Urban Agglomeration Ecological Welfare Performance and Spatial Convergence Research in the Yellow River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Research Method
3.2.1. Two-Phase US-NSBM Model
3.2.2. Dagum Gini Coefficient and Decomposition
3.2.3. β Convergence Model
4. Results
4.1. EWP Measurement Result
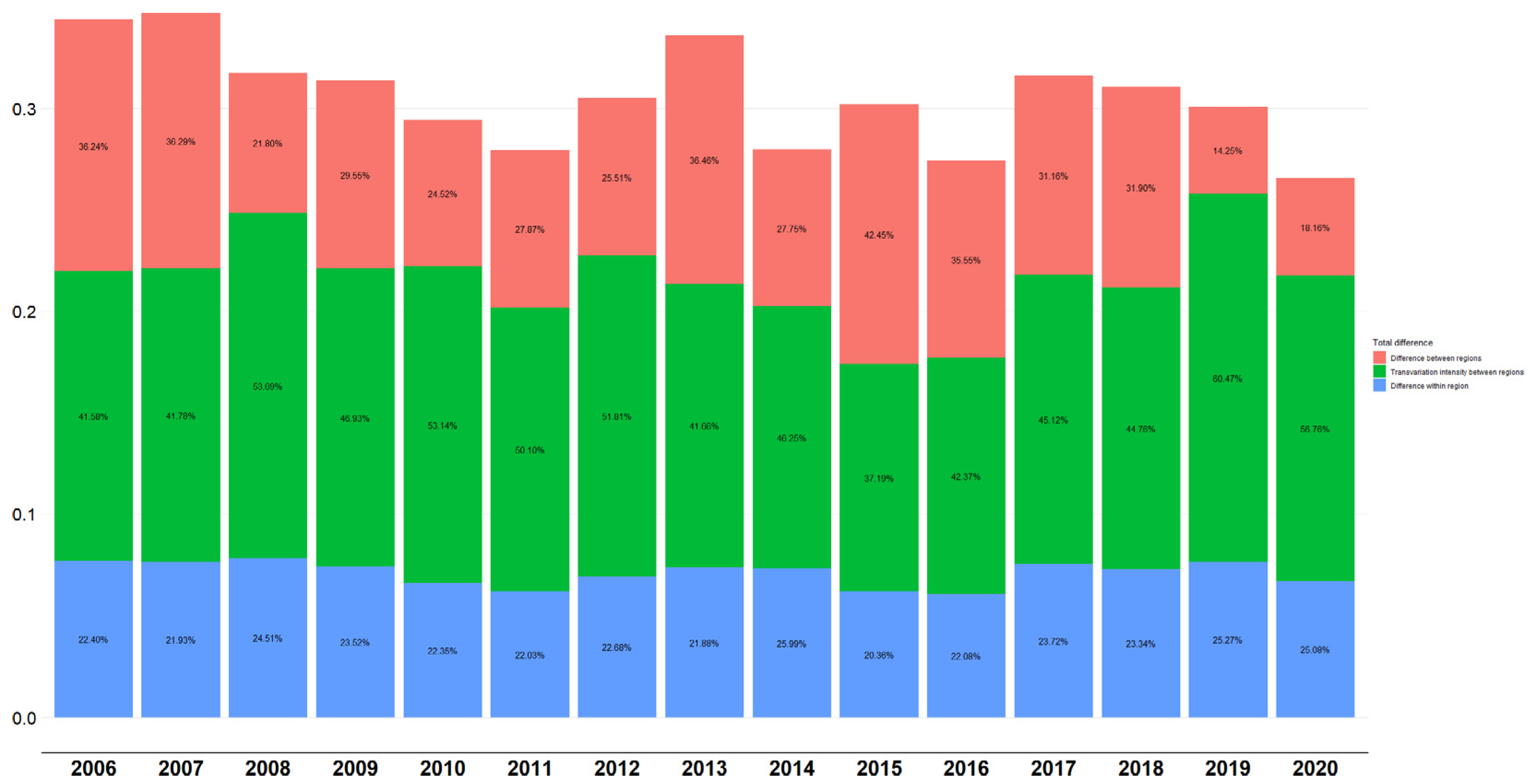
4.2. Urban Agglomeration Ecological Welfare Efficiency Difference and Decomposition along the Yellow River Basin
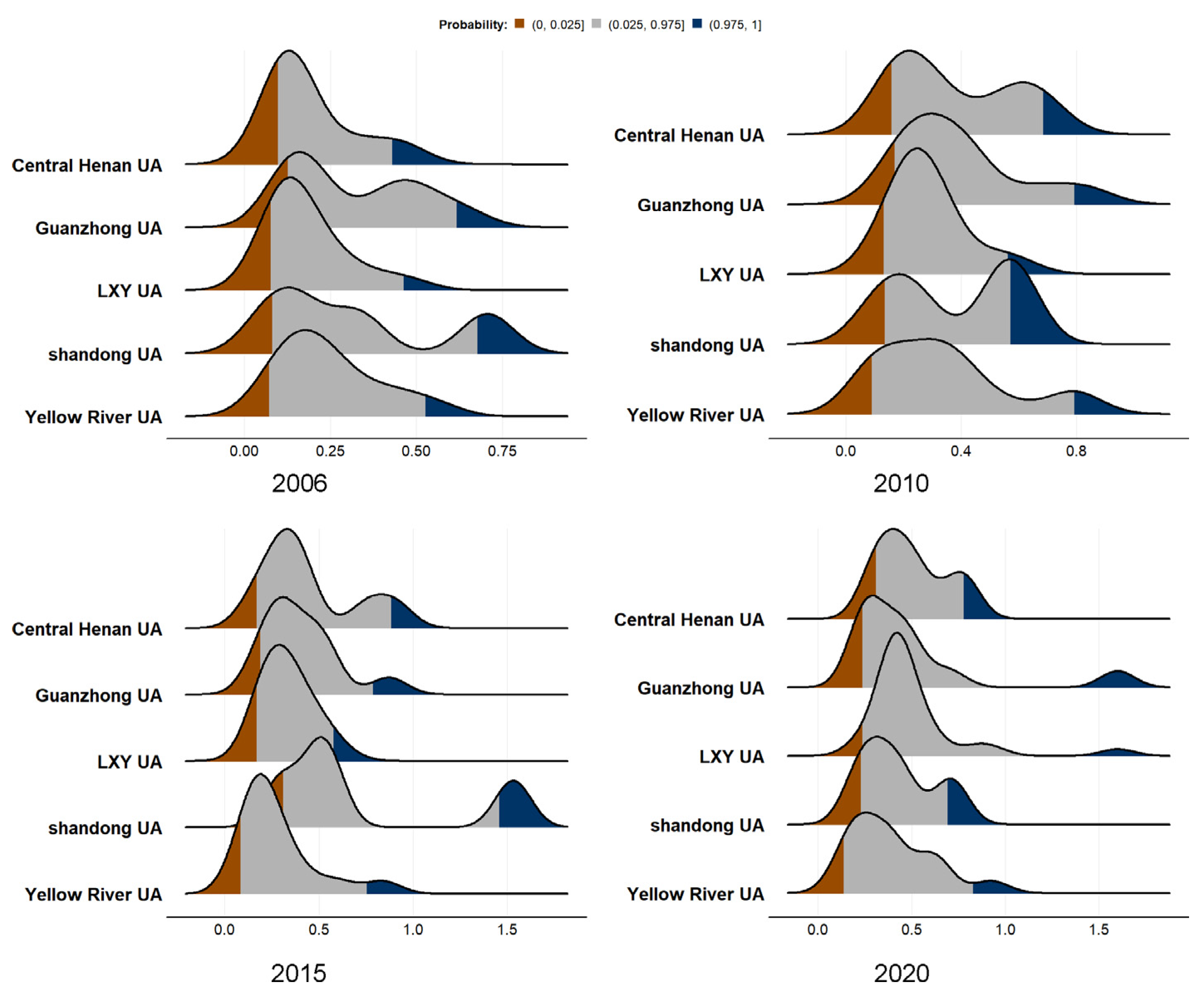
4.3. β Convergence and Result Analysis
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pirgmaier, E. The neoclassical trojan horse of steady-state economics. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 133, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, G.; Szigeti, C. The historical ecological footprint: From over-population to-consumption. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, H.E. Economics in a full world. Sci. Am. 2005, 293, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, H.E. From a failed-growth economy to a steady-state economy. Solutions 2010, 1, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, H.E. A further critique of growth economics. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 88, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.J.; Zhang, S. Research on ecological wellbeing performance and its relationship with economic growth. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 24, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; Daly, L.; Fioramonti, L. Modelling and measuring sustainable wellbeing in connection with the UN sustainable development goals. Am. Econ. Rev. 2016, 64, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.W. The proximity of nations to a socially sustainable steady-state economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1213–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.; Yu, D. Urban agglomeration: An evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhao, X. Evaluation of urban green development transformation process for Chinese cities during 2005–2016. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.P.; Zhang, Q. The strategic design and supporting system construction of high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Reform 2019, 308, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zuo, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z. The world dynamics of economic growth: The economics of the steady state. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, H.E. The world dynamics of economic growth: The economics of the steady state. Am. Econ. Rev. 1974, 64, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, W.E. Ecological footprints and appropriated carrying capacity: What urban economics leaves out. Environ. Urban. 1992, 4, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernage, M.; Rees, W. Our Ecological Footprint: Reducing Human Impact on the Earth; New Society Publishers: Gabriola, BC, Canada, 1998; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bergh, J.C.; Verbruggen, H. Spatial sustainability, trade and indicators: An evaluation of the ‘ecological footprint’. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T.; Rosa, E.A.; York, R. Environmentally efficient well-being: Is there a Kuznets curve? Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, S.; Thompson, S.; Michaelson, J.; Marks, N.; Steuer, N. The Happy Planet Index 2.0: Why Good Lives Don’t Have to Cost the Earth; New Economics Foundation: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgenson, A.K.; Dietz, T. Economic growth does not reduce the ecological intensity of human well-being. Sustain. Sci. 2015, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, D.J.; Shi, Q.H.; Cheng, M. Which countries are more ecologically efficient in improving human well-being? an application of the index of ecological well-being performance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.J. Evaluation of urban ecological well-being performance of Chinese major cities based on two-stage super-efficiency network SBM Model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 64, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.J.; Zhong, S.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhao, X.M.; Dong, X. Ecological well-being performance growth in China (1994–2014): From perspectives of industrial structure green adjustment and green total factor productivity. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Common, M. Measuring national economic performance without using prices. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, K.W.; Rosa, E.A. The environmental efficiency of well-being: A cross-national analysis. Soc. Sci. Res. 2011, 40, 931–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T.; Rosa, E.A.; York, R. Environmentally efficient well-being: Rethinking sustainability as the relationship between human well-being and environmental impacts. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 2009, 16, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, C.; Che, L.; Wang, B. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban green development efficiency in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 724–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Yu, Z.; Wu, M.; Ning, J.; Lv, T. The spatiotemporal evolution and trend prediction of ecological wellbeing performance in China. Land 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, W. Exploring the spatial-temporal disparities of urban land use economic efficiency in China and its influencing factors under environmental constraints based on a sequential slacks-based model. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10171–10190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C. Construction land utilization efficiency based on SBM-Undesirable and Meta-frontier model. Am. Econ. Rev. 2017, 39, 836–845. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shuai, C.; Shen, L.; Ren, H.; Wang, Y. Have cities effectively improved ecological well-being performance? Empirical analysis of 278 Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jia, G. Environmental efficiency analysis of China’s regional industry: A data envelopment analysis (DEA) based approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Han, J.; Guan, D.; Mi, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q. The comprehensive environmental efficiency of socioeconomic sectors in China: An analysis based on a non-separable bad output SBM. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 1091–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tone, K. Variations on the theme of slacks-based measure of efficiency in DEA. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 200, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Yin, Z. A network DEA model with super efficiency and undesirable outputs: An application to bank efficiency in China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordhaus, W.D.; Tobin, J. Is growth obsolete? The measurement of economic and social performance. Stud. Income Wealth 1973, 38, 509–532. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, J.; Daly, H. For the Common Good, Redirecting the Economy toward Community, the Environment and a Sustainable Future; Beacon Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, A.D.; Najam, A. The human development index: A critical review. Ecol. Econ. 1998, 25, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranis, G.; Stewart, F.; Samman, E. Human development: Beyond the human development index. J. Hum. Dev. 2006, 7, 323–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagum, C. A New Approach to the Decomposition of the Gini Income Inequality Ratio. Empir. Econ. 1997, 22, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skidmore, M.; Toya, H.; Merriman, D. Convergence in government spending: Theory and cross-country evidence. Kyklos 2004, 57, 587–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Specification and estimation of spatial panel data models. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2003, 26, 244–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, W. Green efficiency of water resources in Northwest China: Spatial-temporal heterogeneity and convergence trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.H. An empirical research on industry structure and economic growth. Stat. Res. 2010, 27, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Lee, L. Estimating a spatial autoregressive model with an endogenous spatial weight matrix. J. Econom. 2015, 184, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Stage | Category | Secondary Indicators | Tertiary Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | Inputs | Resource consumption | Land consumption |
| Energy consumption | |||
| Water consumption | |||
| Outputs | Desirable outputs | GDP per capita | |
| Undesirable outputs | Per capita wastewater | ||
| Per capita SO2 | |||
| Per capita soot/dust | |||
| Stage | Inputs | Economic growth | GDP per capita |
| Outputs | Economic welfare | per capita disposal income | |
| Per capita consumption | |||
| Engel coefficient | |||
| Social welfare | Doctors per 10,000 people | ||
| Number of college students per 10,000 people | |||
| Basic medical coverage rate | |||
| Teacher–student ratio | |||
| Basic pension coverage rate | |||
| Unemployment insurance coverage rate | |||
| Environmental welfare | Greening coverage of built-up areas | ||
| Number of parks per 10,000 people | |||
| Forest coverage rate | |||
| PM2.5 |
| LXY UA | Guanzhong UA | Shandong UA | Central Henan UA | Yellow River UA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 0.182 | 0.3165 | 0.3202 | 0.1925 | 0.2444 |
| 2007 | 0.2262 | 0.4259 | 0.3428 | 0.2809 | 0.274 |
| 2008 | 0.2055 | 0.2908 | 0.2558 | 0.2432 | 0.2102 |
| 2009 | 0.2462 | 0.3081 | 0.4025 | 0.3146 | 0.2199 |
| 2010 | 0.2815 | 0.3852 | 0.3758 | 0.3768 | 0.3322 |
| 2011 | 0.2716 | 0.3898 | 0.3772 | 0.3417 | 0.3426 |
| 2012 | 0.2808 | 0.3539 | 0.3926 | 0.4133 | 0.3265 |
| 2013 | 0.2675 | 0.4289 | 0.4312 | 0.3487 | 0.2402 |
| 2014 | 0.3906 | 0.4227 | 0.5295 | 0.4629 | 0.3145 |
| 2015 | 0.3322 | 0.4043 | 0.7168 | 0.4397 | 0.2787 |
| 2016 | 0.344 | 0.394 | 0.7768 | 0.3882 | 0.3229 |
| 2017 | 0.3777 | 0.5499 | 0.6692 | 0.4638 | 0.3724 |
| 2018 | 0.3871 | 0.6267 | 0.6005 | 0.4417 | 0.3944 |
| 2019 | 0.3438 | 0.3568 | 0.3803 | 0.4348 | 0.3895 |
| 2020 | 0.5045 | 0.4919 | 0.4248 | 0.5029 | 0.3925 |
| average | 0.3094 | 0.4097 | 0.4664 | 0.3764 | 0.3103 |
| Year | Overall | LXY UA | Guanzhong UA | Shandong UA | Central Henan UA | Yellow River UA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 0.343 | 0.2918 | 0.3148 | 0.4025 | 0.2998 | 0.3104 |
| 2007 | 0.3469 | 0.2718 | 0.3615 | 0.3258 | 0.3504 | 0.3254 |
| 2008 | 0.3175 | 0.2967 | 0.2861 | 0.3064 | 0.3135 | 0.3078 |
| 2009 | 0.3134 | 0.2804 | 0.2153 | 0.2981 | 0.2928 | 0.3539 |
| 2010 | 0.2941 | 0.2094 | 0.2722 | 0.2765 | 0.2933 | 0.3579 |
| 2011 | 0.2794 | 0.1898 | 0.2432 | 0.2761 | 0.2679 | 0.3561 |
| 2012 | 0.3048 | 0.2265 | 0.2744 | 0.2876 | 0.3003 | 0.3762 |
| 2013 | 0.3357 | 0.2465 | 0.3902 | 0.1529 | 0.3248 | 0.3542 |
| 2014 | 0.2798 | 0.2879 | 0.2165 | 0.2042 | 0.2216 | 0.2869 |
| 2015 | 0.3021 | 0.2064 | 0.2435 | 0.33 | 0.2917 | 0.3503 |
| 2016 | 0.2741 | 0.2231 | 0.2013 | 0.2864 | 0.1916 | 0.3194 |
| 2017 | 0.3163 | 0.294 | 0.3322 | 0.1728 | 0.2235 | 0.3111 |
| 2018 | 0.3104 | 0.2638 | 0.3654 | 0.2558 | 0.2221 | 0.2998 |
| 2019 | 0.3007 | 0.2645 | 0.2676 | 0.2223 | 0.2331 | 0.3779 |
| 2020 | 0.2654 | 0.2134 | 0.3345 | 0.2352 | 0.19 | 0.3001 |
| average | 0.3056 | 0.2511 | 0.2879 | 0.2688 | 0.2678 | 0.3325 |
| Overall | Central Henan UA | Guanzhong UA | LXY UA | Shandong UA | Yellow River UA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDM | SEM | OLS | OLS | SAR | SEM | |
| −0.6486 *** | −0.712 *** | −0.625 *** | −0.373 ** | −0.479 *** | −0.826 *** | |
| (−20.64) | −0.0507 | −0.0502 | −0.138 | −0.0758 | −0.0622 | |
| −1.2863 ** | ||||||
| (−2.52) | ||||||
| rho | −1.3133 *** | −1.000 *** | ||||
| (−5.05) | −0.222 | |||||
| lambda | −1.7574 *** | −0.950 *** | ||||
| (−7.21) | −0.229 | |||||
| Time-fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Space-fixed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Hausman | 152.17 *** | 202.06 *** | 38.58 *** | 38.58 *** | 20.62 *** | 79 *** |
| R-LM (SAR) | 145.4474 (0.000) | 0.8574 (0.354) | 0.0272 (0.869) | 0.7062 (0.401) | 3.102 * | 0.4989 |
| R-LM (SEM) | 7.4974 (0.00) | 227.0485 (0.000) | 0.0596 (0.807) | 0.1995 (0.655) | 2.1367 | 115.8193 *** |
| R² | 0.127 | 0.2388 | 0.446 | 0.508 | 0.2412 | 0.3596 |
| Overall | Central Henan UA | Guanzhong UA | LXY UA | Shandong UA | Yellow River UA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDM | SDM | SEM | OLS | SAR | SEM | |
| −0.657 *** | −0.749 *** | −0.329 *** | −0.301 *** | −0.572 *** | −0.846 *** | |
| −0.0307 | −0.0516 | −0.0574 | −0.101 | −0.081 | −0.0621 | |
| −0.370 * −0.191 | −0.604 *** −0.207 | |||||
| POP | 1.074 *** 0.0145 | 1.861 *** −0.159 | −0.296 ** | 0.0183 | 0.460 *** | 0.0622 |
| −0.303 −0.0484 | −0.447 −0.123 | −0.13 | −0.249 | −0.125 | −0.0543 | |
| ADV | 0.238 ** 2.547 *** | 0.275 * 1.078 * | −0.0734 | 1.235 * | 0.382 | 0.850 *** |
| −0.101 −0.715 | −0.162 −0.623 | −0.108 | −0.708 | −0.585 | −0.27 | |
| inc | −0.00556 −0.0165 | 0.0347 0.128 | −2.211 * | −1.442 | −0.908 | 0.182 |
| −0.0116 −0.0607 | −0.0302 −0.208 | −1.337 | −2.113 | −1.195 | −0.94 | |
| mar | −0.0354 −0.0073 | 0.685 ** −0.049 | 0.0103 | 0.0407 | −0.0153 | −0.00268 |
| −0.0345 −0.395 | −0.33 −0.0506 | −0.0165 | −0.0269 | −0.0135 | −0.00978 | |
| ope | 0.0194 0.357 | 0.0237 −0.277 | 1.169 | −0.882* | 1.68 | 1.006 |
| rho lambda | −0.0524 −0.455 0.431 *** −0.0901 | −0.0687 −0.433 0.292 *** −0.101 | −2.005 −1.276 *** | −0.477 | −1.371 0.222 ** −0.112 | −0.913 −0.954 *** |
| Time-fixed | Yes Yes | Yes Yes | −0.218 Yes | Yes | Yes | −0.227 Yes |
| Space-fixed | Yes Yes | Yes Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Hausman | 112.47 *** | 112.47 *** | 417.11 *** | 21.91 ** | 17.01 ** | 383.13 *** |
| R-LM (SAR) | 11.3282 *** | 15.4693 *** | 0.0555 | 0.5497 | 4.3260 ** | 0.0018 |
| R-LM (SEM) | 46.2743 *** | 371.3759 *** | 10.6024 *** | 0.0953 | 0.0955 | 73.2107 *** |
| R² | 0.4059 | 0.228 | 0.3161 | 0.3039 | 0.3914 | 0.3928 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Wang, Y. Urban Agglomeration Ecological Welfare Performance and Spatial Convergence Research in the Yellow River Basin. Land 2022, 11, 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11112073
Liu N, Wang Y. Urban Agglomeration Ecological Welfare Performance and Spatial Convergence Research in the Yellow River Basin. Land. 2022; 11(11):2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11112073
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ningyi, and Yongyu Wang. 2022. "Urban Agglomeration Ecological Welfare Performance and Spatial Convergence Research in the Yellow River Basin" Land 11, no. 11: 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11112073
APA StyleLiu, N., & Wang, Y. (2022). Urban Agglomeration Ecological Welfare Performance and Spatial Convergence Research in the Yellow River Basin. Land, 11(11), 2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11112073






