Phosphorus Dynamics along River Continuum during Typhoon Storm Events
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Field Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
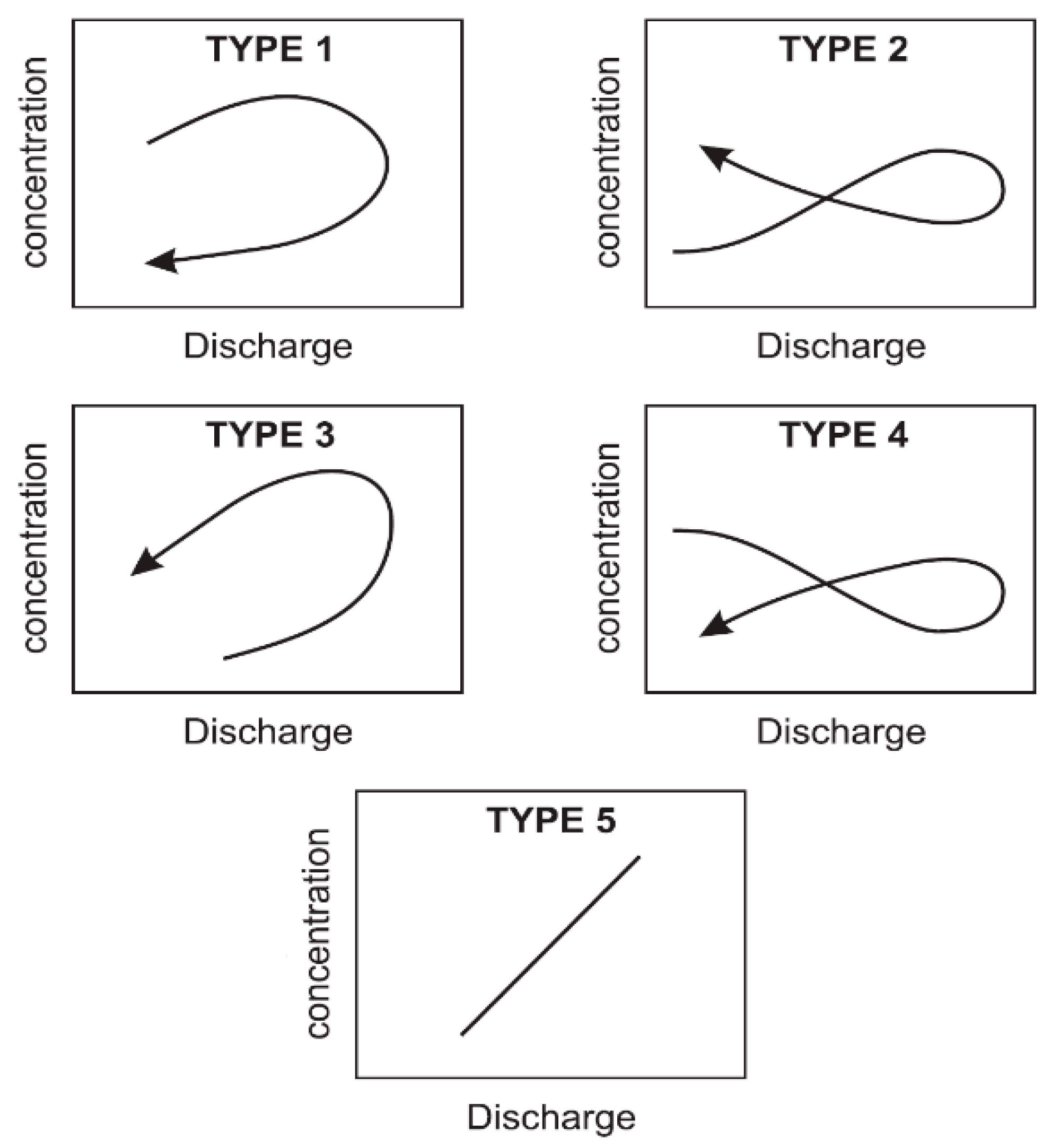
2.4. Hysteresis Loop Analysis
3. Results
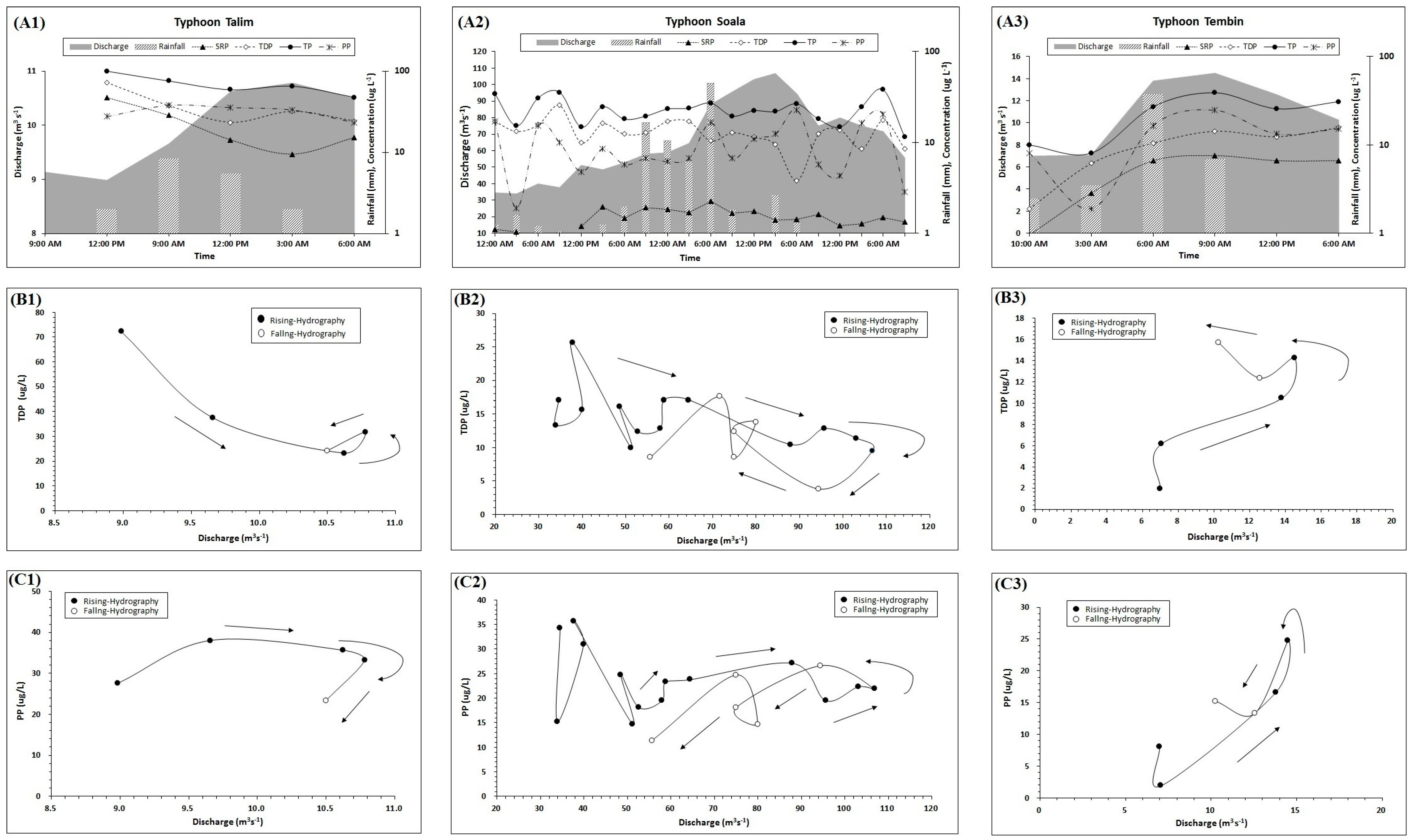
3.1. Storm Characteristics
3.2. Flow-Weighted Phosphorus Concentrations and Fluxes
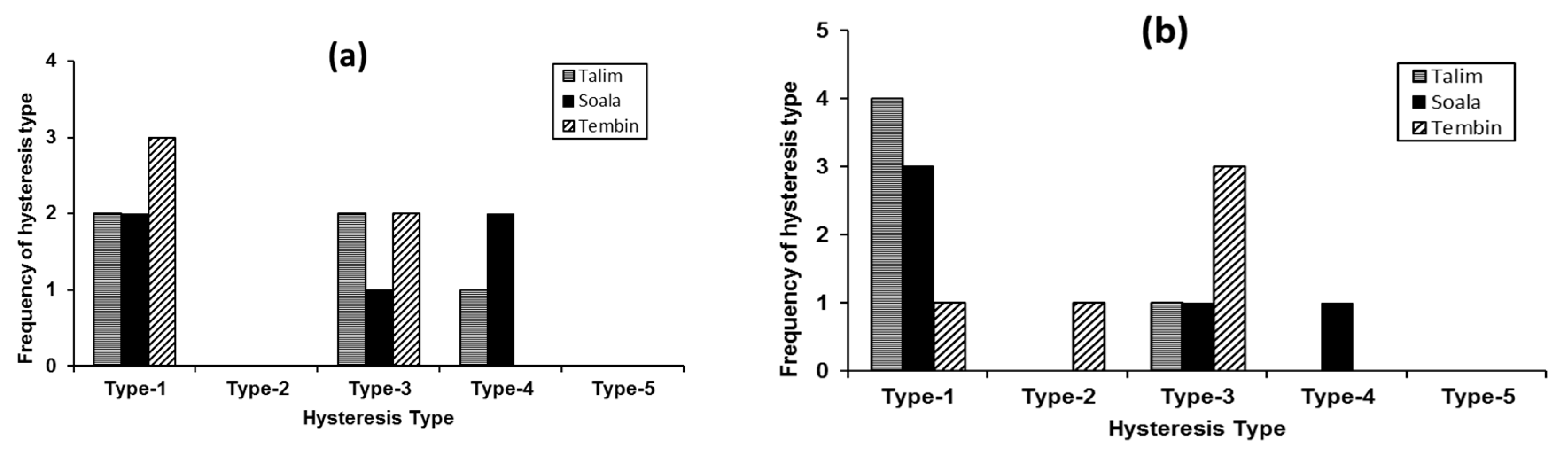
3.3. Hysteresis Patterns of Phosphorus
3.4. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Phosphorus Fractions
3.5. Hydrological Factors Controlling P Transport
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Compton, J.; Mallison, D.; Glenn, C.; Filippelli, G.; Föllmi, K.; Shields, G.; Zanin, Y. Variations in the global phosphorus cycle. In Marine Authigenesis: From Global to Microbial: 66 (SEPM Special Publication); SEPM (Society of Sedimentary Geology): Tulsa, OK, USA, 2000; pp. 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Teubner, K. Phytoplankton, pelagic community and nutrients in a deep oligotrophic alpine lake: Ratios as sensitive indicators of the use of P-resources (DRP:DOP:PP and TN:TP:SRSi). Water Res. 2003, 37, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E. Anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen and phosphorus and riverine export for Illinois, USA. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, T.V.; David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E. Timing of riverine export of nitrate and phosphorus from agricultural watersheds in Illinois: Implications for reducing nutrient loading to the Mississippi River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4126–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidon, P.; Tedesco, L.P.; Pascual, D.L.; Campbell, M.A.; Casey, L.R.; Wilson, J.; Gray, M. Seasonal changes in stream water quality along an agricultural/urban land-use gradient. Proc. Indiana Acad. Sci. 2008, 117, 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kronvang, B.; Laubel, A.; Grant, R. Suspended sediment and particulate phosphorus transport and delivery pathways in an arable catchment, Gelbaek stream, Denmark. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.W.; Wilcock, R.J. Particulate phosphorus transport within streamflow of an agricultural catchment. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, R.W.; Jensen, H.S.; Marino, R.; Postma, H. Transport to and processing of P in near-shore and oceanic waters. In Phosphorus in the Global Environment: Transfers, Cycles and Management; Tiessen, H., Ed.; John Willey & Son, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 323–345. [Google Scholar]
- Meybeck, M. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus transport by rivers. Am. J. Sci. 1982, 282, 401–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, W.A.; Warwick, M.S. Intensive measurements of nutrient dynamics in the River Swale. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 210, 111–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fukushima, T.; Onda, Y.; Gomi, T.; Fukuyama, T.; Sidle, R.; Kosugi, K.; Matsushige, K. Nutrient runoff from forested watersheds in central Japan during typhoon storms: Implications for understanding runoff mechanisms during storm events. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.F.; Shiah, F.K.; Lai, C.C.; Kuo, H.Y.; Wang, K.W.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, T.Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ko, C.Y. Evaluation of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of Fei-Tsui Reservoir basin, Taiwan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhao, C.; Bai, J.; Lou, H.; Chen, K.; Wu, L.; Dong, G.; Zhou, Q. Assessment of Non-Point Source Total Phosphorus Pollution from Different Land Use and Soil Types in a Mid-High Latitude Region of China. Water 2016, 8, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehetner, F.; Vemuri, M.L.; Huh, C.A.; Kao, S.J.; Hsu, S.C.; Chen, Z.S. Soil and phosphorus re-distribution along a steep tea plantation in Feitsui Reservoir catchment of northern Taiwan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2008, 54, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, D.; Walling, D.E.; Leeks, G.J.L. Mobilisation and transport of sediment-associated phosphorus by surface runoff. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 196, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, M.J.; Smith, J.T.; Neal, C. The value of high-resolution nutrient monitoring: A case study of the River Frome, Dorset, UK. J. Hydrol. 2009, 378, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Liu, J.H.; Kuo, J.T.; Lin, C.F. Estimation of phosphorus flux in rivers during flooding. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 5653–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.F.; Lin, J.Y. Estimating the gross budget of applied nitrogen and phosphorus in tea plantations. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachter, R.; Ngatiah, J.M.; Stamm, C. Transport of phosphate from soil to surface waters by preferential flow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.Y.; Huang, J.C.; Kao, S.J.; Tung, C.P. Temporal variation of nitrate and phosphate transport in headwater catchments: The hydrological controls and land use alteration. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 2617–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Blanco, M.L.; Taboada-Castro, M.M.; Taboada-Castro, M.T. Sediment and phosphorus loss in runoff from an agroforestry catchment, NW, Spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 1611–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Hsu, L.H.; Yang, Y.T. Temporal and spatial characteristics of typhoon extreme rainfall in Taiwan. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 90, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.Y.; Chou, C. Changes in precipitation frequency and intensity in the vicinity of Taiwan: Typhoon versus non-typhoon events. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 014023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; Meijgaard, E. Increase in hourly precipitation extremes beyond expectations from temperature changes. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.K.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.W.; Hegerl, G.C. Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature 2011, 470, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.; Neelin, J.D.; Chen, C.A.; Tu, J.Y. Evaluating the rich-get-richer mechanism in tropical precipitation change under global warming. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 1982–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA (American Public Health Association); AWWA (American Water Works Association); WEF (Water Environment Federation). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; APHA; AWWA; WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagstad, N.; Deelstra, J.; Eggestad, H.O. Discharge and measurement, sampling techniques and their influences on calculated sediment and phosphorus loss from agricultural area. In Sediment and Phosphorus: Erosion and Delivery, Transport and Fate of Sediments and Sediment-Associated Nutrients in Watersheds; NERI Technical Report 178; National Environmental Research Institute: Silkeborg, Denmark, 1996; pp. 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bowes, M.J.; House, W.A.; Hodginson, R.A.; Leach, D.V. Phosphorus-discharge hysteresis during storm events along a river catchment: The River Swale, UK. Water Res. 2005, 39, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, C.E.M.; Freer, J.E.; Johnes, P.J.; Collins, A.L. Using hysteresis analysis of high-resolution water quality monitoring data, including uncertainty, to infer controls on nutrient and sediment transfer in catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, W.A.; Warwick, M.S. Hysteresis of the solute concentration/discharge relationship in rivers during storms. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, M.; Errea, M.P.; Beguería, S.; Arnáez, J.; Martí-Bono, C.; García-Ruiz, J.M. Catchment soil moisture and rainfall characteristics as determinant factors for discharge/suspended sediment hysteretic loops in a small headwater catchment in the Spanish Pyrenees. J. Hydrol. 2004, 288, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.P. Sediment concentration versus water discharge during single hydrologic events. J. Hydrol. 1989, 111, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashige, Y. Mechanisms of sediment supply in headwater rivers. Trans. Jpn. Geomorphol. Union 1994, 15A, 109–129. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, S. Effects of the Phosphorus Forms of the Watershed on the Speciation of Phytoplankton: A Case Study of the Two Subtropical Deep Reservoirs in Taiwan. Crit. Trans. Water Environ. Resour. Manag. 2004, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Lin, T.C.; Hwong, J.L.; Lin, N.H.; Wang, C.P.; Hamburg, S. Typhoon impacts on stream water chemistry in a plantation and an adjacent natural forest in central Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 2009, 378, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hong, H. Phosphorus export during storm events from a human perturbed watershed, southeast China: Implications for coastal ecology. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 166, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, M.J.; House, W.A.; Hodgkinson, R.A. Phosphorus dynamics along a river continuum. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, P.N.; Walling, D.E. The phosphorus content of fluvial sediment in rural and industrialized river basins. Water Res. 2002, 36, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Sharpley, A.N.; Saporito, L.S.; Buda, A.R.; Bryant, R.B. Application of manure to no-till soils: Phosphorus losses by sub-surface and surface pathways. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2009, 84, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.F.; Yusop, Z.; Toriman, M.E. Stormwater runoff quality and pollutant loading from commercial, residential, and industrial catchments in the tropic. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8321–8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.; Williams, R.J.; Neal, M.; Bhardwaj, L.C.; Wickham, H.; Harrow, M.; Hill, L.K. The water quality of the River Thames at a rural site downstream of Oxford. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 251, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.F.; Yusop, Z. Sizing first flush pollutant loading of stormwater runoff in tropical urban catchments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4047–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Zhuo, M.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y. Quality characterization and impact assessment of highway runoff in urban and rural area of Guangzhou, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 140, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Blanco, M.L.; Taboada-Castro, M.M.; Taboada-Castro, M.T. Phosphorus transport into a stream draining from a mixed land use catchment in Galicia (NW Spain): Significance of runoff events. J. Hydrol. 2013, 481, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Shaner, P.J.L.; Wang, L.J.; Shih, Y.T.; Wang, C.P.; Huang, G.H.; Huang, J.C. Effects of mountain tea plantations on nutrient cycling at upstream watersheds. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4493–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, M.J.; Jarvie, H.P.; Halliday, S.J.; Skeffington, R.A.; Wade, A.J.; Loewenthal, M.; Gozzard, E.; Newman, J.R.; Palmer-Felgate, E.J. Characterising phosphorus and nitrate inputs to a rural river using high-frequency concentration–flow relationships. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stutter, M.I.; Langan, S.J.; Cooper, R.J. Spatial contributions of diffuse inputs and within-channel processes to the form of stream water phosphorus over storm events. J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, D.; Walling, D.; Collins, A.; Leeks, G.L. Phosphorus storage in fine channel bed sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2006, 6, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, D.J.; Walling, D.E.; Collins, A.L.; Leeks, G.J.L. The content and storage of phosphorus in fine-grained channel bed sediment in contrasting lowland agricultural catchments in the UK. Geoderma 2009, 151, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Jurgens, M.D.; Williams, R.J.; Neal, C.; Davies, J.J.L.; Barrett, C.; White, J. Role of river bed sediments as sources and sinks of phosphorus across two major eutrophic UK river basins: The Hampshire Avon and Herefordshire wye. J. Hydrol. 2005, 304, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Site | Sampling Site Coordinate | Stream | Area (km2) | Percentage of Land Use (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Forest | Road | Water | Building | Other | ||||
| S1 | 24°56′31.1″ N 121°42′46.6″ E | Xia-Keng-Zi | 5.58 | 19.1 | 72.7 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| S2 | 24°56′9.3″ N 121°42′46.0″ E | Bei-Shih | 110.47 | 4.8 | 90.6 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.7 |
| S3 | 24°55′56.5″ N 121°42′19.1″ E | Dai-Yu | 78.86 | 2.1 | 95.5 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.7 |
| S4 | 24°55′57.8″ N 121°41′24.5″ E | Bei-Shih | 195.52 | 4.1 | 91.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 1.5 |
| S5 | 24°55′46.7″ N 121°41′29.9″ E | Jin-Gua | 22.92 | 5.4 | 92.3 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 1.0 |
| Typhoon | Parameter | Unit | Site | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |||
| Talim 19 June–21 June | Rdep | (mm) | 46.5 | 46.5 | 34.5 | 46.5 | 53.5 |
| Rdur | (h) | 67 | 67 | 67 | 67 | 67 | |
| I | (mm/h) | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.51 | 0.69 | 0.80 | |
| Imax | (mm/h) | 4.5 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 4.5 | 4.0 | |
| Qave | (m3·s−1) | 0.28 | 5.51 | 2.85 | 9.74 | 2.33 | |
| Qpeak | (m3· s−1) | 0.31 | 6.20 | 3.95 | 10.97 | 5.30 | |
| ADD | (day) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | |
| API5 | (mm) | 45.1 | 45.1 | 23.0 | 45.1 | 152.5 | |
| Soala 31 July–3 August | Rdep | (mm) | 669 | 669 | 922 | 669 | 687 |
| Rdur | (h) | 117 | 117 | 117 | 117 | 117 | |
| I | (mm/h) | 5.70 | 5.70 | 7.90 | 5.70 | 5.90 | |
| Imax | (mm/h) | 39.0 | 39.0 | 59.5 | 39.0 | 46.5 | |
| Qave | (m3· s−1) | 1.88 | 37.6 | 21.95 | 73.08 | 10.29 | |
| Qpeak | (m3 ·s−1) | 3.27 | 65.36 | 49.59 | 115.68 | 29.55 | |
| ADD | (day) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| API5 | (mm) | 130.9 | 130.9 | 227.8 | 130.9 | 116.5 | |
| Tembin 28 August–29 August | Rdep | (mm) | 63.5 | 63.5 | 63.0 | 63.5 | 54.0 |
| Rdur | (h) | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 | |
| I | (mm/h) | 1.87 | 1.87 | 1.85 | 1.87 | 1.59 | |
| Imax | (mm/h) | 20.5 | 20.5 | 19.0 | 20.5 | 14.0 | |
| Qave | (m3· s−1) | 0.29 | 5.74 | 2.46 | 10.22 | 0.99 | |
| Qpeak | (m3· s−1) | 0.49 | 9.79 | 5.79 | 17.33 | 2.35 | |
| ADD | (day) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| API5 | (mm) | 64.0 | 64.0 | 85.0 | 64.0 | 63.7 | |
| Site | Typhoon | Flow-Weighted Concentration | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | TDP | SRP | PP | Temp. | pH | EC | TSS | NVSS | ||
| μg/L | μg/L | μg/L | μg/L | °C | μmho/cm | mg/L | mg/L | |||
| S1 | Talim | 21.37 | 13.30 | 7.44 | 8.07 | 22.67 | 7.69 | 115.82 | 3.55 | 2.29 |
| Soala | 28.34 | 14.87 | 1.64 | 13.47 | 23.00 | 7.16 | 63.89 | 120.58 | 107.75 | |
| Tembin | 22.96 | 12.63 | 4.82 | 10.32 | 23.71 | 7.55 | 85.26 | 13.02 | 4.37 | |
| mean | 27.56 | 14.65 | 2.22 | 12.92 | 23.00 | 7.22 | 68.80 | 106.75 | 94.98 | |
| Base flow | 46.59 | 26.51 | 4.04 | 20.09 | 25.20 | 7.86 | 134.0 | 1.43 | - | |
| S2 | Talim | 22.50 | 12.41 | 6.12 | 10.09 | 23.25 | 7.49 | 69.61 | 3.18 | 1.92 |
| Soala | 21.35 | 11.99 | 1.24 | 9.35 | 23.17 | 6.93 | 36.33 | 187.12 | 185.53 | |
| Tembin | 18.01 | 12.99 | 5.77 | 5.02 | 24.62 | 7.48 | 62.23 | 15.90 | 5.13 | |
| mean | 21.28 | 12.07 | 1.82 | 9.21 | 23.25 | 7.00 | 40.05 | 165.28 | 163.28 | |
| Base flow | 17.59 | 12.96 | 5.70 | 4.64 | 25.30 | 7.99 | 62.00 | 1.95 | - | |
| S3 | Talim | 21.33 | 15.58 | 6.03 | 5.76 | 23.13 | 7.63 | 79.12 | 3.28 | 2.05 |
| Soala | 25.90 | 14.61 | 1.57 | 11.29 | 23.45 | 7.03 | 34.22 | 346.80 | 326.37 | |
| Tembin | 19.58 | 9.06 | 5.57 | 10.52 | 24.32 | 7.60 | 63.43 | 16.71 | 9.86 | |
| mean | 25.30 | 14.42 | 2.06 | 10.88 | 23.47 | 7.10 | 38.60 | 308.37 | 289.87 | |
| Base flow | 29.48 | 15.69 | 3.56 | 13.79 | 25.10 | 7.89 | 83.00 | 2.41 | - | |
| S4 | Talim | 84.75 | 53.95 | 29.47 | 30.80 | 25.21 | 8.46 | 67.89 | 5.85 | 3.83 |
| Soala | 22.97 | 12.59 | 1.47 | 10.39 | 23.92 | 6.44 | 35.46 | 170.00 | 156.49 | |
| Tembin | 20.16 | 8.65 | 5.42 | 11.52 | 24.63 | 7.51 | 65.60 | 17.96 | 9.76 | |
| mean | 27.69 | 15.64 | 3.86 | 12.04 | 24.06 | 6.65 | 39.47 | 149.74 | 137.39 | |
| Base flow | 24.41 | 17.24 | 29.94 | 7.17 | 26.40 | 9.20 | 74.00 | 2.90 | - | |
| S5 | Talim | 34.95 | 23.30 | 14.69 | 11.66 | 22.91 | 7.70 | 76.47 | 5.00 | 3.53 |
| Soala | 26.32 | 15.14 | 1.70 | 11.18 | 24.26 | 6.98 | 35.21 | 608.50 | 572.73 | |
| Tembin | 24.74 | 8.97 | 4.30 | 15.77 | 24.56 | 7.58 | 69.69 | 17.07 | 7.70 | |
| mean | 27.12 | 15.76 | 3.04 | 11.35 | 24.13 | 7.06 | 40.19 | 533.22 | 501.52 | |
| Base flow | 72.27 | 36.85 | 8.55 | 35.42 | 24.90 | 8.05 | 81.00 | 3.92 | - | |
| Site | Typhoon | Percentage of Ratio (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRP:TDP | TDP:TP | DOP:TDP | PP:TP | SRP:TP | DOP:TP | ||
| S1 | Talim | 55.93 | 62.23 | 44.07 | 37.77 | 34.78 | 27.43 |
| Soala | 11.01 | 52.47 | 88.99 | 47.53 | 5.78 | 46.69 | |
| Tembin | 38.17 | 55.04 | 61.83 | 44.96 | 20.95 | 34.19 | |
| S2 | Talim | 49.32 | 55.15 | 50.68 | 44.85 | 27.20 | 27.94 |
| Soala | 10.38 | 56.18 | 89.62 | 43.82 | 5.83 | 50.35 | |
| Tembin | 44.40 | 72.14 | 55.60 | 27.86 | 32.03 | 40.10 | |
| S3 | Talim | 38.73 | 73.01 | 61.27 | 26.99 | 28.28 | 44.73 |
| Soala | 10.76 | 56.41 | 89.24 | 43.59 | 6.07 | 50.34 | |
| Tembin | 61.50 | 46.26 | 38.50 | 53.74 | 28.45 | 17.81 | |
| S4 | Talim | 54.63 | 63.66 | 45.37 | 36.34 | 34.78 | 28.88 |
| Soala | 11.71 | 54.79 | 88.29 | 45.21 | 6.41 | 48.37 | |
| Tembin | 62.72 | 42.89 | 37.28 | 57.11 | 26.90 | 15.99 | |
| S5 | Talim | 63.04 | 66.65 | 36.96 | 33.35 | 42.02 | 24.63 |
| Soala | 11.25 | 57.53 | 88.75 | 42.47 | 6.48 | 51.05 | |
| Tembin | 47.99 | 36.25 | 52.01 | 63.75 | 17.38 | 18.84 | |
| Typhoon | Upstream Site (S1) P Loading (kg) | Upstream Sites (S1, S2 & S3) P Loading (kg) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | TDP | SRP | PP | TSS | TP | TDP | SRP | PP | TSS | |
| Talim | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.3 × 102 | 24.8 | 15.2 | 6.9 | 9.6 | 3.6 × 103 |
| Soala | 11.7 | 6.1 | 0.6 | 5.6 | 5.0 × 104 | 317.8 | 178.4 | 18.8 | 139.4 | 3.3 × 106 |
| Tembin | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.9 × 102 | 13.5 | 8.3 | 4.0 | 5.1 | 1.2 × 104 |
| Downstream Site (S2) P Loading (kg) | Downstream Site (S4) P Loading (kg) | |||||||||
| Talim | 16.0 | 8.8 | 4.3 | 7.2 | 2.3 × 103 | 107.0 | 68.1 | 37.2 | 38.8 | 7.4 × 103 |
| Soala | 177.3 | 99.6 | 10.3 | 77.7 | 1.6 × 106 | 322.7 | 176.8 | 20.7 | 145.9 | 2.4 × 106 |
| Tembin | 7.9 | 5.7 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 7.0 × 103 | 15.7 | 6.7 | 4.2 | 8.9 | 1.4 × 104 |
| Parameter | Storm Characteristics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rdep | Rdur | I | Imax | Qave | Qpeak | ADD | API5 | |
| Event Mean Concentration (mg/L) | ||||||||
| TP | 0.134 | 0.491 | 0.134 | −0.011 | −0.021 | 0.007 | 0.142 | 0.307 |
| TDP | −0.155 | 0.416 | −0.155 | −0.170 | −0.054 | −0.086 | 0.487 | 0.025 |
| DOP | 0.372 | 0.775 ** | 0.372 | 0.386 | 0.421 | 0.393 | 0.034 | 0.332 |
| SRP | −0.852 | −0.472 | −0.852 ** | −0.895 ** | −0.468 | −0.464 | 0.797 ** | −0.607 * |
| PP | 0.134 | 0.057 | 0.134 | −0.011 | −0.036 | 0.021 | −0.146 | 0.271 |
| TSS | 0.931 ** | 0.472 | 0.931 ** | 0.903 ** | 0.582 * | 0.611 * | −0.818 ** | 0.704 ** |
| Fluxes (kg) | ||||||||
| TP | −0.063 | −0.246 | −0.063 | −0.150 | −0.004 | 0.032 | 0.140 | −0.025 |
| TDP | 0.020 | −0.076 | 0.020 | −0.082 | 0.022 | 0.063 | 0.135 | 0.102 |
| DOP | 0.062 | −0.047 | 0.062 | −0.047 | 0.072 | 0.115 | 0.078 | 0.163 |
| SRP | 0.142 | −0.086 | 0.142 | 0.062 | 0.117 | 0.171 | 0.028 | 0.102 |
| PP | −0.073 | −0.399 | −0.073 | −0.174 | −0.034 | 0.009 | 0.071 | −0.062 |
| TSS | 0.170 | −0.340 | 0.170 | 0.054 | −0.111 | −0.071 | −0.261 | 0.300 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chow, M.F.; Huang, J.-C.; Shiah, F.-K. Phosphorus Dynamics along River Continuum during Typhoon Storm Events. Water 2017, 9, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070537
Chow MF, Huang J-C, Shiah F-K. Phosphorus Dynamics along River Continuum during Typhoon Storm Events. Water. 2017; 9(7):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070537
Chicago/Turabian StyleChow, Ming Fai, Jr-Chuan Huang, and Fuh-Kwo Shiah. 2017. "Phosphorus Dynamics along River Continuum during Typhoon Storm Events" Water 9, no. 7: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070537
APA StyleChow, M. F., Huang, J.-C., & Shiah, F.-K. (2017). Phosphorus Dynamics along River Continuum during Typhoon Storm Events. Water, 9(7), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070537







