Abstract
A spatial analysis was carried out to evaluate the compatibility of human activities and biophysical characteristics in the Mexican Caribbean Sea, in order to identify the most viable areas for energy generation from ocean currents and the areas where the population would most benefit from such energy projects. Of the study area, 82% have some form of protection legislation. Tourism is the main economic activity in the area and this is reflected in a wide range of activities and services that often overlap within the same spatial area. In the case study, the use of renewable ocean energies is seen as an important innovation to reduce fossil fuel dependency. These energies have the potential to meet the demands of the region. However, it is vital to seek for potential areas for this type of energy harvesting where the social, economic and environmental impacts would be minimal. The lack of marine policies and land-use planning processes in Mexico is a major obstacle in avoiding land use conflicts.
1. Introduction
In Mexico, oil and natural gas reserves are decreasing, from peak production in 2004; the oil era is in its final stage [1]. Figures from the Ministry of Energy [2] show that at the beginning of 2019 the proven reserves, of 6.66 billion barrels of oil and 9.7 trillion cubic feet (tcf) of gas, would last for approximately 9 and 5 years, respectively if the current rate of extraction continued (oil: 1.833 mb/day; gas: 4.847 bcf/day in 2018) [1]. An energy transition is thus needed in Mexico, from fossil fuels to sustainable energy. This would contribute significantly to achieving the climate goals set out in the General Law on Climate Change, reduce the looming energy poverty and facilitate access to energy in the region studied [3]. Renewable sources of energy from the ocean are an innovative source of great importance, thanks to their magnitude and the fact that they are found in all latitudes, that that would allow us to reduce fossil fuel consumption and meet increasing energy demands [4,5,6]. According to estimates, ocean currents and tidal energy have an annual global potential of 800 TWh and 300 TWh, respectively [4]. However, only 1TWh of energy is currently generated from the ocean globally [7]. Marine renewable energies are generally considered to have a low environmental impact, thanks to their low or zero greenhouse gas emissions [8]. However, some fundamental questions arise, including the formulation of standards for this industry [9], economic aspects, and environmental consequences of any mass deployment of energy generation from these sources.
Due to their inherent reliability, predictability and sustainability, ocean currents are an attractive option within marine renewables. In locations where flow acceleration is exacerbated as a consequence of the geomorphology and topography of the seabed, such as straits and channels, there is greater potential for exploitation [4,10]. The marine currents that flow through the Cozumel Channel in the Mexican Caribbean Sea have been the subject of a study by the Mexican Centre for Ocean Energy Innovation (CEMIE-Océano), defining it as a key site and pilot area for the installation of an energy harvesting device of this type. [11] examined areas, where it is possible to harvest energy for low-current hydrokinetics for approximately 50% of the time, finding that near-permanent energy extraction of ~32–215 W/m2 would be possible in the Mexican Caribbean Sea. Fossil fuels are the main energy source in this area (59%), mostly coming from natural gas, and mainly used in the transport sector, and have a very negative impact on the environment [12,13].
Our oceans are spaces where there is great diversity of economic activities, such as tourism, fishing and transport. The lack of adequate regulations and the absence of marine policies in land-use planning in Mexico may generate local conflicts, with the result that changes or adaptations are needed in some of these activities so that they can continue to thrive [14].
Marine Spatial Planning (MSP) is a tool that is widely used to carry out a diagnosis of an area to define and analyse existing and future conditions [14]. For the deployment and operation of current energy projects in the Mexican Caribbean Sea, MSP can be very useful in identifying the areas most feasible for renewable energy conversion [14]. As they take into account the integrity of marine-coastal ecosystems as well as human activities, MSP help to avoid many antagonistic conflicts.
As part of the strategy for energy transition, this study describes a geospatial analysis, using MSP, carried out in the Mexican Caribbean Sea, in order to foresee possible environmental, social and economic impacts in areas where harnessing of energy from ocean currents is most feasible. With this information, more harmonious, sustainable and integrated decision-making is possible.
2. Materials and Methods
The study area (Figure 1) is in the northwest of Quintana Roo state, Mexico, encompassing parts of six municipalities which vary considerably in size, economic development and social characteristics. As any energy generation devices must be connected to the mainland to transfer the electricity to the national grid, a 10 km strip, along the coast was chosen, from the town of Holbox, in the north, to the town of Tulum, in the south, 895 km in all [15]. The marine area was delimited by the Cozumel Channel, and the boundary of the Caribbean Sea Ecoregion, as established by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), which is roughly 55 km off the coast (http://www.cec.org/ accessed on 1 May 2020).
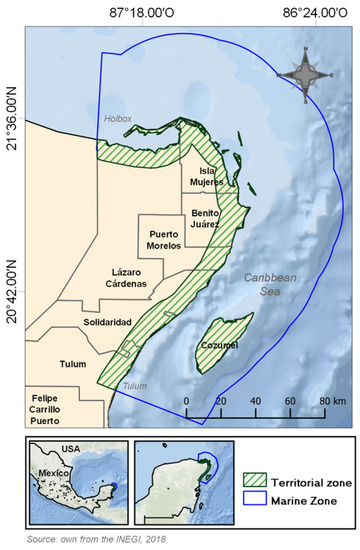
Figure 1.
Study Area.
2.1. Biophysical Characteristics for Marine Energy Extraction
The Mexican Caribbean is a region of great environmental interest, with a range of sensitive coastal and marine ecosystems that are vulnerable to changes in the environment. These are of importance, both economically and socially, due to their biological productivity and the human activities that take place here [16]. These ecosystems include coral reefs, seagrass meadows, coastal beaches and dunes, coastal lagoons and mangroves. They are interconnected and act as habitats for a wide range of marine and terrestrial flora and fauna. Some of these species are at risk, according to NOM-059-SEMARNAT-2010, including the four species of sea turtles that nest in the area (Eretmochelys imbricata, Caretta caretta, Chelonia mydas and Dermochelys coriacea), and four of the six mangrove species found here (Rhizophora mangle, Laguncularia racemosa, Avicennia germinans and Conocarpus erectus) [15,17,18].
The study area harbors significant biodiversity, particularly on the coral reefs that belong to the Mesoamerican Reef System (MAR), and stretch 300 km, from Cabo Catoche in the north to Xcalak in the south. Mangroves, seagrass beds and deep-sea flora and fauna communities are also plentiful [19,20,21]. Several legal instruments currently exist which aim to protect areas of Mexico, like this, that are rich in significant ecosystems and biodiversity characteristics.
The terrestrial part of the study area is low lying, flat land, and includes three islands: Cozumel, Mujeres and Contoy. There are diverse geographical features including bays, dune systems, coves, cays, coastal reef lagoons, islands and sea cliffs [16].
In the study area, land use consists mainly of human settlements, natural ecosystems and secondary vegetation (Figure 2). Land use is important in relation to the need to connect the marine energy produced to the electricity grid. The characteristics of the area near to the plant must be considered when the installation of the electrical infrastructure required is being planned. It is also important to identify the areas of urban development that require electricity. In areas that already have an environmental impact, it is easier to plan the infrastructure needed to connect the plant to the existing electricity grid, thus avoiding more environmentally sensitive areas that can be preserved in better condition, and areas of potential socio-environmental conflict.
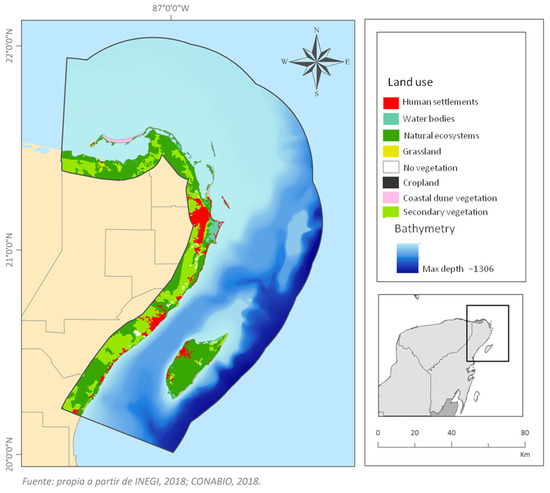
Figure 2.
Biophysical characteristics.
The bathymetry of the marine area helps identify currents and their power [4]. In the marine part of the study area the continental shelf covers approximately 6% of the ecoregion; 20 km wide near Cancun and less than 3 km in the Sian Ka’an region. The continental slope has depths of up to 3000 m (36%); and an abyssal plain over 3000 m deep [21].
Within the Caribbean Sea ecoregion there are two important channels: the Cozumel channel, approximately 50 km long and 18 km wide (Alcérreca-Huerta et al., 2019), with a depth of ~400 m; and the channel to the east of Cozumel Island, ~1000 m deep (Figure 2). The Yucatan Current flows through both channels, with an oceanic transport of 23 Sv and an average velocity of 1.5 m s−1 [22]. A part of this current flows eastward from the island of Cozumel, while ~5 Sv and 20% of the mean transport of the current flows through the Cozumel Channel [23]. The channels merge eastward at a depth of 2040 m, to form the Yucatan Channel (196 km wide), where velocities increase to 2.5 m s−1 [4,24]. This zone is the connection between the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, with a water flux of 23.8 ± 1 Sv [25] and depths of over 3500 m [26]. The widths of the channels are 50 and 100 km, respectively, and the currents recorded in both are semi-permanent and intense, always greater than 0.6 m s−1, with maximum speeds near the surface. The speed and variability of these currents mean this area has potential for energy generation and has therefore been identified as a suitable area for energy harvesting [22,26]. Silva et al. [27] identified potential sites in the study area for the harvesting of marine renewable energies from five potential energy sources: thermal gradients (Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion, OTEC), winds (Nearshore Wind Power Converters, NSWPC), waves (Wave Energy Converters, WEC), salinity gradient (Pressure Retarded Osmosis, PRO), and marine currents (Marine Current Energy Converters, MCEC) (Figure 3). This last was calculated for 2 to 7 km off the coastline, at 50 m depth.
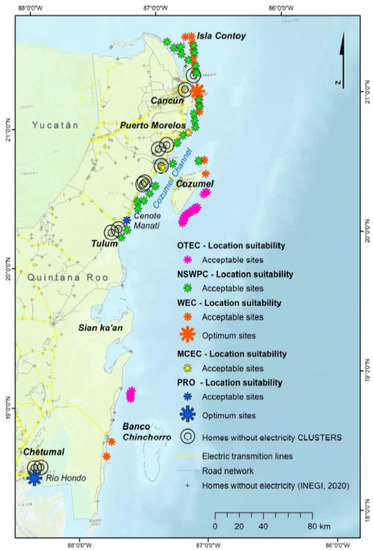
Figure 3.
Suitable locations for energy in the study area for five potential energy sources from [27]. Sites for Marine Current Energy Converters (MCEC) are shown by yellow asterisks.
The study area has a warm humid climate, with an average annual temperature of 26 °C, with summer rainfall, occasionally accompanied by extreme weather events such as tropical storms and hurricanes (June to September) [28,29]. The risk level for hurricane formation in the region is classified as very high, making this a potential threat to the operation of some ocean energy technologies [30]. The average annual surface water temperature is 27 °C and 7.7 °C at a depth of 700 m [30].
2.2. Marine Spatial Planning
The methodology of this work was based on the UNESCO [31] guide for Marine Spatial Planning (MSP), in which a spatial diagnosis is developed to plan integrated management in a given marine area. This consists of a definition and analysis of existing conditions in the Mexican Caribbean Sea and a compatibility analysis between existing characteristics/activities and energy needs.
2.2.1. Analysis of Existing Conditions in the Mexican Caribbean Sea
The various activities that take place in the region were defined, as well as the physical or social characteristics that could be related to the potential ocean energy harvesting. Scientific literature, Governmental databases (CONAPESCA, CONANP, INEGI, CONABIO), and websites of regional, local hotels, companies and NGOs were consulted to compile information in three key categories, as shown in Table 1:

Table 1.
Characteristics/activities assessed for compatibility in the Caribbean Sea.
Category (1) includes the protected areas and areas of environmental importance, significant for their biodiversity, richness, abundance, endemism, etc. (Table 2). In Mexico, Natural Protected Areas (NPA) are used as a conservation tool to protect marine and terrestrial ecosystems that shelter wild flora and fauna, natural landscapes, ecological processes, recreation opportunities, etc. as goods and ecosystem services that provide benefits for local inhabitants, for the region, and for the country. In the Mexican Caribbean, all these protected areas are important support instruments for the integrated management of coastal zones, and are designed to stimulate good practices in fisheries management, tourism, governance, etc. A considerable part of these areas has some kind of protection policy. They may be legally protected or categorised as environmentally important (although they have significant environmental characteristics, they do not have official regulations governing them). The specific objectives of each protected area depend on the goals proposed for each. Their administration is the responsibility of three governmental agencies: The National Commission on Natural Protected Areas (CONANP), Ministry of Ecology and the Environment of Quintana Roo (SEMAQRoo) and The National Commission of Aquaculture and Fisheries (Conapesca), each of which has its own respective legislation, as well as of civil organisations, whose practices are aligned to the legal and regulatory framework (Table 2).

Table 2.
Types of Protected Areas.
Category (2) concerning human activities, economic activities, activities that concern the preservation of cultural heritage, and recreational activities are shown. Tourism and fishing are the most important activities, because of the economic and social benefits they generate. In 2018, Quintana Roo received 16,675 million visitors, (top ranking, nationally), generating almost 9 billion USD [32]. About half of the employed population in Quintana Roo work in tourism [33]. With respect to fishing, the state ranks 21st nationally, producing 3571 tonnes in 2018, generating over $181 million Mexican pesos. Its share of national production was 0.17% in 2018, with octopus, grouper and lobster being the main commercial species [34].
Category (3) contains port and urban infrastructure, important in both the installation of marine energy harvesting devices, which requires the transport of technical personnel and supplies, as well as the existing port and urban infrastructure, such as access roads, dock facilities or the feasibility of building a dock, and proximity to services.
The information available was downloaded in vector and raster format and integrated with processed information to generate maps for geospatial analysis to calculate delimited areas and generate assessment categories through ArcMap 10.4 software. The information without a spatial format was processed and edited in spreadsheets for subsequent conversion to vector data in the Mexico_ITRF2008_UTM_Zone_16N coordinate system. The location software Google Earth was used to rectify the maps or to obtain specific coordinates for specific locations.
2.2.2. Analysis of Existing Characteristics/Activities in the Mexican Caribbean Sea
From the overlaid vector layers, new maps were generated to show the degree of compatibility between the 21 characteristics/activities described (Table 1). This information was organised and analysed by means of three matrices: compatibility between objectives, spatial intersection and objectives compatibility special intersection, in three consecutive steps:
- The compatibility between the objectives of the characteristics/activities was analysed by first constructing a compatibility matrix (Table 3). Three degrees of compatibility were considered: (a) compatible objectives, when the two characteristics/activities evaluated can be developed in the same time and space, represented by green cells; (b) poorly compatible objectives, when there may be conflicts when developing both characteristics/activities in the same time and space, yellow cells, and; (c) incompatible objectives, when the characteristics/activities cannot, or should not, be developed in the same time and space, red cells. The frequency, or number of cells, with which each degree of compatibility occurred was also calculated.
 Table 3. Compatibility matrix between the objectives of the characteristics/activities.
Table 3. Compatibility matrix between the objectives of the characteristics/activities. - The spatial information was analysed to construct a second intersection matrix, in which the number of spatial intersections between the types of characteristics/activities with the same and other types, was calculated to determine the number of coincidences (Figure 4, letter “a”). For this, the “Selection by location” tool of ArcGis 10.4 was used. With this information, the percentage of spatial intersections between each of the features/activities presented in the area was counted.
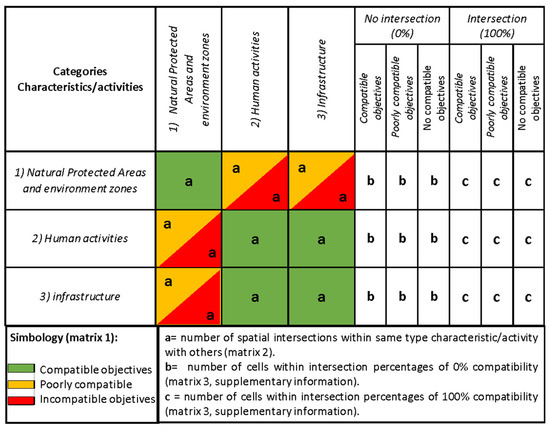 Figure 4. Summary of matrices that show the degree of compatibility between the characteristics/activities objectives in the Mexican Caribbean represented by colors: green for compatible, orange for poorly compatible and red for incompatible objectives (matrix 1). Number of spatial intersections (matrix 2), and number of cells with intersection percentages of 0 and 100% (matrix 3 in Supplementary materials).
Figure 4. Summary of matrices that show the degree of compatibility between the characteristics/activities objectives in the Mexican Caribbean represented by colors: green for compatible, orange for poorly compatible and red for incompatible objectives (matrix 1). Number of spatial intersections (matrix 2), and number of cells with intersection percentages of 0 and 100% (matrix 3 in Supplementary materials). - Finally, a third matrix was obtained calculating the frequency of cells with 0% and 100% intersection percentages, and then the frequency of cells for each percentage of the compatibility degree matrix (Compatible, Poorly compatible and Incompatible) was calculated. Subsequently, the percentages of intersection 0, 100 and >0 to 100 were calculated, for all the characteristics/activities found in the area, for each degree of compatibility of objectives (compatible, poorly compatible and not compatible) (Figure 4, letters “b” and “c”). These results were then summarised in a table of compatibility degree percentages identifying two types: the percentage of intersection (>0–100%) and the percentage of non-intersection (0%) of characteristics/activities.
In order to identify areas with potential for energy harvesting from ocean currents with respect to all the activities in the study area, a map was generated to spatialize the information obtained in the compatibility matrix. The same colour code (green, potential areas; yellow, little potential; and red, no potential) was used to indicate the respective areas. Then the “merge” polygon tool was used to construct a single layer for each degree of compatibility obtained in the matrix. Since it is not possible to merge points and polygons with the tool used, the characteristics/activities were assigned the specific colour according to the compatibility matrix.
2.2.3. Energy Supply Needs of Communities
For this analysis, government databases for the study area [35,36,37] and a civil organization [38] were consulted. Information on access to electricity, the degree of social marginalization, and features of the electricity infrastructure (power plants, electricity substations, electricity grid) were compiled. Using the INEGI Catalogue of localities [39] settlements were identified that are less than 10 km from the coast, at less than 100 m above sea level and with more than 100 inhabitants. These socio-economic criteria have previously been used for the deployment of marine energy harvesting devices [30,40].
The information was organized into databases in.cvs format for specialization in a GIS, by category and by municipality, using ArcMap 10.4 software. Subsequently, a digital map of the study area was produced showing the spatial distribution of electricity needs (% of dwellings without electricity) and the degree of social marginalization of the municipalities. Regarding settlements, 34 were found to be less than 10 km from the coast, with more than 100 inhabitants, where the implementation of ocean energy technologies would be beneficial.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Existing Conditions in the Mexican Caribbean
3.1.1. Protected Areas and Areas of Environmental Importance
- (a)
- Protected Areas
82% of the study area is under legal protection, 77% is marine territory and 5% terrestrial. There are six types of protected areas: federal Natural Protected Areas (NPAs), state NPAs, Voluntary NPAs, fisheries refuge zones (FRZs), refuge areas for the protection of aquatic species (RAs) and protected beaches (Figure 5). In total, 77 protected areas were recorded in the area (Table 2). Some of these overlap, so that in the same location more than one legal regulation is applicable, as is the case of refuge areas that are in federal NPAs or FRZs.
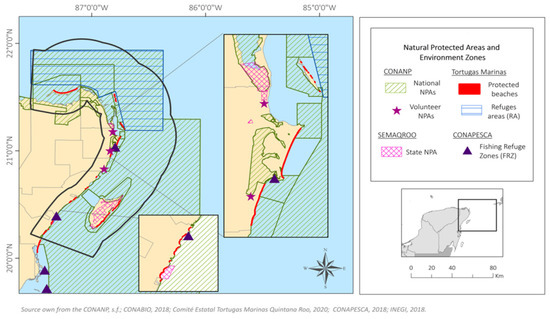
Figure 5.
Protected Areas.
81% of the study area is part of a federal NPA, protecting 92% of the marine territory; the rest of the territory is administered by the Law of National Waters and other laws, such as the General Law of Ecological Balance and Environmental Protection (Ley General de Equilibrio Ecologico y Protección al Ambiente, LGEEPA). Refuge Areas (RA) cover 32% of the area, with their objectives focused on one or more species. There are two marine RAs in the study area: one for the protection of the Whale Shark (north) and one for the protection of Akumal Bay marine species (south). Both are located within a Federal NPA, and so their protection programme is governed by the corresponding NPA Management Plan; Article 68 of the General Wildlife Law. The rest of the areas (state and voluntary NPAs; PRZs and protected beaches) make up less than 2% of the study area, for example, state NPAs cover 1.32%, with the largest covering the forests and wetlands of Cozumel.
The objectives of the Fisheries Refuge Zones (FRZ) are to conserve and promote the reproduction, growth and recruitment of fishery resources [41]. In the north these are: (1) the FRZ Canal Nizuc, in the municipality of Benito Juárez and (2) the FRZ Akumal, off the coast of Tulum. In the first, no commercial, didactic, promotional, sport-recreational or fishing for self-consumption is allowed of any species or aquatic flora and fauna. In the second, fishing is allowed periodically, with specific fishing gear for commercial, sport-recreational fishing, or for self-consumption.
Finally, voluntary NPAs and protected beaches together represent only 0.04% of the study area. NPAs of this type are private properties, where the owners are interested in conservation. In accordance with the law established by SEMARNAT, they are granted a certificate. In the study area, these NPAs are terrestrial and owned by community landowners, or “ejidatarios”. Protected beaches, on the other hand, are nesting sites for sea turtles and are coordinated by a turtle camp, generally managed by CONANP or a civil organization, under NOM-059-SEMARNAT-2010. They are guarded and monitored during the nesting season (if they are not within an NPA).
- (b)
- Areas of Environmental Importance
These are defined following studies involving national and international agencies, with the aim of conserving and maintaining the connectivity of sites considered a priority for hosting ecosystems and wildlife under threat. In the study site, three types of environmentally important areas were identified: Sites of Marine Priority (SMP), Important Bird Areas (IBAs) and RAMSAR sites (Figure 6). These cover 28.5% of the study area, mainly marine territory (Figure 5).
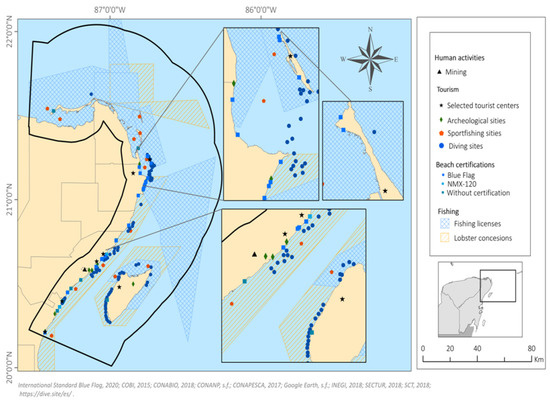
Figure 6.
Areas of environmental importance.
The SMPs were defined in 2005, based on the Priority Marine Regions (PMRs) [42,43]. They are the result of collaborative work between various governmental organisations and civil associations (CONABIO, CONANP, Pronatura and TNC), and aim to conserve sites of coastal and marine biodiversity in Mexico. There are 11 SMPs in the study area, of which two are entirely marine and nine are coastal, covering 24% of the study area. The “Coastal Wetlands and the Continental Shelf of Cabo Catoche”, SMP 68, is the largest in the area located in the municipalities of Lázaro Cárdenas and Isla Mujeres (continental zone).
IBAs are part of an internationally initiated project that aims to create a regional network of important areas for bird conservation [44]. Some are the result of collaboration between governmental bodies and civil organisations (CIPAMEX, CONABIO and SEO Birdlife). Seven IBAs are located in the study area, and it is worth noting that nearly half of the bird species recorded in Mexico (483) have been recorded in Quintana Roo [45]. The seven IBAs cover 9.7% of the study area, mostly terrestrial (60%). The entire islands of Cozumel and Contoy are IBAs (Figure 6).
The RAMSAR sites are recognised internationally by the “RAMSAR Convention” as being of international importance, and their objective is the conservation and wise use of wetlands. All RAMSAR sites in the country have been designated as federal NPAs, which is why they were considered as sites of environmental importance (since there is no exclusive legislation for wetlands in the country). Eight RAMSAR sites are located in the study area (Figure 6).
As with the protected areas, some of the sites of environmental importance overlap spatially, which is why these areas could be considered to be more important, such as the islands of Cozumel and Contoy, declared SMPs, IBAs and RAMSAR sites. 82% of the surface area of environmentally important sites is a protected area.
3.1.2. Human Activities
- (a)
- Tourist activities
Tourism is the activity that generates most employment and income in the state. It is the core of the Mexican Caribbean economy and demand for energy here is high. The region is known as the “Riviera Maya”, and has fourteen established tourist destinations on the coast of Quintana Roo, of which six are located in the study area. These include Cancun, Mexico’s main “sun and beach” destination, and are known as Selected Tourist Centres (STCs). They each have one, or more, of the following conditions: (1) over 2000 hotel rooms, (2) permanent or periodically significant tourist inflows, (3) participation in the “Mundo Maya” or “Centros de Playa” development programmes, and (4) are part of a tourist complex planned by the Fondo Nacional de Fomento al Turismo (Fonatur). In 2018, the six STCs in the study area received over 12 million tourists, 70% to Cancun [46] (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
Human Activities.
The STCs are also classified as “Beach Centres”, as the “sun and beach binomial” is the fundamental feature of recreation and leisure in the study area [47]. The coastline of the study area varies from solitary beaches to modern architectural complexes, including hotels and marinas, where a range of leisure and recreational activities take place [48].
Beaches with and without certification were considered. In the study area, there are 23 certified beaches. Of these there are two types of certification: Blue Flag, an international distinction awarded to beaches for their environmental education and information, water quality, environmental management, safety and services; and secondly, the “Playa Limpia Sustentable” certification, of the Mexican government, NMX-120, which defines the environmental quality, health, safety and services for beach sustainability.
There are also 10 beaches without certification that are registered as “sites of tourist interest” by the Mexican Institute of Transport in its National Road Network. (http://189.254.204.50:83/ accessed on 1 November 2020). These are mostly in the south of the study area, between Akumal and Playa del Carmen (Figure 7). Of the certified beaches, 43% are located in Cancun, and 87% coincide with one of the six STS within the study area.
Diving in the study area is a high value activity that is growing in popularity. It is closely related to the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System. One of the dive magazines most internationally circulated, “Scuba Diving Mag”, describes the Mayan Riviera as a world-class diving destination, with Isla Mujeres and Cozumel defined as “Best Diving Destinations” in the categories l arge animals and advanced diving, respectively [48,49,50]. Most dive sites are found off the coasts of Cozumel (34%), Solidaridad (19%) (mainly off Playa del Carmen), Akumal (13%), Benito Juárez (13%), Isla Mujeres (11%) and Puerto Morelos (7%) (Figure 7). Since there is no official repository of dive sites, the maps provided by diving companies in the study area were used to identify 90 dive sites. All of these are located within an ANP, so although the dive service is private, it is regulated by CONANP.
Sport fishing is a very important activity in the region and is regulated by CONAPESCA and SEMARNAT. In 2017, 3373 permits were granted in Quintana Roo, representing just over half a million Mexican pesos as revenue for the state. The state was ranked nationally in seco nd and fif th place, respectively, for number of permits and amount of money collected [34]. Annually, Quintana Roo hosts at least 25 tournaments, 21 of which are of international stature. According to the 2020 calendar published by CONAPESCA, 26 tournaments were planned in the state, of which 58% would be within the study area [32,51]. The study site has 13 of the 15 sport fishing locations reported in the state.
Finally, there are nine archaeological zones (A.Z.) in the study area, of which Tulum is by far the most visited; in fact it is the third most important A.Z. in Mexico. the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) records the number of visitors to archaeological sites, and figures for seven of the nine sites in 2018 are seen in Table 4.

Table 4.
Number of visitors to archaeological sites 2018.
- (b)
- Fishing
In the study area, fishing is both coastal and oceanic. In 2017, in Quintana Roo, 3800 tones were fished, with grouper being the species with the highest volume reported, 530 tones, followed by lobster, 490 tones. The total value of the production that year was almost 200 million Mexican pesos. There are 2910 fishermen, 889 coastal vessels, 29 larger vessels, and 10 fishing plants registered in the state [34].
In Quintana Roo there are nine areas where fishing is permitted and all of them converge in the authorized environmental buffer zones of a natural protected area, so they must comply with the provisions of the LGEEPA and the Management Plan of the respective NPAs. There are 24 permitted fishing zones in force in the study area, 92% are based in Puerto Juárez, 4% at the dock in Cozumel, and 4% at the dock in Isla Mujeres. 67% of these permits are for fishing. 67% of permitted fishing is for deep-sea shrimp, 13% for Caribbean lobster and sea scales, 4% for lobster and 4% for octopus.
CONAPESCA has extended the concessions for fishing cooperatives to carry out commercial lobster fishing, which has become a growing market in Quintana Roo.
3.1.3. Infrastructure
- (a)
- Port infrastructure
In the study area there are 20 ports for tourist, industrial, fishing, military and ferry terminals, as well as 39 piers and 11 marinas. In 2018, Quintana Roo had eight registered tourist marinas, with facilities for pleasure boats or yachts, both public and private (SCT 2014) and twelve berths for tourist cruise ships and ferries [46]. Six ports have cruise ship docking infrastructure, three of which are on the island of Cozumel, the most important tourist port in Mexico in terms of the number of ships that dock. In 2019 1366 cruisers arrived, carrying 4,569,853 tourists [52]. Puerto Morelos is deemed a tourist destination with port infrastructure, but it is exclusively for cargo, although there are plans to expand it, to receive cruise ships.
Connections between the islands and the mainland are needed for the transport of people, both tourists and workers. 10 ferry terminals exist, among which the most important routes are: Chiquilá-Holbox; Cancún-Isla Mujeres; Isla Mujeres-Isla Contoy; and Playa del Carmen–Cozumel (Figure 8). According to estimates from the port administration agency [53], approximately 11 million passengers, tourists and local inhabitants [52], used these ferries (Table 5). Given the uneven economic activity associated with COVID-19 mobility restrictions, the data for 2020 is poorly representative of normal maritime mobility in the study area.
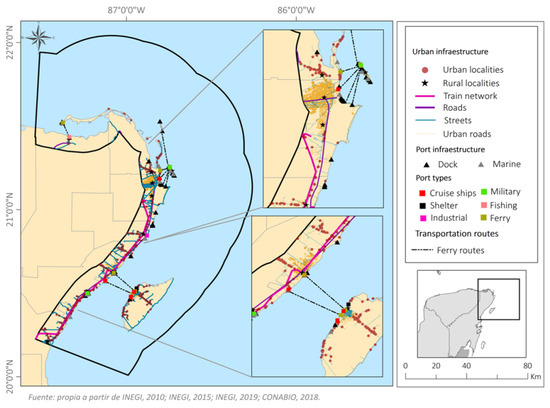
Figure 8.
Urban infrastructure.

Table 5.
Maritime passenger movement.
- (b)
- Urban Infrastructure
The study area contains 917 localities, with 1.4 million inhabitants, only nine of which are urban: Cancun, Playa del Carmen, Cozumel, Tulum, Puerto Aventuras, Alfredo V. Bonfil, Puerto Morelos, Isla Mujeres and Zona Urbana Ejido Isla Mujeres. However, 98.7% of the state population live in these centres. Similarly, of the total number of inhabited private dwellings, 90% are in these areas (Table 6) [39].

Table 6.
Rural and urban localities within the study area.
A motorway runs along the coastline in the study area, with occasional intersecting roads giving access to the sea and inland. The main roads connect Cancun, Playa del Carmen and Cozumel, where the major tourist developments are found. From the end of the 19th century to the middle of the 20th century, railway lines were built mainly for commercial transport, but they are all abandoned nowadays. Currently the “Tren Maya” a railway line linking Cancun and Chetumal, and these two cities with neighbouring states, is under construction, due to be completed in 2023.
3.2. Compatibility Analysis of Existing Activities in the Caribbean Sea
The results of the analysis showing compatibility and the number of spatial intersections between the objectives of the 21 activities which currently occur in the study area are shown in Table 7. Activities related to protected areas/areas of environmental importance have objectives which are compatible with those in archaeological sites and certified beaches. These are shown in green.

Table 7.
Interaction between compatibility (colours) and the number of spatial intersection (represented by “a” in Figure 4) between characteristics/activities. The colours represent the degree of compatibility between the objectives of the characteristics/activities. Compatible objectives (green), Poorly compatible objectives (yellow) and Incompatible objectives (red). Categories: 1: Natural Protected Areas and Environmental zones, 2, Human activities, 3. Infra structure.
Poorly compatible objectives (yellow) are seen between the activities of protected areas/areas of environmental importance with those of socio-economic activities, such as tourism and fishing (Figure 9).
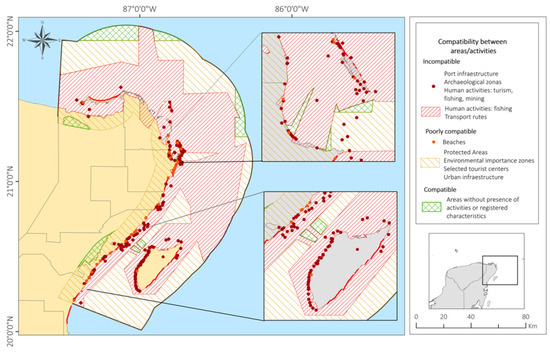
Figure 9.
Compatibility Map.
Objectives that are non-compatible (red) are related to protected areas/areas of environmental importance with activities of tourist destinations, tourist beaches, marinas and other port infrastructure (Figure 9). Incompatibility of objectives was also found between tourist beaches and protected beaches (sea turtle nesting), as well as between port infrastructure, even piers and marinas, with other marine activities, such as diving and both commercial and sport fishing.
With geospatial analysis, intersections between the types of activity and land uses in a given area can be identified (Table 7, Figure 9). Table 8 summarises the percentage of spatial intersections between characteristics and activities into two types: no intersection (=0% intersections) or to some degree (>0% intersections), according to the degree of compatibility of the land use objectives.

Table 8.
Summary of the results of the interaction between compatibility and spatial intersection (Table 7 and Supplementary Materials).
There are two wildlife refuge areas in the study area that intersect completely with the federal NPAs, the SMPs, the tourist destinations and the areas with lobster concessions. The objectives and activities of the first two are compatible, but of the third and fourth the objectives and activities are contradictory, and poorly compatible, respectively.
Regarding the port and urban infrastructure, there are 19 decks and 20 marinas for the berthing of maritime transport in the study area. For decks, 15 coincide with federal NAPs, 11 are in SMPs, 12 in tourist destinations, and 16 in areas with fishing permits. 66.9% (see Figure S1, Table 8) of the characteristics/activities of poor compatibility intersect in one or more occasions. Tourist destinations and fishing zones are highly compatible with port and urban infrastructure.
All Fishing Refuge Zones and Wildlife Refuge Areas intersect with Lobster Concession sites, whose management objectives are poorly compatible (2 and 3 times respectively, see Figure S1). The same is true for Permitted Fishing and Lobster Concessions (seven times, Figure S1), which intersect in their entirety with Federal NPAs, which they have poorly compatible management objectives.
50.5% of activities with non-compatible management objectives intersect on one or more occasions. For example, the total number of Fisheries Refuge Zones (2) were found to intersect with Selected Tourism Destinations (2), with which they have non-compatible management objectives (Figure S1).
It was also found that some characteristics/activities which are seen in large land and marine areas, such as federal NPAs, RAMSAR Sites and Marine Protected Sites have up to 100% intersections with other characteristics/activities in the categories: (1) protected areas and areas of environmental importance and (2) human activities (Figure S1). However, these intersections occurred with characteristics/activities with compatible conservation objectives.
3.3. Energy Needs of the Population
The municipality of Isla Mujeres is that with the highest percentage of households without electricity (6.05%) in the study area, followed by the Lázaro Cárdenas (3.58%) and Tulum (2.35%) municipalities [36]. The spatial relationship of energy needs with social marginalization shows that there is a high degree of marginalization in Lázaro Cárdenas, while the other municipalities have Low, or Very Low, degrees of marginalization [35] (Figure 10, Table 9).
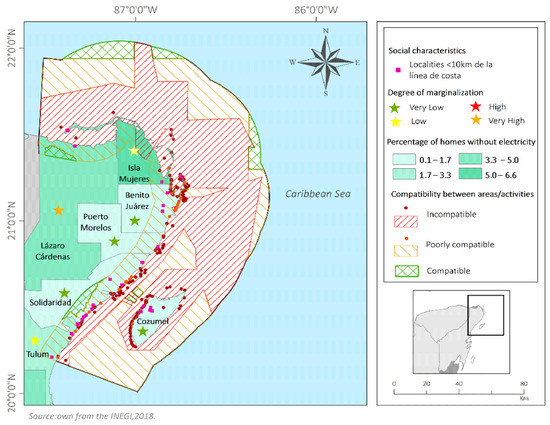
Figure 10.
Percentage of households without electricity.

Table 9.
Municipalities in Quintana Roo with the highest percentage of inhabited private dwellings without electricity and their degrees of marginalisation. Own elaboration with information obtained from [35,36,39].
The highest concentration of transmission grids, substations and power plants was found in the municipality of Benito Juárez, followed by Solidaridad and Cozumel. Isla Mujeres and Lázaro Cárdenas are the municipalities with fewest of these features.
Analysis of the criteria of priority (greatest social benefit) and proximity (close to the ocean) shows that in the three municipalities with greatest energy needs, Isla Mujeres, Lázaro Cárdenas and Tulum, there are 13 coastal localities with over 100 inhabitants that are less than 10 km from the coastline (Figure 10, Table 9).
4. Discussion
There is ample evidence of a future crisis in energy based on fossil fuels [1,56]. Added to this, greenhouse gas emissions, global warming and environmental contamination, increase the need to develop alternative technologies that allow us to harness energy from the ocean [3,56]. Energy from ocean currents is a promising option, given the widespread availability of the resource, worldwide [5,6]. In Mexico today, large coastal areas are still without electric energy supply, causing great socioeconomic inequalities [4,57].
There are many types of devices being developed to harness ocean energy [56], and the exploration of potential areas for energy harvesting must also be prioritised [27]. The ocean currents in the Mexican Caribbean were analysed to find the areas where conditions are most favourable for energy generation [4,57,58]. A subsequent geospatial analysis shows the great diversity in terms of human development and biodiversity in the study area. In 82% of the study area, 77 NPAs and areas of environmental importance exist, overlapping with each other. Legal regulatory instruments exist within these areas that establish the activities that drive economic development and the generation of services. In some cases, the objectives of the various activities that take place there are compatible, but in others this is not so and can mean that environmental degradation is likely in protected areas.
In regard to human activities, tourist activities in the region are very diverse, from beach visits to sport fishing and visits to archaeological sites. Limestone extraction, in one specific area, near Playa del Carmen, in the municipality of Solidaridad is a special case. Since 1986 the renovation of local, state and federal authorization has meant the mining activities were expanded every 15 years. However, since 2016 these permits have not been renewed, as the activity is incompatible with local regulations and with the 2009 ecological zoning policy of the municipality. In 2017 the environmental authorities partially closed down a coastal rock mining following inspections of the site after an application for a renovation of the permit was turned down. The main environmental damage caused by the mining is the complete removal of vegetation.
Regarding existing infrastructure, it is important that any infrastructure related to a marine energy generation project does not affect existing transport routes, nor put at risk the activities currently taking place in the area.
Section 5 of the “Tren Maya”, the new rail line presently under construction, runs through the study area, connecting Tulum, Playa del Carmen, Puerto Morelos and Cancún. The infrastructure associated with the construction of the railway is severely modifying subsurface water flows that are of utmost importance for the preservation of coastal wetlands.
Socio-environmental conflicts are defined as “mobilizations of local communities, social movements, which may include support for national or international networks against particular economic activities, infrastructure construction or waste disposal/pollution, whereby environmental impact is a key element of their claims” [59]. In the study area there are several hotspots where there is already dissatisfaction with public policies associated with national level projects. Tourism and fishing depend on healthy ecosystems, as scenic beauty and biodiversity are the main factors in the development of these activities. On the other hand, these activities can produce negative environmental impacts if they are not properly regulated. As an example, the Atlas of Environmental Justice [59] describes the “recreational tourism” on Holbox Island, related to the “La Ensenada” project as a cause for concern. A luxury tourism development was planned which would entail 70 community landowners, or “ejidatarios” being dispossessed of their land with a payment of less than 5% of the value of the land. Although the project has been stopped and the conflict is reported to have ended in 2016, this area is vulnerable to this type of conflict due to its status as a tourist attraction [60].
The second area of conflict is related to the “extraction of minerals and construction materials”, classified as medium intensity, described earlier. The extraction of limestone near Playa del Carmen from previously undeveloped areas of jungle has exceeding the limits authorised and affected the communities living in the region. The main impacts are pollution, loss of biodiversity, landscape degradation, water contamination [61].
As marine currents influence the distribution of commercially important species and impact on the marine and coastal environment, a current energy project could only be successful in an area where there are no repercussions for fishing, commercial and recreational. Bárcenas et al. [58] analysed the areas where marine energy harnessing would be feasible in part of our study area, considering environmental conditions and a range of floating and fixed devices. Their work, in front of Cozumel island suggests that the areas with greatest potential are at 30–50 metres depth. They also examined the NPAs, land use policies of the area (one regional, for the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean, and the other at local scale), shipping routes, infrastructure, tourist areas, military facilities, academic and research institutions, concluding that restrictions are needed in these areas and that it is important to take into consideration information from maps and internet pages for decision making regarding possible marine energy projects.
In Mexico the environmental impact assessment of marine energy power generation projects is still in process [62]. This work should be carried out prior to the installation of any marine energy project to minimize anthropogenic impacts. The areas with greatest need of electricity in the study area are in the north, Isla Mujeres, followed by locations in the interior and centre of Lázaro Cárdenas, and finally in Tulum, in the south (Figure 10, Table 9). Any project focused on improving socioeconomic change needs the participation of local actors for its acceptance, development and success. If it does not have this, socio-environmental conflicts may arise which limit the possible benefits of the project.
5. Conclusions
With geo-visualization tools, a diagnosis was made of areas in which marine energy generation is feasible as a way of ensuring environmental friendliness and economic viability. The extraction of marine energy through currents, would require a stable, safe physical space. Power generation projects must be able to be properly integrated into existing socio-environmental processes, for example, in the case of diving and sport fishing activities where safety must be guaranteed.
The development of human activities in the study area should be achieved by seeking a positive impact on the populations with the greatest need for electricity. The generation of electricity through ocean energy will have to coexist with economic activities both in the marine and terrestrial space.
The results of the present work provide a tool for spatial and marine planning that would enable the development and installation of such projects, that considers the needs of all, without forgetting that a potential energy generation project can be seen as an opportunity for socioeconomic development. This can serve as a basis for similar studies in other parts of the world, and to enable decision-makers and stakeholders in Mexico to make better use of the Mexican Caribbean’s biological resources for a fairer society and a less polluted world.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land11050665/s1. Figure S1: Matrix 3 for the calculation of intersection percentages of 0% and 100%, related to the frequency of intersections between the characteristics/activities objectives.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.B.-O. and G.M.-G.; methodology, I.B.-O.; software, I.B.-O.; validation, R.S., formal analysis, I.B.-O., G.M.-G. and L.M.-P.; investigation, I.B.-O., G.M.-G., L.M.-P. and R.S.; resources, G.M.-G. and R.S.; data curation, I.B.-O. and L.M.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, I.B.-O. and G.M.-G.; writing—review and editing, I.B.-O., G.M.-G., L.M.-P. and R.S.; visualization, I.B.-O. and G.M.-G.; supervision, G.M.-G.; project administration, G.M.-G. and R.S.; funding acquisition, G.M.-G. and R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Mexican Centre for Innovation in Ocean Energy (CEMIE-Océano, CONACYT project 249795).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by CEMIE-Océano. We also thank Maribel Badillo Alemán and Alfredo Gallardo Torres for the technical support in the Biological Conservation Laboratory.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kühne, K.; Sanchez, L.; Roth, J.; Tornel, C.; Ivetta, G. Beyond Fossil Fuels: Fiscal Transition in Mexico; International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD): Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2019; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Sener. Reporte de Avance De Energías Limpias Primer Semestre 2018; Secretaría de Energía del Gobierno de México: Ciudad de México, México, 2018; p. 21. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/418391/RAEL_Primer_Semestre_2018.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Congreso de la Unión. Ley General de Cambio Climático (LGCC). In Diario Oficial de la Federación-06-2012, ú ltima reforma DOF-06-11-2020; Congreso de la Unión: Ciudad de México, México. Available online: https://www.diputados.gob.mx/LeyesBiblio/pdf/LGCC_061120.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2021).
- Alcérreca-Huerta, J.C.; Encarnacion, J.I.; Ordoñez-Sánchez, S.; Callejas-Jiménez, M.; Barroso, G.G.D.; Allmark, M.; Mariño-Tapia, I.; Casarín, R.S.; O’Doherty, T.; Johnstone, C.; et al. Energy yield assessment from ocean currents in the insular shelf of Cozumel Island. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, R.; Viteri, D. Energía Undimotriz, alternativa para la producción de Energía Eléctrica en la Provincia de Santa Elena. Rev. Cient. Tecnol. UPSE 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hucherby, J.; Jeffrey, H.; de Andres, A.; Finlay, L. An International Vision for Ocean Energy, Version III: February 2017; Ocean Energy Systems Technology Collaboration Programme: Paris, France, 2011; Volume 7, p. 28. Available online: www.ocean-energy-systems.org (accessed on 20 March 2021).
- International Renewable Energy Agency. Renewable Energy Highlights—July 2020. Available online: https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2021/Apr/IRENA_-RE_Capacity_Highlights_2021 (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Pérez, H.B.; Ramírez, J.C.C.; Andrade, M.Á.G.; Pulido, E.P.O. Evaluación de una política de sustitución de energías fósiles para reducir las emisiones de carbono. Trimest. Econ. 2017, 84, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Noble, D.R.; O’shea, M.; Judge, F.; Robles, E.; Martinez, R.; Khalid, F.; Thies, P.R.; Johanning, L.; Corlay, Y.; Gabl, R.; et al. Standardising marine renewable energy testing: Gap analysis and recommendations for development of standards. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Haas, K.A.; Fritz, H.M. Theoretical assessment of ocean current energy potential for the Gulf Stream system. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2013, 47, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Fontes, J.V.; Felix, A.; Mendoza, E.; Cueto, Y.R.; Silva, R. On the marine energy resources of Mexico. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Acosta-Olea, R.; Barbosa-Pool, G.R.; Aguilar-Aguilar, J.O.; Chargoy-Rosas, M.A.; Quinto-Diez, P. Indicadores de Desarrollo Energético Sustentable. Caso: Quintana Roo, México. Quivera Univ. Autónoma Estado México 2016, 18, 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, L.; 3 desafíos del sector eléctrico de la Península de Yucatán y cómo superarlos. El Financiero Península Home Page (Mérida, Yucatán, México). 28 de enero de 2019. Available online: https://www.elfinanciero.com.mx/peninsula/3-desafios-del-sector-electrico-de-la-peninsula-de-yucatan-y-como-superarlos/ (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Aldana, O.; Hernández, A. La Planificación Espacial Marina: Marco Operativo Para Conservar la Diversidad Biológica Marina y Promover el Uso Sostenible del Potencial Económico de los Recursos Marinos en el Caribe. In Adaptación Basada en Ecosistemas: Alternativa para la Gestión Sostenible de los Recursos Marinos y Costeros del Caribe; Instituto de Oceanología: La Habana, Cuba, 2016; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-959-298-036-5. [Google Scholar]
- Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad (Conabio). Geoportal del Sistema Nacional de Información sobre Biodiversidad Home Page. In Subdirección de Sistemas de Información Geográfica. Available online: http://www.conabio.gob.mx/informacion/gis/ (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Rioja-Nieto, R.; Garza-Pérez, R.; Álvarez-Filip, L.; Mariño-Tapia, I.; Enríquez, C. The Mexican Caribbean: From Xcalak to Holbox. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Warwick, UK, 2018; Volume I: Europe, the Americas and West Africa, pp. 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisión Nacional de Áreas Naturales Protegida (Conanp). Programa de Manejo de la Reserva de la Biosfera Caribe Mexicano; Comisión Nacional de Áreas Naturales Protegidas, Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales del Gobierno de México: Ciudad de México, México, 2018; p. 375. Available online: https://simec.conanp.gob.mx/pdf_libro_pm/191_libro_pm.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Sandoval Herazo, E.J.; Lizardi Jiménez, M.A. Hydrocarbons: Pollution at the Mexican Caribbean. Rev. Digit. Univ. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardisson, P.L.; May-Kú, M.A.; Herrera-Dorantes, M.T.; Arellano-Guillermo, A. El Sistema Arrecifal Mesoamericano-México: Consideraciones para su designación como Zona Marítima Especialmente Sensible. Hidrobiologica 2011, 21, 261–280. [Google Scholar]
- Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad (Conabio). Mares Mexicanos. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/articulos/mares-mexicanos; http://www.biodiversidad.gob.mx/pais/mares/Nuestros; (accessed on 19 March 2021).
- Wilkinson, T.; Wiken, E.; Bezaury Creel, J.; Hourigan, T.F.; Agardy, T.; Herrmmann, H.; Janishevsji, L.; Madden, C.; Morgan, L.; Moreno, P. Ecorregiones Marinas de América del Norte; Comisión para la Cooperación Ambiental: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2009; p. 200. ISBN 978-2-923358-72-7. [Google Scholar]
- Badan, A.; Candela, J.; Sheinbaum, J.; Ochoa, J. Upper-layer circulation in the approaches to Yucatan channel. In Circulation in the Gulf of Mexico: Observations and Models; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 161, pp. 57–69. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2005GMS...161...57B/abstract (accessed on 20 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Chávez, G.; Candela, J.; Ochoa, J. Subinertial flows and transports in Cozumel Channel. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, A.J.; Sheinbaum, J.; Candela, J.; Ochoa, J.; Badan, A. Analysis of flow variability in the Yucatan Channel. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheinbaum, J.; Candela, J.; Badan, A.; Ochoa, J. Flow structure and transport in the Yucatan Channel. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 10-11–10-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athié, G.; Candela, J.; Sheinbaum, J.; Badan, A.; Ochoa, J. Yucatan Current variability through the Cozumel and Yucatan channels. Cienc. Mar. 2011, 37, 471–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Zúñiga, A.; Guimarais, M.; Barcenas, J.F.; Chávez, V.; Martínez, M.L.; Wojtarowski, A. Marine energy in the Mexican Caribbean: Needs and resources. In Proceedings of the SEEP2021, Boku, Vienna, Austria, 13–16 September 2021; pp. 600–605. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, M.L. Evaluación Del Riesgo y Vulnerabilidad Ante la Amenaza de Huracanes en Zonas Costeras del Caribe Mexicano: Chetumal y Mahahual. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Quintana Roo, Chetumal, México, 2014; p. 398. Available online: http://repobiblio.cuc.uqroo.mx/handle/20.500.12249/98 (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (Inegi). Inegi Home Page. Climatología; Mapas Climatológicos. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/temas/climatologia/ (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Garduño-Ruiz, E.P.; Silva, R.; Rodríguez-Cueto, Y.; García-Huante, A.; Olmedo-González, J.; Martínez, M.L.; Wojtarowski, A.; Martell-Dubois, R.; Cerdeira-Estrada, S. Criteria for optimal site selection for ocean thermal energy conversion (Otec) plants in Mexico. Energies 2021, 14, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission; Directorate General for Fisheries and Maritime, Affairs. MSPglobal: International Guide on Marine/Maritime Spatial Planning. 2021. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000379196 (accessed on 4 April 2021).
- Secretaría de Desarrollo Agropecuario Rural y Peasa. PESCA DEPORTIVA. 2018. Available online: https://qroo.gob.mx/sedarpe/pesca-deportiva/ (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Inegi. Censos Económicos 2014. 2014. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/programas/ce/2014/ (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Conapesca. Anuario Estadístico de Acuacultura y Pesca. 2018. Available online: https://nube.conapesca.gob.mx/sites/cona/dgppe/2018/ANUARIO_2018.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Conapo. Índice de Marginación por Entidad Federativa y municipio 2015|Consejo Nacional de Población|Gobierno|gob.mx. 2015. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/conapo/articulos/indice-de-marginacion-por-entidad-federativa-y-municipio-2020-271404?idiom=es (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Encuesta Intercensal 2015. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/programas/intercensal/2015/ (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Sener. Programa Nacional para el Aprovechamiento Sustentable de la Energía 2014–2018. Avances y Resultados 2018, 42.
- Geocomunes, C. Geovisualizador-Alumbrar las Contradicciones del Sistema Eléctrico Nacional y de la Transición Energética|Geocomunes. Available online: http://geocomunes.org/Visualizadores/SistemaElectricoMexico/ (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- Inegi. Catálogo Único de Claves de Áreas Geoestadísticas Estatales, Municipales y Localidades. 2020, pp. 1–8. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/app/ageeml/ (accessed on 6 February 2021).
- Hernández-Fontes, J.V.; Martínez, M.L.; Wojtarowski, A.; González-Mendoza, J.L.; Landgrave, R.; Silva, R. Is ocean energy an alternative in developing regions? A case study in Michoacan, Mexico. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conapesca. Zonas de Refugio Pesquero Vigentes en México al 11 de Diciembre de 2019. 2019; pp. 1–5. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/516926/ZRP_VIGENTES_191211__2_.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Conabio, The Nature Conservancy-Programa México, Pronatura. Sitios Prioritarios Marinos Para la Conservación de la Biodiversidad. 2007. Available online: http://geoportal.conabio.gob.mx/metadatos/doc/html/spm1mgw.html (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Semarnat. Regiones Marinas Prioritarias. 1998. Available online: http://dgeiawf.semarnat.gob.mx:8080/ibi_apps/WFServlet?IBIF_ex=D3_BIODIV01_14&IBIC_user=dgeia_mce&IBIC_pass=dgeia_mce (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Conabio. Regionalización. Áreas de Importancia para la Conservación de las Aves (AICAS). 2004. Available online: http://conabioweb.conabio.gob.mx/aicas/doctos/aicas.html (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Pozo, C.; Armijo, N.; Calmé, S. Mexico. Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad. Riqueza Biológica de Quintana Roo: Un Análisis Para su Conservación; Comisión Nacional Para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad (Conabio): Mexico City, Mexico, 2011; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sectur. Compendio Estadistico del Turismo en México. 2018. Available online: https://www.datatur.sectur.gob.mx/SitePages/CompendioEstadistico.aspx (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Sectur. Centros de Playa. 2014. Available online: https://www.sectur.gob.mx/programas/programas-regionales/centros-de-playa/ (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Uqroo. Tourism Competitiveness Study of the Riviera Maya destination. 2013; p. 548. Available online: https://www.sectur.gob.mx/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/PDF-Riviera-Maya.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Gobierno de Quintana, R. Quintana Roo, Mejor Destino de Buceo del Mundo. 2019. Available online: qroo.gob.mx (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Santander, L.C.; Propín, E. Impacto ambiental del turismo de buceo en arrecifes de coral. Cuadernos Turismo 2009, 24, 207–227. [Google Scholar]
- Conapesca. Calendar of the Mexican Caribbean Sport Fishing Tournaments 2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.pescandoenelcaribe.com/torneos.html (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Sct. Movimiento Marítimo de Pasajeros por Tipo de Embarcación, Litoral y Puerto, Serie Anual de 2015 a 2019. 2019, p. 240. Available online: www.sct.gob.mx/fileadmin/DireccionesGrales/DGP/PDF/DEC-PDF/Anuario_2019.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Apiqroo. Postal de estadísticas. 2017. Available online: http://servicios.apiqroo.com.mx/estadistica/index.php (accessed on 2 April 2021).
- Sectur. Movimiento de Cruceros en los Principales Puertos del país: Anual. 2021. Available online: https://www.datatur.sectur.gob.mx/SitePages/CompendioEstadistico.aspx (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Semar. Actividades en Crucero 2021–2022. 2022. Available online: https://www.datatur.sectur.gob.mx/SitePages/Actividades%20En%20Crucero.aspx (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Ibrahim, W.I.; Mohamed, M.R.; Ismail, R.M.T.R.; Leung, P.K.; Xing, W.W.; Shah, A.A. Hydrokinetic energy harnessing technologies: A review. Energy Reports. 2021, 7, 2021–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Reyes, L.A.; Beltrán-Telles, A.; Bañuelos-Ruedas, F.; Reta-Hernández, M.; Ramírez-Arredondo, J.M.; Silva-Casarín, R. Level-Shift PWM Control of a Single-Phase Full H-Bridge Inverter for Grid Interconnection, Applied to Ocean Current Power Generation. Energies 2022, 15, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcenas Graniel, J.F.; Fontes, J.V.H.; Gomez Garcia, H.F.; Silva, R. Assessing hydrokinetic energy in the mexican caribbean: A case study in the cozumel channel. Energies 2021, 14, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejatlas. Atlas de Justicia Ambiental. 2021. Available online: https://ejatlas.org/?translate=es (accessed on 24 March 2021).
- Ejatlas. Proyecto la Ensenada en Holbox, México | EJAtlas. 2018. Available online: https://ejatlas.org/conflict/proyecto-la-ensenada-en-holbox-mexico?translate=es (accessed on 24 March 2021).
- Ejatlas. MINA CALICA DE VULCAN Materiales Empresa EN PAPAA DEL CARMEN, MÉXICO | EJAtlas. 2020. Available online: https://ejatlas.org/conflict/devastacion-mina-calica-de-vulcan-materials-company-en-playa-del-carmen?translate=es (accessed on 24 March 2021).
- IMP. Gaceta IMP. Available online: https://backend.aprende.sep.gob.mx/media/uploads/proedit/resources/gaceta_instituto_mex_7bdb5f2f.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).