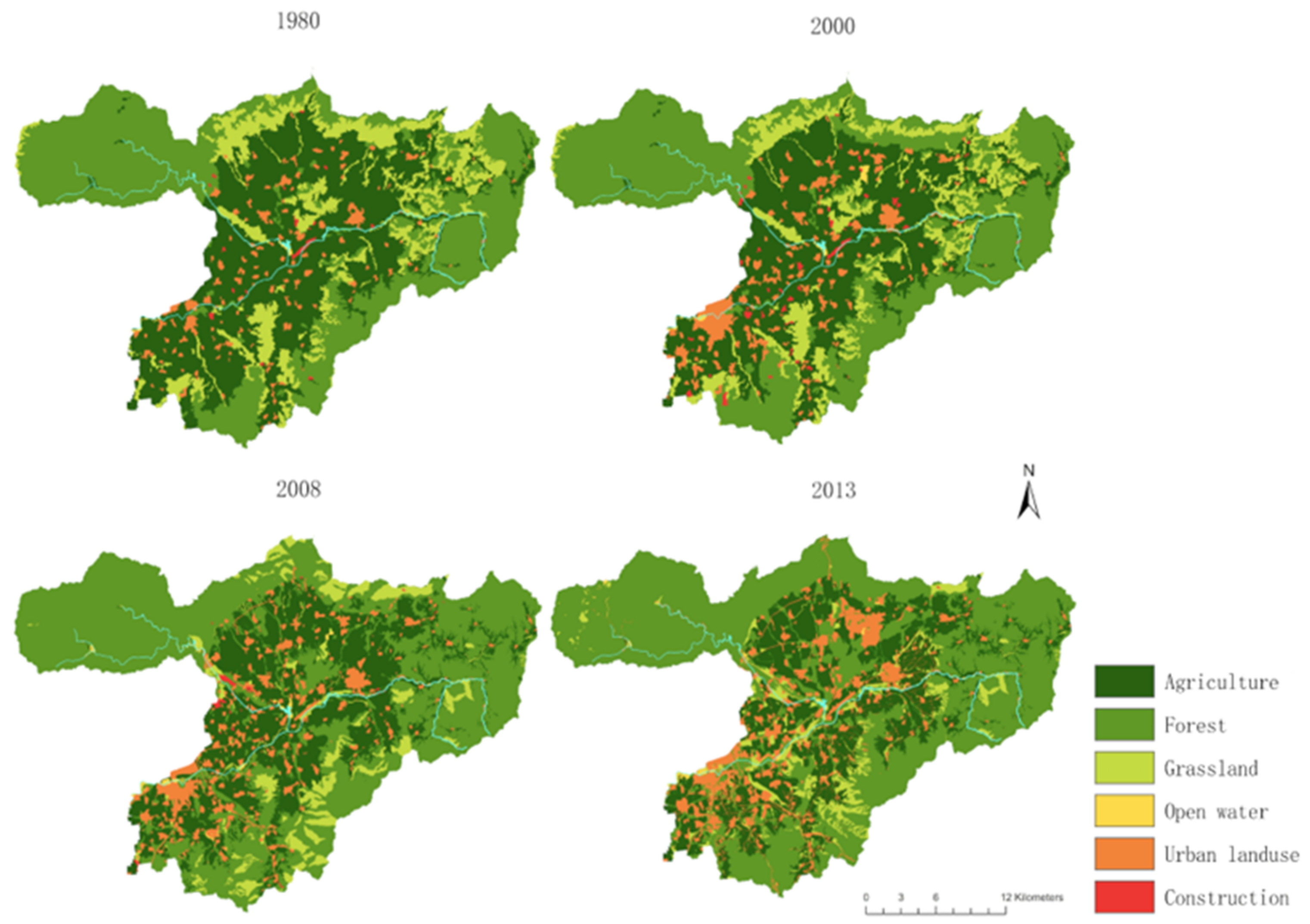






| Year | 1980 | 2000 | 2008 | 2013 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | A% | A% | △% | A% | △% | A% | △% |
| Arable land | 40.45 | 35.51 | −12.23 | 29.61 | −26.82 | 26.12 | −35.43 |
| Forest | 40.95 | 44.26 | +8.09 | 55.63 | +35.85 | 58.63 | +43.16 |
| Grassland | 14.95 | 13.48 | −9.82 | 6.88 | −54.00 | 5.48 | −63.37 |
| Open water | 0.12 | 0.27 | +135.71 | 0.62 | +430.28 | 0.51 | +335.49 |
| Settlement | 3.23 | 5.70 | +76.44 | 6.99 | +116.19 | 9.26 | +186.48 |
| Construction | 0.30 | 0.77 | +157.58 | 0.28 | −6.18 | 0.01 | −95.51 |
| Land-Use Type | Partition Coefficients Suited for Central Europe | Partition Coefficients Suited for North China | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1s | a1w | a2s | a2w | a3 | a4 | a1s | a1w | a2s | a2w | a3 | a4 | |
| Excavation | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 1 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 |
| Meadow | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 |
| Orchard | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 |
| Deciduous forest | 1 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 |
| Mixed forest | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 |
| Shrubs | 1 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 |
| Sparse vegetation | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, C.; Honti, M.; Cheng, J.; Wang, T. Impact of Land Use and Climate Change on Streamflow: An Assessment Using a Semi-Empirical Model in the Guishui Watershed of North China. Land 2024, 13, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060725
Gao C, Honti M, Cheng J, Wang T. Impact of Land Use and Climate Change on Streamflow: An Assessment Using a Semi-Empirical Model in the Guishui Watershed of North China. Land. 2024; 13(6):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060725
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Chunni, Mark Honti, Jinhua Cheng, and Tao Wang. 2024. "Impact of Land Use and Climate Change on Streamflow: An Assessment Using a Semi-Empirical Model in the Guishui Watershed of North China" Land 13, no. 6: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060725
APA StyleGao, C., Honti, M., Cheng, J., & Wang, T. (2024). Impact of Land Use and Climate Change on Streamflow: An Assessment Using a Semi-Empirical Model in the Guishui Watershed of North China. Land, 13(6), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13060725






