Abstract
Maintaining and enhancing the quality of civil defense services are of importance to citizens’ life in any city. During the past few decades, the expansion of settlements in Al-Riyadh City has led to a shortage in the distribution of the civil defense centers (CDCs) there. The main aim of this study is to implement the Weighted Sum Method (WSM) and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to evaluate the distribution of the CDCs in Al-Riyadh City. Eight criteria (i.e., distance from the existing civil defense center, accident density, population density, distance from the road, distance from commercial centers, distance from educational services, distance from industrial areas, and distance from residential areas) were used. The areas under the curve (AUC) of the Prediction Rate Curve (PRC) show that almost all of the AHP models are better than the WSM model. We suggest establishing five CDCs in Al-Riyadh City in areas that are lacking CDCs and characterized by a high population density and consequently a high rate of accidents. We recommend highly long-term planning for establishing new CDCs in cities where there is rapid areal expansion (e.g., Al-Riyadh City).
Keywords:
GIS; AHP; multi criteria decision making; MCDM; civil defense centers; LAND use; Saudi Arabia; suitability map 1. Introduction
Civil defense is a set of measures to protect citizens and public and private property from the dangers of fires, disasters, wars, and various accidents. It plays a key role in any country by assisting those who are afflicted and providing safety for transportation, communications, and evacuation plans as defined by the civil defense system [1]. Efficient utilization of these resources is a major responsibility of decision-makers in a country and can have a considerable impact on the quality of the service provided by civil defense. The tasks of civil defense can be summarized as: (i) providing relief to those affected by emergency situations; (ii) firefighting, fire extinguishing, rescue, and ambulance services; (iii) establishing operating rooms and civil defense centers (CDCs) and identifying those affected; (iv) storing various materials and equipment needed in war emergencies and catastrophic situations; (v) preparing and implementing the necessary procedures and providing cash support; and (vi) implementing plans for evacuation and providing shelter in emergency situations [2].
Selecting sites for the optimal location of civil defense centers is an important application for geographic information systems (GISs), which can play a significant role in decision-making [3]. The main task of the civil defense center is acting in the event of fire and other emergencies, where the time of arrival of help during a disaster is the dominant criterion. The determination of the optimal location for emergency facilities such as CDCs has a long history in the field of management and operations research using different methods [4]. Several studies have been conducted in the field of the selection and evaluation of civil defense centers [5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. The authors of [12] used the travel-time method to determine the geographical variation in hospital use in Estonia, while [13] used both travel-time and straight-line techniques to determine health service areas in southwest England. Some of these studies used Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) to select the best location for CDCs.
MCDA methods have been applied in different studies. For example, [14] used Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) to develop land suitability maps for selected crops. In addition, [15] used AHP to select suitable areas for professional adventure tourism to help in formulating tourism development strategies. The authors of [16,17] used MCDA for winter wheat cultivation and viticulture, respectively. The authors of [18,19,20] used Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to locate groundwater potential zone watersheds using a GIS and remote sensing. For evaluating the quality of life, [21] used AHP and the location–allocation method to improve the spatial distribution of services and enhance the quality of life in districts. In addition, AHP has been used in environmental and watershed management [22,23].
For civil defense, MCDA methods have been used. Many researchers have used a GIS to determine locations for fire stations [24]. For example, [25,26] used the Fuzzy AHP method to select the optimal location of new fire stations. We have stated some of the common MCDA methods that have been used around the world in Table 1. This study aims to implement the Weighted Sum Method (WSM) and AHP methods to select suitable sites for CDCs in Al-Riyadh City.

Table 1.
Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) methods used in various studies.
Our study utilizes, for the first time, MCDA represented by AHP and the WSM to determine new CDC locations in Al-Riyadh City. In addition to the Introduction, this paper consists of four sections structured as follows. Section 1 focuses on a description of the study area. Section 2 deals with the methods and data used. Results and a discussion are presented in Section 3. Finally, Section 4 summarizes the main conclusions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Al-Riyadh City is the capital of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the largest city in the Arabian Peninsula (Figure 1). It covers a total area of ~2894 km2. The city lies at an altitude of 600 m above sea level (Figure 1). It is characterized by a desert climate with hot summers, short and mild winters, and low humidity levels throughout the year. The temperature changes substantially between night and day, typically 28 °C and 43 °C, respectively. The city of Al-Riyadh, in general, has low rainfall, which falls mainly in March and April. However, the city is exposed periodically to heavy rain events leading sometimes to flash floods [48]. It is also exposed to dust storms, which sometimes severely affect visibility, reducing it to less than 10 m [49].
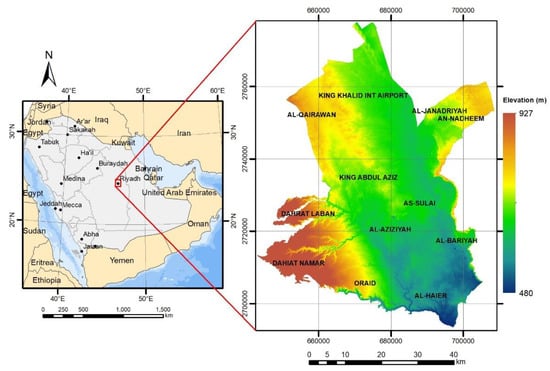
Figure 1.
Location of Al-Riyadh City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Al-Riyadh City has experienced rapid population and areal growth since 1900 [50] with an annual rate of growth of more than 8% (Figure 2; [50]). The population growth of Al-Riyadh City over the 12 years from 2007 to 2019 was ~2.6 million (from 6 to 8.6 million) [51]. As the population grows and the city of Al-Riyadh expands, there will be a need for more CDCs. Hence, it is imperative to effectively determine new locations for emergency facilities to adequately serve civilians and ensure that lives and urban infrastructure are protected.
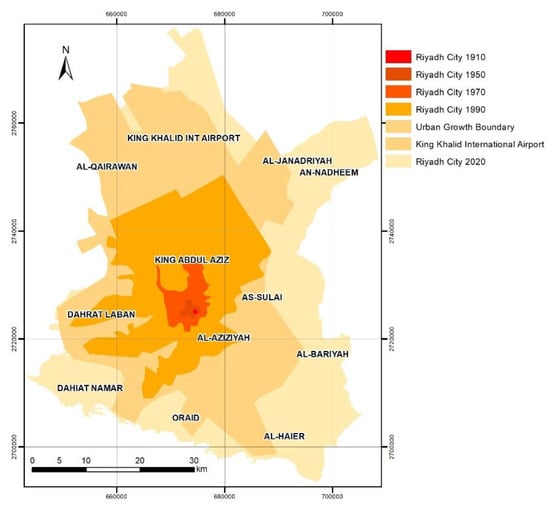
Figure 2.
Al-Riyadh City and the urban growth boundaries (1910, 1950, 1970, and 1990) [52].
2.2. Geodatabase
Before selecting effective criteria to determine suitable sites for CDCs, we reviewed several papers, e.g., [25,53,54]. A geospatial database for Al-Riyadh City was constructed and several thematic layers were used. The layers include road and street networks, the administrative division of city districts, land use, and population density. This dataset was obtained from the Municipality of Al-Riyadh, which is affiliated with the Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs and the General Directorate of Civil Defense (Table 2). We followed the workflow shown in Figure 3. to find suitable areas for new CDCs. We used the assembled maps to generate the eight factors (Table 2 and Appendix A) used to determine suitable sites. For instance, the land use map was used to estimate the layers C5, C6, C7, and C8.

Table 2.
Coding criteria and data sources of the prediction-factor layers.
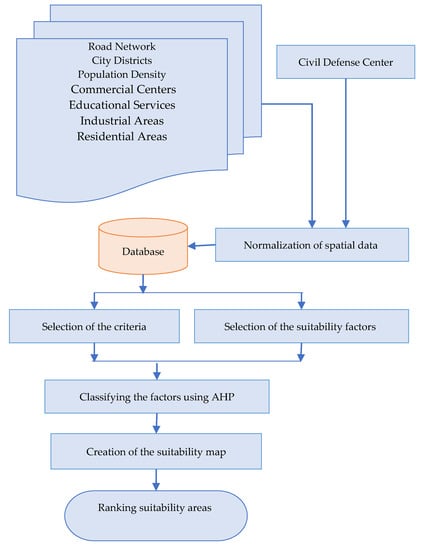
Figure 3.
The workflow used.
As we have several prediction factors in the models, multicollinearity tests were tried between these factors to detect and remove highly correlated factors [55]. Table 3 shows that there are no very high correlations between the factors. The maximum correlation is between distance from commercial centers (factor C5) and distance from educational services (factor C6). This is 0.767. The correlation between accident density (factor C2) and population density (factor C3) is 0.692, which can be considered a bit high.

Table 3.
Correlation between layers C2–C8.
2.3. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis
MCDA has been widely used as key tool in many studies (Table 1). Such a technique can be implemented through the application of a scientifically determined and well-structured method. We used two of the common methods (i.e., WSM and AHP) to design new CDCs in Al-Riyadh City. Below, we summarize the methods used.
2.3.1. Weighted Sum Method (WSM)
The WSM is a simple method using multiple factors with the same weighting value. Therefore, significant inadequacy in inputs is not considered [56]. In this study, each factor was coded (Table 2) and classified into five classes (Table 4). These were 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 for the non-suitable, less suitable, moderately suitable, suitable, and most suitable locations for CDCs, respectively. The suitability of each class for a CDC location was used for weighting classes (Table 4). The summation of all factors was taken based on Equation (1) [57].
where n is the number of factors, is the actual value of the i-th and j-th criteria, and is the weight of the j-th criterion.

Table 4.
Classified criteria.
For smooth classification of data, we reclassified all used layers into five classes (Table 4). The map version of the classified layers is presented in Appendix A.
2.3.2. AHP Method
AHP was first proposed by [56] and provides a scheme for working in a hierarchical structure to solve complex problems where the used parameters in each layer are compared in pairs. This allows us to assess the comparative standard coefficient weights with alternative schemes [58,59]. The AHP method is flexible and structured because it relies on a simple principle of finding the relationship between standards and alternatives. The comparison method for each pair is the most commonly used process for the calculation of criteria weight coefficients in MCDA applications [60]. The eight criteria for CDC suitability are coded in Table 4.
The preferences matrix is a result of a pairwise comparison of all the elements in a specific hierarchy level. Equation (2) illustrates the structure of an (n × n) square matrix where (n) is the number of elements that have been compared. Equation (3) is an expression of the principle of preference, where two elements that are identical to each other are expressed according to the preference by the number 1. Therefore, the elements in the diagonal of the matrix are equal to 1. Equation (4) explains how to calculate preferences in the other elements.
2.4. Civil Defense Site Selection and Validation
Six (i.e., one WSM and five AHP) suitability maps were estimated to select suitable CDCs. The highest weight pixels are nominated as suitable sites. To validate the suitability of the nominated defense centers in Al-Riyadh City, we used an existing defense center map as a reference [61] and ignored the distance from the civil defense center (C1) factor in the six models.
The Area Under the Curve (AUC) of the Prediction Rate Curve (PRC) is a common quantitative measurement used to evaluate site selection models. It is used to evaluate suitability models in different fields, such as landslide prediction [61]. A PRC is usually represented by a two-dimensional plot, where the x-axis is the suitability index rank of CDCs (%) and the y-axis is the cumulative percentage of the CDC percentages. Ref. [62] reported that an AUC of N50% for a model is reasonable for acceptability. The higher the AUC, the more suitable is the model. We evaluated our models used to select the suitable sites for CDCs by using the AUC of the PRC for all suitability maps. To validate the six suitability maps, we calculated the AUC of the PRC using the existing 70 CDCs within Al-Riyadh City. Then, the AUC of the PRC was used to select the best suitability maps (Results section; Figure 4).
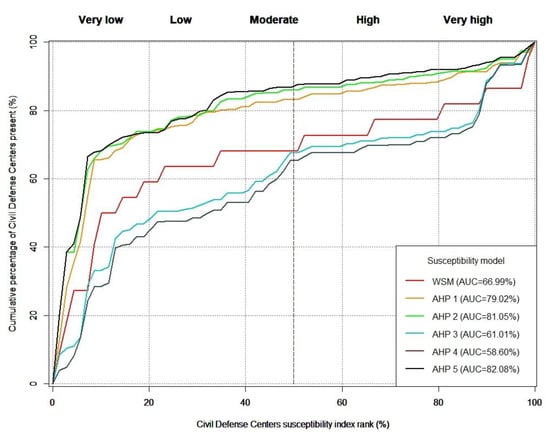
Figure 4.
PRC plot evaluation of the six CDC models.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. WSM and AHP Assessment
For the WSM, only one set of weights was tested (as the weights of the predictive factors for the WSM are equal to each other). For the AHP method, we tested several weights to create the spatial distributions of the CDC maps within Al-Riyadh City experimentally. Table 5 shows the WSM and the best weights of the predictive factors for the AHP models (five sets) used to estimate the CDC suitability maps. Figure 5 shows the spatial distributions of the CDC maps within Al-Riyadh City. For each model, each predictive factor has its specific weight, which differs from one model to another. Six maps were created using the WSM and AHP methods based on eight predictive factors (Table 2). Each map includes five classes, which are very low, low, moderate, high, and very high CDC suitability (Table 2 and Table 4). The AHP maps were created with the best AUC of the PRC. The spatial distributions of the five classes for the CDC maps (WSM and five AHP) show some similarity. They can be classified into two groups—group 1 (i.e., Figure 5a,d,e) and group 2 (i.e., Figure 5b,c,f), where each group has high similarity for the maps (Figure 5). The very high suitability class of group 1 shows a restricted distribution in a very small zone within the center of Al-Riyadh City, while the very high suitability class of group 2 shows a wide distribution within Al-Riyadh City. That is clear in the AUC of the PRC for the six tested models (Figure 4), where we assumed that the weight of the accident density (C2) factor is low for the AHP-3, AHP-4, and WSM models, while it is high for the AHP-1, AHP-2, and AHP-5 models (Table 5). Therefore, we found that the reason for the decreasing AUC of the PRC for the AHP-3, AHP-4, and WSM models and the increasing AUC of the PRC for the AHP-1, AHP-2, and AHP-5 models is the lack of recent information on accident density (C2), which has changed with the rapid expansion of Al-Riyadh City.

Table 5.
The weight of the predictive factors suggested for the six models (WSM and five AHP).
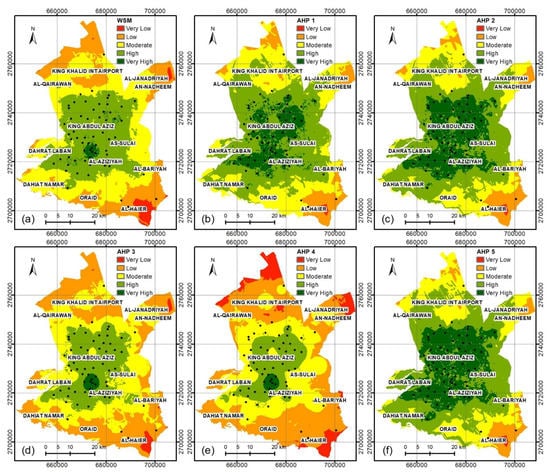
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of the CDCs of the study area using models (a) WSM, (b) AHP-1, (c) AHP-2, (d) AHP-3, (e) AHP-4, and (f) AHP-5.
3.2. Re-Estimation and Validation of the Most Successful Models
In Figure 4, we calculated the AUC of the PRC to validate the six tested CDC models (Figure 5), where the AUC of the PRC for the WSM, AHP-1, AHP-2, AHP-3, AHP-4, and AHP-5 maps were 66.99%, 79.02%, 81.05%, 61.01%, 58.6%, and 82.08%, respectively. The best overall models are AHP-5, AHP-2, and AHP-1, while the worst models are AHP-4 AHP-3, and WSM. We re-estimated the suitability map of CDC sites for models AHP-1, AHP -2, and AHP-5 by integration of the existing civil defense center factor with the other factors for these three models (Figure 6).
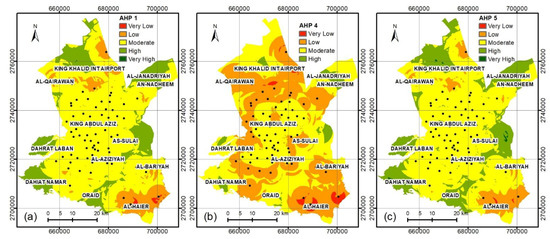
Figure 6.
Best spatial distribution of the CDC maps after adding the existing CDC factor to the three models, which are (a) AHP-1, (b) AHP-4, and (c) AHP-5.
Based on the results, we assumed that the civil defense center factor has the highest weight, and the normalized weight for the AHP-1, AHP-2, and AHP-5 models is 0.411, 0.434, and 0.474, respectively. We compared the three nominated models to display their spatial distribution within Al-Riyadh City (Figure 7). All these models are normally distributed. It can be seen that the AHP-5 model is positive in skewness, where the skew is towards a high and very high ranking, while the AHP-2 model is negative in skewness. The AHP-1 model is symmetrically distributed for the weight of the rank. Table 6 shows the new suggested weights for the three nominated models after normalizing the weights of the eight factors.
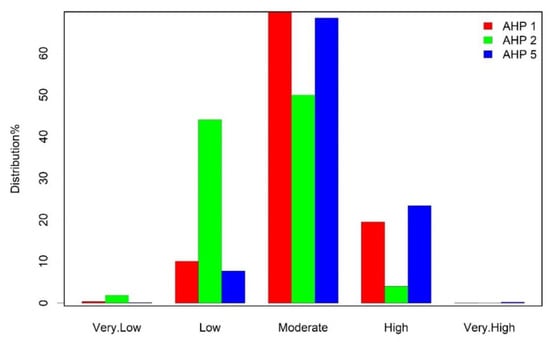
Figure 7.
Bar graph showing the spatial suitability categories for CDCs in Al-Riyadh City.

Table 6.
The weights of the predictive factors suggested for the best three AHP models.
We used the eight effective factors (i.e., C1–C8) that allow for the selection of proposed locations of CDCs in Al-Riyadh City. The use of these factors is satisfactory considering the distribution of weights (Appendix B).
The AUC of the PRC for the best three tested models, after adding the existing CDC factor (i.e., AHP-1, AHP-2, and AHP-5; Figure 8), show lower values than the three models before adding the existing CDC factor (Figure 4). The main reason is that the existing CDCs were established on the basis of two main factors, which are distance from residential areas (C8) and distance from the road (C4). Other factors were disregarded. Therefore, the distribution of the CDCs is random. The decision-makers did not constrain their choices using the other affecting factors (i.e., distance from the civil defense center, accident density, population density, distance from the road, distance from commercial centers, distance from educational services, and distance from industrial areas). The reason is that the CDCs were established in multiple stages. For example, in the year 2000 five CDCs were established [63]. Moreover, the growth of Al-Riyadh City occurred in five stages (Figure 2).
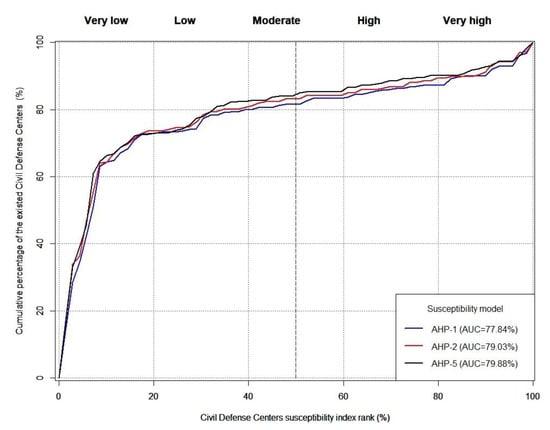
Figure 8.
PRC plot evaluation of the three best CDC models after adding the existing CDC factor.
The distance from the existing CDC factor did not improve the CDC maps obtained from models AHP-1, AHP-2, and AHP-5. On the contrary, adding this layer degraded the results of these three models (Figure 4 and Figure 8).
Based on the best CDC distribution map (i.e., AHP-5), we suggest establishing five new CDCs in Al-Riyadh City (Figure 9 and Appendix C). These new suggested CDCs are on the outskirts of the city. All the areas are characterized by high rates of accidents and a high population density. For example, 18,255 people live in Dahiat Namar, in the southwest of Al-Riyadh City, which suffers from 186 accidents per year. It includes several commercial, residential, and governmental buildings, hotels, water sewage treatment plants, police stations, and schools.
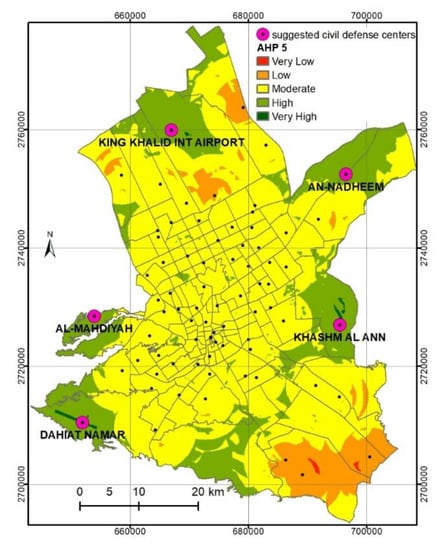
Figure 9.
The best spatial distribution of the AHP-5 model overlain by the suggested new five CDCs.
The highest correlation was found between layers C6 and C5, which represent the distance from commercial and educational centers, respectively (Table 5 and Table 6). This pair of layers had similar influences on the determination of the validity of the existing and proposed new defense centers. This allowed us to reduce the weight used by neglecting one of these layers as they act as one layer. Thus, layer C5 can be neglected as it has a strong correlation with the other layers and will depend on layer C6 (Table 3). Similarly, the layers accident density (C2) and population density (C3) have a moderate correlation (Table 3). This is logical because accidents have a direct relationship with population density. Additionally, there is a moderate correlation between distance from educational services (C6) and distance from residential areas (C8; Table 3), which is also logical because educational services are close to residential areas.
The PRC plots show that the AUC of all models increased after adding the five suggested CDCs, where AHP-1, AHP-2, and AHP-5 increased by ~0.68, 1.9, and 1.86, respectively (Figure 8 and Figure 10).
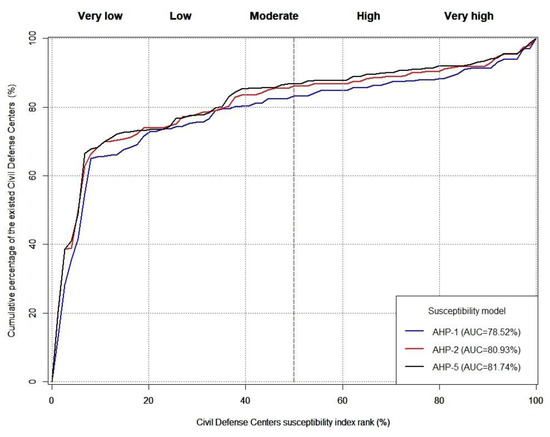
Figure 10.
PRC plot evaluation of the three best CDC models after adding the existing and proposed CDCs.
This work is in agreement with [22] that the AHP method is more robust than WSM in spite of the complexity of AHP. We agreed with [53,54,64,65,66] that the population density is the most effective criterion to determine the CDCs’ location.
4. Conclusions
An integrated approach using AHP and GIS was used in this study to provide the best model for optimally locating new civil defense centers (CDCs) in Al-Riyadh City. After evaluating the existing CDCs, it was found that they were established based on two main factors, which are distance from residential areas and distance from the road. Other factors were neglected. We tested eight factors within six models to select new proposed CDCs. Our results indicate that models AHP-1, AHP-2, and AHP-5 are acceptable estimators of the optimal localities of CDCs and the best one is model AHP-5. Adding the existing civil defense center factor led to deterioration of the results of models AHP-1, AHP-2, and AHP-5. This study recommends redistributing the CDC centers in Al-Riyadh City. Adding new CDCs is important to overcome the negative impact of the growth of Al-Riyadh City and to save the lives and property of civilians. In addition, there is a need for a clear scientific strategy for regularly locating new CDCs consistent with the rapid expansion of Al-Riyadh City. Our methods are applicable to other cities within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia to select the best CDC sites. Including other factors, such as distance from the water supply network, is possible for future studies. In addition, to obtain better results, we recommended analyzing different types of hazards separately using multiple effective factors. The results can then be integrated in a single map.
Author Contributions
B.B., A.A.O. and A.K.O. wrote the manuscript; B.B., A.A.O. and H.B. conducted the analysis; B.B., A.A.O., A.K.O., A.A. and H.B. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Researchers Supporting Project (number RSP-2021/296), King Saud University, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the General Directorate of Civil Defense, the Municipality of Al-Riyadh, and the Royal Commission for Riyadh city for providing the data used in this study. The fourth author would like to thank CARA for supporting his research. Special thanks to Professor Gillian Foulger from the Department of Earth Sciences, University of Durham for fixing the language of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
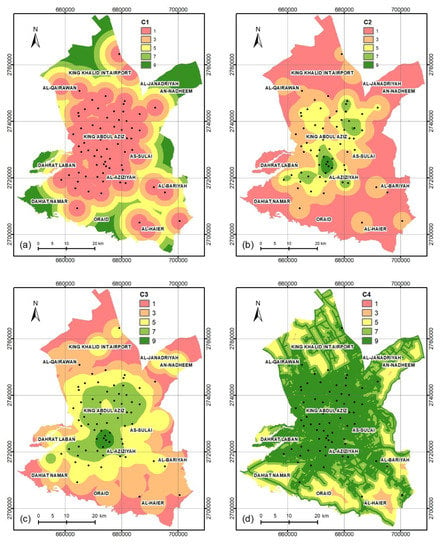
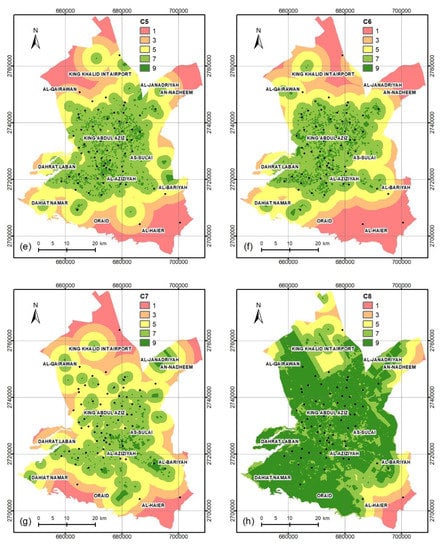
Figure A1.
The eight criteria layers: (a) distance from the civil defense center; (b) accident density; (c) population density; (d) distance from the road; (e) distance from commercial centers; (f) distance from educational services; (g) distance from industrial areas; (h) distance from residential areas.
Appendix B. AHP Weights of the Eight Selected Factors
| WSM | WSM | AHP 1 | AHP 1 | ||||||||||||
| C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | ||
| C2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C2 | 1 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/5 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/7 |
| C3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C3 | 5 | 1 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1/9 | 1/3 | 1/7 |
| C4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C4 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| C5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C5 | 5 | 5 | 1/5 | 1 | 1/7 | 1/3 | 1/5 |
| C6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C6 | 7 | 9 | 1/3 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 1/7 |
| C7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C7 | 5 | 3 | 1/5 | 3 | 1/3 | 1 | 1/9 |
| C8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C8 | 7 | 7 | 1/3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 1 |
| AHP 2 | AHP 2 | AHP 3 | AHP 3 | ||||||||||||
| C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | ||
| C2 | 1 | 1 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | C2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| C3 | 1 | 1 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | C3 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| C4 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 1/3 | C4 | 1 | 1/9 | 1 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| C5 | 9 | 9 | 1/7 | 1 | 1/9 | 7 | 1/9 | C5 | 1/3 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| C6 | 9 | 9 | 1/7 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 1/9 | C6 | 1/2 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| C7 | 9 | 9 | 1/7 | 1/7 | 1/5 | 1 | 1/9 | C7 | 1/2 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| C8 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 1 | C8 | 1/2 | 1/9 | 1/7 | 1 | 1/5 | 1 | 1 |
| AHP 4 | AHP 4 | AHP 5 | AHP 5 | ||||||||||||
| C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | ||
| C2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | C2 | 1 | 1 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/3 | 1 | 1/9 |
| C3 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | C3 | 1 | 1 | 1/7 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1 | 1/9 |
| C4 | 1 | 1/9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C4 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 1/3 |
| C5 | 1/3 | 1/9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C5 | 9 | 9 | 1/9 | 1 | 1/9 | 1 | 1/9 |
| C6 | 1/2 | 1/9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C6 | 3 | 9 | 1/9 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1/9 |
| C7 | 1/2 | 1/9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C7 | 1 | 1 | 1/9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1/9 |
| C8 | 1/2 | 1/9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | C8 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 1 |
Appendix C. The Coordinates of the Five Proposed New CDCs
| No. | Location (UTM Z38N) | District Name | |
| X(m) | Y(m) | ||
| 1 | 652,000 | 2,710,500 | Dahiat Namar |
| 2 | 695,500 | 2,727,000 | Khashm Al Ann |
| 3 | 667,000 | 2,760,000 | King Khalid Int Airport |
| 4 | 696,500 | 2,752,500 | An-Nadheem |
| 5 | 654,000 | 2,728,500 | Al-Mahdiyah |
References
- Civil Defense—Saudi Arabia. Available online: https://www.998.gov.sa/English/CDIntroduction/Pages/conceptofCD.aspx (accessed on 25 April 2020).
- Fire Fighting. Available online: https://www.998.gov.sa/English/FireFighting/Pages/FireFighting.aspx (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Li, X.; Yeh, A.G.O. Integration of genetic algorithms and GIS for optimal location search. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2005, 19, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri, M.A.; Mortagy, A.K.; Alsayed, C.A. A multi-objective model for locating fire stations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 110, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitarafan, M.; Hosseini, S.B.; Abazarlou, S.; Mahmoudzadeh, A. Selecting the optimal composition of architectural forms from the perspective of civil defense using AHP and IHWP methods. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2015, 11, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminasab, H.; Hashemkhani Zolfani, S.; Bitarafan, M.; Chatterjee, P.; Abhaji Ezabadi, A. The Role of Façade Materials in Blast-Resistant Buildings: An Evaluation Based on Fuzzy Delphi and Fuzzy EDAS. Algorithms 2019, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitarafan, M.; Hosseini, S.B.; Sabeti, N.; Bitarafan, A. The architectural evaluation of buildings’ indices in explosion crisis management. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Kim, M.-K.; Bae, J.; Sohn, H.-G. Selection of appropriate location for civil defense shelters using genetic algorithm and network analysis. J. Korean Soc. Surv. Geod. Photogramm. Cartogr. 2018, 36, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wen, J.; Jiang, Y. Agent-based evacuation simulation for spatial allocation assessment of urban shelters. In Proceedings of the ISPRS International Conference on Intelligent Earth Observing and Applications, Guilin, China, 23–25 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kaili, D.; Qingming, Z.; Shiguo, L. GIS-Based Responsibility Area Subdivision for Metropolitan Emergency Shelters—Case Study of Wuchang District, Wuhan City. In Proceedings of the 6th International Association for China Planning Conference (IACP), Wuhan, China, 17–19 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. GIS-based design of urban emergency shelter in Songbei Harbin. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 2012, 129, 617–622. [Google Scholar]
- Rooväli, L.; Kiivet, R.A. Geographical variations in hospital use in Estonia. Health Place 2006, 12, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, H.; Roderick, P.; Martin, D.; Barnett, S. Distance, rurality and the need for care: Access to health services in South West England. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2004, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mugiyo, H.; Chimonyo, V.G.P.; Sibanda, M.; Kunz, R.; Nhamo, L.; Masemola, C.R.; Dalin, C.; Modi, A.T.; Mabhaudhi, T. Multi-criteria suitability analysis for neglected and underutilised crop species in South Africa. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Z. Suitability evaluation for mountain-based adventure tourism: A case study of Xinjiang Tianshan, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafadi, K.; Mohammed, S.; Habib, H.; Kiwan, S.; Hennawi, S.; Sharaf, M. An integration of bioclimatic, soil, and topographic indicators for viticulture suitability using multi-criteria evaluation: A case study in the Western slopes of Jabal Al Arab—Syria. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 1466–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Alsafadi, K.; Ali, H.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Kiwan, S.; Hennawi, S.; Harsanyie, E.; Pham, Q.B.; Linh, N.T.T.; Ali, R.; et al. Assessment of land suitability potentials for winter wheat cultivation by using a multi criteria decision Support- Geographic information system (MCDS-GIS) approach in Al-Yarmouk Basin (S syria). Geocarto Int. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhanu, K.G.; Hatiye, S.D. Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Proxy Data: Case study of Megech Watershed, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 28, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Alazba, A.A. Integrated remote sensing and GIS-based approach for deciphering groundwater potential zones in the central region of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Dilawar, A. Mapping favorable groundwater potential recharge zones using a GIS-based analytical hierarchical process and probability frequency ratio model: A case study from an agro-urban region of Pakistan. Geosci. Front. 2020, 11, 1805–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Karim, A.A.; Awawdeh, M.M. Integrating GIS accessibility and location-allocation models with multicriteria decision analysis for evaluating quality of life in Buraidah city, KSA. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othman, A.A.; Al-Maamar, A.F.; Al-Manmi, D.A.M.; Veraldo, L.; Hasan, S.E.; Obaid, A.K.; Al-Quraishi, A.M.F. GIS-based modeling for selection of dam sites in the Kurdistan Region, Iraq. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Othman, A.A.; Obaid, A.K.; Al-Manmi, D.A.; Al-Maamar, A.F.; Hasan, S.E.; Liesenberg, V.; Shihab, A.T.; Al-Saady, Y.I. New Insight on Soil Loss Estimation in the Northwestern Region of the Zagros Fold and Thrust Belt. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H. GIS-based Fire Risk Assessment and Fire Station Site Selection—Taking Dujiangyan City as An Example. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Taiyuan, China, 16–18 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nyimbili, P.H.; Erden, T. GIS-based fuzzy multi-criteria approach for optimal site selection of fire stations in Istanbul, Turkey. Socio-Econ. Plann. Sci. 2020, 71, 100860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, A.E.; Taş, İ. Using GIS techniques for assessment of accessible forest lands by firefighting teams considering fire risk degrees. Eur. J. For. Eng. 2021, 6, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, B.; Díaz-Cuevas, P.; Ferreira, P.; Djebli, A.; Pérez, J.P. Mapping concentrated solar power site suitability in Algeria. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 838–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Tarabees, E. Integrated evaluation of urban development suitability based on remote sensing and GIS techniques: Contribution from the analytic hierarchy process. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 4, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkanou, K.; Karymbalis, E.; Papanastassiou, D.; Soldati, M.; Chalkias, C.; Gaki-Papanastassiou, K. Assessment of neotectonic landscape deformation in Evia Island, Greece, using GIS-based multi-criteria analysis. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. Ordered weighted averaging with fuzzy quantifiers: GIS-based multicriteria evaluation for land-use suitability analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2006, 8, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Karim, A.; Alogayell, H.M.; Alkadi, I.I.; Youssef, I. Mapping of GIS-Land Use Suitability in the Rural–Urban Continuum between Ar Riyadh and Al Kharj Cities, KSA Based on the Integrating GIS Multi Criteria Decision Analysis and Analytic Hierarchy Process. Environments 2020, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinci, H.; Özalp, A.Y.; Turgut, B. Agricultural land use suitability analysis using GIS and AHP technique. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 97, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, H.; Keihanfard, S.; Ahmad, B.B.; Amiri, M.J.T. Evaluating Boolean, AHP and WLC methods for the selection of waste landfill sites using GIS and satellite images. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4221–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raškauskaite, R.; Grigonis, V. An approach for the analysis of the accessibility of fire hydrants in urban territories. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murad, A.A. Using geographical information systems for defining the accessibility to health care facilities in Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia. Geospat. Health 2014, 8, S661–S669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlson, L.C.; Baker, O.N.; Schuur, J.D. A geospatial analysis of freestanding and hospital emergency department accessibility via public transit. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 20, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima, J.P.; Abitante, J.D.C.; Pons, N.A.D.; Senne, C.M. A spatial fuzzy multicriteria analysis of accessibility: A case study in Brazil. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.; Chen, N.; Islam, M.M.; Dewan, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Washakh, R.M.A.; Nepal, N.; Tian, S.; Faiz, H.; Alam, M.; et al. Location-allocation modeling for emergency evacuation planning with GIS and remote sensing: A case study of Northeast Bangladesh. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, P.; Thomas, I.; Geraets, D.; Goetghebeur, E.; Janssens, O.; Peeters, D.; Plastria, F. Locating fire stations: An integrated approach for Belgium. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 2012, 46, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tali, J.A.; Divya, S.; Nusrath, A. Location-allocation model applied to urban public services: Spatial analysis of fire stations in Mysore Urban Area Karnataka, India. Indones. J. Geogr. 2020, 35, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaeinejad, A.; Bolouri, S.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Panahi, M.; Lee, C.W. The Capacitated Location-Allocation Problem Using the VAOMP (Vector Assignment Ordered Median Problem) Unified Approach in GIS (Geospatial Information Systam). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Zeinivand, H.; Besharat, M. Flood hazard zoning in Yasooj region, Iran, using GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 1000–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, Y. An integrated spatial clustering analysis method for identifying urban fire risk locations in a network-constrained environment: A case study in Nanjing, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong, J.R.; Boakye, K.; Edziyie, R.; Owusu, A.Y.; Tiwari, C. Emergency fire response in Ghana: The case of fire stations in Kumasi. Afr. Geogr. Rev. 2017, 36, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, M.; Akcay, C. Construction site layout planning using GIS overlay analysis—A case study. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. On the use of weighted linear combination method in GIS: Common and best practice approaches. Trans. GIS 2000, 4, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hong, Y.; Yu, X.; Cerato, A.B.; Zhang, X.; Komac, M. Landslides susceptibility mapping in Oklahoma state using gis-based weighted linear combination method. In Landslide Science for a Safer Geoenvironment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Gan, T.Y. Irrigation water management in arid regions of Middle East: Assessing spatio-temporal variation of actual evapotranspiration through remote sensing techniques and meteorological data. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almannaa, M.H.; Alsahhaf, F.A.; Ashqar, H.I.; Elhenawy, M.; Masoud, M.; Rakotonirainy, A. Perception analysis of E-scooter riders and non-riders in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: Survey outputs. Sustainability 2021, 13, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, S.B. Managing urban growth and development in the Riyadh metropolitan area, Saudi Arabia. Habitat Int. 2004, 28, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King Abdullah Petroleum Studies and Research. Available online: https://datasource.kapsarc.org/explore/dataset/saudi-arabia-population-by-administrative-region-nationality-and-sex/information/?disjunctive.administrative_region&disjunctive.gender (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Riyadh Municipality. Available online: https://www.alriyadh.gov.sa/ar/riyadh/popudev (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Chaudhary, P.; Chhetri, S.K.; Joshi, K.M.; Shrestha, B.M.; Kayastha, P. Application of an Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) in the GIS interface for suitable fire site selection: A case study from Kathmandu Metropolitan City, Nepal. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 2016, 53, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, T.; Coşkun, M.Z. Multi-criteria site selection for fire services: The interaction with analytic hierarchy process and geographic information systems. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsley, D.A.; Kuh, E.; Welsch, R.E. Regression Diagnostics: Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780471691174. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishburn, P.C. Assignments Letters to the Editor. Oper. Res. 1967, 15, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Huq, M.E.; Cai, B.; Altan, O.; Li, Y. Integrated remote sensing and GIS approach using Fuzzy-AHP to delineate and identify groundwater potential zones in semi-arid Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 134, 104868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balezentiene, L.; Streimikiene, D.; Balezentis, T. Fuzzy decision support methodology for sustainable energy crop selection. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 17, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis: A survey of the literature. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 703–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.A.; Gloaguen, R.; Andreani, L.; Rahnama, M. Improving landslide susceptibility mapping using morphometric features in the Mawat area, Kurdistan Region, NE Iraq: Comparison of different statistical models. Geomorphology 2018, 319, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-J.-F.; Fabbri, A.G. Validation of spatial prediction models for landslide hazard mapping. Nat. Hazards 2003, 30, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jazirah. Available online: https://www.al-jazirah.com/2001/20011104/lp5.htm (accessed on 6 July 2021).
- Jozaghi, A.; Alizadeh, B.; Hatami, M.; Flood, I.; Khorrami, M.; Khodaei, N.; Tousi, E.G. A comparative study of the AHP and TOPSIS techniques for dam site selection using GIS: A case study of Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Iran. Geosciences 2018, 8, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noori, A.; Bonakdari, H.; Morovati, K.; Gharabaghi, B. The optimal dam site selection using a group decision-making method through fuzzy TOPSIS model. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2018, 38, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, H.-L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.-Y.; Cui, Y.-J. Study and implementation of fire sites planning based on GIS and AHP. Procedia Eng. 2011, 11, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).