HYDRUS Simulation of Sustainable Brackish Water Irrigation in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
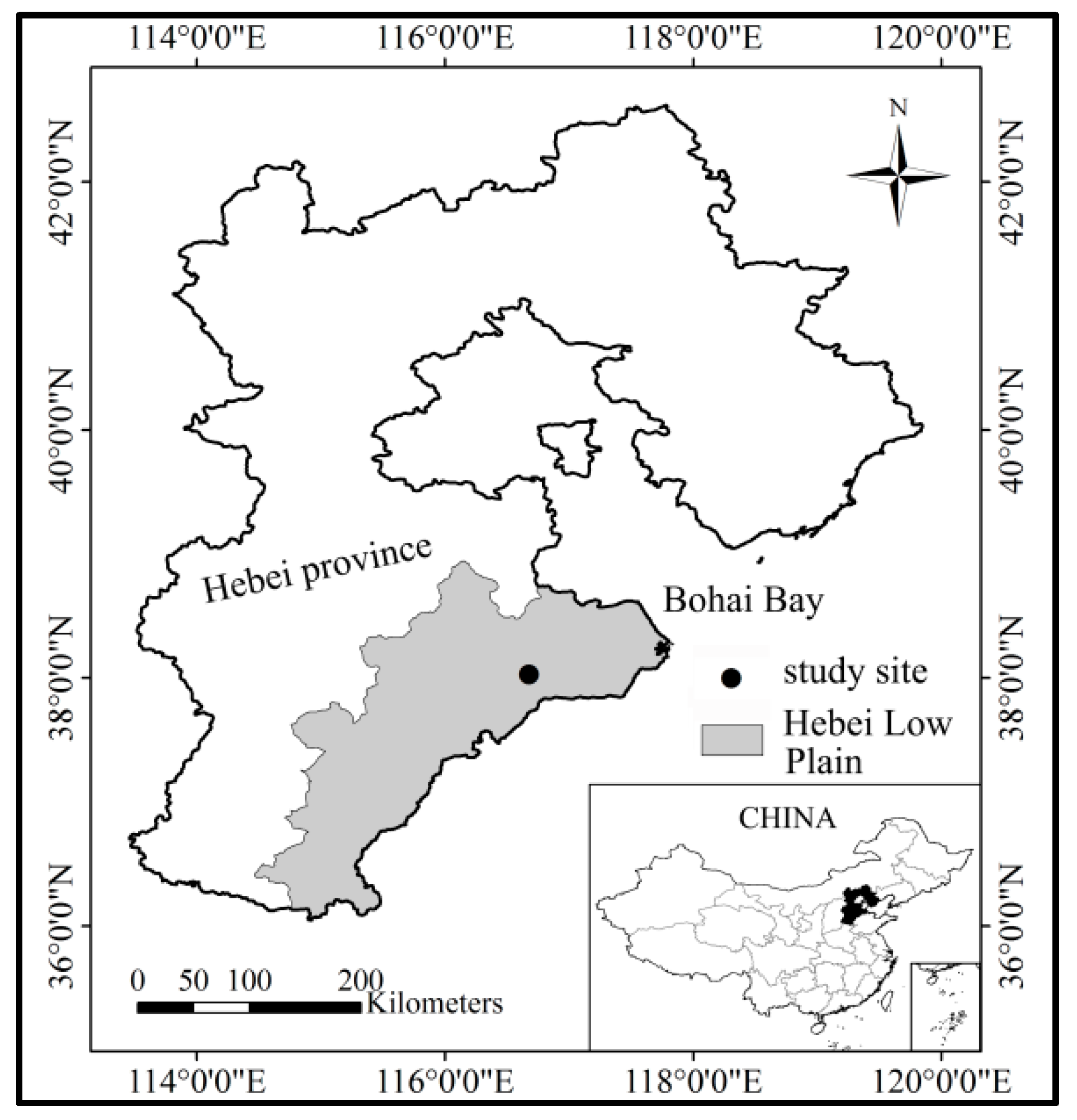
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
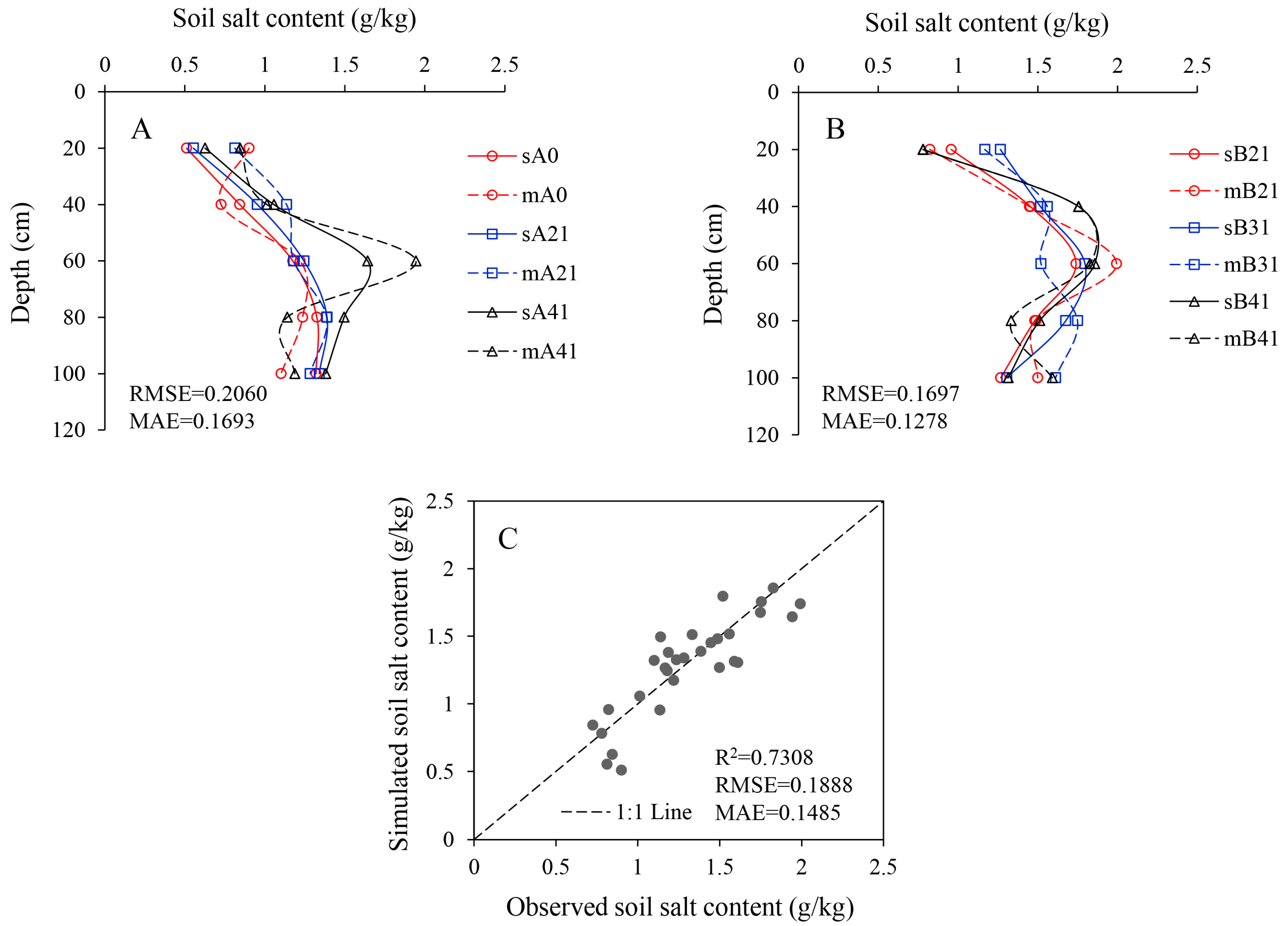
2.3. Model Calibration and Validation
2.4. Long-Term Irrigation Scheme Design
3. Results
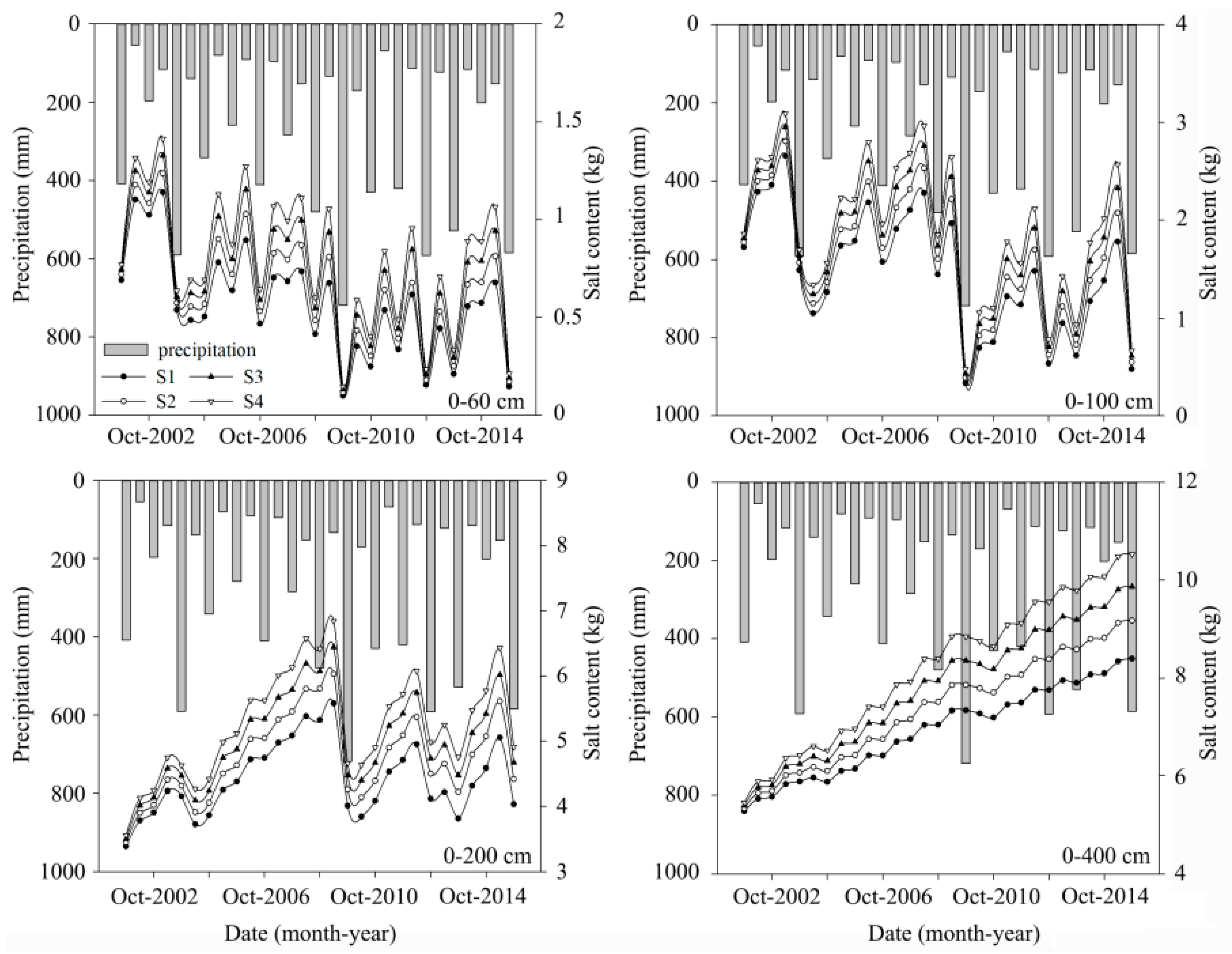
3.1. Soil Profile Salinity Variation
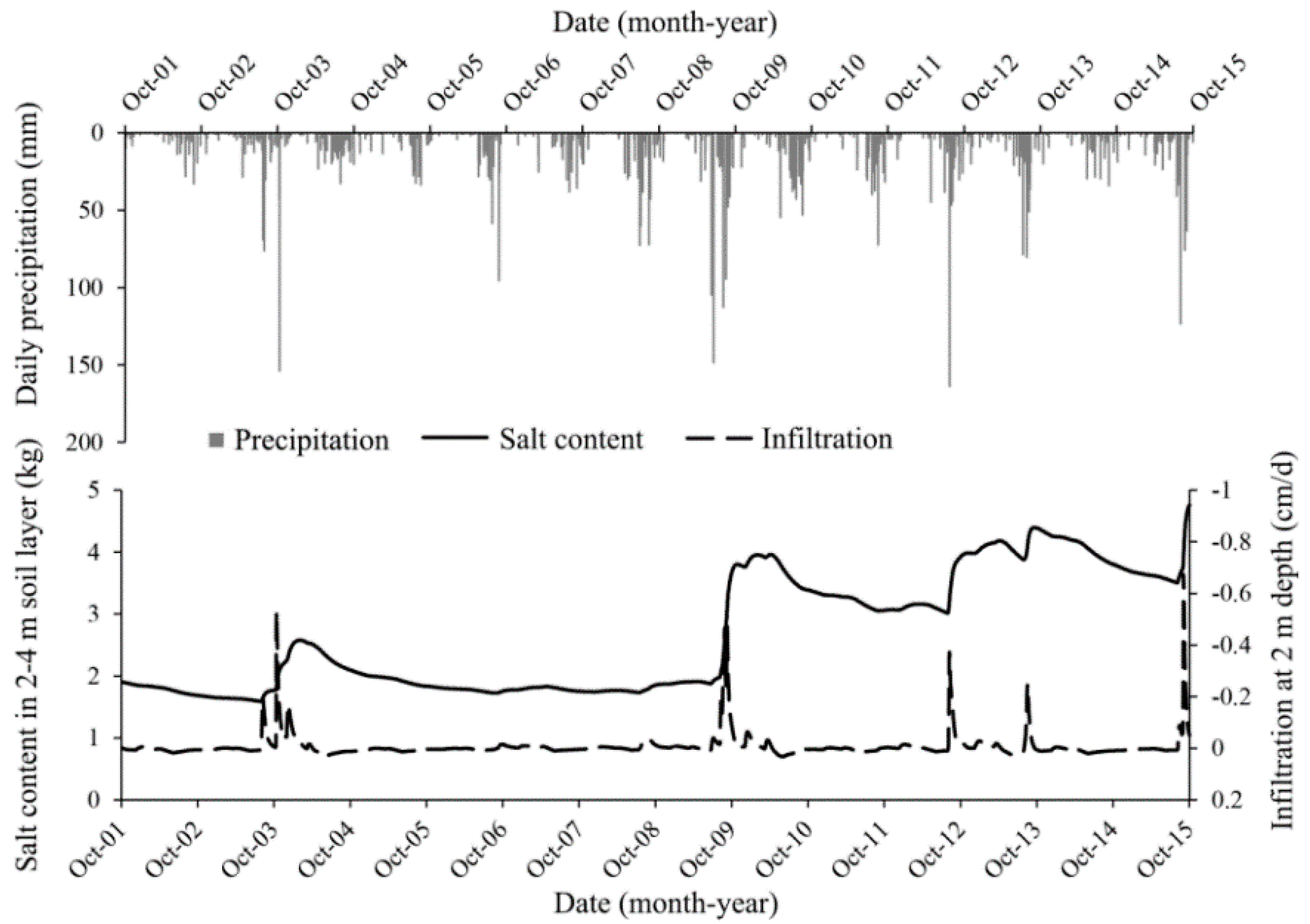
3.2. Effect of Precipitation on Salt Leaching
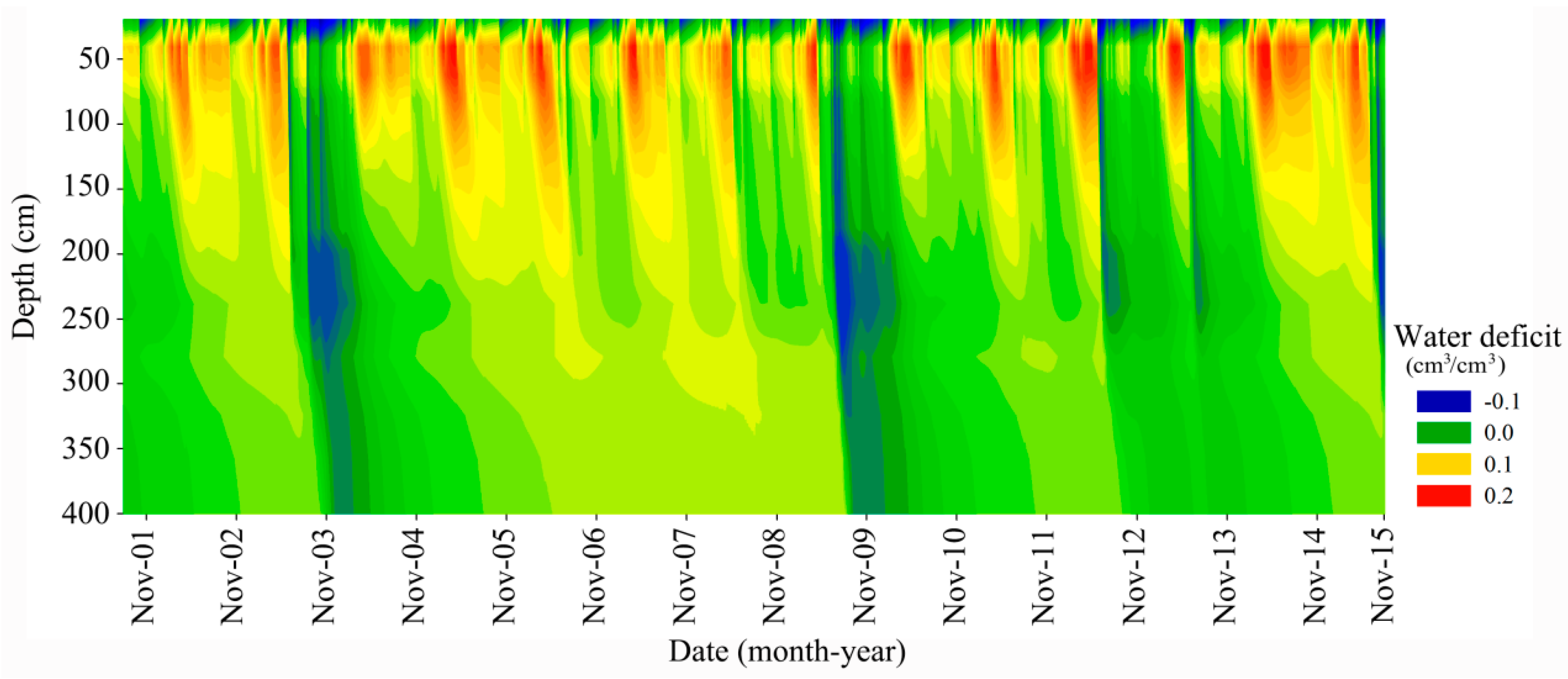
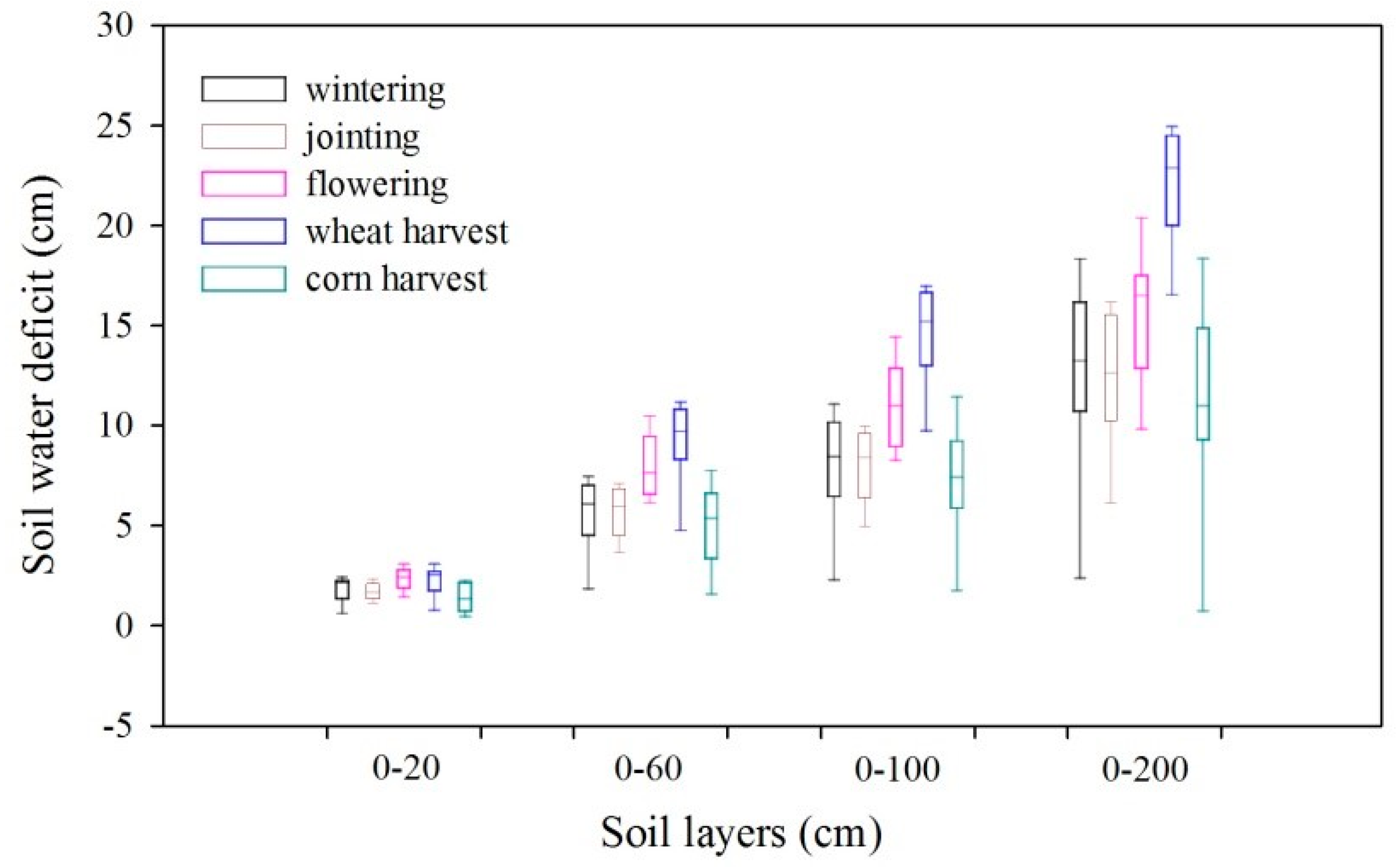
3.3. Soil Water Deficit and Critical Salt Leaching Season
4. Discussions
4.1. Brackish Water Irrigation Reliability
4.2. Heavy Rains Critical for Leaching Salt
4.3. Other Considerations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Water balance of global aquifers revealed by groundwater footprint. Nature 2012, 488, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatalovic, M. Irrigation reform needed in Asia. Nature 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S. Quaternary Aquifer of the North China Plain-assessing and achieving groundwater resource sustainability. Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sophocleous, M. Review: Groundwater management practices, challenges, and innovations in the High Plains aquifer, USA-lessons and recommended actions. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S. The Development and Prospect of Saline Soil Research in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 45, 837–843. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wada, Y.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Non-sustainable groundwater sustaining irrigation: A global assessment. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, G.L.; Zheng, C.M. Sustainability of groundwater resources in the North China Plain. In Sustaining Groundwater Resources; Anthony, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J. China faces up to groundwater crisis. Nature 2010, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiwo, J.P.; Yang, Y.H.; Li, H.L. Comparison of GRACE with in situ hydrological measurement data shows storage depletion in Hai River basin, Northern China. Water SA 2009, 35, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.L.; Scanlon, B.R.; Han, D.M. Impacts of thickening unsaturated zone on groundwater recharge in the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Liu, J.; Cao, G.; Kendy, E.; Wang, H.; Jia, Y. Can China cope with its water crisis?—Perspectives from the North China Plain. Groundwater 2010, 48, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Fei, Y.H. Sustainable exploitable potential of shallow groundwater in the North China Plain. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2014, 22, 890–897. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J. Study and Assessment on Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater in North China Plain; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 362–370. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Shao, L.W.; Sun, H.Y. Effect of brackish water irrigation on soil salt balance and yield of both winter wheat and summer maize. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2016, 24, 1049–1058. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.W.; Til, F.K.; Chen, S.Y. Effects of saline irrigation on soil salt accumulation and grain yield in the winter wheat-summer maize double cropping system in the low plain of North China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2886–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Yang, J.S.; Liu, G.M.; Yao, R.J.; Yu, S.P. Impact of irrigation volume and water salinity on winter wheat productivity and soil salinity distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.J.; Chen, Q.J.; Li, L.T.; Yu, Z.R.; Niu, L. Effect of slight saline water irrigation on soil salinity and yield of crop. Trans. CSAE 2010, 26, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tarek, S.; Berndtsson, R.; Magnus, P.; Ahmed, M. Influence of geometric design of alternate partial root-zone subsurface drip irrigation (APRSDI) with brackish water on soil moisture and salinity distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 103, 182–190. [Google Scholar]
- Mass, E.V.; Hoffman, G.J. Crop salt tolerance-current assessment. J. Irrig. Drain Div. 1977, 103, 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa, M.S.; Josan, A.S.; Hira, G.S.; Singh, N.T. Effect of sustained saline irrigation on soil salinity and crop yields. Irrig Sci. 1986, 7, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askri, B.; Ahmed, A.T.; Abichou, T. Effects of shallow water table, salinity and frequency of irrigation water on the date palm water use. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, K.A.; Woodbury, A.D. Transient, spatially varied groundwater recharge modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4593–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Sejna, M. HYDRUS: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, T.B.; Simunek, J.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Martins, J.C.; Prazeres, A.; Castanheira, N.L.; Pereira, L.S. Field evaluation of a multicomponent solute transport model in soils irrigated with saline waters. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.Z.; Ren, S.M.; Yang, P.L.; Huang, L.M. Modeling the risk of the salt for polluting groundwater irrigation with recycled water and ground water using HYDRUS-1D. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.J.; Huang, J.S.; Gao, Z.Y. Study on water and salt transportation of different irrigation modes by the simulation of HYDRUS model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 44, 826–834. [Google Scholar]
- Goncalves, M.C.; Šimůnek, J.; Tiago, B.; Pires, F.P. Multicomponent solute transport in soil lysimeters irrigated with waters of different quality. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzari, S.; Hachicha, M.; Bouhlila, R. Characterization and modeling of water movement and salts transfer in a semi-arid region of Tunisia (BouHajla, Kairouan)—Salinization risk of soils and aquifers. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 86, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Liu, G.M.; Yang, J.S.; Huang, G.H.; Yao, R.J. Evaluating the effects of irrigation water salinity on water movement, crop yield and water use efficiency by means of a coupled hydrologic/crop growth model. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 185, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zeng, W.Z.; Wu, J.W. Effects of different irrigation strategies on soil water, salt, and nitrate nitrogen transport. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2015, 22, 589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.Z. Hebei Soil Species; Hebei Science and Technology Publishing: Shijiazhuang, China, 1992. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Chen, X.L. Study on the utilization and transformation of shallow groundwater. Hebei Hydraul. Sci. Technol. 1999, 20, 6–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Šimůnek, J.; Šejna, M.; Van Genuchten, M.T. The Hydrus-1D Software Package for Simulating the One-dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-saturated Media; University of California-Riverside Research Reports: Riverside, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Xu, C.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Soil salt leaching under different irrigation regimes: HYDRUS-1D modelling and analysis. J. Arid Land. 2014, 6, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.L.; Shen, Y.J.; Pei, H.W. Estimating groundwater recharge using deep vadose zone data under typical irrigated cropland in the piedmont region of the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.K.; Yang, Y.M.; Yang, Y.H. HYDRUS-1D model simulation of soil water and salt movement under various brackish water use schemes in North China Low-plain. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2016, 24, 1059–1070. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.J.; Yi, J.; Zhang, J.G.; Zhao, Y.; Si, B.C.; Hill, R.L.; Cui, L.L.; Liu, X.Y. Modeling of Soil Water and Salt Dynamics and Its Effects on Root Water Uptake in Heihe Arid Wetland, Gansu, China. Water 2015, 7, 2382–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums. J. Appl. Phys. 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchtenn, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddes, R.A.; Kowalik, P.J.; Zaradny, H. Simulation of Field Water Use and Crop Yield; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Wesseling, J.G.; Elbers, J.A.; Kabat, P. SWATRE: Instructions for Input, Internal Note, Winand Staring Centre, Wageningen, the Netherlands; International Water Logging and Salinity Research Institute: Lahore, Pakistan, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Belmans, C.; Wesseling, J.G.; Feddes, R.A. Simulation model of the water balance of a cropped soil: SWATRE. J. Hydrol. 1983, 63, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, R.K.M.; Porter, J.R. The Physiology of Crop Yield, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, S.W.; Gilley, J.R.; Splinter, W.E. A simplified model of corn growth under moisture stress. Trans. ASAE 1977, 20, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.D.; Wang, Q.J. Response to salt stress about winter wheat in Huanghuaihai Plain. Trans. CSAM 2010, 41, 99–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Pei, D. Evapotranspiration, yield and crop coefficient of irrigated maize under straw mulch conditions. Prog. Geol. 2002, 21, 583–592. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, A.W.; Sun, J.S.; Liu, Y. Irrigation Water Quota of Main Crops in North China; China Agricultural Science and Technology Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 60–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Kandiah, A.; Mashali, A.M. The Use of Saline Waters for Crop Production; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 48; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bresler, E.; McNeal, B.L.; Carter, D.L. Saline and Sodic Soils: Principles Dynamics-modeling; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.F.; Zhang, G.Y.; Li, Y.Z. Comparative and relationship of the different methods to expressing soil salinity. In Movement of Water and Salt in Saline Soil; Beijing Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 57–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shao, L.W.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.W. Effect of deficit irrigation with brackish water on growth and yield of winter wheat and summer maize. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2011, 19, 579–585. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, M.G.; Leij, F.J.; van Genuchten, M.T. Rosetta: A computer program for estimating soil hydraulic parameters with hierarchical pedotransfer functions. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.A.; Wang, Q.J.; Huang, M.B. Soil Physics; High Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 203–205. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.Y.; Shen, Y.J.; Yu, Q. Effect of precipitation change on water balance and WUE of the winter wheat–summer maize rotation in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 29 Rev. 1; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Rameshwaran, P.; Tepe, A.; Yazar, A.; Ragab, R. Effects of drip-irrigation regimes with saline water on pepper productivity and soil salinity under greenhouse conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 199, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Huo, Z.L.; Zhang, L.D. Impact of saline water irrigation on water use efficiency and soil salt accumulation for spring maize in arid regions of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 163, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.C.; Li, Y.Y.; Yang, J.S. Effect of brackish water irrigation and straw mulching on soil salinity and crop yields under monsoonal climatic conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiremit, M.S.; Arslan, H. Effects of irrigation water salinity on drainage water salinity, evapotranspiration and other leek (Allium porrum L.) plant parameters. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 201, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Lei, J.Q.; Zhao, Y. Effect of saline water irrigation on soil development and plant growth in the Taklimakan Desert Highway shelterbelt. Soil Till. Res. 2015, 146, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.J.; Mao, Z.Q.; Yu, Z.R.; Driessen, P.M. Effects of saline water irrigation on soil salinity and yield of winter wheat–maize in North China Plain. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2008, 22, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Kang, Y.H.; Wan, S.Q. Reclamation of very heavy coastal saline soil using drip-irrigation with saline water on salt-sensitive plants. Soil Till. Res. 2015, 146, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Hou, Z.N.; Wu, L.S. Evaluating salinity distribution in soil irrigated with saline water in arid regions of northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 2001–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.B.; Li, R. Estimation of effective hydraulic parameters in heterogeneous soils at field scale. Geoderma 2016, 264, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, A.K.; Šimůnek, J.; Hanjra, M.A.; Avliyakulov, M.; Forkutsa, I. Effects of the shallow water table on water use of winter wheat and ecosystem health: Implications for unlocking the potential of groundwater in the Fergana Valley (Central Asia). Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhao, C.Y.; Šimůnek, J.; Feng, G. Evaluating the impact of groundwater on cotton growth and root zone water balance using Hydrus-1D coupled with a crop growth model. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouse, P.J.; Ayars, J.E.; Simunek, J. Simulating root water uptake from a shallow saline groundwater resource. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekakis, E.H.; Antonopoulos, V.Z. Modeling the effects of different irrigation water salinity on soil water movement, uptake and multicomponent solute transport. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.B.; Shao, M.A. Effects of temperature changes on soil hydraulic properties. Soil Till. Res. 2015, 153, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.A.; Bachmann, J. Effect of temperature on capillary pressure. In Environmental Mechanics: Water, Mass and Energy Transfer in the Biosphere: The Philip Volume; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridasan, M.; Jensen, R.D. Effect of temperature on pressure head–water content relationship and conductivity of two soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1972, 36, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, H.R. Water temperature fluctuations and effect on irrigation infiltration. Trans. ASAE 1992, 35, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharabaghi, B.; Safadoust, A.; Mahboubi, A.A.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Unc, A.; Ahrens, B.; Sayyad, G. Temperature effect on the transport of bromide and E. coli NAR in saturated soils. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Depth (cm) | Texture | Soil Particle Size Distribution (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.002 mm | 0.002–0.05 mm | 0.05–2 mm | ||
| 0–20 | Sandy loam | 16.6 | 27.3 | 56.1 |
| 20–60 | Sandy loam | 17.3 | 22.1 | 60.6 |
| 60–200 | Sandy loam | 18.8 | 26.4 | 54.8 |
| 200–260 | loam | 19.5 | 37.2 | 43.3 |
| 260–320 | Sandy loam | 15.9 | 26.2 | 57.9 |
| 320–400 | Sandy loam | 16.0 | 32.0 | 52.0 |
| Crop Water Potential | h0 (cm) | hopt (cm) | h2H (cm) | h2L (cm) | h3 (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter wheat | 0 | −1 | −500 | −900 | −16 000 |
| Summer maize | −15 | −30 | −325 | −600 | −8 000 |
| Soil Depth (cm) | Model Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θr (cm3/cm3) | θs (cm3/cm3) | α (cm−1) | n | Ks (cm/d) | l | |
| 0–20 | 0.0437 | 0.3938 | 0.0108 | 1.3592 | 37.54 | 0.5 |
| 20–60 | 0.0748 | 0.4706 | 0.0078 | 1.2932 | 26.66 | 0.5 |
| 60–200 | 0.0758 | 0.4517 | 0.0093 | 1.2461 | 24.55 | 0.5 |
| 200–260 | 0.0602 | 0.3989 | 0.0108 | 1.5027 | 14.17 | 0.5 |
| 260–320 | 0.0534 | 0.4045 | 0.0194 | 1.4456 | 31.88 | 0.5 |
| 320–400 | 0.0551 | 0.4000 | 0.0153 | 1.4623 | 23.21 | 0.5 |
| Year | Hydrological Year | Precipitation (mm) | Winter Wheat | Summer Maize | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation (mm) & Water Quality (g/L) | Irrigation (mm) & Water Quality (g/L) | ||||||
| Winter | Jointing | Flowering | Grain-filling | Sowing | |||
| 2000–2001 | Normal | 525.8 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | 70(0.84) | |
| 2001–2002 | Very dry | 251.6 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | 60(0.84) | 70(0.84) |
| 2002–2003 | Wet | 707.2 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | 70(0.84) | |
| 2003–2004 | Normal | 482.2 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | ||
| 2004–2005 | dry | 338.9 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | 70(0.84) | |
| 2005–2006 | Normal | 502.3 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | ||
| 2006–2007 | dry | 379.5 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | 70(0.84) | |
| 2007–2008 | Wet | 632.6 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | ||
| 2008–2009 | Very wet | 852.8 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | ||
| 2009–2010 | Wet | 600.8 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | |||
| 2010–2011 | Normal | 488.8 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | 60(0.84) | 70(0.84) |
| 2011–2012 | Wet | 705.0 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | ||
| 2012–2013 | Wet | 651.7 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | ||
| 2013–2014 | Very dry | 316.9 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | 70(0.84) | |
| 2014–2015 | Wet | 738.4 | 60(2) | 60(2/3/4/5) | 60(0.84) | 70(0.84) | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, K.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, Q.; Liu, X.; Gao, F. HYDRUS Simulation of Sustainable Brackish Water Irrigation in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain. Water 2017, 9, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070536
He K, Yang Y, Yang Y, Chen S, Hu Q, Liu X, Gao F. HYDRUS Simulation of Sustainable Brackish Water Irrigation in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain. Water. 2017; 9(7):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070536
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Kangkang, Yonghui Yang, Yanmin Yang, Suying Chen, Qiuli Hu, Xiaojing Liu, and Feng Gao. 2017. "HYDRUS Simulation of Sustainable Brackish Water Irrigation in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain" Water 9, no. 7: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070536
APA StyleHe, K., Yang, Y., Yang, Y., Chen, S., Hu, Q., Liu, X., & Gao, F. (2017). HYDRUS Simulation of Sustainable Brackish Water Irrigation in a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain. Water, 9(7), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070536





