Geochemical Distribution of Ni, Cr, and Co in the Main Soil Types of the Čemernica River Basin in Serbia (In a Serpentine Environment)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Sampling, Pre-Treatment, and Analysis of Soil
2.3. Fractionation of the Studied Metals
2.4. Indices for Soil Contamination Assessment
2.4.1. Risk Assessment Code (RAC)
2.4.2. Soil Contamination Factor (CF)
2.4.3. Enrichment Factor (EF)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality Control of Analysis
3.2. Basic Characteristics of Soil in the Study Area
3.2.1. Fluvisol
3.2.2. Vertisol
3.2.3. Leptosol on Serpentinite
3.2.4. Leptosol on Sandstone
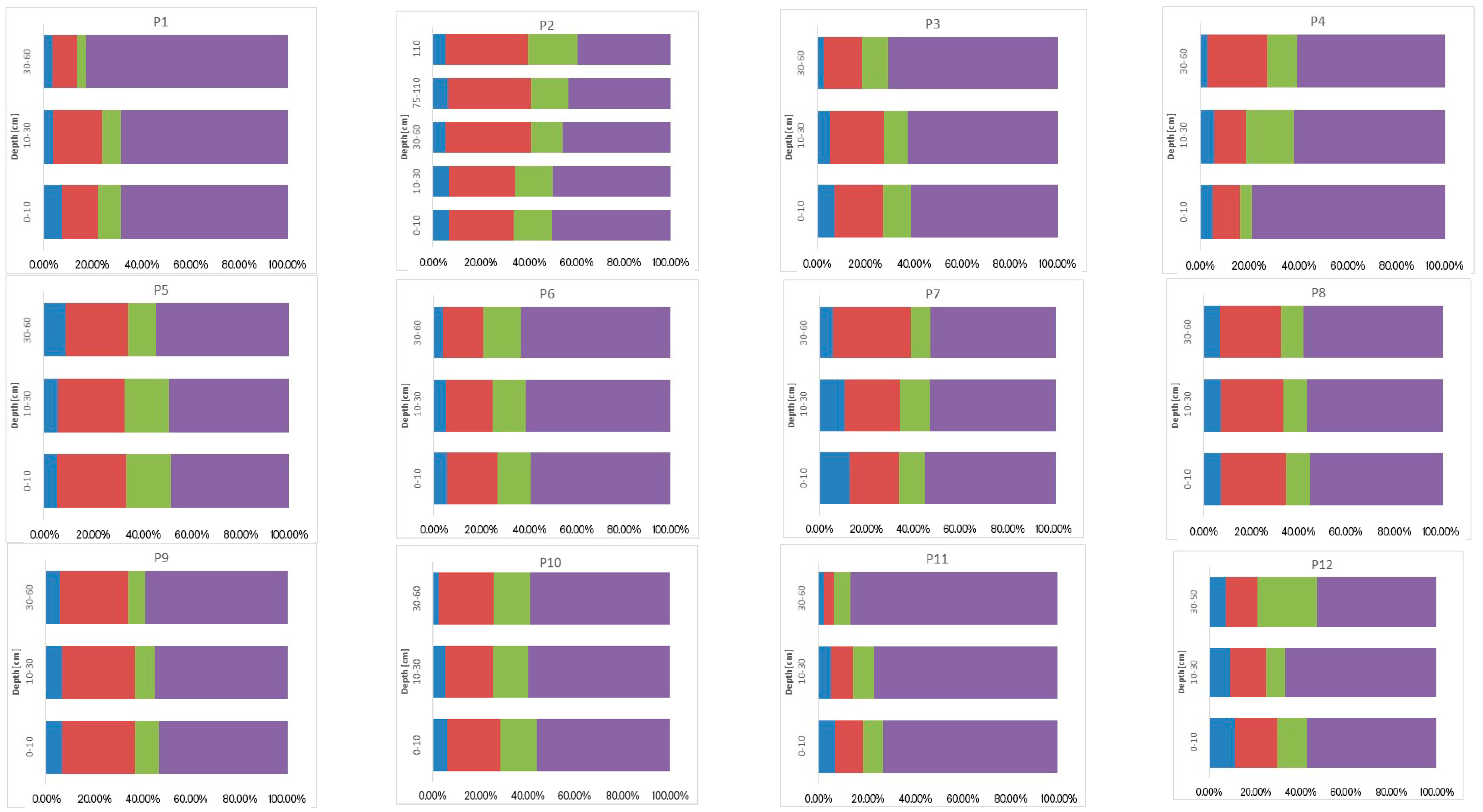
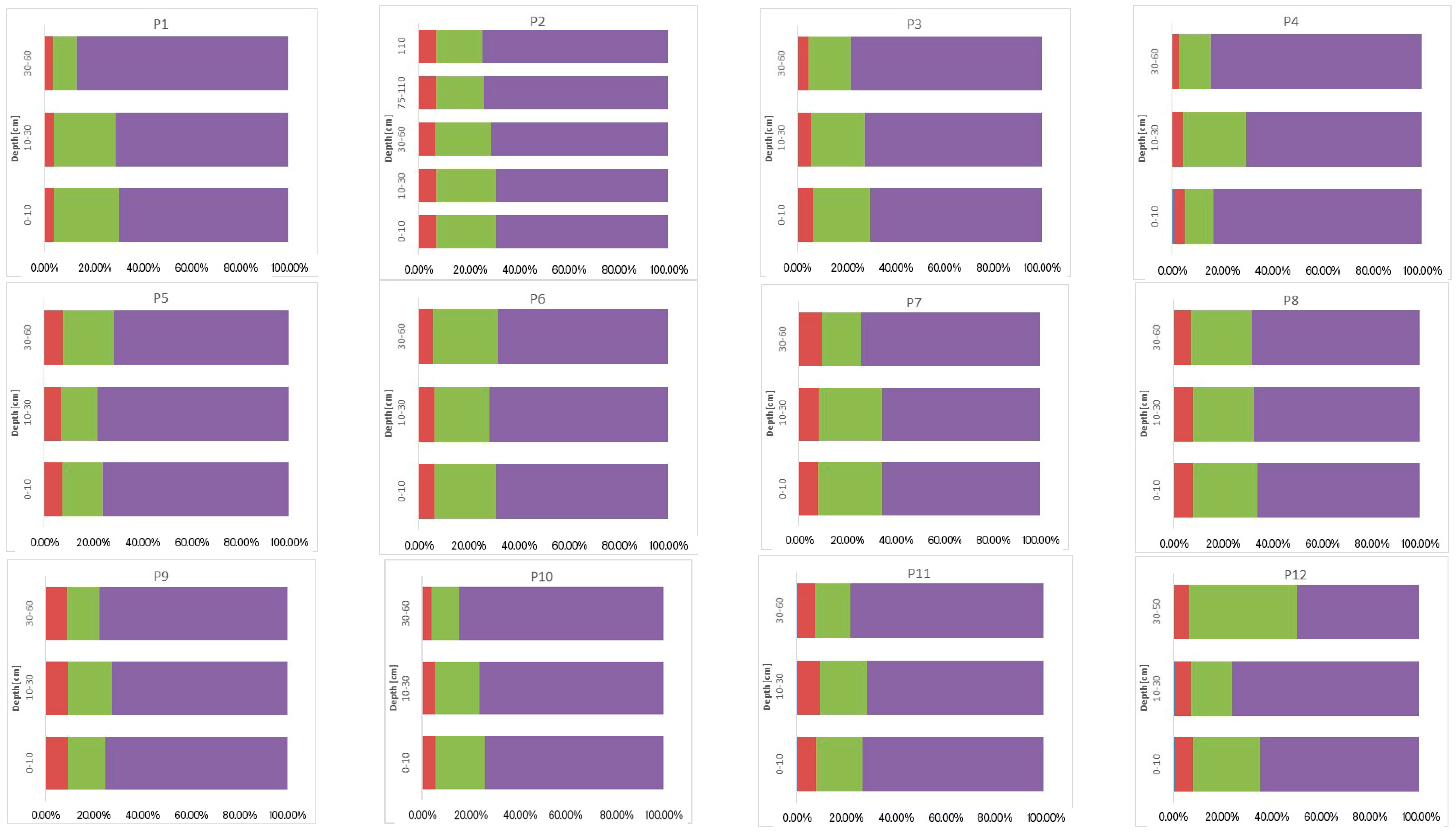
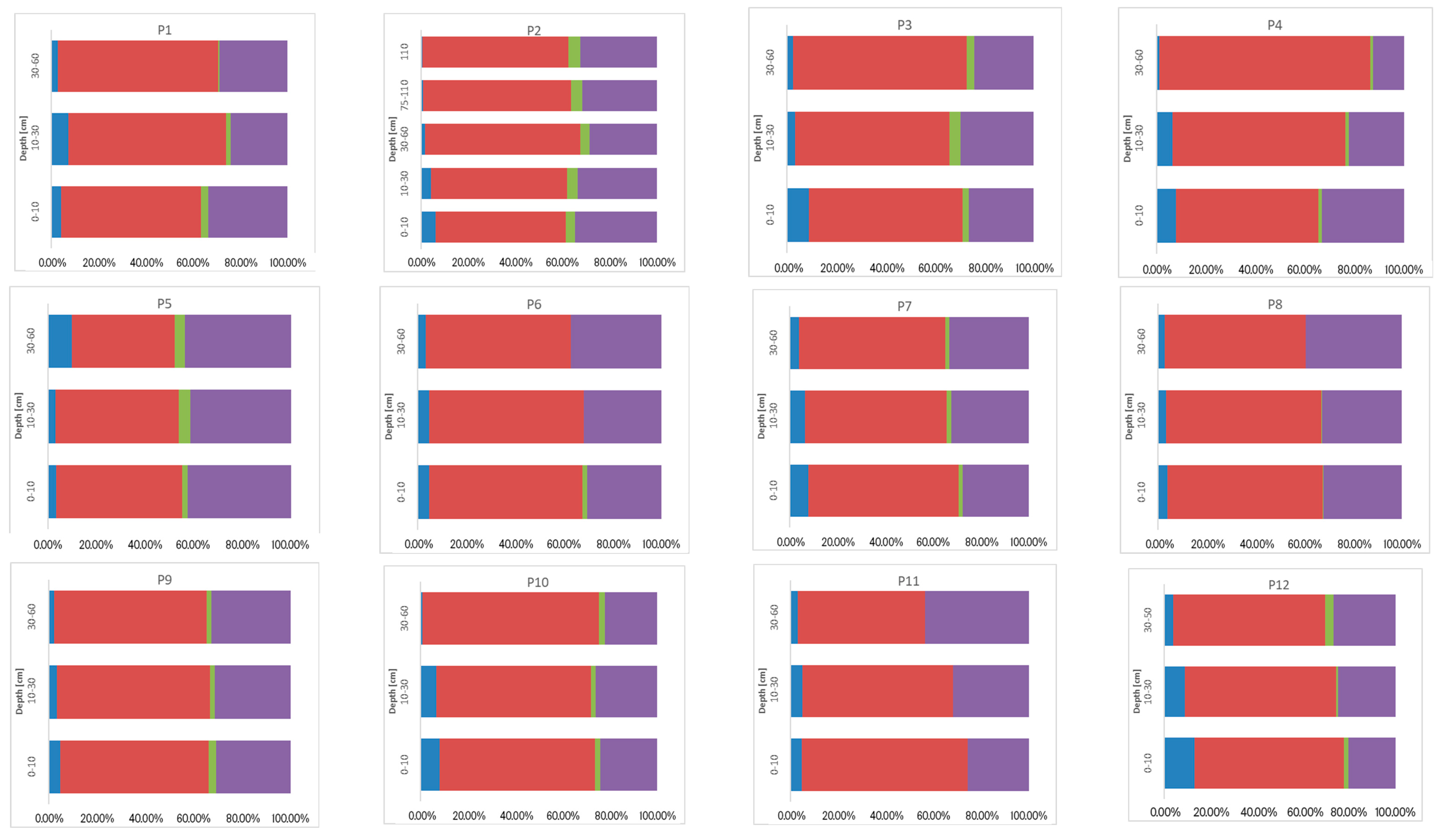
3.3. Sum of Fractions (∑F1–F4), Concentration of Ni, Cr, and Co, and Their Vertical Distribution in Soil
3.4. Geochemical Fractions and Vertical Distribution of Ni, Cr, and Co
3.4.1. Available DTPA-Extracted Ni, Cr, and Co
3.4.2. Chemical Binding Forms of Ni, Cr, and Co in the Soils Studied
3.4.3. Influence of the Properties of Studied Soil Types on the Chemical Binding Forms of Ni, Cr, and Co
3.5. Risk Assessment Code, Soil Contamination Index, and Risk Assessment Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lago-Vila, D.M.; Arenas-Lago, A.; Rodríguez-Seijo, M.L.; Andrade, C.; Vega, V.A. Cobalt, chromium and nickel contents in soils and plants from a serpentinite quarry. Solid Earth Discuss 2015, 6, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antić-Mladenović, S. Chemistry of Nickel and Chromium in Soils with Their High Geochemical Content. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Belgrade, Beograd, Serbia, 2004. (In Serbian). [Google Scholar]
- Mrvić, V.; Antonović, G.; Čakmak, D.; Perović, V.; Maksimović, S.; Saljnikov, E.; Nikoloski, M. Pedological and Pedogeochemical map of Serbia. In Proceedings of the 1st International Congress on Soil Science, XIII National Congress in Soil Science: “Soil-Water-Plant”, Belgrade, Serbia, 23–26 September 2013; pp. 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Dozet, D.; Nešić, L.; Belić, M.; Bogdanović, D.; Ninkov, J.; Zeremski, T.; Dozet, D.; Banjac, B. Origin and Content of Nickel in Alluvial-Deluvial Soils of Srem Ratar. Povrt. Field Veg. Crop Res. 2011, 48, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Poznanović Spahić, M.; Sakan, S.; Cvetković, Ž.; Tančić, P.; Trifković, J.; Nikić, Z.; Manojlović, D. Assessment of contamination, environmental risk, and origin of heavy metals in soils surrounding industrial facilities in Vojvodina, Serbia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinklebe, J.; Antić-Mladenović, S.; Frohne, T.; Staerk, H.-J.; Tomić, Z.; Ličina, V. Nickel in a serpentine-enriched Fluvisol: Redox affected dynamics and binding forms. Geoderma 2016, 263, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, S.; Sagar, B.; Sijan, D.; Sudip, S.; Rajendra, J.; Arjun, P.T.; Hak, Y.K.; Mahesh, K.J. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar]
- Belanović Simić, S.; Miljković, P.; Baumgertel, A.S.; Ljubičić, J.; Cakmak, D. Environmental and health risk Assessment of potentially toxic elements in the soil near the former antimony mine in western Serbia. Soil 2023, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, P.S. Trace Elements in Soils; Wiley: London, UK, 2010; p. 618. [Google Scholar]
- Rinklebe, J.; Shaheen, S.M. Geohemical distribution of Co, Cu, Ni, and Zn in soil profiles of Fluvisols, Luvisols, Gleysols, and Calcisols originating from Germany and Egypt. Geoderma 2017, 307, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmaz, A.; Yaman, M. Distribution of Chromium, Nickel, and Cobalt in Different Parts of Plant Species and Soil in Mining Area of Keban, Turkey. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, M.M.; Montero, M.A.; Pina, S.; García-Sánchez, E. Mineralogy and Distribution of Cd, Ni, Cr, and Pb in Biosolids-Amended Soils From Castellón Province (NE, Spain). Soil Sci. 2009, 174, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Kwon, E.E.; Biswas, J.K.; Tack, F.M.G.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J. Arsenic, chromium, molybdenum, and selenium: Geochemical fractions and potential mobilization in riverine soil profiles originating from Germany and Egypt. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushkar, B.; Sevak, P.; Parab, S.; Nilkanth, N. Chromium pollution and its bioremediation mechanisms in bacteria: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, M.; Chen, X.; Deng, T.; Sun, S.; Tang, Y.; Morel, J.L. Chromium biogeochemical behaviour in soil-plant systems and remediation strategies: A critical review. J. Hazard Mat. 2020, 424, 127233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoli, N.; Uzoho, B.; Ahukaemere, C.; Egboka, N.; Irokwe, I. Chemical fractionation and mobility of nickel in soils in relation to parent materials. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021, 67, 1075–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakor, M.; Hochwimmer, B.; Brearley, F.Q. Geochemical assessment of metal transfer from rock and soil to water in serpentine areas of Sabah (Malaysia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrvić, V.; Antonović, G.; Martinović, L.J. Fertility and Content of Toxic and Dangerous Materials in Soil of Central Serbia; Institute of Soil Science: Belgrade, Serbia, 2009. (In Serbian) [Google Scholar]
- Čakmak, D.; Perović, V.; Antić-Mladenović, S.; Kresović, M.; Saljnikov, E.; Mitrović, M.; Pavlović, P. Contamination, risk, and source apportionment of potentially toxic microelements in river sediments and soil after extreme flooding in the Kolubara River catchment in Western Serbia. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1981–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, F.; Belanović-Simić, S.; Čavlović, D.; Miljković, P.; Caković, M.; Jovanović, N.; Marković, A.; Grujić, T.; Lukić, S. Practices for Phytoremediation of Soil in Serbia. South-East Eur. 2024, 15, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Local Ecological Action Pla from City Čačak. 2003. Available online: https://www.cacak.org.rs/documents/Community_profile_242.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources; World Soil Resources Reports No. 103; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10390:2022; Soil, Treated Biowaste and Sludge-Determination of pH. SRPS: Belgrade, Serbia, 2021.
- ISO 11260:2018; Soil Quality-Determination of Effective Cation Exchange Capacity and Base Saturation Level Using Barium Chloride Solution. SRPS: Belgrade, Serbia, 2018.
- ISO 10694:2005; Soil Quality-Determination of Organic and Total Carbon after Dry Combustion (Elementary Analysis). SRPS: Belgrade, Serbia, 2005.
- ISO 22036:2008; Soil Quality-Determination of Trace Elements in Extracts of Soil by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES). SRPS: Belgrade, Serbia, 2008.
- ISO 14870:2005; Soil Quality-Extraction of Trace Elements by Buffered DTPA Solution. SRPS: Belgrade, Serbia, 2005.
- U.S. EPA. Method 3050B: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils; Revision 2; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Official Gazette of RS, no. 23/1994. Regulation on Permissible Quantities of Hazardous and Harmful Substances in Soil and Irrigation Water and Methods for Their Testing, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Water Management. Belgrade. Available online: https://pravno-informacioni-sistem.rs/eli/rep/sgrs/ministarstva/pravilnik/1994/23/1/reg (accessed on 18 March 1994).
- Official Gazette of RS, no. 30/2018 and 64/2019. Regulation on the Limit Values of Pollutant, Harmful and Dangerous Substances in the Soil (in Serbian: Uredba o Granicˇnim Vrednostima Zagad¯ujuc’ih, Štetnih i Opasnih Materija u Zemljištu). Available online: https://www.ekologija.gov.rs/sites/default/files/old-documents/Zemljiste/Uredbe/Uredba-o-granicnim-vrednostima.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Sakan, S.; Popović, A.; Anđelković, I.; Đorđević, D. Aquatic sediments pollution estimate using the metal fractionation, secondary phase enrichment factor calculation, and used statistical methods. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, L.; Craboledda, L.; Lucchese, M.; Cirillo, R.; Dotta, L.; Zanette, M.L.; Orio, A.A. Heavy metal speciation in the sediments Northern Adriatic sea: A new approach for environ-mental toxicity determination. Heavy Met. Environ. 1985, 2, 454–456. [Google Scholar]
- Sakan, S.; Frančišković-Bilinski, S.; Đorđević, D.; Popović, A.; Škrivanj, S.; Bilinski, H. Geochemical Fractionation and Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Sediments from Kupa River, Croatia. Water 2020, 12, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, Z.; Hossaini, S.M.T.; Renella, G. Risk assessment for sediment and stream water polluted by heavy metals released by a municipal solid waste composting plant. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 169, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Al-Mamun, M.H.; Masunaga, S. Potential ecological risk of hazardous elements in different land-use urban soils of Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoller, W.H.; Gladney, E.S.; Duce, R.A. Atmospheric Concentrations and Sources of Trace Metals at the South Pole. Science 1974, 183, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garrett, R.G. Background and threshold: Critical comparison of methods of determination. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Shih, K.; Zeng, E.Y.; Cheng, H. Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6150–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinklebe, J.; Shaheen, S.M. Assessing the mobilization of cadmium, lead, and nickel using a seven-step sequential extraction technique in contaminated floodplain soil profiles along the Central Elbe River, Germany. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnik, V.G.; Bauer, T.V.; Minkina, T.M. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils of the flood plain of the Seversky Donets River (Russia) based on geostatistical methods. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antić-Mladenović, S.; Rinklebe, J.; Frohne, T.; Stärk, H.J.; Wennrich, R.; Tomić, Z.; Ličina, V. Impact of controlled redox conditions on nickel in a serpentine soil. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohne, T.; Rinklebe, J.; Diaz-Bone, R.A. Contamination of floodplain soils along the Wupper River, Germany, with As, Co, Cu, Ni, Sb, and Zn and the impact of predefinite redox variations on the mobility of these elements. Soil Sediment Contam. 2014, 23, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.C.; Wall, A.J.; Hiller, S.; Clark, L. Insights into Sequential Chemical Extraction Procedures from Quantitative XRD: A Study of Trace Metal Partitioning in Sediments Related to Frog Malformities. Chem. Geol. 2002, 184, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheila, A.; Maria, A.T.; Gonçalves, M.S.; Santos, M.M. A nickel availability study in serpentinised areas of Portugal. Geoderma 2011, 164, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Kostić, N.; Wilson, J.M.; Živković, M.; Bain, D. Mineralogy and Geochemical Speciation of Heavy Metals in Some Serpentine Soils of Serbia. In Proceedings of the 16th World Congress of Soil Science, Montpellier, France, 20–26 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tsadilas, C.D.; Rinklebe, J.; Selim, H.M. Nickle in Soils and Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; p. 327. [Google Scholar]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Blsson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 52, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Shan, X. Distribution and Speciation of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments from Guanting Reservoir, Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2002, 37, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Haider, F.U.; Ahmad, M.; Hussain, S.; Maqsood, M.F.; Ishfaq, M.; Shahzad, B.; Waqas, M.M.; Ali, B.; Tayyab, M.N.; et al. Chromium toxicity, speciation, and remediation strategies in soil-plant interface: A critical review. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1081624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avudainayagam, S.; Megharaj, M.; Owens, G.; Kookana, R.S.; Chittleborough, D.; Naidu, R. Chemistry of chromium in soils with emphasis on tannery waste sites. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 178, 53–91. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J. Geochemical fractions of chromium, copper, and zinc and their vertical distribution in floodplain soil profiles along the central Elbe River, Germany. Geoderma 2014, 228–229, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrović, M.; Blanusa, T.; Pavlović, M.; Pavlović, D.; Kostić, O.; Perović, V.; Jarić, S.; Pavlović, P. Using Fractionation Profile of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils to Investigate Their Accumulation in Tilia sp. Leaves in Urban Areas with Different Pollution Levels. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.T.; Conklin, M.H.; Fuller, C.C.; O’Day, P.A. Processes of nickel and cobalt uptake by a manganese oxide forming sediment in Pinal Creek, Globe Mining, Arizona. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4719–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendling, L.A.; Kirby, J.K.; McLaughlin, M.J. A novel technique to determine cobalt exchangeability in soils using isotope dilution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; McLaren, R.G.; Metherell, A.K. Fractionation of cobalt and manganese in New Zealand soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jović, M.; Šljivić-Ivanović, M.; Dimović, S.; Marković, J.; Smičiklas, I. Sorption and mobility of Co(II) in relation to soil properties. Geoderma 2017, 297, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smičiklas, I.; Dimović, S.; Jović, M.; Milenković, A.; Šljivić-Ivanović, M. Evaluation study of cobalt(II) and strontium(II) sorption–desorption behavior for selection of soil remediation technology. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3853–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil | Depth [cm] | Statistic | pH in KCl | SOM | Clay * | Total Sand * | CEC | Fe * | Mn * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluvisol | 0–10 n = 3 | Mean | 5.48 | 5.05 | 35.00 | 28.30 | 32.61 | 25,711.40 | 820.09 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.75 | 1.04 | 9.82 | 5.47 | 7.70 | 1301.21 | 124.94 | ||
| Minimum | 4.78 | 3.88 | 24.80 | 22.00 | 24.90 | 24,533.85 | 682.96 | ||
| Maximum | 6.27 | 5.86 | 44.40 | 31.80 | 40.30 | 27,108.37 | 927.46 | ||
| 10–30 n = 3 | Mean | 5.00 | 3.38 | 37.27 | 26.47 | 30.53 | 26,243.36 | 898.66 | |
| Std. Dev. | 0.70 | 0.81 | 11.12 | 6.73 | 6.61 | 2827.05 | 204.07 | ||
| Minimum | 4.35 | 2.45 | 26.50 | 18.70 | 23.60 | 23,296.82 | 744.42 | ||
| Maximum | 5.75 | 3.88 | 48.70 | 30.60 | 36.70 | 28,933.43 | 1130.06 | ||
| 30–60 n = 3 | Mean | 4.64 | 1.61 | 48.43 | 19.53 | 35.69 | 29,961.66 | 606.34 | |
| Std. Dev. | 0.77 | 0.53 | 4.97 | 4.90 | 7.00 | 3209.20 | 111.37 | ||
| Minimum | 4.02 | 1.20 | 42.70 | 13.90 | 27.60 | 26,572.12 | 529.09 | ||
| Maximum | 5.50 | 2.21 | 51.30 | 22.80 | 40.20 | 32,953.44 | 734.01 | ||
| Mean of type soil | 5.18 a | 2.86 a,b | 40.08 a | 25.16 c | 32.71 a | 26,742.44 b | 757.99 b | ||
| Vertisol | 0–10 n = 4 | Mean | 5.36 | 2.51 | 39.38 | 30.93 | 28.10 | 20,477.53 | 636.72 |
| Std. Dev. | 1.16 | 0.35 | 10.39 | 9.13 | 1.70 | 5612.38 | 67.14 | ||
| Minimum | 4.45 | 2.21 | 26.50 | 24.80 | 26.90 | 13,206.83 | 539.53 | ||
| Maximum | 7.06 | 2.84 | 50.60 | 44.50 | 29.30 | 26,867.86 | 693.20 | ||
| 10–30 n = 4 | Mean | 5.39 | 2.46 | 40.38 | 30.75 | 28.28 | 20,671.16 | 685.39 | |
| Std. Dev. | 1.25 | 0.47 | 10.46 | 9.30 | 4.23 | 5441.04 | 129.69 | ||
| Minimum | 4.32 | 1.85 | 27.40 | 23.70 | 25.30 | 13,987.21 | 517.28 | ||
| Maximum | 7.19 | 2.94 | 49.30 | 44.40 | 31.30 | 27,251.79 | 832.42 | ||
| 30–60 n = 4 | Mean | 5.26 | 1.37 | 43.52 | 29.38 | 30.69 | 22,422.16 | 590.51 | |
| Std. Dev. | 1.43 | 0.43 | 6.45 | 7.20 | 3.40 | 7875.85 | 104.35 | ||
| Minimum | 4.10 | 0.83 | 34.70 | 23.80 | 28.30 | 17,079.24 | 496.76 | ||
| Maximum | 7.34 | 1.89 | 50.20 | 39.50 | 33.10 | 33,959.81 | 711.30 | ||
| Mean of type soil | 5.33 a | 2.12 b | 41.09 a | 30.35 b,c | 29.02 a | 21,190.28 c | 637.54 b | ||
| Leptosol on serpentinite | 0–10 n = 3 | Mean | 5.71 | 5.95 | 28.47 | 40.47 | 30.39 | 34,450.97 | 908.66 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.42 | 1.55 | 8.38 | 14.52 | 5.08 | 6639.60 | 183.43 | ||
| Minimum | 5.40 | 4.33 | 21.60 | 24.10 | 26.80 | 27,047.90 | 788.82 | ||
| Maximum | 6.18 | 7.40 | 37.80 | 51.80 | 34.00 | 39,878.83 | 1119.82 | ||
| 10–30 n = 3 | Mean | 5.64 | 4.05 | 29.83 | 35.37 | 29.86 | 39,132.03 | 887.76 | |
| Std. Dev. | 0.43 | 1.09 | 9.58 | 10.97 | 3.17 | 1944.27 | 220.72 | ||
| Minimum | 5.25 | 2.86 | 22.60 | 23.20 | 27.60 | 37,695.44 | 705.86 | ||
| Maximum | 6.11 | 4.99 | 40.70 | 44.50 | 32.10 | 41,344.43 | 1133.31 | ||
| 30–60 n = 3 | Mean | 5.81 | 1.70 | 32.74 | 39.63 | 32.43 | 44,388.30 | 893.08 | |
| Std. Dev. | 0.47 | 1.18 | 16.05 | 15.89 | 8.53 | 5847.84 | 44.19 | ||
| Minimum | 5.30 | 0.72 | 21.33 | 23.10 | 26.40 | 37,826.88 | 859.56 | ||
| Maximum | 6.22 | 3.02 | 51.10 | 54.80 | 38.50 | 49,050.33 | 943.16 | ||
| Mean of type soil | 5.72 a | 3.90 a | 30.35 b | 38.49 b | 30.89 a | 39,323.77 a | 896.50 a | ||
| Leptosol on sandstone | 0–10 n = 2 | Mean | 4.17 | 2.61 | 21.05 | 55.90 | 16.25 | 15,665.28 | 726.19 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.35 | 0.45 | 4.74 | 2.97 | 0.73 | 4243.01 | 144.40 | ||
| Minimum | 3.92 | 2.30 | 17.70 | 53.80 | 15.70 | 12,665.02 | 624.08 | ||
| Maximum | 4.41 | 2.93 | 24.40 | 58.00 | 16.80 | 18,665.54 | 828.29 | ||
| 10–30 n = 2 | Mean | 4.16 | 1.72 | 22.55 | 50.85 | 13.80 | 18,201.00 | 780.30 | |
| Std. Dev. | 0.34 | 0.17 | 4.45 | 0.35 | 1.60 | 3161.56 | 220.13 | ||
| Minimum | 3.92 | 1.60 | 19.40 | 50.60 | 12.70 | 15,965.45 | 624.64 | ||
| Maximum | 4.40 | 1.85 | 25.70 | 51.10 | 14.90 | 20,436.56 | 935.95 | ||
| 30–60 n = 2 | Mean | 4.20 | 1.21 | 21.10 | 51.05 | 15.34 | 15,046.70 | 704.33 | |
| Std. Dev. | 0.47 | 0.58 | 0.85 | 4.45 | 1.79 | 1430.90 | 61.41 | ||
| Minimum | 3.86 | 0.80 | 20.50 | 47.90 | 14.10 | 14,034.90 | 660.90 | ||
| Maximum | 4.53 | 1.62 | 21.70 | 54.20 | 16.60 | 16,058.50 | 747.75 | ||
| Mean of type soil | 4.17 b | 1.85 b | 21.57 c | 52.60 a | 15.13 b | 16,304.33 d | 736.94 b | ||
| Soil | Depth [cm] | PTE | Concentration (mg kg−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | Sum of Fractions | DTPA | Total | |||
| Fluvisol (P1, P2, P3) | 0–10 | Ni | 12.88 ± 6.15 | 42.92 ± 34.76 | 25.12 ± 19.93 | 105.74 ± 38.44 | 186.66 ± 99.24 | 13.56 ± 3.52 | 191.44 ± 86.24 |
| Cr | 0.26 ± 0.13 | 7.71 ± 5.54 | 30.53 ± 13.09 | 88.00 ± 40.49 | 126.50 ± 59.14 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 132.68 ± 53.39 | ||
| Co | 1.96 ± 0.97 | 17.62 ± 2.99 | 0.97 ± 0.21 | 9.28 ± 0.92 | 29.84 ± 3.89 | 1.82 ± 2.57 | 26.66 ± 2.78 | ||
| 10–30 | Ni | 11.67 ± 8.11 | 50.14 ± 31.45 | 25.36 ± 20.18 | 116.66 ± 32.30 | 203.82 ± 91.75 | 14.11 ± 5.95 | 202.65 ± 67.68 | |
| Cr | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 7.96 ± 5.48 | 31.87 ± 12.60 | 95.73 ± 36.17 | 135.77 ± 54.15 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 135.44 ± 37.68 | ||
| Co | 1.88 ± 1.04 | 23.21 ± 5.70 | 1.29 ± 0.39 | 10.50 ± 0.07 | 36.88 ± 6.26 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 30.33 ± 2.62 | ||
| 30–60 | Ni | 10.44 ± 7.22 | 60.17 ± 58.70 | 25.48 ± 20.48 | 154.11 ± 7.03 | 249.79 ± 92.17 | 9.04 ± 4.16 | 251.43 ± 81.73 | |
| Cr | 0.08 ± 0.10 | 7.87 ± 4.81 | 26.13 ± 16.20 | 116.07 ± 20.07 | 150.26 ± 40.75 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 176.65 ± 58.27 | ||
| Co | 0.89 ± 0.14 | 25.71 ± 1.67 | 1.00 ± 0.70 | 10.22 ± 0.74 | 37.82 ± 1.64 | 0.33 ± 0.15 | 26.03 ± 2.45 | ||
| Mean of type soil | Ni | 13.47 b | 67.05 b | 34.15 b | 132.09 b | 249.76 | 11.27 | 215.48 | |
| Cr | 0.25 b | 8.70 b | 30.27 b | 106.04 b | 145.26 | 0.01 | 148.25 | ||
| Co | 0.89 b | 19.86 b | 1.46 a | 10.44 b | 32.66 | 0.19 | 27.67 | ||
| Vertisol (P4, P5. P6, P7) | 0–10 | Ni | 5.71 ± 1.48 | 18.05 ± 10.16 | 10.67 ± 7.57 | 53.45 ± 22.19 | 87.88 ± 28.11 | 5.03 ± 1.82 | 94.19 ± 34.47 |
| Cr | 0.25 ± 0.19 | 3.65 ± 0.86 | 11.10 ± 2.22 | 43.87 ± 12.96 | 58.86 ± 11.67 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 70.07 ± 19.28 | ||
| Co | 1.27 ± 0.63 | 12.26 ± 2.91 | 0.37 ± 0.08 | 6.85 ± 1.41 | 20.74 ± 4.25 | 0.39 ± 0.31 | 17.69 ± 5.21 | ||
| 10–30 | Ni | 5.10 ± 1.31 | 16.80 ± 8.95 | 12.99 ± 5.54 | 43.76 ± 9.41 | 78.65 ± 21.77 | 4.36 ± 1.52 | 86.16 ± 19.76 | |
| Cr | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 3.26 ± 0.76 | 11.40 ± 1.65 | 37.81 ± 7.88 | 52.60 ± 7.09 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 65.62 ± 10.57 | ||
| Co | 1.06 ± 0.46 | 12.49 ± 4.38 | 0.37 ± 0.31 | 6.17 ± 0.75 | 20.08 ± 4.58 | 0.35 ± 0.25 | 18.68 ± 4.65 | ||
| 30–60 | Ni | 5.31 ± 1.89 | 27.95 ± 15.27 | 13.36 ± 7.64 | 65.23 ± 37.04 | 111.85 ± 58.91 | 3.56 ± 2.97 | 110.46 ± 57.21 | |
| Cr | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 3.93 ± 0.80 | 12.40 ± 3.33 | 52.67 ± 24.20 | 69.13 ± 24.51 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 77.96 ± 32.95 | ||
| Co | 0.87 ± 0.32 | 22.26 ± 25.93 | 0.46 ± 0.40 | 6.97 ± 1.36 | 30.55 ± 27.46 | 0.37 ± 0.52 | 26.50 ± 22.67 | ||
| Mean of type soil | Ni | 5.37 b.c | 20.93 b.c | 12.34 b | 54.15 b | 92.79 | 4.32 | 96.96 | |
| Cr | 0.17 b | 3.59 b | 11.70 c | 45.61 c | 61.07 | 0.01 | 71.21 | ||
| Co | 1.07 b | 15.98 b.c | 0.41 b | 6.73 c | 24.19 | 0.38 | 20.96 | ||
| Leptosol on serpentinite (P8, P9, P10) | 0–10 | Ni | 50.99 ± 23.13 | 208.10 ± 108.02 | 93.96 ± 50,61 | 427.27 ± 187.55 | 780.32 ± 354.33 | 55.17 ± 7.87 | 745.06 ± 309.47 |
| Cr | 0.66± | 29.45± | 77.33± | 277.97± | 385.41± | 0.03± | 437.87± | ||
| 0.12 | 12.05 | 11.71 | 61.01 | 63.31 | 0.02 | 65.18 | |||
| Co | 4.31± | 48.31± | 1.45± | 21.75± | 75.83± | 0.89± | 65.07± | ||
| 2.22 | 8.12 | 1.25 | 2.96 | 12.22 | 0.43 | 9.93 | |||
| 10–30 | Ni | 48.64 ± 23.48 | 198.63 ± 111.46 | 81.01 ± 36.69 | 436.44 ± 174.90 | 764.73 ± 323.26 | 44.91 ± 6.10 | 734.75 ± 285.15 | |
| Cr | 0.58± | 30.20± | 83.33± | 291.92± | 406.02± | 0.02± | 432.24± | ||
| 0.23 | 13.14 | 18.38 | 47.26 | 68.93 | 0.02 | 82.62 | |||
| Co | 3.14± | 47.19± | 1.12± | 22.04± | 73.50± | 0.58± | 63.65± | ||
| 1.31 | 5.62 | 0.80 | 3.85 | 9.20 | 0.24 | 4.86 | |||
| 30–60 | Ni | 75.22 ± 43.37 | 325.34 ± 262.08 | 114.44 ± 120.92 | 597.91 ± 611.61 | 1085.31 ± 1038.08 | 50.82 ± 26.84 | 950.02 ± 506.94 | |
| Cr | 0.58± | 29.69± | 72.54± | 353.39± | 456.19± | 0.01± | 459.36± | ||
| 0.29 | 11.55 | 22.08 | 76.99 | 53.15 | 0.02 | 41.57 | |||
| Co | 1.45± | 54.01± | 1.36± | 24.22± | 81.03± | 0.31± | 65.79± | ||
| 0.53 | 21.28 | 1.34 | 1.75 | 21.34 | 0.20 | 15.64 | |||
| Mean of type soil | Ni | 47.70 a | 222.94 a | 98.63 a | 491.77 a | 861.04 | 42.30 | 106.3 | |
| Cr | 0.61 a | 30.82 a | 79.02 a | 307.13 a | 417.58 | 0.02 | 94.22 | ||
| Co | 2.87 a | 48.94 a | 1.25 a | 22.87 a | 75.92 | 0.57 | 117.11 | ||
| Leptosol on sandstone (P11, P12) | 0–10 | Ni | 4.01± | 6.44± | 4.52± | 25.49± | 40.46± | 3.02± | 46.88± |
| 2.63 | 4.29 | 2.88 | 5.36 | 15.17 | 2.00 | 19.65 | |||
| Cr | 0.14± | 2.06± | 6.60± | 18.88± | 27.67± | 0.03± | 32.17± | ||
| 0.02 | 0.65 | 3.68 | 4.50 | 8.85 | 0.01 | 14.42 | |||
| Co | 1.72± | 11.79± | 0.20± | 3.98± | 17.70± | 0.54± | 14.37± | ||
| 1.49 | 2.49 | 0.28 | 0.39 | 4.66 | 0.36 | 5.22 | |||
| 10–30 | Ni | 3.21± | 5.23± | 3.44± | 27.95± | 39.83± | 2.25± | 48.85± | |
| 2.34 | 3.77 | 1.36 | 8.60 | 16.07 | 1.51 | 15.42 | |||
| Cr | 0.13± | 2.11± | 4.80± | 20.59± | 27.63± | 0.02± | 35.93± | ||
| 0.02 | 0.54 | 1.70 | 9.97 | 12.22 | 0.01 | 17.51 | |||
| Co | 1.26± | 10.89± | 0.10± | 4.64± | 16.89± | 0.38± | 15.14± | ||
| 0.87 | 3.80 | 0.14 | 0.69 | 5.49 | 0.24 | 4.51 | |||
| 30–60 | Ni | 1.88± | 3.70± | 6.62± | 26.89± | 39.08± | 1.03± | 42.80± | |
| 1.46 | 2.89 | 5.80 | 7.62 | 2.54 | 0.56 | 6.94 | |||
| Cr | 0.09± | 1.75± | 8.40± | 16.44± | 26.68± | 0.01± | 30.82 | ||
| 0.00 | 0.22 | 7.35 | 1.35 | 6.23 | 0.02 | 2.70 | |||
| Co | 0.48± | 8.43± | 0.28± | 4.74± | 13.93± | 0.14± | 12.35± | ||
| 0.17 | 2.91 | 0.40 | 0.67 | 2.81 | 0.01 | 1.44 | |||
| Mean of type soil | Ni | 3.04 c | 5.12 c | 4.86 b | 26.77 b | 39.79 | 2.10 | 46.17 | |
| Cr | 0.12 b | 1.93 c | 6.17 c | 18.19 c | 41.58 | 0.02 | 32.93 | ||
| Co | 1.07 b | 10.06 c | 0.17 b | 4.44 d | 15.74 | 0.33 | 13.94 | ||
| PTEs Fractions | pHinKCl | SOM | Sand tot | Silt | Clay | CEC | Fe tot | Mn tot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | F1 | 0.131 | 0.340 * | 0.464 ** | −0.171 | −0.43 ** | −0.373 * | −0.343 * | 0.029 |
| F2 | 0.715 ** | 0.163 | −0.253 | −0.02 | 0.296 | 0.613 ** | 0.30 | 0.062 | |
| F3 | 0.328 * | −0.146 | −0.321 * | −0.042 | 0.384 * | 0.259 | −0.159 | −0.232 | |
| F4 | −0.70 ** | −0.129 | 0.227 | 0.071 | −0.293 | −0.48 ** | −0.075 | 0.051 | |
| Ni total | 0.427 ** | 0.199 | −0.106 | 0.097 | 0.068 | 0.505 ** | 0.708 ** | 0.293 | |
| Cr | F1 | −0.265 | −0.182 | 0.379 * | −0.175 | −0.334 * | −0.607 ** | −0.577 ** | −0.146 |
| F2 | 0.334 * | 0.19 | 0.544 ** | −0.417 ** | −0.391 * | −0.277 | −0.233 | 0.079 | |
| F3 | −0.121 | 0.287 | 0.2 | 0.117 | −0.287 | −0.152 | −0.243 | 0.241 | |
| F4 | 0.033 | −0.317 | −0.339 * | 0.002 | 0.381 * | 0.214 | 0.304 | −0.246 | |
| Cr total | 0.431 ** | 0.369 * | −0.013 | 0.141 | −0.06 | 0.508 ** | 0.842 ** | 0.451 ** | |
| Co | F1 | −0.083 | 0.274 | 0.219 | −0.035 | −0.228 | −0.34 | −0.326 * | −0.098 |
| F2 | −0.547 ** | −0.115 | −0.061 | 0.181 | −0.028 | 0.039 | 0.312 | 0.256 | |
| F3 | 0.558 ** | −0.018 | −0.465 ** | 0.167 | 0.435 ** | 0.514 ** | −0.112 | −0.248 | |
| F4 | 0.484 ** | 0.011 | 0.083 | −0.217 | 0.023 | −0.02 | −0.168 | −0.172 | |
| Co total | 0.243 | 0.296 | −0.105 | 0.22 | 0 | 0.460 * | 0.861 ** | 0.451 ** | |
| Index | PTEs | Index Scale | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Risk | Low | Moderate | High (Considerable) | Very High | ||
| RAC | Ni | - | 94.9 | 5.1 | - | - |
| Cr | 100 | - | - | - | - | |
| Co | 7.8 | 87.1 | 5.1 | - | - | |
| CF | Ni | - | 12.8 | 41 | 18 | 28.2 |
| Cr | - | 46.2 | 30.7 | 23.1 | - | |
| Co | - | 76.9 | 20.5 | 2.6 | - | |
| EF | Ni | 82.1 | 12.8 | 5.1 | - | - |
| Cr | 66.7 | 30.7 | 2.6 | - | - | |
| Co | 82.1 | 17.9 | - | - | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tošić Jojević, S.; Mrvić, V.; Stajković-Srbinović, O.; Jovković, M.; Antić Mladenović, S.; Krpović, M.; Belanović Simić, S. Geochemical Distribution of Ni, Cr, and Co in the Main Soil Types of the Čemernica River Basin in Serbia (In a Serpentine Environment). Land 2024, 13, 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122075
Tošić Jojević S, Mrvić V, Stajković-Srbinović O, Jovković M, Antić Mladenović S, Krpović M, Belanović Simić S. Geochemical Distribution of Ni, Cr, and Co in the Main Soil Types of the Čemernica River Basin in Serbia (In a Serpentine Environment). Land. 2024; 13(12):2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122075
Chicago/Turabian StyleTošić Jojević, Sonja, Vesna Mrvić, Olivera Stajković-Srbinović, Marina Jovković, Svetlana Antić Mladenović, Matija Krpović, and Snežana Belanović Simić. 2024. "Geochemical Distribution of Ni, Cr, and Co in the Main Soil Types of the Čemernica River Basin in Serbia (In a Serpentine Environment)" Land 13, no. 12: 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122075
APA StyleTošić Jojević, S., Mrvić, V., Stajković-Srbinović, O., Jovković, M., Antić Mladenović, S., Krpović, M., & Belanović Simić, S. (2024). Geochemical Distribution of Ni, Cr, and Co in the Main Soil Types of the Čemernica River Basin in Serbia (In a Serpentine Environment). Land, 13(12), 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122075






