Research on the Interactive Coupling Relationship between Land Space Development and Eco-Environment from the Perspective of Symbiosis: A Practical Analysis of Henan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analytical Framework
2.1. Symbiotic Relationship between LSD and Eco-Environment
2.2. Coupling Symbiosis Mechanism of LSD and Eco-Environment
3. Materials and Methods
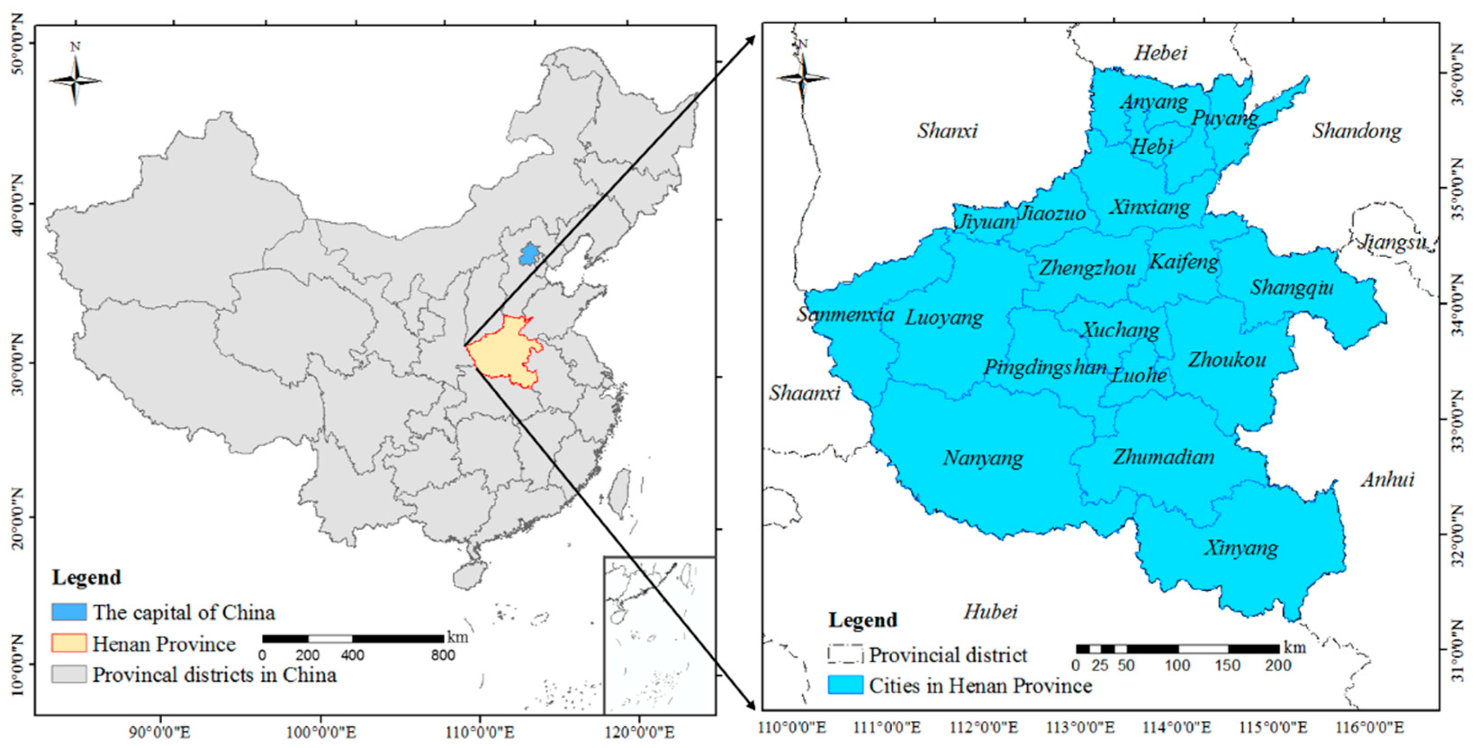
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Source and Processing
3.3. The Indexes for Evaluation of LSD and Eco-Environment
3.4. Comprehensive Index Evaluation Model of LSD and Eco-Environment
3.5. Coupling Coordination Degree Model of LSD and Eco-Environment
3.5.1. Coupling Degree Model
3.5.2. Coordination Degree Model
3.5.3. Classification of Coupling Coordination Degree
3.6. Spatial Correlation Analysis Model between LSD and Eco-Environment
4. Results
4.1. Temporal Evolution Characteristics of LSD and Eco-Environment
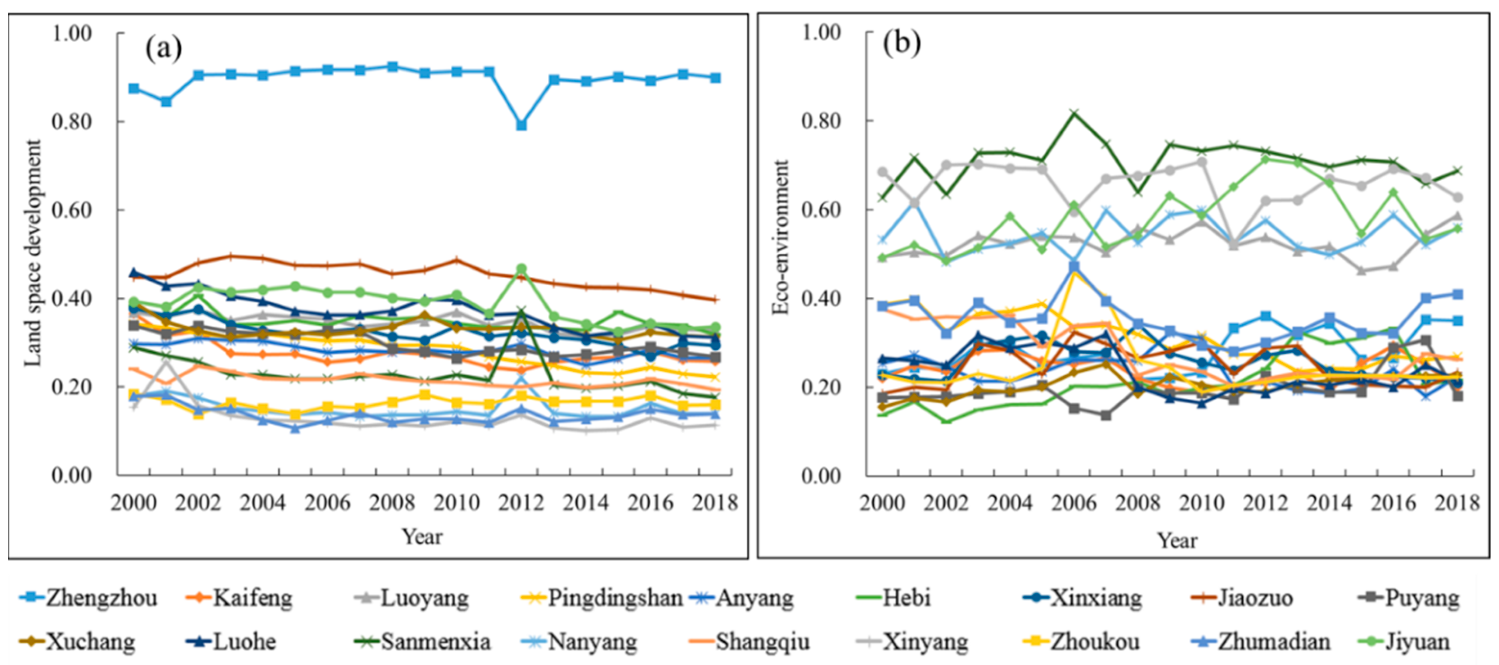
4.1.1. Evolution Trends of LSD and Eco-Environment
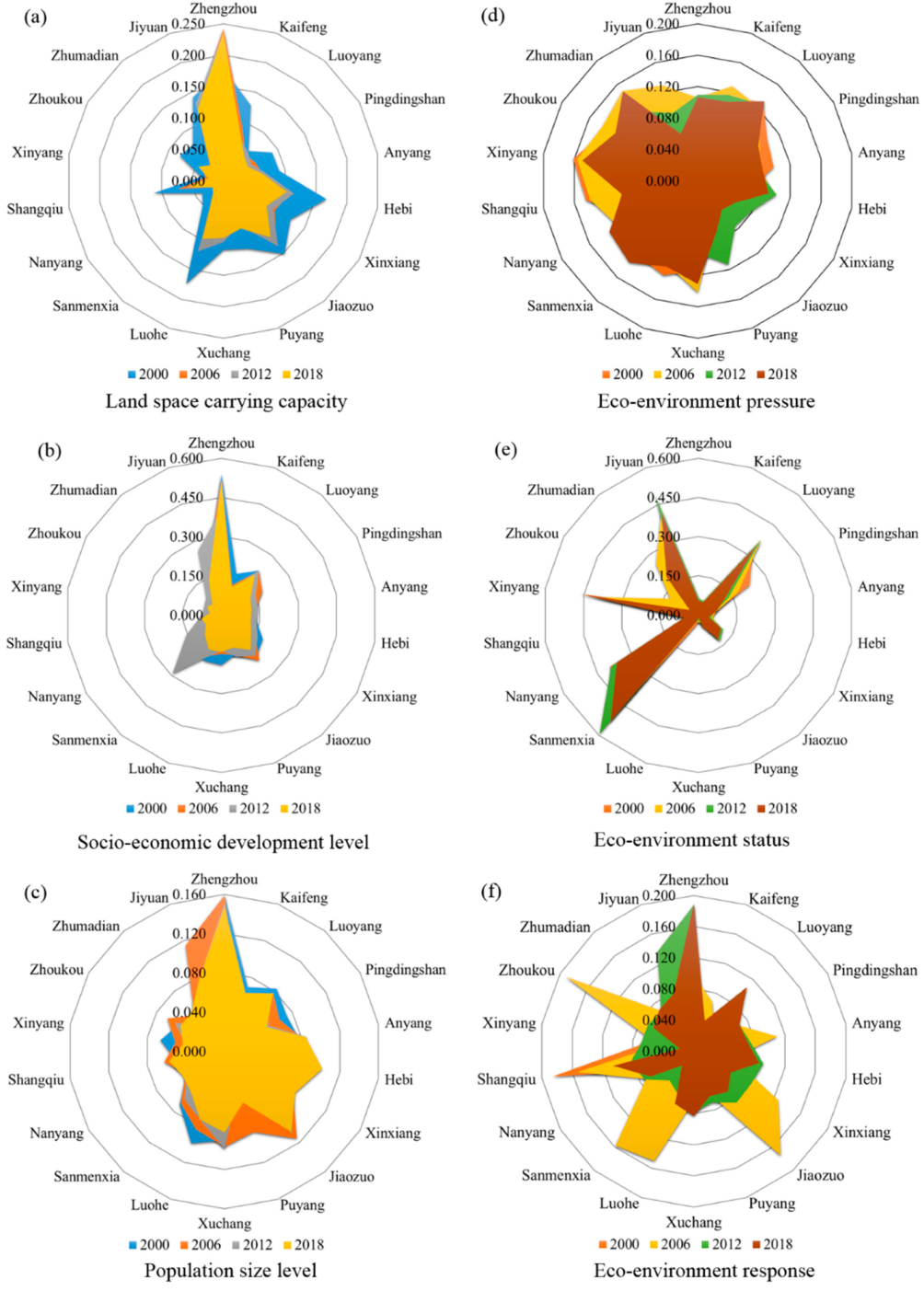
4.1.2. Evolution Trends of Subsystem between LSD and Eco-Environment
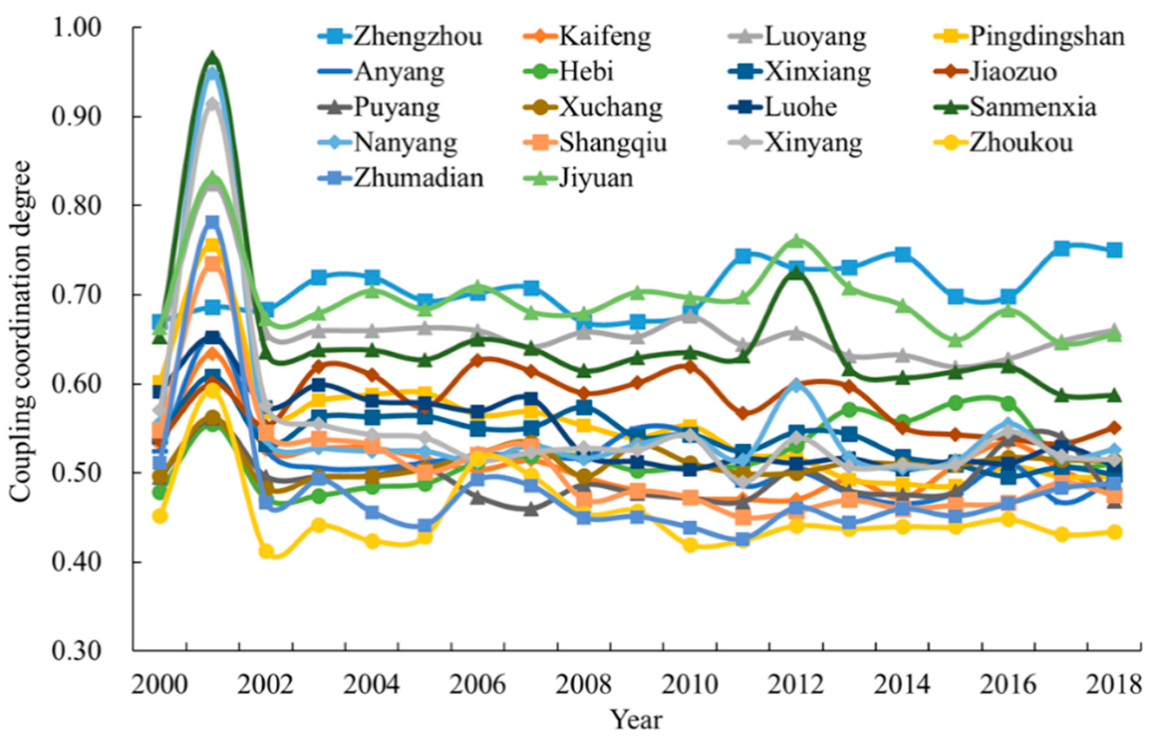
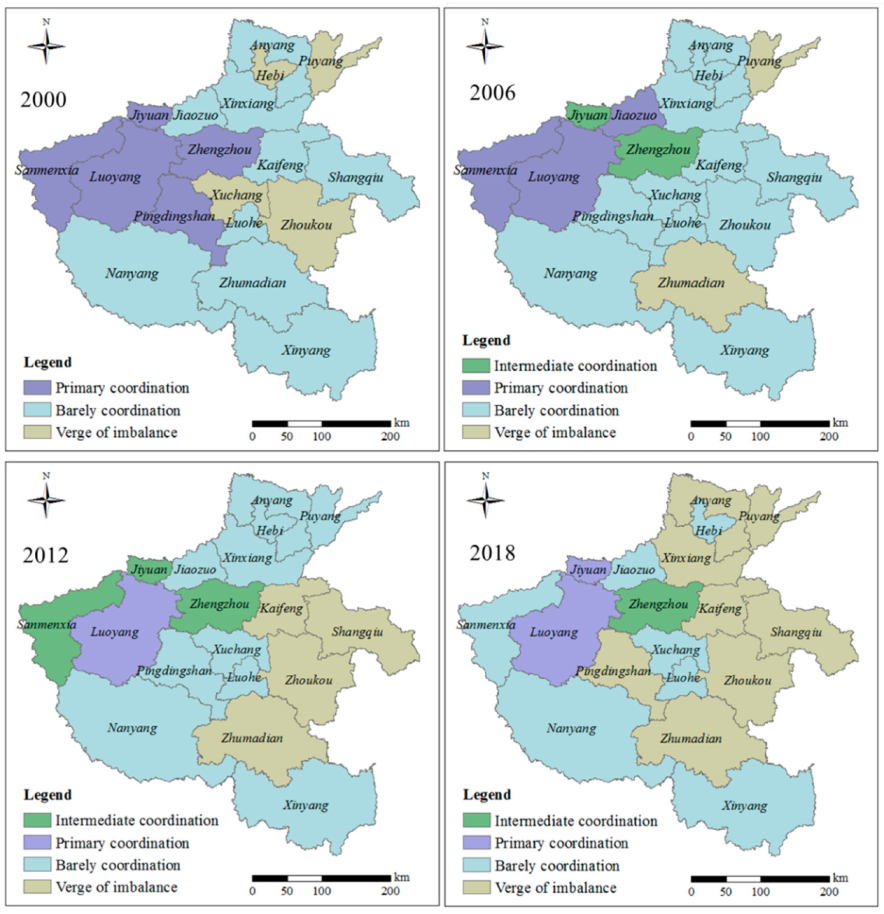
4.2. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Coupling Coordination Degree between LSD and Eco-Environment
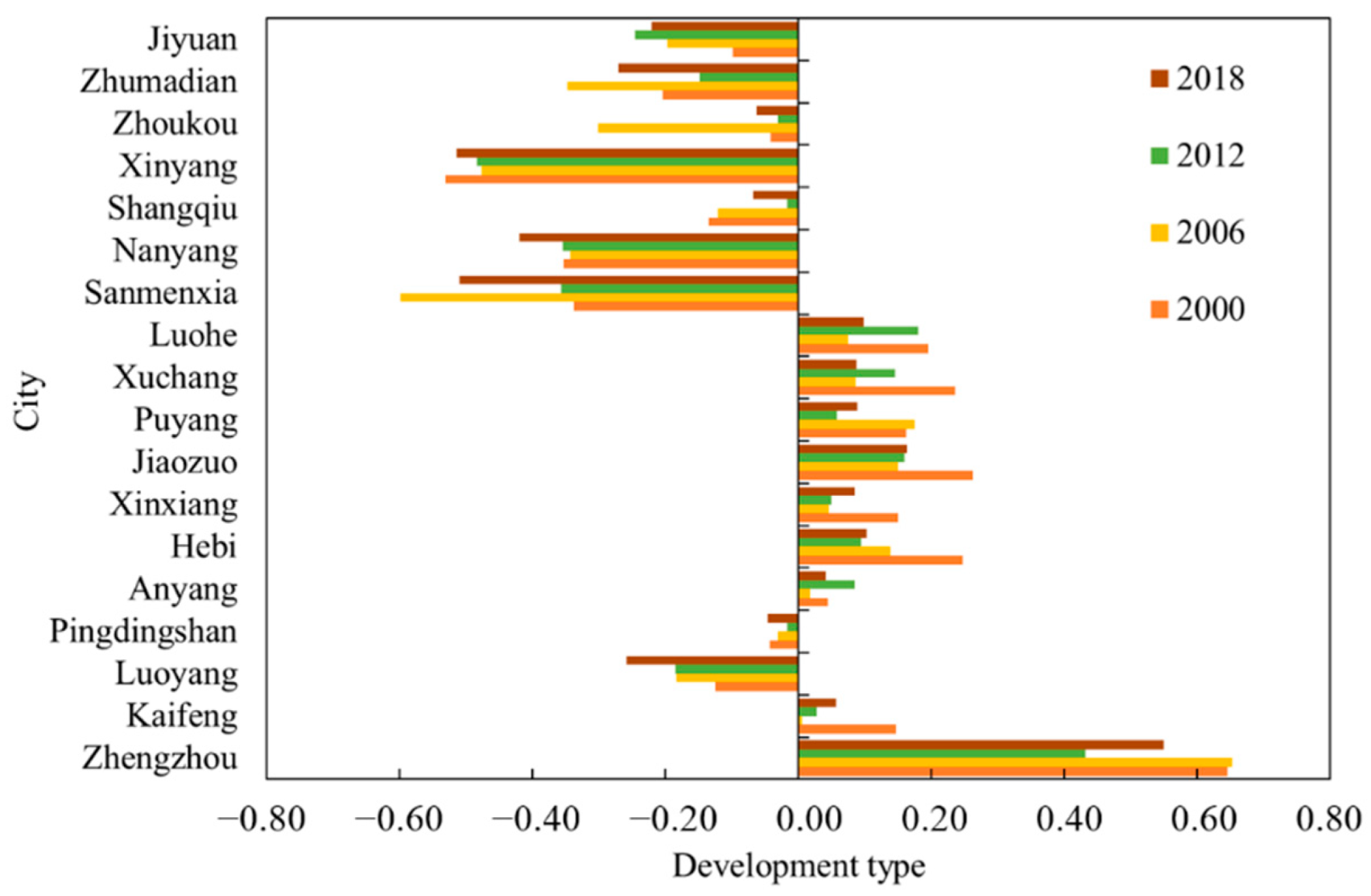
4.3. Development Type Characteristics of LSD and Eco-Environment
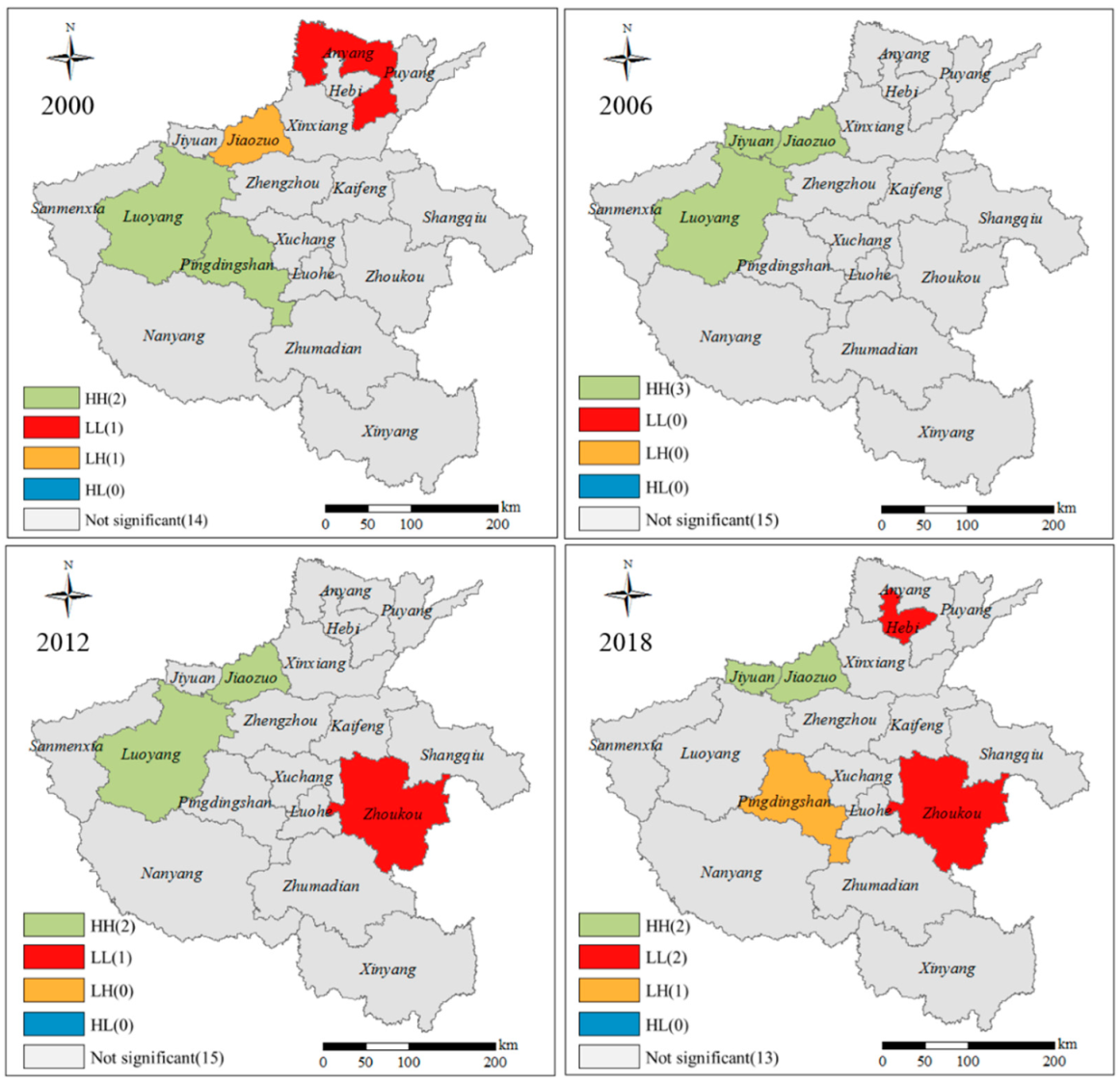
4.4. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Spatial Correlation between LSD and Eco-Environment
5. Discussion
5.1. Rationality of the Interactive Coupling between LSD and Eco-Environment
5.2. Insights into the Relative Relationship between LSD and Eco-Environment
5.3. Policy Implications and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuang, W. Issues regarding spatial pattern change of national land space and its overall implementation on beautiful vision in new era. Resour. Sci. 2019, 41, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Coupling coordinative degree and interctive coercing relationship between urbanization and eco-environment in pearl river delta. Hum. Geogr. 2015, 30, 64–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Hu, W.; Mei, Y. Spatiotemporal pattern of coupling coordination degree between land intensive use and regional ecological efficiency in China. Trans. CSAE 2020, 36, 234–243. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Keola, S.; Andersson, M.; Hall, O. Monitoring Economic Development from Space: Using Nighttime Light and Land Cover Data to Measure Economic Growth. World Dev. 2015, 66, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Xu, W.; Fan, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Spatial coupling differentiation and development zoning trade-off of land space utilization efficiency in eastern China. Land Use Policy 2019, 85, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, X.; He, W. A land space development zoning method based on resource–environmental carrying capacity: A case study of henan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, Q. Examining the relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment using a coupling analysis: Case study of Shanghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Kreuger, A.B. Economic growth and the environment. Quart. J. Econ. 1994, 110, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Huang, B.; Lin, C.T. Environmental awareness and environmental Kuznets curve. Econ. Model. 2019, 77, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Xiao, J. Evaluation of coupling coordination between urbanization and eco-environment in six central cities, Wuling Mountain area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5973–5987. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ariken, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Fang, C.; Kung, H.-T. Coupling coordination analysis of urbanization and eco-environment in Yanqi Basin based on multi-source remote sensing data. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiao, F.; Ren, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Coupling coordination relationship between urbanization and atmospheric environment security in Jinan City. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersperger, A.M.; Oliveira, E.; Pagliarin, S.; Palka, G.; Verburg, P.; Bolliger, J.; Grădinaru, S. Urban land-use change: The role of strategic spatial planning. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2018, 51, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Luo, D.; Guo, K. Analysis of Factors Affecting the Coordinated Development of Urbanization and the Ecological Resource Environment in Southwest China Based on Data Mining. J. Urban. Plan. Dev. 2021, 147, 04021034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C. Understanding the relation between urbanization and the eco-environment in China’s Yangtze River Delta using an improved EKC model and coupling analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; He, S.; Li, G. Interaction between urbanization and the eco-environment in the Pan-Third Pole region. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, S.; Tosun, B. Environmental Pollution Index and economic growth: Evidence from OECD countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 36870–36879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Hua, G.; Wu, Q. What is the relationship among environmental pollution, environmental behavior, and public health in China? A study based on CGSS. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20299–20312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, I.; Sanz-Sánchez, M.J. Effects of historical land-use change in the Mediterranean environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, B.; Kwan, M.P. How does urban expansion impact people’s exposure to green environments? A comparative study of 290 Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, C.; Liu, F. Interprovincial two-stage water resource utilization efficiency under environmental constraint and spatial spillover effects in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Tian, S. How to sustainably use water resources—a case study for decision support on the water utilization of xinjiang, china. Water 2020, 12, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, R.; Xu, M.; Cao, G. Dynamic assessment of island ecological environment sustainability under urbanization based on rough set, synthetic index and catastrophe progression analysis theories. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 178, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.L.; Barbir, J.; Sima, M.; Kalbus, A.; Nagy, G.J.; Paletta, A.; Villamizar, A.; Martinez, R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Pereira, M.J.; et al. Reviewing the role of ecosystems services in the sustainability of the urban environment: A multi-country analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Zhang, H.; Tong, J.; Ma, J.; Zhi, Y. Water resource constraint on urbanization in Yangtze River Economic Belt. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 39–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Tong, L.; Qiu, F.; Guo, F. Eco-environment effect of urban expansion in Songhua River Basin. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Chidthaisong, A.; Limsakul, A.; Varnakovida, P.; Ekkawatpanit, C.; Diem, P.K.; Diep, N.T.H. How do disparate urbanization and climate change imprint on urban thermal variations? A comparison between two dynamic cities in Southeast Asia. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raihan, A.; Tuspekova, A. Dynamic impacts of economic growth, energy use, urbanization, agricultural productivity, and forested area on carbon emissions: New insights from Kazakhstan. World Dev. Sustain. 2022, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijima, M.; Nishide, K.; Ohyama, A. Economic models for the environmental Kuznets curve: A survey. J. Econ. Dyn Control 2010, 34, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veziroglu, A.; Macario, R. A system dynamics model for the reduction of health expenditures through transition to hydrogen vehicles (Srth): Case studies in the USA, China, and India. Int. J. Green. Energy 2014, 11, 695–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvieco, E. Integration of linear programming and GIS for land-use modelling. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1993, 7, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiagha, S.H.R.; Akrami, H.; Hashemi, S.S. A multi-objective programming approach to solve grey linear programming. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2012, 2, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoseiri, K.; Ghannadpour, S.F. Multi-objective vehicle routing problem with time windows using goal programming and genetic algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2010, 10, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Tang, B.; Yeung, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheung, G. A system dynamics model for the sustainable land use planning and development. Habitat Int. 2009, 33, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, T.J.; Janssen, R.; Herwijnen, M.V. A Genetic Algorithm Approach to Multi-Objective Land Use Planning; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 2293–2313. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, K.Y.; Pinheiro, P.O.; Minet, L.; Hatzopoulou, M.; Weichenthal, S. Extending the spatial scale of land use regression models for ambient ultrafine particles using satellite images and deep convolutional neural networks. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Hayashi, Y.; Cao, X.; Imura, H. Application of an integrated system dynamics and cellular automata model for urban growth assessment: A case study of Shanghai, China. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2009, 91, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Lei, X.; Jia, K.; Wu, Y. Simulating urban land use change by incorporating an autologistic regression model into a CLUE-S model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Cai, Y. The New Progresses and Development Trends in the Research of Physio-Geographical Regionalization in China. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 1400–1407. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.; Shi, P.; Bao, S.; Zhang, X.; Nie, X. Optimization of Urban Land Development Spatial Allocation Based on Ecology-Economy Comparative Advantage Perspective. J. Urban. Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 05018006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Coupling coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment in Chinese provincial capital cities-assessment and policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ouyang, X.; Zhu, X. Land space simulation of urban agglomerations from the perspective of the symbiosis of urban development and ecological protection: A case study of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fei, Z.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, Y. Rural settlement space reconstruction strategy and implementation based on symbiosis theory on village scale. Trans. CSAE 2014, 30, 205–214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Li, X.; Fan, H.; He, W. Spatial analysis of production-living-ecological functions and zoning method under symbiosis theory of Henan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 69093–69110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Territorial Multi-functionality Evaluation and Decision-making Mechanism at County Scale in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 1379–1389. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y. Quantitative investigation of the interactive coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 2244–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Shemshadi, A.; Shirazi, H.; Toreihi, M.; Tarokh, M.J. A fuzzy VIKOR method for supplier selection based on entropy measure for objective weighting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 12160–12167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X. Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Wu, Y. Research on the coupling coordination of a sea-land system based on an integrated approach and new evaluation index system: A case study in Hainan province, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Cui, Y. Evaluating the coordinated development of economic, social and environmental benefits of urban public transportation infrastructure: Case study of four Chinese autonomous municipalities. Transp. Policy 2018, 66, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Liu, M.; Shao, Q.; Sun, X.; Wu, J.; Xiang, Z.; Yang, W. Research on eco-environmental vulnerability evaluation of the Anning River Basin in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. The nexus between regional eco-environmental degradation and rural impoverishment in China. Habitat Int. 2020, 96, 102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, S.; Wang, Y.; Miao, C. Spatiotemporal differentiation and influencing factors of the coupling and coordinated development of new urbanization and ecological environment in the Yellow River Basin. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 159–171. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Cui, X.; Li, G.; Bao, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Sun, S.; Liu, H.; Luo, K.; Ren, Y. Modeling regional sustainable development scenarios using the Urbanization and Eco-environment Coupler: Case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Cui, X.; Deng, X.; Liang, L. Urbanization and eco-environment coupling circle theory and coupler regulation. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Huang, Z.; Xu, D.; Shi, X.; Liu, H.; Tan, L.; Ge, J. The spatial characteristics and drive mechanism of coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment in the Pan Yangtze River Delta. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 163–186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shu, C.; Xie, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Q. Is Urban Land Development Driven by Economic Development or Fiscal Revenue Stimuli in China? Land Use Policy 2018, 77, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.O.; Wu, H.; Hao, Y. How does China’s land finance affect its carbon emissions? Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2020, 54, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, R.; Deng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Evaluating the relationships among economic growth, energy consumption, air emissions and air environmental protection investment in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, G. Environmental decentralization, environmental protection investment, and green technology innovation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12740–12755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, X. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of “production-living-ecological” functions in Henan Province, China. Transac. CSAE 2021, 37, 243–252. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


| Number | City | Population (10,000 Persons) | Total Area (sq.km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zhengzhou | 787 | 7567 |
| 2 | Kaifeng | 526 | 6240 |
| 3 | Luoyang | 714 | 15,236 |
| 4 | Pingdingshan | 553 | 7910 |
| 5 | Anyang | 592 | 7352 |
| 6 | Hebi | 166 | 2140 |
| 7 | Xinxiang | 617 | 8291 |
| 8 | Jiaozuo | 377 | 3973 |
| 9 | Puyang | 399 | 4271 |
| 10 | Xuchang | 498 | 4979 |
| 11 | Luohe | 284 | 2692 |
| 12 | Sanmenxia | 231 | 9936 |
| 13 | Nanyang | 1198 | 26,511 |
| 14 | Shangqiu | 926 | 10,704 |
| 15 | Xinyang | 885 | 18,916 |
| 16 | Zhoukou | 1162 | 11,961 |
| 17 | Zhumadian | 920 | 15,086 |
| 18 | Jiyuan | 71 | 1899 |
| Target Level | Sub-System | Indicators (Unit) | Serial Number | Weight | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land space development | Land space carrying capacity | Urban land proportion (%) | L1 | 0.0814 | + |
| Rural land proportion (%) | L2 | 0.0298 | + | ||
| Traffic land density (%) | L3 | 0.0605 | + | ||
| Built-up area per 10,000 people (km2/person) | L4 | 0.0783 | − | ||
| Socio-economic development level | Economic density (yuan/km2) | L5 | 0.0791 | + | |
| Gross industrial production per area (yuan/km2) | L6 | 0.0724 | + | ||
| Proportion of secondary and tertiary industries (%) | L7 | 0.0440 | + | ||
| Per capita retail sales (yuan/person) | L8 | 0.0994 | + | ||
| Per capita disposable income ratio in urban and rural areas (%) | L9 | 0.0543 | + | ||
| Number of college students per 10,000 people (person) | L10 | 0.1643 | + | ||
| Number of hospital beds per 10,000 people (unit) | L11 | 0.0559 | + | ||
| Population size level | Population density (person/km2) | L12 | 0.0325 | + | |
| Population urbanization rate (%) | L13 | 0.0602 | + | ||
| Natural population growth rate (%) | L14 | 0.0325 | − | ||
| Proportion of employees in secondary and tertiary industries (%) | L15 | 0.0554 | + |
| Target Level | Sub-System | Indicators (Unit) | Serial Number | Weight | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eco-environment | Eco-environment pressure | Per capita industrial wastewater discharge (t/person) | E1 | 0.0366 | − |
| Per capita industrial sulfur dioxide emission (t/person) | E2 | 0.0312 | − | ||
| Per capita comprehensive water (t/person) | E3 | 0.0510 | − | ||
| Input intensity of chemical fertilizer (kg/hm2) | E4 | 0.0578 | − | ||
| Eco-environment status | Forest coverage (%) | E5 | 0.1659 | + | |
| Per capita total water resources (m3/person) | E6 | 0.1521 | + | ||
| Per capita ecological land area (km2/person) | E7 | 0.1855 | + | ||
| Habitat abundance index (−) | E8 | 0.1170 | + | ||
| Eco-environment response | Harmless treatment rate of domestic waste (%) | E9 | 0.0322 | + | |
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste (%) | E10 | 0.0315 | + | ||
| Proportion of total environmental investment (%) | E11 | 0.1393 | + |
| Category | Interval | Sub-Category | F(x) and G(y) | Development Type Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coupling coordination stage | 0.9 < D ≤ 1 | Advanced coordination | F(x) − G(y) > 0.1 |F(x) − G(y)| < 0.1 F(x) − G(y) < −0.1 | Coupling coordination—Eco-environment lagging Coupling coordination—Balanced development Coupling coordination—Development lagging |
| 0.8 < D ≤ 0.9 | Well coordination | |||
| 0.7 < D ≤ 0.8 | Intermediate coordination | |||
| 0.6 < D ≤ 0.7 | Primary coordination | |||
| Coordination transition stage | 0.5 < D ≤ 0.6 | Barely coordination | F(x) − G(y) > 0.1 |F(x) − G(y)| < 0.1 F(x) − G(y) < −0.1 | Coordination transition—Eco-environment lagging Coordination transition—Balanced development Coordination transition—Development lagging |
| 0.4 < D ≤ 0.5 | Verge of imbalance | |||
| Maladjusted recession stage | 0.3 < D ≤ 0.4 | Mild imbalance | F(x) − G(y) > 0.1 |F(x) − G(y)| ≤ 0.1 F(x) − G(y) ≤ −0.1 | Maladjusted recession—Eco-environment lagging Maladjusted recession—Balanced development Maladjusted recession—Development lagging |
| 0.2 < D ≤ 0.3 | Moderate imbalance | |||
| 0.1 < D ≤ 0.2 | Serious imbalance | |||
| 0 < D ≤ 0.1 | Extreme imbalance |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Li, X.; Fan, H. Research on the Interactive Coupling Relationship between Land Space Development and Eco-Environment from the Perspective of Symbiosis: A Practical Analysis of Henan, China. Land 2022, 11, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081252
Xie X, Li X, Fan H. Research on the Interactive Coupling Relationship between Land Space Development and Eco-Environment from the Perspective of Symbiosis: A Practical Analysis of Henan, China. Land. 2022; 11(8):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081252
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xiaotong, Xiaoshun Li, and Huiping Fan. 2022. "Research on the Interactive Coupling Relationship between Land Space Development and Eco-Environment from the Perspective of Symbiosis: A Practical Analysis of Henan, China" Land 11, no. 8: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081252
APA StyleXie, X., Li, X., & Fan, H. (2022). Research on the Interactive Coupling Relationship between Land Space Development and Eco-Environment from the Perspective of Symbiosis: A Practical Analysis of Henan, China. Land, 11(8), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081252





