Abstract
A growing body of research has sought to determine how different factors have affected urbanization in developed countries over the past decades. Yet, few studies have systematically examined urbanization’s driving forces, particularly in emerging economies. In 2008–2009, the Chinese government announced an economic stimulus program to revitalize an economy struck by the 2007–2008 Global Financial Crisis. This study aims to identify how urbanization’s driving forces evolved under a drastic change in fiscal policy and revisit the conventional urbanization theories in the Chinese context. Using a dataset covering 31 Chinese provinces and spanning the periods 2005–2011 and 2013–2015, we employ panel data regressions to analyze whether such a fiscal arrangement affected urbanization in China. Throughout the entire period, the fiscal stimulus program caused a change in the drivers for urbanization at the national and regional levels. Before the implementation of the program, industrialization drove urbanization. After the program’s implementation, land financialization was crucial in promoting urbanization across the country. Our findings challenge the conventional urbanization theory—industrialization is always the primary driving force of urbanization in emerging economies. Land financialization, a kind of tertiary production, can also drive urbanization significantly.
1. Introduction
Urbanization is a major driver of social and economic development. It constitutes a rise in the population living in cities and the expansion of urban land and infrastructure [1]. Rapid urbanization represents one of developing countries’ most distinctive features. While most developed countries took about two centuries to achieve significant urbanization rates, China’s urbanization took only half that time to reach comparable levels. China’s urbanization occurred in a compressed amount of space and time, propelled by a “transactional transition” that reflects recent fundamental changes in the flows of people, commodities, capital, and information—between and within the countries [2]. In this era of globalization, intensive foreign capital inflows, high international trade volumes, sharp population growth, and massive rural-to-urban migration have helped shape China’s urbanization in various ways.
For developed countries, some studies have documented the driving forces behind urbanization at the national, supra-national, and global levels [3,4,5] and have established the relationship between various factors and urbanization. For example, Wong, Hesse, and Sigler [6] and Kutz and Lenhardt [7] explored the impact of the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) on the urbanization of Luxembourg, Singapore, and Morocco. Luxembourg and Singapore experienced rapid urban growth driven by investors’ demand, fostering the urbanization process. On the other hand, with less-developed financial systems, the Moroccan government transformed housing policy away from homeownership access. It sought to establish a new urban model to attract international investors to invest in the local property market, while such a motive hampered local urbanization. However, few studies systematically investigate the drivers of urbanization in emerging economies [8]. As a major developing economy, China provides a unique case for studying urbanization. By figuring out which factors contribute to urbanization, the Chinese government can increase healthy economic growth and alleviate negative impacts such as overcrowding and environmental degradation. Differences in local government structures, social–cultural backgrounds, historical and geographical factors, and the divide between coastal and inland urbanization played a role in this history—so did fiscal policy.
To what extent did massive post-crisis fiscal spending affect China’s urbanization? In November 2008, the government spent CNY four trillion as a fiscal stimulus. Local governments financed the stimulus through bank loans, and continue to do so. The upsurge in domestic investment occurred due to the extensive scale finance of state-owned enterprises and large infrastructure projects across China [9]. Such a massive stimulus should have affected China’s urbanization dynamics. The Chinese fiscal policy plays a pivotal role in determining urbanization. The fiscal stimulus packages (FSP) implemented after the GFC emphasize large-scale urban development projects, speeding up land financialization in urban spaces through land mortgages and municipal corporate bonds. However, land financialization brings the uncoordinated development of the population flows and the conversion of land use from non-urban to urban uses across the country [10].
Given the drastic change in fiscal policy after the 2007–2008 GFC and its associated impact on urban development, we raise the following research questions: Has China’s primary urbanization driver changed by the FSP? If the answer is yes, how does land financialization, the key feature of the FSP and a kind of tertiary production, enhance urbanization in China and its macro-regions significantly in the aftermath of the GFC?
Many traditional urbanization theories emphasize how industrialization is crucial in facilitating urbanization. Still, limited research examines whether the primary urbanization’s driver can be something other than the manufacturing sectors. Therefore, this study contributes to the literature in two ways. First, we find that before launching the FSP, industrialization was the primary driver of China’s urbanization. Yet, after the FSP implementation, land financialization was pivotal in facilitating urbanization across China. Our findings challenge the conventional urbanization theory—industrialization is always the primary driving force of urbanization in emerging economies. Land financialization, a kind of tertiary production, can also drive urbanization significantly. Second, unlike many qualitative studies that use case studies to demonstrate how land financialization fundamentally affects regional/city urbanization, we provide a systematic analysis and quantitative evidence to prove land financialization’s contribution to urbanization.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theories of Urbanization
Urbanization reflects the systematic increase in proportion to a country’s population residing in urban areas. It describes the process of the population moving from rural to urban localities. Such a movement often contributes substantially to the socio-economic development of both places and the persons moving. The early years of urbanization centered around theories from classical economics, the political setting of wages, and the feedback in urban demand that urban agglomeration attracts.
Based on demographic dynamics, van den Berg [11] proposed a standard trajectory for the population base of core cities and their periphery. His model specifies four stages of urban development. In the first stage, the core city grows fast, and the periphery declines or remains steady in population. This is the stage of urbanization. During the second stage, suburbanization occurs. The core city’s population starts to slow down while the population of the periphery considerably increases. The proportion of the population living in the periphery gradually rises. In the third stage, deurbanization occurs—the absolute population growth declines in the core city, its periphery, and thus the entire urban agglomeration. In the final stage, reurbanization entails a regrowth of population in the core city and a slow decline of the population in the periphery. This stage ends the cycle, which eventually leads back to the first stage—urbanization. Still, Parr [12] provides an alternative model, criticizing the repeating nature of the van den Bergian model assumption that after the reurbanization stage a new urbanization stage will start.
In addition, classical economic theories of urbanization dominated the early research on urbanization. These theories specifically looked at the association between structural economic change and the spatial dynamics of labor markets. For example, the Lewis–Fei–Ranis model presents a two-sector model of the economy [13,14]. The rural subsistence sector exhibits zero marginal labor productivity because farmers use traditional methods on overpopulated lands. In contrast, a high-productivity modern, urban, and industrial sector gradually draws in labor, seeking higher wages and a better quality of life. As the modern, urban sector expands, labor leaves behind the relatively unproductive agricultural sector, searching for higher wages in urban-based manufacturing. Thus, income differentials arising early in industrialization drive urbanization.
Todaro’s model of rural-to-urban migration represents another classic in the urbanization literature [15]. Farmers and country residents file into cities not because cities provide higher incomes, but instead because cities offer the hope of higher incomes—whether these migrants rationally form these expectations or not. Political—rather than economic—factors drive income differentials in these models. Namely, “a politically determined minimum urban wage at levels substantially higher than agricultural earning” pushes labor in cities [16]. However, Li, Cheong, Shen, and Fu [17] argue that Lewis–Fei–Rans’ and Todaro’s models undermine the advancement of agriculture sectors in improving rural household income. The rise in rural household income will increase the possibility of rural households migrating from urban to rural areas.
2.2. China’s Urbanization: A Preliminary Assessment
China’s urbanization process can be understood as an essential part of the general political, economic, social, and development processes that have shaped unique configurations in the post-1978 reform era [18]. Despite the globalizing forces, such as foreign direct investment and export and decentralization of fiscal and administrative powers from central to local governments over the past four decades, the Party-state played powerful and multiple roles as the decisionmaker, participant, and regulator in the urbanization process [19].
China’s urbanization has its salient features because of the unique household registration (hukou) system, which divided the entire population into two classes of citizenship: urban and rural residents. The Chinese people enjoyed various political, economic, and social rights based on different hukou types. Only residence permit holders could live in particular urban areas, and rural residents could not just move wherever they wanted. Contrasted with the high labor mobility assumption of the Lewis–Fei–Ranis and Todaro’s models, China’s hukou scheme prevented much of the mass rural-to-urban migration and urban development that might have otherwise occurred [20]. From 1949 to 1984, the Chinese government restricted rural residents from moving into cities for residency and employment. Since 1984, a cohort of peasants has been allowed to migrate to cities to look for job opportunities and live there [2]. Due to the vast amount of manufacturing foreign direct investment flown into China, they worked in the production plants in the coastal cities to earn higher wages than in their hometowns. Yet, they were not entitled to any social benefits in the cities because they did not have the urban hukou. Due to the country’s massive industrialization, China’s urbanization lifted off. In the mid-2000s, urbanization progressed faster than economic growth [21].
Land development, commodification, and marketization have become significant forces in the new wave of urbanization in major large cities. After the 2007–2008 GFC, the Chinese government implemented a four trillion FSP to promote economic growth. In unison, many local governments converted rural land to urban land for fiscal revenue generation to finance economic development. Consequently, the land economy played an instrumental role in China’s urbanization in the 2010s [22,23].
To conclude, China’s urbanization is mainly influenced by the globalizing forces, the increased market forces, and the active role of the state in the post-1978 period. More importantly, the Chinese government put forward the National New-type Urbanization Plan (2014–2020) to rationalize its urbanization process in March 2014. The hukou reform, rural land marketization, improvement in urban public services for urban residents, and reducing disparities between urban and rural areas are significant parts of the state-led urbanization plan, which provides a new approach to China’s urbanization [2,24].
2.3. Roles of Industrialization and Land Financialization in Urbanization—A Missing Determinant?
2.3.1. The Influence of Industrialization on Urbanization
The discussed literature provides considerable evidence that industrialization and land financialization can play significant roles in urbanization. In the United States, Atack, Margo, and Rhode [25] found that the development of the national transportation system facilitated rural people to go to big cities to look for manufacturing jobs in the nineteenth century. Over time, industrialization and urbanization became tightly connected. For newly industrialized economies, Turok and McGranahan [5] explain how industrialization promotes robust urbanization through the rapid development of non-agricultural sectors, the division of labor, and economies of scale. Economic globalization has encouraged the influx of manufacturing and service sector jobs from developed countries. The immigration of agricultural workers from rural areas to urban places and large-scale investment in public infrastructure has shaped the recent urbanization experience in Africa and Asia.
While these country examples provide some general information about the urbanization process, they poorly serve scholars looking at the urbanization of developing countries such as China. Some authors offer their perspectives on China’s urbanization pattern to its trade at home and abroad. Scott and Storper [26] and He and Zhu [27] argue that many metropolitan regions in China serve as the primary loci of national growth. Guo et al. [1] indicate that export-oriented industrialization explains part of this growth. The economic gains from proximity (agglomeration), technological advances, and a raft of urban-friendly market and trade reforms also help explain some metropolitan areas’ urbanization patterns. Many scholars have claimed that urbanization and industrialization grew together in other countries [28,29]. Still, He et al. [30] show how such a correspondence between industrialization and urbanization did not necessarily occur in China because of the hukou system. China’s case shows how different industrialization types lead to various production and product methods. Such differences may drastically influence a path of urbanization when the country—at the same time—also experiences radical changes in its economic structure and systems. Despite these studies, Li and Haynes [31] indicate many researchers underestimate the prominent role of industrialization on urbanization.
The 2007–2008 financial crisis affected how urbanization has occurred in China. Following the crisis, many labor-intensive industries have moved inland from coastal regions [32,33]. The relocation of manufacturing firms has attracted foreign and domestic capital inland, created new factory jobs, and stimulated local consumer markets. Such a move has allowed rural migrants to work closer to home—staying in their home provinces instead of going to other provinces. Migrants returning home have helped promote local economic development by investing in fixed assets, starting new businesses, and bringing capital, skills, and technology from the larger cities [34]. Local governments, in turn, have benefitted from increased tax revenue, increases in staffing (to meet the rising demand for public services), and a boom in business and community infrastructure, making the quality of life and commerce at home more attractive [35]. As such, the financial crisis has engendered gradual “counter-urbanization” over the previous decade.
2.3.2. The Impact of Land Financialization behind Urbanization
In addition, some scholars look at land policy and find out how land financialization stimulates urbanization. Wu [36] defines land financialization “as a tendency to use the land as a financial asset to create financial capital to fund urban development projects.” In China, the shift from agricultural to urban-centered production necessarily required urbanization. Manufacturers, industrialists, and higher value-added service sectors could not use agricultural land. Yet, unlike in other countries, local governments had more robust fiscal and financial needs for land. During urbanization, they become the dominant force to convert the land from the agricultural sector into non-agricultural and commercial uses. Driven by local officials’ pro-growth political and economic policies, many local governments marketed land to attract foreign capital and mobilize bank loans [37,38]. Such investments further increased tax revenue—making the land financially and fiscally more attractive.
More importantly, the central government adopted the fiscal FSP in 2008–2009, leading to land financialization. As Wu [36] emphasizes, after adopting the fiscal policy, the local government and many state-owned enterprises served as the major actors in land development. The local government deploys land mortgages, local government financing vehicles, and chengtou bonds (municipal corporate bonds) to use the land as collateral to access more available credits under fiscal expansion. Yet, the central authorities have recently cracked down on such finance—prompting local governments to replace the off-balance-sheet debt incurred by local governments through financing vehicles tied up with these land purchases with municipal bonds instead. Despite the new regulations, land financialization remains one of the drivers of urbanization and a significant contributor to fiscal revenue [9].
Briefly, as Li et al. [39] note, very few pieces of research pay attention to unveiling the picture indicating the complex dynamics of phenomenal urbanization within China and its macro-regions. The FSP undoubtedly had an impact on such urbanization. The effects of the massive government stimulus spending on urbanization in China remain insufficiently explored.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
Drawing upon the existing literature, we look at major forces driving urbanization and consider regional variations. Our dataset covers 31 Chinese provinces, municipalities, and autonomous regions. We segment the provincial-level dataset into sub-datasets of three different macro-regions—Eastern, Central, and Western China—based on the Seventh Five-Year Plan (1986–1990) adopted by the Chinese government. Several provinces, municipalities, or autonomous regions with similar characteristics are grouped in each macro-region. This regional delineation has been widely used in academic research on Chinese regional economies [40]. In this study, we follow this delineation to perform our inter-regional analysis.
Our data come from the China Statistical Yearbook, China Provincial and Municipal Statistical Yearbook, China Textile Industry Development Report, China Rubber Industry Yearbook, The Yearbook of China’s Electronics Industry, China Land and Resources Statistical Yearbook, China Rural Statistical Yearbook, and various provincial/municipality financial reports. From the 2013 China Land and Resources Statistical Yearbook, the Ministry of Land and Resources did not provide data on land conveyance fees (LCF) in 2012. Hence, we exclude our statistical analysis in the year 2012. In addition, due to the data limit of LCFs and annual export values of textile products (TP), rubber products (RP), and electronic products (EP), we cannot perform the analysis at the city level. Yet, fruitful insights into the driving forces of China’s urbanization can still be obtained from the provincial-level data analysis.
Since the Chinese government implemented the 2008–2009 economic stimulus program, we split our sample into two periods to examine the FSP’s effect. The first period started from 2005 to 2009, representing before the FSP, while the second period spanned 2010–2011 and 2013–2015, which stands for after the FSP. The two periods have the same sample size, facilitating their statistical comparison to trace the effect of the FSP on urbanization. In addition, such data allow us to cover multi-provincial and province-specific factors driving Chinese urbanization. We posit that the level of a province’s (or group of provinces’) urbanization (UL)—as our dependent variable—depends on various factors measuring each province’s social development and economic transformation.
3.2. Measures
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
We want to know the extent of urbanization in a province or region. A province’s urbanization level refers to the proportion of a province’s urban population relative to its total population. Table 1 describes our variables’ specifics, the measurements, data sources, and development of hypotheses. In line with international practice, the Chinese government implemented the actual population counts—mainly residents—rather than de-jure population counts derived from lists such as hukou holders (or individuals authorized and registered to live in a particular area). We chose the study period from 2005 onwards [41].
3.2.2. Independent Variables
We also grouped our independent variables into two major urbanization drivers: industrialization and land financialization.
In the past decades, the Chinese government decentralized authority and responsibilities to local governments in providing industrialization incentives to stimulate local innovation, formulate strategic industrial policies, and develop local economies [2,42]. The decentralization process encourages industrialization, enhancing urbanization by expanding service industries, economies of scale, and technological advancement. As such, we posit that ID has a positive causal link with UL.
In addition, the government’s incentives to use the land to attract investment and tax revenue also play a part in China’s provincial urbanization. We use land conveyance fees as an independent proxy of land financialization for how land policy has affected urbanization. Unlike other countries, the land is vital in China’s urban and economic development production factors [32,33,38]. An LCF measures the intensity of that land use and, thus, the effect of land financialization. We hypothesize a positive link exists between LCFs and UL.
3.2.3. Control Variables
We classified our control variables into economic development, foreign direct investment, industrial structure, and investment in fixed assets in rural areas. Here, we explain why we choose those variables.
Economic development represents the first driver of such urbanization. For economic development (ED), we use per capita gross regional product measured as CNY in 2005 to represent the level of economic development. In line with scholars such as Todaro [15], we hypothesize that such ED positively correlates with UL.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) acts as one of the globalizing forces in the Chinese urbanization process. Chen and Wu [43] emphasized the role of differing FDI in urbanization across Chinese regions. Such FDI focused on labor-intensive, export-oriented manufacturing sectors. Thus, FDI has fueled Chinese urbanization for decades, and it is the most commonly used indicator to measure the extent of urbanization force [44]. We expect FDI to correlate with UL positively.


Table 1.
Measurement, data sources, and supporting references for the variables employed in this study.
Table 1.
Measurement, data sources, and supporting references for the variables employed in this study.
| Variable | Full Name of the Variable | Measurement | Expected Sign | Data Source | Supporting Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL | Urbanization level | The proportion of the total de facto population residing in an “urban place” in a province | Dependent variable | China Statistical Yearbook | Chan [41] |
| ED | Economic development | Natural logarithm of real regional domestic product per capita at 2005 constant price | + | China Statistical Yearbook | Todaro [15] |
| ID | Industrialization level | Revenue from the principal business of industrial enterprises above the designated size over gross regional product | + | China Statistical Yearbook | He, Wei, and Xie [42] |
| FDI | Foreign direct investment | Foreign direct investment flow divided by gross regional product | + | Provincial/ Municipality Statistical Yearbook and China Statistical Yearbook | Chen and Wu [43] |
| TP | Textile and apparel product export | Share of annual export value of textile and apparel products divided by gross regional product | + | China Textile Industry Development Report | Song, Thisse, and Zhu [45] |
| RP | Rubber and plastic product export | Share of annual export value of rubber and plastic products divided by gross regional product | + | China Rubber Industry Yearbook | Song, Thisse, and Zhu [45] |
| EP | Electronic product export | Share of annual export value of electronic products divided by gross regional product | + | The Yearbook of China’s Electronics Industry | Song, Thisse, and Zhu [45] |
| LCF | Land conveyance fee | Share of land conveyance fee divided by general public budget revenue | + | China Land and Resources Statistical Yearbook and various provincial/municipality financial reports | Pan et al. [38] |
| RI | Investment in the fixed asset in rural areas | Investment in the fixed asset in rural areas over gross regional product | − | China Rural Statistical Yearbook | Wu et al. [46] |
Notes: + and − indicate the positive and negative association, respectively.
To estimate the effect of industrial structure on China’s urbanization, we also use TP, RP, and EP as the explanatory variables to proxy the impacts of industrial structure on urbanization determinants. We posit that TP, RP, and EP positively correlate with our urbanization measure UL. At the very least, China’s textile and apparel manufacturing industries mainly focus on labor-intensive production methods and high mobility in response to changing costs in other areas. On the other hand, China’s rubber and plastic manufacturing sectors focus on capital-intensive methods and target domestic markets. China’s high-tech electronics industry encompasses the assembly work of a wide range of electronic products from the region, making its production lines hard to relocate. Though many export-led sectors could have attracted migrant workers in varying degrees, authors such as Song, Thisse, and Zhu [45] point to textiles and apparel products, rubber and plastic products, and electronic products as the vanguard for urbanization in China.
We employ the investment in fixed assets in rural areas (RI) as an independent proxy to estimate the effect of urbanization. As for RI, we use this measure to pick up the massive relocation of manufacturing plants from coastal areas to inland provinces. As previously noted, many returning migrant workers brought capital, knowledge, and other assets [46,47]. Thus, such fixed asset investments in rural areas hope to pick up those counter-urbanizing influences that keep Chinese families and workers in the countryside. If true, our variable RI should negatively correlate with UL.
The measurement, data sources, and supporting literature for the variables employed in this study are summarized and presented in Table 1.
3.3. Methods
We used panel data methods to test the above-stated hypotheses. Our data’s potential regional variations require us to use two statistical models: fixed-effect models (FE) and random-effect models (RE). We used the Hausman specification test results to decide which specification method best fits our needs and data. Equation (1) shows the log-linear form we tested.
where the subscripts i and t denote the number of provinces and time, respectively, α and βi are coefficients to be estimated, and εit is the random error.
ULit = αi + β1EDit + β2IDit + β3FDIit + β4TPit + β5RPit + β6EPit + β7LCFit + β8RIit + εit
We used two-stage least squares estimation (2SLS) to deal with the potential endogeneity problem between economic growth and urbanization. Scholars such as Liu et al. have found that urbanization could have promoted Chinese economic growth by deepening domestic demand through higher densities and volumes of transactions. Chen and Wu [43] point to a foreign direct investment channel, claiming that highly urbanized areas would attract the FDI, which draws rural migrants searching for work in labor-intensive manufacturing or service industries. Reinforcing itself, such migration would encourage urbanization, leading to the migration–FDI cycles. Such two-way causality represents the endogeneity that makes 2SLS estimation necessary. Hence, we instrument the lagged variable of FDI to be an exogenous variable in Equation (1).
We applied three specification tests to test the quality of our instrumental variable. First, we tested for over-identification. Using the Hansen test in the generalized method of moments estimation, we studied if our additional instrument is exogenous. If we can reject the null hypothesis of zero covariance between our instrument and the error term, we know at least one instrument is invalid [48]. Second, we looked for weak instruments to study whether the instrument has a low correlation with the endogenous variables. To verify weak instruments’ existence, we needed to test if a first-stage partial F test is less than 10 [49]. Finally, we conducted a Durbin–Wu–Hausman test to examine whether the residuals from Equation (1) on all the exogenous variables have a significant coefficient when added to the original model specification. The null hypothesis is that if the coefficient on the residuals from the first-stage regression is not significantly different from zero, then the regressors are exogenous. Otherwise, the regressors are endogenous.
4. Results
To demonstrate the influence of the CNY four trillion fiscal stimulus on China’s economic structure, Figure 1 indicates the manufacturing industry and gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) percentages over China’s gross domestic product (GDP) from 2006 to 2018. The share of the manufacturing industry in China’s GDP gradually decreased from 42.0% in 2006 to 32.8% in 2018. Moreover, the contribution of gross fixed capital formation to China’s GDP increased sharply from 39.9% in 2006, peaked at 47.0% in 2011, and steadily declined to 42.7% in 2016. Subsequently, it rose from 43.2% in 2017 to 44.0% in 2018.
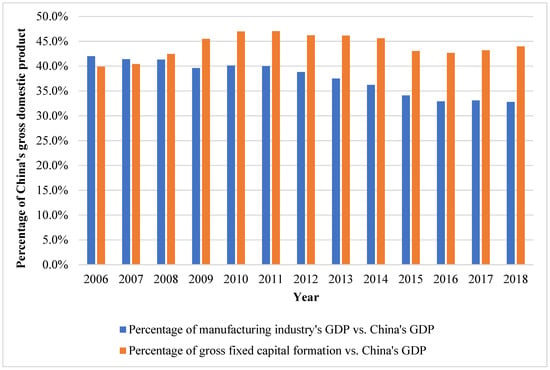
Figure 1.
The percentages of the manufacturing industry’s GDP and gross fixed capital formation over China’s GDP.
In addition, before the Chinese government implemented the FSP, the share of the manufacturing industry’s GDP in China’s GDP surpassed the contribution of gross fixed capital formation over China’s GDP. However, after the CNY four trillion stimulus package launched in 2008, the manufacturing industry’s contribution to China’s GDP was remarkedly lower than the share of GFCF over China’s GDP. As such, the deployment of the fiscal stimulus plan significantly affected China’s economic structure.
Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5 show our regression results for China and its macro-regions. Out of the FE and RE specifications, our Hausman test results favor random effects specifically. In other words, breaking up urbanization and our other variables by larger regions had little extra explanatory power. Before the FSP’s implementation (namely the period 2005–2009), based on Models 2, 8, 14, and 20, the adjusted R2 values for the whole of China and Eastern, Central, and Western China are 0.698, 0.693, 0.818, and 0.663, respectively. Similarly, after the FSP launched (namely the period 2010–2011 and 2013–2015), the adjusted R2 values of the whole of China and Eastern, Central, and Western China are 0.594 (Model 5), 0.716 (Model 11), 0.623 (Model 17), and 0.648 (Model 23), which suggest that the estimated equations are capturing the significant determinants of urbanization.

Table 2.
Panel data regression results (fixed-effects (FE) and random-effects (RE)) and two-stage least squares (RE (2SLS)) estimation for the whole of China.

Table 3.
Panel data regression results (fixed-effects (FE) and random-effects (RE)) and two-stage least squares (RE (2SLS)) estimation for Eastern China.

Table 4.
Panel data regression results (fixed-effects (FE) and random-effects (RE)) and two-stage least squares (RE (2SLS)) estimation for Central China.

Table 5.
Panel data regression results and two-stage least square estimation (2SLS) for Western China.
After performing the 2SLS estimation, Models 3, 9, 15, and 21 report 2SLS estimate results before the FSP, whereas Models 6, 12, 18, and 24 summarize the 2SLS estimate after the FSP. We find that our 2SLS estimate results are robust for China and its three macro-regions. Overall, the instrument test results were satisfactory and indicate that all regression models are acceptable.
The Hansen’s J statistics for China and Eastern, Central, and Western China before the FSP are 7.251, 12.368, 5.333, and 7.979, and insignificant (p < 0.05). Hansen’s J-statistics for China and Eastern, Central, and Western China after the FSP are 11.738, 12.001, 8.717, and 10.002, which are also insignificant (p < 0.05). Hence, no over-identification problem is found. We checked the partial F statistic from the first-stage regression to test for weak instruments and found no irregularities in all cases in our study period. We conducted the Durbin–Wu–Hausman test and demonstrated that all models’ residuals from Equation (1) on the lagged variable for FDI are insignificant (p < 0.05). Taken together, our estimation results indicate that the lagged variable for FDI is not related to error terms and is strictly exogenous.
5. Discussion
Our statistical results regarding drivers for urbanization are analyzed more here. For all our statistical models, we find a positive correlation between our proxy for economic development and urbanization. Before the FSP, ED had a significant positive influence on UL in China (p < 0.001) and Eastern (p < 0.01), Central (p < 0.001), and Western China (p < 0.001). In addition, the effect of ED on UL after the FSP was positive and significant in China as a whole (p < 0.001) and Eastern (p < 0.05), Central (p < 0.05), and Western China (p < 0.001). Our regression results unsurprisingly support Todaro’s findings [15]. Chinese villagers migrated to urban areas because of higher personal economic development prospects. These prospects include higher incomes, greater employment opportunities, and better living conditions. The effect of the economic development level on urbanization is also prominent at the national and regional levels.
Before the FSP, ID is found to be an essential determinant of urbanization in any regression model on national and regional contexts. ID is positively and significantly correlated with UL in China (p < 0.001) and Eastern (p < 0.001), Central (p < 0.05), and Western China (p < 0.01). After the FSP, ID has a positive but insignificant relationship with UL in China (p > 0.05), while ID has a significant positive impact on Eastern China (p < 0.001). However, the association between ID and UL is negative and insignificant in Central (p > 0.05) and Western China (p > 0.05). Echoing Guo et al. [1], industrialization has strengthened urbanization in China. Rural migrant workers took new techniques and connections they learned in China’s manufacturing industries’ urban cores back to new urban areas—at least, they did so before the FSP. However, following the FSP, we discover that industrialization has no direct impact on urbanization. Our findings contrast with previous research that emphasizes the synchronization of modern urbanization and industrialization [25,28,29]. According to He et al. [42], China’s industrialization–urbanization nexus does not hold. The primary reason could be the profound impact of the hukou system, which serves as a significant institutional barrier preventing a cohort of rural people from relocating to many urban areas.
There was an observed effect of FDI on UL changes after the FSP. During the whole study period, in Eastern China, FDI negatively correlated with UL (p < 0.05). For China as a whole, though, and in Central China, FDI had no association with UL. In Western China, FDI positively and statistically significantly correlated with UL before the FSP (p < 0.01). This relationship disappeared during and after the FSP. This finding contradicts previous studies, such as that by Chen and Wu [43]. The possible changes in FDI sectoral contribution and FDI types have markedly influenced China’s regional urbanization dynamics.
The effect of TP on UL differs across China at the national and regional levels. Before the FSP, the association between TPs and UL in China (p > 0.05) and Central (p > 0.05) and Western China (p > 0.05) is negative yet insignificant. However, after the FSP, TP exerts a negative and profound influence on UL in China (p < 0.01) and Western China (p < 0.05). During the entire study period, no association exists between TP and UL in Eastern China. After the FSP, our results reveal the relocation of foot-loose textile and apparel production plants from China to Southeast Asia, restricting China’s urbanization.
Our results also show that the link between RP and UL varies in China and its three macro-regions in different periods. Before the FSP, RP have a negatively significant association with UL in China (p < 0.01) and Eastern China (p < 0.01). Yet, there exists a significant negative correlation between RPs and UL for Central (p > 0.05) and Western China (p > 0.05). After the FSP, RPs exerts a negative and profound impact on UL in Eastern China (p < 0.05). Our findings support that some rubber product manufacturers gradually moved out of China or successively relocated their production lines from coastal areas to inland regions, which led to the relocation of rural migrant workers from the eastern coastal region and the search for new job opportunities in inland areas.
Moreover, before the FSP, we find that EP only profoundly and negatively impacts UL in Eastern China (p < 0.01). After the FSP, our estimation results indicate that EP has a positive and significant statistical relationship with UL in China (p < 0.01) and Central (p < 0.001) and Western China (p < 0.01), but there exists a negative and insignificant correlation between EP and UL in Eastern China (p > 0.05). In contrast to the findings of Song, Thisse, and Zhu [45], our findings show that changes in industrial structure have a complex relationship with urbanization. Following the global financial crisis, some electronic companies relocated to a few inland cities to conduct export sales and build domestic market-oriented production networks. The positive and robust impact of the export-driven development of electronic products on urbanization in Central and Western China draws people away from developed coastal megacities and toward developing inland areas.
Before the FSP, our findings show a positive and significant correlation between LCF and UL is found in China (p < 0.05) and Western China (p < 0.05), while LCF has a positive yet insignificant relationship with UL in Eastern (p > 0.05) and Central China (p > 0.05). Yet, after the FSP, LCF has a negative and significant association with UL in China (p < 0.001) and Eastern (p < 0.001), Central (p < 0.001), and Western China (p < 0.001). Consistent with He, Huang, and Wang [37] and Pan et al. [38], our estimation results strongly support that land financialization became one of the major urbanization determinants after implementing the FSP. Our statistical results also show that the influence of land financialization on urbanization varies across the country and its macro-regions. Regional variation does matter on this topic.
Moreover, the resulting urbanization can be viewed as a state formation project interacting with political, economic, and social forces. During urbanization, many local governments actively involved in real estate and infrastructure development projects attempted to deploy land as an essential asset and used land conveyance fees as collateral for heavy fixed asset investment. In addition, they have developed numerous new urban spaces [50] which promote spatial production, distribution, and exchanges at increasing geographical scales [51,52]. High land costs markedly increased migrants’ housing prices and living costs, constraining the migrants’ rural–urban settlement decision and consequently affecting the inter-regional migration and urbanization at the regional level.
Finally, before the FSP, the correlation between RI and UL is consistent among China’s three macro-regions. RI has a positive and insignificant effect on UL in China (p > 0.05) and Eastern (p > 0.05), Central (p > 0.05), and Western China (p > 0.05). Nonetheless, RI and UL have a negative statistical relationship in China (p < 0.001) and Eastern (p < 0.01), and Western China (p < 0.01), while there exists a positive but insignificant association between RI and UL. Because of the closure or relocation of manufacturing plants in the eastern coastal region over the last decade, a growing number of rural migrant workers have returned to their hometowns in inland provinces. This has facilitated the counter-urbanization process throughout China [47].
Overall, before the FSP, industrialization played a critical role in promoting urbanization. Yet, after the FSP, land financialization became the significant urbanization determinant. Implementing the FSP encouraged massive infrastructure investment, significantly changing the country’s urbanization dynamics.
6. Conclusions
This study systemically examines the role of industrialization and land financialization behind China’s urbanization before and after the FSP and revisits the conventional urbanization theories. We deployed a dataset for all Chinese provinces and used econometric methods to enhance the nuanced understanding of urbanization’s role in China’s regional development. First, our results indicate that the region-specific drivers for urbanization remarkably changed when the Chinese government underwent the 2008–2009 economic stimulus program. Before launching the CNY four trillion stimulus packages, industrialization was one of the major driving forces for China’s urbanization. However, while the economic stimulus packages have been implemented, the Chinese government focuses on utilizing financial resources in real estate and infrastructure development. As a result, land financialization becomes crucial in enhancing urbanization across the country. Second, the conventional urbanization theories emphasize that industrialization is always the primary driving force of urbanization in emerging economies. However, our findings show that land financialization, a kind of tertiary production, can also drive urbanization significantly in China.
The findings of this study have two significant policy implications. Based on our results, economic development is the only determinant that facilitates urbanization in China at both the national and regional levels. As the Chinese government actively promotes people-oriented urbanization, we suggest Chinese economists and regional planners consider not only the country’s current macroeconomic and demographic situation but also the local context of each macro-region to improve the well-being of the entire population. Second, amid COVID-19, the Chinese government pledged a stimulus package of CNY 4 trillion (USD 559 billion) worth of cost cuts, which was the most extensive economic rescue plan because the global economy remained weak. This package includes another CNY 1.6 trillion in special-purpose bonds to finance infrastructure construction [53]. Many local governments, particularly in inland provinces, still rely on land financing to implement new urbanization plans. This may pressure local public fiscal and financial governance [9]. The central government can regularly evaluate local governments’ financial capacity and effectively allocate financial resources to support urban infrastructure and public services.
Yet, our study has the following limitations: (1) in the absence of the possible interesting variables, such as demographic structure, education, and technology levels of each macro-region, there may be possible omissions in our selection of independent variables; and (2) due to a lack of data at the prefectural-level city level, we can only explore the regional differences. The prevalent division of three macro-regions may not fully reflect intra-regional variations. A detailed analysis can divulge some potential differences which are not visible at the existing levels of data aggregation.
In many developing countries, particularly in Southeast and South Asia, identifying the driving forces of urbanization can fully maximize the positive impacts and mitigate urbanization’s adverse effects. Policies should be implemented carefully, thoroughly considering the positive and negative spillovers pertinent to the urbanization process. Our research provides a quantitative synthesis of China’s urbanization. Future research is needed to determine the driving force of a country’s/urbanization region’s shifts from primary to tertiary industry or from manufacturing to tertiary industry. This approach may broaden the scope and strengthen the theoretical foundation of various broadly conceived analytical frameworks of the overall urbanization process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.W.H.W., H.F.L. and S.X.B.Z.; methodology, D.W.H.W. and H.F.L.; software, D.W.H.W.; validation, D.W.H.W. and H.F.L.; formal analysis, D.W.H.W.; investigation, D.W.H.W.; resources, D.W.H.W.; data curation, D.W.H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, D.W.H.W.; writing—review and editing, D.W.H.W., H.F.L., S.X.B.Z. and A.C.L.T.; visualization, D.W.H.W.; supervision, H.F.L. and S.X.B.Z.; project administration, D.W.H.W.; funding acquisition, D.W.H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant datasets in this study are described in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for the helpful comments that improved this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guo, J.H.; Yu, Z.Q.; Ma, Z.H.; Xu, D.Y.; Cao, S.X. What factors have driven urbanization in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 6508–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Hui, C.M.; Choguill, C.; Jia, S.H. The new urbanization policy in China: Which way forward? Habitat Int. 2015, 47, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S. Urbanization as a global historical process: Theory and evidence from Sub-Saharan Africa. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2012, 38, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.F. Chinese urbanization and urban policy. In China Review; Lau, C.M., Shen, J.F., Eds.; The Chinese University Press: Hong Kong, China, 2000; pp. 455–480. [Google Scholar]
- Turok, I.; McGranahan, G. Urbanization and economic growth: The arguments and evidence for Africa and Asia. Environ. Urban. 2013, 25, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; Hesse, M.; Sigler, T.J. City-states in relational urbanization: The case of Luxembourg and Singapore. Urban Geogr. 2022, 43, 501–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, W.; Lenhardt, J. “Where to put the spare cash?” Subprime urbanization and the geographies of the financial crisis in the Global South. Urban Geogr. 2016, 37, 926–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, E.; Canning, D.; Fink, G. Urbanization and the wealth of nations. Science 2008, 319, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; He, Z.G.; Liu, C. The financing of local government in China: Stimulus loan wanes and shadow banking waves. J. Financ. Econ. 2020, 137, 42–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.Y.; Guo, X.X.; Zhong, S.H.; Wu, L.N. Land financialization, uncoordinated development of population urbanization and land urbanization, and economic growth: Evidence from China. Land 2020, 9, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, L.; Drewett, R.; Klaassen, L.H.; Rossi, A.; Vijverberg, C.H.T. Urban Europe Vol. 1: A Study of Growth and Decline; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, J. The spatial-cycle model (SCM) revisited. Reg. Stud. 2012, 46, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fei, C.H.; Ranis, G. Development of the Labour Surplus Economy: Theory and Policy; Irwin: Homewood, IL, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, W. Economic development with unlimited supplies of labor. Manch. Sch. 1954, 22, 139–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, P. A model of labor migration and urban unemployment in less developed countries. Am. Econ. Rev. 1969, 59, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.; Todaro, P. Migration, unemployment, and development: A two-sector analysis. Am. Econ. Rev. 1970, 61, 126–141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cheong, T.S.; Shen, J.F.; Fu, D.H. Urbanization and rural-urban consumption disparity: Evid. China 2019, 64, 983–996. [Google Scholar]
- McGee, T.G.; Lin, G.C.S.; Marton, A.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Wu, J.P. China’s Urban Space: Development under Market Socialism; Routledge: Oxon, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.C. Urban transformation in China, 1949–2000: A review and research agenda. Environ. Plan. A 2007, 34, 1545–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.W. The household registration system and migrant labor in China: Notes on a debate. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2010, 36, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Liu, W.D.; Tao, X.L. Evolution and assessment on China’s urbanization 1960–2010: Under-urbanization or over-urbanization? Habitat Int. 2013, 38, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.C.S.; Li, X.; Yang, F.F.; Hu, F.Z.Y. Strategizing urbanism in the era of neoliberalism: State power reshuffling, land development, and municipal finance in urbanizing China. Urban Stud. 2015, 52, 1962–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.L.; Hu, L.Q.; Cook, I.G. China’s urbanization in 1949–2015: Processes and driving forces. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, K.Q.; Yan, L.; Yu, L.; Zhu, Y.L. Citizenization of rural migrants in China’s new urbanization: The roles of hukou system reform and rural land marketization. Cities 2022, 132, 103968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atack, J.; Margo, R.A.; Rhode, P.W. Industrialziation and urbanization in nineteeth century America. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2022, 94, 103678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.; Storper, M. Regions, Globalization, development. Reg. Stud. 2003, 37, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Zhu, S.J. Industrial agglomeration and labor productivity in transition: An empirical study of Chinese manufacturing industries. Post-Communist Econ. 2009, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.M. Fundamentals of China urbanization and policy. China Rev. 2010, 10, 63–94. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, V. The urbanization process and economic growth: The so-what question. J. Econ. Growth 2003, 8, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Chen, T.M.; Mao, X.Y.; Zhou, Y. Economic transition, urbanization and population redistribution in China. Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Q.; Haynes, K.E. Economic structure and regional disparity in China: Beyond the Kuznets transition. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2011, 34, 157–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.W. China’s new urbanization plan: Progress and structural constraints. Cities 2020, 103, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.B.; Wong, W.H.; Wong, W.S.; Jiang, Y.P. Ever-transient FDI and ever-polarizing regional development: Revisiting conventional theories of regional development in the context of China, Southeast and South Asia. Growth Chang. 2020, 51, 338–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yin, X.D.; Zheng, X.; Li, W.W. Lose to win: Entrepreneurship of returned migrants in China. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2017, 58, 341–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.Z.; Wu, C.L.; Zuo, W.M.; Li, S.T. From industrial urbanization, land urbanization to people-centred urbanization: A sociological investigation on the Chinese pathway to urbanization. J. Soc. Dev. 2018, 1, 42–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.L. Land financialization and the financing of urban development in China. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 104412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Huang, Z.J.; Wang, R. Land use change and economic growth in urban China: A structural equation Analysis. Urban Stud. 2014, 51, 2880–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.H.; Zhang, F.M.; Zhu, S.J.; Wojcik, D. Developing by borrowing? Inter-jurisdictional competition, land finance, and local debt accumulation in China. Urban Stud. 2017, 54, 897–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Zou, F.Q.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, J.H. Does financial excess support land urbanization–An empirical study of cities in China. Land 2021, 10, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Sun, M.J. Regional inequality in China, 1978–2006. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2008, 49, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.W. Misconceptions and complexities in the study of China’s cities: Definitions, statistics, and implications. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2007, 48, 383–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Wei, Y.H.; Xie, X.Z. Globalization, institutional change, and industrial location: Economic transition and industrial concentration in China. Reg. Stud. 2008, 42, 923–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Wu, Y. Impact of foreign direct investment and export on urbanization: Evidence from China. China World Econ. 2017, 25, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Wu, Y. Interregional impact of foreign direct investment on China’s inland urbanization. Singap. Econ. Rev. 2019, 64, 997–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.S.; Thisse, J.F.; Zhu, W.X. Urbanization and/ or rural industrialization in China. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2012, 42, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Fu, Q.; Gu, J.X.; Shi, Z.L. Does migration pay off? Returnees, family background, and self-employment in rural China. China Rev. 2018, 18, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.Z.; Wang, S.C. Farmers moving upstairs and capital going down to the countryside: A sociological study of urbanization. Soc. Sci. China 2015, 1, 66–83. [Google Scholar]
- Roodman, D. A note on the theme of too many instruments. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2009, 71, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, D.; Stock, J.H. Instrumental variable regression with weak instruments. Econometrica 1997, 65, 557–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, H. The Production of Space; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, D. Social Justice and the City (Revised Edition); University of Georgia Press: Athens, Greece, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, D. The right to the city. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2003, 27, 939–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South China Morning Post. China Pledges Largest-Ever Economic Rescue Package to Save Jobs and Livelihoods Amid Coronavirus, 28 May 2020. Available online: https://www.scmp.com/economy/china-economy/article/3086569/china-pledges-largest-ever-economic-rescue-package-save-jobs (accessed on 29 July 2020).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).