Spatial Pattern of Soil Erosion in Relation to Land Use Change in a Rolling Hilly Region of Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
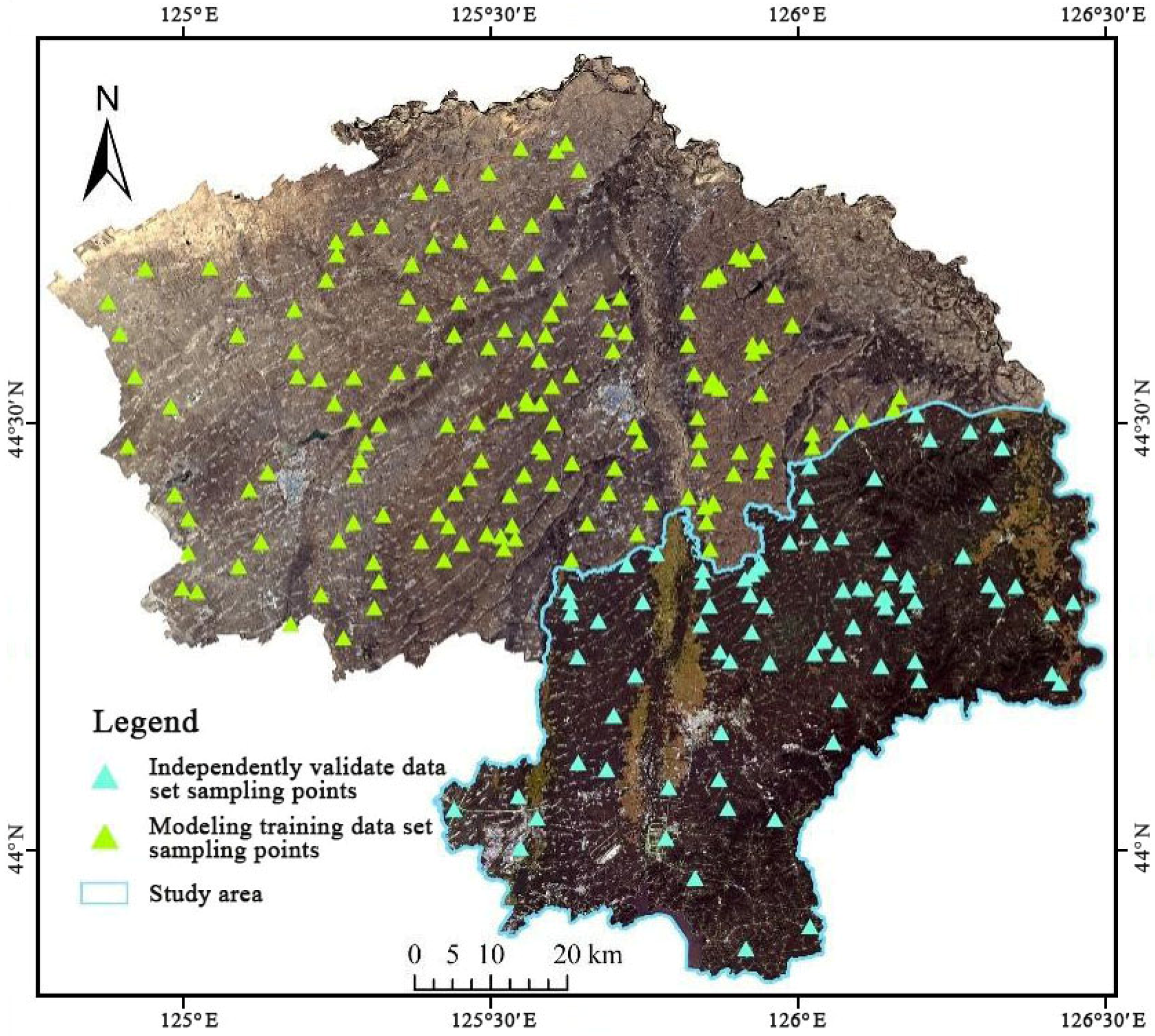
2.1. Study Area, Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. RUSLE Model
2.3.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
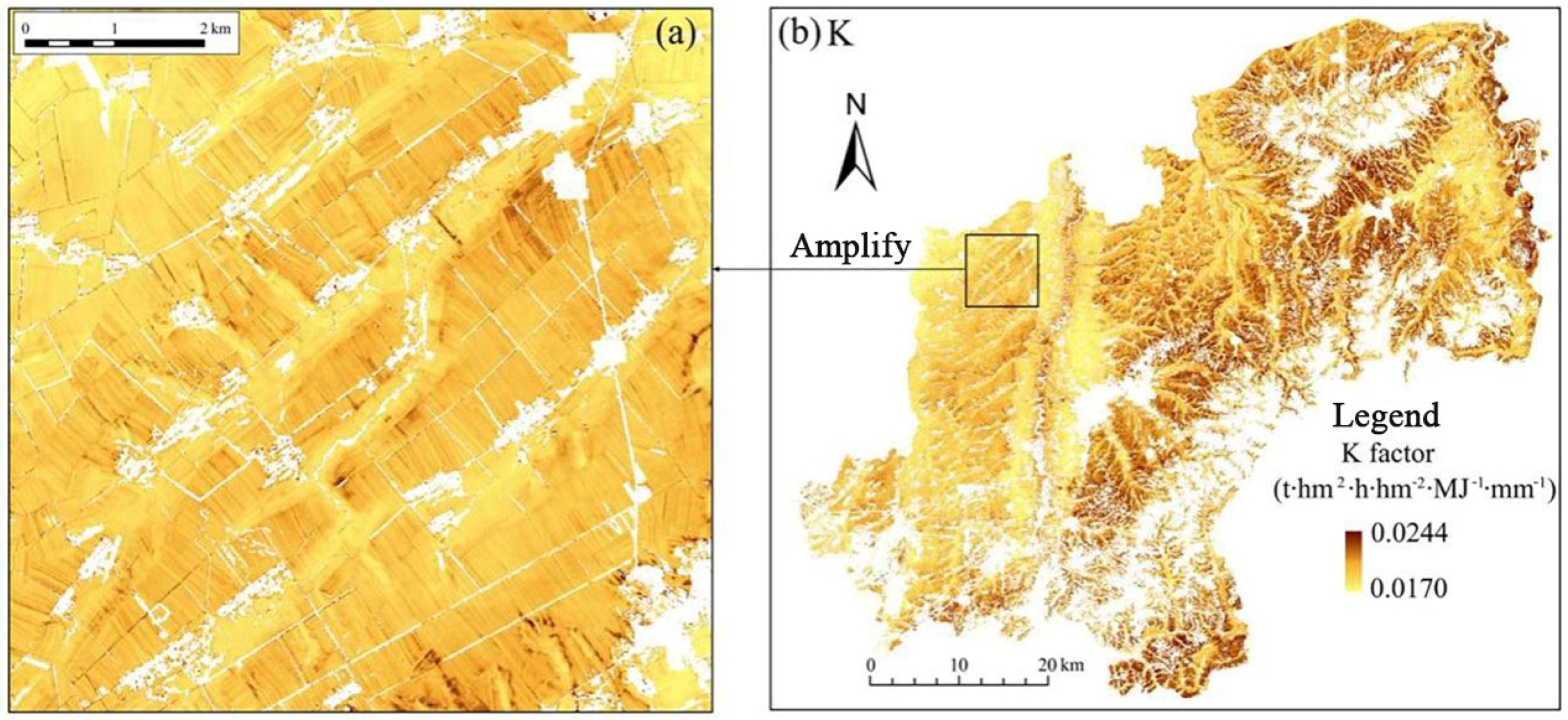
2.3.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
2.3.3. Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS)
2.3.4. Cover and Management Factor (C)
2.3.5. Support Practice Factor (P)
2.4. GWR Model
3. Results and Discussion
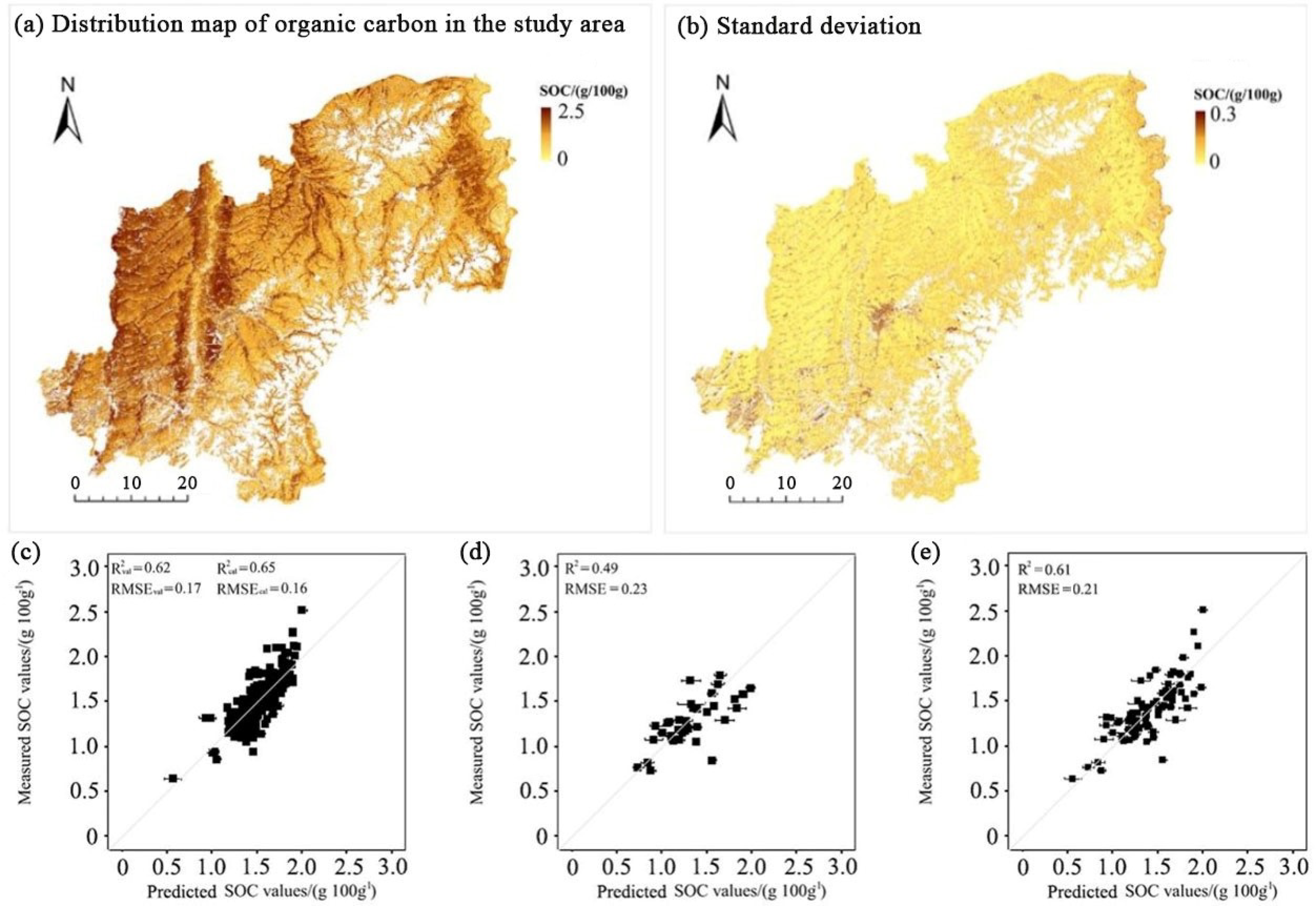
3.1. SOC Inversion Based on Multi-Temporal S2 Remote Sensing Image and Composite Soil Pixels
3.1.1. Determination of the Scope of Bare Cultivated Land
3.1.2. SOC Inversion
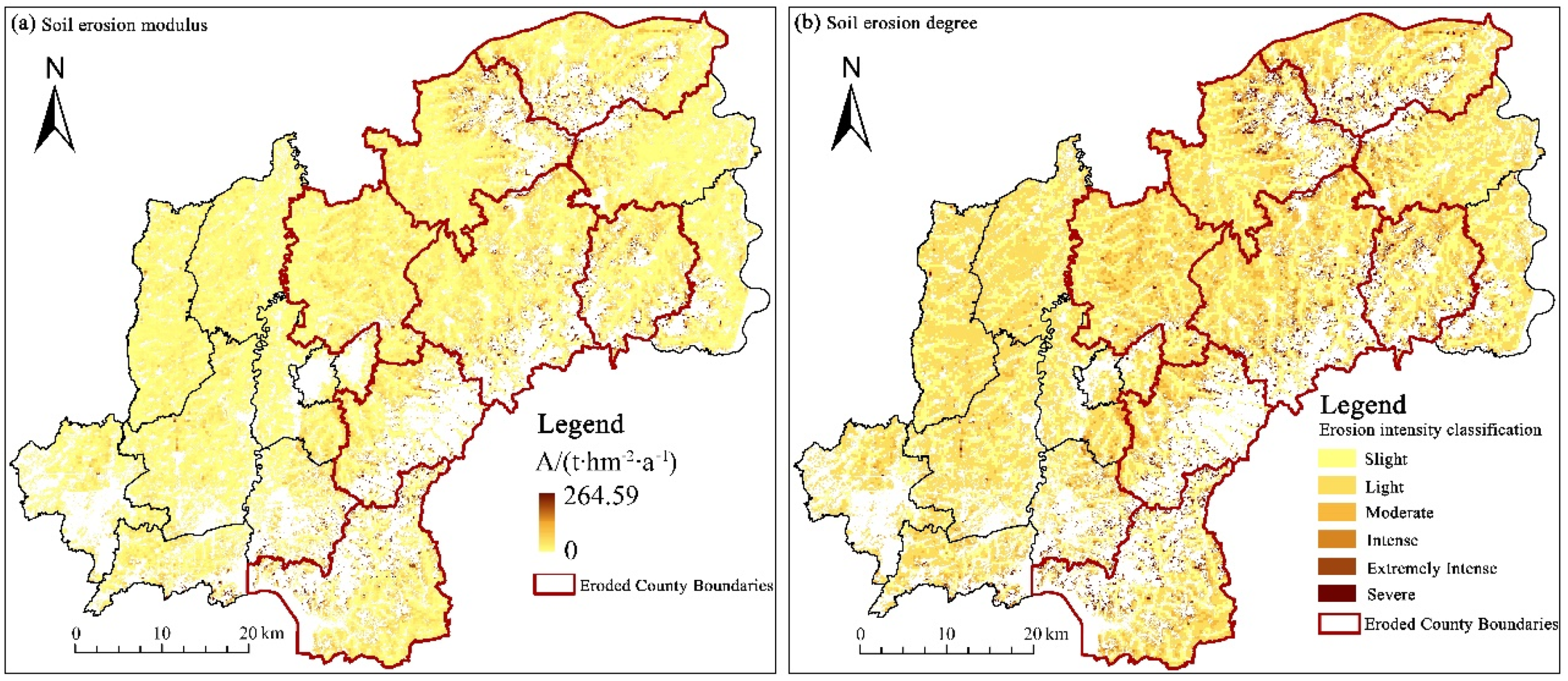
3.2. Spatial Mapping of Soil Erodibility Factor and Soil Erosion Risk
3.3. Land Use Factor Analysis of Cropland Soil Erosion Based on the GWR Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, L.; Celette, F.; Gary, C.; Ripoche, A.; Valdés-Gómez, H.; Metay, A. Management of service crops for the provision of ecosystem services in vineyards: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 251, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhe, A.A.; Barnes, R.T.; Six, J.; Marín-Spiotta, E. Role of soil erosion in biogeochemical cycling of essential elements: Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 46, 521–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Yi, X.Y.; Zhou, R.L.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Drake, S. Wind erosion and sand accumulation effects on soil properties in Horqin Sandy Farmland, Inner Mongolia. Catena 2006, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, J.N.; Govers, G.; Van Oost, K.; Bardgett, R.D. The impact of agricultural soil erosion on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, G.R.; Wells, T. Predicting soil organic carbon movement and concentration using a soil erosion and Landscape Evolution Model. Geoderma 2021, 382, 114759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Nedebock, D.; Chivenge, P.; Chaplot, V. Selective organic carbon losses from soils by sheet erosion and main controls Earth Surf Process. Landforms 2016, 41, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Harvey, C.; Resosudarmo, P.; Sinclair, K.; Kurz, D.; Mcnair, M.; Crist, S.; Shpritz, L.; Fitton, L.; Saffouri, R. Environmental and Economic Costs of Soil Erosion and Conservation Benefits. Science 1995, 267, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.; Baldock, J.; Sanderman, J. The global significance of omitting soil erosion from soil organic carbon cycling schemes. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Jiao, J.Y.; Rayburg, S.; Wang, Q.L.; Su, Y. Soil erosion resistance of “Grain for Green” vegetation types under extreme rainfall conditions on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2016, 141, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Ni, J.R.; Ciais, P.; Piao, S.L.; Wang, T.; Huang, M.T.; Li, T.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Chappell, A.; Van Oost, K. Lateral transport of soil carbon and land-atmosphere CO2 flux induced by water erosion in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6617–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Guo, Q. The assessment of soil loss by water erosion in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.G.; Fang, H.Y.; Wu, H.Q.; Yang, H.Y. Evaluating soil erosion by introducing crop residue cover and anthropogenic disturbance intensity into cropland C-factor calculation: Novel estimations from a cropland-dominant region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 219, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Fu, B.; Qiu, Y. Land-use change in a small catchment of northern Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 86, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alem, B.B. The nexus between land use land cover dynamics and soil erosion hotspot area of Girana Watershed, Awash Basin, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarello, V.; Di Stefano, V.; Ferro, V.; Giordano, G.; Iovino, M.; Pampalone, V. Estimating the USLE Soil Erodibility Factor in Sicily, South Italy. Trop. Agric. 2012, 28, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Jarva, J.; Frank-Kamenetsky, D.; Bogatyrev, I. Integrated geological risk mapping: A qualitative methodology applied in St. Petersburg, Russia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1629–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, P.P.; Tiwari, S.P.; Mandal, D.; Lakaria, B.L.; Madhu, M. Geospatial comparison of four models to predict soil erodibility in a semi-arid region of Central India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 5049–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Begueria, S.; Nadal-Romero, E.; González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Lana-Renault, N.; Sanjuán, Y. A meta-analysis of soil erosion rates across the world. Geomorphology 2015, 239, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Panagopoulos, T.; Loures, L. Simulating the impacts of future land use change on soil erosion in the Kasilian watershed. Land Use Policy 2017, 67, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Burras, C.L.; Kravchenko, Y.S.; Duran, A.; Huffman, T.; Morras, H.; Yuan, X. Overview of Mollisols in the world: Distribution, land use and management. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 92, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ding, G.; Cruse, R.M. Soil erosion control practices in Northeast China: A mini-review. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 117, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd-Brown, K.E.O.; Randerson, J.T.; Hopkins, F.; Arora, V.; Hajima, T.; Jones, C.; Zhang, Q. Changes in soil organic carbon storage predicted by Earth system models during the 21st century. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 2341–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liao, X.; Zhu, H.; Wei, X.; Shao, M. Soil physical and hydraulic properties under different land uses in the black soil region of Northeast China. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 99, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Xie, Y.; Ou, T.; Lu, H. Effects of soil erosion on long-term soil productivity in the black soil region of northeastern China. Catena 2011, 87, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, G.; Jin, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Soil microbial communities are affected more by land use than seasonal variation in restored grassland and cultivated Mollisols in Northeast China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.N.; Srivastava, A.; Dumka, U.C. A Long-Term Spatiotemporal Analysis of Vegetation Greenness over the Himalayan Region Using Google Earth Engine. Climate 2021, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, B.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Onda, Y.; Qiu, G. Sensitivity of the enhanced vegetation index (EVI) and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) to topographic effects: A case study in high-density cypress forest. Sensors 2007, 7, 2636–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, F.S.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, Y. Application of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) for the Detection of Extreme Precipitation Change. Forest 2021, 12, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.Q.; Zhang, H.Q. Change pathway and intersection of rainfall, soil, and land use influencing water-related soil erosion. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Wu, J.S.; Li, W.F. Assessing relationships of ecosystem services on multiscale: A case study of soil erosion control and water yield in the Pearl River Delta. Ecol. Ind. 2019, 99, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Luo, G. Soil erosion evolution and spatial correlation analysis in a typical karst geomorphology using RUSLE with GIS. Solid Earth 2017, 8, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Y.; Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhai, J. Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2014, 121, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Bennett, S.J.; Li, Y. Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: A case study of the Yangou watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.F.; Zang, Y.Z.; Ma, D.D.; Yao, W.Q.; Holden, J.; Irvine, B.; Zhao, G.J. Soil erosion rates assessed by RUSLE and PESERA for a Chinese Loess Plateau catchment under land-cover changes. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2020, 45, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Fu, J.S. Rainfall erosivity estimation under different rainfall amount. Resour. Sci. 2003, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. EPIC–Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator: 1. Model Documentation; USDA Technical Bulletin No. 1768; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.L.; Shu, A.P.; Xu, X.L.; Yang, Q.K.; Yu, B. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soils in China. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Lin, L.R.; Ding, S.W.; Tian, Z.C.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wu, K.R.; Zhao, Y.Z. Characteristics of Soil Erodibility K Value and Its Influencing Factors in the Changyan Watershed, Southwest Hubei, China. Land 2022, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised slope length factor for the universal soil loss equation. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Risse, L.M. Slope gradient effects on soil loss for steep slopes. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.A.; Maes, J.; Geijzendorffer, I.; Metzger, M.J. An assessment of soil erosion prevention by vegetation in Mediterranean Europe: Current trends of ecosystem service provision. Ecol. Ind. 2016, 60, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyas, H.; Kolat, C.; Süzen, M.L. A new approach to estimate cover-management factor of RUSLE and validation of RUSLE model in the watershed of Kartalkaya Dam. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Ding, S.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Study of applying USLE and geographical information system IDRISI to predict soil erosion in small watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 19–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Phinzi, K.; Ngetar, N.S. The assessment of water-borne erosion at catchment level using GIS-based RUSLE and remote sensing: A review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, S.; Charlton, M. Geographically weighted regression. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D 1998, 47, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Pontius, R.G.; Zhang, Z. Geographically weighted regression to measure spatial variations in correlations between water pollution versus land use in a coastal watershed. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 103, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, L.; Schepaschenko, D.; Lesiv, M.; McCallum, I.; Fritz, S.; Comber, A.; Perger, C.; Schill, C.; Zhao, Y.; Maus, V. Building a hybrid land cover map with crowdsourcing and geographically weighted regression. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.S.; Yang, H.; Guo, F.; Han, R.M. Spatial patterns and origins of heavy metals in Sheyang River catchment in Jiangsu, China based on geographically weighted regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, S. Detecting spatially non-stationary and scale-dependent relationships between urban landscape fragmentation and related factors using geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jia, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. A satellite-based geographically weighted regression model for regional PM 2.5 estimation over the Pearl River Delta region in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.; Xu, X.; Kiely, G. Towards spatial geochemical modelling: Use of geographically weighted regression for mapping soil organic carbon contents in Ireland. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Q. Application of geographically weighted regression to identify spatially non-stationary relationships between Fe mineralization and its controlling factors in eastern Tianshan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Castaldi, F.; van Wesemael, B.; Van Oosta, K. Vis-NIR spectroscopic assessment of soil aggregate stability and aggregate size distribution in the Belgian Loam Belt. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, F.; Hueni, A.; Chabrillat, S.; Ward, K.; Buttafuoco, G.; Bomans, B.; Vreys, K.; Brell, M.; van Wesemael, B. Evaluating the capability of the Sentinel 2 data for soil organic carbon prediction in croplands. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2019, 147, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, C.M.; Mendes, W.D.S.; Silvero, N.E.Q.; Poppiel, R.R.; Sayão, V.M.; Dotto, A.C.; dos Santos, N.V.; Accorsi, M.T.; Demattê, J.A.M. Soil degradation index developed by multitemporal remote sensing images, climate variables, terrain and soil atributes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D. Soil Erosion: A Food and Environmental Threat. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.R.; Jalili, K.; Nikkami, D. Land use optimization in watershed scale. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.; Giboire, G.; Marchand, P.; Valentin, C. Dynamic modelling for linear erosion initiation and development under climate and land-use changes in northern Laos. Catena 2005, 63, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneaux, V.; Cheggour, A.; Deschamps, C.; Mouillot, F.; Cerdan, O.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Land use and climate change effects on soil erosion in a semi-arid mountainous watershed (High Atlas, Morocco). J. Arid Environ. 2015, 122, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohrer, N.; Haverkamp, S.; Eckhardt, K.; Frede, H.G. Hydrologic Response to land use changes on the catchment scale. Phys. Chem. Earth B—Hydrol. Oceans Atmos. 2001, 26, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, S.L.; Wang, Y.D.; Gu, Z.Y.; Xiong, S.F.; Huang, X.F.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, S.H.; Guo, L.C.; Cui, J.Y.; et al. Rates and causes of black soil erosion in Northeast China. Catena 2022, 214, 106250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Long, H.L.; Tu, S.S.; Ge, D.Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, L.Z. Spatial identification of land use functions and their tradeoffs/synergies in China: Implications for sustainable land management. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Land Use Types | Unused Land | Forest, Grassland and Water | Arable Land | Construction Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land use intensity grading index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Soil Erosion Intensity Grade | Soil Erosion Modulus/ t hm−2 a−1 | Area/km2 | Proportion of Total Arable Land/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Slight | ≤2 | 697.44 | 31.99 |
| 2. Light | 2–12 | 1117.43 | 51.25 |
| 3. Moderate | 12–24 | 242.93 | 11.14 |
| 4. Intense | 24–36 | 60.70 | 2.78 |
| 5. Extremely Intense | 36–48 | 24.18 | 1.11 |
| 6. Severe | >48 | 37.51 | 1.72 |
| Type Layer | Explanatory Variables | Collinearity Test Results | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | VIF | ||
| Natural conditions | Elevation (X1) | 0.94 | 1.07 |
| Slope (X2) | 0.67 | 1.49 | |
| Precipitation (X3) | 0.44 | 2.27 | |
| SOC content (X4) | 0.50 | 1.99 | |
| Vegetation coverage (X5) | 0.79 | 1.27 | |
| Socioeconomic conditions | Change in the proportion of residential areas (X6) | 0.92 | 1.09 |
| Change of road network density (X7) | 0.88 | 1.14 | |
| Land Use conditions | Change of land use intensity (X8) | 0.93 | 1.08 |
| Change of landscape fragmentation degree of cropland (X9) | 0.98 | 1.02 | |
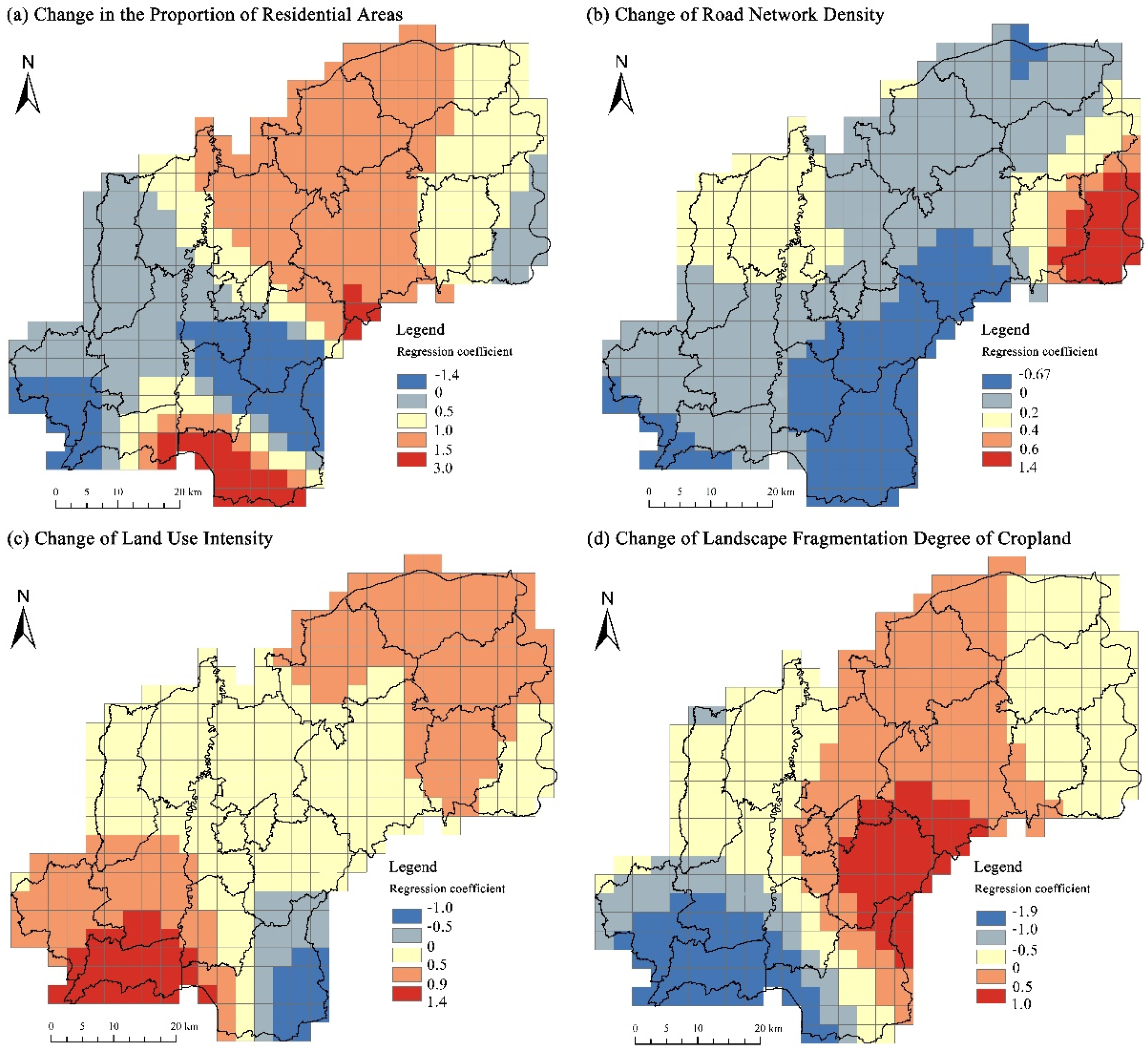
| Explanatory Variables | Minimum | Upper Quartile | Median | Average | Lower Quartile | Maximum | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation | −1.89 | −0.05 | 0.08 | −0.01 | 0.20 | 1.01 | 0.45 |
| Slope | 4.03 | 5.54 | 5.94 | 6.18 | 6.46 | 9.04 | 1.09 |
| Precipitation | −1.76 | −0.92 | −0.55 | −0.56 | −0.17 | 0.63 | 0.51 |
| SOC content | −2.56 | −0.72 | −0.47 | −0.56 | −0.30 | 0.29 | 0.49 |
| Vegetation coverage | −0.57 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.41 | 1.54 | 0.35 |
| Change in the proportion of residential areas | −1.42 | 0.17 | 0.83 | 0.69 | 1.19 | 3.01 | 0.69 |
| Change in road network density | −0.67 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 1.46 | 0.30 |
| Change of land use intensity | −1.98 | −0.68 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.62 | 1.39 | 0.37 |
| Change of landscape fragmentation degree of cropland | −1.92 | −0.37 | −0.16 | −0.17 | 0.25 | 1.04 | 0.59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, D.; Wu, Z.; Shang, P. Spatial Pattern of Soil Erosion in Relation to Land Use Change in a Rolling Hilly Region of Northeast China. Land 2022, 11, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081253
Zhu Y, Li W, Wang D, Wu Z, Shang P. Spatial Pattern of Soil Erosion in Relation to Land Use Change in a Rolling Hilly Region of Northeast China. Land. 2022; 11(8):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081253
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yuanli, Wenbo Li, Dongyan Wang, Zihao Wu, and Peng Shang. 2022. "Spatial Pattern of Soil Erosion in Relation to Land Use Change in a Rolling Hilly Region of Northeast China" Land 11, no. 8: 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081253
APA StyleZhu, Y., Li, W., Wang, D., Wu, Z., & Shang, P. (2022). Spatial Pattern of Soil Erosion in Relation to Land Use Change in a Rolling Hilly Region of Northeast China. Land, 11(8), 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081253





