Mapping Rural Settlements from Landsat and Sentinel Time Series by Integrating Pixel- and Object-Based Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
3. Methods
3.1. Creating Feature Composites from Landsat and Sentinel Time Series
3.2. Generating Objects and Calculating Object-Level Features
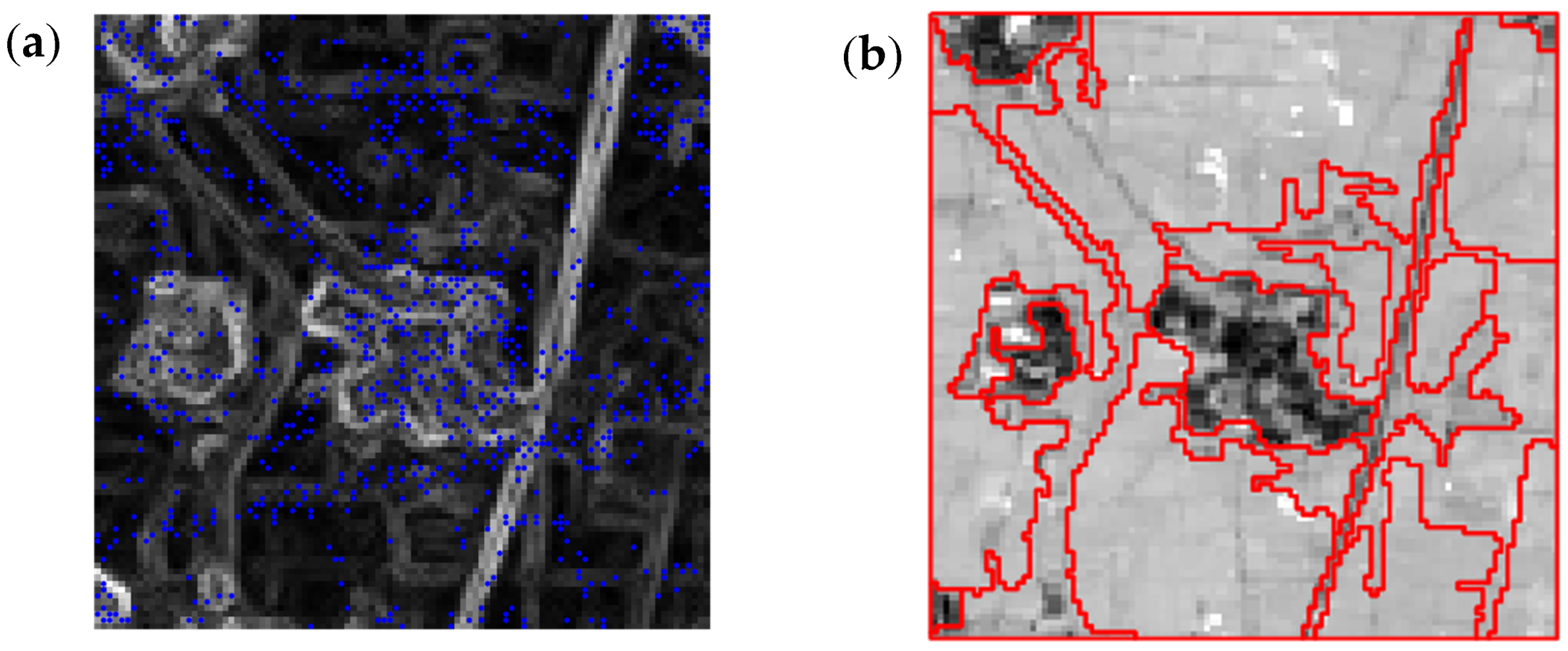
3.3. Automatic Generation of Samples for Different Land Cover Class
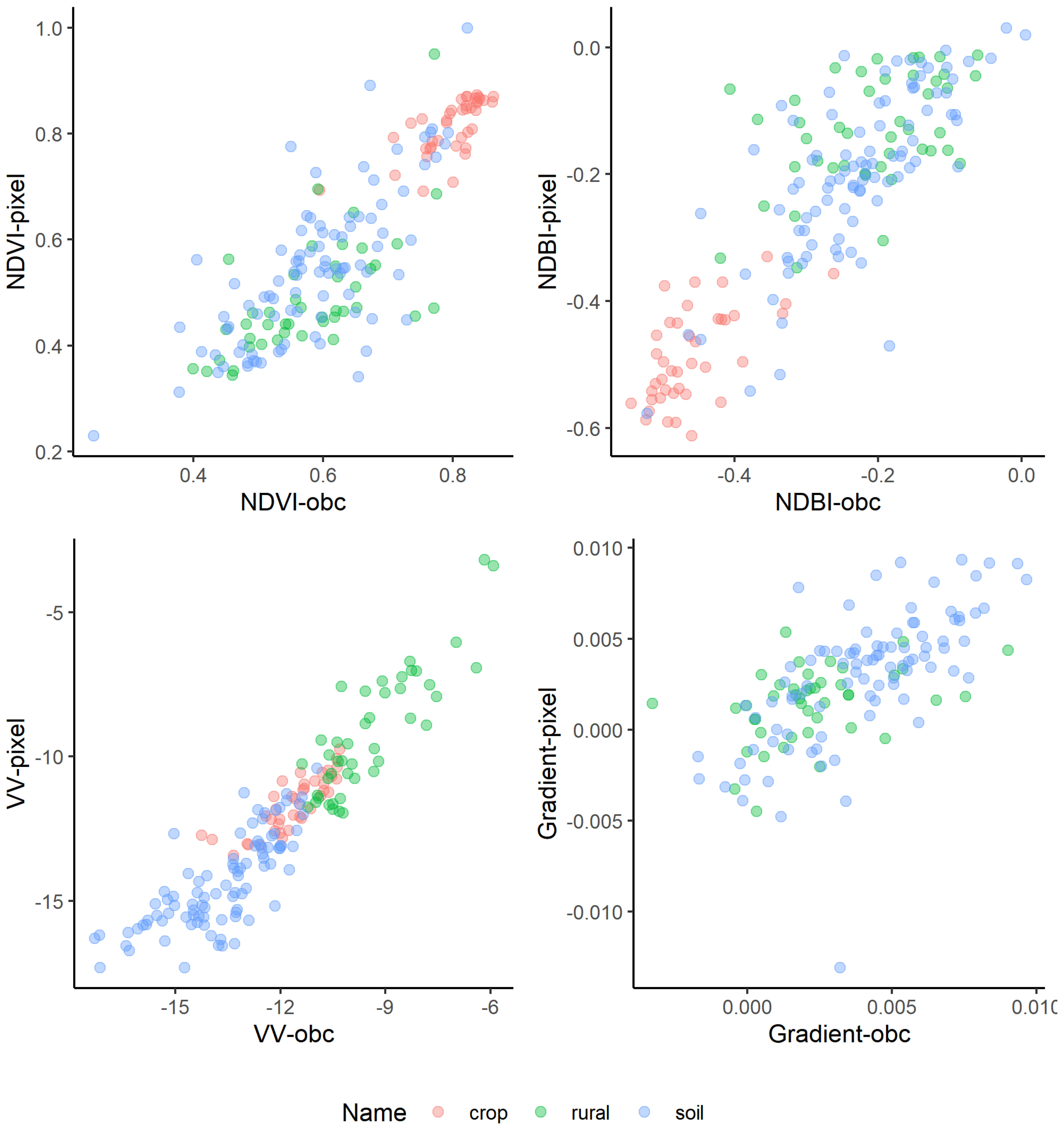
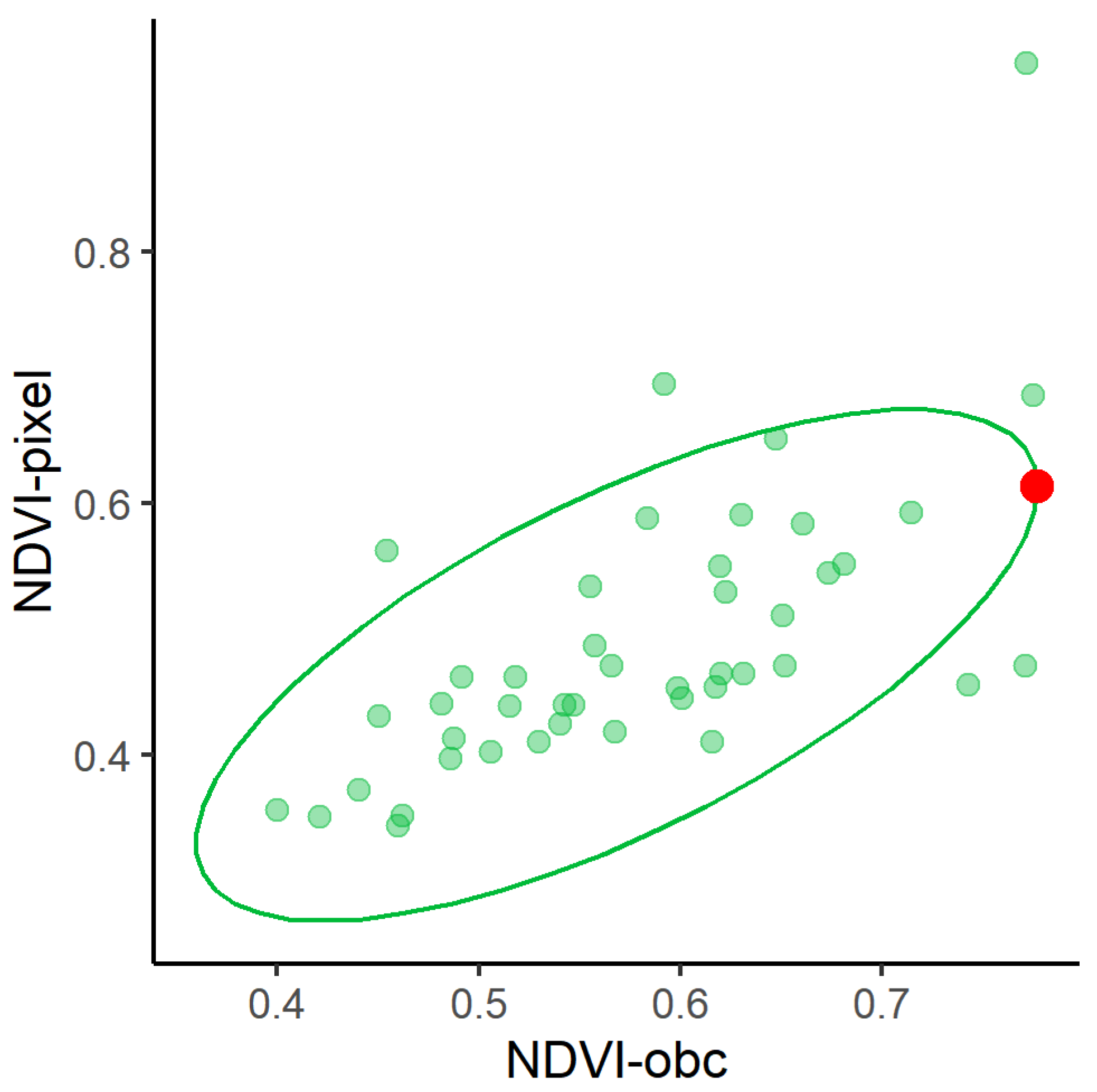
3.4. Determining Pixel- and Object-Based Thresholds
3.5. Accuracy Assessment
4. Results
4.1. The Extracted Results
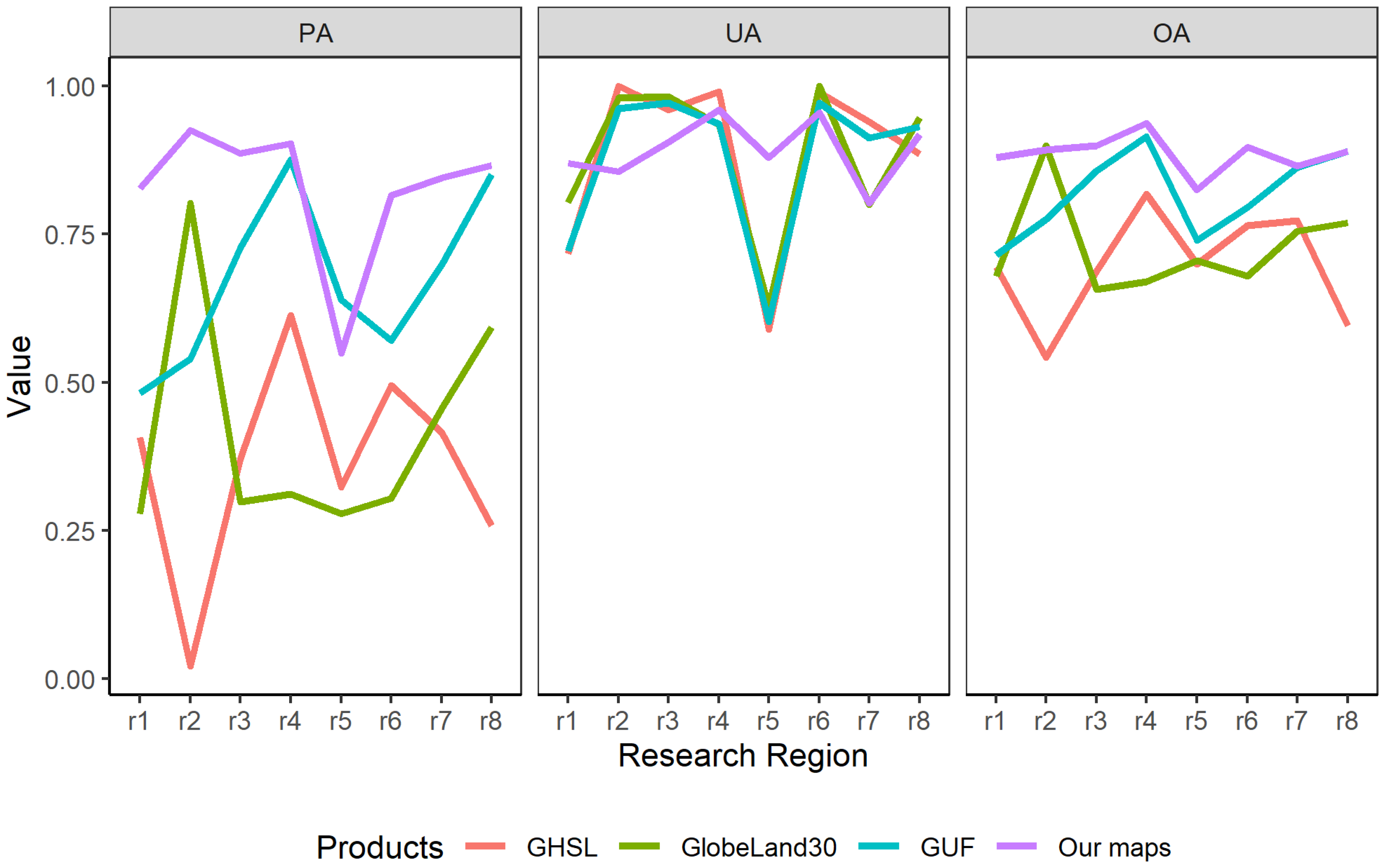
4.2. The Accuracy of Extracted Rural Settlements
5. Discussion
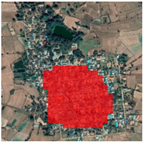
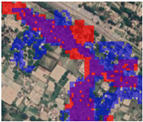
5.1. Comparison between Different Products from the Algorithm Perspective
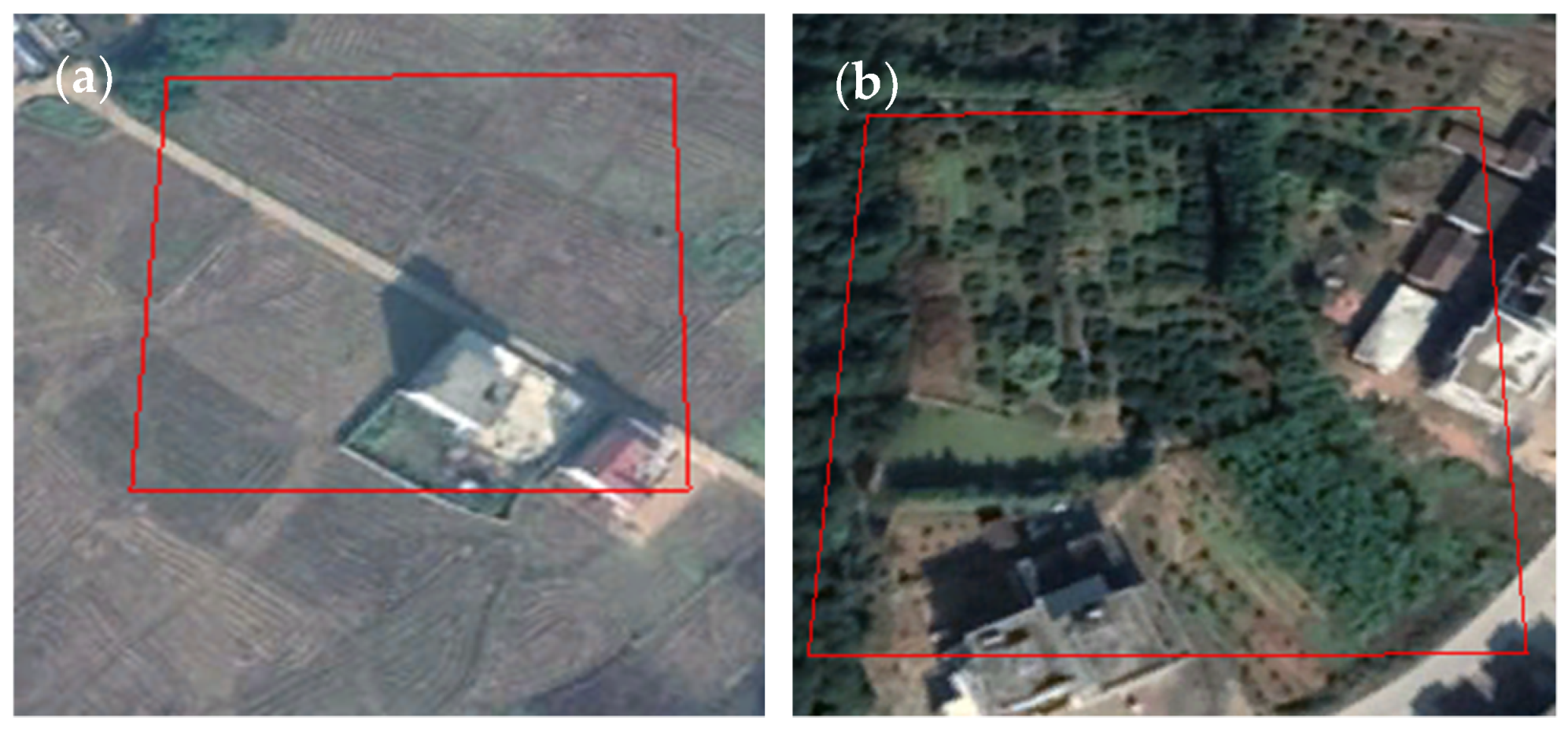
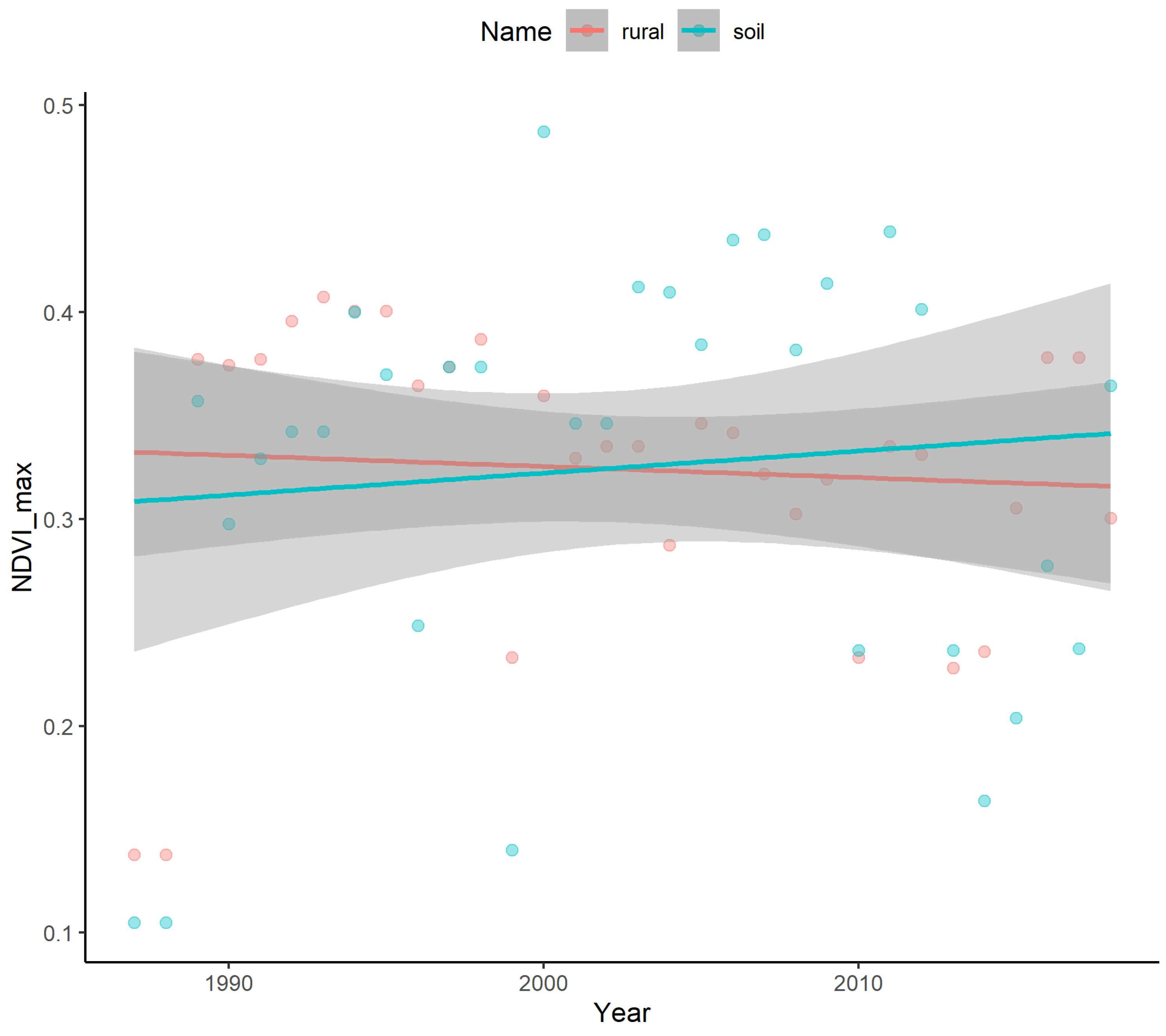
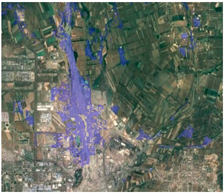
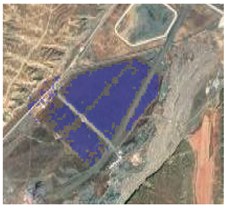
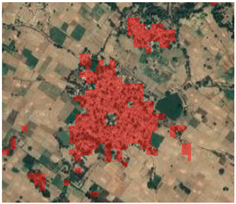
5.2. The Performance of Soil-Minimization Using Gradient Feature
6. Conclusions
- Our obtained rural map achieved higher accuracy than current mainstream settlement layers/products and could provide complementary materials to the existing operational land cover maps. We also find that the current rural settlement product (even our result) has relatively poor performance (settlements lost) in the Indian area. Researchers should pay more attention when using the rural products for this region.
- Our method facilitated the removal of bare soil by using the gradient feature from annual NDVI_max information. This simple and easily obtained index effectively solved soil-impervious misclassification issues.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seitzinger, S.P.; Svedin, U.; Crumley, C.L.; Steffen, W.; Abdullah, S.A.; Alfsen, C.; Broadgate, W.J.; Biermann, F.; Bondre, N.R.; Dearing, J.A.; et al. Planetary Stewardship in an Urbanizing World: Beyond City Limits. Ambio 2012, 41, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmino Costa da Silva, D.; Elhorst, J.P.; Silveira Neto, R.d.M. Urban and Rural Population Growth in a Spatial Panel of Municipalities. Reg. Stud. 2017, 51, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, P.K.; Loboguerrero, A.M.; Campbell, B.M.; Kavikumar, K.S.; Mercado, L.; Shackleton, S. Rural Livelihoods, Food Security and Rural Transformation under Climate Change; Global Commission on Adaptation: Rotterdam, The Netherlands; Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-Resolution Multi-Temporal Mapping of Global Urban Land Using Landsat Images Based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miheretu, B.A.; Yimer, A.A. Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Their Environmental Implications in the Gelana Sub-Watershed of Northern Highlands of Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global Land Cover Mapping at 30 m Resolution: A POK-Based Operational Approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer Resolution Observation and Monitoring of Global Land Cover: First Mapping Results with Landsat TM and ETM+ Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Lin, H.; Lü, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Comber, A. A Modified Change Vector Approach for Quantifying Land Cover Change. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Asrar, G.R.; Smith, S.J.; Imhoff, M. A Global Record of Annual Urban Dynamics (1992–2013) from Nighttime Lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. Mapping Global Urban Areas Using MODIS 500-m Data: New Methods and Datasets Based on “Urban Ecoregions”. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN); Columbia University; International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI); The World Bank; Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT). “Global Rural-Urban Mapping Project (GRUMP), Beta Version: Urban Extents”; Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC), Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Esch, T.; Heldens, W.; Hirner, A.; Keil, M.; Marconcini, M.; Roth, A.; Zeidler, J.; Dech, S.; Strano, E. Breaking New Ground in Mapping Human Settlements from Space—The Global Urban Footprint. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 134, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Florczyk, A.J.; Freire, S.; Halkia, M.; Julea, A.; Kemper, T.; Soille, P.; Syrris, V. Operating Procedure for the Production of the Global Human Settlement Layer from Landsat Data of the Epochs 1975, 1990, 2000, and 2014; JRC Technical Report EUR 27741 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Ispra, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual Maps of Global Artificial Impervious Area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, W. A National Dataset of 30 m Annual Urban Extent Dynamics (1985–2015) in the Conterminous United States. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, R.; Du, W.; Wang, L.; Lu, D. High-Resolution Urban Land Mapping in China from Sentinel 1A/2 Imagery Based on Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer, C.; Dewitz, J.; Yang, L.; Jin, S.; Danielson, P.; Xian, G.; Coulston, J.; Herold, N.; Wickham, J.; Megown, K. Completion of the 2011 National Land Cover Database for the Conterminous United States—Representing a Decade of Land Cover Change Information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 2015, 81, 345–354. [Google Scholar]
- Leyk, S.; Uhl, J.H.; Balk, D.; Jones, B. Assessing the Accuracy of Multi-Temporal Built-up Land Layers across Rural-Urban Trajectories in the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 898–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Weng, Q. Annual Dynamics of Impervious Surface in the Pearl River Delta, China, from 1988 to 2013, Using Time Series Landsat Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 113, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, H.; Lin, H. Urban Impervious Surfaces Estimation from Optical and SAR Imagery: A Comprehensive Comparison. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4010–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T.; Burnett, C.; Pekkarinen, A. Image Segmentation Methods for Object-Based Analysis and Classification. In Remote Sensing Image Analysis: Including the Spatial Domain; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 211–236. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Xia, F. Assessing Object-Based Classification: Advantages and Limitations. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 1, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Gutiérrez, J.; Seijmonsbergen, A.C.; Duivenvoorden, J.F. Optimizing Land Cover Classification Accuracy for Change Detection, a Combined Pixel-Based and Object-Based Approach in a Mountainous Area in Mexico. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, Y.; An, R.; Chen, Y. Enhancing Land Cover Mapping through Integration of Pixel-Based and Object-Based Classifications from Remotely Sensed Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ziv, G.; Adami, M.; Mitchard, E.; Batterman, S.A.; Buermann, W.; Schwantes Marimon, B.; Marimon Junior, B.H.; Matias Reis, S.; Rodrigues, D.; et al. Mapping Tropical Disturbed Forests Using Multi-Decadal 30 m Optical Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teluguntla, P.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Giri, C.; Milesi, C.; Ozdogan, M.; Congalton, R.G.; Tilton, J. Global Food Security Support Analysis Data (GFSAD) at Nominal 1 km (GCAD) Derived from Remote Sensing in Support of Food Security in the Twenty-First Century: Current Achievements and Future Possibilities. In Land Resources Monitoring, Modeling, and Mapping with Remote Sensing; CPC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 131–160. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Jing, L.; Lin, Q.; Li, H.; Xu, R.; Tang, Y.; Ding, H.; Liu, Q. A new region growing-based segmentation method for high resolution remote sensing imagery. IGARSS 2015, 53, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) to Enhance Open Water Features in Remotely Sensed Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Wu, C. BCI: A Biophysical Composition Index for Remote Sensing of Urban Environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
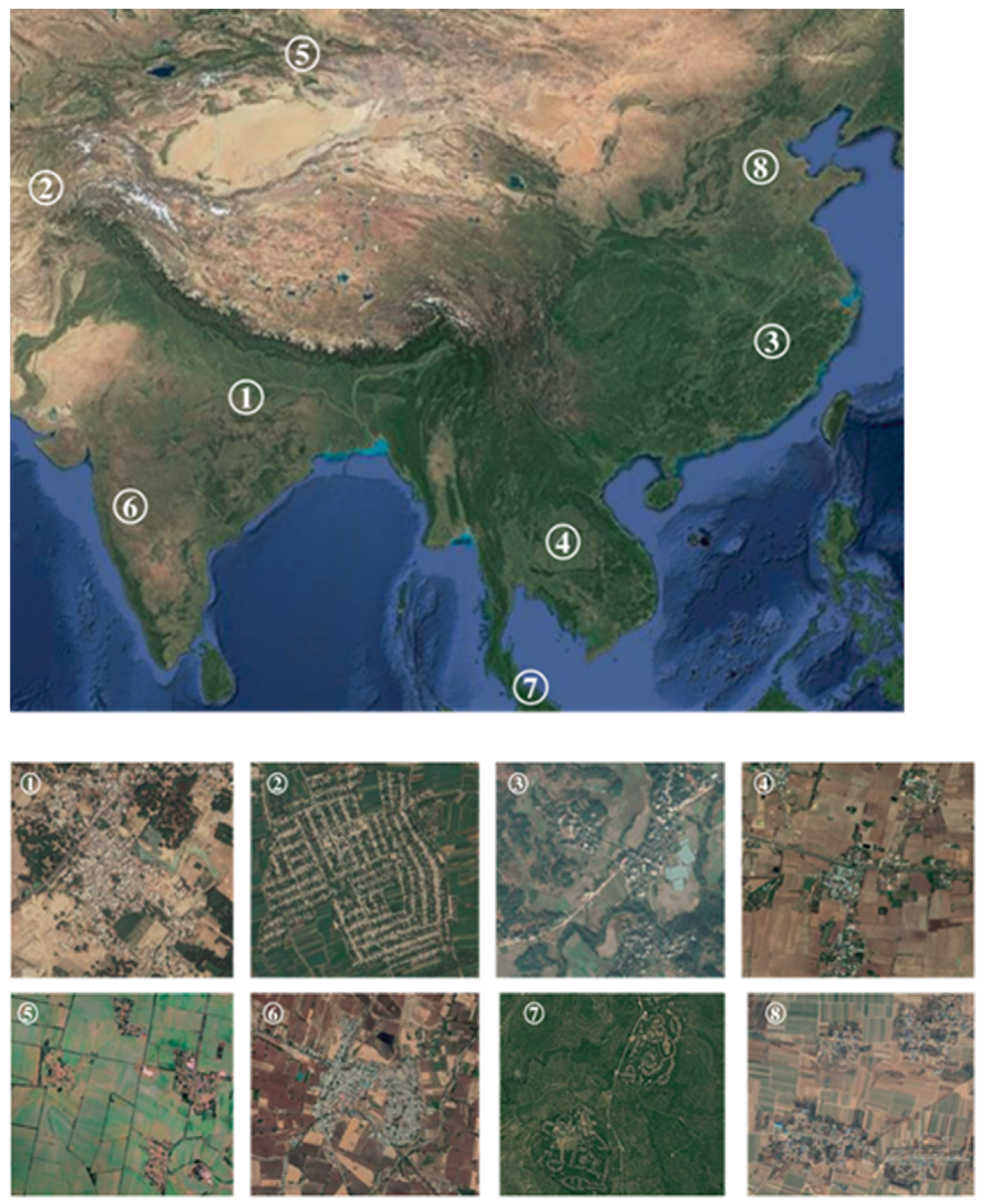
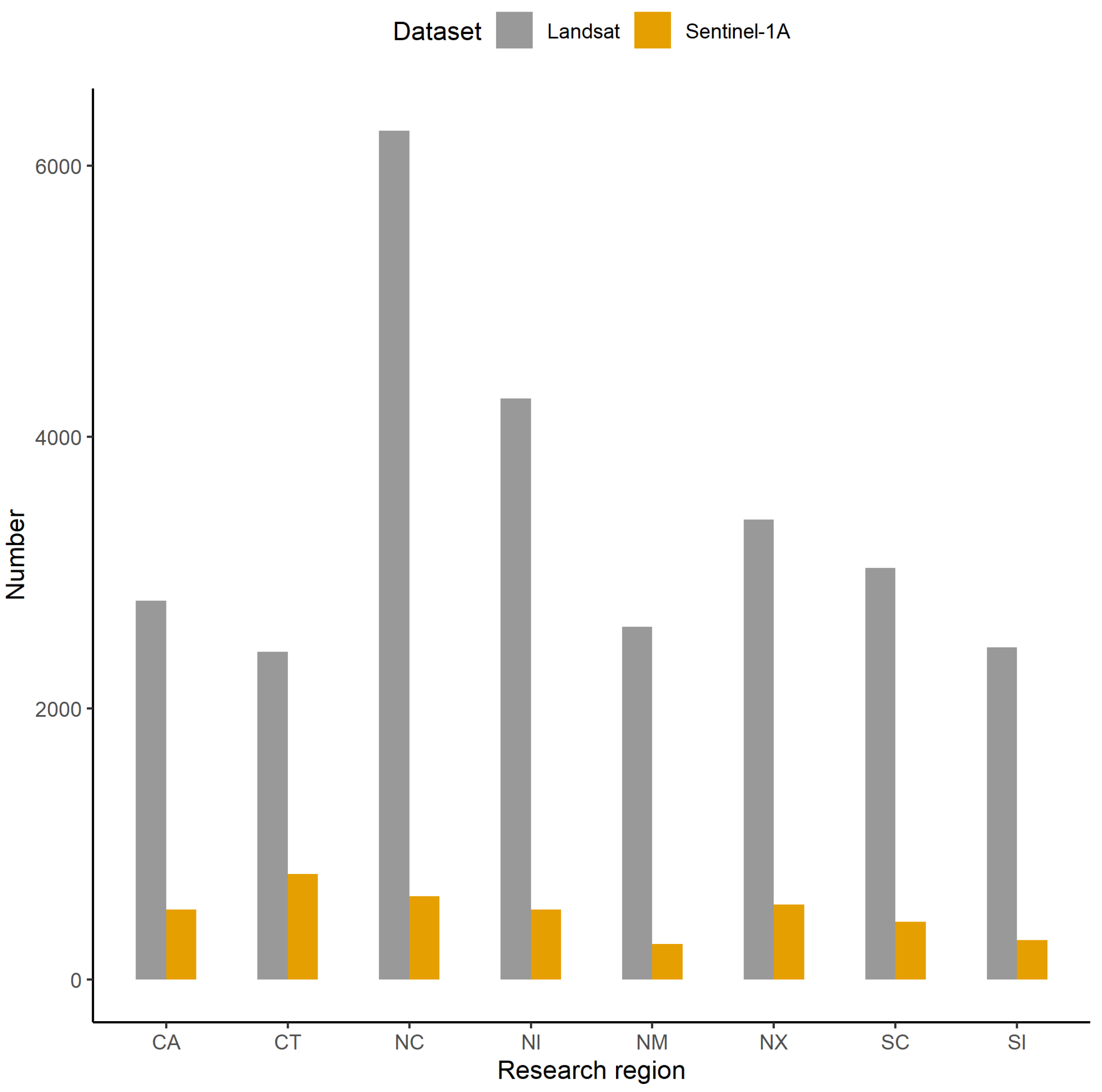


| Research Region | Land Cover Types | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rural Settlements | Crop | Soil | |
| NI | 208 | 1338 | 93 |
| CA | 38 | 229 | 24 |
| SC | 58 | 286 | 0 |
| CT | 37 | 257 | 7 |
| NX | 27 | 91 | 30 |
| SI | 173 | 684 | 72 |
| NM | 23 | 78 | 0 |
| NC | 228 | 385 | 0 |
| Research Region | Google Earth Image | Our Maps | GHSL | GUF | GlobeLand30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NI |  |  |  |  |  |
| CA |  |  |  |  |  |
| SC |  |  |  |  |  |
| CT |  |  |  |  |  |
| NX |  |  |  |  |  |
| SI |  |  |  |  |  |
| NM |  |  |  |  |  |
| NC |  |  |  |  |  |
| Google Earth Image | Our Map (Red) GUF (Blue) | GHSL | GlobeLand30 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
| Google Earth Image | Settlement Extraction with Gradient Feature | Settlement Extraction without Gradient Feature |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, R. Mapping Rural Settlements from Landsat and Sentinel Time Series by Integrating Pixel- and Object-Based Methods. Land 2021, 10, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10030244
Xu R. Mapping Rural Settlements from Landsat and Sentinel Time Series by Integrating Pixel- and Object-Based Methods. Land. 2021; 10(3):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10030244
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Ru. 2021. "Mapping Rural Settlements from Landsat and Sentinel Time Series by Integrating Pixel- and Object-Based Methods" Land 10, no. 3: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10030244
APA StyleXu, R. (2021). Mapping Rural Settlements from Landsat and Sentinel Time Series by Integrating Pixel- and Object-Based Methods. Land, 10(3), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10030244






