Urban Development and the (Re)use of the Communist-Built Industrial and Agricultural Sites after 1990. The Showcase of Bucharest–Ilfov Development Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Context of Spatial Transformations in Romania: From Deindustrialization and Agricultural Restructuring to Post-Communist Urban Development
3. Study Area: Bucharest–Ilfov Development Region
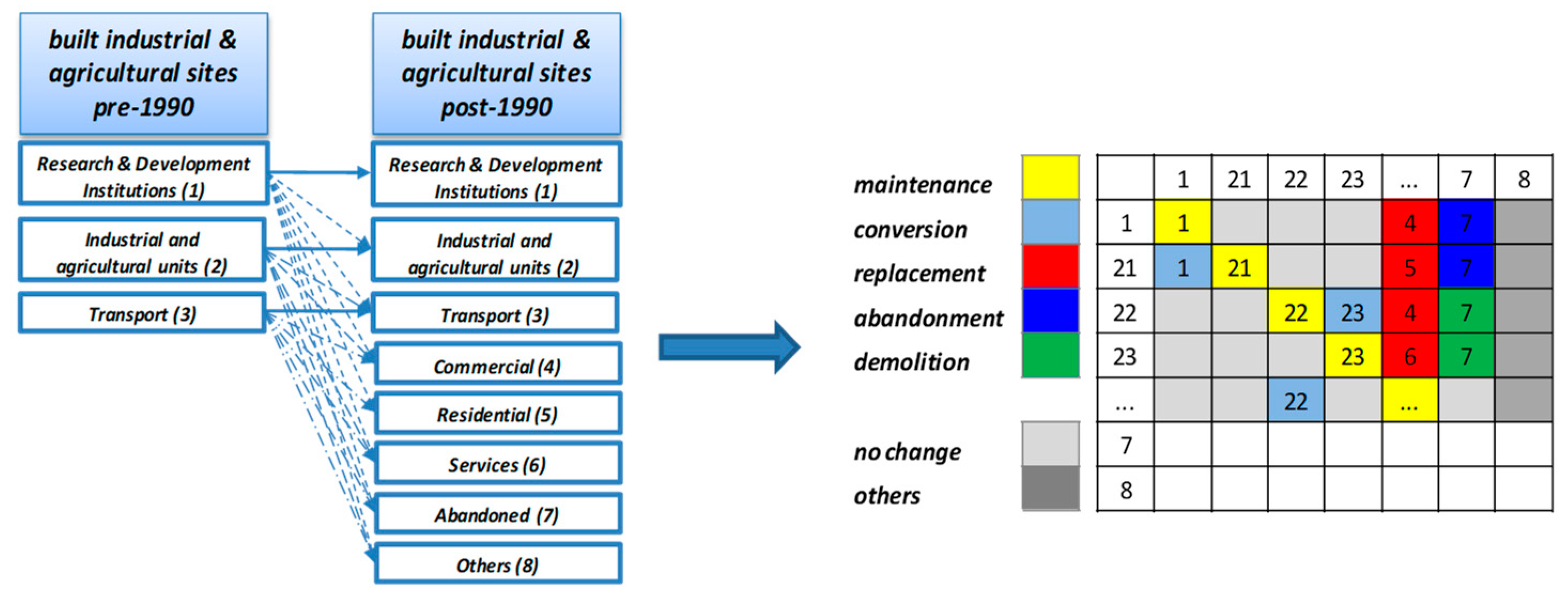
4. Materials and Methods
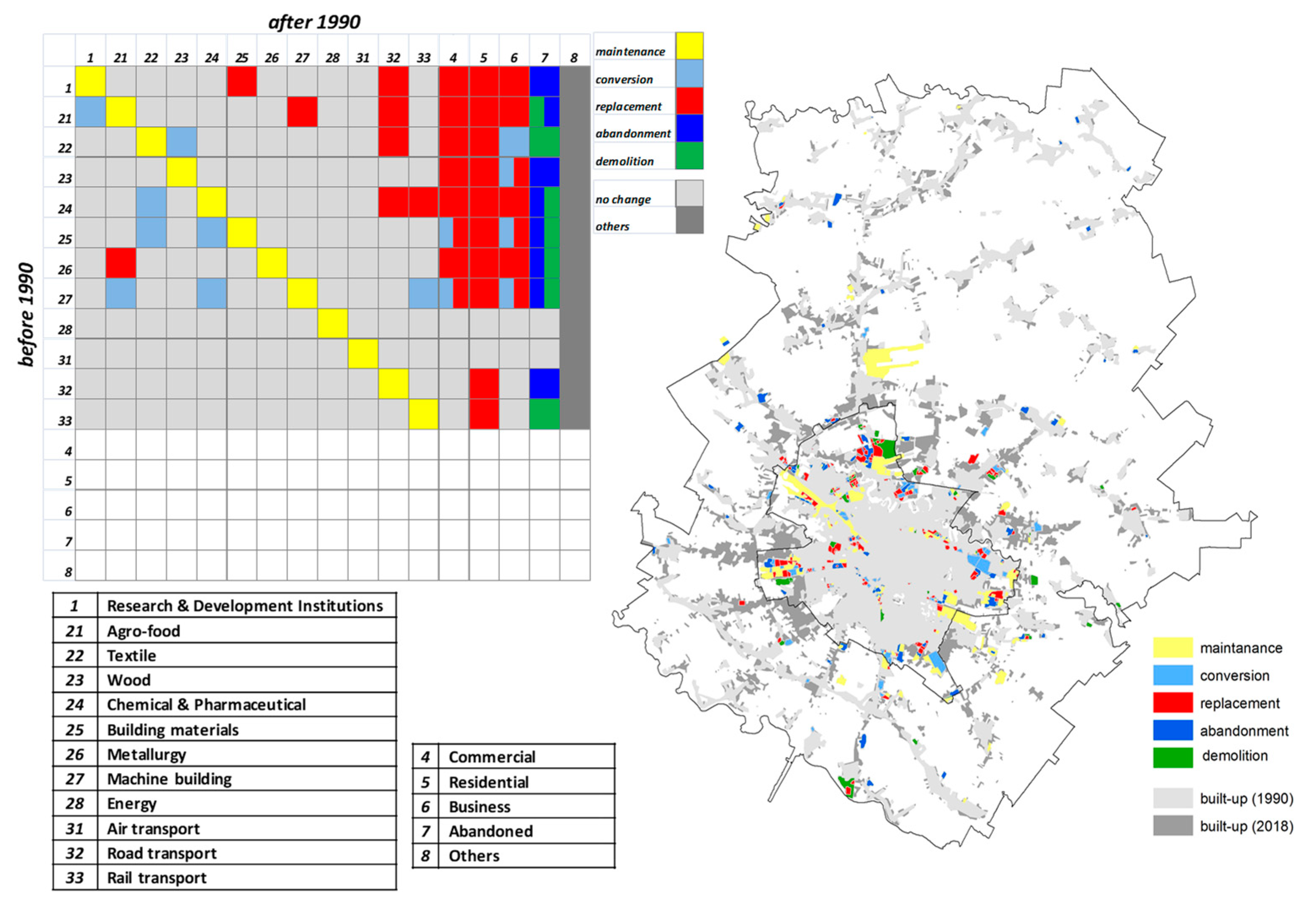
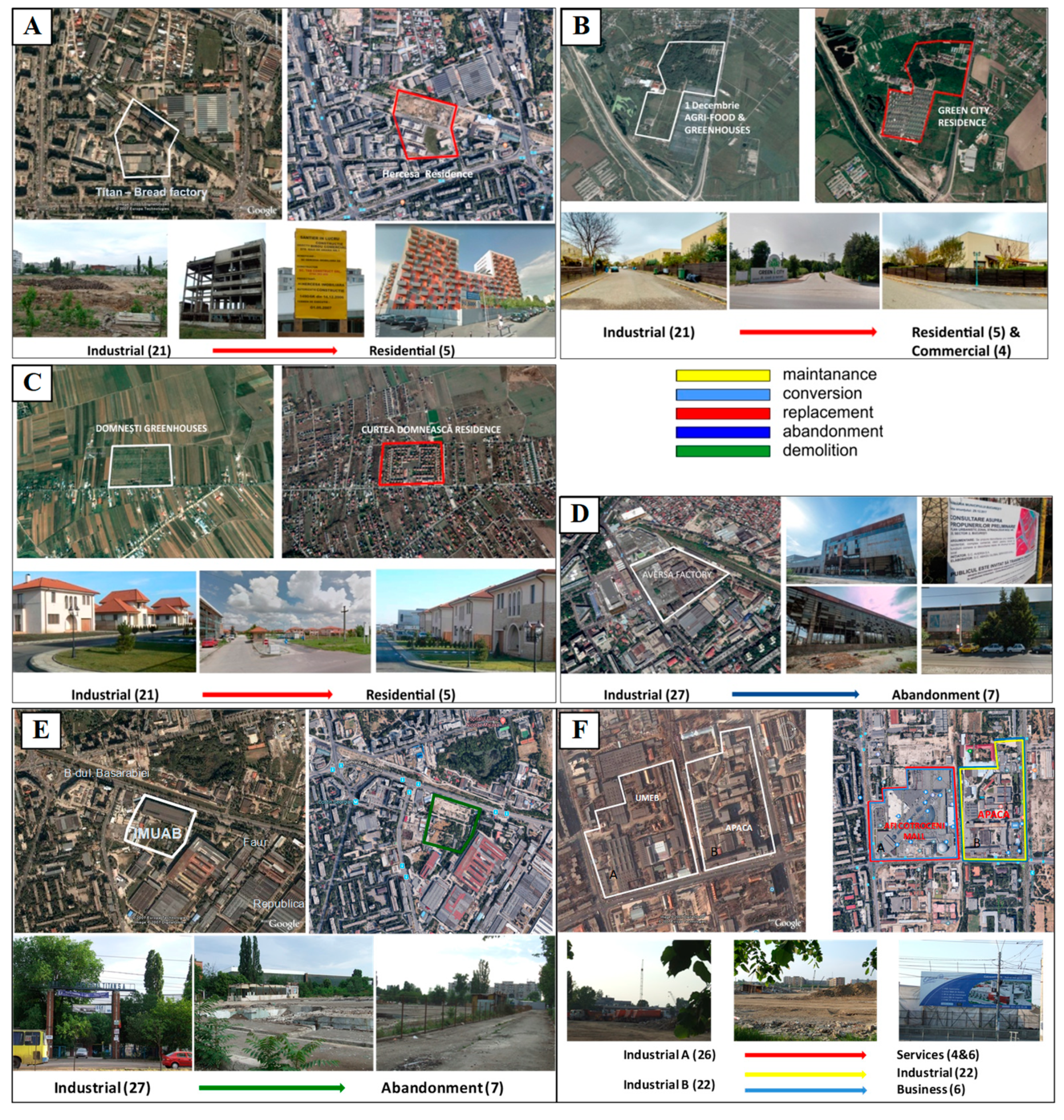
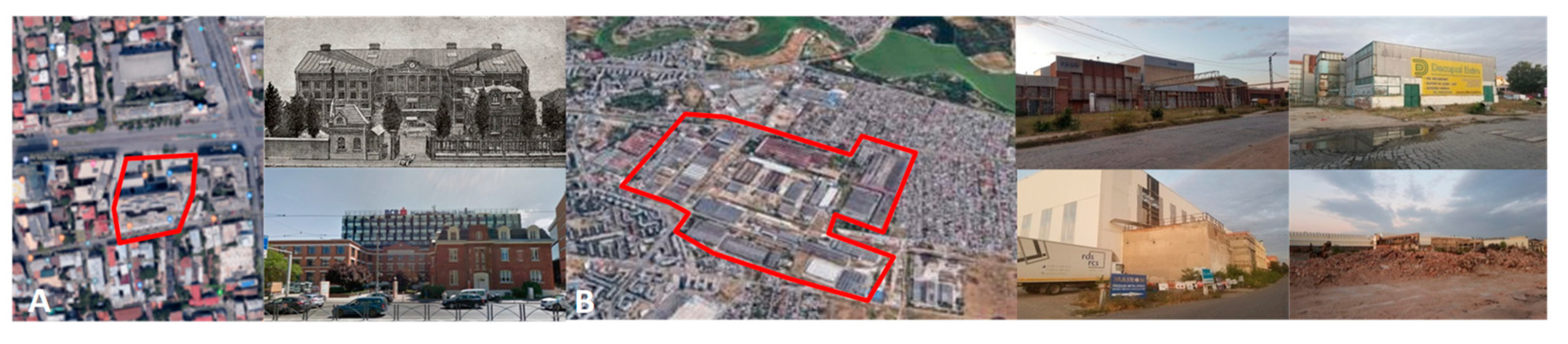
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mengüşoğlu, N.; Boyacioğlu, E. Reuse of industrial built heritage for residential purposes in Manchester. METU J. Fac. Archit. 2016, 30, 117–138. [Google Scholar]
- Popovici, E.A.; Bălteanu, D.; Kucsicsa, G. Assessment of changes in land-use and land-cover pattern in Romania using Corine Land Cover Database. Carpath. J. Earth Environ. 2013, 8, 195–208. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Ayllon, S. Urban transformations as indicators of economic change in post-communist Eastern Europe: Territorial diagnosis through five case studies. Habitat Int. 2017, 71, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrică, B.; Grigorescu, I.; Urucu, V. Dezvoltarea Urbană și Ariile Metropolitane. In Romania—Natură și Societate; Bălteanu, D., Dumitraşcu, M., Geacu, S., Mitrică, B., Sima, M., Eds.; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2016; pp. 250–291. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu, I.; Kucsicsa, G.; Popovici, E.-A.; Mitrică, B.; Dumitraşcu, M.; Mocanu, I. Regional disparities in the urban sprawl phenomenon in Romania using Corine Land Cover database. Rev. Roum. Géogr./Rom. Journ. Geogr. 2018, 62, 169–184. [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu, I.; Kucsicsa, G.; Popovici, E.A.; Mitrică, B.; Mocanu, I.; Dumitraşcu, M. Modelling land use/cover change to assess future urban sprawl in Romania. Geocarto Int. 2021, 36, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buček, J. Urban Development Policy Challenges in East-Central Europe: Governance, City Regions and Financialisation. Quaest. Geogr. 2016, 35, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuissl, H.; Siedentop, S. Urbanisation and Land Use Change. In Sustainable Land Management in a European Context, Human-Environment Interactions; Weith, T., Barkmann, T., Gaasch, N., Rogga, S., Strauß, C., Zscheischler, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 8, pp. 75–99. [Google Scholar]
- Loures, L. Post-industrial landscapes as drivers for urban redevelopment: Public versus expert perspectives towards the benefits and barriers of the reuse of post-industrial sites in urban areas. Habitat Int. 2015, 45, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottero, M.; D’Alpaos, C.; Oppio, A. Ranking of Adaptive Reuse Strategies for Abandoned Industrial Heritage in Vulnerable Contexts: A Multiple Criteria Decision Aiding Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osman, R.; Frantal, B.; Klusáček, P.; Kunc, J.; Martinát, S. Factors affecting brownfield regeneration in post-socialist space: The case of the Czech Republic. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sýkora, L.; Ourednicek, M. Sprawling post-communist metropolis: Commercial and residential suburbanisation in Prague and Brno, the Czech Republic. In Employment Deconcentration in European Metropolitan Areas; Razin, E., Dijst, M., Vázquez, C., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 91, pp. 209–233. [Google Scholar]
- Tosics, I. City development in central and eastern Europe since 1990: The impacts of internal forces. In Transformation of Cities in Central and Eastern Europe: Towards Globalisation; Hamilton, F.E.I., Dimitrowska-Andrews, K., Pichler-Milanovic’, N., Eds.; United Nations University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2005; pp. 44–78. [Google Scholar]
- Tsenkova, S.; Nedovic-Budic, Z. The Urban Mosaic of Post-Socialist Europe: Space, Institutions and Policy; Springer Science & Business Media: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sýkora, L. Post-socialist cities. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 8, pp. 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Sýkora, L.; Bouzarovski, S. Multiple transformations: Conceptualising the post-communist urban transition. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sýkora, L.; Stanilov, K. The challenge of post-socialist suburbanisation. In Confronting Suburbanisation: Urban Decentralization in Post-Socialist Central and Eastern Europe; Sýkora, L., Stanilov, K., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Malý, J.; Dvořák, P.; Šuška, P. Multiple transformations of post-socialist cities: Multiple outcomes? Cities 2020, 107, 102901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, A.; Wolff, M.; Špačková, P.; Radzimski, A. Reurbanisation in Post-socialist Europe - A ComparativeView of Eastern Germany, Poland, and the Czech Republic. Comp. Popul. Stud. 2017, 42, 353–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idczak, P.; Musiałkowska, I.; Mrozik, K. Ecosystem services in the appraisal of the economic performance of urban regeneration projects exemplified by the Jessica Initiative. Econ. Environ. 2019, 70, 114–129. [Google Scholar]
- Jadach-Sepioło, A.; Zathey, M. Alternative between Revitalisation of City Centres and the Rising Costs of Extensive Land Use from a Polish Perspective. Land 2021, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouředníček, M. Differential suburban development in the Prague urban region. Geogr. Ann. Ser. B, Hum. Geogr. 2007, 89, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazur, R.; Feranec, J.; Stych, P.; Kopecká, M.; Holman, L. Changes of urbanised landscape identified and assessed by the Urban Atlas data: Case study of Prague and Bratislava. Land Use Policy 2017, 61, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, H.; Kovacs, Z. The process of suburbanisation in the agglomeration of Budapest. J. Hous. Built Environ. 1999, 14, 119–141. [Google Scholar]
- Soós, G.; Ignits, G. Suburbanisation and its consequences in the Budapest metropolitan area. In Proceedings of the 3rd Euro Conference The European City in Transition, The City and the Region, Weimar, Germany, 14–15 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tosics, I. Spatial Restructuring in Post-Socialist Budapest; Physica-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 131–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, Z.; Farkas, J.Z.; Egedy, T.; Kondor, A.C.; Szabó, B.; Lennert, J.; Baka, D.; Kohán, B. Urban sprawl and land conversion in post-socialist cities: The case of metropolitan Budapest. Cities 2019, 92, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammaru, T.; Leetmaa, K.; Silm, S.; Ahas, R. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of the New Residential Areas around Tallinn. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2009, 17, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leetmaa, K.; Kährik, A.; Nuga, M.; Tammaru, T. Suburbanisation in the Tallinn metropolitan area. In Confronting Suburbanisation: Urban Decentralization in Post-Socialist Central and Eastern Europe; Wiley Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 192–224. [Google Scholar]
- Hirt, S. Post-Socialist Urban Forms: Notes From Sofia. Urban. Geogr. 2006, 27, 464–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, S. Suburbanising Sofia: Characteristics of post-socialist peri-urban change. Urban Geogr. 2007, 28, 755–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, S.; Kovachev, A. The changing spatial structure of post-socialist Sofia. In The Urban Mosaic of Post-Socialist Europe: Space, Institutions and Polic; Tsenkova, S., Nedovic-Budic, Z., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 113–130. [Google Scholar]
- Degórska, B. Spatial growth of urbanised land within the Warsaw Metropolitan Area in the first decade of the 21st century. Geogr. Pol. 2012, 85, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sławiński, T.; Sulmicki, M. The 3S Model of Urban Sprawl in the Warsaw Functional Area. MAZOWSZE Stud. Reg. 2015, 17, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mantey, D.; Sudra, P. Types of suburbs in post-socialist Poland and their potential for creating public spaces. Cities 2018, 88, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudra, P. Spatial dispersion and the concentration of buildings in an urban agglomeration—A typology proposal for the Warsaw Metropolitan Area. Environ. Socio-Econ. Stud. 2020, 8, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurkovich, M.; Gyurkovich, J. New Housing Complexes in Post-Industrial Areas in City Centres in Poland versus Cultural and Natural Heritage Protection—With a Particular Focus on Cracow. Sustainability 2021, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szubert, M.; Warcholik, W.; Żemła, M. The Influence of Elements of Cultural Heritage on the Image of Destinations, Using Four Polish Cities as an Example. Land 2021, 10, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschke, K.; Kirschke, P.; Komarzyńska-Świeściak, E. Adaptive reuse of commercial and public buildings in Wroclaw Old Town in Poland. The occupant’s safety and comfort versus preservation of authenticity of monumental buildings. Teka Kom. Archit. Urban. Studiów Krajobrazowych 2018, 14, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmytkie, R. Suburbanisation processes within and outside the city: The development of intra-urban suburbs in Wrocław, Poland. Morav. Geogr. Rep. 2021, 29, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozik, K.; Podawca, K.; Drożyńska, D. Spatial diversification of the implementation of planning and investment processes in the Poznań Metropolitan Area. Ekon. Sr. 2020, 4, 64–80. [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu, I.; Mitrică, B.; Mocanu, I.; Ticană, N. Urban sprawl and residential development in the Romanian Metropolitan Areas. Rev. Roum. Géogr./Rom. J. Geogr. 2012, 56, 43–59. [Google Scholar]
- Mihai, B.; Nistor, C.; Simion, G. Post-socialist urban growth of Bucharest, Romania—A change detection analysis on Landsat imagery (1984–2010). Acta Geogr. Slov. 2015, 55, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumitrache, L.; Zamfir, D.; Nae, M.; Simion, G.; Stoica, I.V. The Urban Nexus: Contradictions and Dilemmas of (Post) Communist (Sub) Urbanisation in Romania. Human Geogr. 2016, 10, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grigorescu, I.; Kucsicsa, G.; Mitrică, B.; Mocanu, I.; Dumitraşcu, M. Regional Spatial and Statistical Analyses of the Urban–rural Relationships in Romania. Case Study: Romanian Plain. In Smart Geography; Nedkov, S., Zhelezov, G., Ilieva, N., Nikolova, M., Koulov, B., Naydenov, K., Dimitrov, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 155–173. [Google Scholar]
- Kucsicsa, G.; Grigorescu, I. Urban Growth in the Bucharest Metropolitan Area: Spatial and Temporal Assessment Using Logistic Regression. J. Urban. Plan. Dev. 2018, 144, 05017013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, I.-V.; Vîrghileanu, M.; Zamfir, D.; Mihai, B.-A.; Săvulescu, I. Comparative Assessment of the Built-Up Area Expansion Based on Corine Land Cover and Landsat Datasets: A Case Study of a Post-Socialist City. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantal, B.; Greer-Wootten, B.; Klusáček, P.; Krejčí, T.; Kunc, J.; Martinát, S. Exploring spatial patterns of urban brownfields regeneration: The case of Brno, Czech Republic. Cities 2015, 44, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spórna, T. The suburbanisation process in a depopulation context in the Katowice conurbation, Poland. Environ. Socio-Econ. Stud. 2018, 6, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerstetter, D.; Confer, J.; Bricker, K. Industrial Heritage Attractions: Types and Tourists. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 1998, 7, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landorf, C. A Framework for Sustainable Heritage Management: A Study of UK Industrial Heritage Sites. Int. J. Heritage Stud. 2009, 15, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldpaus, L.; Roders, A.R.P.; Colenbrander, B.J.F. Urban Heritage: Putting the Past into the Future. Hist. Environ. Policy Pract. 2013, 4, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Judd, B.; Hawken, S. Adaptive reuse of industrial heritage for cultural purposes in Beijing, Shanghai and Chongqing. Struct. Surv. 2016, 34, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, S.; Gao, L. The Role of Community in Industrial Heritage Redevelopment: Evidence from Taigucang Wharf, Guangzhou, China. Asian J. Tour. Res. 2016, 1, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navratil, J.; Krejci, T.; Martinat, S.; Pasqualetti, M.J.; Klusacek, P.; Frantal, B.; Tochackova, K. Brownfields do not “only live twice”: The possibilities for heritage preservation and the enlargement of leisure time activities in Brno, the Czech Republic. Cities 2018, 74, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frantál, B.; Kunc, J.; Nováková, E.; Klusáček, P.; Martinát, S.; Osman, R. Location Matters! Exploring Brownfields Regeneration in a Spatial Context (A Case Study of the South Moravian Region, Czech Republic). Morav. Geogr. Rep. 2013, 21, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercleux, A.-L.; Merciu, F.-C.; Merciu, G.-L. Models of Technical and Industrial Heritage Re-Use in Romania. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 14, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copić, S.; Tumarić, A. Possibilities of industrial heritage reuse as tourist attractions: A case study of city of Zrenjanin (Vojvodina, Serbia). Geogr. Pannonica 2015, 19, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iancu, F.; Stoica, I. Tourist capitalization of industrial heritage elements: A strategic direction of sustainable development. Case study: Petroșani depression. GeoJ Tour. 2010, 5, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Filimon, L.; Nemes, V.; Olau, P. Urban regeneration in the context of current urban development policies in Romania. Case study: Ştei city (Bihor county, Romania). Rev. Rom. Geogr. Pol. 2012, XIV, 200–210. [Google Scholar]
- Boix, R.; Hervás-Oliver, J.L.; De-Miguel-Molina, B. Micro-geographies of creative industries clusters in Europe: From hot spots to assemblages. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2014, 94, 753–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S. Artists and Shanghai’s culture-led urban regeneration. Cities 2016, 56, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boca, M.C. Urban regeneration and gentrification in Romania. J. Geogr. Politi- Soc. 2018, 8, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boca, M.C. Theoretical and practical aspects of regeneration of decommissioned industrial areas in Oradea, Romania. J. Geogr. Politi- Soc. 2019, 9, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorescu, I.; Geacu, S. The dynamics and conservation of forest ecosystems in Bucharest Metropolitan Area. Urban. For. Urban. Green. 2017, 27, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G. Creative Cities, Creative Spaces and Urban Policy. Urban. Stud. 2009, 46, 1003–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Chan, R. The impact of ‘creative industry clusters’ on cultural and creative industry development in Shanghai. City, Cult. Soc. 2014, 5, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, E. The Adaptive Reuse of Industrial Heritage Buildings: A Multiple-Case Studies Approach. Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Langston, C.; Wong, F.K.; Hui, E.C.M.; Shen, L.-Y. Strategic assessment of building adaptive reuse opportunities in Hong Kong. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klusáček, P.; Alexandrescu, F.; Osman, R.; Malý, J.; Kunc, J.; Dvořák, P.; Frantal, B.; Havlíček, M.; Krejčí, T.; Martinát, S.; et al. Good governance as a strategic choice in brownfield regeneration: Regional dynamics from the Czech Republic. Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Shen, L.-Y.; Langston, C. A fuzzy approach for adaptive reuse selection of industrial buildings in Hong Kong. Int. J. Strat. Prop. Manag. 2014, 18, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I. Critical sustainable development factors in the adaptive reuse of urban industrial buildings. A fuzzy DEMATEL approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, S.; Cocean, P. Urban industrial brownfields: Constraints and opportunities in Romania. Carpath J. Earth Env. 2012, 7, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Merciu, F.C.; Cercleux, A.L.; Peptenatu, D.; Merciu, G.L.; Pintilii, R.; Drăghici, C.C. Revival of industrial towns through cultural regeneration–a viable solution. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Tourism and Economic Development (TED ‘11), Drobeta-Turnu Severin, Romania, 27–29 October 2011; pp. 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Merciu, F.-C.; Merciu, G.-L.M.; Cercleux, A.-L.; Drăghici, C. Conversion of industrial heritage as a vector of cultural regeneration. Procedia. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 122, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Cobârzan, B. Brownfield redevelopment in Romania. Transylv. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2007, 3, 28–46. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, G.; Patraşcoiu, R. Brownfield sites - between abandonment and redevelopment case study: Craiova city. Hum. Geogr. – J. Stud. Res. Hum. Geogr. 2012, 6, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moscovici, A.M.; Banescu, O.A.; Vaduva, R. Integrating brownfield sites into city redevelopment strategies. In Proceedings of the 17th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference, Surveying Geology & Mining, Albena, Bulgaria, 29 June–5 July 2017; Volume 17, pp. 675–682. [Google Scholar]
- Simion, G. Effects of post-socialist deindustrialization in Central and Eastern Europe: Results of an industrial site survey and GIS mapping in Bucharest City, Romania. Hum. Geogr. 2016, 10, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Moţcanu-Dumitrescu, M.A. Bucharest Municipality competitive local economic development through urban regeneration of destructured industrial areas. Urbanism. Arhitectură. Construcţii 2015, 6, 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jucu, I.S. Romanian Post-socialist Industrial Restructuring at the Local Scale: Evidence of Simultaneous Processes of De-/Reindustrialization in the Lugoj Municipality of Romania. J. Balk. Near East. Stud. 2015, 17, 408–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, L.P.; Iticescu, C.; Murariu, G.; Topa, C. Ecological revitalisation of brownfields–a challenge for Romania and Eastern Europe. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2014, 12, 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- Constantinescu, I.P.; Dascălu, D.; Sucală, C. An Activist Perspective on Industrial Heritage in Petrila, a Romanian Mining City. Public Hist. 2017, 39, 114–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzui, A.E.; Mirea, D.A.; Stoiculescu, R.C. The perception upon landscape revitalization of industrial spaces. Case study: The industrial units Belvedere Cigarette Factory and SC Mefin Sinaia. Rom. Rev. Reg. Stud. 2011, 7, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, C. Industrializarea României–de la Dezindustrializare la Reindustrializare. In Romania; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2016; pp. 375–404. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Nae, M.; Dumitrache, L.; Suditu, B.; Matei, E. Housing Activism Initiatives and Land-Use Conflicts: Pathways for Participatory Planning and Urban Sustainable Development in Bucharest City, Romania. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bălteanu, D.; Popescu, M.; Popovici, E.A. Agriculture. In Romania; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2006; pp. 228–235. [Google Scholar]
- Popovici, E.A.; Bălteanu, D.; Kucsicsa, G. Utilizarea Terenurilor și Dezvoltarea Actuală a Agriculturii. In Romania; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2016; pp. 329–374. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Ianoş, I.; Tălângă, C.; Braghină, C.; Gheorghe, C.A. Characteristics of the industrialization process around the moment of collapse of a centralized political system. Romania as a case study. Forum Geogr. 2010, 9, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, C. Industrial Restructuring. In Romania; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2006; pp. 236–256. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, C. Deindustrialization and urban shrinkage in Romania. What lessons for the spatial policy? Transylv. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2014, 10, 181–202. [Google Scholar]
- Săgeată, R.; Popescu, C. Regiunile de Dezvoltare şi Politica de Dezvoltare Regională. In Romania; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2016; pp. 604–608. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu, I.; Sima, M.; Mitrică, B.; Kucsicsa, G.; Dumitraşcu, M. A regional assessment of the man-made hazards. The case of Bucharest–Ilfov Development Region. In Proceedings of the 17th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference vol. 5 Ecology and Environmental Protection, Albena, Bulgaria, 29 June–5 July 2017; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bălteanu, D.; Mitrică, B.; Mocanu, I.; Sima, M.; Popescu, C. Caracterizarea Geografică a Regiunilor de Dezvoltare. In Romania; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2016; pp. 621–652. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Mitrică, B. Changes in the dynamics and demographic structures of the Romanian urban population. An overview of the post-communist period. Romanian J. Geogr. 2014, 58, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrică, B.; Persu, M.R.; Mocanu, I.; Şerban, P.; Grigorescu, I.; Damian, N. Changes in the Dynamics and Demographic Structure of the Romanian Rural Population: An Overview of the Post-communist Period, in vol. In Three Decades of Transformation in the East-Central European Countryside; Banski, J., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 191–215. [Google Scholar]
- Stănculescu, M.S.; Berevoiescu, I. Sărac Lipit, Caut Altă Viață! Fenomenul Sărăciei Extreme și al Zonelor Sărace în România; Nemira Publishing House: Bucharest, Romania, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Erdeli, G.; Simion, G. Local Decentralization and extended suburbanisation: A geographical approach of the metropolisation process in Romania. Bul. Soc. Geogr. Rom. 2006, XII, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Grădinaru, S.R.; Ioja, I.-C.; Onose, D.A.; Gavrilidis, A.A.; Pătru-Stupariu, I.; Kienast, F.; Hersperger, A.M. Land abandonment as a precursor of built-up development at the sprawling periphery of former socialist cities. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucsicsa, G.; Popovici, E.A.; Bălteanu, D.; Dumitraşcu, M.; Grigorescu, I.; Mitrică, B. Assessing the Potential Future Forest-Cover Change in Romania, Predicted Using a Scenario-Based Modelling. Environ. Model. Assess 2019, 25, 471–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.; James, K.; Reed, R. Using building adaptation to deliver sustainability in Australia. Struct. Surv. 2009, 27, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullen, P.A.; Love, P. Adaptive reuse of heritage buildings. Struct. Surv. 2011, 29, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medici, S.; De Toro, P.; Nocca, F. Cultural Heritage and Sustainable Development: Impact Assessment of Two Adaptive Reuse Projects in Siracusa, Sicily. Sustainability 2019, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aigwi, I.E.; Ingham, J.; Phipps, R.; Filippova, O. Identifying parameters for a performance-based framework: Towards prioritising underutilised historical buildings for adaptive reuse in New Zealand. Cities 2020, 102, 102756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borén, T.; Young, C. Conceptual export and theory mobilities: Exploring the reception and development of the “creative city thesis” in the post-socialist urban realm. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2016, 57, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Maps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Year | Scale | ||
| Topographic map | 1974–1978 | 1:25,000 | ||
| Topographic plan | 1967–1985 | 1:2000 | ||
| Satellite images | ||||
| source | year | data | Path/row | resolution |
| LANDSAT 4-5 TM | 1990 | 07 July | 182/029 | 30 m |
| 21 August | 183/029 | |||
| LANDSAT 8 OLI_TIRS | 2016 | 09 April | 182/029 | 30 m |
| 07 July | 183/029 | |||
| SENTINEL—2A, 2B | 2018 | 06 January | 206/050 | 10 m |
| 01 May | 206/050 | |||
| Level I | Level II |
|---|---|
| Research & Development Institutions (1) | |
| Industrial and agricultural units (2) | Agro-food (21) |
| Textile (22) | |
| Wood (23) | |
| Chemical and Pharmaceutical (24) | |
| Building materials (25) | |
| Metallurgy (26) | |
| Machine building (27) | |
| Energy (28) | |
| Transport (3) | Air (31) |
| Road (32) | |
| Rail (33) | |
| Commercial (4) | |
| Residential (5) | |
| Services (6) | |
| Abandoned (7) | |
| Others (8) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grigorescu, I.; Dumitrică, C.; Dumitrașcu, M.; Mitrică, B.; Dumitrașcu, C. Urban Development and the (Re)use of the Communist-Built Industrial and Agricultural Sites after 1990. The Showcase of Bucharest–Ilfov Development Region. Land 2021, 10, 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10101044
Grigorescu I, Dumitrică C, Dumitrașcu M, Mitrică B, Dumitrașcu C. Urban Development and the (Re)use of the Communist-Built Industrial and Agricultural Sites after 1990. The Showcase of Bucharest–Ilfov Development Region. Land. 2021; 10(10):1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10101044
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrigorescu, Ines, Cristina Dumitrică, Monica Dumitrașcu, Bianca Mitrică, and Costin Dumitrașcu. 2021. "Urban Development and the (Re)use of the Communist-Built Industrial and Agricultural Sites after 1990. The Showcase of Bucharest–Ilfov Development Region" Land 10, no. 10: 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10101044
APA StyleGrigorescu, I., Dumitrică, C., Dumitrașcu, M., Mitrică, B., & Dumitrașcu, C. (2021). Urban Development and the (Re)use of the Communist-Built Industrial and Agricultural Sites after 1990. The Showcase of Bucharest–Ilfov Development Region. Land, 10(10), 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10101044








